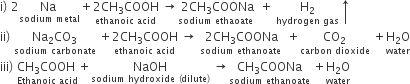Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science
Give two physical characteristics each of acids and bases.
Acids are,
(i) sour in taste.
(ii) change the colour of blue litmus to red.
Bases are,
(i) bitter in taste.
(ii) change the colour of red litmus to blue.
What are indicators? Name four acid-base indicators and mention their colour change.
Indicators are chemical substances which give different colours in acidic or basic solutions.
(i) Methyl orange gives pink colour with acid solution and yellow colour with base solution.
(ii) Phenolphthalein is colourless in acid solution while it turns into pink colour in base solution.
(iii) Litmus solution turns red in acid solution and blue in base solution.
(iv) Bromothymol blue is blue in base solution and is yellow in acid solution.
What are antacids?
What are olfactory indicators?
Onion: Paste or juice of onion loses its smell when added with base. It does not change its smell with acid.
Vanilla: The smell of vanilla vanishes with base, but it’s smell does not vanishes with an acid.
You are given the following solutions:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulphuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), acetic acid (CH3COOH), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), calcium hydroxide [(Ca(OH)2], potassium hydroxide (KOH), magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2] and ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). Give the colour change for each of these solutions with red litmus, blue litmus, phenolphthalein and methyl orange solutions.
|
Given solution |
Red litmus solution |
Blue litmus solution |
Phenolphthalein solution |
Methyl orange solution |
|
HCl |
no change |
turns red |
colourless |
pink |
|
H2SO4 |
no change |
turns red |
colourless |
pink |
|
HNO3 |
no change |
turns red |
colourless |
pink |
|
CH3COOH |
no change |
turns red |
colourless |
pink |
|
NaOH |
turns blue |
no change |
turns pink |
yellow |
|
Ca(OH)2 |
turns blue |
no change |
turns pink |
yellow |
|
Mg(OH)2 |
turns blue |
no change |
turns pink |
yellow |
|
KOH |
turns blue |
no change |
turns pink |
yellow |
|
NH4OH |
turns blue |
no change |
turns pink |
yellow |
Choose the olfactory indicators and give their characteristics: red cabbage extract, onion, vanilla extract, litmus, clove oil.
Olfactory indicators: Onion, vanilla extract, clove.
Characteristics: An olfactory indicator works on the principle that when an acid or base is added, then its characteristic smell can be detected.
(i) Onion has a characteristic smell. When a base (like NaOH) is added to a cloth strip treated with onion extract—then the smell is destroyed. An acid solution (HCl) does not destroy the smell of onion.
(ii) Vanilla extract has a characteristic pleasant smell. If a basic solution like sodium hydroxide solution is added to vanilla extract, then we cannot detect the pleasant smell of vanilla. An acidic solution does not affect the smell of vanilla.
(iii) Similarly odour of clove oil is not affected in acidic solutions.
What do you understand by concentrated and dilute acids?
Concentrated and dilute are nothing burt the percentage of acid in water.
Dilute acid: A dilute acid solution contains only small amount of acid and a large amount of water.
Concentrated acid: A concentrated acid contains a large amount of acid and a small amount of water.
How do metals react with bases?
Only some metals react with bases to form salts. For example, zinc (Zn) on warming with sodium hydroxide gives sodium zincate and hydrogen gas.
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
What is a neutralization reaction? Give some examples.
The reaction between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is known as neutralisation reaction can be written as :
Acid + Base → salt + water
Examples:
(i) Aqueous solution of base, NaOH is neutralized by aqueous hydrochloric acid.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O
(ii) Aqueous solution of sulphuric acid is neutralized by aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide.
H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(ag) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O
What are non-metallic oxides? Substantiate your answer.
Non-metals react with oxygen in the air to produce non-metal oxides. Here are two examples for the non-metals carbon and sulphur.
Non-metallic oxides in water forms acidic solution. For example, carbon dioxide in water forms carbonic acid. We can prove it because aqueous solution of carbon dioxide turns blue litmus red. Further aqueous solution of carbon dioxide is neutralized by a base, calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2], to form salt and water.
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 + H2O → CaCO3 + 2H2O
Take 5 ml hydrochloric acid in a boiling tube or a conical flask. Add a few pieces of zinc granules to it.
(a) What do you observe on the surface of zinc granules?
(b) Name the gas evolved.
(c) What happens when the above gas is passed through soap solution?
(d) What happens when a burning candle is brought near the gas filled tube?
(a) There is effervescence on surface of zinc granules.
(b) Hydrogen gas.
(c) Soap bubbles are formed.
(d) Gas bubbles break up with a pop sound due to burning of hydrogen gas.
Name four acids and bases. Write their formulae.
Acids:
(i) Hydrochloric acid — HCl
(ii) Sulphuric acid — H2SO4
(iii) Nitric acid — HNO3
(iv) Acetic acid — CH3COOH
Bases:
(i) Sodium hydroxide — NaOH
(ii) Calcium hydroxide — Ca(OH)2
(iii) Ammonium hydroxide — NH4OH
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide — Mg(OH)2
Name the various kind of oxides and mention their properties.
Oxides are of three types:
(i) Acidic oxides.
(ii) Basic or metallic oxides.
(iii) Amphoteric oxides.
(i) Acidic oxides: These oxides on treatment with water form acids, e.g., CO2, SO2, etc.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
Properties:
1. Do not react with acids.
2. React with bases and alkalis to form salt & water.
3. Dissolve in water to form acidic solutions.
4. Usually gases at room temp.
(ii) Basic or metallic oxides: The oxides which on treatment with water form alkalies are known as basic oxides. Metallic oxides are generally basic oxides. Such oxides turn red litmus blue, e.g., Na2O, MgO, etc.
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
MgO + 2H2O → Mg(OH)2
Propertes:
1. Do not react with bases.
2. React with acids to form salt & water.
3. Basic Oxides are usually insoluble in water. Those that dissolve in water forms alkaline solutions.
(iii) Amphoteric oxides: The oxides which show the properties of both acidic and basic oxides are known as amphoteric oxides, e.g., Al2O3, SiO2 etc.
