Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 राजनीतिक विज�ञान Biology
List the function of RNA.
RNA acts as genetic material in viruses
It also functions as an adapter and messenger
It also acts as a catalytic molecule and catalyses various biochemical reactions.
List the number of base pairs in :
(i) lambda bacteriophage
(ii) E.coli and
(iii) haploid content of human DNA.
(ii) 4.6 x 106 bp and
(iii) 3.3 x 109 bp.
Comment two chains of DNA have antiparallel polarity.
if one chain has 5’ x 3’ polarity the other chain has 3’ x 5’ polarity.
What is the difference between DNAs and DNAase ?
Whereas
DNAase or Deoxyriconuclease is an enzyme which digests DNA.
Suggest one evidence to prove that RNA was first genetic material.
Why was RNA unstable ?
What made DNA more preferrable as genetic material ?
List three components of transcription unit.
1. A promoter,
2. The structural gene,
3. A terminator.
Name three kinds of polymerases.
2. RNA polymerase II and
3. RNA polymerase III.
What is splicing ?
Sponsor Area
Where are UTRs present in mRNA strand ?
Write significance of UTRs.
What is the exception to the general rule that DNA is the genetic material in all organisms ? Give evidences that support these exceptions.
What do you mean by a term ‘replication fork’ ?
During DNA replication the nature of replication on 5’-3’ strand and 3'-5' strand is?
5' - 3' strand is Continuous replication
3' -5' strand is Discontinuous replication
Name the nitrogen bases present in RNA.
What are the essential requirements of the genetic materials ?
1. A genetic material should be able to express itself and in the form of Mndelian Characters'.
2. It should be capable to make its own copies (Replication).
3. It should also have mechanism to undergo mutations that will generate variation and lead to evolution.
4. It should be stable chemically and structurally.
List the various evidences for genetic role of DNA
(1) It is capable of replication and forms its own carbon copies.
(2) Constancy of amount of DNA per cell.
(3) DNA is much stable during cellular metabolism.
(4) It undergoes mutation and thus paves way for variation and evolution.
(5) Griffith’s transformation experiments on Diplococcus pneumoniae provided direct evidence for DNA as genetic material.
(6) Hershey and Chase with their experiments of transduction concluded that DNA is the genetic material.
(7) The chromosomes act as vehicles of hereditary transmission and DNA is the main component of chromosomes.
(8) It regulates cellular activities.
What does transformation experiment prove ?
What is the contribution of Avery, MacCleod and McCarty ?
(a) How did the transformation experiments of Griffith differ from those of Avery and MacCleod ?
(b) What was the significance of each ?
(b) Griffith showed that a transforming substance existed whereas Avery, MacLeod and McCarty proved that it is DNA.
What was the rationale of using 32P and 35S by Hershey and Chase ? Instead, if we use radiolabelled C and N, will the results be any different ?
If we use radiolabelled C and N then we cannot diffferentiate as both DNA and protein have C and N, so both will be labelled.
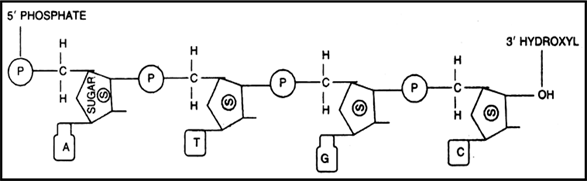
Which three components that make up the nucleotides ?
1. Pentose sugar (Deoxyribose in DNA and Ribose sugar in RNA.)
2. Phosphate group .
3. Nitrogenous bases which are of two types Purines- Adenine (A) , Guanine (G) and
Pyrimidines-Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U).
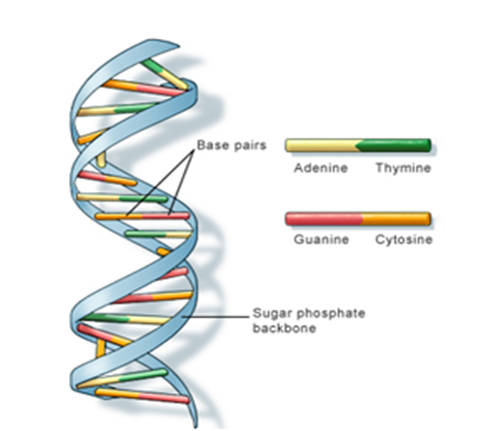
Why is the DNA molecule compared to a spiralling staircase ?
Sketch a double helix of DNA.
The bases forms pairs , adenine pairs with thymine and guanine with cytosine.
The helix is coiled in an right hande fashion. The pitch of helix is is 3.4 nm and there are 10 base pairs in each turn.
The diameter of the helix is 20Å.

Fig. Watson and Crick model of DNA.
If a double stranded DNA has 20 per cent of cytosine, calculate the percent of adenine in the DNA.
%of A= % of T, and
% of G = % of C
Therefore if % of Cytosine is 20% then % of Guanine also will be 20 %
And the remaining 60 % will be 30% of Cytosine and 30 % of Adenine.
If the sequence of one strand of DNA is written as follows : 5’–ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATG C –3’ Write down the sequence of complementary strand in 5’ and 3’ direction.
5’ GCAT GCAT GCAT GCAT GCAT GCAT GCAT 3’
If the sequence of coding strand in a transcription unit is written as follows :
5’– ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC –3’ Write down the sequence of mRNA.
Therefore the sequence of mRNA shall be :
5’– AUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGC –3’.
Sponsor Area
What are Chargaff rules ?
(1) In DNA molecule, A — T base pairs equal in number to G — C base pairs.
(2) A + G = T + C, i.e. Purines and pyrimidines equal in amount.
(3) A = T and C = G (Amount).
(4) The base ratio A + T/G + C may vary from one species to other but is constant for each species. It helps in identifying the source of DNA.
(5) The deoxyribose sugar and phosphate component occur in equal proportions.
Write differences between Prokaryotic DNA and Eukaryotic DNA.
|
Prokaryotic DNA |
Eukaryotic DNA |
|
1. Occurs in the cytoplasm in the region called nucleoid and much less in amount. 2. Circular in form. 3. It has little proteins associated with it. 4. Can code for fewer (3 to 4,000) proteins. 5. No non-coding introns within the coding regions.
|
1. Occurs in the nucleus, mitochondria and plastids and much more in amount . 2. Linear in form in the nucleus, circular in mitochondria and plastids. 3. Nuclear DNA is associated with proteins, extranuclear DNA is not. 4. Can code for many proteins. 5. Non-coding introns occur within coding regions.
|
Differentiate between the followings:
(a) Repetitive DNA and Satellite DNA
(b) mRNA and tRNA
(c) Template strand and Coding strand
| Repetitive DNA | Satellite DNA |
| Repetitive DNA are short sequences which are repeated many times. | Satellite DNA are DNA sequences that contain highly repetitive DNA |
2.
| mRNA | tRNA |
| Messenger RNA acts as a transcript . | tRNA acts as and adator molecule |
| 2.Linear in structure |
2. It has a structure similar to clover leaf . |
3.
| Template strand | Coding strand |
| 1. It acts as an template for the synthesis of mRNA. | 1.It does not act as an template. |
| 2. It has an sequence complementary to the mRNA | 2. It has a sequnce similar to the mRNA. |
| 3. It runs in 3'-5' direction | 3.It runs from 5'-3' direction. |
Which property of DNA double helix led Watson and Crick to hypothesize semi-conservative mode of DNA replication ? Explain.
Differentiate Leading Strand and Lagging Strand.
|
Leading Strand |
Lagging Strand |
|
1. The replication on this strand is continuous. 2. DNA ligase is not required 3. It is synthesized in the 5’ → 3’ direction. |
1. The replication on this strand is discontinuous in the 2. DNA ligase enzyme is required for joining Okazaki fragments. 3. In Okazaki fragments direction is 5’ → 3’ but overall direction is 3’ → 5’. |
Sketch and explain clover leaf model of tRNA.
Transfer RNA or soluble RNA (tRNA or sRNA).
It constitutes 15% of total RNA and is the smallest.
It has an amino acid acceptor end which binds to amino acids and an anticodon arm which has bases complementary to the code. It also has an enzyme activating site and a ribosomal recognition site.
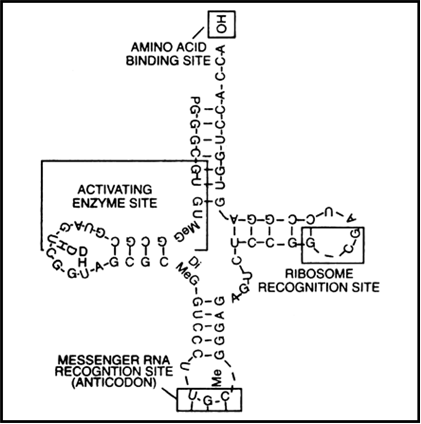
Fig. Clover leaf model of tRNA.
Write a note on repair replication.
Write a note on messenger RNA.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
It forms only 5% of total RNA but is longest of all. It brings instructions from DNA for the formation of a particular polypeptide. The instructions are coded in the form of base sequence called genetic code . Three adjacent nitrogen bases (triplet codons) specify a particular amino acid. it does not contain introns.
Fig. mRNA
It consists of a methyl cap at 5' end , a non coding region near both the ends, by initiation codon and coding region, a termination codon and a poly-A tail at 3' end.
What is the role of m-RNA, t-RNA and rRNA in protein synthesis ?
Or
Why all the three RNAs are needed to synthesise a protein in a cell ?
Role of tRNA. tRNA iacts as an adaptor and carries amino acid to mRNA.
Role of Ribosomal rRNA rRNA is present in ribosomes. It helps in providing site for protein synthesis.
RNA was first genetic material, DNA evolved later on. Explain.
Explain Central Dogma of flow of information.
It is the flow of information from DNA to mRNA (transcription) and then decoding information present in mRNA in the formation of polypeptide chain or protein (Translation). It was proposed by Crick 1958. It was developed by Alec Jeffreys.

Give a schematic structure of transcription unit.
Give a schematic structure of transcription unit.

Schematic structure of a transcription unit
Explain briefly transcription.
(1)The RNA polmerase binds to the promoter and initiates the process of transcription. The DNA strand seperates and one of it functions as template for mRNA synthesis. It is synthesized in the 5’ → 3’ direction. The base pairing is specific A with U ; C with G.
(2) RNA polymerase polymerises the strand using nucleoside triphosphates as substrate.
(3) mRNA detaches when it reaches terminator region the latter restores its original double helical structure.
What are retroviruses ? How has their discovery led to the modification of central dogma in molecular biology ?
Their discovery led to the modification of central dogma they showed that RNA is used as a template to form DNA the reverse of what is shown in central dogma.

What is retrovirus ?
What is genetic code ? List the properties of genetic code.
Properties of genetic code are
(i) The code is triplet .
(ii) The code is specific that is one codon code for only one amino acid.
(iii) The code is de-generate that is some amino acids are coded by more than one codon.
(iv) The codon is contiguos.
(v) The code is nearly universal.
What is RNA polymerase ? Write its functions.
Functions.
It initiates the transcription by attaching to the promoter.
RNA polymerase I transcribes ribosomal RNA
RNA polymerase II transcribes messenger RNA
RNA polymerase III transcribes transfer RNA.
Suppose during transcription of DNA code AAA, a mistake occurs due to which UUG code of RNA is formed. Due to this what change in picking the type of amino acid would occur during synthesis of protein.
What is the role of AUG?
How do mutations affect proteins structure and functions ?
Explain non-sense mutation, mis-sense mutation and silent mutation.
Mis-sense mutation. A mis-sense mutation is one which results in the replacement of one nucleotide giving rise to a new protein.
Silent mutation. The mutation that does not cause any change in the expression of the gene is called silent mutation.
In the medium where E. coli was growing, lactose was added, which induced the lac operon. Then, why does lac operon shut down some time after addition of lactose in the medium?
But with time all the lactose is hydrolysed by the action of enzymes . Therefore in the absence of any more lactose the lac-operon shuts down as the repressor binds to the operator and blocks RNA polymerase from accessing the promoter and transcribing the operon.
Give the chief characteristics of Eukaryotic operon.
1. They have several thousand genes.
2. The information is coded in the linear sequence in DNA.
3. The information in eukaryotic DNA for assembling a protein is not continuous but split.
4. Only exons code the mRNAs and introns do not code.
5. The gene expression is regulated by changing environment in a cell.
Differentiate between Introns and Exons.
| INTRONS | EXONS |
| 1. Non coding sequences | 1. Coding sequences |
| 2. Removed during RNA processing | 2. Not removed during RNA processing |
| 3. Not present in mRNA | 3. Present in mRNA. |
Differentiate induction and repression.
|
Induction |
Repression |
|
1. It is the switching on of an operon which normally remains turned off . 2. Regulator gene produces aporepressor that cannot block operator |
1. It is turning off of an operon which normally remains switched on . 2. In this case, regulator gene produces a repressor that blocks the operator gene. |
Explain (in one or two lines) the function of following :
(a) Promoter
(b) tRNA
(c) Exons.
(b) tRNA works as an adaptor molecule for carrying amino acid and reads the reads the genetic code
(c) Exons are the regions that are transcribed and becomes part of mRNA and code for different regions of the protein.
Why is the Human Genome project called a mega project ?
The biologists who study the developing embryos of multicellular organisms often refer to the development process as “selective gene action”. Why is this term appropriate name ?
Describe the steps in the sequencing of human genome.
1. Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) focussed on identifying all the genes that are expressed as RNAs.
2. Sequence Annotation involved simply sequencing the whole set of genome, that included all the coding and non-coding sequences and then assigning functions to different regions in the sequence.
HGP followed the second technique in which-
(i) The total DNA from the cell is isolated and converted into random fragments of relatively smaller sizes.
(ii) These fragments were then cloned in suitable hosts using specialised vectors; the commonly used hosts were bacteria and yeast and the vectors used were bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC) and yeast artificial chromosomes (YAC).
(iii) The fragments were then sequenced using automated DNA sequences.
(iv) The sequences were then arranged on the basis of certain overlapping regions present in them; this required the generation of overlapping fragments for sequencing.
(v) These sequences were annotated and assigned to the respective chromosomes.
List the applications and future challenges of human genome project.
1. Study all the genes in a genome.
2. Genes concerned with cancer can be found and sequenced. Study the transcripts in a particular tissue or organ or tumor
3. Study of interaction of various genes, proteins and their interaction.
Future challenges of human genome project are
1. Being an enormous task it will require the expertise and creativity of many people from varied disciplines in both the public and private sectors worldwide.
2. New high-throughput technologies and a huge amount of money will be needed for the same.
What is satellite DNA ? Name their two types. Mention the basis for their classification.
Types of satellite DNA are:
(i) micro satellites
(ii) mini satellites
The criteria for their classification includes :
(i) Base composition— A : T rich or G : C rich
(ii) Length of segment
(iii) Number of repetitive units.
What is DNA finger printing ? Mention its applications.
Applications of DNA Fingerprinting
1. Paternity disputes can be solved by DNA fingerprinting.
2. Evolutionary relation between the species.
3. It can be used in determining population and genetic diversities .
4.It is very useful in the detection of crime and legal pursuits.
What are aims of bioinformatics ?
How did Hershey and Chase differentiate between DNA and protein in their experiment while proving that DNA is the genetic material?
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase worked with viruses that infect bacteria called bacteriophages.
To differentiate between DNA and protein they grew bacteriophages on medium that contained on radioactive sulfur (S35)or radioactive phosphorous (P32). It produces two types of viruses
i. Viruses (grown on radioactive phosphorus medium) with radioactive DNA and non -radioactive protein as DNA has phosphorous.
ii. Viruses (grown on radioactive sulphur ) contained radioactive protein but not radioactive DNA because DNA does not contain sulphur.
These viruses were allowed to infect bacteria. The infected bacteria contained radioactive DNA and not protein. Therefore, DNA is the genetic material that passed from virus to bacteria and not protein.
Hershey-Chase Experiment
List the characteristics of DNA molecule.
1. The two chains are spirally coiled about around a common axis to form a regular, right-handed double helix.
2. The double helix has a major groove and minor groove alternately.
3. The helix is 20 A wide; its one complete turn is 34 A long, and has 10 base pairs ; and the successive base pairs are 3.4 A apart.
4. The two chains are complementary to each other with respect to base sequence.
5. The two strands are hydrogen bonded : A on one chain is joined to T on the other chain by hydrogen bonds; C on one chain is linked to G on the other chain by 3 hydrogen bonds.
6. The two strands run in antiparallel direction.
7. The amount of A + G = the amount of T + C; the amount of A = the amount of T : the amount of G = the amount of C. Sugar and phosphate groups occur in equal proportion.
8. The DNA molecule is remarkably stable due to hydrogen bonding hydrophobic reactions.
9. The DNA molecule can replicate and repair itself, and can also transcribe RNAs.
10. The amount of DNA per nucleus is constant in all the body cells of a given species.
Describe briefly the mechanism of DNA replication.
Replication is the process by which DNA copies itself.
Mechanism of DNA replication
1. It starts at a specific point called the origin. Bacterial and viral DNA have single origin whereas eukaryotic DNA has many origins.
2. The two strands of the DNA double helix unwind in some regions and form replication fork.
The DNA polymerases attach and start polymerizing the DNA in a 5'-3' direction . Thus on one strand the polymerisation is continuous and in the other it is discontinuos in the form of short fragments called Okazakki fragments which is later joined by enzyme DNA Ligase.
Make a table showing genetic codes and the corresponding amino acids coded by genetic codes.
Sponsor Area
Mention the steps of translation.
Translation. During translation process, proteins are made by the ribosomes on mRNA strand.
The main steps are:
1. Activation of amino acid.
2. Transfer of activated amino acid to tRNA.
3. Initiation of synthesis when the ribosome binds to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG).
4. Elongation of polypeptide chain. in which the tRNA and amino acid complex bind to the codon in mRNA by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon. Ribosome moves from codon to codon and amino acids are added one by one.
5. Termination of chain- when the release factor binds to termination codon releasing the complete releasing polypeptide.
Write salient features of human genome project.
Salient features of Human Genome are
1. The human genome contains 3164.7 million nucleotides (base pairs).
2. The size of the genes varies; an average gene consists of 3000 bases, while the largest gene, dystrophin consists of 2.4 million bases.
3. The total number of genes is estimated to be 30000 and 99.9% of the nucleotides are the same in humans.
4. The functions of over 50% of the discovered genes are not known.
5. Only less than 2% of the genome codes for proteins.
6. Repetitive segments forms large portion of the human genome.
7. Repetitive sequences throw light on chromosome structure and dynamics and evolution, though they are thought to have no direct coding functions.
8. Chromosome No. 1 has 2968 genes and Y-chromosome has the least number (231 genes).
9. Scientists have identified about 1.4 million locations, where DNA differs in single base in human beings these are called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
10. Repeated sequences make up a large portion of human genome.
List the steps involved in DNA fingerprinting.
(i) DNA is isolated.
(ii) DNA is digested by restriction endonucleases,
(iii) The fragments od DNA are seperated by electrophoresis,
(iv) The fragments are then traferred to to synthetic membranes, such as nitrocellulose or nylon.
(v)It is hybridized using labelled VNTR probe.
(vi) Hybridised DNA fragments are detected by autoradiography.
Briefly describe the following:
(a) Transcription
(b) Polymorphism
(c) Translation
(d) Bioinformatics
(b) Polymorphism - is the variation at genetic level which is caused due to mutation.
