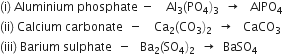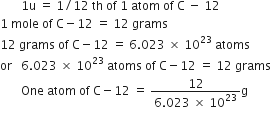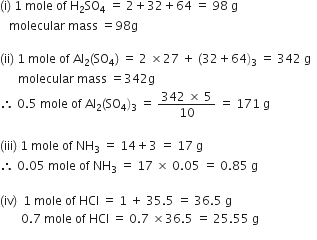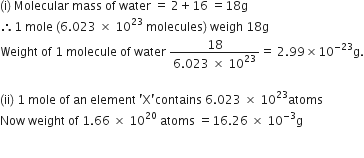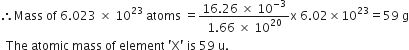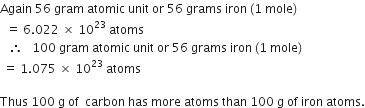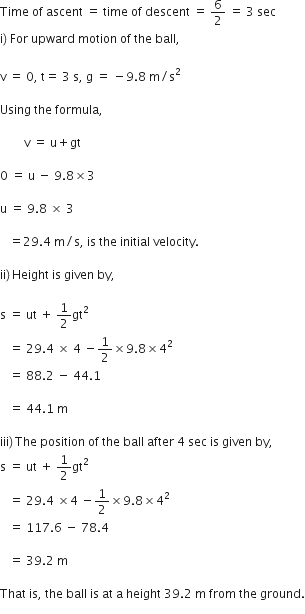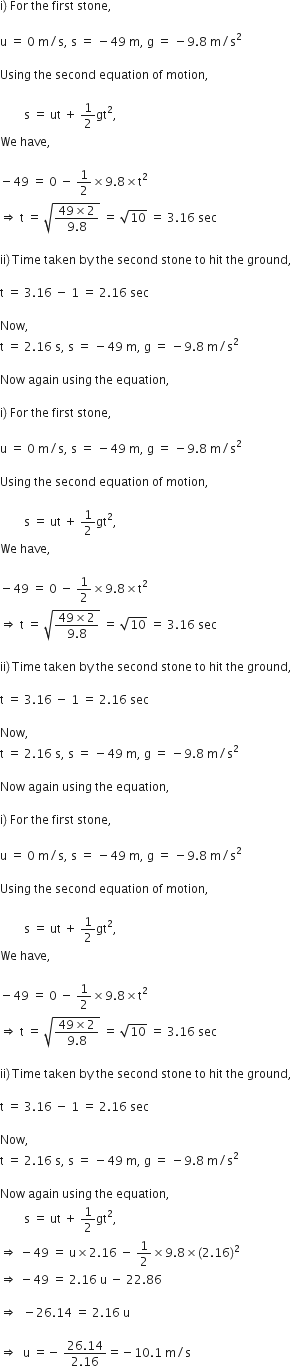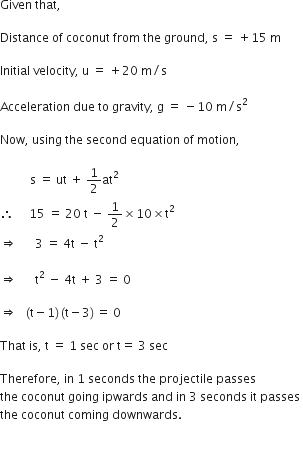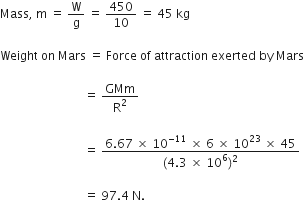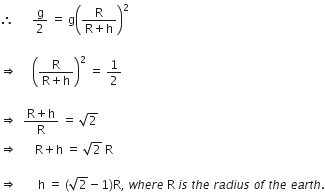Science Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 9 About 2.html
A 0.24 g sample of compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
We have given,
Mass of boron = 0.096g
Mass of oxygen = 0.144g
Mass of sample =0.24g
Thus, percentage of boron by weight in the compound =
Thus, percentage of oxygen by weight in the compound =
When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen ? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
When 3.0 g carbon is burnt in 8.00 g oxygen, 11.00 g carbon dioxide is formed. It means all of carbon and oxygen are used up and carbon and oxygen are combined in the ratio of 3 : 8 to form carbon dioxide. Thus when there is 3 g carbon and 50.0 g oxygen, then also only 8 g oxygen will be used and 11.0 g carbon dioxide will be formed. The remaining oxygen is not used us. This indicates law of definite proportions which says that in compounds, the combining elements are present in definite proportions by mass.
What are polyatomic ions? Give examples.
A group of atoms carrying a charge is known as a
polyatomic ion. For example, hydroxide ion (OH–), carbonate ion (CO3–2).
Write the chemical formulae of the following:
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium carbonate
Chemical formulae of the following is:
(a) Magnesium chloride – MgCl2
(b) Calcium oxide – CaO
(c) Copper nitrate – Cu(NO3)2
(d) Aluminium chloride – AlCl3
(e) Calcium carbonate – CaCO3
Give the names of the elements in the following compounds.
(a) Quick lime
(b) Hydrogen bromide
(c) Baking powder
(d) Potassium sulphate.
(a) Quick lime(CaO) – Calcium and oxygen
(b) Hydrogen bromide(HBr) – Hydrogen and bromine
(c) Baking powder(NaHCO3) – Sodium, Hydrogen, Carbon and Oxygen
(d) Potassium sulphate (K2SO4)– Potassium, Sulphur and Oxygen
Calculate the molar mass of the following substances:
(a) Ethylene
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3.
(a) Ethylene, C2H2 = 2 x 12 + 2 x 1 = 26 u
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8 = 8 x 32 = 256 u
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 = 4 x 31 = 124 u
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl = 1 x 1 + 1 x 35.5 = 36.5 u
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3 = 1 x 1 + 1 x 14 + 3 x 16 = 63 u
What is the mass of:
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite.
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms = 14 u = 14 gm
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms = 4 x 27 = 108 u = 108 gm
(c) 1 mole of sodium sulphite, Na2 SO3 = (2 x 23 + 1 x 32 + 3 x 16) = 126 u
10 moles of sodium sulphite = 126 x 10 = 1260 u = 1260 gm.
Convert into mole
(a) 12 gm of oxygen gas
(b) 20 gm of water
(c) 22 gm of carbon dioxide.
(a) Formula of oxygen is O2.
1 mole of oxygen gas = 32 gm
12 gm of oxygen gas = 12/32 = 0.375 mole
(b) Formula of water is H2O.
18 gm of water = 1 mole
20 gm of water = 20/18 = 1.1 mole
(c) Formula of carbon dioxide CO2.
44 gm of carbon dioxide = 1 mole
22 gm of carbon dioxide = 0.5 mole
What is the mass of?
(a) 0.2 mole oxygen atoms.
(b) 0.5 mole of water molecules.
(a) 1 mole of oxygen atoms = 16 gm
0.2 moles of oxygen atoms = 16 x 0.2 = 3.2 gm
(b) 1 mole of water molecules = 18 gm
0.5 mole of water molecules = 0.5 x 18 =9.0 gm
Calculate the number of molecules of sulphur (S8) present in 16 gm of solid sulphur.
1 mole of S8 contain 6.023 X 1023 molecules
therefore, 256 gm S8 has = 6.023 X 1023 S8 molecules
16 gm S8 has = (6.023 X 1023 X 16)/256
= 3.76 X 1023 molecules
Calculate the number of aluminium ions present in 0.56 gm of aluminium oxide.
1 mole of aluminium oxide, Al2O3 = 2 X 27+3 X 16 = 102 u = 102 gm
So,
102 gm has Al2O3 has = 6.023 X 1023 Al2O3 molecules
0.56 gm Al2O3 has 6.023 X1023 X 0.56
102
= 3.01 X 1021 Al2O3 molecules
1 molecules of Al2O3 gives =2Al3+ ions
Hence 0.56 gm Al2O3 gives = 2 X 3.01 X 1021 Al3+ ions
= 6.023 X 1021 aluminium ions
Explain law of conservation of mass.
Law of consveration of mass state that mass can neither be created nor be destroy in chemical reaction. For example, take a solution of lead nitrate in water. Weigh it. Let it be x gm. Then add a given amount of solution (y gm) of sodium chloride. It will be found that a white precipitate is formed. Weigh the total solution. It will be found that total weight of the contents is (x + y) gm, i.e., equal to the total weight of the two solutions taken. Hence, it can be inferred that mass is neither created nor lost even during a chemical change. Similar results are obtained when any other chemical reaction has taken place. Only care to be taken is that no material is allowed to escape during the reaction.
50 g of 10% lead nitrate is mixed with 50 g of 10% sodium chloride in a closed vessel. After the reaction has taken place, it was found that 6.83 g of lead chloride was precipitated. Besides, the reaction mixture contained 90 g water and sodium nitrate. Calculate the amount of sodium nitrate formed.
50 g of 10% lead nitrate means the solution contains 5 g lead nitrate and 45 g water. Similarly, 50 g of 10% sodium chloride means the solution contains 5 g sodium chloride and 45 g water.
Thus total content before reaction = 5+5+90 = 100 g
After reaction, amount of water = 90 g
Amount of precipitate = 6.83 g
Since according to law of conservation of mass, the total mass of reaction mixture = 100 g
So, Amount of sodium nitrate = 100 - 90 - 6.83
= 3.17 g
Name and explain two important laws of chemical combination ?
(i) Law of constant proportion. According to law of constant composition or proportion, all pure samples of a compound contain the same elements combined together in the same proportion by mass. For example, a sample of water would always contain hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 1 : 8 by mass irrespective of the source of water. If we decompose 100 grams of pure water by passing electricity through it then we get 11 grams of hydrogen and 89 grams of oxygen showing that hydrogen and oxygen are combined together in water in the same constant proportion of 1 : 8 by weight.
(ii) Law of multiple proportions. According to law of multiple proportions, when two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the weights of one of these elements which combine with a fixed weight of the other element, bear a simple ratio to one another. For example, hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water (H2O) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) under different conditions. In water 2 grams of hydrogen combine with 16 grams of oxygen while in hydrogen peroxide, 2 grams of hydrogen combine with 32 grams of oxygen. Now the weights of oxygen which combine with a fixed weight of hydrogen (2 grams) in water and hydrogen peroxide respectively are 16 and 32 grams which are in simple ratio of 16 : 32 or 1 : 2.
What are the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter?
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms.Each substances is made by extremely small particles called atoms.
The postulates of this theory may be stated as follows:
(i) All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
(ii) Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
(iii) Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
(iv) Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
(v) Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
(vi) The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
How will you explain the laws of constant proportion on the basis of Dalton’s atomic theory?
Explanation on the basis of Dalton’s atomic theory:
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, each element consists of atoms which are similar and have same weights. Further atoms of one element combine with atoms of another to form compounds. for example that x atoms of element A combine with y atoms of element B and the compound formed is AxBy (Dalton’s atomic theory).
If ‘a’ stands for the atomic mass of A and ‘b’ for that of B,then
Now a and b (atomic masses of elements) are fixed, x and y are also fixed whole numbers according to atomic theory. Therefore per cent of A and B in the compound is also constant. This shows that the composition of various elements in a compound is also fixed. This is the law of constant proportion.
Hydrogen and oxygen combine in two different ways to produce water and hydrogen peroxide. Which of Dalton’s law does this observation confirm? Explain.
In water 1 g of hydrogen combines with 8 g of oxygen. And in hydrogen peroxide, 2 g of hydrogen combines with 16 g of oxygen. The ratio of oxygen in water and hydrogen peroxide combining with the same amount of hydrogen i.e., 1 g is 8 : 16 or 1 : 2—a small integral ratio. This is law of multiple proportions which defines as under.
When two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a given mass of the other element in different compounds are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
Sponsor Area
State drawbacks of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter.
Some of the drawbacks of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter are:
1. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, matter is indivisible, i.e., which cannot be divided. But now it is known that under special circumstances, atoms can be divided into still smaller particles called electrons, protons and neutrons.
2. Dalton’s atomic theory fails to explain why substances like charcoal, graphite and diamond have different properties when all these substances are made up of the same type of atoms, called carbon atoms.
3. Dalton’s atomic theory postulated that all the atoms of the same element have exactly the same mass. It is now known that isotopes are atoms of the same element but have different masses.
4. It is now known that some atoms called isobars have same masses but these belong to different elements. Whereas Dalton’s atomic theory says that atoms of different atoms have different mass.
Give an illustration based on atomic theory for the difference between an element, compound and mixture.
|
Characteristic |
Compound |
Element |
|
Define |
A compound contains atoms of different together in a fixed ratio. |
An element is a pure chemical substance made of the same type of atom |
|
Distinguishing features |
Compounds contain different elements in a fixed ratio arranged in a defined manner through chemical bonds. |
Elements are distinguished by their atomic number (number of protons in their nucleus). |
|
Ability to breakdown |
A compounds can be separated into the simpler substance by chemical method reaction only. |
A element cannot be broken down into the simpler substance by chemical reactions. |
|
Types |
The list of compounds is endless. |
There are about 117 elements that have observed, can be classified as metal, non-metal or metalloid. |
|
Representation |
A compound is represented by using formula. |
An element is represented by using symbols |
|
Examples |
Water (H2O), sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) etc. |
Iron (Fe), silver (Ag), gold (Au), nickel (Ni) etc. |
Give one major drawback of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter.
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, matter is indivisible, i.e., which cannot be divided. But now it is known that under special circumstances, atoms can be divided into still smaller particles called electrons, protons and neutrons. This was the major drawback of Dalton's atomic theory of matter.
A sample of ammonia contains 9 g hydrogen and 42 g nitrogen. Another sample contains 5 g hydrogen. Calculate the amount of nitrogen in the second sample.
The ratio of hydrogen and nitrogen in the first sample of ammonia is 9:42 or 3:14.
According to ‘law of definite proportions' the second sample of ammonia should also contain hydrogen and nitrogen in the ratio 3:14.
![]()
Carbon and oxygen combine in two different ways to form carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. In carbon monoxide, 12 g carbon combines with 16 g oxygen. In carbon dioxide 12 g carbon combines with 32 g oxygen. Which law of combination is illustrated by this experiment? Explain.
The above experiment illustrates law of multiple proportions. 16 g and 32 g of oxygen respectively are required to combine with a fixed weight, i.e., 12 g of carbon to form carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The ratio of oxygen which combines with a fixed weight of carbon is 16 : 32 or 1 : 2, a simple whole number. This is law of multiple proportions.
In a reaction, 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Mass of reactants = Mass of sodium carbonate + Mass of ethanoic acid
= 5.3+6.0 = 11.3 g
Mass of products = Mass of carbon dioxide + Mass of water + Mass of sodium ethanoate
= 2.2 + 0.9 +8.2 = 11.3 g
Since the mass of products is equal to mass of reactants. Thus mass is neither creater nor lost during the given chemical change or the observation made is in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio of 1 : 8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?
We know that, 1 g of hydrogen reacts with oxygen =8g
Therefore, 3g of hydrogen reacts with oxygen =8x 3 =24g
Thus, 24g of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas.
Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This is law which result of the law of conservation of mass.
Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound. This theory explain the law of definite proportions.
What is an atom?
The smallest particle that retains properties of an element. Atom is Composed of electrons and a nucleus.
In what form atoms of a solid exist?
Atoms of a solid exist in closely packed and compressed to each other. A solid element is a cluster of atoms. The properties of an element in the solid state is not of single atom of that element but due to cluster of atoms. For example, diamond and graphite though both are composed of carbon atoms but due to different arrangements of carbon atoms in these, they differ in their physical and chemical properties.
What is the arrangement of atoms in elements ?
Atoms are very small atoms, they are smaller than anything that we can imagine or compare with. More than millions of atoms when stacked would make a layer barely as thichk as a sheet of paper. Nowdays, It is possible to take in depth photographs of the surfaces of the elements. The surface images of silicon with a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) shows that the silicon atoms are arranged in a regular pattern.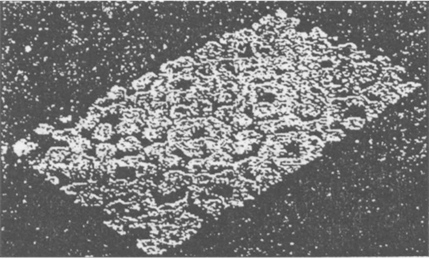
How were the names of elements derived?
In the beginning, the names of elements were derived from the name of the place they were found for the first time or from some specific colours. For example, the name of copper was taken from Cyprus, a place where it was found. Gold was taken from the English word meaning yellow.
What is the present accepted or IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system of symbols of elements?
Many of the symbols are the first one or two letters of the element’s name in English. The first letter of a symbol is always written as a capital letter (upper case) and the second letter as a small letter (lower case). For example, Hydrogen is written as H and Aluminium is written as Al.
Some symbols are formed from the first letter of the name and a letter, appearing later in the name. Examples : Chlorine, Cl and Zinc, Zn.
Some other symbols are taken from the names of elements in Latin, German or Greek. For example, the symbol of iron is Fe from Latin name ferrum.
What do you mean by symbols of elements?
In order to write the chemical reactions conveniently, each element is represented by a ‘letter’ or a group of two letters called symbol. Thus hydrogen is represented as ‘H’. Calcium is represented as ‘Ca’.
Give a list of a few elements with their symbols.
Symbol of Common Elements
|
Element |
Symbol |
Element |
Symbol |
|
|
Hydrogen |
H |
Iron |
Fe |
|
|
Carbon |
C |
Silicon |
Si |
|
|
Nitrogen |
N |
Gold |
Au |
|
|
Oxygen |
O |
Silver |
Ag |
|
|
Sulphur |
S |
Mercury |
Hg |
|
|
Phosphorus |
P |
Sodium |
Na |
|
|
Chlorine |
Cl |
Potassium |
K |
|
|
Calcium, Barium |
Ca,Ba |
Magnesium, Lead |
Mg, Pb |
|
|
Copper |
Cu |
Nickel |
Ni |
|
|
Manganese |
Mn |
Tin |
Sn |
Calculate the relative molecular mass of water.
Atomic mass of hydrogen =1u,
Atomic mass of oxygen =16u
SO the molecular mass of water, which contains two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen is
= 2 x1+1 x16 = 18u
Calculate the molecular mass of HNO3.
The molecular mass of HNO3 = the atomic mass of H+ the atomic mass of N +3 x the atomic mass of O =1+14+48 =63u
Write the names of symbols of five elements where the symbols are taken from their name in English.
i) Copper (Cu)
ii)Calcium (Ca)
iii)Oxygen (O)
iv)Magnesium (Mg)
v)Zinc (Zn).
Write the names and symbols of five elements where the symbols are taken from their name in a language other than English.
Silver (Ag), Gold (Au), Lead (Pb), Iron (Fe), Sodium (Na).
Write the symbols of the following chemical elements :
Mercury, Potassium, Silver, Boron, Chlorine, Gold, Lead, Copper, Aluminium.
Mercury (Hg),
Potassium (K),
Silver (Ag),
Boron (B),
Chlorine (Cl),
Gold (Au),
Lead (Pb),
Copper (Cu),
Aluminium (Al).
State the contribution of Dalton’s atomic theory to the mass of atom. What steps were taken to resolve this issue?
Dalton’s atomic theory states that each atom has a characteristic mass and all atoms of an element are identical. Since, the mass of an atom is very very small, it was a difficult task to determine the mass of an individual atom. Therefore, it was decided to measure the atomic mass of an atom. Atomic mass is the relative atomic mass of an atom as compoared to some particular atom. For example, carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon monoxide. It is observed that 3 g of carbon combines with 4 g of oxygen. In other words.
carbon is 4/3 times its mass of oxygen, since, oxygen combines with a large number of elements, oxygen atom was taken as standard and 1/16 of mass of oxygen was taken as one atomic mass unit (u).
Now a days 1/12 of the mass of C-12 isotope of carbon is taken as the standard reference for measuring atomic masses.
Sponsor Area
Define and explain atomic mass unit.
The atomic mass unit (abbreviated as amu) is unit that is used to express the atomic masses of atoms and molecule at massed of compounds. One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12. The atomic masses of all elements have been found relative to an atom is basically the one twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12 isotope.
1/12th of carbon atom is basically the one twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon -12 isotope.
How do atoms exist?
Individual atoms of most elements do not exist independently. These either aggregate to form elements or form molecules or ions which also aggregate in large numbers to form the matter that is available to us.
Give atomic masses of some common elements.
Atomic masses of some common elements
|
Element |
Symbol |
Mass (u) |
Element |
Symbol |
Mass(u) |
|
Aluminium |
Al |
27.0 |
Magnesium |
Mg |
24.3 |
|
Argon |
Ar |
39.9 |
Manganese |
Mn |
54.9 |
|
Arsenic |
As |
74.9 |
Mercury |
Hg |
200.6 |
|
Barium |
Ba |
137.3 |
Neon |
Ne |
20.1 |
|
Boron |
B |
10.8 |
Nickel |
Ni |
58.7 |
|
Bromine |
Br |
79.9 |
Nitrogen |
N |
14.0 |
|
Cesium |
Cs |
132.9 |
Oxygen |
O |
16.0 |
|
Calcium |
Ca |
40.1 |
Phosphorus |
P |
31.0 |
|
Carbon |
C |
12.0 |
Platinum |
Pt |
195.1 |
|
Chlorine |
Cl |
35.5 |
Potassium |
K |
39.1 |
|
Chromium |
Cr |
52.0 |
Silicon |
Si |
28.1 |
|
Cobalt |
Co |
58.9 |
Silver |
Ag |
107.9 |
|
Copper |
Cu |
63.5 |
Sodium |
Na |
23.0 |
|
Fluorine |
F |
19.0 |
Sulphur |
S |
32.1 |
|
Gold |
Au |
197.0 |
Tin |
Sn |
118.7 |
|
Helium |
He |
4.0 |
Why is it not possible to see an atom with naked eyes?
The size of an atom is very very small. Further atoms of most elements do not exist independently. So it is impossible to see an atom with naked eyes.
What are molecules? Give an account of the arrangement of the constituent atoms in the molecules.
A molecule is the smallest-particle of an element or of a compound which is stable under ordinary conditions and can exist freely and shows all the properties of that element or compound.
A molecule may be made up of one, two or more atoms. Molecules with only one atom are called monoatomic, e.g., helium, argon, neon.
Molecules with two atoms are diatomic. These may have similar or different atoms, e.g., chlorine (Cl2), oxygen (O2), hydrochloric acid gas (HCl). Similarly, there are molecules containing three atoms (H2O, CO2), four atoms (P4, NH3) and so on.
Arrangement of atoms in molecules:
The atoms in a molecule are chemically bonded in a definite pattern. This arrangement of atoms is given by the structural formula of the compound. For example, structural formula for water is H—O—H. This is a simple illustration for the structure of water. In fact water and all other molecules exhibit definite spatial arrangements depending on the nature of chemical bonding between atoms.
Fig. 3.3 shows molecular model for water, ammonia and sulphur.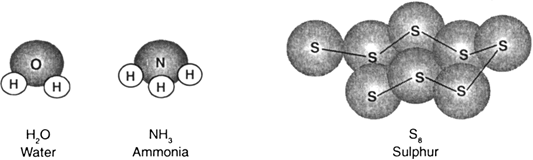
Could you make a distinction between a molecule and a compound?
A molecule is usually formed when at least two atoms of the same or different kinds combine. If two or three atoms of the same kind of element combine, then it is referred to as molecule of an element or simply molecule. For example, molecule of oxygen (O2) is formed by the combination of two oxygen atoms. Molecule formed by the union of two or more atoms of different elements is called a molecule of a compound or simply compound. For example, a molecule or a compound of carbon dioxide is formed by the union of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. However, the noble gases consists of molecules of single atoms only. For example, helium exists as He.
Comment on the statement. “A molecule is the smallest particle of a substance (element or compound) which has the properties of the substance and is stable.”
It is true that a molecule is the smallest particle of a substance which has the properties of that substance and is stable. In case of gases as example oxygen, a molecule (O2) is stable and gives properties of oxygen gas, whereas atom ‘O’ is not stable and does not represent oxygen gas. In case of noble gases such as helium, a molecule is of monoatomic helium atom (He) and represents helium gas and is also stable. In case of a compound, e.g., carbon dioxide, properties of carbon dioxide molecule are the properties of carbon dioxide gas. A molecule of carbon dioxide is stable.
Here are molecules of different substances. Differentiate between these. (i) Chlorine molecule, (ii) Argon molecule, (iii) Hydrogen chloride molecule, (iv) Nitrogen molecule, (v) Neon molecule, (vi) Sulphur dioxide molecule, (vii) Hydrogen molecule.
(ii) Argon molecule and (v) Neon molecule are monoatomic molecules. Here molecule is formed of only single atom.
(i) Chlorine molecule, (iv) Nitrogen molecule and (vii) Hydrogen molecule are diatomic molecules. These are formed by the union of two atoms of the same element.
(iii) Hydrogen chloride and (vi) Sulphur dioxide are molecular compounds and are formed by the union of different kinds of atoms.
Define atomicity of an element and give one example each of mono, dia and triatomic molecules.
The number of atoms combined together to form a stable molecule of an element is called its atomicity.
For example helium (He), neon (Ne) is a monoatomic and its atomicity is 1. In same manner oxygen (O2) diatomic, therefore its atomicity is 2.
What is the basic unit of all material substances?
Since all matters are composed of tiny particles called atoms or molecules. Therefore, the basic unit of all material substance is atom and molecule.
Name some molecules containing more than four atoms. What are these called?
Molecules containing more than four atoms are called polyatomic molecules. Examples are : sulphur (S8), ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH), sugar (C12H22O11), a form of carbon called buckminsterfullerene (C60).
What is the ultimate particle on which depends the properties of a material substance?
The properties of matter depend upon the properties of atoms or molecules of which they are composed.
Which of the following statements is more correct? Explain.
(i) Two atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of oxygen to give one molecule of water.
(ii) Two molecules of hydrogen combine with one molecule of oxygen to give two molecules of water.
The (ii) statement that two molecules of hydrogen combine with one molecule of oxygen to give two molecules of water is correct because oxygen and hydrogen exist as molecules and not as atoms.
Explain the difference between 2Cl and Cl2.
2Cl indicates 2 atoms of chlorine and Cl2 indicates one molecule of chlorine.
Name two molecules each having one atom, two atoms, three atoms and four atoms.
Helium (He) and Neon (Ne) are monoatomic molecules.
Chlorine (Cl2) and Oxygen (O2) are diatomic molecules.
Water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are triatomic molecules.
Ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are tetra-atomic molecules.
Give an account of existence of various elements and compounds.
Metals exist as atomic crystals and do not form molecules. Generally, metals and other elements like carbon and silicon do not have single molecular structure but consist of a very large indefinite number of atoms bonded together. A form of carbon bonded with sixty atoms is called buckminsterfullerence.
Non-metals exist as molecules containing one or more atoms. For example, argon exists as Ar and nitrogen as N2.
Compounds containing non-metals only exist as molecules. For example, compound of nitrogen and hydrogen is a ammonia molecule. Compound of carbon and oxygen is a carbon dioxide molecule.
Compounds containing metal and non-metal exist as ions. For example, compound of sodium and chlorine consists of positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.
If A and B are two kinds of atoms, then state whether A and B are metals or non-metals in the following representative compounds or materials:
It can defined by the bonding properties and valency of metal and non-metal.
(a) A is a non-metal.
(b) A is a metal or non-metal like carbon or silicon.
(c) B is a non-metal.
(d) A and B, both are non-metals.
(e) A is a metal and B is a non-metal.
(f) A and B are non-metals.
(g) A is a metal and B is a non-metal.
(h) B is a non-metal.
Define atomicity.
The number of atoms constituting a molecule is knowns as its atomicity. For example in hydrogen molecule ( H2 ), its atomicity is 2 becuase it is made of 2 hydrogen atom.
How does an atom differ from a molecule?
An atom is the smallest particle of an element which may or may not have independent existence. On the other hand, ‘molecule’ is the smallest particle of the element or compound which is capable of independent existence. For example, helium (He) is an atom and can exist as such, whereas hydrogen atom (H) cannot exist as such but exists as a molecule, i.e., H2. A molecule may be made up of similar atoms (homo atomic molecule) or dissimilar atoms (hetero atomic molecule such as HCl).
How many kinds of atoms are present in a molecule of copper carbonate (CuCO3) ?
Copper carbonate is a hetero atomic molecule. It contains three types of atoms, i.e., one atom of copper, one atom of carbon and three atoms of oxygen.
Separate the following stable elements into atoms and molecules : Oxygen, Nitrogen, Argon, Sodium, Neon, Chlorine.
Atoms : Argon, Sodium, Neon.
Molecules : Oxygen, Nitrogen, Chlorine.
How many hydrogen and oxygen atoms are obtained when one molecule of water decomposes.
![]()
When water molecule decomposes it gives hydrogen and oxygen. according to law of conversation of mass " mass neither be created nor be destroy but change into one form to other form. Thus, 2 molecules of water gives 2 molecules of hydrogen, i.e., 4 atoms of hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen, i.e., two atoms of oxygen. Hence, one molecule of water on decomposition gives 2 atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen.
What is the difference between:
(i) an atom of hydrogen and a molecule of hydrogen ?
(ii) a molecule of oxygen and a molecule of water ?
(i) An atom of hydrogen is the smallest particle of hydrogen element which does not have independent existence. A molecule of hydrogen has two hydrogen atoms bonded together and is the smallest particle of hydrogen element which has independent existence.
(ii) A molecule of oxygen has two atoms of oxygen only. It is the smallest particle of oxygen element which can exist independently. A molecule of water is a compound obtained from two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
What is an ion?
An ion is a charged particle. It can be either positively charged or negatively charged. A negatively charged ion is called an anion and a positively charged ion is called a cation. Ions may consist a single charged atom or a group of atoms that have a net-charge on them. Such a group of atoms carrying a net charge is known as a polyatomic ion. For example, Na+ is a single charged atom and is known as sodium cation. Cl– is a single charged atom and is known as chloride anion. NO-3 is a group of atoms carrying net negative charge and is known polyatomic anion.