Properties:
1. React with both acids and bases to form salt & water
What are acids? How are they produced?
(a) Acids are sour in taste and change the colour of blue litmus to red, Acid contain H+ ion in solution.
(b) They are produced when oxides of non-metals react with water.
Common acids are: (i) HCl—Hydrochloric acid, (ii) H2SO4—Sulphuric acid, (iii) HNO3— Nitric acid etc.
Mention important characteristics of acids.
Characteristics of acids:
(i) They are sour in taste.
(ii) They turn blue litmus to red.
(iii) Acids react with metals to evolve hydrogen gas.
2HCl + Mg → MgCl2 + H2 ↑
H2SO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + H2 ↑
2HCl + 2Na → 2NaCl + H2 ↑
(iv) Acids react with bases to form salt and water. This is called neutralisation.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
H2SO4 + Ca(OH)2 → CaSO4 + 2H2O
(v) Acids react with basic oxides to form salt and water.
CaO + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O
Na2O + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(vi) Acids react with carbonates to form salt, water and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 ↑
MgCO3 + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2O + CO2 ↑
Why the vessels of copper and brass need ‘Kalai’?
Hence “Kalai” is needed to prevent them from corrosion.
How can you test the presence of an acid in any substance?
Acid can be tested in many ways:
i) Test with litmus paper: Place a drop of the given substance on a moist litmus paper. If the colour changes to red, it is an acid.
ii) Test with metals: Acids react with metals to produce salt and hydrogen gas. So if the given substance gives a gas with metals and the gas burns with explosion, then it is acid.
Acid +metal → salt +hydrogen gas
example: 2HCl + Mg → MgCl2 + H2 ↑
Sponsor Area
Why are acids not stored in metal containers? Containers/vessels made from which material are safe to store acids.
Metals like sodium, magnesium and calcium, react vigorously with mineral acids and give hydrogen.
Aluminium, zinc, and iron react less vigorously with mineral acids. However, some metals like copper, silver and gold do not react with acids. Some metals like sodium and calcium react with sulphuric violently and are unsafe. So mineral acids (except carbonic acid) react with metal and produce corrosion on the surface of metal container. Therefore, acid are not stored in metal containers.
Vessels made from glass or ceramic are considered safe for storing mineral acids.
A solution turns red litmus paper blue. What does this indicate about the chemical nature of the solution?
The changing colour of litmus from red to blue is a characteristic of the substances called bases or alkalies. Metal hydroxide like potassium hydroxide change the colour of red litmus to blue litmus.
What are bases? Give the characteristic of bases.
Bases are the hydroxide of metals, which give hydroxide ion after dissociation in aqueous solution.
Characteristics of bases.
(i) They are bitter in taste.
(ii) They change red litmus to blue.
(iii) They react with acids to form salt and water.
(iv) Common bases are soluble in water and are known as alkalies.
Name some common bases?
Some common bases are:
| Common name |
Chemical name |
Chemical formula |
|
(i) Caustic soda |
Sodium hydroxide |
NaOH |
|
(ii) Caustic potash |
Potassium hydroxide |
KOH |
|
(iii) Lime water |
Calcium hydroxide |
Ca(OH)2 |
|
(iv) Milk of magnesia |
Magnesium hydroxide |
Mg(OH)2 |
Indicate the colour changes for the following samples:
|
Sample |
Indicator |
|
Dilute sulphuric acid |
Methyl orange |
|
Moist ammonia gas |
Phenolphthalein |
|
Moist chlorine |
Red litmus |
|
Moist carbon dioxide |
Blue litmus |
|
Dilute magnesium hydroxide |
Phenolphthalein |
|
Lemon juice |
Blue litmus |
|
Vinegar (Acetic acid) |
Blue litmus |
|
Water into which SO2 gas has been bubbled for sometime |
Phenolphthalein |
|
Water containing Na2O |
Phenolphthalein |
|
Milk of magnesia |
Methyl orange |
|
Sample |
Colour change |
|
Dilute sulphuric acid |
Methyl orange turns pink |
|
Moist ammonia gas |
Phenolphthalein turns pink |
|
Moist chlorine |
Red litmus remains red |
|
Dilute magnesium hydroxide |
Phenolphthalein turns pink |
|
Lemon juice |
Blue litmus changes to red |
|
Vinegar |
Blue litmus changes to red |
|
Water into which SO2 gas has been bubbled for some time |
Phenolphthalein becomes colourless |
|
Water containing Na2O |
Phenolphthalein turns pink |
|
Milk of magnesia |
Methyl orange turns yellow |
How are indicators used to differentiate between an acid and a base?
What colour change would you observe of red litmus with aqueous magnesium hydroxide?
Name a metal which gives hydrogen gas with sodium hydroxide?
Name one oxide which reacts with water to give an acid.
SO2 + H2O = H2SO3
Name one oxide which reacts with water to give a base.
Na2O + H2O → NaOH
What is the name given to a reaction between an acid and a base?
What is common to all acids?
(2) Acids have sour taste.
Do all compound containing hydrogen are acidic?
for example (CH4 methane) contain acid but it is not a acid.
Sponsor Area
Name the scale used for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution?
If the pH increases from 7 to 14, what does it show in terms of OH- ion concentration?
Out the following substances, choose the one with lowest value of pH: vinegar, lemon juice, tap water, hydrochloric acid.
Which of the following has highest value of pH? Aerated drink, saliva (after meal), saliva (before meal), vinegar
Which of the following has highest value of pH? Milk of magnesia, Milk of lime, Pure water, Sodium hydroxide
What is the optimal pH range for living organisms?
At what pH in the mouth is tooth decay faster and why?
Name a salt of the following family: Sodium nitrate, sodium chloride, sodium sulphate
Name a salt of the following family: Sodium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, potassium chloride
Name the gas responsible for extinguishing fire in a soda-acid fire extinguisher.