(c) Translation is the process by which proteins are synthesized based on the code in mRNA transcript.
(d) Bioinformatics- The term Bioinformatics is derived from two words : “Biology” and “Informatics” which uses computer-assisted interdisciplinary science to acquire, manage, store, access and process biological data.
Describe Griffith’s experiment to demonstrate that DNA is the basic genetic material. What observation was given by Avery, McCarty and MacCleod?
Griffith’s experiment demonstrated DNA as genetic material.
His experiment involved the following steps
1. He grew Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) bacteria on culture plates, some produce smooth shiny colonies (S) because of the mucous coat while othersproduce rough colonies (R).
2.When he infected mice with the S strain (virulent) they died from pneumonia infection but mice infected with the R strain did not.
3.He killed bacteria by heating and observed that heat-killed S strain bacteria did not kill the mice. But when he injected the mice with heat-killed S strain and live R strain then the mice dies.
Thus he concluded that transformation of R-strain into S-strain was due to the transfer of genetic material.
Avery, MacCleod and McCarty showed that the“transforming agent” is DNA.
How is long DNA molecule adjusted in a nucleus.
The Long DNA molecule is adjusted in the nucleus in the following way-:
The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer. The structure formed is called nucleosome that contains 200bp of DNA helix.
The nucleosomes repeating units form chromatin in the nucleus. Nucleosomes look like bead on string in chromatin.
The chromatin (bead on string structure) are packed to form the chromatin fibres that coil further to give metaphase chromosomes.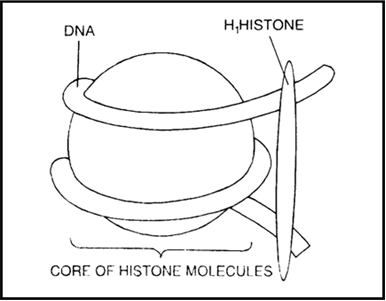
Nucleosome
Write a note on semiconservative mode of DNA replication.
Name two major enzymes of DNA replication ?
1.DNA polymerase that polymerizes the DNA strand.
2. DNA ligase which joins the Okazakki fragments.
One of the codons on mRNA is AUG.What is unique about this code
AUG codon is unique because it has double specificity, that is it codes for Methionine as well as it acts as an initiator codon to start translation
What is the inducer in the lac operon? How does it ensure the “switching on” of genes?
Draw a schematic representation of Lac operon of how does this operon get switched ‘on’ or ‘off.
Or
Explain how the gene expression is regulated?
Inducer in lac operon is lactose which binds to the repressor and prevents it from binding to the operator and blocking transcription. 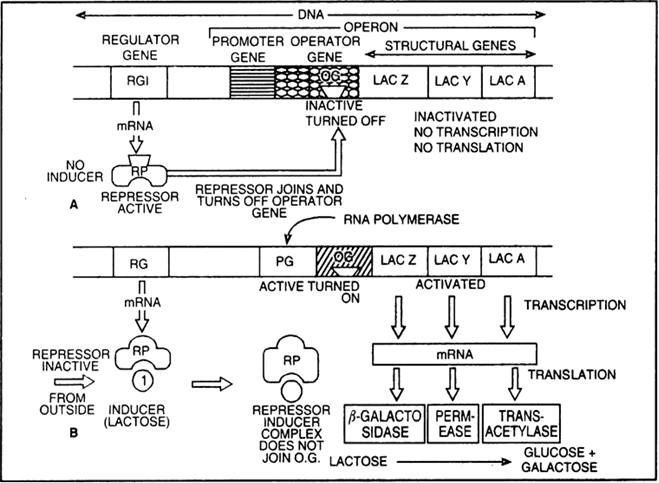
Fig. Lac operon
(a) Why is DNA molecule more stable genetic material than RNA ? Explain.
(b)‘Unambigous’, ‘degenerate’ and ‘universal’ are some of the salient features of genetic code. Explain.
(b)The terms used in genetic code means
Unambiguous means that each codon codes for only one amino acid.
Degenerate means that one amino acid can be coded by mopre than one codon.
Universal means that a given codon in DNA and mRNA specifies the same amino acid in all organisms from viruses, bacteria to human beings.
Provide experimental evidence for semi-conservative mode of replication of DNA.
Meselson and Stahl (1958) experimentally proved that the DNA replication is semi-conservative.
1. E. coli bacterium was grown for many generations in a culture medium in which the nitrogen source contained heavy isotope N15 thus the labelling of bacterial DNA was done.
2. Later on these bacteria were cultured in N14 non-radioactive isotope.
3. DNA was analysed to determine the distribution of radioactivity.
The experiment showed that one strand of each daughter DNA molecule was radioactive whereas the other was non-radioactive.
5. During second replication in N14 medium the radioactive and nonradioactive strand separated and served as template for the synthesis of nonradioactive strands.
6. Out of four DNA molecules two are completely non-radioactive and the other two have half of molecule as non-radioactive.
7. This evidence shows that DNA replication is semi-conservative.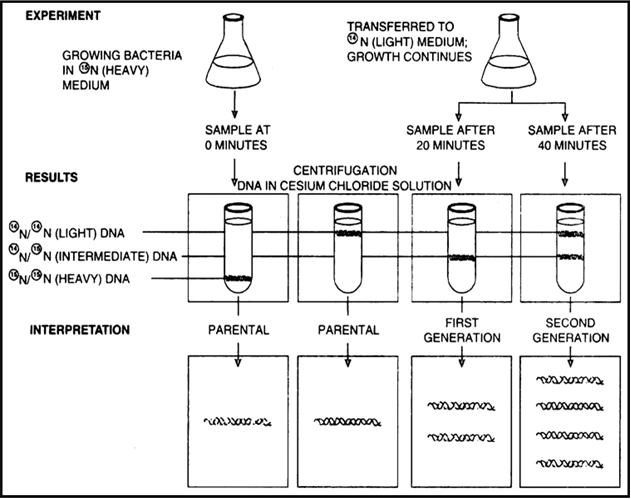
Meselson and Stahl’s experiment to prove the semi-conservative replication of DNA
Describe various goals of human genome project (HGP).
The goals of human genome project were to
(i) Identify all the genes in human DNA;
(ii) Determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA
(iiii) Store this information in databases and improve tools for analysis
(iv) Transfer related technologies to other sectors, such as industries;
(v) Address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the project.
Nucleotide arrangement in DNA can be seen by :
-
X-ray crystallography
-
Electron microscope
-
Ultracentrifuge
-
Light microscope.
A.
X-ray crystallography Central dogma of cytogenetics is : - RNA → DNA → Protein
- DNA → RNA → Protein
- Protein → RNA → DNA
- DNA → RNA → Protein → DNA.
B.
DNA → RNA → Protein DNA copies itself by the process of : - Translation
- Transcription
- Replication
- Both (A) and (B).
C.
Replication Which of the following is specifically used in genetic engineering ? - polymerase
- Gyrase
- Restriction endonuclease
- DNAse.
C.
Restriction endonucleaseGroup the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides:
Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine.
Nitrogenous bases are – Adenine, Thymine, Uracil and cytosine.
Nucleosides are – Guanosine and cytidine.
Depending upon the chemical nature of the template (DNA or RNA) and the nature of nucleic acids synthesised from it (DNA or RNA), list the types of nucleic acid polymerases.
Depending upon the chemical nature of the template (DNA or RNA) and the nature of nucleic acids synthesised from it (DNA or RNA), there are four different types of nucleic acid polymerases.
(1) DNA-dependent DNA polymerases. These use DNA as a template for synthesizing a new strand of DNA.
(2) DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. These use a DNA template strand for synthesizing RNA.
(3) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. These use RNA template synthesize RNA.
(4) RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. These use RNA template to synthesize DNA.
List two essential roles of ribosome during translation.
Ribosome plays an essential role during translation in the following two ways:
i. It acts as the site for protein synthesis. The two subunits help in the synthesis of protein, the smaller subunit forms a protein synthesizing complex with mRNA , whereas the larger subunit acts as an amino acid binding site.
ii. Ribosome acts as a catalyst for forming peptide bond.
Name the scientist who suggested that the genetic code should be made of a combination of three nucleotides.
George Gamow suggested that the genetic code should be made up of a combination of three nucleotides.
Explain the basis on which he arrived at this conclusion.
He proposed that if 20 amino acids are to be coded by 4 bases, then the code should be made up of three nucleotides. 43 = 64, if it was 2 codon then 42 = 16 which is less than 20 and a 4 codon would give 256 amino acids which is much more than required. So, the codon was proposed to be triplet.
Explain the process of DNA replication with the help of a schematic diagram.
DNA replication is the phenomenon in which a duplicate copy of DNA is synthesized
The steps involved in the process of DNA replication are as follows:
i) DNA replication occurs in S-phase of the cell cycle.
ii) Enzyme involved: DNA polymerase (DNA-dependent DNA polymerase)
iii) Replication requires energy
Source of energy -Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs)
dNTPs have dual purposes: act as substrates as well as provide energy
Replication initiates at specific regions in DNA called the origin of replication.
DNA polymerase polymerises a large number of nucleotides in a very short time.
During the course of replication, two parent strands do not completely open, but a small opening form in which replication occurs. This small opening forms a replication fork.
DNA polymerase can polymerize only in one direction, i.e,'
Therefore, replication occurs smoothly into end of DNA (continuous replication, but occurs discontinuously into end).
The discontinuous fragments so formed are joined by DNA ligase
In which phase of the cell cycle does replication occur in Eukaryotes? What would happen if cell-division is not followed after DNA replication?
DNA replication occurs in S phase of cell cycle in eukaryotes. If cell division is not followed after DNA replication then the replicated chromosomes (DNA) would not be distributed to daughter nuclei. A repeated replication of DNA without any cell division results in the accumulation of DNA inside the cell. This would increase the volume of the cell nucleus, thereby causing cell expansion.
Name the transcriptionally active region of chromatin in a nucleus.
Euchromatin is the transcriptionally active region of chromatin in a nucleus.
A DNA segment has a total of 1000 nucleotides, out of which 240 of them are adenine containing nucleotides. How many pyrimidine bases this DNA segment possesses?
According to Chargaff’s base pairing rule, The ratio of purines (A and G) to pyrimidines (C and T) is equal.
Thus, the number of adenine (A) will be equal to the number of thymine (T).
Therefore, if the number of A is 240, T will also be 240 as A = T
Thus A + T = 240 + 240 = 480
The number of cytosine (C) will be equal to the number of guanine (G).
Thus, G + C = Total number of nucleotides - Nucleotides containing A and T = 1000 - 480 = 520
Since G = C = 260 (520 divided by 2)
Thus, the number of pyrimidines that the segment possess = C + T
= 260 + 240 = 500
Sponsor Area
How did Hershey and Chase established that DNA is transferred from virus to bacteria?
Hershey and Chase worked on bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria).
When a bacteriophage infects a bacterium, the viral genetic material gets attached with the bacterial genetic material and then, bacteria treats the viral genetic material as its own to synthesize more viral particles.
Hershey and Chase experiment were to discover whether it was a protein or DNA that entered the bacteria from virus. They carried out the following steps:
i. They labelled some phages with radioactive sulphur and the others with radioactive phosphorus.
ii. These radioactive phages were used to infect E. coli.
iii. Then, E.coli was blended and centrifuged to remove viral particles.
iv. It was observed that bacteria with radioactive DNA were radioactive while those with radioactive proteins lost their radioactivity.
This showed that it is the DNA that enters the bacteria from viruses and not proteins. Hence, it was concluded that DNA is the genetic material.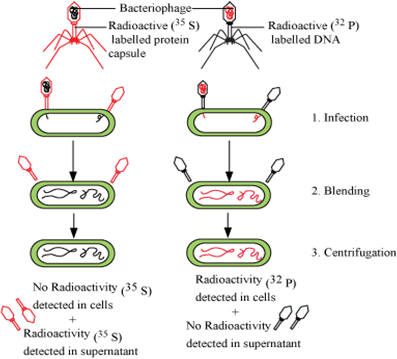
Name the enzyme and state its property that is responsible for continuous and discontinuous replication of the two strands of a DNA molecule.
The enzyme involved in the process of replication is DNA dependent DNA polymerase. This enzyme catalyzes polymerization only in one direction, i.e., 5’ → 3’. As a result on template strand with 3’ → 5’ the replication is continuous while on the template strand with polarity 5’→3’ replication is discontinuous.
Why is the enzyme cellulase needed for isolating genetic material from plant cells and not from the animal cells?
Cellulase is the enzyme that digests cell wall. Since plant cells have cell wall, so to digest the cell wall, cellulase is required. Animals do not have cell wall so, no cellulase required.
Describe the structure of a RNA polynucleotide chain having four different types of nucleotides.
RNA polynucleotide consists of namely
(i) Sugar = Ribose (ii) Phosphate group (iii) Nitrogenous bases like
Adenine - A
Uracil - U
Cytosine - C Guanine - G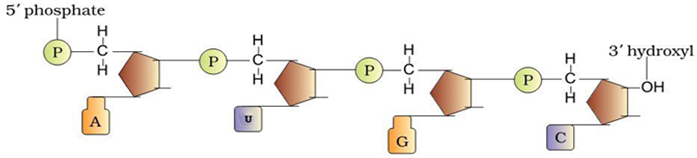
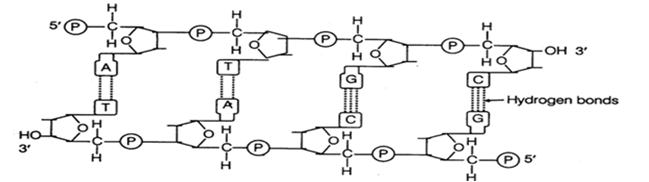
Draw a schematic diagram of a part of double stranded dinucleotide DNA chain having all the four nitrogenous bases and showing the correct polarity.
Double stranded dinucleotide DNA chain having all the four nitrogenous bases with polarity.
It is established that RNA is the first genetic material. Explain giving three reasons.
RNA was the first genetic material in cells because:
i. RNA is capable of both storing genetic information and catalyzing chemical reactions
ii. Essential life processes (such as metabolism, translation, splicing, etc.), evolved around RNA.
iii. It has the tendency of self-replication.
(a) Name the enzyme responsible for the transcription of tRNA and the amino acid the initiator tRNA gets linked with.
(b) Explain the role of initiator tRNA in initiation of protein synthesis.
(a) RNA polymerase III is responsible for transcription of t-RNA and methionine is the amino acid that gets linked with the initiator t-RNA.
(b) Initiator t-RNA carries amino acid methionine at its amino acid binding site and has anticodon UCA at its anticodon binding site. Initiator t-RNA binds with the codon (AUG) present on the mRNA and in this way the initiator t-RNA plays a role in initiation of protein synthesis.State the aim and describe Messelson and Stahl experiment.
Messelson and Stahl in 1958 performed and experiment to prove that the DNA replicates in a semi-conservative fashion.
Experimental proof
(1) They grew E.coli in a medium containing 15NH4Cl (15N is the heavy isotope of nitrogen) as the only nitrogen source for many generations. As a result, 15N was incorporated into
the newly-synthesized DNA. This heavy DNA could be distinguished from the normal by centrifugations in CsCl (cesium chloride) density gradient.
(2) Then, they transferred the E. coli cells to a medium with normal 14NH4Cl and the DNA samples were extracted at various time intervals. The DNA samples taken were double-stranded helix. The various samples were separated on the basis of CsCl gradients for measuring the density of DNA.
(3) Since E.coli divides in 20 min, they extracted DNA from the culture one generation after the transfer from N15 to N14 medium after 20 min. After 40 minutes, the DNA of the second generation was extracted from the 14NH4Cl medium and was found to have equal amounts of hybrid and light DNA. Thus it was proved that DNA replication is semiconservative since the samples contained both N15 and N14 strands that is both hybrid and light.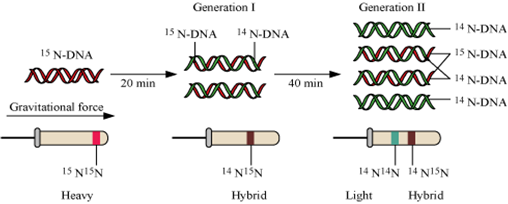
Mention the role of the codons AUG and UGA during protein synthesis.
How do histones acquire positive charge?
The base sequence in one of the strands of DNA is TAGCATGAT.
(i) Give the base sequence of its complementary strand.
(ii) How are these base pairs held together in a DNA molecule?
(iii) Explain the base complementarity rules. Name the scientist who framed this rule.
(i) The base sequence of the complementary strand will be - ATCGTACTA.
(ii) The base pairs in the DNA molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds. There are two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine and three hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine.
(iii) Base Complementarity Rule: A purine always pairs with a pyrimidine in a DNA molecule i.e.
A will pair with T and G will pair with C.
The ratio of A and T or C and G will always be 1.
Erwin Chargaff framed the base complementarity rule.
What is a cistron?
How do m-RNA, t-RNA and ribosomes help in the process of translation?
Translation is the process of polymerising amino acid to form a polypeptide chain.
The triplet sequence of base pairs in mRNA defines the order and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
The process of translation involves the following three steps: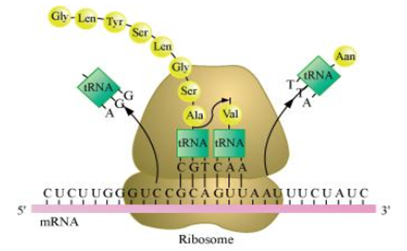
(i) Initiation
(ii) Elongation
(iii) Termination
- During the initiation of the translation, tRNA gets charged when the amino acid binds to it using ATP.
- The start (initiation) codon (AUG) present on mRNA is recognised only by the charged tRNA.
- The ribosome acts as an actual site for the process of translation and contains two separate sites in a large subunit for the attachment of subsequent amino acids.
- The small subunit of ribosome binds to mRNA at the start codon (AUG) followed by the large subunit. Then, it initiates the process of translation.
- During the elongation process, the ribosome moves one codon downstream along with mRNA so as to leave the space for binding of another charged tRNA.
- The amino acid brought by tRNA gets linked with the previous amino acid through a peptide bond and this process continues to result in the formation of a polypeptide chain.
- When the ribosome reaches one or more stop codon (VAA, UAG and UGA), the process of translation gets terminated.
- The polypeptide chain is released and the ribosomes get detached from mRNA.
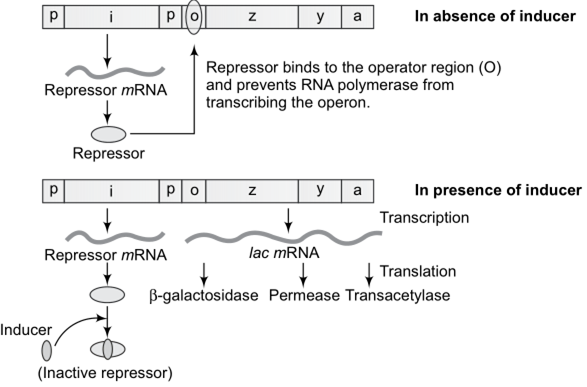
Describe how the lac operon operates, both in the presence and absence of an inducer in E.coli.
The lac operon consists of one regulatory gene (the i gene) and three structural genes (z, y, and a).
The i gene codes for the repressor of the lac operon.
The z gene codes for beta-galactosidase (β-gal), which is primarily responsible for the hydrolysis of the disaccharide, lactose
into its monomeric units, galactose and glucose.