What are ionic compounds?
An ionic compound is a compound formed by ions bonding together through electrostatic forces. Such compounds are formed from combination of metals with non-metals. For example, sodium chloride is an ionic compound. Its constituent particles are positively charged sodium ions (Na+) and negatively charged chloride ions (Cl–).
Name the ions in the following compounds:
Sodium fluoride, potassium bromide, calcium oxide, silver sulphide.
Sodium fluoride — Sodium cation and fluoride anion
Potassium bromide — Potassium cation and bromide anion.
Calcium oxide — Calcium cation and oxide anion
Silver sulphide — Silver cation and sulphide anion
What do you understand by formula of a molecule?
Chemical formula: It is an expression which states the number and type of atoms present in a molecule of a substance. For example, there are 6C atoms and 14 H atoms in a hexane molecule, which has molecular formula C6H14.
What is valency? What is its use?
Valency define as, the combining capacity of an element. It can be used to find out how many atoms of an element will combine with the other element to form a chemical formula. For example, hydrogen has a valency of +1 and chlorine has a valency of –1, so one atom of hydrogen combines with one atom of chlorine to form hydrochloric acid. Further oxygen has a valency of –2, so one atom of oxygen combines with 2 atoms of hydrogen to form water molecule, H2O.
Give symbols and valencies for the common ions as given below:
Potassium, Barium, Aluminium, Calcium, Cobalt, Copper, Fluorine, Gold, Lead, Zinc, Iodine, Sulphide.
|
Name of ion |
Symbol |
Valency |
|
Potassium |
K+ |
+ 1 |
|
Barium |
Ba2+ |
+ 2 |
|
Aluminium |
Al3+ |
+ 3 |
|
Calcium |
Ca2+ |
+ 2 |
|
Cobalt |
Co2+ |
+ 2 |
|
Copper |
Cu2+ |
+ 1, +2 |
|
Fluoride |
F– |
–1 |
|
Gold |
Au+1,+2 |
+1,+2 |
|
Lead |
Pb+1,+2 |
+ 1, +2 |
|
Zinc |
Zn+2 |
+ 2 |
|
Iodide |
I–1 |
–1 |
|
Sulphide |
S–2 |
–2 |
Do all elements have a charged valency? Explain.
All elements do not form ions so their valencies do not have a charge. For example, carbon and silicon have a valency of 4 and nitrogen has a valency of 3. Further molecules containing only non-metals are formed without a charged valency. For example, in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), carbon has a valency of 4 and chlorine has a valency of 1.
Give the name and valency of the following polyatomic ions :
Ammonium, Hydroxide, Nitrate, Carbonate, Sulphate, Sulphite, Bicarbonate, Phosphate.
|
Polyatomic ion |
Symbol |
Valency |
|
Ammonium |
(NH4)+1 |
+ 1 |
|
Hydroxide |
(OH)– |
–1 |
|
Nitrate |
(NO3)–1 |
– 1 |
|
Carbonate |
(CO3)–2 |
–2 |
|
Sulphate |
(SO4)–2 |
–2 |
|
Sulphite |
(SO3)–2 |
-2 |
|
Bicarbonate |
(HCO3)–1 |
–1 |
|
Phosphate |
(PO4)–3 |
-3 |
How is a molecular formula of a compound written?
In order to write formula of a compound comprised of cations and anions, the valencies of the ion must be known. Let us consider a compound composed of cation A with valency x+ and anion B with valency y– . Then the following steps may be followed to write a molecular formula.
(i) Write down the symbols of the cation and anion side by side.
A B
(ii) Write their valencies at top corners as
Ax+ By–
(iii) Interchange between the ions their valencies and these are placed on the lower side of each radical or used as subscripts.
Ay Bx(iv) If a radical is multi-atomic, use a small bracket around it.
(v) Eliminate the common factor, if any, from the numbers used in subscripts.
vi) The valencies or charges on the ion must balance.
vii) When a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the name or symbol of the metal is written first. For example: calcium oxide (CaO), sodium chloride (NaCl), iron sulphide (FeS), copper oxide (CuO) etc., where oxygen, chlorine, sulphur are non-metals and are written on the right, whereas calcium, sodium, iron and copper are metals, and are written on the left.
viii) In compounds formed with polyatomic
ions, the ion is enclosed in a bracket
before writing the number to indicate the
ratio. Thus calcium phosphate, compound of calcium ion (valency 2+) and phosphate ion (valency 3–) is written as Ca3(PO4)2.
The same method is used to write formula even for non-ionic substances.
Write ‘step-wise’ the formulae for the following:
(a) Zinc Sulphate (b) Ammonium carbonate
(c) Methane (d) Potassium sulphide
(e) Cupric chloride (f) Hydrogen sulphate.
(a) Zinc sulphate (b) Ammonium carbonate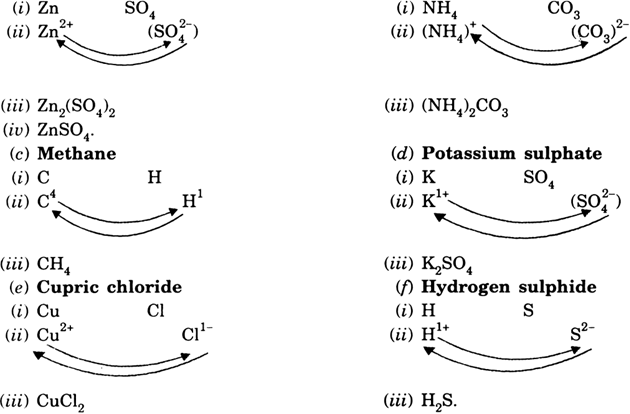
Calcium pyrophosphate is represented by the formula Ca2P2O7. Write the formula of ferric pyrophosphate.
Calcium has a valency of +2. There are two Ca atoms. Thus Ca carries a total of +4 charges. Therefore, pyrophosphate has a valency of -4. Since ferric ion has a valency of +3, the formula of ferric pyrophosphate is Fe4(P2O7)3.
Write the formula of aluminium chloride, aluminium sulphate, sodium chloride and sodium sulphate.
Aluminium chloride = AlCl3
Aluminium sulphate = Al2(SO4)3
Sodium chloride = NaCl
Sodium sulphate = Na2SO4
Valencies or charges of some ions are given below:
|
Ions |
Valency/charge |
|
Aluminium ion |
3+ |
|
Nitride ion |
3– |
|
Magnesium ion |
2+ |
|
Sulphate ion |
2– |
|
Fluoride ion |
1– |
|
Potassium ion |
1+ |
Using the above information, write down the chemical formulae of the following:
(i) Aluminium nitride (ii) Magnesium nitride
(iii) Aluminium sulphate (iv) Potassium fluoride
(v) Magnesium fluoride (vi) Potassium nitride.
|
Name of compound |
Cation |
Anion |
Chemical formula
|
|
(i) Aluminium nitride |
Al3+ |
N3- |
AlN |
|
|
Mg2+ |
N3- |
Mg3N2 |
|
(iii) Aluminium sulphate |
Al3+ |
SO42- |
Al2(SO4)3 |
|
(iv) Potassium fluoride |
K+ |
F- |
KF |
|
(v) Magnesium fluoride |
Mg2+ |
F- |
MgF2 |
|
(vi) Potassium nitride |
K+ |
N3- |
K3N |
If the calcium salt of a hypothetical anion Z has the molecular formula Ca3Z2. What is the valency of Z and what would be molecular formula of the aluminium salt of Z?
In a ionic compound the charge excange, thus Valency of Z = –3
Valency of Al = +3
Formula of aluminium salt of Z = AlZ.
The formula of sulphuric acid is H2SO4 and the formula of metal chloride is MCl3. Write the formula of metal sulphate.
Valency of SO4–2 is –2 and that of metal is +3 [since it combines with 3 chloride ions (–1)].
∴
Metal sulphate = M2(SO4)3.
Give the chemical name, chemical formulae for the following compounds.
Baking soda, Washing soda, Blue vitriol, Green vitriol, Gypsum, Oil of vitriol or white vitriol, Soda ash, Marble chips, Lime water.
|
Common name |
Chemical name |
Chemical formula |
|
Baking soda |
Sodium bicarbonate |
NaHCO3 |
|
Washing soda |
Sodium carbonate |
Na2CO3. 10H2O |
|
Blue vitriol |
Copper sulphate |
CuSO4 . 5H2O |
|
Green vitriol |
Ferrous sulphate |
FeSO4 . 7H2O |
|
Gypsum |
Calcium sulphate |
CaSO4.2H2O |
|
Oil of vitriol |
Sulphuric acid |
H2SO4 |
|
Soda ash |
Sodium carbonate |
Na2CO3 |
|
Marble chips |
Calcium carbonate |
CaCO3 |
|
Lime water |
Calcium hydroxide |
Ca(OH)2 |
What is molecular formula? Explain with example what information can be derived from a molecular formula?
Molecular formula of a substance is the symbolic representation of its molecule. It gives the number and kind of atoms united chemically. For example, water is given by H2O. H2SO4 represents one molecule of sulphuric acid.
Significance of a formula
To signify the information derived from a formula let us consider carbon dioxide whose formula is CO2. It indicates :
(i) The elements present in carbon dioxide are ‘carbon’ and ‘oxygen’.
(ii) One molecule of carbon dioxide is given by CO2.
(iii) On molecule of carbon dioxide has one atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen.
(iv) In carbon dioxide, carbon and oxygen are in a weight ratio of 12 : 32.
(v) Mass of one molecule (relative weight or molecular weight) of carbon dioxide is 44 u, 12 u contributed from carbon atom and 32, from the two oxygen atoms.
(vi) It shows that the valency of oxygen here is 2 and that of carbon is 4.
(vii) Molecule of CO2 is not charged and is not an ion.
Sponsor Area
The chemical formula for calcium oxide is CaO and not Ca2O2. Comment.
The chemical formula of calcium oxide is CaO because writing formula of a compound, valencies are divided by highest common factor. Similarly formula for aluminium nitrate is AlN and not Al3N3.
Write down the formulae of (i) aluminium oxide, (ii) aluminium chloride, (iii) hydrogen sulphide, (iv) calcium hydroxide, (v) ammonium sulphate, (vi) calcium bicarbonate, (vii) ammonium phosphate, (viii) silver nitrate.
(i) Aluminium oxide — Al2O3
(ii) Aluminium chloride — AlCl3
(iii) Hydrogen sulphide — H2S
(iv) Calcium hydroxide — Ca(OH)2
(v) Ammonium sulphate — (NH4)2SO4
(vi) Calcium bicarbonate — Ca(HCO3)2
(vii) Ammonium phosphate — (NH4)3PO4
(viii) Silver nitrate — AgNO3
Write down the name of the compounds represented by the following formulae : (i) Al2(SO)3, (ii) MgCl2, (iii) K2SO4, (iv) KNO3, (v) CaCO3, (vi) (NH4)2CO3, (vii) H2CO3, (viii) SO2
i) Al2(SO4)3 — Aluminium sulphate
(ii) MgCl2 — Magnesium chloride
(iii) K2SO4 — Potassium sulphate
(iv) KNO3 — Potassium nitrate
(v) CaCO3 — Calcium carbonate
(vi) (NH4)2CO3 — Ammonium carbonate
(vii) H2CO3 — Hydrogen carbonate
(viii) SO2 — Sulphur dioxide
Write down the formulae of
(i) sodium oxide
(ii) aluminium chloride
(iii) sodium sulphate
(iv) magnesium hydroxide.
The formulae of given compounds are:
(i) sodium oxide — Na2O
(ii) aluminium chloride — AlCl3
(iii) sodium sulphate — Na2SO4
(iv) magnesium hydroxide — Mg(OH)2
Write down the names of compounds represented by the following formulae:
(i) Al2(SO)3, (ii) CaCl2, (iii) K2SO4, (iv) KNO3, (v) CaCO3.
(i) Al2(SO4)3 —Aluminium sulphate
(ii) CaCl2 — Calcium chloride
(iii) K2SO4 — Potassium sulphate
(iv) KNO3 — Potassium nitrate
(v) CaCO3 — Calcium carbonate.
Define ' Molecular Mass'
The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of substance. it is therefore the relative mass of a molecule expressed in atomic mass units.
What is relative formula mass?
The formula mass of a substance is the sum of atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound. Formula mass is used for substances whose constituent particles are ions. In ionic compound, one molecule may contain several positive and negative ions. One molecule of sodium chloride contains six Na+ and 6 C1– ions. But formula unit is NaC1. So formula mass is used in ionic compounds.
Atomic masses of few elements are given:
|
Element |
Atomic mass (u) |
|
Hydrogen (H) |
1 |
|
Carbon (C) |
12 |
|
Oxygen (O) |
16 |
|
Nitrogen (N) |
14 |
|
Sodium (Na) |
23 |
|
Magnesium (Mg) |
24 |
|
Chlorine (Cl) |
35.5 |
|
Fluorine (F) |
19 |
Find the molecular mass or formula mass of the following compounds:
H2, O2, Cl2, CH4, CH3OH, CO2, HCl, Na2O, MgCl2, NaF, Na2CO3, NaNO3.
Molecular mass of given compounds :
Give an account of the ‘mole concept’.
A mole signifies a collection of 6.023 x 1023 atoms, molecules, ions, etc. Thus, 1 mole of oxygen atom refers to 6.023 x 1023 atoms of oxygen.
A mole also refers to the mass in grams numerically equal to the molecular mass or atomic mass in atomic mass units. Thus, mole signifies both number and amount in grams. For example,
One mole of hydrogen molecule refers to
(i) 6.02323 x 1023 molecules of hydrogen.
(ii) 2.016 g (equivalent to molecular mass in u i.e., 2.016 u) of hydrogen.
What is the utility of the mole concept?
Utility of mole concept.
(i) From the number of moles of a substance, we can calculate the number of elementary particles because the number of moles of a substance is directly proportional to the number of elementary particles.
(ii) One mole of a gas occupies 22.4 litres at S.T.P. (273 K and 1 atm).
(iii) One mole of any gas under the same conditions of temperature and pressure occupies the same volume.
(iv) One mole is equal to molecular mass in grams which is equal to 6.023 x 1023 atoms, molecules, ions etc. Thus, we can calculate absolute masses of atoms and molecules.
What is Avogadro number constant?
The number 6.023 x 1023 is referred to as Avogadro number constant and is denoted by symbol NA.
Define the term gram atom. How is it related to the mole and Avogadro number?
Gram atom or Gram atomic mass. The atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is called gram atomic mass or gram atom.
1 gram atom of any element contains 6.023 x 1023 (Avogadro number) atoms of the
element. It is equal to 1 mole of atoms.
1 gram atomic mass = 6.023 x 1023 atoms = 1 mole.
(Avogadro number)
The gram atomic mass of an element is equal to the masses of its 6.023 x 1023 atoms. Examples. One gram atom of hydrogen atom weighs one gram and contains 6.023 x 1023 hydrogen atoms. 1 mole of hydrogen atom also weighs 1 gram.
Define the term:Gram molecular mass. How is it related to the mole and Avogadro number?