What happens when copper sulphate is heated?
Name the raw materials used for preparing bleaching powder.
Ca(OH)2 +Cl2 → CaOCl2 +H2O
When carbon dioxide is bubbled into lime water, a white cloud appears. Name the chemical name of white cloud.
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
Ca(OH)2 (aq) +CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) +H2O(l)
A substance burns in air to give a white product which dissolves in water to form alkaline solution. Name the likely substance.
MgO +H2O → Mg(OH)2 (alkaline solution)
Name a metal which gives H2 gas on reaction with sodium hydroxide.
Hence, Zinc is the metal which gives hydrogen gas with sodium hydroxide.
Name the main constituent of baking powder.
Which salt is used to remove permanent hardness of water?
Name the salt that is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
An acidic solution has pH 4. It is diluted with water. Its pH will increase or decrease?
Write two examples of hydrated salts?
i)Washing soda( Na2CO3 · 10H2O)
ii)Blue vitriol( CuSO4 · 5H2O)
Which compound of calcium is used for disinfecting water?
Name the gas evolved when dilute HCl reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. How is it recognised?
HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
CO2 gas is evolved. It turns lime water milky.
What do you call the property of losing water of crystallisation?
What would be the pH of a salt of weak acid and strong base?
What would be the pH of a salt of strong acid and strong base?
Choose a strong acid among the following acids: HCl, CH3COOH, H3PO4, H2CO3
pH values of same concentration of hydrochloric acid, gastric juice and lemon juice are 1.2, 3.5 and 4.5 respectively. Which is less acidic?
What is the pH range of our body at which it works?
When copper sulphate is heated, it loses water of crystallisation. What is the colour change?
Sponsor Area
A yellow colour solution of an indicator turns reddish pink in acidic solution and remains as such in a basic solution. What is this solution?
For a good growth, a farmer has decided to add lime to the soil. What can you say about the nature of soil?
The soil must be acidic.
Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus red when hydrochloric acid does. Give one reason.
What will happen when dry ammonia gas is passed over dry litmus paper?
When H2O is present, ammonia can dissociate into ammonium ions and hydroxide ions, hence turning the red litmus paper blue. If water is not present, ammonia gas remains in it's gaseous state and there will be no change when dry ammonia gas is passed over dry litmus paper.
Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Therefore, the pH of the milk will drop (decrease). As the more acidic the substance the lower the pH.
Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Uses of baking soda:
(i) It is used in bakery.
(ii) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
Uses of washing soda:
(i) It is used in the manufacture of glass, soap and paper.
(ii) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
Give two physical characteristics each of acids and bases.
Physical characteristics of acid and base are:
Acids are
(i) sour in taste.
(ii) change the colour of blue litmus to red.
Bases are
(i) bitter in taste.
(ii) change the colour of red litmus to blue.
Explain the reaction of dilute acids with metals and metal oxides.

Metal Oxides and Acids: Metal oxides dissolve in dilute acids to give salt and water.
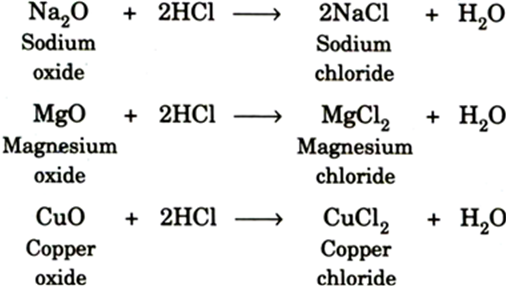
Name the gas evolved when a metal carbonate or metal hydrogen carbonate reacts with acids. Explain the chemical reaction.
hydrogencarbonate react with acid its gives salt, carbon dioxide and water.
Na2CO3 (s)+2HCl(aq)→ 2NaCl(aq) +H2O(l) +CO2
NaHCO3(s)+ HCl(aq)→NaCl(aq) +H2O(l) +CO2
CaCO3(s)+2HCl(aq)→CaCl2(aq) +H2O(l) +CO2
When hydrochloric acid is added to marble pieces, a gas (A) is evolved. On passing gas A through lime water, a white precipitate of (B) is formed. When excess of A is passed, B dissolves due to the formation of soluble C. Identify A, B and C. Explain the reactions.
Chemical Reactions:
Marble is calcium carbonate. It reacts with HCl to give CO2
CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
Marble (A)
CO2 when passed through lime water [Ca(OH)2] gives a white precipitate of CaCO3.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2(g) CaCO3(s) + H2O
White ppt.
(B)
On passing excess CO2, CaCO3 dissolves forming soluble Ca(HCO3)2.
CaCO3 + CO2 Ca(HCO3)2 (aq)
Calcium
hydrogen
carbonate
(C)
A — Carbon dioxide
B — Calcium carbonate
C — Calcium hydrogen carbonate
Complete and balance the following equations:
(i) H2CO3 + NaOH →
(ii) CH3COOH + NH4OH →
(iii) HNO3 + KOH →
(iv) H2SO4 + NaOH →
(a) What are these reactions called?
(b) Name the salt formed in each case.
(ii) CH3COOH + NH4OH →CH3COONH4 +H2O
(iii) HNO3 + KOH → KNO3 +H2O
(iv) H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 +2H2O
(a) All the above are Neutralization Reactions.
b)Name of salts in reactions:
(i) Sodium carbonate, (ii) Ammonium acetate,
(iii) Potassium nitrate, (iv) Sodium sulphate.
What is common between bases and metal oxides? How will you prove your answer?
Both Metal oxides and bases react with acids to give salt and water.
Base + acid → Salt + water
Metal oxide + acid → Salt + water
Illustration: Take small amount of copper oxide in a beaker. Note its colour. It is white. Now add dilute hydrochloric acid slowly white stirring. It will be seen that the colour of the solution changes slowly from white to blue-green. The blue-green colour of the solution is due to the formation of copper chloride in the solution.