The y gene codes for permease, which increases permeability of the cell to β-galactosides. The a gene encodes a transacetylase.
Hence, all the three gene products in lac operon are required for metabolism of lactose.
Lactose is the substrate (inducer) for the enzyme beta-galactosidase and it regulates switching on and off of the operon.
The repressor of the operon is synthesised all-the-time or constitutively from the i gene.
The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon.
In the absence of inducer the the repressor is active and the RNA polymerase cannot access the promoter region and hence the transcription does not take place.
In the presence of an inducer, such as lactose or allolactose, the repressor is inactivated by interaction with the inducer. This allows RNA polymerase access to the promoter and transcription proceeds.
(a) Draw a neat labelled diagram of a nucleosome.
(b) Mention what enables histones to acquire a positive charge.(a) Diagram of Nucleosome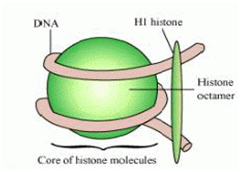
(b) Histones are positively charged because they are rich in the basic amino acid residues like lysine and arginine which carry positive charges in their side chains.
List the salient features of double helix structure of DNA.
Watson and Crick proposed the double helix for structure of DNA. Its features are:
(i) It is made of two polynucleotide chains, where the sugar-phosphate constitutes the backbone, and the bases project inside.
(ii) The two chains have anti-parallel polarity. It means, if one chain has the polarity 5'-3', the other has 3'-5'.
(iii) The bases in two strands are paired through hydrogen bond (H-bonds) forming base pairs (bp). Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine from opposite strand and vice-versa. Similarly, Guanine is bonded with Cytosine with three H-bonds. As a result, always a purine comes opposite to a pyrimidine. This generates approximately uniform distance between the two strands of the helix.
(iv) The two chains are coiled in a right-handed fashion. The pitch of the helix is 3.4 nm (a nanometre is one billionth of a metre, that is 10-9 m) and there are roughly 10 bp in each turn turn. Consequently, the distance between a bp in a helix is approximately equal to 0.34 nm.
(v) The plane of one base pair stacks over the other in double helix.How are the structural genes activated in the lac operon in E.coli
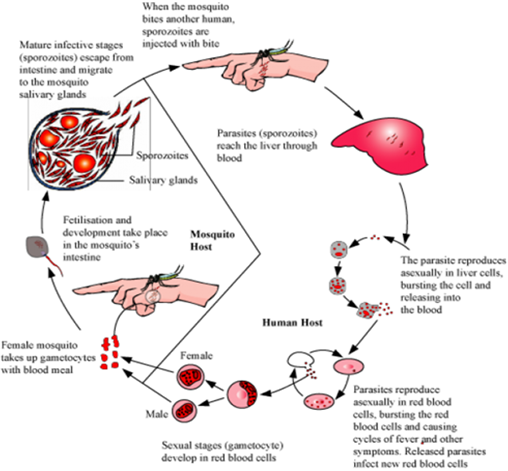
Trace the life-cycle of malarial parasite in the human body when bitten by an infected female Anopheles.
Describe Frederick Griffith’s experiment on Streptococcus pneumonia. Discuss the conclusion he arrived at.
(a) Frederick Griffith worked on Streptococcus pneumoniae to find the process of transformation in the bacteria. When Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria were grown on a culture plate, some of the bacteria produced smooth shiny colonies (S) due to the presence of polysaccharide coat while others produced rough colonies (R) as they lacked polysaccharide coat.
Griffith then injected mice with this S strain (polysaccharide coat) as well as with R strain bacteria. He found that mice infected with virulent strain died from pneumonia, but mice infected with R strain did not develop pneumonia.
S strain → Injected into mice →Mice died of pneumonia
R strain →Injected into mice →Mice lived
Griffith then killed the S strain bacteria by heating them and injected these heat-killed bacteria into the mice. He observed that heat-killed S strain bacteria did not kill the mice. But when a mixture of heat-killed S and live R bacteria was injected into mice, the mice died.
S strain →injected into mice →Mice lived
S strain (heat-killed) + R strain (live) → Injected into mice → Mice died
It was because the DNA from the heat-killed S strain got transferred into live R strain and transformed the R strain into virulent type which caused pneumonia in the mice and led to their death. This process is called transformation.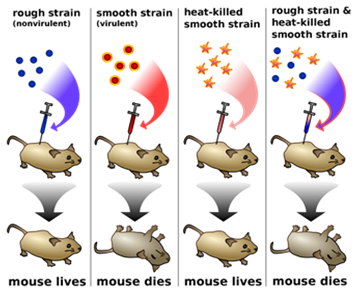
Following are the features of genetic codes. What does each one indicate ? [2]
Stop codon; Unambiguous codon; Degenerate codon; Universal codon.
Stop codon -
Unambiguous codon
Degenerate codon
Universal codon
Tips: -
i. Stop codon - In genetic code. a stop codon or (termination codon) is a Nucleotide triplet with messenger RNA that signals a termination of the translation.
ii. Unambiguous codon - One codon codes for only one amino acid, hence, it is unambiguous and specific.
iii. Degenerate codon - Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the code is degenerate.
iv. Universal codon - because a codon in one organism will code for the same amino acid in another organism.
(a) What do 'Y' and 'B' stand for in 'YAC' and 'BAC' used in Human Genome Project (HGP). Mention their role in the project.
(b) Write the percentage of the total human genome that codes for proteins and the percentage of discovered genes whose functions are known as observed during HGP.
(c) Expand 'SNPs' identified by scientists in HGP.
(a) Y stands for Yeast in YAC (Yeast artificial chromosome) and
B stands for Bacteria in BAC (Bacterial artificial chromosome)
YAC and BAC are used as vectors in the Human genome project.
(b) Less than 2% of the genome codes for proteins. 21.4% is discovered genes whose functions are known as observed during HGP.
(c) SNP stands for Single Nucleotide Polymorphism.
(a) Name the stage in the cell cycle where DNA replication occurs.
(b) Explain the mechanism of DNA replication. Highlight the role of enzymes in the process.
(c) Why is DNA replication said to be semiconservative ?
(a) DNA replication takes place in the S phase or Synthetic phase of the Cell cycle.
(b) The process of Replication;
1. The double-helix structure of the DNA unzips. This is carried out by an enzyme called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary basesof DNA together
2. The DNA do not separate completely but at some point. The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a ‘Y’ shape called a replication ‘fork’. The two separated strands act as templates for making the new strands of DNA.
3. One of the strands is oriented in the 3’ to 5’ direction and is called the leading strand. The other strand is oriented in the 5’ to 3’ direction and is the lagging strand. As a result of their different orientations, the two strands are replicated differently:
4. Leading Strand:
A short piece of RNA called a primer (produced by an enzyme called primase) comes along and binds to the end of the leading strand. The primer acts as the starting point for DNA synthesis.
DNA polymerase binds to the leading strand and then ‘walks’ along it, adding new complementary nucleotide bases (A, C, G and T) to the strand of DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction. This sort of replication is called continuous.
Lagging strand:
Numerous RNA primers are made by the primase enzyme and bind at various points along the lagging strand. Chunks of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, are then added to the lagging strand also in the 5’ to 3’ direction. This type of replication is called discontinuous as the Okazaki fragments will need to be joined up later.
5. Once all of the bases are matched up (A with T, C with G), an enzyme called exonuclease strips away the primer(s).
6. Finally, an enzyme called DNA ligase seals up the sequence of DNA into two continuous double strands. The result of DNA replication is two DNA molecules.
(c) The newly formed two DNA strands consist of one new and one old chain of nucleotides. This is why DNA replication is described as semi-conservative, half of the chain is part of the original DNA molecule, half is new
Discuss the role the enzyme DNA ligase plays during DNA replication.
The DNA ligase helps to join or seal the Okazakki fragment or discontinuos DNA strands present on the lagging strands.
Describe the experiment that helped demonstrate the semi-conservative mode of DNA replication
Meselson and Stahl (1958) experimentally proved that the DNA replication is semi-conservative. It had the following steps;
1. E. coli bacterium was grown for many generations in a culture medium in which the nitrogen source contained heavy isotope N15 , thus the labelling of bacterial DNA was done.
2. Later on these bacteria were cultured in N14 non-radioactive isotope.
3. DNA was analysed to determine the distribution of radioactivity.
4. The experiment showed that one strand of each daughter DNA molecule was radioactive whereas the other was non-radioactive.
5. During second replication in N14 medium, the radioactive and nonradioactive strand separated and served as a template for the synthesis of nonradioactive strands.
6. Out of four DNA molecules, two are completely non-radioactive and the other two have half of molecule as non-radioactive.
This showed that DNA replication is semi-conservative.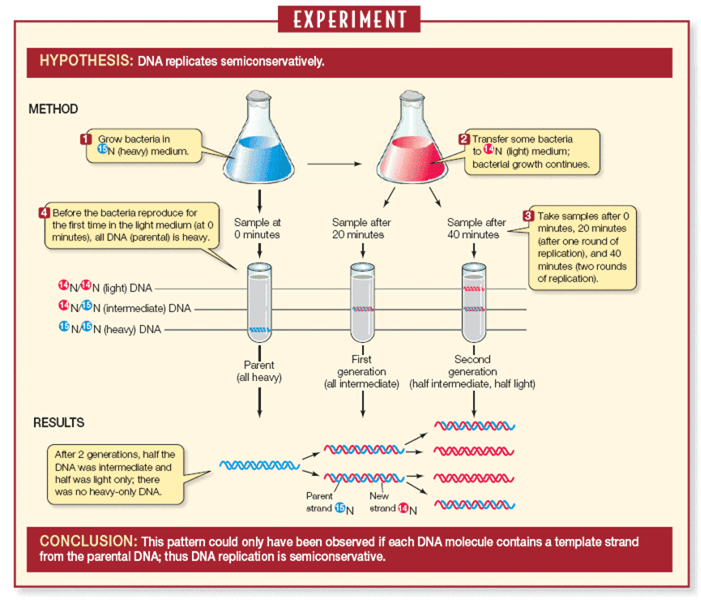
(a) How are the following formed and involved in DNA packaging in a nucleus of a cell?
(b) Differentiate between Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
i. Histone octomer - The histones are positively charged, basic proteins called histones. Histones are rich in basic amino acids like lysines and arginines. Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called an histone octamer.
ii. Nucleosome - The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form the structure called nucleosome. A typical nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNa helix.
iii. Chromatin - The nucleosome are the repeating units and together form chromatin. The nucleosome appear like beads on strings on the chromatin.
The chromatin is packaged to form chromatin fibres that further coil and condense at metaphasic stage of cell division to form chromosome. This involves non-histone proteins for packaging called the No-histone Chromosomal (NHC) proteins.
(b)
| Euchromatin | Heterochromatin |
| Region of the chromatin which is loosely packed. | Region of the chromatin which is densely packed |
| Stains light | Stains dark. |
Mention the contribution of genetic maps in human genome project.
The contribution of genetic maps in human genome project.
1. The gene mapping has made it possible to sequence the whole human genome.
2. Genetic maps have been used to find the exact chromosomal location.
3. The distances between markers and genes could be measured using the gentic maps.
A. Name the enzyme that catalyses the transcription of hnRNA.
B. Why does the hnRNA need to undergo changes ? List the changes hnRNA undergoes and where in the cell such changes take place.
A. hnRNA is designated as heterogeneous nuclear RNA. Transcription of hnRNA is catalyses by – RNA polymerase II.
B. During primary transcription formation the mRNA contains both coding and non-coding regions called as exons and introns. The sequence is then subjected to splicing (process of removal of introns form primary transcript).
hnRNA then undergo capping and tailing.
Capping is a process where addition of methyl guanosine triphosphate takes place at 5' end of hnRNA, while tailing is done by the addition 200- 300 adenylate residues at 3' end. The final mRNA is then transported outside of nucleus by nuclear pore to the cytoplasm for translation.
Unambiguous, universal and degenerate are some of the terms used for the genetic code. Explain the salient features of each one of them.
Unambiguous nature - It means that one codon codes for only single amino acid and are specific.
Degenerate – coding of some amino acids are done by more than one sets of codon therefore, they are termed as degenerate.
Universal - sequence of codon represents specific amino acids and are unique to all organisms
A number of passengers were severely burnt beyond recognition during a train accident. Name and describe a modern technique that can help hand over the dead to their relatives.
The technique that can help in the identification of victims is DNA fingerprinting which distinguishes between individuals of same species by using their DNA as sample. The chemical structure of DNA is same in everyone (99.9%) except the order of base pairs, i.e. only 0.1% of DNA makes every individual unique. DNA fingerprinting exploits the highly variable repeating sequences, i.e. VNTRs for profiling. These VNTRs are highly conserved among members of the same species. Technique
This technique has following steps:
(i) DNA Isolation DNA is extracted from the cells in a high speed centrifuge.
(ii) Amplification Many copies of the extracted DNA can be made by the use of polymerase chain reaction.
(iii) Digestion of DNA by restriction endonucleases.
(iv) Separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis.
(v) Blotting Transfer of separated DNA fragments to synthetic membranes (like nylon or nitrocellulose).
(vi) Hybridisation, with the help of a radio labelled VNTR probe (small segments of DNA which help to detect the presence of a gene in a long DNA sequence). These probes target a specific nucleotide sequence that is complementary to them.
(vii) Autoradiography Detection of hybridised DNA fragments by autoradiography.
The presence of similarities between the victims and their relatives determines their association on the basis of which dead bodies can be identified and handed over to their families.
Name the scientist who is associated with the following:
Reverse Transcription
State two postulates of Oparin and Haldane with reference to origin of life.
Oparin and Haldane proposed that life originated from pre-existing non-organic molecules and the diverse organic molecules were formed from these inorganic constituents by chemical evolution
Differentiate between the genetic codes given below : (a) Unambiguous and Universal (b) Degenerate and Initiator
(a) Unambiguous and Universal : - Unambiguous : - The code is specific, i.e. one codon codes for only one amino acid. Universal : - The code is same in all organisms. (b) Degenerate and Initiator : - Degenerate : - When an amino acid is coded by more than one codon, it is said to be degenerate. Initiator : - AUG is an initiator codon i.e. it initiates the translation process & also codes for methionine.
(a) List the two methodologies which were involved in human genome project. Mention how they were used.
(b) Expand ‘YAC’ and mention what was it used for.
(a) 2 Methodologies of HGP : - (1) Expressed Sequence Tags (EST's) : - This method focusses on identifying all the genes that are expressed as RNA.
(2) Sequence Annotation : - It is an approach of simply sequencing the whole set of genome that contains all the coding and non-coding sequences, and later assigning different regions in the sequence with functions.
(b) 'YAC' → Yeast Artificial Chromosome : - It is used as a cloning vector for cloning DNA fragments in suitable host so that DNA sequencing can be done.
(a) Explain the significance of palindromic nucleotide sequence in the formation of recombinant DNA.
(b) Write the use of restriction endonuclease in the above process.
(a) The palindromic sequences i.e. the sequence of base pairs read the same on both the DNA strands, when orientation of reading is kept the same.
(b) On finding the palindrome, the endonuclease binds to the DNA.
* It cuts the opposite strands of DNA, but between the same bases on both the strands & forms STICKY ENDS. This sticky ends facilitate the action of enzyme DNA ligase and helps in the formation of recombination DNA.
Describe the roles of heat, primers and the bacterium Thermus aquaticus in the process of PCR.
Role of Heat : - It helps in denaturation process in PCR. The ds DNA is heated in this process at very high temperature (95ºC) so that both the strands separates. Role of primers : - Primers are chemically synthesised small oligonucleotides of about 10-18 nucleotides that are complementary to a region of template DNA and helps in the extension of new chain. Role of Bacterium Thermus aquaticus : - From this bacterium, a thermostable Taq DNA polymerase is isolated which can tolerate high temperatures and forms new strand.
Write the different components of a lac-operon in E. coli. Explain its expression while in an ’open’ state.
The lac operon (Inducible operon) Operon : - The concept of operon was first proposed in 1961, by Jacob and Monod Components of an operon : - (i) Structural genes : - The fragment of DNA which transcribe mRNA for polypeptide synthesis.
(ii) Promoter : - The sequence of DNA where RNA polymerase binds and initiates transcription.
(iii) Operator : - The sequence of DNA adjacent to promoter is called OPERATER.
(iv) Regulator gene : - It is the gene that codes for repressor protein which binds to operator due to which operon is switched ‘‘off’’
(v) Inducer : - Lactose is inducer which helps in switching ‘‘on’’ of operon. Lac operon consists of there structural genes (z, y, a), operator (o), promoter (p), regulatory gene (i)
When lactose is absent:- When lactose is absent, i.e. gene produces repressor protein. This repressor protein binds to operator and as a result prevents RNA polymerase to bind to operon. The operon is switched off. When lactose is present : -
• Lactose act as inducer which binds to the repressor and forms inactive repressor.
• The repressor cannot bind to operator.
• Now the RNA polymerase binds to operator and transcribes lac mRNA.
• Lac mRNA is polycistronic i.e. produces all three enzymes β−galactosidase, permease and trans-acetylase.
• The lac operon is switched on.
Write the dual purpose served by Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in the polymerisation.
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (DTPs) purpose:
(i) DTPs serves as substrates i.e. nucleotides during replication.
(ii) DTPs supply energy for polymerisation reaction by breaking of high energy terminal phosphates bond.
Although a prokaryotic cell has no defined nucleus, yet DNA is not scattered throughout the cell. Explain.
The DNA (negatively charged) is scattered in the cytoplasm means that it is naked and is not covered by any membrane. The prokaryotes use an arrangement that helps to pack genetic material tightly into a specific region known as nucleoid because prokaryote does not have a well-defined nucleus. So DNA is not scattered but present in the form of a membrane-less structure called nucleoid.
This nucleoid floats in the cytoplasm and can be found anywhere in the cytoplasm. Also, the DNA in form of single chromosomes is attached to mesosome at a point.
List any two applications of DNA fingerprinting technique.
Since DNA from every tissue (such as blood, hair - follicle , skin, bone, saliva, sperm etc.), from an individual, show the same degree of polymorphism, they become very useful identification tool in forensic
applications to identify criminals. Further, as the polymorphisms are inheritable from parents to children, DNA fingerprinting is the basic of paternity testing, in case of disputes.
State the ‘Central dogma’ as proposed by Francis Crick. Are there any exceptions to it? Support your answer with a reason and an example.
Francis Crick proposed the Central dogma in molecular biology, which states that the genetic information
flows from DNA → RNA → Protein.
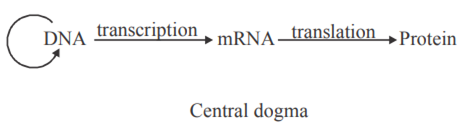
In some viruses, central dogma is seen in the reverse direction, that is from RNA to DNA. as RNA is the main genetic material.
Eqs: Retrovirus (HIV) and the process is Reverse transcription.
Explain how the biochemical characterisation (nature) of ‘Transoforming Principle’ was determined. which was not defined from Griffith’s experiments.
Transforming Principle :
In 1928, Frederick Griffith, in a series of experiments with Streptococcus pneumoniae (bacterium responsible for pneumonia), witnessed a miraculous transformation in the bacteria. During the cource of his experiment, a living organism (bacteria) had changed in physical form.