The molecular mass of a substance (compound) expressed in grams is called its gram molecular mass. Ionic compounds do not contain molecules (they consist of ions) and therefore, molecular masses of ionic compounds are equal to their formula masses.
A gram molecular mass of a compound is equal to the mass of 6.023 x 1023 molecules or 1 mole of the substance.
Examples;
(i) A gram molecular mass of hydrogen molecules (molecular mass = 2)
weighs 2 grams and contains 6.023 x 1023 hydrogen molecules.
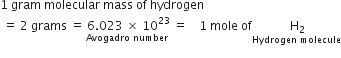
(ii) A gram molecular mass of sodium chloride (molecular or formula mass = 58.5) weighs 58.5 grams and contains 6.023 x 1023 sodium chloride units.
How do you account for the fact that gram atomic mass or gram molecular mass of any substance contains the same number of particles?
Atomic mass of any substance indicates the times it is heavier than 1/12th of C-12 atom. Now atomic mass of H atom is one u, it means that one C-12 atom is 12 times as heavy as one H atom or to say 1000 C-12 atoms are 12 times as heavy as 1000 H atoms or 6.023 x 1023 C-12 atoms (12 grams C-12 are found to contain 6.023 x 1023 atoms) are 12 times as heavy as 6.023 x 1023 H atoms. Since atomic mass of C-12 is 12 u and that of H atom is 1 u, it can be inferred that weight equal to atomic mass of C-12 or H atom contains the same number of atoms. Thus, it can be shown that gram atomic mass or gram molecular mass of all substances have the same number, i.e., 6.023 x 1023 particles.
Define mole and Avogadro's number? Will the weight of 1 mole of sodium and 1 mole of oxygen be the same?
Mole: Mole is the measurement in chemistry. It is used to express the amount of a chemical substance.
One mole is defined as the amount of substance of a system which contains as many entities like, atoms, molecules, and ions as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon - 12'.
Avogadro number: The number of the particles present in one mole of any substance is equal to 6.022x1023. This is called Avogadro's number or Avogadro's constant.
1 mole of sodium (6.023 x 1023 atoms) weighs 23 g (atomic mass). And 1 mole of oxygen (6.023 x 1023 molecules) weighs 32 g (molecular mass). Thus, particles present in 1 mole of oxygen and sodium is same such as (6.023 x 1023 atoms) but the weight could not be same.
What is an ion ?
The metal and non-metal contain charged species. The charged species are known as ion. It can be negtive or positive. A negatively charged ion is called anion and the postively charged ion is called cation.
How many moles of chlorine atoms are present in one mole of the following compounds:
(i) Cl2O7 (ii) HCl (iii) BaCl2 (iv) AlCl3 (v) FeCl3 (vi) CCl4.
(i) 2 moles of chlorine atoms in one mole of Cl2O7
(ii) 1 mole of chlorine atoms in one mole of HCl
(iii) 2 moles of chlorine atoms in one mole of BaCl2
(iv) 3 moles of chlorine atoms in one mole of AlCl3
(v) 3 moles of chlorine atoms in one mole of FeCl3
(vi) 4 moles of chlorine atoms in one mole of CCl4.
What gives the number and kind of atoms in each molecule of a substance?
Molecular formula gives information of the number and kind of atoms in each molecule of a substance.
What is the weight of 0.5 mole of oxygen?
Mass = molar mass x number of moles
m= M x n =16 x0.5 = 8 g
Tips: -
16 gram.
How many moles does 11 g of carbon dioxide make?
Molecular weight of carbon dioxide is 44g/mol.
Such that CO2 contains 1 carbon and 2 oxygen atom. Thus,
1 x12 +2x16 =44 (mass of carbon =12, mass of oxygen =16)
Now by dividing the given grams (11g) by the molecular weight of CO2:
11/44 =0.25 mol
How many moles of oxygen atoms are present in 1 mole of KMnO4?
Four moles of oxygen atoms are present in 1 mole of KMnO4.
Calculate the mass of 6.022 x1022 atoms of He.
6.022 x1022 atom of Helium weight 4g
Therefore 6.022 x 1022 atoms of Helium will weighs
4 x6.022 x1022/6.022 x1023 =0.4g
What is the percentage of oxygen in water?
Total molecular mass of water =18 g
mass of oxygen is =16g
Thus, the percentage of oxygen in water is,
16/18 x100 =88.9%
Water always contains hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 1 : 8 by mass irrespective of the source of water. Does it conform to some law in chemical combination?
The above statement conforms to Law of Constant Proportion.
Name the smallest particle that has all the properties of an element.
Atom is smallest particles of an element.
Name the smallest particle that has all the properties of a compound.
Molecule is smallest particle of compound.
Sponsor Area
Identify the triatomic molecule from the following : HCl, S8, He, H2S, CH3OH.
What is gram molecular mass of CaCO3. (Atomic mass of Ca, C and O are 40, 12 and 16 amu respectively)?
Gram molecular mass of CaCO3 :
Mass of Calcium =40
Mass of carbon =12
Mass of oxygen =16
Thus,
40 +12 +3 x16 =100grams.
What is the ‘term’ called ‘the mass in grams’ of 1 mole of a substance?
Molar mass or gram molecular mass.
How many mole atoms of sulphur are present in two moles of sulphuric acid, H2SO4?
In 2 moles of sulphuric acid (2H2SO4) 2 moles of sulphur is present.
Give the molecular mass and molar mass of C2H6.
mass of carbon atom =12 u
mass of hydrogen atom =1 u
therefore molecular mass of C2H6
12 x2 +1x6 =30 u
Hence, molecular mass of C2H6 = 30 u
Molar mass of C2H6 = 30 g mol–1
How many molecules are present in one molar mass of a substance?
In one molar mass of a substance 6.022 x 1023 molecules are present.
What is the approximate size of an atom?
The diameter of an atom ranges from about 0.1 to 0.5 nanometers (1 × 10-10 m to 5 × 10-10 m)
Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, CO2, CH4, CH6, C2H4, NH3, CH3 OH.
Mass of hydrogen =1 u
Molecular mass of H2 = 1+1 =2 u
Mass of oxygen=16u
Molecular mass of O2 = 16+16 = 32 u
Mass of Chlorine=35.5u
Molecular mass of Cl2 = 35.5 + 35.5 = 71 u
Mass of carbon =12u
Mass of oxygen=16u
Molecular mass of CO2 = 12 +32 = 44 u
Mass of carbon = 12u
Mass of hydrogen=1u
Molecular mass of C2H6 = 12 X 2 + 1 X6 = 30 u
Mass of carbon = 12u
Mass of hydrogen=1u
Molecular mass of C2H4 = 12 X 2 + 1 X 4 = 28 u
Mass of hydrogen=1u
Mass of carbon =12u
Molecular mass of NH3 = 1 X 14 + 1 X 3 = 17 u
Mass of carbon = 12u
Mass of hydrogen=1u
Mass of oxygen=16u
Molecular mass of CH3OH = 1 X 12 + 1 X 3 + 1 X 16 +1 X 1 = 32 u
Calculatte the formula unit masses of Zno, Na2O, K2CO3 given atomic masses of Zn = 65 u, Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u and O = 16 u.
We have given,
Atomic masses of elements: Zn = 65 u, Na = 23 u, K = 39u, C = 12 u and O = 16u
Formula unit mass of ZnO = 65 + 16 = 81 u
Formula unit mass of Na2O =23 X 2 +16 = 62 u
Formula unit mass of K2CO3 = 39 X 2 + 12 X 1 + 16 X 3 = 138 u
If one mole of carbon atoms weights is 12 grams, then what is the mass ( in grams) of 1 atom of carbon?
1 mole of carbon atoms = 6.022 X 1023 atoms
Now,
6.022 X 1023 atoms of carbon weights = 12g
So, One atom of carbon weights =12/6.022 X 1023 = 1.99 X 1023g.
Dalton’s atomic theory provided explanation for the various laws of ______________.
combinations
,combinations
A mole does not signify
atomic mass unit
6.022 x 1023 ions
22.4 litres of a gas at STP
gram molecular mass
A.
atomic mass unit
Select the ionic compound
sulphur molecule, S8
phosphorus molecule, P4
methane, CH4
copper nitrate, Cu(NO3)
D.
copper nitrate, Cu(NO3)
One atomic mass unit is equal to weight of
One atom of hydrogen
1/16th of oxygen atom
1/12th fo natural carbon atom
1/12 of C-12 isotope of carbon
D.
1/12 of C-12 isotope of carbon
How does the force of gravitation between two bodies change when the distance between them is reduced to half?
According to the law of gravitation, the force of attraction between two bodies is,
![]()
When the distance is reduced to half,
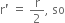
![]()
Thus, graviational force becomes four times the original force.
Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why, then, does not a heavy object fall faster than a light object?
The gravitational force acting on the body is given by,
![]()
![]()
We can see that, F ∝ m but g does not depend on m.
Hence, all bodies fall with the same rapidness when there is no air resistance.
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the Earth = 6 x 104 kg and radius of earth is 6.4 x 106 m)
Given,
Mass of the body (m) = 1 kg
Mass of the earth (M) = 6 x 1024kg
Radius of the earth (R) = 6.4 x 106m
Magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and 1 kg body,
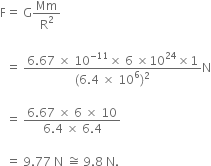
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon, with a force that is greater, or smaller, or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth ? Why?
According to Newton's third law, these two forces are equal and opposite. The earth attracts the moon with the same force as the force with which the moon attracts the earth.
If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
According to Newton's third law, the moon attracts earth with a force equal to that with which the earth attracts the moon. But, the mass of Earth is much massive than that of the moon. So, the acceleration produced in the earth,
(a ∝1/m)
is not noticeable.
What happens to the force between two bodies, if
(i) the mass of one body is doubled?
(ii) the distance between the bodies is doubled and tripled?
(iii) the masses of both bodies are doubled?
Gravitational Force, F = G ![]()
(i) The force gets doubled on increasing the mass of the body (m1 or m2).
New force becomes,
![]()
a) When distance between the bodies is doubled,
i.e. the force becomes one fourth of the original force.
b) When the distance between the two bodies is tripled,
i.e. the force becomes one ninth of the original force.
(iii) When the masses of both sids are doubled,
i.e, the force becomes four times the original force when masses of both bodies are doubled.
What is the importance of universal law of gravitation?
The universal law of gravitation successfully explained many phenomena occurring in nature.
Some of these phenomena are as follows:
1. The force that binds us to the earth.
2. The motion of the moon around the earth.
3. The motion of planets around the sun.
4. The tides due to the moon and the sun.
What is the acceleration of free fall?
Near the surface of the earth, its value is 9.8 ms-2.
What do we call the gravitational force between the earth and an object?
Gravitational force between the earth and an object is called weight of the object.
Amit buys few grams of gold at poles as per the instruction of one of his friends. He hands over the same when he meets him at equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why?
The friend of Amit will not agree with the weight of the gold bought. The value of 'g' at the equator is less than that at the poles. Hence, the few gram of gold at poles will measure less when taken to the equator.
Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
The sheet of paper crumpled into a ball will fall faster. The sheet of paper will experience a larger air resistance due to its larger surface area. Therefore, the sheet falls slowly.
Gravitational force on the surface of the moon is only 1/6 as strong as gravitational force on the earth. What is the weight in newtons of a 10 kg object on the moon and on the earth? What is its mass on each?
Mass of the object on the moon = 6 kg.
Mass of the object on the earth = 6 kg.
Weight of the object on the earth = mg = 10 x 9.8 = 98 N.
Weight of the object on the moon
![]()
Therefore, the weight of object on earth and moon is different.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 m/s. Calculate
(i) the maximum height to which it rises,
(ii) the total time it takes to return to the surface of the earth.
(i) Upward velocity is taken positive and acceleration due to gravity is taken negative, according tho the cartesian sign convention.
So,
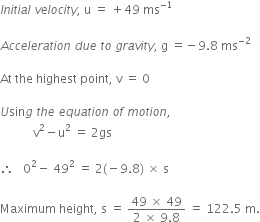
(ii) Let t be the time taken by the stone to reach the highest point.
According to the equation,
v = u + gt
![]()
Since time of ascent = time of descent
![]()
A stone is released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 m. Calculate its final velocity.
Given, a stone is released from the top of a tower.
Initial velocity, u = 0 m/s
Acceleration due to gravity, g = -9.8 m/s2
Distance covered by the ball during the course of it's motion = 19.6 m
Now, usign the equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2ags
We have,
v2 - 02 = 2 * (-9.8) * (-19.6)
i.e., v2 - 02 = (19.6)2
i.e., v = - 19.6 m/s
The negative sign indicates that the velocity is acting in the downward direction
A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Taking g = 10 m/s2, find maximum height reached by the stone. What is the net displacement and total distance covered by the stone?
Given, a stone is thrown vertically upwards.
Initial velocity, u = 40 m/s
Acceleration due to gravity, g = -10 m/s2
When the stone reaches a maximum heigh, v = 0
Now, using the equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2 gs
We have,
02 - 402 = 2 (-10) h
i.e., h = (40*40)/ 20 = 80 m
Total distance covered = h + h = 80 + 80 = 160 m
Net displacement = 80 - 80 = 0.
Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg and of the sun = 2 x 1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 x 1011 m.
Given,
Mass of the earth, Me = 6 ![]()
Mass of the Sun, Ms = ![]()
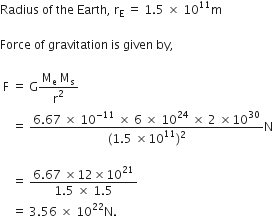
A stone is allowed to fall from the top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Find when and where the two stones meet?
Suppose the two stones meet at a height x from the ground, after time t from the start.
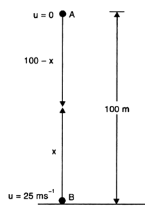
Hence, the two stones meet after 4 sec at a height of 20 m from the ground or 80 m from the top.
In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
The upward force exerted by a liquid on an object is known as buoyant force. Buoyant force acts in the vertically upward direction, through the centre of gravity of the displaced fluid which is called centre of buoyancy.
Why does a block of plastic piece released under water come to the surface of water?
The upthrust or the buoyant force exerted by water brings the plastic block to the surface of water.
The volume of 50 g substance is 20 cm3. If the density of water is 1 g cm-3, will the substance float or sink?
Mass of a substance = 50 g
Volume of substance = 20 cm3
As the denisty of substance is greater than that of water, so the substance will sink in water.
The volume of a 500 g sealed packet is 350 cm3. Will the packet float or sink in water if the density of water is 1 g cm-3? What will be the mass of the water displaced by this packet?
Mass of a packet = 500 g
Volume of packet = 350 cm3![]()
The sealed packet will sink in water because its density (1.43 g cm-3) is more than that of water (1 g cm-3).
Distinguish between the terms gravitation and gravity, giving suitable examples.
Gravitation: Every single body in this universe attracts every other body with a force known as gravitational force. Gravitation is the force of attraction between any two bodies in the universe.
Given are some of the examples on which gravitational force acts.
Attraction between the sun and the earth, attraction between a table and a chair lying in a room, attraction between the earth and a satellite revolving around it, etc.