CuO + 2HCl CuCl2 + H2O
Metal oxide Acid Salt Water
HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O
Acid base salt water
Write the balanced chemical equations for the reactions that take place when zinc, magnesium and sodium react with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid.
Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 +H2
Reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid.
Mg +2HCl MgCl2 +H2
Reaction of Sodium with hydrochloric acid.
2Na +2HCl2NaCl +H2
How are metal carbonates formed? Give an example along with the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
When metal oxides react with carbon dioxide, they produce metal carbonates.
For example:
i) CaO +CO2 CaCO3
ii) Na2O +CO2 Na2CO3
Metal carbonate can be prepared form hydroxide.
For example:
i) Ca(OH)2 +CO2 CaCO3 +H2O
Mention names of two oxides each which on reaction with water give acids and bases respectively.
CO2 +H2O H2CO3
SO2 +H2O H2SO3
(b) Magnesium oxide (MgO) and calcium oxide (CaO) with water give bases.
MgO + H2O Mg(OH)2
CaO +H2O Ca(OH)2
You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
acid + metal → salt + Hydrogen gas
Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
(ii) Illustration: Set up an apparatus as shown. Take some zinc granules in the test tube. Add about 5 ml dilute hydrochloric acid slowly. Soon the reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid starts and hydrogen gas is evolved.
(iii) Test for H2 gas: H2 gas is not soluble in water. When passed through soap solution, it gets trapped into bubbles which burn with explosion.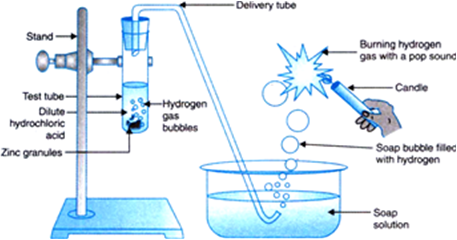
Fig. 2.1. Reaction of zinc granules with dilute hydrochloric and testing hydrogen gas by burning.
2HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2 ↑
Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
What are acids and bases (According to Arrhenius)?
According to Arrhenius, acids are compounds that break up in water to give off hydronium (H+) ions. A common example of an Arrhenius acid is hydrochloric acid (HCl):
HCl ⇔ H+ + Cl-
Arrhenius bases are defined as compounds that cause the formation of the hydroxide ion when placed in water. One example of an Arrhenius base is sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
NaOH ⇔ Na+ + OH-
Does acid solution conduct electricity?
Out of tap water and pure water, which is a better conductor?
How will you prepare dilute acid solution?
We should always add acid to water, otherwise, so much heat is produced during the dilution process that the container, specially that of glass, may break. The hot contents may also cause an explosion and spill on our clothes and body. This may cut our clothes and also result into serious acid burns.
Which of the following aqueous solutions will conduct electricity? Glucose, Hydrochloric acid, Acetic acid, Alcohol, Sulphuric acid, Sodium hydroxide.
Describe an activity to show that acids produce ions only in aqueous solutions.
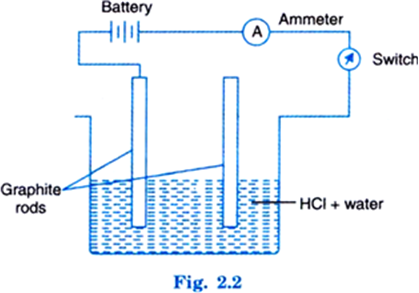
Now switch on the circuit. It will be seen that the pointer of ammeter moves. This shows that current is passing through circuit. This is possible when ions are present in solution.
Now take dry HCl in acetone or any other organic liquid. Arrange the system as before. It will be seen that pointer of the ammeter does not move when circuit is completed. This means no current is passing and solution does not contain ions. Hence, it is inferred that acids produce ions in water solution only.
Explain, why does dry hydrochloric acid not conduct electricity but its aqueous solution conducts electricity.
Electric current flows through the solution by ions. Since dry hydrochloric acid does not give any ions, it does not conduct current. Whereas in the presence of water, H+ ions and CI– ions are produced which are responsible for flow of current.
HCl + H2O → H3+O + Cl–
Tap water conducts electricity whereas distilled water does not. Why?
Distilled water is free from all kinds of salts and hence does not conduct electricity.
Which of the following substances in water will not show acidic properties? Explain.
Sugar, Alcohol, Acetic acid, Urea, Nitric acid, Cabron dioxide
What is the essence of all neutralization reactions?
When a strong acid is neutralized by a strong base there are no excess hydrogen ions left in the solution. The solution is said to be neutral as it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The pH of such a solution is close to a value of 7; the exact pH value is dependent on the temperature of the solution.
Neutralization is an exothermic reaction. The standard enthalpy change for the reaction
H+ + OH− → H2O is -55.90 kJ/mol.
What do you mean by dilution of an acid or base? Why is it done?
Why do HCl, HNO3 etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
HCl (aq) → H+ + Cl-
When alcohols and glucose are mixed with water then they do not form ions. Hence they do not show acidic character.
Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
What is a universal indicator?
What is pH scale? How is it calibrated?
Sponsor Area
What is pH?
pH the symbol for the logarithm of the reciprocal of hydrogen ion concentration in gram atoms per liter,used to express the acidity or alkalinity of a solution on a scale of 0 to 14, where less than 7 represents acidity, 7 neutrality, and more than 7 alkalinity.
What is the pH of neutral water? What does it mean?
10–7 moles per litre.
How do you measure the strength of an acid or a base?
If we take one molar concentration (1 mole acid dissolved in 1 litre of solution) of hydrochloric acid and acetic acid, then the acid which gives rise to more of H+ ions is a stronger acid and the one that gives less H+ ions is a weaker acid. In this case, it is found that hydrochloric acid is a strong acid. Similarly one can find whether it is a strong base or a weak base. (Here number of OH- ions is counted.)
1 mole per litre of (A) has pH equal to 13 and 1 mole per litre of (B) has pH equal to 11. Which is stronger? Whether these are bases or acids?