He concluded that the R strain bacteria had somehow been transformed by the heat - killed S strain bacteria. Some ‘transforming principle’, transferred from the heat-killed S strain, had enabled the R strain to synthesise a smooth polysaccharide coat and become virulent. This must be due to the transfer of the genetic material. However, the biochemical nature of the genetic material was not defined from his experiments.
Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod and Maclyn McCarty worked to determine the biochemical nature of ‘tranforming principle’ in Griffith’s experiment.
They purified biochemicals (proteins, DNA, RNA, etc.) from the heat-killed S cells to see which ones could transform live R cells into S cells. They discovered that DNA alone from S bacteria caused R bacteria to become transformed.
They also discovered that protein - digesting enzymes (proteases) and RNA - digesting enzymes (RNases) did not affect transformation, so the transforming substance was not a protein or RNA. Digestion with DNase did inhibit transformation, suggesting that the DNA caused the transformation.
They concluded that DNA is the hereditary material, but not all biologist were convinced.
Which of the following is required as inducer(s0 for the expression of lac operon?
-
galactose
-
lactose
-
lactose and galactose
-
glucose
B.
lactose
Lac operon is and inducible operon. Lactose is the substrate for the enzyme  -galactosidase and it also regulates switching on and off of the operon. Hence, it is termed as inducer.
-galactosidase and it also regulates switching on and off of the operon. Hence, it is termed as inducer.
The two polypeptides of human insulin are linked together by
-
phosphodiester bonds
-
covalent bonds
-
disulphide bridges
-
hydrogen bonds
C.
disulphide bridges
The insulin chains are held together by disulphide bridges.
Which of the following is the starter codon?
-
UGA
-
UAA
-
UAG
-
AUG
D.
AUG
AUG is a start codon. Others are stop codon.
Which one of the following is not applicable to RNA?
-
Complementary base pairing
-
5, phosphoryl and 3' hydroxyl ends
-
Heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
-
Chargaff's rule
D.
Chargaff's rule
Chargaff's Rule is not applicable to RNA. He is the generalisations formulated about DNA structure. The rule states that DNA from any cell of all organisms should have a 1:1 ratio (base pair rule) of pyrimidine and purine bases, i.e. the amount of guanine is equal to cytosine and the amount of adenine is equal to thymine. Further complementary base pairing is sometimes, visible is RNA as well (in doubled stranded RNAs of viruses) hence option (a) is not taken into consideration.
Balbiani rings rigs are sites of
-
Lipid synthesis
-
Nucleotide synthesis
-
Polysaccharide synthesis
-
RNA and protein synthesis
D.
RNA and protein synthesis
A Balbiani ring is a large chromosome puff. Balbiani rings are diffused uncoiled regions of the polytene chromosome that are sites of RNA transcription and protein synthesis.
Satellite DNA is important because it
-
codes for proteins needed in cell cycle.
-
shows high degree of polymorphism in population and also the same degree of polymorphism in an individual, which is heritable from parents to children.
-
does not code for proteins and is same in all members of the population.
-
codes for enzymes needed for DNA replication.
B.
shows high degree of polymorphism in population and also the same degree of polymorphism in an individual, which is heritable from parents to children.
Satellite DNA forms that minor peak after centrifugation of DNA. These are repetitive DNA sequences that do not code for any protein. They show high degree of polymorphism and heritable from parents to children, thus form the basis of DNA fingerprinting.
Which one of the following shows coiled RNA stands and capsomeres?
-
Polio virus
-
Tabacco mosaic virus
-
Measles virus
-
Retrovirus
A.
Polio virus
In TMV RNA is a single-stranded (ss) helically coiled structure containing about 2130 capsomeres, a basic subunit of the capsid (an outer covering of protein that protects the genetic material of a virus).
There are about 16 capsomeres present in each helical turn.
Which one of the following a wrongly matched?
-
Transcription - Writing information from DNA to t-RNA
-
Translation - Using information in m - RNA to make protein
-
Repressor protein - Binds to operator to stop enzyme synthesis
-
Operon- Structural genes, operator and promoter
A.
Transcription - Writing information from DNA to t-RNA
Transcription is a process of RNA synthesis from a DNA template. It involves three main events, i.e., initiation (binding of RNA polymerase to as DNA), elongation (development of a short stretch of DNA) and termination (recognition of release of RNA polymerase). Expect trans cuiprion are correctly matched.
Transformation was discovered by
-
Meselson and Stahi
-
Hershey and Chase
-
Griffith
-
Watson and crick
C.
Griffith
The transformation was discovered by F Griffith (1928). He isolated the DNA as genetic material that inherits the genetic information between two generation by using two strain of Pneumococcus bacteria which infect mice. i.e., type III S (smooth) and type IIR (rough) strain
The first human hormone produced by recombinant DNA technology is
-
insulin
-
estrogen
-
thyroxin
-
progesterone
A.
insulin
Insulin is peptide hormone, which controls the level of blood sugar. It is formed by joining of two polypeptide chain by disulphide bonds
An analysis of chromosomal DNA using the Southern hybridization technique does not use
-
electrophoresis
-
blotting
-
autoradiography
-
PCR
D.
PCR
Southern hybridization is a technique used in molecular biology for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples in which DNA sequence in DNA samples in which excepting PCR we use all three methods such electrophoresis, blotting and autoradiography. Because PCR is the method used for the amplification of DNA sample. In vitro, clonal propagation is characterised by PCR and RPAD.
Removal of RNA polymerase -III from nucleoplasm will affect the synthesis of
-
tRNA
-
rRNA
-
mRNA
-
rRNA
A.
tRNA
RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA, RNA poly II synthesis mRNA while RNA poly I synthesis of mRNA while RNA poly I synthesis rRNA in eukaryotes
PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism are the methods for
-
Study of enzymes
-
Genetic transformation
-
DNA sequencing
-
Genetic Fingerprinting
D.
Genetic Fingerprinting
The hypervariable regions of DNA have Variable Number of Tandem repeats (VNTRs) of short nucleotide sequences which are specific for each individual (except for monozygotic twins). Variations also occur due to mutations, small deletions or insertions. Therefore, DNA cut by a particular endonuclease will have different lengths in different persons. This phenomenon is called Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism. It is the basis of genetic (Or DNA) fingerprinting and is useful in identifying individuals from their semen, blood or tissues or any other DNA sample and resolution of parent-hood disputes.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is also useful in genetic fingerprinting as it can amplify the DNA sample even if available in a very small amount
Which one of the following is not a part of a transcription unit in DNA?
-
The inducer
-
A terminator
-
A promoter
-
The structural gene
C.
A promoter
Transcription unit consists of promoter, structural gene and terminator. The inducer (lactose/allolactose) is not a component of transcription unit.
A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called
-
vector
-
selectable marker
-
plasmid
-
probe
D.
probe
Probes are 15-30 bases long radioactive labelled oligonucleotides (RNA or DNA) used to detect complementary nucleotide sequences, used for diseases diagnosis etc.
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesised in
-
lysosomes
-
nucleolus
-
nucleoplasm
-
ribosomes
B.
nucleolus
In eukaryotes, the site of synthesis of most of the ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is nucleolus. The nucleolar organiser contains many copies of ribosomal DNA (repetitive DNA). The RNA cistron of nucleolar DNA forms 45 S precursor with the help of RNA polymerase. This 45 S RNA undergoes to give 18S, 28S and 5.8 S rRNA units. Out of different rRNAs, the 5S rRNA is not synthesized in nucleolus. It is synthesized outside it.
Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR?
-
It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells
-
It serves as a selectable marker
-
It is isolated from a virus
-
It remains active at hight temperature
It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells
It serves as a selectable marker
It is isolated from a virus
It remains active at hight temperature
D.
It remains active at hight temperature
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is used to amplify a DNA segment or to synthesize in vitro the multiple copies of gene (or DNA) of interest, using two sets of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase. This enzyme is isolated from a bacterium Thermus aquatics and it remains active during the high temperature but high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNA
Given below is the diagrammatic representation of one of the categories of small molecular weight organic compounds in the living tissues. Identify the category shown and the one blank component X in it
-
Category Component
Nucleoside Uracil
-
Category Component
Cholesterol Guanin -
Category Component
Amino acid NH2 -
Category Component
Nucleotide Adenine
A.
Category ComponentNucleoside Uracil
Nucleoside is made up of ribose sugar and nitrogenous base only. Uracil forms nucleoside with only ribose sugar. So, the option with category nucleoside component uracil is correct.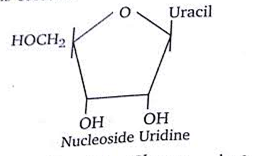
Removal of introns and joining of exons in a defined order during transcription in called
-
looping
-
inducing
-
slicing
-
splicing
D.
splicing
The primary transcript from a typical eukaryotic gene contains introns as well as exons. During RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are joined in a defined order, to produce functional RNA.
Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are
-
T-DNA
-
BAC and YAC
-
Expression vectors
-
T/A cloning vectors
B.
BAC and YAC
Commonly used vector for human genome sequencing are BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) and YAC BAC is a DNA construct, based on a functional fertility plasmid (Fplasuid) used for transforming and cloning in bacteria (e.coil) and YAC are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is then ligated into a bacterial plasma.
Read the following four statement.
1. In transcription, adenosine pairs with uracil
2. Regulation of lac operon by repressor is referred to as positive regulation.
3. The human genome has approximately 50,000 genes.
4. Haemophilia is sex-linked recessive disease.
How many of the above statements are right?
-
Two
-
Three
-
Four
-
One
A.
Two
Transcription is the process of synthesis of RNA on the DNA template. During transcription adenosine pairs with uracil.
Repressor gene determines the transcription of structural gene. It codes for repressor protein. After synthesis the repressor molecule is diffused from the ribosome and bind to the operator in absence of inducer.
The human genome has approximately 30000 genes with ~ 3.2 billion base pairs.
Select the correct option.
-
Direction of RNA Synthesis
Direction of reading of the template DNA strand
5’-3’
3’-5’
-
Direction of RNA Synthesis
Direction of reading of the template DNA strand
3’-5'
5’-3'
-
Direction of RNA Synthesis
Direction of reading of the template DNA strand
5’-3’
5’-3'
-
Direction of RNA Synthesis
Direction of reading of the template DNA strand
3’-5'
3’-5’
D.
|
Direction of RNA Synthesis |
Direction of reading of the template DNA strand |
|
3’-5' |
3’-5’ |
RNA polymers catalyse polymerization only in one direction, that 5'->3' and the strand that has 3'-5', act as a template.
What is it that forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting?
-
The relative proportions of purines and pyrimidines in DNA
-
The relative difference in the DNA occurrence in blood, skin and saliva
-
The relative amount of DNA in the ridges and grooves of the fingerprints
-
Satellite DNA occuring as hightly repeated short DNA segments
D.
Satellite DNA occuring as hightly repeated short DNA segments
DNA fingerprint is individual-specific DNA identification which is made possible by the finding that no two people are likely to have the same of copies of repetitive DNA sequences of regions. The chromosomes of every human cells contains short, highly repeated DNA sequence (15 nucleotide) called minisatelite scattered throughout.
The figure below shows three steps (A, B, C) of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Select the option giving correct identification together with what it represents?
-
B – Denaturation at a temperature of about 98°C separatiing the two DNA strands
-
A – Denaturation at a temperature of about 50°C
-
C – Extension in the presence of heat stable DNA polymerase
-
A – Denaturation at a temperature of about 50°C
C.
C – Extension in the presence of heat stable DNA polymerase
There are three steps in polymerase chain reaction namely.
(i) Denaturation- at  for DNA strand separation.
for DNA strand separation.
(ii) Annealing - binding of primer.
(iii) Extension in presence of DNA polymerase which is heat stable.
Select the correct option:
| Column I | Column II | |
| A | Synapsis aligns homologous chromosomes | 1. Anaphase-II |
| B | Synthesis of RNA and protein | 2. Zygotene |
| C | Action of enzyme recombinase | 3. G2-phase |
| D | Centromeres do not separate but chromatids move towards opposite poles | 4. Anaphase-I |
| 5. Pachytene |
-
Codes
A B C D
2 1 3 4 -
Codes
A B C D
2 3 5 4 -
Codes
A B C D
1 2 5 4 -
Codes
A B C D
2 3 4 5
B.
CodesA B C D
2 3 5 4
Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E.coli that involves the lac I gene product is
-
Positive and inducible because it can be induced by lactose
-
Negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription
-
Negative and repressible because repressor protein prevents transcription.
-
Feedback inhibition because excess of
 -galactosidase can switch off trascription.
-galactosidase can switch off trascription.
B.
Negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription
Lac I gene produces an inhibitor or repressor and negative regulation of lac operon is induced. The repressor binds to the operator gene and stops its working. Repressor is meant to block the operator gene so that structural genes are unable to form mRNA thus stopping the transcription of genes.
In sea Urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in this DNA are:
-
G 34%, A 24.5%, T 24.5%
-
G 17%, A 16.5%, T 32.5%
-
G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
-
G 8.5%, A 50%, T 24.5%
C.
G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
Charagaff's rule states that purine and pyrimidine base paires are present in equal amount, i.e.
A = T, G = C
(A + T) = (G + C)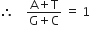
Cytosine = 17%
If A+G+C+T = 100 and G = C, A = T then
A+17+7+T = 100 G = 17%
G = 17%
A + T + 34 = 100
A + T = 100 - 34
A + T = 66
A = T = 33% = 66
Hence, if cytosine is 17%, then G = 17% A and T will be 33% each.
What are those structures that appear as 'beads-on-string' in the chromosomes when viewed under electron microscope?
-
Nucleotides
-
Nucleosomes
-
Base pairs
-
Genes
B.
Nucleosomes
Nucleosome is sub-microscopic sub-unit of chromatin which is formed by wrapping of DNA over a core of histone proteins. The term was coined by Oudet et. al, (1975). It is oblate structure with a length of 10 nm and a thickness of 5-5.7 nm. Its core is called nu-body. The latter is formed of four pairs of histone molecules - H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. DNA makes 1.75 turns over the octamer to form a nucleosome. Two adjacent nucleosomes are connected by a short segment of unbound DNA called linker DNA. A fifth type of histone called H1 is attached over the linker DNA. Nucleosomes appear as 'beads-on-string' in the chromosomes under electron microscope.
The process of RNA interference has been used in the development of plants resistant to
-
fungi
-
viruses
-
insects
-
nematodes
D.
nematodes
The process of RNA interference (RNA) has been used in the development of plants resistant to nematodes like Molodegyne incognitia, which infects the roots of tobacoo plants and causes a great reduction in yied. RNAi takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense. This method involves silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRNA (sliencing).
Which one of the following also acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell?
-
sn RNA
-
hn RNA
-
23 S rRNA
-
5 S rRNA
C.
23 S rRNA
23 SrRNA in bacteria is the enzyme ribozyme for the formation of a peptide bond. 23 S rRNA is found large sub- unit (70 S) of ribosome of bacteria.
Silencing of mRNA has been used in producing transgenic plants resistant to
-
bollworms
-
nematodes
-
White rusts
-
bacterial blight
B.
nematodes
RNA interference (RNAi) takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence. This method involves silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary ds RNA molecule that binds to an prevents translation of the mRNA (silencing). The source of the complementary RNA could be from an infection by viruses having RNA genome of mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate. Using Agrobacterium vectors, nematode -specific genes were introduced into the host plant. The introduction of DNA was such t hat it produced both sense and anti -sense RNA in the host cells. These two RNA's being complementary to each other formed a dsRNA that initiated RNAi and thus, silenced the specific mRNA of the nematode. The result was that the parasite could not survive in a transgenic host expressing specific interfering RNA. The transgenic plant, therefore, got itself protected from the parasite.
The unequivocal proof of DNA as the genetic material came from the studies on a
-
bacterium
-
fungus
-
viroid
-
Bacterial virus
D.
Bacterial virus
The unequivocal (leaving no doubt; unambiguous) proof that DNA is the genetic material came from the experiments of Alfred Hershey and Martha chase. They worked with viruses that infect bacteria called bacteriophages.
Which one of the following techniques made it possible to genetically engineer living organism
-
Recombinant DNA techniques
-
X -ray diffraction
-
Heavier isotope labelling
-
Hybridization
A.
Recombinant DNA techniques
Recombinant DNA technology is joining together of DNA molecules from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations.
Which one of the following is used as a vector for cloning the gene into higher organisms?
-
Baculovirus
-
Salmonella typhimurium
-
Rhizopus nigricans
-
Retrovirus
D.
Retrovirus
Retroviruses are RNA-containing animal viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate. Retroviruses in animals have the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells. A better understanding of the act of delivering genes by pathogen into useful vectors for delivering genes of interest of humans. Retroviruses have been disarmed and are now used to deliver desirable genes into animals cells.
The one aspect which is not a salient feature of genetic code is its being
-
degenerate
-
ambiguous
-
universal
-
specific
D.
specific
The genetic code is degenerate, i.e, a given amino acid can be specified by more than one codons.
The genetic code inside the cell medium is said to be non-ambiguous because a particular condon always codes are same amino acid. But in certain rare cases the genetic code is found to be ambiguous, i.e some condon code for different amino acids under different conditions. The genetic code is almost universal.
Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle be some particular restriction enzyme?
-
5'-CGTTCG -3'
3'-ATCCTA-5' -
5'-GATATG-3'
3'-CTACTA-5' -
5'-GAATTC-3'
3'CTTAAG-5' -
5'-CACGTA-3'
3'-CTCAGT-5'
C.
5'-GAATTC-3'
3'CTTAAG-5'
The palindromic base sequence is a sequence in double -stranded nucleic acids that read the same on both strands when reading one strand from left to right and the other from right to left (i.e both strands read 5' ->3'). Out of the given options
5' - GAATTC - 3'
3' - CTTAAG-5'
Is a palindromic sequence that can be cut at about the middle by a particular restriction enzyme.
DNA and RNA segment tagged wit a radioactive molecule is called
-
vector
-
probe
-
clone
-
plasmid
B.
probe
The probe is a defined nucleic acid molecule that can be used in molecular hybridization sequence that is complementary to it, by virtue of a label carried by the probe. The label may be radioactive or non- radioactive. Nucleic acid probes have a wide range of applications such as in the detection of microorganisms in clinical specimens, in food and water samples, in the detection of genetic diseases, etc.
Genetic engineering has been successfully used for producing
-
transgenic mice for testing safety to polio vaccine before use in humans
-
transgenic models for studying new treatments for certain cardiac diseases
-
transgenic cow -Rosie which produces high-fat milk for making ghee
-
animals like bulls for farm work as they have a super power
A.
transgenic mice for testing safety to polio vaccine before use in humans
Transgenic mice are being developed for use in testing the safety of vaccines before they are used on humans. Transgenic mice are being used for testing toxicity of drugs. Transgenic animals are made that carry genes, which make them more sensitive animals. They are then exposed to the toxic substances and the effects studied. Toxicity testing in such animals will allow us to obtain results in less time.
Satellite DNA is useful tool in
-
Organ transplantation
-
sex determination
-
forensic science
-
genetic engineering
C.
forensic science
Britten and his coworkers (1996-68) have demonstrated that many vertebrate DNAs reassociate, especially, If broken into smaller pieces. This observation gave rise to the hypothesis that certain short sequences of bases are repeated hundred or more time in such DNAs. Such DNAs have been called repetitive or satellite DNAs have been called repetitive or satellite DNAs. All eukaryotes except years contain satellite DNA. Satellite DNA region like VNTR/RFLP are the basis of DNA fingerprinting (forensic science).