Gravity: Gravity is the attraction between the earth and any object lying on or near its surface. A body thrown up falls back on the surface of the earth due to earth's force of gravity.
Gravity is a special case of gravitation.
Give some examples of the gravitational force in nature.
The gravitational force plays an important role in nature. Below are mentioned some examples where gravitaional force comes into play:
1. All the planets revolve around the sun due to the gravitational force between the sun and the planets. Thus, the gravitational force is responsible for the existence of the solar system.
Fig. Our solar system. Gravitational force holds together the sun and the planets.
2. The motion of the moon around the earth is due to the gravitational force between the moon and the earth.
3. Tides in oceans are formed due to the gravitational force between the moon and the water in oceans.
4. The earth holds the atmosphere (envelope of gases) near its surface due to its gravitational force.
5. The gravitational force of the earth is responsible for rainfall and snowfall.
What is centripetal force? From where does the moon get the centripetal force required for its motion around the earth?
Centripetal force:
i) When a body moves along a circular path with a uniform speed, its direction of motion changes at every point.
ii) The change in direction involves change in velocity or acceleration. The force that provides this acceleration and keeps the body moving along the circular path, acts towards the centre. This force is called centripetal (centre seeking) force.
iii) Therefore, a force which is required to make a body move along a circular path with uniform speed is called centripetal force.
iv) Centripetal force always acts along the radius and towards the centre of the circular path.
v) The figure given below shows that it is the centripetal force which continuously deflects a particle from its straight line path to make it move along a circle. 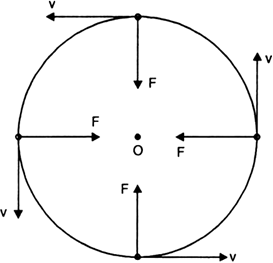
Fig. Centripetal force.
Example:
The moon needs a centripetal force, for its circular motion around the earth. This centripetal force is provided by the gravitational attraction exerted by the earth on the moon.
State Kepler’s law of planetary motion.
Kepler's laws of planetary motion:
John Kepler derived three laws, which govern the motion of planets. These laws are called Kepler's law and can be stated as follows:
1. Law of orbits (first law):
Each planet revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit with the sun S situated at one of the two foci, as shown in Fig. below. 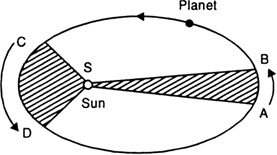
Fig. Motion of a planet in an ellipse.
2. Laws of areas (second law):
The line joining the planet and the sun sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time. Thus, if the time of travel from A to B is the same as that from C to D, then the shaded areas SAB and SCD are equal.
3. Law of periods (third law):
The cube of the mean distance r of a planet from the sun is proportional to the square of its orbital period T.
![]()
How did Newton guess the inverse square rule obeyed by the gravitational force?
Kepler's third law of planetary motion was used by Newton to guess how the force of gravitation of the earth is weakened by distance.
Suppose a planet revolves around the sun in a circular orbit of radius r with speed v, then the force acting on the planet is given by,
![]() ...(1)
...(1)
If 'T' is the period of revolution of the planet around the sun, then its orbital velocity will be

![]()
According to Kepler's third law,
![]()
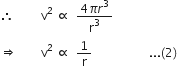
According to the inverse-square law of gravitaion, the force of gravitation on a planet should decrease as the square of the distance of the planet from the sun.
Thus, Newton formulated the universal law of gravitation.
State Newton's universal law of gravitation. Hence define universal gravitational constant. Give the value of G.
Newton's universal law of gravitation
The gravitational law states that every body in the universe attracts every other body with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The direction of the force is along the line joining the centres of two bodies.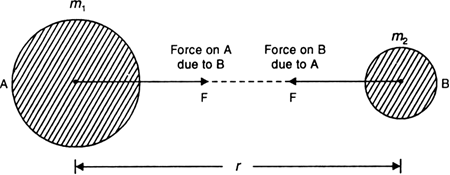
Fig. Law of gravitation.
As shown in Fig. above, consider two bodies A and B of masses m1 and m2.
Let r be the distance between their centres.
If F is the force with which the two bodies attract each other, then according to the law of gravitation,
![]()
![]()
Combining the two factors, we get
![]()
![]()
where G is a proportionality constant, called universal gravitational constant.
The value of G is 6.754×10−11 m3 kg−1 s−2.
Determine the units of G in SI system of measurement.
According to Newton's law of gravitation,
Gravitational force is given by,
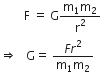
In SI system, force F is measured in Newton; distance r in metres and masses m1 and m2 in kilo gram.
Therefore,
SI unit of ![]()
Name the scientist who first determined the value of G experimentally. What is the value of G accepted presently?
Henry Cavendish first determined the value of G experimentally in the year 1778, using a sensitive balance.
The presently accepted value of G = 6.673 x 10–11 Nm2 kg-2.
Why is G called ‘a universal gravitational constant’?
The value of G does not depend on the nature of the intervening medium. Also, G is constant for any object in the universe. Hence, is is known as 'universal gravitational constant'.
Do the gravitational forces obey Newton's third law of motion?
Yes, the gravitational forces obey Newton's third law of motion.
Body A attracts body B with a force FBA and body B attracts body A with a force FBA. These two forces are equal and opposite, forming action and reaction pair. Hence gravitational forces obey Newton's third law of motion.
What is the importance of the universal law of gravitation in nature?
The universal law of gravitation successfully explained many phenomena occurring in nature.
Some of these phenomena are as follows:
1. The force that binds us to the earth.
2. The motion of the moon around the earth.
3. The motion of planets around the sun.
4. The tides due to the moon and the sun.
State the universal law of gravitation.
Universal law of gravitation states that every body in the universe attracts every other body with a force which is directly proportional to product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
This force acts along the line joining the centres of the two bodies.
Write the formula to find the magnitude of gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.
Consider, the earth as a sphere of mass M and radius R.
If an object of mass m is placed on the surface of the earth, then the magnitude of the gravitational force between the body and the earth is,
![]()
The mass of planet Jupiter is 1.9 x 1027 kg and that of the sun is 1.99 x 1030 kg. The mean distance of the Jupiter from the sun is 7.8 x 1011 m. Calculate the gravitational force which the sun exerts on Jupiter.

F is the gravitaional force which the Sun exerts on Jupiter.
Suppose you and your friend have mass 50 kg each. Suppose also that both of you are standing such that your centres of gravity are 1 m apart. Calculate the force of gravitation between you and your friend. Calculate also the force of gravity acting on you. Take the mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg, radius of the earth = 6.4 x 10 6 m and G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2.
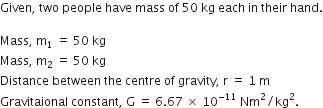
Therefore,
Force of gravitation,
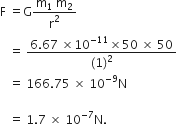

A sphere of mass 40 kg is attracted by a second sphere of mass 60 kg with a force equal to 4 x 10–5 N. If G = 6 x 10–11 Nm2/kg 2, calculate the distance between the two spheres.
Given,
Mass of the first sphere, m1 = 40 kg
Mass of the second sphere, m2 = 60 kg
Forcing acting between the bodies, F = 4 x 10–5 N
Gravitaional constant, G = 6 x 10–11 Nm2/kg2.
Now, using the formula,
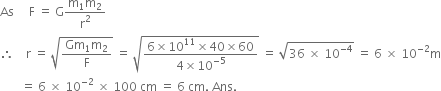
Therefore, the distance between the two spheres is 6 cm.
Compare the gravitational forces exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth. Which exerts a greater force and by how many times?
Mass of the earth, M = 6 x 1024 kg
Mass of the sun, Ms = 2 x 1030 kg
Mass of the moon, Mm = 7.3 x 1022 kg
Distance of Earth from the sun, rs = 1.5 x 1011 m
Distance of Earth from the moon, rm = 3.84 x 108 m
Gravitational force exerted by the sun on the earth,
![]()
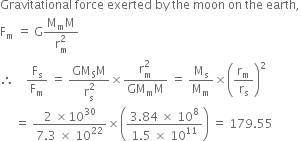
Thus the sun exerts force, about 180 times the force exerted by the moon on the earth.
The mass of the earth is 6 x 1024 kg and that of the moon is 7.4 x 1022 kg. If the distance between the earth and the moon be 3.84 x 105 km, calculate the force exerted by the earth on the moon. The value of G = 6.7 x 10–11 Nm2 kg–2.

The distance between the earth and the moon is,
r = 3.84 x 105 m
= 3.84 x 105 x 1000 m
= 3.84 x 108 m
The value of G = 6.7 x 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
The force exerted by the earth on the moon is,
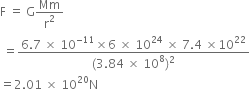
Thus the force exerted by the earth on the moon is 2.01 x 1020 N.
Suppose that the two giant planets of the solar system, Jupiter and Saturn, are in the same line as seen from the earth. It happens occasionally that some planets appear in the same line from the earth. Find the total gravitational force due to them on a person of mass 50 kg on the earth. Compare this with the force of gravity on the same person. Could the force due to planets be important?
The given question has been illustrated in the figure below.
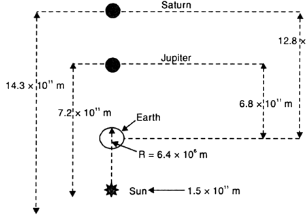
The force due to planets, is very small and hence is negligible.
What were the views of Aristotle regarding the rate of fall of bodies on the surface of the earth?
In the early days, it was observed that a piece of stone dropped from a certain height, reaches the Earth earlier than a light piece of paper dropped from the same height. This led the great greek philospher, Aristotle to conclude that, a heavier body falls faster on the earth in comparison to a lighter body. So a body having mass twice as that of another body will fall twice fast than the lighter body.
But, in 1590, Galileo disapproved this belief. He proved that all bodies irrespective of their mass and nature, fall at the same rate towards the earth.
How did Galileo prove that different bodies fall towards the earth at the same rate?
Galileo proved that all bodies fall at the same rate towards the earth. This experiment was done as mentioned below:
Galileo climbed to the top of the leaning tower of Pisa in the presence of a large gathering. He dropped spheres of different masses and materials simultaneously from the top. To a surprise of the gathering, all the spheres reached the earth's surface at the same time.
So, he concluded that the acceleration of an object, falling freely towards the earth does not depend on the mass of the object.
How did Robert Boyle prove experimentally that in vacuum, all bodies fall at the same rate?
Boyle's experiment: 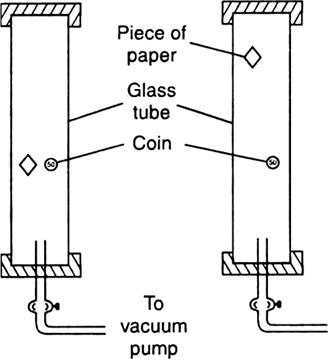
Fig. Boyle's experiment of coin and paper (a) in vacuum, (b) in air.
i) Robert Boyle took a long glass tube, a heavy coin and a piece of paper were placed inside it as shown in the Fig. below
ii) The ends of the tube were closed and air of the tube was removed by a vacuum pump.
iii) When the tube was quickly inverted, it was observed that both the coin and the paper hit the bottom at the same time.
iv) On repeating the experiment with air inside the tube, it was observed that the piece of paper falls slowly while the coin hits the bottom immediately.
v) thus, Galileo's assertion was proved, that in vacuum all bodies irrespective of their mass fall towards the earth with the same acceleration.
What do you mean by the term free fall?
When the objects fall towards the Earth solely under the effect of gravitational force, the fall is known as free fall. The effect of air resistance is neglected in these cases.
E.g., The motion of a small heavy body in air, may be taken as a free fall as the resistance of air on it is very small.
Define acceleration due to gravity. Deduce an expression for it in terms of mass of the earth (M) and universal gravitational constant (G).
Acceleration due to gravity:
Acceleration produced in the motion of a body falling under the force of gravity is called acceleration due to gravity.
It is denoted by ‘g’.
Relation between g and G
Consider the earth as a sphere of mass M and radius R, as shown in Fig. 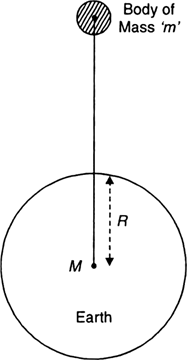
Fig. To determine ‘g’.
Consider a body of mass 'm' situated at distance 'r' from the centre of the earth.
According to Newton's law of gravitation, the force of attraction between the earth and the body is given by,
![]()
This force of gravity produces on acceleration ‘g’, called acceleration due to gravity in the body of mass m.
Hence, from Newton's second law,
F = Mass x Acceleration = mg ...(2)
From equations (1) and (2), we get
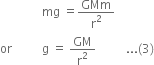
The above derived equation gives acceleration due to gravity at points far away from the earth.
If body is located on the surface of the earth, then r = R, the radius of the earth.
The above equation becomes,
![]()
This equation gives acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth.
The value of 'g' is almost constant near the surface of the earth because the radus of the earth does not change much over it's entire surface.
The value of ‘g’ on earth’s surface = 9.8 ms-2.
Why do we take distance 'r' of the body from the centre of the earth for points outside or on the surface of the body?
We take distance 'r' of the body from the centre of the Earth because for gravitational force at points outside or on the surface, the spherical body behaves as if the entire mass of the body is concentrated at its centre.
What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity?
Whenever an object falls towards the Earth under the influence of gravitational force, an acceleration is involved. This is known as acceleration due to gravity.
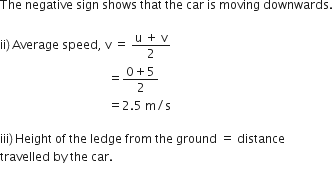
A car falls off a ledge and drops to the ground in 0.5 second. Let g = 10 ms–2.
(i) What is its speed on striking the ground?
(ii) What is its average speed during the 0.5 second?
(iii) How high is the ledge from the ground?
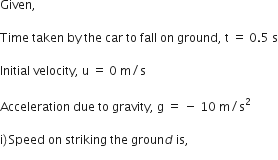
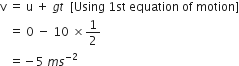
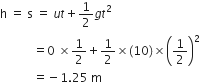
The negative sign in the distance implies that the car is moving downwards.
A particle is thrown up vertically with a velocity of 50 m/s. What will be its velocity at the highest point of its journey? How high would the particle rise? What time would it take to reach the highest point?
According to the cartesian sign convention,
Upward velocity is taken positive, and
acceleration due to gravity is taken negative.
So,
Velocity with which the particle is thrown, u = +50 m/s
Acceleration due to gravity, g = -10 m/s2
At the highest point, v = 0.
Using the formula,
v = u + gt
![]() 0 = 50 - 10 x t
0 = 50 - 10 x t
![]()
![]()
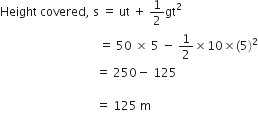
A helicopter is ascending with a velocity of 2 m/s at a height of 24 m when it drops a mail packet. The packet contains material, which can be damaged if it hits ground with velocity of magnitude greater than 72 km / h. Was the packet damaged? Explain your answer.