The pH of a hydrochloric acid solution is 3. Does it mean that it has only hydronium ions. If not, how are OH– ions generated?
Write a note on pH scale.
A measure of acidity or alkalinity of water soluble substance ( pH stands for potential of hydrogen). A pH value is a number from 1 to 14 with 7 as the middle (neutral) point. Values below 7 indicate acidity which increases as the number decrease, 1 being the most acidic values above 7 indicate alkalinity which increases as the number increase, 14 being the most alkaline. 
|
pH value |
Nature of solution |
|
0–2 |
Strongly acidic |
|
2–4 |
Moderately acidic |
|
4–7 |
Weakly acidic |
|
7 |
Neutral |
|
7–10 |
Weakly basic |
|
10–12 |
Moderately basic |
|
12–14 |
Strongly basic |
(i) An aqueous solution has a pH value of 7.0. Is this solution acidic, basic or neutral?
(ii) Which has a higher pH value, 1 M HCl or 1 M NaOH?
(i) Neutral.
(ii) 1 M NaOH has higher pH value.
A group of students measured the pH of some substance they found in their home. Their results are given in the table below:
|
Substance |
pH |
|
Apples |
3.0 |
|
Black coffee |
4.5 |
|
Lemon juice |
2.5 |
|
Milk |
6.5 |
|
Sugar |
7.0 |
|
Toothpaste |
9.0 |
|
Vinegar |
3.0 |
|
Washing soda |
11.5 |
|
Blood |
7.3 |
|
Saliva |
6.5 |
|
Urine |
6.0 |
|
Tomato juice |
4.2 |
|
Vinegar |
2.4 |
(i) Which solution is the most acidic?
(ii) Which solution is the most basic?
(iii) Which substance is the neutral?
(i) Vinegar.
(ii) Washing soda.
(iii) Sugar.
Given below are the pH values of four different liquids. 7.0, 14.0, 4.0, 2.0, Which of these could be that of
(i) Lemon juice (ii) Distilled water
(iii) 1 M NaOH (iv) Tomato juice.
Given below are the pH values of four different liquids. 7.0, 14.0, 4.0, 2.0, Which of these could be that of
(i) Lemon juice (ii) Distilled water
(iii) 1 M NaOH (iv) Tomato juice.
(i) Lemon juice 2.0
(ii) Tomato juice 4.0
(iii) Distilled water 7.0
(iv) 1 M NaOH 14.0
What is acid rain. How does it affect our aquatic life?
What is the importance of pH in tooth decay?
You are provided with different solutions A, B, C, D, E having pH values as 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 respectively. Which solution has highest hydrogen ion concentration and which solution has lowest hydrogen ion concentration?
| Solution | pH |
| A | 3 |
| B | 5 |
| C | 7 |
| D | 9 |
| E | 11 |
What is a universal indicator? How is it used?
Universal indicator is a mixture of many different dyes which give different colour at different H+ ion concentration or pH values. The colours produced by universal indicator at various pH values is given beloe:
|
≈ pH |
Colour |
≈ pH |
Colour |
≈ pH |
Colour |
|
0 |
Dark |
5 |
Orange yellow |
10 |
Navy blue |
|
1 |
Red |
6 |
yellow |
11 |
Purple |
|
2 |
Red |
7 |
Green |
12 |
Dark purple |
|
3 |
Orange red |
8 |
Greenish blue |
13 |
Violet |
|
4 |
Orange |
9 |
Blue |
14 |
Violet |
hus, if on putting the drop of a solution on the universal indicator paper, the paper turns orange, the pH will be about 4 and the solution will be acidic. If the solution turns universal indicator purple, then the pH will be about 11 and the solution will be moderately basic.
Describe the importance of pH in every day life.
1. pH in our digestive system: Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid of pH about 1.4. This dilute hydrochloric acid helps in digesting our food without harming the stomach. Sometime, excess of acid is produced in the stomach for various reasons such as overeating. The excess acid in the stomach causes indigestion which produces pain and irritation. In order to cure indigestion and get rid of pain, we can take bases called antacids. Being basic in nature, antacids react with excess acid in the stomach and neutralize it. The two common antacids used for curing indigestion due to acidity are Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia) and Sodium hydrogen carbonate.
2. pH change as the cause of tooth decay: When we eat food containing sugar, then the bacteria present in our mouth break down the sugar to form acids such as lactic acid. Thus, acid is formed in the mouth after a sugary food has been eaten. This acid lowers the pH in the mouth making it acidic. Tooth decay starts when the pH of acid formed in the mouth falls below 5.5. This is because then the acid becomes strong enough to attack the enamel of our teeth and corrode it. This sets in tooth decay.
The best way to prevent tooth decay is to clean the mouth thoroughly after eating food by rinsing it with lots of clean water. Many tooth pastes contain bases to neutralise the mouth acid. The pH of tooth paste is about 8.0. Therefore, using the tooth paste, which is generally basic, for cleaning the tooth can neutralise the excess acid in mouth and prevent tooth decay.
3. Soil pH and plant growth: Most of the plants grow best when the pH of the soil is close to 7. If the soil is too acidic or too basic the plants grow badly or do not grow at all. The soil may be acidic or basic naturally. The soil pH is also affected by the use of chemical fertilisers in the fields.
Most often the soil in the fields in too acidic. If the soil is too acidic, (having low pH), then it is treated with materials like quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate). If the soil is too alkaline then its basicity is reduced by adding decaying organic matter which are acidic.
4. pH change and survival of animals: Our body works well within a narrow pH range of 7.0 to 7.8. If due to some reason, this pH range gets disturbed in the body of a person, then many ailments can occur. The aquatic animals (like fish) can survive in river water within a narrow range of pH change.
When the pH of rain water is about 5.6, it is called acid rain. Too much acid rain can lower the pH of river water to such an extent (and make it so acidic) that the survival of aquatic animals becomes difficult. The high acidity of river water can even kill the aquatic animals (like fish).