Which one of the following does not follow the central dogma of molecular biology?
-
Pea
-
Mucor
-
Chlamydomonas
-
HIV
D.
HIV
The central dogma a proteins synthesis is expressed as
Temin described the presence of an enzyme, ie, reverse transcriptase or RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, which controls the synthesis of DNA from a single strand of RNA. D-Baltimore also described the presence of this enzyme in RNA tumour viruses. The presence of this enzyme changed the central dogma of protein synthesis into central dogma reverse.
Which of the following is used in gene cloning?
-
Nucleoids
-
Lomasomes
-
Mesosomes
-
Plasmids
D.
Plasmids
Plasmids are extrachromosomal genetic elements (DNA) found in bacterial cells. These can exist and replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. Nowadays plasmids are widely used as vectors to produce recombinant DNA for gene cloning.
Which of the following is used in gene cloning?
-
Nucleoids
-
Lomasomes
-
Mesosomes
-
Plasmids
D.
Plasmids
Plasmids are extrachromosomal genetic elements (DNA) found in bacterial cells. These can exist and replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. Nowadays, plasmids are widely used as vectors to produce recombinant DNA for gene cloning.
Which one of the following is now being commercially produced by biotechnological procedures?
-
Nicotine
-
Morphine
-
Quinine
-
Insulin
D.
Insulin
Nowadays, genetically engineered insulin is being produced at commercial level. the biotechnological procedure involves the synthesis of two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B insulin chains. The two DNA sequences or genes are made to fuse with plasmids and later allowed to form insulin chains.
In eukaryotic cell transcription, RNA splicing and RNA capping take place inside the
-
ribosomes
-
nucleus
-
dictyosomes
-
ER
A.
ribosomes
Transcripiton involves the transfer of genetic information from DNA to functional mRNA. In eukaryotes, the modification of newly formed primary mRNA transcripts (pre- m-RNA) to produce functional mRNA is called RNA processing or post-transcriptional modification. it occurs in the nucleus and involves gene-splicing (i.e removal of introns from primary transcript and splicing together of exons) and capping involves the formation of a cap at 5' end by condensation of guanylate residues. The fully processes mRNA molecules are exported from the nucleus to the ribosomes for translation in the cytoplasm.
The lac operon consists of
-
four regulatory genes only
-
one regulatory gene and three structural genes
-
two regulatory genes and two structural genes
-
three regulatory genes and three structural genes
B.
one regulatory gene and three structural genes
Lac operon is the operon that regulates lactose metabolism in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Its form wast first postulated in 1961 by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod to explain the control of β- galactosidase synthesis and for this work, they were awarded Nobel Prize. Lac operon system or inducible operon system consists of regulator gene (i) promoter gene (z, y and a), repressor protein and inducer.
Drosophila
Sickle cell anaemia is
-
an autosomal-linked dominant trait
-
caused by substitution of valine by glutamic acid in the β-globin chain of haemoglobin
-
caused by a change in a base pair of DNA
-
characterised by elongated sickle-like RBCs with a nucleus
C.
caused by a change in a base pair of DNA
Sickle-cell anaemia is caused by a change in a single base DNA. It is genetic disease reported from negroes. The individuals of stickle-cell anaemia are immune to malaria.
There is no DNA in
-
an enucleated ovum
-
mature RBCs
-
a mature spermatozoan
-
hair root
A.
an enucleated ovum
The chromatin material inside the nucleus is composed of DNA, some proteins and RNA. In fact it is DNA- protein complex basically. Thus, in an enucleated ovum, DNA will be absent.
Study the pedigree chart given below.
what does it show?
-
Inheritance of a sex-linked inborn error of metabolism like phenylketonuria
-
Inheritance of a condition like phenylketonuria as an autosomal recessive trait
-
The pedigree chart is wrong as this is not possible
-
Inheritance of recessive sex-linked diseases like haemophilia
D.
Inheritance of recessive sex-linked diseases like haemophilia
In the given pedigree chart, squares are representing males and circles females. In an F1 generation, 1-male and 1- female are diseased and in next generation the only male is diseased. This shows the inheritance of a recessive sex-linked disease.
Which one of the following is the correct matching of three items and their grouping category?
-
Items
Group
Malleus, incus, cochlea
Ear ossicles
-
Items
Group
IIium, ischium, pubis
Coxal bones of pelvic girdle
-
Items
Group
Actin, myosin,
Rhodopsin
Muscle proteins
-
Items
Group
Cytosine, uracil, thiamine
Pyrimidines
D.
|
Items |
Group |
|
Cytosine, uracil, thiamine |
Pyrimidines |
There are found total five nitrogenous, bases in nucleic acids. Out of this adenine, guanine (purines) and cytosine, thymine (pyrimidines) are present in DNA, while RNA contains uracil in place of thymine (both pyrimidines) along with rest 3 similar to DNA.
Removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in transcription unit is called
-
splicing
-
tailing
-
transformation
-
capping
A.
splicing
In some eukaryotes, genes consist of coding nucleotides sequences, which are separated from each other by blocks of non-coding sequences. The coding sequences here are called exons and non-coding sequences are called introns. The primary transcript from a typical eukaryotic gene contains introns as well as exons. The introns are removed from this primary transcript by a process called RNA splicing.
Whose experiments cracked the DNA and discovered unequivocally that is genetic code is a triplet?
-
Nirenberg and Mathaei
-
Hershey and Chase
-
Morgan and Sturtevant
-
Beadle and Tatum
A.
Nirenberg and Mathaei
The existence of a triplet code was simply an assumption till 1961 when Nirenberg and Methaei proved its existence by experiment. They were able to synthesise artificial mRNA, which contained only one nitrogenous base, ie, uracil. This synthetic poly-U sequence was then placed in a cell-free system containing protein synthesizing enzymes (extracted from bacterium E. coil) and 20 amino acids together with necessary ATP. During the process, a small polypeptide molecule was produced, which was formed by the linking of phenylalanine. This issuggested that UUU is code for phenylalanine. Nirenberg got Nobel Prize for his contributions.
select the incorrect statement from the following
-
Linkage is an exception to the principle of independent assortment in heredity
-
galactosemia is an inborn error of metabolism
-
small population size results in a random genetic drift in a population
-
baldness is a sex-limited trait
D.
baldness is a sex-limited trait
Baldness is not a sex -limited trait.
The linkage is an exception to the principle of independent assortment in heredity. Galactosemia is a hereditary disease that is caused by the lack of a liver enzyme required to digest galactose.
Small population size results in a random genetic drift in population.
Semiconservative replication of DNA was first demonstrated in
-
Drosophila melanogaster
-
Escherichia Coli
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae
-
Salmonella typhimurium
B.
Escherichia Coli
Semiconservative replication of DNA was first demonstrated in E.coil. According to the semiconservative mode proposed by Waston and Crick, each strand of the two double helices formed would have one old and one new strand. The semiconservative nature of DNA of replication was proved by the experiment of Meselson and Stahl (1958).
Transgenic plants are
-
produced by a somatic embryo in an artificial medium
-
generated by introducing foreign DNA into a cell and regenerating a plant from that cell
-
Produced by protoplast fusion in the artificial medium
-
grown in the artificial medium after hybridization in the field
B.
generated by introducing foreign DNA into a cell and regenerating a plant from that cell
The plants obtained through genetic engineering contain a gene or genes usually from an unrelated organism, such genes are called transgenes and the plants containing transgenes are known as transgenic plants. These plants are often called as genetically modified or GM crops, eg, Flavor saur transgenic for identification, expressing the gene activity in time to produced several chemicals likes fatty acids sugars cellulose, rubber, etc.
What is not true for genetic code?
-
A condon in mRNA is read in a non-contiguous fashion
-
It is nearly universal
-
It is degenerate
-
It is unambiguous
A.
A condon in mRNA is read in a non-contiguous fashion
The general features of genetic code are:
(i) The genetic code is written in linear form, using the ribonuclotide bases that compose mRNA molecule as letters.
(ii) Each word of codon consists of three letters, ie, the codon triplet.
(iii) The genetic code inside the cell medium is said to be non-ambiguous.
(iv) The code is degenerate, ie, a given amino acid can be specified by more than one codons.
(v) The codon contains start and stops signals.
(vi) The code is said to be commaless.
(vii) The code is said to be commaless.
Given below is the diagram of a bacteriophage in which one of the options, all the four parts A, B, C and D are correct?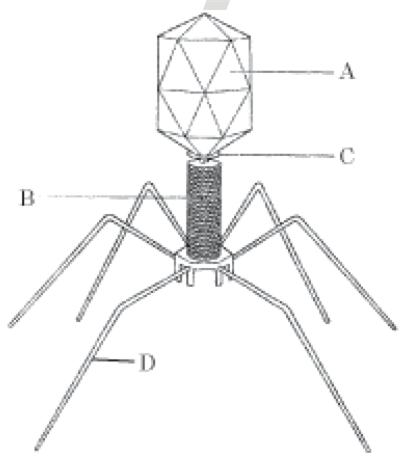
-
A
B
C
D
Tail fibres
Head
Sheath
Collar
-
A
B
C
D
Sheath
Collar
Head
Tail fibres
-
A
B
C
D
Head
Collar
Sheath
Tail fibres
-
A
B
C
D
Collar
Tail fibres
Head
Sheath
C.
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Head |
Collar |
Sheath |
Tail fibres |
Plasmids are the extrachromosomal DNA found in bacterial cells. These are commonly used as vectors in genetic engineering programmes because these have the capacity of binding with eukaryotic DNA.
A bacteriophage is a virus that is parasitic within a bacterium. These also, are the important tools in genetic engineering s cloning vectors.
Gel electrophoresis is used for
-
cutting of DNA into fragments
-
separation of DNA fragments according to their size
-
construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
-
isolation of DNA molecule
B.
separation of DNA fragments according to their size
When genomic DNA extracted from any tissue of a plant or animal species is digested with a restriction enzyme, it is cleaved into segments. The segments of different size can be separated through gel electrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis involves the movement of fragments or molecules from a well created on edge of the gel.
Polymase is formed by
-
several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
-
many ribosomes attached to a strand of endoplasmic reticulum
-
a ribosome with several subunits
-
ribosomes attached to each other in a linear arrangement
A.
several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
In prokaryotes, ribosomes attach to the 5 end of mRNA as soon as transcription begins. A bunch of ribosome moves along a single m RNA molecules adding 15 amino acids second to the polypeptide chain, almost the same speed at which RNA polymerase transcribes the mRNA. The group of ribosomes together with single mRNA molecules, they are translating is called polysome. The use of polysomes si advantageous to a cell since the overall rate of protein synthesis is increased compared to the rate that would occur if there were no polysomes.
In eukaryotic cells, the ribosomes are attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum by ribophorin protein.Electron microscopy reveals that membranes of homogenised reveal that membranes of homogenised endoplasmic reticulum disrupt to form closed vesicles called microsomes.
In the DNA molecule
-
the total amount of purine nucleotides and pyrimidine nucleotides is not always equal
-
there are two strands, which run parallel in the 5' →3' direction
-
the proportion of adenine in relation to thymine varies with organism
-
the are two strands, which run antiparallel-one in 5'-3' direction and other in 3' →5'
D.
the are two strands, which run antiparallel-one in 5'-3' direction and other in 3' →5'
In DNA molecule the adjacent deoxyribonucleotides are joined in a chain by phosphodiester bridges or bonds, which link the 5' carbon of deoxyribose of one mononucleotide unit with 3' carbon of deoxyribose of next mononucleotide unit, According to Waston and Crick DNA molecule consists of two such polynucleotide chains wrapped helically around each other, with the sugar-phosphate chain on the outside and purine and pyrimidine on the inside of helix. Two strands run antiparallel, ie, one strand have phosphodiester linkage in 3'→5' direction while another strand has phosphodiester linkage in 5' →3' direction.
Chargaff (1950) suggested that despite wide compositional variations exhibited by different types of DNA the total amount of purines equalled the total amount of purines equaled the total amount of pyrimidines (A + G = T + C)
Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it?
-
Thymine, Uracil - Pyrimidines
-
Uracil, Cytosine - Pyrimidines
-
Guanine, Adenine - Purines
-
Adenine, Thymine - Purines
D.
Adenine, Thymine - Purines
DNA and RNA the principal genetic materials of living organisms are chemically called nucleic acids. These are polymers of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of phosphoric acid, a Pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous bases are of two types, ie, Purine and pyrimidines.
Prices are heterocyclic and two rings compound, eg, adenine, guanine.
Pyrimidines are single ring compound, eg, thymine, cytosine, uracil.
Cry-I endotoxins obtained from Bacillus thringiensis are effective against
-
mosquitoes
-
flies
-
nematodes
-
boll worms
B.
flies
Insect-resistant transgenic plants contain either a gene from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis or some other gene. The cry gene of bacillus thuringiensis produces a protein which forms crystalline inclusion in the bacterial strains. Cry-I endotoxins are effective gains Lepidoptera (eg flies). Cry- V and Cry-VI proteins are effective against are ingested by insects, they are dissolved in the alkaline juices present in the midgut lumen. The gut proteases process them hydrolytically to release the core toxic fragments. The toxic fragments are believed to bind to specific high-affinity receptors present in the brush border of midgut epithelial cells and causing their swelling and eventual lysis.
What is antissense technology?
-
A cell displaying a foreign antigen used for synthesis of antigens
-
Production of somaclonal variants in tissue cultures.
-
When a piece of RNA that is complementary to sequence is used to stop expression of a specific gene.
-
all mutations, whether dominant or recessive are expressed in haploids
C.
When a piece of RNA that is complementary to sequence is used to stop expression of a specific gene.
The antisense RNA technology simply involves the synthesis of RNA molecules that are complementary to the mRNA molecules produced by transcription of a given gene. Usually t his antisense RNA will not contain the regulatory sequences required for translation but even if does it will not usually specify a functional product. Instead, most antisense RNAs contain multiple termination codons in all three reading frames. However, when antisense RNA molecules are present in the same cytosol with sense (mRNA) molecules of a gene, the antisense RNA and mRNA molecules will anneal to form duplex RNA molecules. These duplex RNA molecules cannot be translated thus, the presence of antisense RNA will block translation of the mRNA of the affected gene.
The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with
-
DNA ligase
-
endonucleases
-
DNA polymerase
-
exonucleases
A.
DNA ligase
DNA ligase is used to seal the nicks that remain in recombinant DNA molecule. In fact, DNA ligase joins together the neighbouring nucleotides flanking a discontinuity in a DNA strand by forming a phosphodiester bond. A recombinant DNA molecules is a vector into which the desired DNA fragment has been inserted to enable its cloning in an appropriate host.
Endonucleases are the enzymes that produce internal cuts called cleavage in DNA molecules. A class of endonucleases cleaves DNA only within or near those sites, which has specific base sequences, such endonucleases are known as restriction endonucleases.
Exonucleases are enzymes that remove one or more nucleotide from the free ends.
DNA polymerase is the enzyme, which causes polymerization of nucleotides during DNA replication.
Telomere repetitive DNA sequences control the function of eukaryotic chromosomes because they
-
act as replicons.
-
are RNA transcription initiator
-
help chromosome pairing
-
prevent chromosome loss
D.
prevent chromosome loss
Telomeres are ends of a chromosome, have repetitive DNA sequences and are stable and resistant to exonuclease digestion hence, essential for chromosome stability.
Molecular basis of organ differentiation dpends on the modulation in transcription by
-
RNA polymerase
-
ribosome
-
transcription factor
-
anticodon
C.
transcription factor
Transcription factor is molecular basis of organ differentiation.
Differentiation of organs and tissues in a developing organism, is associated with
-
developmental mutations
-
differential expression of genes
-
lethal mutations
-
deletion of genes
B.
differential expression of genes
Differentiation of organs and tissues in a developing organism, is associated with differential expression of genes. In regulation of gene expression the chromosomal proteins play an important role. The chromosomal proteins are of two types histones and non-histones. The regulation of gene expression involves an interaction between histones and non-histones.
The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain growth
-
result in transcription
-
polymerize in the 3’ - to - 5’ direction and forms replication fork
-
prove semi-conservative natuire of DNA replication
-
polymerize in teh 5’ - to - 3’ direction and explain 3’ - to - 5’ DNA replication
A.
result in transcription
The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain growth polymerize in the 5' - to -3' direction. The replicated DNA results in transcription.
The two polynucleotide chains in DNA are
-
parallel
-
discontinuous
-
antiparallel
-
semiconservative
C.
antiparallel
In 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick suggested that in a DNA molecule there are two polynucleotide chains arranged antiparallel or in opposite directions.
A sequential expression of a set of human genes occurs when a steroid molecule binds to the
-
transfer RNA
-
messenger RNA
-
DNA sequence
-
ribosome
C.
DNA sequence
The steroid hormone receptor protein complex activate transcription of target gene by binding to specific DNA sequence.
Which antibiotic inhibits interaction between t-RNA and m-RNA during bacterial protein synthesis?
-
Erythromycin
-
Neomycin
-
Streptomycin
-
Tetracycline
D.
Tetracycline
Tetracyclin interfere with the attachment of t-RNA carrying the amino acid to the m-RNA-ribosome complex preventing the addition of amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. Streptomycin interfere with the initial steps of protein synthesis by changing the shape of 30S portion of 70S prokaryotic ribosome.
Erythromycin refers with 50S portion of the 70S prokaryotic ribosome.
In which mode of inheritance do you expect more maternal influence among the off spring?
-
Autosomal
-
Cytoplasmic
-
Y-linked
-
X-linked
B.
Cytoplasmic
The more maternal influence can be expected in the cytoplasmic inheritance (i.e. the inheritance of genes contained in the cytoplasm of a cell, rather than the nucleus. The reason is that the female reproductive cell or the egg has a large amount of cytoplasm containing many such organelles which contain their own genes and can reproduce independently (e.g., mitochondria and chloroplast) and which are consequently incorporated into the cytoplasm of all the cells of the embryo. The male reproductive cells (sperm or pollen) consist almost solely of a nucleus. Cytoplasmic organelles are thus, not inherited from the male parent.
This is why, the cytoplasmic inheritance is also called maternal inheritance.
Genes located on Y-chromosome are called Y-genes and their inheritance is called Y-linked inheritance. This carries the paternal influences.
A gene located in the X-chromosomes is said to be X-linked and its inheritance is called X-linked inheritance. In this, a male transmits his X-chromosome only to his daughters while a female transmits one of her X-chromosomes to the offspring of both sexes.
Amino acid sequence, in protein synthesis is decided by the sequence of
-
t-RNA
-
m-RNA
-
c-DNA
-
r-RNA
B.
m-RNA
In the process of protein synthesis, the messenger RNA (m-RNA) is responsible for carrying the genetic code transcribed from DNA to specialized sites within the cell (called ribosomes) where the information is translated into protein composition. The sequence of amino acids in a particular protein is determined by the sequence of t-RNA, c-DNA or r-RNA do not decide the amino acid sequence in protein synthesis.
Antiparallel strands of a DNA molecule means that
-
one strand turns anti-clockwise
-
the phosphate groups of two DNA strands, at their ends, share the same position
-
the phosphate groups at thestart of two DNA strands are in opposite position (pole)
-
one strand turns clockwise
C.
the phosphate groups at thestart of two DNA strands are in opposite position (pole)
J.D. Watson and F.H.C. Crick (1953) showed that DNA has a double helical structure with two polynucleotide chains structure with two polynucleotide chains connected by hydrogen bonds and running in opposite directions (antiparallel). The antiparallel strands of a DNA molecule means that the phosphate groups at the start of two DNA strands are in opposite position (pole).