(Take g = 10 m/s2)
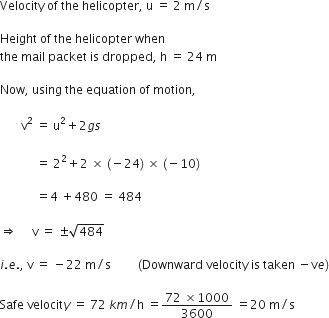
The packet reaches the ground with a velocity (22 m/s), which is greater than the safe velocity of 20 m/s. So the packet is damaged.
A ball is dropped from the jumping board of a swimming pool, which is at a height of 20 m. A second ball is thrown from the same board after one second with initial velocity u. Both the balls hit the water together. What was the initial velocity with which the second ball was thrown ? Do they hit water with the same velocity ? Explain your answer.
(i) Given that,
s = -20 m, u = 0 m/s and g = -10 m/s2
Now, according to the third equation of motion,
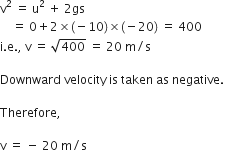
ii) Now,
Distance travelled by the ball, s = -40 m
u = 0 and g = -10 m/s2
Now, using the third equation of motion,
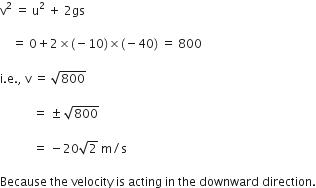
A rocket is launched to travel vertically upwards with a constant velocity of 20 m/s. After travelling for 35 seconds the rocket develops a snag and its fuel supply is cut off. The rocket then travels like a free body. What is the total height achieved by it ? After what time of its launch will it come back to the earth ?
Given that,
Upward distance covered by the rocket in first 35 s, 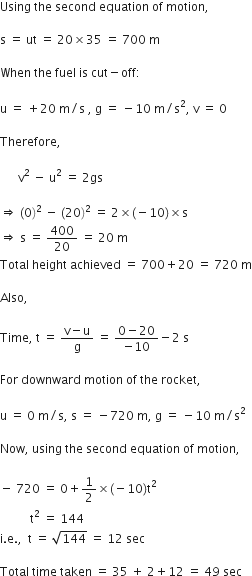
A helicopter is on a mission to drop food for people stranded on a boat. It is at a height of 20 m and moving with a steady horizontal velocity of 2 m/s when it spots the nearest end of the boat immediately below it. It drops the packets then. If the length of the boat is 5 m, will the people in the boat receive the packets?
For the vertical motion of the food packet:
u = 0, s = -20 m, g = -10 m/s2
Now, using the second eqaution of motion,

A man is standing at the top of a 60 m high tower. He throws a ball vertically upwards with a velocity of 20 m/s. After what time will the ball pass him going downward ? How long after its release will the ball reach the ground ? (Take g = 10 m/s2)
(i) When the ball passes the man, net displacement = 0
That is, s = 0 m
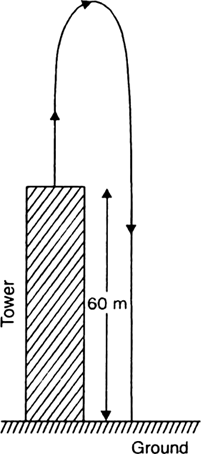
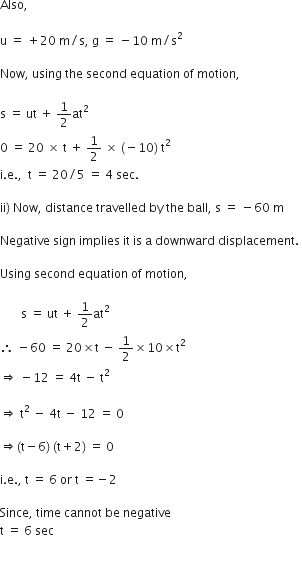
Take data in Fig. 10.12 and find the value of ‘a’.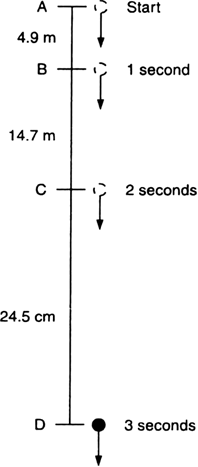
From A to B,
u = 0 m/s, s = - 4.9 m, t = 1 sec
Now, using the 2nd equation of motion,
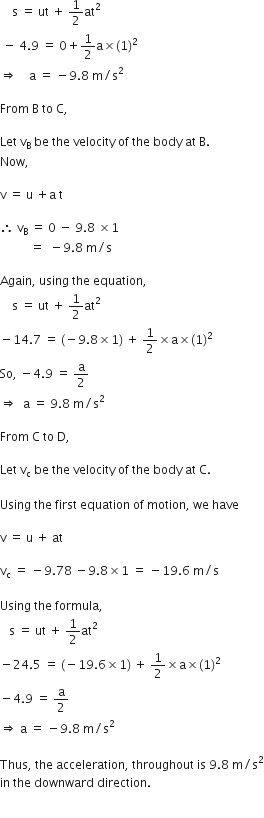
A particle is thrown up vertically with a velocity of 50 m/s. Make a table showing the distance covered by the particle, the velocity and acceleration at the end of each second of its journey. Use this data to draw distance-time, velocity-time and acceleration-time graphs.
Displacement covered is s.
Velocity attained is given by,
v = u - gt
Acceleration, a = -g
Given:
Initial velocity, u = 50 ms-1
Acceleration due to gravity, a = -10 ms-2
|
Time |
Displacement |
Distance |
Velocity |
Acceleration |
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
0 m 45 m 80 m 105 m 120 m 125 m 120 m 105 m 80 m 45 m 0 |
0 45 m 80 m 105 m 120 m 125 m 130 m 145 m 170 m 205 m 250 m |
50 ms–1 40 ms–1 30 ms–1 20 ms–1 10 ms–1 0 -10 ms–1 -20 ms–1 -30 ms–1 -40 ms–1 -50 ms–1 |
-10 m/s2 -10 m/s2 -10 m/s 2 -10 m/s2 -10 m/s 2 -10 m/s2 -10 m/s 2 -10 m/s-2 -10 m/s 2 -10 m/s 2 -10 m/s 2 |
Fig. (i) Distance-time graph.
Fig. (ii): Velocity-time graph
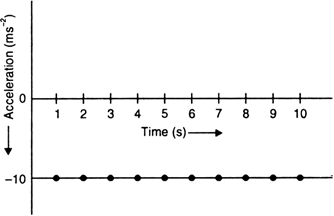
Fig. (iii) Acceleration-time graph.
A particle is dropped from a tower 180 m high. How long does it take to reach the ground ? What is its velocity when it touches the ground ?
Given that,
Distance from which the ball is dropped, s = -180 m (negative sign for downward displacement)
Initial velocity, u = 0 m/s
Acceleration due to gravity, g = - 10 m/s2
Using the second equation of motion,
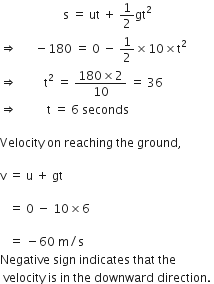
Define mass of a body. What is its SI unit ? Is it a scalar or vector quantity?
The amount of matter which is contained in abody is called it's mass. Mass gives a measure of inertia of the body.
Greater the mass of a body, greater is its inertia.
SI unit of mass is kilogram (kg).
Mass of a body is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude and no direction.
Can the mass of a body be zero?
No, the mass of a body can never be zero. There is always a matter within the minute particle.
Is the mass of an object a constant quantity?
Yes, the mass of an object does not vary from place to place. Whether the object is on Earth, moon or outer space, an object contains same quantity of matter.
Define weight of a body. Write an expression for it.
The force with which a body is attracted towards the centre of the earth is known as the weight of a body.
When a body falls towards the earth, the gravitational force of the earth produces an acceleration 'g' in the motion of the body.
According to Newton's second law, the force of attraction on the body of mass m is,
F = Mass x Acceleration due to gravity
= mg
This force is known as the weight of the body.
So substituting weight(W) with F, we get
The weight of a body varies from place to place, as 'g' varies.
Is the weight of a body a scalar or vector quantity ? Give the SI unit for weight.
SI unit of weight is Newton(N), wich is same as that of force.
Define one kilogram-weight. How many newtons are there in 1 kg-wt?
The force of gravity acting on a body of mass 1 kg is called as one-kilogram weight.
1 kg-wt = 1 kg x 9.8 m/s2
= 9.8 N.
How does the weight of a body depend on its mass at a given place?
At a given place, the value of ‘g’ is constant.
Therefore, at a given place, the weight of a body is directly proportional to its mass,
That is,
W ∝ m
It is due to this reason that at a given place we can use the weight of a body as a measure of its mass.
What do you mean by weight of an object on the moon ? Why is the weight of an object on the moon is less than that on the earth?
The force with which the object is attracted towards the centre of the moon is the weight of an object on the moon.
The mass and radius of the moon is less than that of the earth. Due to this the moon exerts lesser force of attraction on the object. Hence, the weight of an object on the moon is less than that on the earth.
The gravitational force of the moon is about one sixth of that on the earth.
Example. Suppose the weight of a certain object is 6 kg-wt on the earth. If the same object is weighed on the moon, then the weight will be just 1 kg-wt.
Show that weight of an object on the moon is 1/6 th its weight on the earth. Given that the mass of the earth is 100 times the mass of the moon and its radius is 4 times that of the moon.
Let,
Mass of the object = m
Mass of the Earth = Me
Mass of the moon = Mm
Radius of the Earth = Re
Radius of the moon = Rm
Me = 100 Mm and Re = 4 Rm
Weight of the object on earth is the force with which the earth attracts the object towards it.

What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight?
|
Differences between mass and weight: |
|
|
Mass |
Weight |
|
1. Mass is the quantity of matter contained in a body and is the measure of its inertia. 2. Its value remains constant at all places. 3. It is a scalar quantity. 4. It is measured by a pan balance. 5. Mass of a body is never zero. 6. Its unit is kg. |
1. Weight of a body is the force with which a body is attracted towards the centre of the earth. 2. Its value (W = mg) changes from place to place due to the change in the value of acceleration due to gravity ‘g’. 3. It is a vector quantity. 4. It is measured by a spring balance. 5. Weight of a body is zero at the centre of the earth because there ‘g’ becomes zero. 6. Its unit is newton or kg-wt. |
Why is the weight of an object on the moon 1/6th its weight on the earth?
Mass of the moon is 1/100 times and radius of moon is 1/4 times that of the earth.
Therefore, the gravitational attraction on the moon is about one sixth of that on the earth. Hence, the weight of an object on the moon is 1/6 th of the weight on the earth.
(i) Define centre of gravity of a body.
(ii) What is the difference between centre of gravity and centre of mass?
(i) Centre of gravity: The point at which the resultant of all the parallel forces due to gravity experienced by various particles of the body acts or at which the whole weight of the body acts is called the centre of gravity.
If a force equal to the weight of the body is applied at this point vertically upwards, the body will remain in equilibrium.
Hence a body can be supported at its centre of gravity.
Fig. (i): Centre of Gravity of Some Regular Bodies
Fig. | Body | Centre of gravity |
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) | Right cylinder Circular disc Triangular lamina A solid cone Rectangular lamina Circular ring | Mid. point Centre of the disc The point of intersection of medians. Point on the axis at a distance h/4 from the base of the cone, h being its height. Point of intersection of diagonals Centre of the ring (outside the body) |
(ii) Centre of mass is a point at which whole of the mass of the body may be assumed to be concentrated to describe its motion as a particle.
Discuss the various factors on which the value of g depends.
Variation of acceleration due to gravity depends on a following factors:
Value of g varies from place to place.
(i) Effect of shape of earth: Acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface is given by,
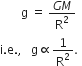
That is, earth is not a perfect sphere.
The Earth is slightly compressed at the poles and bulges out at the equator. So equatorial radius Re is about 21 km greater than the polar radius Rp.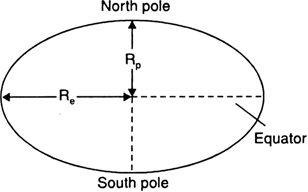
As, 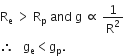
Thus, the value of g is maximum at the poles and minimum at the equator.
The weight of the body increases as we move from the equator to the poles.
(ii) Effect of altitude (Height):
The value g at a height h from the earth's surface is given by,
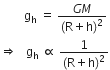
Clearly, with increase in heigh h, acceleration due to gravity decreases.
That is why the value of g is lesser at mountains than at plains.
At a height equal to the radius of the earth, h = R = 6400 km.
So,
![]()
Hence the weight of a body becomes one-fourth at distance 2R from the centre of the earth of its weight at the earth's surface.
(iii) Effect of depth:
At a depth d, a body experiences force of gravity only due to the inner spherical portion of radius (R – d) of the earth.
Acceleration due to gravity at depth d is,
![]()
Clearly, the acceleration due to gravity decreases with the increase of depth d.
At the centre of the earth, d = R, so
![]()
Hence the weight of a body at the centre of the earth is zero.
What is the effect of the distribution of mass inside the earth on the value of g? What is its utility?
Acceleration due to gravity in any region of the Earth is the force acting on a unit mass. If in any region the value of g is found to be large, it indicates the presence of deposits of some heavy ore in that region.
Mass of an object is 10 kg. What is its weight on the earth? Take g = 9.8 m/s2.
Given,
Mass of m = 10 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Weight, W = mg
= 10 x 9.8 N
= 98 N.
An object weighs 10 N when measured on the surface of the earth. What would be its weight when measured on the surface of the moon?
Weight of object on the earth, Wm = 10 N
Weight of object on the moon = ![]()
That is,
Weight of the object on the moon,
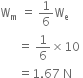
A man weighs 600 N on the earth, what is his mass? (Take g = 10 m/s2). If he was taken to the moon, his weight would be 100 N. What is his mass on the moon? What is the acceleration due to gravity on the moon?
Weights of man on earth, W = 600 N
Acceleration due to gravity 'g' on earth, g = 10 m/s2
![]()
We know that,
Mass remains constant everywhere.
Therefore,
Mass of man on moon, m = 60 kg
Weight of man on moon, W = 100 N
Acceleration due to gravity on moon is,
![]()
If your weight is 60 kg on earth, how far must you go from the centre of the earth so that you weigh 30 kg?
Weight of a body varies inversely as the square of the distance from the centre of the earth.
Therefore,
![]()
![]()
![]() (Re = Radius of the earth)
(Re = Radius of the earth)


So, at a distance of 9.05 x 106m from the centre of the earth, 100 kg -wt will become 30 kg-wt.
A body weighs 63 N on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it due to the earth at a height equal to half the radius of the earth?

![]() Gravitational force at height equal to half the radius of the earth.
Gravitational force at height equal to half the radius of the earth.
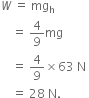
At what height from the surface of the earth, will the value of g be reduced by 36% from the value at the surface ? Radius of the earth = 6400 km.
Given,
At height h, the value of g reduces by 36%.
i.e., it becomes 64% of that at the surface.