Acids are also present on other planets. For example, the atmosphere of planet Venus is made up of thick white and yellowish clouds of sulphuric acid. Hence, life cannot exist on the planet Venus.
Tooth enamel is one of the hardest substances in our body. How does it undergo damage due to eating chocolates and sweets? What should we do to prevent it?
You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
How are salts formed? What determines their pH value in aqueous solution?
Among the following salts, which salts are acidic, basic or neutral?
Sodium chloride, potassium nitrate, aluminium chloride, zinc sulphate, sodium acetate, sodium carbonate, copper sulphate, sodium sulphate, ammonium chloride.
Acidic salts: Aluminium chloride, zinc sulphate, copper sulphate, ammonium chloride.
Basic salts: Sodium acetate, sodium carbonate.
Neutral salts: Sodium chloride, potassium nitrate, sodium sulphate.
A drop of phenolphthalein indicator is added to each of three test tubes A, B, C containing solution of sodium sulphate, potassium acetate and ammonium chloride respectively. In which test tube the colour of solution will turn pink? Explain.
Given below a few salts. Write the corresponding acid and base from which these salts are formed, indicating the strength of the corresponding acid and base.
i)CaCl2
ii)(NH4)2 SO4
iii)CH3COONa
iv) KNO3
v)C6H5OOK
i) CaCl2: Calcium chloride is a salt of strong acid, hydrochloric acid (HCl) and a weak base, calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2].
ii) (NH4)2SO4: Ammonium sulphate is a salt of strong acid, sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and weak base, ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
iii) CH3COONa: Sodium acetate is a salt of weak acid, acetic acid (CH3COOH) and strong base, sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
iv) KNO3: Potassium nitrate is a salt of strong base, potassium hydroxide (KOH) and strong acid, nitric acid (HNO3).
v) C6H5COOK: Potassium benzoate is a salt of weak acid, benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) and strong base, potassium hydroxide (KOH).
Select the neutral, acidic and basic salts among the following:
Na2SO4, CH3COONa, AlCl3, KCl, Na2CO3, (NH4)SO4, MgCl2, K2SO4, KHCO3
Acidic salts: AlCl3, (NH4)2SO4, MgCl2
Basic salts: CH3COONa, Na2CO3, KHCO3.
The tanks in which milk is stored for retail selling are cleaned with sodium hydroxide solution everytime fresh milk is filled in them. Give the reason for this practice.
Distinguish clearly between the following terms by giving suitable examples:
(a) Acid and Alkali
(b) Organic acid and Mineral acid
(c) Base and Alkali.
(a) Distinguish between Acid and Alkali
|
Acid |
Alkali |
|
1. The compound formed by the reaction of |
1. The hydroxide of metals which dissolve in |
|
acidic oxide with water is called acid. |
water are known as alkalies. |
|
Examples: HCl, HNO3, H2SO4. |
Examples: NaOH, KOH, NH4OH. |
(b) Distinguish between Organic acid and Mineral acid
|
Organic Acid |
Mineral Acid |
|
1. Organic acid contains — COOH functional group. |
1. Mineral acid contains hydrogen ion (H+). |
|
2. These acids are weak. Examples: Ethanoic acid, Lactic acid, citric acid. |
2. These acids are strong. Examples: Hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acid. |
(c) Distinguish between Base and Alkali
|
Base |
Alkali |
|
1. A base is defined as a substance which contains hydroxyl group. Examples: NaOH, KOH, Al(OH)3. |
1. The hydroxide of metal which dissolves in water, is known as alkali. Examples: NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2 etc. |
Name a normal (neutral) salt, acidic salt and basic salt of element sodium. Explain.
Neutral or normal salt of sodium: Sodium chloride (NaCl). It does not hydrolyse in water and so solution of NaCl contains no extra H+ or OH– ions.
Acidic salt of sodium: Sodium hydrogen sulphate (NaHSO4). It hydrolyses in water to give
strong acid, H2SO4.
Basic salt of sodium: Sodium acetate (NaOOCCH3). It hydrolyses in water to give strong base, NaOH.
When carbon dioxide is bubbled into lime water, a white cloud appears.
(i) Write an equation to show the reaction between carbon dioxide and water.
(ii) Name and write the formula of the product.
(iii) What is the chemical name for limewater.
(iv) Write the equation for the chemical reaction between limewater and the product of water + CO2 Name the product.
(i) Reaction between carbon dioxide and water.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
(ii) Carbonic acid, H2CO3.
(iii) Calcium hydroxide
(iv) Ca(OH)2 + H2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2H2O.
The main product is calcium carbonate.
What happens when the extinguisher cylinder is inverted and the stopper is opened by pushing the plunger?
2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2 ↑
What is water of crystallization? Give two examples.
Name five hydrated salts.
(i) Ferrous sulphate, FeSO4 · 6H2O
(ii) Magnesium sulphate, MgSO4 · 7H2O
(iii) Barium chloride, BaCl2 · 2H2O
(iv) Calcium sulphate, CaSO4 · 2H2O
(v) Sodium thiosulphate, Na2S2O3 · 7H2O.
Name the compound which is an essential ingredient in our daily life. Give its chemical name.
Or
What is the chemical composition of table salt?
Explain the term: Deliquescence.
Why does common salt become moist in rainy season?
Or
Ordinary common salt contains another substance which is deliquescent. Name the substance and write its formula.
Common salt contains some impurity such as magnesium chloride (MgCl2) which is deliquescent and is responsible for sodium chloride to become moist in rainy season.
How is common salt obtained from sea water?
State some important uses of sodium chloride.
(i) It is an essential constituent of our daily life and is used for making food items.
(ii) It is used for the manufacture of soap.
(iii) Mixed with ice, it is used as a freezing mixture.
(iv) It is used as a preservative for meat, fish and pickles.
(v) It is used for the industrial preparation of a number of compounds like hydrochloric acid, washing soda, caustic soda etc.