The association of histone H1 with a nucleosome indicates:
-
Transcription is occurring
-
DNA replication is occurring
-
The DNA is condensed into a Chromatin Fibre
-
The DNA double helix is exposed
C.
The DNA is condensed into a Chromatin Fibre
Thalassemia and sickle cell anemia are caused due to a problem in globin molecule synthesis. Select the correct statement
-
Both are due to a qualitative defect in globin
chain synthesis -
Both are due to a quantitative defect in globin chain synthesis
-
Thalassemia is due to less synthesis of globin molecules
-
Sickle cell anemia is due to a quantitative problem of globin molecules
C.
Thalassemia is due to less synthesis of globin molecules
AGGTATCGCAT is a sequence from the coding strand of a gene. What will be the corresponding sequence of the transcribed mRNA?
AGGUAUCGCAU
UGGTUTCGCAT
UCCAUAGCGUA
ACCUAUGCGAU
A.
AGGUAUCGCAU
Coding strand and mRNA has same nucleotide sequence except, ‘T’ – Thymine is replaced by ‘U’–Uracil in mRNA.
Many ribosomes may associate with a single mRNA to form multiple copies of a polypeptide simultaneously. Such strings of ribosomes are termed as
Polysome
Polyhedral bodies
Nucleosome
Plastidome
A.
Polysome
The phenomenon of association of many ribosomes with single m-RNA leads to the formation of polyribosomes or polysomes or ergasomes.
Which of the following is true for nucleolus?
Larger nucleoli are present in dividing cells
It is a membrane-bound structure
It is a site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis
It takes part in spindle formation
C.
It is a site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis
The nucleolus is a non-membranous structure and is a site of r-RNA synthesis.
Which of the following is commonly used as a vector for introducing a DNA fragment in human lymphocytes?
Retrovirus
Ti plasmid
pBR 322
λ phage
A.
Retrovirus
Retrovirus is commonly used as vector for introducing a DNA fragment in human lymphocyte.
Gene therapy: Lymphocyte from the blood of the patient are grown in culture outside the body, a functional gene is introduced by using a retroviral vector, into these lymphocyte.
Select the correct match
Ribozyme - Nucleic acid
F2 × Recessive parent - Dihybrid cross
G. Mendel - Transformation
T.H. Morgan - Transduction
A.
Ribozyme - Nucleic acid
A ribozyme is a catalytic RNA, which is a nucleic acid.
The experimental proof for semiconservative replication of DNA was first shown in a
Fungus
Bacterium
Virus
Plant
B.
Bacterium
Semi-conservative DNA replication was first shown in Bacterium Escherichia coli by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl.
Which of the following pairs is wrongly matched?
Starch synthesis in pea: Multiple alleles
ABO blood grouping: Co-dominance
T.H. Morgan: Linkage
XO type sex determination: Grasshopper
A.
Starch synthesis in pea: Multiple alleles
Starch synthesis in pea is controlled by a pleiotropic gene.
hnRNA undergoes two additional processes. Out of them in one process an unusual nucleotide (methyl GPT) is added to the 5' end of the molecule. What would you call this?
Tailing
Splicing
Termination
Capping
D.
Capping
The process of addition of methyl GPT at the 5' end of hnRNA is known as capping. Enzyme guanly transferase catalyses this process.
Cap is essential for the formation of mRNA- Ribosome complex. Translation is not possible if cap is lacking, because cap is identified by 18 SrRNA of ribosome unity.
Variation in gene frequencies within a population can occur by chance rather than by natural selection. This is referred to as
Genetic flow
Genetic drift
Random mating
Genetic load
B.
Genetic drift
Variation in gene frequencies within populations can occur by chance and is called genetic drift.
Which of the following DNA sequences qualifies to be designated as a palindrome?
5'-GACCAG'3 in one strand
3'GACCAG-5' in one strand
5-GACGAG-3', 3'-CIGGIC-5'
5'-AGCGCT-3', 3'-TCGCGA-5'
D.
5'-AGCGCT-3', 3'-TCGCGA-5'
The palindromic sequence is the sequence of nucleotides whose reading is same when read from both 5'→3' and '3→5' direction. It is the mirror image of the sequence in its first half.
Munch hypothesis is based on
Translocation of food due to Turgor Pressure (TP) gradient and imbibition force
Translocation of food due to Turgor Pressure (TP) gradient
Translocation of food due to imbition force
None of the above
B.
Translocation of food due to Turgor Pressure (TP) gradient
Munch hypothesis is based on the movement of phloem sap along a turgor pressure gradient. The mass flow of organic solutes takes place from the site of higher concentration, (source) to the site of lower concentration (sink).
Biolistic technique is used in
Gene transfer process
Tissue culture process
Hybridisation process
Germplasm conservation process
A.
Gene transfer process
Biolistics is a technique for introducing genetic material into living cells, especially plant cells in which DNA- coated microscopic particles are fired into the cell using a special gun.
Genetic material found in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is
Double stranded RNA
Single stranded RNA
Double stranded DNA
Single stranded DNA
B.
Single stranded RNA
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is the causal organism of AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome). It is a retrovirus belonging to the family-Retroviridae. The core of HIV contains two molecules of single-stranded RNA (as genetic material) and reverse transcriptase.
DNA replication occurs in
G1-phase
S-phase
G2-phase
M-phase
B.
S-phase
The s-phase of the cell cycle is also called 'synthesis phase, in which the cell synthesizes the replica of its genome, ie, DNA replication occurs during this stage, which ultimately results to the duplication of chromosomal material.
The vector for T-DNA is
Thermus aquaticus
Salmonella typhimurium
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Escherichia coli
C.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
The vector is a plasmid or virus DNA used to introduce genes into a host cell, where the genes may be amplified, gene cloning or otherwise manipulated.
Viroids have
ssRNA not enclosed by a protein coat
ssDNA not enclosed by a protein coat
dsDNA enclosed by a protein coat
dsRNA enclosed by protein coat
A.
ssRNA not enclosed by a protein coat
Viroids are small, single-stranded, circular RNA molecules not enclosed by a protein coat. They were discovered by TO Diener in 1971. Viroid replication requires host-encoded RNA polymerase.
Probes, used in DNA fingerprinting, are initially
Single-stranded RNA
Mini-satellite
19base long oligonucleotide
All of the above
B.
Mini-satellite
Probes used for DNA fingerprinting are usually prepared from mini-satellite or microsatellite DNA.
Satellite DNA is a useful tool in
Organ transplantation
Sex determination
Forensic science
Genetic engineering
C.
Forensic science
All eukaryotes except yeast contain satellite DNA. Satellite DNA regions like NTR/RFLP are the basis of DNA fingerprinting (forensic science).
Select the correct statement from the one’s given below with respect to dihybrid cross.
Tightly linked gene on the same chromosome show higher recombinations
Genes for apart on same chromosomes show very few recombination
Genes loosely linked on the same chromosomes show similar recombination as lightly linked ones
Tightly linked genes on the same chromosomes show very few recombination
D.
Tightly linked genes on the same chromosomes show very few recombination
Morgan and his group found that when genes were grouped on the same chromosomes some genes were very tightly linked while other were loosely linked.
Maximum green house gases are released by
India
Britain
USA
France
C.
USA
According to Homes at all 1933, USA is responsible for the largest portion of man-made the contribution to the greenhouse effect 21% followed by Russia 14%
Allelic sequence variation where more than one variant allele at a locus in a human population with a frequency greater than 0.01 is referred to as
DNA polymorphism
Multiple allelism
SNP
EST
A.
DNA polymorphism
Allelic sequence variation is described as DNA polymorphism if more than one variant (allele) at a locus occurs in the human population with a frequency greater than 0.01. In simple terms, if an inheritable mutation is observed in a population at high frequency. It is referred to as DNA polymorphism.
The statement All biological catalysts are protein is no longer valid after the discovery of
ribonuclease
ribozyme
RNAs
DNAs
B.
ribozyme
A ribozyme is an RNA molecule (non-proteinaceous) and is capable of catalysing reactions.
The chromosome of cell duplicate during the
S-phase of cell cycle
G1-phase of cell cycle
G2-phase of cell cycle
Prophase of cell division
A.
S-phase of cell cycle
S-phase (synthesis phase) is the part of the interphase of cell cycle occurring between G, and Gy-phase. This is the phase in which DNA replication takes place, i.e. chromosomes are replicated.
The fact that DNA is a genetic material was established by the experiment of
Meselson and Stahl
Hershey and Chase
Avery, Macleod and McCarty
Rosalind Franklin and Kornberg
B.
Hershey and Chase
The experiment of Hershey and Chase by bacteriophage first time proved that DNA is a genetic material.
Which of the following is the Pribnow box?
5′-TATAAT-3′
5′-TAATAT-3′
5′-AATAAT-3
5′-ATATTA-3′
A.
5′-TATAAT-3′
The promoters are bacterial and viral genes usually contains a consensus sequence of 5'- TATAA-3' forming RNA polymerase binding site or the Pribnow box, after its discoverer. Pribnow box lies within the promoter about 10 base pairs before the starting point of transcription.
The genome of Caenorhabditis elegans consists of
3 billion base pairs and 30,000 genes
12 million base pairs and 6000 genes
4.7 million base pairs and 4000 genes
97 million base pairs and 18,000 genes
B.
12 million base pairs and 6000 genes
Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic (1mm) nematode that normally lives in soil. It has become one of the model organism in biology.
The part of the bacterial chromosomes sharing homology with genome fragment transferred from the recipients to cell during emrozygote formation is known as
Eugenic
Exogenate
Endogenate
Dysgenic
C.
Endogenate
ENdogenate is the native DNA of the recipient bacterial cell which shares homology with the DNA Fragment inserted into it.
Exogenate is the DNA fragment that has been transferred into a recipient cell.
Eugenic is the study or practice of attempting to improve the human gene pool by encouraging reproduction among people with desirable traits. Dysgenics is the study of factors causing propagation of undesirable or disadvantageous genes and traits.
In 1944, Avery, McCarty and MacLeod isolated substance from heat killed a virulent form of bacteria and added to the non-virulent form of bacteria which changed the non-virulent to virulent from this substance can be destroyed by
DNAse
Protease
Lipase
Amylase
A.
DNAse
Avery, MacLeod and McCarty carried out an experiment from which they reported that DNA is a substance that causes bacterial transformation from non-virulent to virulent bacteria, but DNAase acts as a waste management endonucleases responsible for DNA fragmentation.
Match the following column I with column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Carcinogen | 1. Cancerous Tumour |
| B. Anaphase -I | 2. Disjunction |
| C. Mitosis | 3. Synapse |
| D. Zygotene | 4. Plectonemic Coiling |
A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
A-2, B-3, C-1, D-4
A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
A.
A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
Carcinogen causes cancerous tumour disjunction of chromosomes takes place in anaphase I and II when chromosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell.
Plectonemic coiling refers to inter-twining of a double helix DNA molecule in such a way that for its correction unwinding of DNA helix molecule is required, this take place in mitosis in which sister chromatids are tightly coiled upon each other. In the zygotene stage, homologs login to synapse by coming to approximate alignment.
The codon for anticodon 3-UUUA-5' is
3-AAU-5
5-UAAA-3
5-AAAU-3
3-UAAU-5'
C.
5-AAAU-3
In RNA the thymine of DNA is replaced by uracil. Codon and anticodon both found on RNA and are complementary to each other so, the codon for anticodon 3-UUUA-5' will be 5-AAUU-3.
A kind of biotechnology involving manipulation of
DNA is
DNA replication
Genetic engineering
Denaturation
Renaturation
B.
Genetic engineering
In genetic engineering DNA technology is applied to several biotechnological processes for obtaining particular biochemical improvement of the genetic makeup of an organism and fighting genetic defects.
A polygenic inheritance in human beings is
Skin colour
Sickle cell anaemia
Colour blindness
Phenylketonuria
A.
Skin colour
Genes that when acting individually have a small effect but that collectively produce a significant phenotypic expression are called polygenes, e.gr inheritance of kernel colour in wheat and skin colour in human.
Nucleic acid segment tagged with a radiactive molecule is called
Clone
Probe
Plasmid
Vector
B.
Probe
The probe is 15-30 bases long radioactive labelled oligonucleotides (RNA or DNA) used to detect complementary nucleotide sequence, used for disease diagnosis, etc.
The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain growth
Results in transcription
Polymerise in the 3' to 5' direction and forms replication fork
Prove semi-conservative nature of DNA replication
Polymerise in the 5' to 3' direction and explain 3' to 5 DNA replication
A.
Results in transcription
The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain growth polymerise in the 5' to 3' direction. The replicated DNA result in transcription.
One gene-one enzyme relationship was established for the first time in
Neurospora crassa
Salmonella typhimurium
Escherichia coli
Diplococcus pneumoniae
A.
Neurospora crassa
One gene-one enzyme relationship was initially proposed by Beadle and Tatum and based on the experiments conducted on Neurospora crassa. They were awarded by Nobel Prize in 1958 for this achievement.
Balbiani rings are the structural features of
allosomes
polytene chromosomes
autosomes
lampbrush chromosomes
B.
polytene chromosomes
Balbiani rings are large RNA puffs reported in the salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus insect during larval development.
Jumping genes in maize were discovered by
Hugo de Vries
Barbara McClintock
T H Morgan
Mendel
B.
Barbara McClintock
Barbara McClintock discovered 'Jumping genes' or 'movable genetic elements' in maize. These can move from one location to another on the chromosome.
R W Hedges and A E Jacob (1974) introduced the term 'transposon' to jumping genes.
Hugo de Vries introduced the term 'mutation'.
T H Morgan proposed the 'gene theory' and crossing over.
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822- 1884) is known as the 'Father of Genetics'. It leads to the formulation of laws of inheritance which was carried out by Mendel.
DNA element with ability to change position is called
cistron
transposon
intron
recon
B.
transposon
Transposon is a DNA segment or genetic element moving from one chromosome to another. It was introduced by R W Hedges and A E Jacob in 1974.
Cistron is the functional unit of DNA molecules as it codes for a particular gene product.
Recon is the cross- over unit or it is segment of DNA which participates in crossing over.
Introns are the interrupted genes which do not form the part of mRNA and are further removed from primary mRNA during gene expression in eukaryotes.
Initiation codon is
UUU
UGA
AUG
UAG
C.
AUG
AUG codes for Methionine (Met) that is used as a start signal in protein syntheis. Hence, it is an initiation codon.
Also, in prokaryotes, codons GUG and UUG are the start codons.
UAA (ochre), UAG (amber) and UGA (opal) are the non- sense codons as they do not code for any amino acid. Their main function is to terminate the message for gene controlling protein synthesis. Therefore, termed as chain termination or stop codons.
UUU (uracil) codes for phenylalanine.
DNA mutiplication is called
translation
replication
transduction
transcription
B.
replication
DNA multiplication takes place by replication at S- phase of interphase during cell cycle. It is semi- conservative in nature.
Transcription is the mode by which DNA passes its genetic information to mRNA. It is the first step in protein synthesis which takes place in nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
Translation is the synthesis of a chain of polypeptide by mRNA. It takes place at the site of ribosomes and involves three steps- Initiation, Elonagtion and Termination.
Transduction is the transfer of genes from one bacterial cell to another by means of a virus.
A eukaryotic gene contains two kinds of base sequences. Which of these plays an important role in protein synthesis?
Introns
Exons
Both (a) and (b)
None of these
B.
Exons
In eukaryotic genes some non- coding parts are interspersed between coding parts. These non- coding parts are called introns and coding sequence are known as exons, ie, exons play an important role in protein synthesis.
Repressor protein is produced by
regulator gene
operator gene
structural gene
promoter gene
A.
regulator gene
The regulator gene is responsible for the synthesis of a protein called repressor. It may be active or inactive (aporepressor). The active repressor is normally seen in inducible systems while aporepressor is seen in repressible system. The repressor has an affinity for operator gene.
The back bone of RNA consists of which of the following sugar?
Deoxyribose
Ribose
Sucrose
Maltose
B.
Ribose
The back bone of RNA is made up of ribose sugar (5- carbon) whereas DNA is made up of deoxyribose sugar.
Stop codons are
AUG, GUG
UAA, UGA, UAG
UAC, UGG
AGU, AGA, UAC
B.
UAA, UGA, UAG
UAG, UAA, UGA are three stop codons or non- sense codons. They do not code for any amino acid.
AUG works as an initiation codon in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In rare cases, GUG is used as an initiation codon in bacterial protein synthesis.
AUG is used to code for tyrosine, UGG codes for tryptophan, AGU codes for serine and AGA codes for argenine.
RNA is not found in
chromosome
plasmalemma
nucleolus
ribosome
B.
plasmalemma
RNA is not found in plasmalemma. It is the cell membrane which also lines the connecting plasmodesmata.
Sequence of DNA (non-coding) is known as
exon
intron
cistron
none of these
B.
intron
Introns are DNA sequence lying within a coding sequence (exons) but not usually encoding cell product and resulting so called split genes. Cistron is a segment of linear DNA encoding a specific and functional product, usually protein.
Which one of the following makes use of RNA as a template to synthesize DNA?
Reverse transcriptase
DNA dependant RNA polymerase
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
A.
Reverse transcriptase
In 1970 H. Temin and D. Baltimore independently discovered the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This enzyme uses RNA as a template for the synthesis of C-DNA (Complementary DNA).
RNA C- DNA
During transcription holoenzyme RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle like structure at that point. What is that sequence called?
CAAT box
GGTT box
AAAT box
TATA box
D.
TATA box
TATA box is present in eukaryotic promoter region. It has a resemblance with pribnow box of prokaryotes. TATA box was identified by Dr. Hogness and so, it is also called as Hogness box. It is a 7 bp long region located 20 bp upstream to the start point. During the process of transcription, the RNA polymerase (a holoenzyme which has a core unit and a sigma factor for proper initiation of transcription) binds to TATA box due to which DNA assumes a saddle like structure at this place.
E. coli cells with a mutated Z gene of the lac operon cannot grow in medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because
in the presence of glucose, E. coli cells do not utilize lactose
they cannot transport lactose from the medium into the cell
the lac operon is constitutevely active in these cells
they cannot synthesize functional - galactosidase
D.
they cannot synthesize functional - galactosidase
Lac operon is a cluster of genes encoding three proteins that bacteria use to obtain energy from the sugar lactose. There are three structural genes in lac operon.

(i) Lac Z (3063bp)- This genes codes for enzyme - galactosidase. It breaks lactose into glucose and galactose. Therefore, E. coili cells with a mutated Z genes cannot grow in medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because they cannot synthesize functional - galactosidase.
(ii) Lac Y (800 bp)- This gene codes for enzyme galactose permease. It is a membrane bound protein and helps in the transport of metabolites.
(iii) Lac A (800bp)- This gene codes for enzyme - galactose transacetylase. It transfers an acetyl group from acetyl Co- A to - galactosidase.
What's the difference between RNA and DNA?
Base
Sugar
Sugar and base
Phosphate
C.
Sugar and base
DNA has deoxy ribose pentose sugar and four nitrogenous bases i.e. Adenine (A), Guanine (G), both are purines; Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T), both are pyrimidines.
RNA has ribose pentose sugar and four nitrogenous bases as in DNA except Uracil (U) in place of Thymine (T).