Then,
![]()
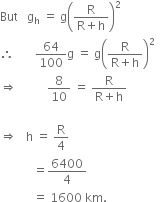
Find the percentage change in the weight of a body when it is taken from the equator to poles. The radius of the earth at the poles is 6357 km, the radius at the equator is 6378 km.
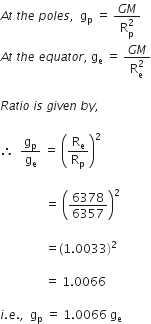
The percentage increase in weight the body is taken from the equator to the poles,
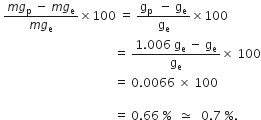
Define the term thrust. Give its SI unit
The force acting on an object perpendicular to the surface is called thrust.
Thrust is a type of force. So, it's SI unit is Newton.
Define the term pressure. Give its SI unit.
Pressure: The thrust acting per unit area of a surface is called pressure.
Mathematically, ![]()
If a force F acts normally over an area A of a surface, then the pressure,
![]()
The SI unit of pressure is newton per square metre (Nm-2).
It is also called pascal (Pa).
Describe some practical applications from daily life which make use of the concept of pressure.
Practical applications based on the concept of pressure are as given below:
1. A sharp knife cuts better than a blunt one. The area of a sharp edge is much less than the area of blunt edge. Therefore, the effective force per unit area is more for the sharp edge than the blunt edge. Hence, a sharp edge cuts better.
2. Railway tracks are laid on large sized wooden sleepers. Therefore, the force due to the weight of the train is on a larger area. Hence, this reduces the pressure considerably. This prevents sinking of the ground under the weight of the train.
3. Pins and nails are made to have pointed ends. Their pointed ends have very small area. When a force is applied over the head of a pin or a nail, it transmits a large pressure (force/area) on the surface and hence easily penetrates through the surface.
When you stand on loose sand, your feet go deep into the sand. Now, lie down on the sand. You will find that your body will not go deep in the sand. Give reason for the difference in the two cases.
The force exerted on the sand is equal to the weight of our body in both the cases.
When we stand on loose sand, our weight acts on a smaller area of the sand. Hence, a large pressure (= force/area) is exerted onto sand and our feet penetrate deeper into the sand.
When we lie down, our weight acts on a larger surface area of the sand. Hence, a smaller pressure is exerted onto sand and our feet stay on the ground only.
A force of 40 N is applied on a nail, whose tip has an area of cross-section of 0.001 cm2. Calculate the pressure on the tip.
Given,
Force, F = 40 N
Area of cross-section, A = 0.001 cm2
= 0.001 x 10-4 m2
So, Pressure is given by, ![]()
A block of wood is kept on a table top. The mass of wooden block is 5 kg and its dimensions are 40 cm x 20 cm x 10 cm. Find the pressure exerted by the wooden block on the table top if it is made to lie on the table top with its sides of dimensions (i) 20 cm x 10 cm and (ii) 40 cm x 20 cm.
Mass of the wooden block = 5 kg
Dimensions of the block = 40 cm x 20 cm x 10 cm
Force exerted by the block on the table top,
F = Weight of block = mg = 5 x 9.8 = 49 N
(i) Let us consider the side of dimension 20 cm x 10 cm
Therefore,
Area = Length x Breadth = 20 cm x 10 cm
= 0.20 x 0.10 m = 0.02 m2
That is,
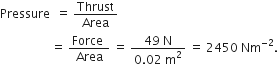
(ii) Consider the block lies on its side 40 cm x 20 cm,
Area = Length x Breadth
= 40 cm x 20 cm
= 0.40 m x 0.20 m = 0.08 m2
When the block lies on its side 40 cm x 20 cm, it exerts the same force F.

What is difference between the pressure exerted by a solid and a fluid?
A solid exerts pressure on a surface due to its weight.
Fluids also have weight. Hence, the fluids also exert pressure on the walls of the container in which they are kept. A fluid exerts pressure in all the directions.
What do you understand by buoyancy and centre of buoyancy?
The upward force acting on a body immersed in a fluid is called upthrust or force of buoyancy and the phenomenon is called buoyancy.
When a body is immersed partially or wholly in a fluid, it displaces fluid. The displaced fluid tends to regain its original condition. Durig this time, it exerts an upward force on the body which is called as Buoyancy.
For example, a cork taken inside water comes to the surface after experiencing an upward thrust.
The buoyancy acts through the centre of gravity of the displaced fluid which is called centre of buoyancy.
Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
The thin string exerts a large pressure on our hand due to the smaller area covered. Hence, we feel the weight of the bag and feel uncomfortable.
What do you mean by buoyancy?
The upward force acting on a body immersed in a fluid is called upthrust or force of buoyancy. The phenomenon is called buoyancy.
The magnitude of buoyant force depends upon the density of the fluid.
When does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water?
(i) An object sinks in water if its density is greater than that of water. Upthrust of water on an object is less than the weight of the object. Hence, it sinks.
(ii) An object floats on water when its density is less than that of water. When the upthrust of water on the object is greater than the weight of the object, the object floats.
State Archimedes' principle.
Archimede's principle states that when a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Briefly explain how can Archimedes' principle be verified experimentally?
Or
Describe a simple activity to show that a body loses weight when immersed in a fluid.
Archimedes principle can be explained experimentally.
Look at the fig. below.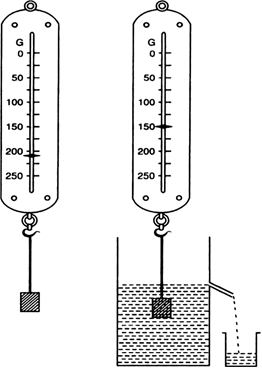
Fig. 10.22. Verification of Archimedes' principle.
i) Take an overflow can and fill it with water.
ii) Hang a piece of stone on spring balance.
iii) Weigh the piece of stone hung from the spring balance.
iv) Take a beaker and weigh it.
v) Place the beaker below the spout of the overflow can.
vi) Immerse the stone in the overflow can and collect the water which overflows and read the weight of stone when it is immersed in water.
vii) We find that, the weight of stone in water is less than the weight of stone in air.
viii) Now weigh the beaker with the water.
ix) It is observed that the loss in weight of the stone is equal to the weight of the water collected in the beaker, i.e., the weight of the water displaced.
Hence, Archimedes principle is proved.
State Archimedes' principle. Write two applications of this principle.
Archimedes' principle states that when a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward thrust equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
The applications of Archimedes’ principle are:
(i) Archimedes' principle is used in designing ships and submarines.
(ii) Lactometers based on Archimedes' principle are used to measure purity of a sample of milk.
(iii) Hydrometers used to measure density of liquids are based on Archimedes' principle.
You find your mass to be 42 kg on a weighing machine. Is your mass more or less than 42 kg?
The weighing machine reads slightly less than the actual value. This is because of the upthrust of air acting on our body. Hence, our actual weight is more than 42 kg.
You have a bag of cotton and an iron bar, each indicating a mass of 100 kg when measured on a weighing machine. In reality one is heavier than other. Can you say which one is heavier and why?
In reality, cotton bag is heavier than the iron bar. The cotton bag experiences larger upthrust of air than on the iron bar. So, the weighing machine indicates a smaller mass for cotton bag than its actual mass.
Define the terms density and relative density. Give their units.
Density of a substance is defined as its mass per unit volume.
Mathematically, we can write,
The SI unit of density is kilogram per cubic metre (kg m–3).
Relative density of a substance is the ratio of the density of the substance to the density of water.
Therefore,
Since the relative density is a ratio of two similar quantities, it has no units.
State the laws of floatation of a body in a liquid.
The laws of floatation are:
i) A body will sink in a liquid if its density is greater than the density of the liquid.
(ii) A body will float in a liquid if its density is less than the density of the liquid.
(iii) A body will be in equilibrium at any submerged depth, if the density of the body is equal to the density of the liquid.
Density of gold is 19300 kg/m3. What will be the mass of a gold brick with dimensions of 5 cm x 10 cm x 20 cm?
Dimension of the brick = 5 cm x 10 cm x 20 cm
Therefore,
Volume =
= 5 x 10 x 20 cm3
= 5 x 10 x 10-6 m3
= 10-3 m3
So, Mass = Volume x Density
= 10-3 x 19300
= 19.3 kg
The density of gold is 19300 kg/m3 and that of water is 1000 kg/m3. What is the relative density of gold?
Given,
Density of gold = 19300 kg/m3
Density of water = 1000 kg/m3
Therefore,
Relative density of gold = Density of gold
Density of water
= 19300 kg/m3
1000 kg/m3
= 19.3
Relative density of silver is 10.8. The density of water is 103 kg m–3. What is the density of silver in S.I. unit?
Given,
Relative density of silver = 10.8
Density of water = 103 kg/m3
Now, using the formula of relative density,
Relative density = Density of silver
Density of water
So,
Density of silver = R. D. x Density of water
= 10.8 c 102 kg m-3
The density of silver is 10.8 x 103 kg m-3
What is difference between gravitation and gravity?
| Gravitation | gravity |
| 1. Gravitation is the force of attraction between any two bodies in general. | 1. Gravity refers to the force of attraction between any body and the earth. |
| 2. The value of G never varies and is constant for all bodies at all places. | 2. Value of 'g' is different at both equator and poles. |
| 3. G = | 3. g = 9.8 m/s2 |
State the Universal law of gravitation.
Newton's law of gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The force is along the line joining the centres of two objects.
We cannot move finger without disturbing stars. Why?
There exists a gravitaional force between all objects in the universe. When we move our fingers, force of attraction changes when the distance between two bodies changes.
Therefore, the position of the stars also changes.
How the gravitational force between two objects depends on the distance between them? What happens to the gravitational force between two objects when the distance between them is doubled?
Gravitational force F between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
That is,
![]()
When the distance between two objects is doubled, the force becomes one-fourth of its original value.
What is the value of the universal gravitational constant?
The value of universal gravitational constant is 6.67 x 10–11 Nm2/kg2.
Does the value of ‘G’ depend on the medium present between the two bodies?
No, the value of ‘G’ is independent on the medium present between the two bodies.
The value of G on the surface of the earth is 6.67 x 10–11 Nm2/kg2. What is its value on the moon?
G is a universal constant.
So, its value on the moon = 6.67 x 10–11 Nm2/kg2.
What does the small value of G indicate?
The small value of 'G' indicates that the force of gravitational attraction between two ordinary sized objects is a very weak force.
The value of G is very small but all the objects near the surface of the earth fall towards it. Why?
Mass of the Earth is very large. Therefore, the force of gravitation is sufficiently large to make all objects near its surface to fall towards it.
In which direction does the force of gravitational attraction act?
The force of gravitational attraction acts along the line joining the centres of mass of the two bodies.
Does ‘G’ change with increasing height above the earth’s surface?
Value of G remains constant. Therefore, the value of G does not change with increasing or decreasing height.
The moon's mass is approximately 1% of the earth's mass. How does the gravitational pull of the earth on the moon compare with the gravitational pull of the moon on the earth?
The gravitaional pull on both moon and Earth are equal because the value of 'g' is constant.
Does the gravitational force between two bodies change, if a material body is placed between them?
Tips: -
Does the gravitational force between two bodies depend upon the presence of other bodies in the surroundings?
No, gravitaional force does not depend upon the presence of other bodies in the surroundings. It remanins constant.
Do all bodies fall with the same acceleration in the absence of air resistance?
Yes, all bodies fall with the same acceleration in the absence of air resistance and this acceleration is called 'acceleration due to gravity'.
Define acceleration due to gravity.
An object which is falling freely under the effect of gravity gets accelerated. This acceleration is called as 'acceleration due to gravity'.
If the numerical value of acceleration due to gravity at a place is 9.8, what are its units?
The unit of 'g' is m/s2.
What are the values of g and G at the centre of the earth?
At the centre of the earth,
g = zero
G = 6.67 x 10–11 Nm2/kg2.
Which is scalar and which is vector amongst g and G?
Acceleration due to gravity(g) is acting vertically downwards. Therefore, g is a vector quantity. But, 'G' is a scalar quantity.
Write down the formula for acceleration due to gravity.
where,
G is the universal gravitaional constant,
M is the mass of the Earth, and
R is the radius of the Earth.
Explain why a 10 kg stone will fall with the same acceleration as 1 kg stone?
since the acceleration due to gravity is given by,
where, M is the mass of the Earth.
Therefore, 'g' does not depend on the mass of the body. So both the stones will fall with the same acceleration.
Name the factors on which the value of g depends.
The value of g depends on,
(i) the shape of the earth,
(ii) latitude,
(iii) altitude, and
(iv) depth.
What is the effect of altitude (height) on acceleration due to gravity?
'Acceleration due to gravity' decreases with altitude.
What is the effect of latitude and shape of earth on the value of g?
The value of 'g' is minimum at the equator and gradually increases from equator to poles.
What is the effect of rotation of the earth on the acceleration due to gravity?
The value of 'g' decreases due to rotation of the earth. This effect is zero at poles and maximum at the equator.
A man can jump six times as high on the moon as that on the earth. Why?
A man can jump six times as high on the moon than on the earth because the value of 'g' on the surface of the moon is about one-sixth of its value on the surface of the earth.
Define centre of mass of a body.
Centre of mass of a body is the point where the whole mass of the body is assumed to be concentrated.
On which factors does the position of centre of mass depend?
The position of centre of mass depends on,
(i) shape of the body and
(ii) distribution of mass in the body.
Where does the centre of mass of a triangular lamina lie?
The centre of mass of a triangular lamina is at the centroid of the triangular lamina.
Where does the centre of mass of a cone lie?
The centre of mass of a cone lies on the line joining the apex to the centre of the base at a distance equal to 1/4 of the length of this line from the base.
Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body?
No, it is not necessary that centre of mass of a body lies inside the body.
For example, the centre of mass of a ring lies in its hollow portion.
What is the mass of a body at a height above the earth's surface of one earth radius when its mass on earth's surface is m kg?
Given that mass of the body on the surface of the Earth = m kg
Mass of the object is constant everywhere.
So, mass of the body at a height 'h' above the Earth's surface = m kg
Define weight of a body.
Weight of a body is the force with which a body is attracted towards the centre of the earth.
What is the relation between mass and weight of a body?
The relation between mass and weight of a body is given by,
W = mg
Is weight a vector or a scalar quantity?
Weight is a vector quantity because weight always acts in the direction of force.
What is the SI unit of weight?
Weight has the same unit as that of force.
SI unit of weight is Newton.
A body has a weight of 10 kg on the surface of the earth. What will be its weight when taken to the centre of the earth?
At the center of the earth, acceleration due to gravity = 0.
Weight is dependent on the value of 'g'.
So, weight at the centre of earth = 0
Where on the earth surface is the weight of a body (i) maximum, and (ii) minimum?
The value of acceleration due to gravity influence the weight of a body.
(i) The value of g is maximum at the poles. Therefore, weight of the body is maximum on the poles.
(ii) The value of 'g' is minimum at the equator. Therefore, weight of the body is minimum.
A body of weight 600 N rests on the floor of a lift. If the lift begins to fall freely under gravity, what is the force with which the body presses on the floor?