An alkali is an important base used for the laboratory work. Name the base and state how it can be prepared from common salt?
An important alkali commonly needed for laboratory work is sodium hydroxide. It can be prepared from sodium chloride by the process of electrolysis.
Electrolysis of aqueous solution of sodium chloride: When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride commonly called brine, it decomposes into chloride and sodium. Sodium is collected at the cathode where it reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide. Chlorine is collected at the anode and is evolved as chlorine gas.
2NaCl 2Na+2Cl
At Cathode: 2Na +2H2O→2NaOH(aq) +H2(g)
At Anode: Cl +Cl → Cl2(g)
The overall reaction is
2NaCl(aq) +2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) +Cl2(g) +H2(g)
What is washing soda? Give its one characteristic property and one important use.
Chemically, washing soda is a carbonate of sodium with chemical formula Na2CO3 · 10H2O. It is alkaline in nature.
Na2CO3 +10H2O → Na2CO3.10H2O (washing soda)
It is very useful as a cleansing (detergent) agent.
It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
Discuss the manufacture of sodium carbonate with a suitable flow diagram.
Now-a-days sodium carbonate is manufactured on a large-scale by Solvay ammonia process and involves the following steps:
(a) Carbon dioxide obtained from limestone is passed through a concentrated solution of sodium chloride (NaCl) (brine) saturated with ammonia. The reaction of CO2 and ammonia gives ammonium bicarbonate which on reaction with sodium chloride gives sodium bicarbonate (NaHCOg). Sodium bicarbonate gets precipitated because of its low solubility in water.
i) NH3(g) +H2O(l) +CO2(g) →NH4HCO3(aq)
ii) NH4HCO3(aq) +NaCl(aq) → NH4Cl(aq) +NaHCO3(s)
The filtrate containing ammonium chloride is reacted with lime to form ammonia which is again used to saturate brine solution (NaCl).
(b) Sodium bicarbonate is obtained as a white crystalline solid by filtration and is well washed so as to free it from ammonium compound.
(c) Sodium bicarbonate is heated to convert it into sodium carbonate.
2NaHCO3(s)+ heat → Na2CO3 +H2O(l) +CO2(G)
Ammonium chloride and carbon dioxide are used again and again and so the manufacture of sodium carbonate involves only sodium chloride and limestone as the cheap raw materials. The overall flow chart is given below in Figure Thus only limestone and sodium chloride are consumed and washing soda can be continuously manufactured.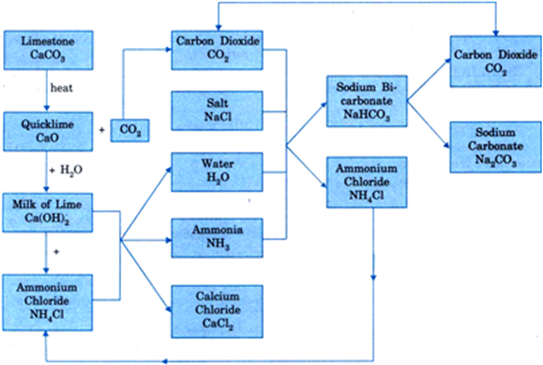
Give the different commercial forms of sodium carbonate.
The commerical forms of sodium carbonate:
(i) Soda ash—Na2CO3
(ii) Washing soda crystals—Na2CO3 · 10H2O
(iii) Carbonate powder—Na2CO3 · H2O.
Give the important properties and uses of sodium carbonate.
Properties of sodium carbonate: It dissolves in water with evolution of heat. Its aqueous solution is alkaline due to hydrolysis and its solution turns red litmus blue.
Na2CO3(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(ag) + CO2(g)
Upon cooling its hot concentrated solution, this gives Na2CO3 · 10H2O (decahydrate). When this variety is exposed to air, it efflorescences and finally changes into monohydrate Na2CO3 · H2O. Upon strong heating, this changes into anhydrous form. It reacts with mineral acids to give carbon dioxide gas.
Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l).
Uses:
(i) It is used in the manufacture of glass, soap powder, caustic soda and borax.
(ii) It is employed as a base in acid base titrations.
(iii) It is used as washing soda in detergents.
(iv) It is used in the softening of water.
Potassium carbonate cannot be made by Solvay’s process using potassium chloride in place of sodium chloride. Why?
In the Solvay process, why does the reaction between sodium chloride and ammonium hydrogen carbonate run to completion?
The reaction is:
NaCl(ag) + NH4HCO3(aq) → NH4Cl(ag) + NaHCO3(s)
This reaction runs to completion because sodium bicarbonate formed is insoluble and is continuously removed from reaction mixture.
What is efflorescence?
A certain compound is alkaline in nature. On exposure to air, it turns into white opaque powder. Identify the compound and mention its two uses.
The alkaline compound is sodium carbonate.
Uses of sodium carbonate:
i) Sodium carbonate is used in glass, soaps and paper industries.
ii)It is used in the manufacture of sodium compounds such as boarx/
Sodium carbonate solution is alkaline. Explain.
Sodium carbonate reacts with water (in solution) and forms sodium hydroxide.
Na2CO3 + H2O → 2NaOH + CO2
Thus the alkaline nature of sodium carbonate solution is due to the presence of NaOH in it.
Give your remarks on:
“Soda ash is the same as washing powder.”
Name the compound which is the primary product of the Solvay process and which is used in fire extinguishers.
Illustrate how is sodium bicarbonate used in a fire extinguisher.
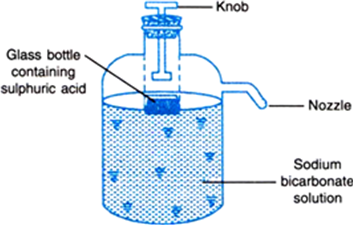
Fig. 2.4. A soda-acid fire extinguisher.
A soda acid fire extinguisher consists of a metal container filled with a solution of sodium bicarbonate. A glass bottle kept inside the container has sulphuric acid in it. When the knob of the extinguisher is pressed, the bottle breaks. The acid comes in contact with sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide is produced.