In split genes the coding sequences are called
introns
exons
cistrons
operons
B.
exons
Split genes were discovered by Phillip Sharp and Robert Richard. The part of DNA which express itself by making mRNA is called exon. One exon is separated from others by inactive part of DNA called intron. This is called split DNA.
DNA replication generally proceeds in a
5 3 direction
3 5 direction
3 3 direction
5 5 direction
A.
5 3 direction
DNA is made up of double helix of two complementary strands. Both the strands get seperated during replication. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, hence, a process is known as semi- conservative replication.
DNA synthesis or replication always proceeds in 5' 3' direction because DNA polymerase acts on the 3'- OH of the existing strand for adding the free nucleotides.
DNA polymerase enzyme is required for synthesis of
DNA from RNA
RNA from DNA
DNA from DNA
RNA from RNA
C.
DNA from DNA
The enzyme needed for replication of DNA i.e. formation of DNA from DNA is DNA polymerase III. DNA replication is initiated by RNA primer which is later removed by DNA polymerase I.
Which type of DNA is found in bacteria
Helical DNA
Membrane bound DNA
Straight DNA
Circular free DNA
D.
Circular free DNA
Bacteria are prokaryotic in nature, in which typical chromosomes are lacking. DNA is circular and naked as it is not surrounded by histones (basic proteins which are responsible for coiled structure of nucleosome).
The chemical knifes of DNA are
polymerases
ligases
endonucleases
amylases
C.
endonucleases
A restriction enzyme or restriction endonuclease is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within the molecule known restriction sites.
Refer to the given figure and select the correct option regarding its parts labelled as A, B and C.
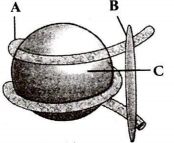
A-Histone octamer, C-DNA
B-H1 histone, C-Histone octamer
A-H1 histone, B-DNA
A-Histone octamer, C-H1 histone
B.
B-H1 histone, C-Histone octamer
The given figure shows nucleosome. Here A is DNA, B is H1 histone and C is histone octamer.
Radio-tracer technique shows that DNA is in
single-helix stage
double-helix stage
multi-helix stage
none of these
D.
none of these
DNA is a helical structure. It could be through X- ray diffractions patterns of DNA studied by Wilkins and Franklin.
Assertion: The honeybee queen copulates only once in her life time.
Reason: The honeybee queen can lay fertilised as well as unfertilised eggs.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Queen is the only fertile female in beehive, having immensely developed ovaries. She lives for several successive years laying about 2000 or more eggs a day. The queen has a remarkable capacity of controlling the fertilisation of its eggs. A fertilised egg is laid in a worker or queen cell, while an unfertilised egg in a drone cell, the latter develops parthenogenetically. The queen mates only once in her life time. The sperms stored in her spermatheca fertilise her eggs as long as she lives.
In a 3.2 Kbp long piece of DNA, 820 adenine bases were found. What would be the number of cytosine bases?
780
1560
740
1480
A.
780
Total DNA = 3.2 Kbp = 3200 bp
Adenine = 820
According to Chargaff's rule
[A] = [T]; [G] = [C]
So, Thymine = 820
Therefore, total A + T content = 820 + 820 = 1640
Also, A + T = 3200 - (G + C)
So, G + C content = 3200 - 1640 = 1560
So, Cytosine = = 780
Some of the steps of DNA fingerprinting are given below. Identify their correct sequence from the options given.
A. Electrophoresis of DNA fragments
B. Hybridisation with DNA probe
C. Digestion of DNA by restriction endonucleases
D. Autoradiography
E. Blotting of DNA fragmentsto nitrocellulose membrane
C - A - B - E - D
C - A - E - B - D
A - E - C - B - D
A - C - E - D - B
B.
C - A - E - B - D
The technique of DNA fingerprinting involves following steps:
(i) Isolation of DNA from sample cell
(ii) Amplification of DNA using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), (if DNA is less in amount).
(iii) Digestion of this DNA by restriction endonucleases (C)
(iv) These DNA fragments are electrophoresed in agarose gel. These fragments can be visualised using EtBr - UV system (A)
(v) Separated DNA fragments are transferred to nitrocellulose membrane using Southern Blotting (E).
(vi) Probing for VNTRs is done using labelled DNA probes (B).
(vii) The hybridised fragment can be detected by autoradiography (D).
Which of the following set of options is used in translation
hnRNA, tRNA, rRNA
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
mRNA, tRNA, hnRNA
hnRNA, rRNA, tRNA
B.
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
hnRNA (heterogeneous nuclear RNA) does not function until it undergoes processing. Post-transcriptional processing converts hnRNA into functional RNA, which then participates in translation (protein synthesis). mRNA, tRNA and rRNA are the functional RNAs which take part in translation.
If the sequence of bases in the coding strand of a double stranded DNA is 5'-GTTCGAGTC-3', the sequence of bases in its transcript will be
5'-GACUCGAAC-3'
5'-CAAGCUCAG-3'
5'-GUUCGAGUC-3'
5'-CUGAGCUUG-3'
C.
5'-GUUCGAGUC-3'
During transcription, one of the two DNA strands functions as template strand and the other functions as coding strand. Template strand serves as template for transcription whereas coding strand does not take part in transcription. Hence, the mRNA produced has base sequence complementary to template strand while similar to coding strand except that thymine (T) is replaced by uracil (U). Here,
Coding strand 5' GTTCGAGTC 3'
Template strand 5' CAAGCTCAG 3'
Transcript 5' GUUCGAGUC 3'
Assertion: One codon may code for more than one amino acid.
Reason: A codon is degenerate and ambiguous.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
D.
If both assertion and reason are false.
The relationship between the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide and nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA is called genetic code. The genetic code is triplet. One codon codes for only one amino acid, hence it is unambiguous and specific. Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the code is degenerate.
What is incorrect about the following figure representing DNA replication?

The direction of DNA replication in strand (i)
The direction of DNA replication in strand (ii)
Discontinuous replication of strand (i)
Discontinuous replication of strand (ii)
C.
Discontinuous replication of strand (i)
DNA polymerase can polymerize nucleotides only in 5' 3' direction on 3' 5' strand because it adds them at the 3' end. Since the two strands of DNA run in antiparallel directions, the two templates provide different ends for replication.
Replication over the two templates thus proceeds in opposite directions. One strand with polarity 3' 5' forms its complementary strand continuously because 3' end of the latter is open for elongation. It is called leading strand.
Replication is discontinuous on the other template with polarity 5' 3' because only a short segment of DNA strand can be built in 5' 3' direction due to exposure of a small stretch of template at one time. Short segments of replicated DNA are called Okazaki fragments.
The binding site of tRNA with mRNA & amino acids respectively are
mRNA with DHU loop and amino acid with CCA end.
mRNA with CCA end and amino acid with anticodon loop
mRNA with anticodon loop and amino acid with DHU loop
mRNA with anticodon loop and amino acid with CCA end
D.
mRNA with anticodon loop and amino acid with CCA end
The binding site of tRNA with mRNA is anticodon loop and with amino acid is CCA end.

During protein synthesis in an organism at one point the process comes to a halt. Select the group of the three codons from the following, from which any one of the three could bring about this halt.
UUU, UCC, UAU
UUC, UUA, UAC
UAG, UGA, UAA
UUG, UCA, UCG
C.
UAG, UGA, UAA
Non-sense codon or terminator codon are the codons that do not code for any amino acid. It is a set of three nucleotides for which there is no corresponding tRNA molecule to insert an amino acid into the polypeptide chain. Protein synthesis is hence terminated and the completed polypeptide released from the ribosome. Three stop codons are UAA (ochre), UAG (amber) and UGA (opal).
Mutations which generate any of these three codons in a position which normally contains a codon specifying an amino acid are known as nonsense mutations.
Assertion: An organism with lethal mutation may not even develop beyond the zygote stage.
Reason: All types of gene mutations are lethal.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Mutations are sudden and abruptive qualitative or quantitative change in the genetic material of an organism. According to their effects on the phenotype mutations may be classified as lethals, subvitals and supcrvitals. Lethal mutations results in death of the cells or organism in which they occur. The organism may not even develop beyond the zygote stage. Subvital reduces the chances of survival. Supervital mutations results in the improvement of biological fitness under certain conditions. There may also be mutations which arc neither harmful nor beneficial to the organisms in which they occur.
Assertion : Replication and transcription occur in the nucleus but translation occurs in the cytoplasm.
Reason : mRNA is transferred from the nucleus into the cytoplasm where ribosomes and amino acids are available for protein synthesis.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
DNA replication is the process of forming a copy of DNA. Transcription is the formation of RNA over DNA template. They both occur in nucleus as the required material DNA and RNA are present in the nucleus.
Translation is the process of protein synthesis. It is separated from transcription in both space and time. It prevents the intermixing of raw materials, protect DNA from respiratory enzymes and ribosomal machinery from nuclease.
Which one of the following pairs of terms/ names mean one and the same thing?
Gene pool - genome
Codon - gene
Cistron - triplet
DNA fingerprinting - DNA profiling
D.
DNA fingerprinting - DNA profiling
Gene pool is the total gene present in a population. Genome is the total genetic constitution of an organism. Codon is the basic unit of genetic code, a sequence of three adjacent nucleotide in DNA or mRNA that code for an amino acid. Gene is the basic unit of heredity; a sequence of DNA nucleotide that encodes a protein.
Cistron is a segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a polypeptide chain. Triplet is a three nucleotides sequence coding for an amino acid.
Therefore, codon triplet
cistron gene
DNA fingerprinting is technically called DNA profiling or DNA typing.
What is true about tRNA?
It binds with an amino acid at it 3' end
It has five double stranded regions
It has a codon at one end which recognizes the anticodon on messenger RNA
It looks like clover leafin the three dimensional structure
A.
It binds with an amino acid at it 3' end
tRNA has four recognition sites among these one is the amino acid attachment site. It has the amino acid attachment site with the 3' terminal - CCA sequence.
Which one of the following correctly represents the manner of replication of DNA?
D.

DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division. It takes place discontinuously. This process consists of 4 main steps:
- Replication Fork formation
- Primer binding
- Elongation
- Termination
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides which are synthesized discontinuously. One strand may synthesize a continuous strand. Both new strands are synthesized in 5' 3' direction. Thus one strand is synthesized forwards and the other backwards.
Which one of the following codons codes for the same information as UGC?
UGU
UGA
UAG
UGG
A.
UGU
UGU codes for the same information as UGC as both code for cystine. UGA and UAG are nonsense codons and UGG codes for tryptophan.
All eukaryotic genes contain two kinds of base sequences. Which of the following plays role in protein synthesis ?
Introns
Exons
Electrons
Both (a) and (b)
B.
Exons
All eukaryotic genes contain two kinds of base sequences ie, introns and exons. Exons are the coding regions which are interrupted by non- coding regions, that is, introns. Exons consist of the information which is required to encode a protein. Introns are removed to make a functioning messenger RNA that can be translated into a protein.
The direction of DNA replication is from :
amino acid end
3' end towards 5' end
5' end towards 3' end
amino terminus to carboxy terminus
C.
5' end towards 3' end
The synthesis of new DNA strand takes place by addition of DNA nucleotides to 3'- OH group of the last nucleotide. of the growing strand. Thus, the synthesis takes place in 5' ➔ 3' direction.
In operon concept, regulator gene functions as:
repressor
regulator
inhibitor
initiator
A.
repressor
Operon is defined as a set of genes transcribed under the control of an operator gene. It is a segment of DNA containing adjacent genes including structural genes, an operator gene, and a regulatory gene. An operon is thus a functional unit of transcription and genetic regulation. In operon model, regulator gene directs the synthesis of proteins. It may be an active repressor or an inactive repressor.
In the lactose operon of Escherichia coli what is the function of promoter
Binding of Gyrase enzyme
Binding of RNA polymerase
Codes for RNA polymerase
Processing of messenger RNA
B.
Binding of RNA polymerase
Promoters contain specific DNA sequences such as response elements that provide a secure initial binding site for RNA polymerase and for proteins called transcription factors that recruit RNA polymerase.
Sex factor in bacteria is
F-replicon
chromosomal replicon
RNA
sex pillies
A.
F-replicon
In bacteria, besides nuclear DNA, there is some extrachromosomal or extranuclear DNA which is known as plasmid. Term plasmid was given by Lederberg (1952). On the basis of their function, the plasmids are of 3 types :
(i) F or fertility factor : Responsible for transfer of genetic material
(ii) R or resistance factor Provides resistance against drugs.
(iii) Colicinogenic factor : Provides colicines which kill other bacteria (other than which produce these colicines).
Most simple amino acid is
lysine
glycine
aspartic acid
nucleic acid
B.
glycine
Glycine is the amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest possible amino acid. The chemical formula of glycine is NH2‐CH2‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids, and is notable as the only one that is achiral.
Which of the following be named for DNA produced from RNA?
A- DNA
B- DNA
C- DNA
Z- DNA
C.
C- DNA
The DNA synthesized on template of RNA by the enzyme reverse transcriptase is called complementary DNA (C-DNA).
A-DNA is a right-handed double helix fairly similar to the more common B-DNA form, but with a shorter, more compact helical structure whose base pairs are not perpendicular to the helix-axis as in B-DNA.
In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure found in nature, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove.
Z- DNA is the double helix that has a left- handed rather than the usual right handed twist and the suagr- phosphate backbone followsa zig-zag course.
The length of DNA having 23 base pair is
78 Ao
78.4 Ao.
74.8 Ao
78.2Ao
D.
78.2Ao
The paired bases are 'stacked' on the inside of the double helix with one base pair every 3.4 Angstrom (0.34 nM). There are slightly more than 10 base pairs (bp) per full turn of helix.
Number of nitrogenous bases in a codon is
3
2
1
5
A.
3
The codon is set of 3 pairs of nitrogen bases. Three bases actually code for an amino acid but the DNA requires that the three bases that are doing the coding are linked to their pair. A-T, T-A, G-C. C-G.
So it takes six nitrogen bases to code for one amino acid. So a codon codes for an amino acid and requires a total of six nitrogen bases.
Chromosomes can be stained with one of the following chemicals
acetocarmine
safranine
light green
eosin
A.
acetocarmine
Acetocarmine is a saturated solution of carmine in 45 percent acetic acid used especially for the rapid staining of fresh unfixed chromosomes.
In a DNA molecule, distance between two bases is
2 nm/ 20 Å
0.2 nm/ 2 Å
3.4 nm/ 34 Å
0.34 nm/ 3.4 Å
C.
3.4 nm/ 34 Å
DNA is a double-stranded polynucleotide arranged in a double helix. The two strands are entwined around one another, each complete coil measures 3.4 nm (10 bases long). Each strand links to the other by pairs of organic bases, where the pairings are always cystosine with guanine and thymine with adenine. The two strands that form the uprights run antiparallel, ie, in opposite directions.
Balbiani rings are the sites of
DNA replication
RNA and protein synthesis
synthesis of lipids
synthesis of polysaccharides
B.
RNA and protein synthesis
Balbiani rings are large puffs on the polytene chromosomes in the dipteran Chironomus tentans. These puffs are used for the studies of the structure of active genes and the synthesis and transport of specific RNA- protein particles.
Which of the following is structural subunit of DNA?
Protein
Carbohydrate
RNA
Nucleotide
D.
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are the single units that make up nucleic acids like RNA and DNA, they are building blocks of life. Each nucleotide contains three items :
(i) A heterocyclic nucleobase (purines or pyrimidines).
(ii) A pentose sugar (ribose for RNA, deoxyribose for DNA).
(iii) A monophosphate, diphosphate or triphosphate.
DNA sequences that code for protein are known as
introns
exons
control regions
intervening sequences
B.
exons
An exon is any part of a gene that will encode a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term exon refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts.
What is ribozyme?
Ribozyme is RNA molecule with catalytic activity and have generated intense interest for their potential to be developed as RNA restriction enzymes. In bacteria the RNA can catalyse the reaction independently of protein.
Structural element of chromatin is
histone
acid protein and DNA
nuclear matrix
nucleosomes
D.
nucleosomes
Chromatin is composed of nucleosome which contains eight histone molecule around which DNA is wound. Some portion of chromatin takes darker stain during interphase called heterochromatin while the portion which take lighter stain are called euchromatin.
Out of A-T, G-C pairing, bases of DNA may exist in alternate valency state owing to arrangement called
tautomerisational mutation
analogue substitution
point mutation
frameshift mutation
A.
tautomerisational mutation
In the early 1950s, guanine and thymine were generally portrayed in the enol form, although there was little data to support the predominance of one form over the other. James Watson and Francis Crick discovered that by using the keto forms instead of the enol forms, they could 'form' two base pairs, an adenine thymine pair and a guanine-cytosine pair, that had the same overall size and shape. These base pairs formed the basis for Watson and Crick's model of DNA.
The process of changing keto form in to enol form of a given organic compound is known as tautomerisational mutation.
The chemical nature of chromatin is as follows
nucleic acids
nucleic acid and histone proteins
nucleic acids, histone and non-histone proteins
nucleic acids and non-histone proteins
C.
nucleic acids, histone and non-histone proteins
Chromatin is the material, of which eukaryotic chromosomes are composed. Chemically, chromatin consists of nucleic acids, histone and non-histone proteins.
Which one of the following triplet codon is a chain termination codon?
UGU
AAU
UUG
UAG
D.
UAG
UAA, UGA and UAG are chain termination codons whereas AUG is chain initiation codon.
What will be the codons in mRNA if the DNA codes are ATG - CAG?
TAC - GTC
UAC - GUC
UCA - TUA
TCA - GTC
B.
UAC - GUC
The DNA strand and mRNA are complementary except that thymine in RNA is replaced by uracil.
Melting of DNA at an elevated temperature (70°C) is primarily due to the breakdown of
phosphodiester bonds
glycosidic bonds
disulphide bonds
hydrogen bonds
D.
hydrogen bonds
Denaturation is the loss of function of a protein caused due to loss of structure. Heat can cause denaturation of DNA. It can disrupt the hydrogen and ionic bonds thus causing the 3 -D-structure to unravel.
Which one of the following triplet codon is known as initiation codon?
UUU
UAA
AUG
UGA
C.
AUG
AUG and GUG are called initiation codons because they initiate the polypeptide chain. UAA (Ochre), UAG (Amber) and UGA (Opal) are termination codons. If these codons are present in mRNA, the protein synthesis stops abruptly, whether the protein synthesis is complete or not.
UUU codes for phenylalanine.
A-DNA is
left-handed helix with 12 nucleotide pairs per turn
right-handed helix with 11 nucleotide pairs per turn
right handed helix with 12 nucleotide pairs per turn
left-handed helix with 11 nucleotide pairs per tum
B.
right-handed helix with 11 nucleotide pairs per turn
In A-DNA a single turn of right handed helix contains 11 base pairs which are tilted 20.2° away from perpendicular to helix axis, diameter is 23 Å and the axial rise or distance between successive base pairs is 2.56 Å.
What would be the percentage of thymine in a double stranded DNA sample which contains 20% cytosine of the total bases?
10%
20%
30%
40%
C.
30%
In DNA, purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine) occur in equal amount.
Adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. Hence, in a DNA sample if,
C = 20% then, G = 20%
So, A or T = = 30%
The diagram shows an important concept in the genetic implication of DNA. Fill in the blanks A to C

A - transcription, B - replication, C - James Watson
A - translation, B - transcription, C - Erevin Chargaff
A - transcription, B - translation, C - Francis Crick
A - translation, B - extension, C - Rosalind Franklin
C.