The weight of the body during a free fall is zero. So, the force with which the body presses on the floor is also zero.
Name one factor on which the value of ‘g’ depends.
The value of ‘g’ depends on the distance from the centre of the earth.
The mass of a body is 9.8 kg on the earth. What would be its mass on the moon where the value of g is approximately 1.63 m/s2.
Mass of the body is constant everywhere.
Therefore, mass of body will remain same on the moon i.e. 9.8 kg.
How does the mass of a body change when it is taken into deep space?
Mass of the body remains constant. So, mass of a body will not change when taken into deep space.
Two balls are released simultaneously from a certain height, one allowed to fall freely and other thrown with some horizontal velocity. Will they hit the ground together?
When two balls are released simultaneously in a free fall, the balls will hit the ground at the same rate. Free fall is independent of the mass of the body.
Why does a mug full of water feel lighter inside water?
A mug full of water feels lighter inside water because of upthrust exerted by water on the mug is more than the weight of the mug.
How does the gravitational force change between two objects when:
(i) the distance between them is reduced to half,
(ii) the mass of each is reduced to half. Justify your answer in each case.
As per Newton's law of gravitation, the force of attraction between two bodies is given by,
![]()
(i) Here, distance between the bodies is reduced to half.
i.e., ![]()
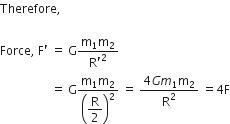
i.e, gravitational force increases four times when distance is reduced to half.
(ii) Given, mass of each body is reduced to half.
That is,
![]()
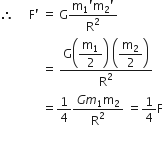
Hence, the gravitational force becomes one-fourth of the original value.
Why is the gravitational force between ordinary sized objects not noticeable?
Gravitational force between ordinary sized objects is hardly observable. This is because of the very small value of force of gravitation between two ordinary sized objects is very small and cannot be easily detected.
Explain why a small piece of stone is not attracted towards another big piece of stone on the earth's surface?
Because of very small value of G, the force of attraction between any two such ordinary sized bodies is so small that it cannot produce motion in them.
According to Newton's third law of motion, action and reaction are equal and opposite, then why do we see a stone falling to the earth and not the earth rising towards the stone?
Any object which is falling towards the Earth exerts an equal and opposite force towards the earth. But, we see a stone falling towards the earth and not the movement of the Earth towards the stone. This is because of the large mass of the Earth as compared to that of the stone. Hence, the acceleration produced in the stone is very large as compared to that of the earth.
So the stone readily falls towards the earth while the earth does not rise at all.
What is the effect of gravitational force between two objects of comparable masses? Give an example.
When two masses are comparable, the force of gravitation between two objects produces comparable accelerations in them. Therefore, the two objects move towards each other.
For example, binary stars, Sirius and its companion move around each other because their masses are comparable.
Give some points of differences between g and G.
|
Acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ |
Universal gravitational constant ‘G’ |
|
1. It is the acceleration acquired by a body due to earth's gravitational pull on it. 2. ‘g’ is not a universal constant. It is different at different places on the surface of the earth. Its value varies from one celestial body to another.
|
1. It is numerically equal to the force of attraction between two masses of 1 kg each separated by a distance of 1 m. 2. ‘G’ is a universal constant i.e., its value is same viz., 6.67 x 10–11 N-m2 kg–2 everywhere in the universe. 3. It is a scalar quantity. |
Under what conditions our weight becomes zero?
Our weight becomes zero when we fall freely under gravity.
Also, at the centre of the Earth, weight becomes zero because acceleration due to gravity is zero at the centre of the Earth.
Why do we feel giddy while moving on a merry-go-round?
While going up, our weight increases and it decreases when awe are going down. Therefore, we feel giddy in a merry-go-round.
An astronaut feels weightlessness in a spacecraft. Give reason.
An astronaut is in a state of free fall in a spacecraft. A body falling freely does not experience any force on his body. Hence, a state of weightlessness is felt for an astronaut in a spacecraft.
Why is the value of g more at the poles than at the equator?
Acceleration due to gravity is given by,
g = ![]()
We can see that value of 'g' is inversely proportional to the radius, R.
And, the value of R at the equator is greater than at the poles. Hence 'g' at poles is greater than g at the equator.
Why does a body weigh more at the poles than at the equator?
Acceleration due to gravity is greater at poles than that at the equator.
That is, gp > ge
So,
Weight at poles > Weight at equator.
Where does a body weigh more ? At the sea level or on the mountains?
A body weigh more at the sea-level. 'g' decreases with height.
The weight of a body is less inside the earth than on the surface. Why?
The value of attracting mass M decreases when we go inside the Earth. Therefore, the value of g decreases. So, the weight of the body(mg) is less inside the Earth than on the surface.
If the earth stops rotating about its axis, what will be the effect on the value of g? Will the effect be same at all places?
If the Earth stops rotating about it's axis, value of 'g' will increase at all places except at the poles. The variation will be different at different places. Value of 'g' will be maximum at the equator.
Which force is responsible for the motion of the planets around the sun?
Gravitational force of attraction of the sun keeps the planets moving in their orbits, just as the moon revolves round the earth due to gravitational attraction of the earth.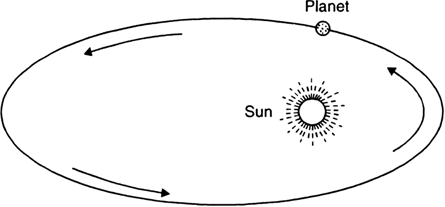
Fig. Orbital motion of a Planet around the Sun.
A satellite does not need any fuel to circle around the earth. Why?
The gravitational force between satellite and earth provides the centripetal force required by the satellite to move in a circular orbit. Hence no fuel is required for its orbital motion.
What is difference between centre of gravity and centre of mass?
Centre of mass: The point at which whole of the mass of the body is concentrated to describe its motion as a particle.
Centre of gravity: The point at which the entire weight of a body may be thought of as centered, so that, if supported at this point the body would balance perfectly.
Why does a projectile fired along the horizontal does not follow a straight line path?
A projectile which is fired horizontally is being constantly acted upon by acceleration due to gravity, acting vertically downwards. Hence, it does not follow a straight line path.
You must have seen two types of balances. A grocer has a balance with two platforms, or pans, and a needle moving on a scale. Some junk dealers (kabadi walas) may be using a spring balance to weigh used newspapers. Suppose the two balances give the same measure for a given body on the earth. Now, you take the balances to moon. Would the two balances give the same measure ? Explain your answer.
No, the two balance would measure different on the moon.
The pan balance measures inertial mass while the spring balance measures gravitational mass or weight of the body. Both masses are equivalent when measured on the earth. But, on the moon the value of 'g' becomes one-sixth of that on the earth. So, spring balance will measure one-sixth of the reading on the pan balance.
You buy a bag of sugar of weight W at a place on the equator. You take this to Antarctica. Would its weight be the same there ? If not, would it increase or decrease?
The value of g is less at equator than at poles. Weight of a body is dependent on the value of 'g'. And, Antarctica lies in the polar region of the earth.
Therefore, weight of the bag of sugar in Antarctica would increase.
In what sense does the moon fall towards the earth? Why does it not actually fall on the earth's surface?
Moon is orbiting around the Earth in a circular orbit. The centripetal force which is provided by the force of attraction of the Earth will enable the moon to go in a circular orbit. So, at each point of its orbit, the moon falls towards the earth instead of going straight.
The earth attracts an apple. Does the apple also attract the earth ? If it does, why does the earth not move towards the apple?
The Earth attracts an apple and so does the apple attracts the earth with an equal and opposite force. Mass of the Earth is extremely massive as compared to that of the moon. So, the acceleration produced is very small as compared to that in the apple. Hence, the motion of the earth towards the apple is not noticeable.
If the force of gravity somehow vanishes today, why would we be sent flying in space?
In the absence of force of gravity, the centripetal force required to keep us rotating along with the earth would not be available. Then, we would be flying off along the tangent into the space.
Suppose the mass of the earth somehow increases by 10% without any change in its size. What would happen to your weight? Suppose the radius of the earth becomes twice of its present radius without any change in its mass, what will happen to your weight?
Weight = Force of gravity
![]()
Clearly, when the mass M of the earth increases by 10%, our weight also increase by 10% because weight is directly proportional to mass.
Also, weight is inversely proportional to the square of radius. Therefore, when radius R of the earth becomes twice of its present radius, our weight become 1/4 of its present value.
Suggest a method for calculating the mass of the moon.
The acceleration produced on the surface of moon is given by,
![]()
![]()
Thus knowing acceleration a, radius Rm of the moon and G, the mass of the moon can be determined.
A ball moving on a table reaches the edge and falls. Sketch the path it will follow while falling.
The ball carries a horizontal velocity and a vertical downward acceleration due to gravity.
Under the combined effect of these two motions, the ball moves along a parabolic trajectory as shown in the fig. below. 
A sharp knife cuts better than a blunt one. Why?
The surface area of sharp edged knife is much less than the blunt edge. For the same total force applied, the effective force per unit area (or pressure) is more for the sharp edge than for the blunt edge. So sharp edge cuts better.
Define the terms thrust and pressure. State their SI units.
The total force acting on a body perpendicular to its surface is called thrust.
SI unit of thrust is newton (N).
Thrust acting per unit on the surface area is called pressure.
Pressure = Thrust
Area
The SI unit of pressure is Nm–2 or pascal (Pa).
Define the terms (i) thrust (ii) pressure and (iii) relative density.
(i) Thrust: The total force acting on a body perpendicular to its surface is called thrust.
(ii) Pressure: Thrust acting per unit on the surface area is called pressure.
(iii) Relative density: The relative density of a substance is the ratio of the density of the substance to the density of water.
Relative density = Density of substance
Density if water at
Since, relative density is a pure ratio, it has no units.
Newton's law of gravitation is applicable to
bodies of the solar system only
bodies on the earth
planets only
All bodies of the universe.
D.
All bodies of the universe.
The relation between ‘g’ and ‘G’ is
- G R2
R2 - g = G MR2
- G
MR2
A.
The relation between ‘g’ and ‘G’ is
The value of universal gravitational constant in SI system is
6.67 x 10–3
6.67 x 10–6
6.67 x 10–11
6.67 x 10–5.
C.
6.67 x 10–11
6.67 x 10–3
Tips: -
6.67 x 10–6
All bodies whether large or small fall with the
same force
Same acceleration
same velocity
same momentum.
B.
Same acceleration
When an object falls freely to the earth, the force of the gravity is
opposite to the direction of motion
in the same direction as that of motion
zero
constant.
B.
in the same direction as that of motion
Newton's law of gravitation
can be verified in the laboratory
cannot be verified but is true
is valid only on earth
is valid only in the solar system
A.
can be verified in the laboratory
The acceleration due to gravity
has the same value everywhere in space
has the same value everywhere on earth
varies with the latitude on the earth
None of them
C.
varies with the latitude on the earth
The weight of an object
is the gravity of the matter it contains
refers to its inertia
is the same as its mass but expressed in different units
is the force with which it is attracted to the earth.
D.
is the force with which it is attracted to the earth.
When an object is thrown up, the force of gravity is
opposite to the direction of motion
in the same direction as the direction of motion
constant
increases as it rises up
A.
opposite to the direction of motion
In vacuum all freely falling objects
have the same speed
have the same velocity
have the same acceleration
have the same force.
C.
have the same acceleration
At the top of its path, a projectile has
no acceleration
acceleration in the upward direction
acceleration in the downward direction
acceleration in the horizontal direction
C.
acceleration in the downward direction
Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio 1:8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3g of hydrogen gas?
It is given that the ration of hydrogen and oxygen by mass to form water is 1:8. Then, the mass of oxygen gas required to react completely with 1g of hydrogen gas is 8g. Therefore, the mass of oxygen gas required to react completely with 3g of hydrogen gas is = 8 x 3g=24g.
Which postulate of Dalton's atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory which is result of the law of conservation of mass is “Atoms are indivisible particles, which can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Which postulate of Dalton's atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory which can explain the law of definite proportion is “The relative number and kind of atoms in a given compound remains constant”.
Write down the formulae of:
(i) sodium oxide
(ii) aluminium chloride
(iii) sodium sulphide
(iv) magnesium hydroxide.
(i) Sodium oxide = NaO
(ii) Aluminum chloride =AlCl3
(iii) Sodium sulphide = Na2S
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide = Mg(OH)2
Write down the names of compounds represented by the following formulae:
(i) Al2(SO4)3
(ii) CaCl2
(iii) K2SO4
(iv) KNO3
(v) CaCO3.
(i) Al(SO4)3→ Aluminium sulphate
(ii) CaCl2→ Calcium chloride
(iii) K2SO4→ Potassium sulphate
(iv) KNO3→ Potassium Nitrate
(v) CaCO3→ Calcium carbonate
What is meant by the term chemical formula?
The chemical formula of a compound means the symbolic representation of the composition of a compound. From the chemical formula of a compound, we can know the number and kinds of atoms of different elements that constitute the compound. For example, from the chemical formula CO2 of carbon dioxide, we come to know that one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms are chemically bonded together to form one molecule of the compound, carbon dioxide.
How many atoms are present in a
![]()
(i) In an H2S molecule, three atoms are present; two of hydrogen and one of sulphur.
(ii) In an ![]() five atoms are present; one of phosphorus and four of oxygen.
five atoms are present; one of phosphorus and four of oxygen.
Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, CO2, CH4, C2H6, C2H4, NH3, CH3OH.
Molecular mass of H2 = 2 × Atomic mass of H = 2 × 1 = 2u
Molecular mass of O2 = 2 × Atomic mass of O = 2 × 16 = 32u
Molecular mass of Cl2 = 2 × Atomic mass of Cl = 2 × 35.5 = 71 u
Molecular mass of CO2 = Atomic mass of C + 2 × Atomic mass of O = 12 + 2 × 16 = 44 u
Molecular mass of CH4 = Atomic mass of C + 4 × Atomic mass of H = 12 + 4 × 1 = 16 u
Molecular mass of C2H6 = 2 × Atomic mass of C + 6 × Atomic mass of H = 2 × 12 + 6 × 1 = 30u
Molecular mass of C2H4 = 2 × Atomic mass of C + 4 × Atomic mass of H = 2 × 12 + 4 × 1 = 28u
Molecular mass of NH3 = Atomic mass of N + 3 × Atomic mass of H = 14 + 3 × 1 =17 u
Molecular mass of CH3OH Atomic mass of C+4 ×Atomic mass of H+Atomic mass of O = 12 + 4 × 1 + 16 = 32 u.
Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, ![]() , given atomic masses of Zn = 65 u. Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u, and O = 16 u.
, given atomic masses of Zn = 65 u. Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u, and O = 16 u.
Formula unit mass of ZnO = Atomic mass of Zn + Atomic mass of O = 65 + 16 = 81 u
Formula unit mass of Na2O = 2 × Atomic mass of Na + Atomic mass of O = 2 × 23 + 16 = 62u
Formula unit mass of K2CO3 = 2 × Atomic mass of K + Atomic mass of C + 3 × Atomic mass of O = 2 × 39 + 12 + 3 × 16 = 138u.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area