A - transcription, B - translation, C - Francis Crick
Central dogma
DNA mRNA Protein
Which enzyme/s will be produced in a cell in which there is a non-sense mutation in the lac Y gene?
- galactosidase
Lactose permease
Transacetylase
Lactose permease and transacetylase
A.
- galactosidase
-galactosidase is a structural gene present in segment of DNA, which carry codes for the synthesis of protein. Mutation in the lac Y gene of E. coli needs residues of cytoplasmic enzyme - galactosidase.
Lactose permease is a membrane protein, which is a major facilitator superfamily.
Transacetylase is an enzyme transferring acetyl groups from one compound to another.
Formation of polysome does not require
rRNA
mRNA
tRNA
snRNA
D.
snRNA
Polysome or polyribosomes are a cluster of ribosomes that bound to mRNA molecule that translates the genetic information coded in the mRNA during protein synthesis.
snRNA is used for splicing. mRNA, tRNA and rRNA are required for the formation of polysome during translation.
Genes which are located only in the X-chromosome are known as
epistasis genes
holandric genes
operator genes
antiepistasis genes
A.
epistasis genes
According to Barr body concept (applicable only for X-chromosomes) genes present on the Barr body (inactive X-chromosome) are at times hypostatic due to presence of epistatic genes on the active X-chromosome. Thus, epistasis gene is the most appropriate option. Genes which are located on X-chromosome only are called hologynic genes and those found on Y-chromosome only are called holandric genes.
Epistatis is the phenomenon where the effect of one gene is dependent on the presence of one or modifier genes. Operator gene in Lac operon, is a segment to which a repressor binds.
Which codon is not an indicator of completion of protein synthesis?
UAG
AUG
UAA
UGA
B.
AUG
Stop codon or termination codon is a nucleotide triplet within mRNA that signals a termination of translation. It signals the termination of this process by binding release factors which cause the ribosomal subunits to dissociate, releasing the amino acid chain. There are three stop codons (for RNA/DNA) respectively i.e.,
For DNA :- UAG (amber), UAA (ochre) and UGA (opal)
For RNA :- TAG (amber), TAA (ochre) and TGA (opal).
AUG acts as the strandard start (or initiation) codon for both DNA and RNA respectively.
If the sequence of bases in the coding strand of a double-stranded DNA is 5'-GTTCGAGTC-3', the sequence of bases in its transcript will be
5'-GACUCGAAC-3'
5'-CAAGCUCAG-3'
5'-GUUCGAGUC-3'
5'-CUGAGCUUG-3'
C.
5'-GUUCGAGUC-3'
DNA is made up of two polynucleotide chains having antiparallel polarity. Therefore, when one chain has 5' 3' polarity the other chain will have 3' 5' polarity. Thus, if the sequence of the bases in the coding strand of a double- stranded DNA is 5' GTTCGAGTC-3' its complementary strand will have 3'-CAAGCTCAG-5'.
In case of transcript, i.e., mRNA, the sequence will be 5'-GUUCGUGUC-3' (Uracil is present instead of thymine).
Nucleosome contains
Only histone protein
Both DNA and histone protein
Only DNA
Both DNA and RNA
B.
Both DNA and histone protein
A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. It contains both DNA and histone protein. It is the negatively charged DNA wrapped around the positively charged his octamer. It consists of 200bp of DNA helix.

What will be the percentage of guanine in a DNA molecule having 20% adenine?
20%
30%
40%
60%
B.
30%
According to Chargaff's rule,
A (Adenine)= T (Thymine); C (Cytosine)= G (Guanine)
If the % of A = 20 %
Then, T is also 20 % or A + T = 40 %
Therefore, G + C = 100 - 40 = 60%
Hence, G = 30%
Central dogma in molecular biology is
RNA DNA Protein
DNA RNA Protein
RNA Protein DNA
DNA Protein RNA
B.
DNA RNA Protein
Francis Crick proposed the central dogma, which states that the genetic information flows from
DNA Protein
In some viruses, the flow of information is in reverse direction, that is from RNA to DNA.
Lactose (Lac) operon is regulated by
lac repressor only
lac repressor and CAP-cGMP complex
lac repressor and CAP-cAMP complex
CAP-cAMP and CAP-cGMP complex
C.
lac repressor and CAP-cAMP complex
The lac operon is regulated by lac repressor and CAP cAMP complex. The inducer - repressor control of the lac operon is an example of negative control of lac-operon, in which expression is normally blocked.
CAP-cAMP system is an example of positive control because expression of the lac operon requires the presence of an activating single. In this case, the interaction of the CAP-cAMP complex with the CAP region takes place.
The enzyme peptidyl transferase of prokaryotes resides in
50 S ribosome
30 S ribosome
40 S ribosome
60 S ribosome
A.
50 S ribosome
The peptidyl transferase is an aminoacyl transferase as well as the primary enzymatic function of the ribosome, which forms peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids using tRNAs during the translation process of protein biosynthesis.
In prokaryotes, the 50 S (23 S component) ribosome subunit contains the peptidyl transferase component and acts as a ribozyme. In eukaryotes, the 60S (28S component) ribosome subunit contains the peptidyl transferase component and acts as the ribozyme.
The tRNA anticodon 3'-UAC-5' will pair with the mRNA codon
5'-AUU-3'
5'-UAC-3'
5'-AUG-3'
3'-GUA-5'
C.
5'-AUG-3'
The tRNA anticodon 3'-UAC-5' will pair with the mRNA codon 5'-AUG -3'. The tRNA acts as an adapter molecule, that would on one hand read the code and on other hand would bind to specific amino acids. tRNA has an anticodon loop that has bases complementary to the code. It also has an amino acid acceptor end to which it binds to amino acids.

Select the correct combination of statements for DNA fingerprinting,
I. It is ELISA based technique.
II. It is PCR based technique.
III. It is used by forensic scientists.
IV. It is based on the fingerprint of the individual.
V. It is a test for paternity
I, II and III
II, III and IV
I, IV and V
I, III and IV
B.
II, III and IV
In DNA fingerprinting PCR is applied. It is used in forensic science and is also used as test for paternity. It involves the use of Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) which differs from person to person in a population except in the case of monozygotic twins.
Which of the following are not the functions of genes?
I. Cell division
II. Structure and metabolism control
III. Carrier of hereditary information
IV. Provide proof for crossing over
I, II, III and IV
I, III and IV
I, II and III
II, III and IV
C.
I, II and III
Gene fucntions are as follows:
(i) Genes are the units of inheritance
(ii) They control the morphology and physiology of individuals.
(iii) Their replication is essential for cell division.
(iv) Reshuffling of genes during sexual reproduction produces variations.
Read the following statements.
I. Satellite DNA is found in the region of euchromatin
II. Prokaryotes contain only non-repetitive DNA
Identify wheather the given statements are true or false
Both the statements are true
I is true and II is false
I is false and II is true
Both the statements are false
C.
I is false and II is true
Satellite DNA is a part of eukaryotic DNA that differs in density from most of its DNA as determined by centrifugation, that consists of short repetitive nucleotide sequences. It is found in the region of heterochromatin. It is the region of chromosomes that are permanently coiled up tightly and inert.
Select the option for correct pairing of nitrogenous bases in dsDNA.
(Py)Adenine = (Pu)Cytosine :: (Pu)Guanine = (Pu)Thiamine
(Pu)Adenine Thiamine(Py) :: (Py)Cytosine = (Py)Guanine
(Py)Adenine (Pu)Thiamine :: (Py)Cytosine (Pu)Guanine
Adenine(Pu) = Thiamine(Py) :: Guanine(Pu) Cytosine(Py)
D.
Adenine(Pu) = Thiamine(Py) :: Guanine(Pu) Cytosine(Py)
The bases in two strands of DNA are hydrogen bonded. A purine base bonds with a pyrimidine base. Adenine binds with thiamine of opposite strands via two hydrogen bonds. Guanine bonds with cytosine similarly via three hydrogen bonds.
The translation unit is represented by the following diagram. Select the correct answer based on this

Promoter/ Terminater/ Coding strand/ Structural gene
Promoter/ Coding strand/ Terminator/ Structural gene
Terminater/ Coding strand/ Structural gene/ Promoter
Promoter/ Structural gene/ Coding strand/ Terminator
D.
Promoter/ Structural gene/ Coding strand/ Terminator
Promoter : Located upstream of initiation codon of structural gene. TATA box in prokaryotes and pribnow box in eukaroytes. Highly conserved sequence.
Structural gene - Sequences involved in actual protein synthesis and are the functional unit of inheritance.
Coding strand - 5'- 3' polarity, sequence same as in mRNA except thymine.
Terminator - This region is downstream of structural gene at the 3'-end of coding strand. It defines end of transcription process.
Given below are the set of statements describing the structural details of Purines (A) and Pyrimidines (BJ.
I. Nine - membered, double ring
II. Six - membered, single ring
III. Contains Nitrogen atoms at four positions
IV. Contains Nitrogen atoms at two positions
Segregate the statements I - IV into categories A and B and choose the correct option.
A B I, IV II, III Only I Only IV Only II Only I I, III II, IV
D.
| I, III | II, IV |
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. It is nine membered, double ring and contains Nitrogen atoms at four positions.
Pyrimidine is a simple aromatic ring composed of two nitrogen atoms and four carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon.
Which type of RNA carries no coding message?
mRNA
tRNA
rRNA
tRNA and rRNA
C.
rRNA
Ribonucleiacid or RNA has following three major classes - mRNA, rRNA and tRNA. mRNA carries a coding message for many amino acids, tRNA carries coding message for only one amino acid and rRNA carries no coding message.
Study the following Columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Hydrogen bond | 1. Adenine - Deoxyribose |
| B. N - glycosidic linkage | 2. Glucose - Fructose |
| C. Phosphodiester bond | 3. Leucine - Glycine |
| D. Peptide bond |
4. Nucleotide - Nucleotide in polynucleotide chain 5. Guanine cytosine on opposite strands of DNA. |
The correct match is
A - 5; B - 1; C - 4; D - 3
A - 2; B - 1; C - 5; D - 3
A - 5; B - 3; C - 4; D - 2
A - 1; B - 4; C - 5; D - 2
A.
A - 5; B - 1; C - 4; D - 3
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Hydrogen bond | 5. Guanine, cytosine on opposite strands of DNA |
| B. N-glycosidic linkage | 1. Adenine-Deoxyribose |
| C. Phosphodiester bond | 4. Nucleotide - Nucleotide in polynucleotide chain |
| D. Peptide bond | 3. Leucine - Glycine |
Select the correct statements out of the four (I-IV) given below about lac operon.
I. Glucose or galactose may bind with the repressor and inactivate it.
II. In the absence of lactose, the repressor binds with the operator region.
III. The Z-gene codes for permease.
IV. This was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monad.
The correct statements are
II and III
I and III
II and IV
I and II
C.
II and IV
Lac operon was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod. It is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in E. coli and many other enteric bacteria.
In lac operon lactose or allolactose binds with the repressor and induces the lac operon system. In the absence of lactose, the repressor binds with the operator region and the Z-genes in this codes for - galactosidase.
Match the following column I with column II
| Column I (Genes) | Column II (Types) |
| A. Genes for glycolysis | 1. Pseudogenes |
| B. Genes for nitrate reductase | 2. Multigenes |
| C. Globin gene family | 3. House keeping genes |
| D. mRNA gene | 4. Inducible genes |
A - 4; B - 3; C - 1; D - 2
A - 3; B - 4; C - 2; D - 1
A - 1; B - 2; C - 4; D - 3
A - 2; B - 1; C - 3; D - 4
B.
A - 3; B - 4; C - 2; D - 1
| Column I (Genes) | Column II (Types) |
| A. Genes for glycolysis | 3. House keeping genes |
| B. Genes for nitrate reductase | 4. Inducible genes |
| C. Globin gene family | 2. Multigenes |
| D. mRNA gene | 1. Pseudogenes |
Consider the following statements about DNA replication.
I. A replisome is the largest functional unit in DNA replication factories.
II. RNA polymerase complexes are responsible for transcribing the newly synthesised RNAs into their mature form.
III. DNA polymerases add new deoxyribonucleotides to the 3' end of a DNA strand.
IV. A replication bubble is a region of single stranded DNA that arises due to unwinding of DNA in same direction by primase
Choose the incorrect statement(s)
I and II
III and IV
I, II and IV
I, II, III and IV
C.
I, II and IV
Out of all 4 statements; Statement 3 is correct. A replisome is the smallest functional unit in DNA replication factories. RNA polymerase complex is responsible for transcribing the newly synthesised DNA into mRNA. A replication bubble is a region of double stranded DNA that arises due to the unwinding of DNA in same direction by helicase.
Which of the following statement is not true about Griffith's experiment?
The experiment was conducted in 1928
The experiment occurs with Streptococcus pneumoniae
R and S-strain of bacteria
The experiment proves the process of transduction
D.
The experiment proves the process of transduction
The experiment prove the transformation of genetic material from one strain of bacteria (S-strain) to A-strain and make it virulent. It was conducted in 1928 and performed with Streptococcus pheumoniae.
In protein synthesis the base sequence of mRNA determines the primary structure of polypeptide chain because
it determine the sequence of alignment of amino acid charged tRNA molecule
there is one to one coding relationship between each base on mRNA and amino acid
each amino acid is defined by a pair of base on mRNA
amino acid molecule align directly on the polynucleotide on mRNA
A.
it determine the sequence of alignment of amino acid charged tRNA molecule
During the process of translation, the codons present on mRNA decides the sequence of amino acids (primary structure) on polypeptide chain. These amino acids later forms secondany structure by forming various bonds.
What do you mean to the mutation in which replacement of a nucleotide occur by another similar type?
Inversion
Transition substitution
Transversion substitution
Insertion frame- shift
B.
Transition substitution
In transition substitution, one nitrogenous base is replaced by another of similar type. e.g., A G; C T
It is induced by tautomerisation (due to rearrangement of H-atoms). The NH2 into -NH or -CO into -COH.
Part of gene which codes for an enzyme is
cistron
codon
exon
intron
A.
cistron
Cistron is that particular length of DNA which is capable of producing a protein molecule or polypeptide chain or enzyme molecule. A cistron is having nitrogenous bases or nucleotides three times in the number of amino acids in a protein molecule.
Which of the following codons does not select any amino acid?
UAG
UAA
UGA
All of these
D.
All of these
Some of the codon like UAA, UAG, UGA cannot select any amino acid and are called chain termination codons or non-sense codons.
Operator genes are controls to which gene mechanism?
Structural gene
Activator gene
Regulator gene
Modulac gene
A.
Structural gene
Operator genes in lac operon controls the activity of structural gene. Operator is a segment of DNA to which a repressor binds. It is a segment present between the promoter and the genes of the operon.
DNA is specific because it has
number of nucleotides
specific nature of phosphate and sugar
arrangement of protein in DNA
specific nature of purine and pyrimidines
B.
specific nature of phosphate and sugar
DNA is specific because of specific nature of nitrogenous bases like purines (cytosine, thymine and uracil).
Role of carbohydrate in protoplasm
as catalyst
for energy
as enzymes
for synthesis
B.
for energy
Carbohydrates are the instant source of energy required for all metabolic processes.
The RNA found in eukaryotic ribosomes are
5 S and 16 S RNA
5 S, 16 S, 18 S RNA
23S, 16 S, RNA
5 S and 28 S RNA
D.
5 S and 28 S RNA
Eukaryotic ribosomes have two unequal subunits, small subunit (40S) and large subunit (60S). Large subunit consists of 28S rRNA and 5S rRNA. It also consists of 5.8S rRNA. Small subunit consists of 18S rRNA.
Which one of the following codons codes for the some information as UGC?
UGU
UGA
UAG
UGG
A.
UGU
Wobble Hypothesis helps to understand why multiple codons can code for a single amino acid. UGC and UGU suggest wobble hypothesis and both stand for same amino acid cystin.
During translation initiation in prokaryotes, a GTP molecule is needed in
association of 30S, mRNA with formyl-met-tRNA
association of 50S subunit of ribosome with initiation complex
formation of formyl-met-tRNA
binding of 30S subunit of ribosome with mRNA
A.
association of 30S, mRNA with formyl-met-tRNA
During the process of translation, an initial complex is formed between mRNA, 30S ribosomal subunit and methionyl tRNA. This complex is formed due to association of IF1, IF2 and IF3 initiation factors and GTP molecule.
In the genetic code dictionary, how many codons are used to code for all the 20 essential amino acids?
61
60
20
64
A.
61
Out of 64 codons, three (UM, UAG, UGA) are chain terminating codons. The translating mechanism is not able to read these codons.
(a) 61 codons are used to code all the 20 essential amino acids.
(b) Out of 64, 3 codons, UAA, UAG, UGA do not code any amino acid molecule
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesized in
nucleolus
nucleosome
cytoplasm
ribosome
A.
nucleolus
Nucleolus is one of the most important site of RNA synthesis. The RNA synthesized by it is rRNA, which comprises about 80% of total RNA content of the cell.
The number of RNA molecules in 60S sub- particles of 80S ribosomes are
five
four
three
two
C.
three
In 80S eukaryotic ribosome, there are two subunits. One large subunit, that is, 60S and one small subunit, that is, 40S.
In animals, 60S subunit is further divided into 28- 29S + 5S + 5.8S and 40S is divided into 18S.
In plants, 60S subunit is divided into 25S +5S +5.8S and 40S subunit is divided into 16- 18S.
Stop codons are
AUG, GUG
UAA, UGA, UAG
UAC, UGG
AGU, AGA, UAC
B.
UAA, UGA, UAG
There are three stop codons or non- sense codons UAG, UAA and UGA.
AUG is an initiation codon in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
UAC codes for tyrosine, UGG codes for tryptophan, AGU codes for serine and AGA codes for argenine.
DNA multiplication is called
translation
replication
transduction
transcription
B.
replication
Replication is the process of DNA multiplication. It is semi- conservative in nature.
Transcription is the mode by which DNA passes its genetic information to mRNA.
Translation is the synthesis of a chain of polypeptide by mRNA.
Transduction is the transfer of genes from one bacterial cell to another by means of a virus.
Enzyme required for transcription is
RNAse
Endonuclease
RNA polymerase
DNA polymerase
C.
RNA polymerase
Transcription is a process of synthesis of RNA from DNA. This synthesis takes place with the help of enzyme RNA Polymerase as a single complementary strand is formed on template DNA strand by linking the free ribotides.

The process of multiplication of DNA from DNA is known as
replication
transversion
transcription
translation
A.
replication
Replication is the process of multiplication of DNA. It is an autocatalytic function of DNA.
Transversion is a mutation in DNA, where a single purine changes to a pyrimidine or vice- versa.
Transcription is a process of synthesis of RNA from DNA.
Translation is a process of synthesis of proteins from RNA.
A eukaryotic gene contains two kinds of base sequences. Which of these plays an important role in protein synthesis?
Introns
Exons
Both 'a' and 'b'
None of the above
B.
Exons
In eukaryotic genes some non-coding parts are interspersed between coding parts. These, non coding parts are called introns and coding sequence are known as exons. Exons play significant role in protein synthesis.
The number of hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine in a DNA molecule is :
two
three
four
eight
A.
two
There are two hydrogen bonds present between Adenine(A) and Thymine (T) whereas there are three hydrogen bonds between Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G).
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area