2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2
The carbon dioxide comes out through the nozzle which is directed towards the fire. Carbon dioxide cuts off the supply of air, after which the fire gets extinguished.
Explain the term ‘carbonation’ in relation to the manufacture of washing soda by Solvay’s process.
NH3(g) +H2O(l) +CO2 → NH4HCO3(aq)
NH4HCO3(aq) +NaCl(aq) → NH4Cl(aq) +NaHCO3(s)
What happens when:
(i) Ammonium bicarbonate is heated?
(ii) Sodium bicarbonate is heated?
(ii) When sodium bicarbonate is heated, carbon dioxide gas is evolved and sodium carbonate is formed.
2NaHCO3(s) + heat → Na2CO3(s) +CO2(l) +H2O
In washing powders certain chemicals are added to impart the under-mentioned properties. Name the chemical used for each property.
(i) Keeps the dirt in water
(ii) Removes dust particles
(iii) Keeps the washing powder dry
(iv) Impart whiteness.
Washing powder contains only about 15–30% detergent by weight. The rest is made up of other chemicals added to impart it the desired property as given below:
(i) Carboxy methyl cellulose (CMC) is added to keep the dirt suspended in water.
(ii) Sodium tripolyphosphate is added to remove dust particles.
(iii) Sodium silicate is added to keep the washing powder dry.
(iv) Sodium borate is a mild bleaching agent and is added to impart whiteness.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(i) Na2CO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) →
(ii) Na2CO3(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) →
(iii) Na2CO3(s) + HCl(aq) →
(i) Na2CO3(g) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(ag) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
(ii) Na2CO3(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) → 2NaHCO3(aq)
(iii) Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(g) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Give a brief account of baking powder.
Baking powder: The soda commonly used in the kitchen for making tasty food item is baking food.
The chemical name of baking powder is sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Preparation: Carbon dioxide is passed through a saturated solution of sodium carbonate. Sodium bicarbonate, being sparingly soluble in water gets precipitated which is washed and dried in air. Requisite amounts of corn starch and hydrogen tartarate are then mixed,
Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O 2NaHCO3(s)
Sodium hydrogen carbonate
It can also be prepared using sodium chloride as raw material.
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 NH4Cl + NaHCO3
Ammonium Sodium
chloride hydrogen
carbonate
Properties: (i) It is alkaline in nature.
(ii) At 100°C, it decomposes with evolution of CO2 gas.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O.
Uses: It is used
(i) As a cooking agent.
(ii) In medicines for neutralising acidity in stomach.
(iii) In soft drinks.
(iv) In fire extinguishers.
Write the chemical formula of washing soda. How can it be obtained from baking soda? Describe a household application of washing soda.
(i) Washing soda is sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 10H2O.
(ii) Baking soda on heating gives sodium carbonate
2NaHCO3 Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
(iii) It is used as cleansing agent.
How is baking powder so useful in the preparation of biscuits and cakes?
immediately to produce carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide gets trapped within batters and expands upon baking, thus useful in the prepartion of biscuits and cakes.
Write the reaction that takes place when sodium oxide reacts with water. How will this solution behave towards phenophthalein and red litmus paper?
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH(aq)
Sodium oxide in water gives sodium hydroxide solution. It is alkaline and turns phenolphthalein solution pink and red litmus paper to blue.
What is the chemical name of baking soda? What happens when it is heated? Write two uses of baking soda.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 +CO2 +H2O
A house-wife found that the cake prepared by her is hard and small in size. Which ingredient has she forgotten to add that would have made the cake fluffy. Give reason.
Baking soda is used in small amount in making bread and cake. It helps to make these soft and spongy. An aqueous solution of baking soda turns red litmus blue. It is also used in soda acid fire extinguisher.
Use this information to answer the following questions:
(i) How does Baking Soda help to make cakes and bread soft and spongy?
(ii) How does it help in extinguishing fire?
(iii) Is the pH value of baking soda solution lesser than or greater than 7? (CBSE Sample Paper)
(i) On heating sodium bicarbonate, the main constituent of baking soda, decomposes to produce CO2. This causes cakes and bread to become light, soft and spongy.
2NaHCO3 +heat → Na2CO3 +H2O +CO2
(ii) Baking soda on reaction with sulphuric acid gives CO2 vigorously. CO2 helps to extinguish fire.
2NaHCO3 + H2SO4→ Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2
(iii) The pH of baking soda solution should be greater than 7.
During summer season, a milk man usually adds a small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. Give one reason.
Name the constituents of baking powder.
What is bleaching powder? How is it prepared?
CaOCl2 (calcium oxychloride) is bleaching powder.
Bleaching powder is produced by the action of chlorine on the dry slaked lime.
for a long time.
Ca(OH)2(s) + Cl2(g) → CaOCl2(s) + H2O(l)
For its manufacture, Bachman’s plants is used which is shown in Figure.
This consists of a vertical cast iron tower fitted with a hopper at the top through which slaked lime is fed and hot air and chlorine enters near the base in opposite direction. The reaction takes place in the different shelves which contains rotating rakes. Bleaching powder is collected in the drum kept at the base.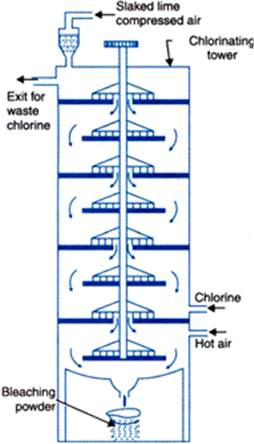
Fig. 2.5. Bachman plant for manufacturing bleaching powder.
Explain the properties of bleaching powder.
(i) Bleaching powder is a yellowish powder with smell of chlorine.
(ii) When in atmosphere, it absorbs moisture but is not deliquescent.
(iii) It is soluble in water but a small insoluble portion is left behind which is the lime present in it.
(iv) Action of carbon dioxide: Upon reaction with carbon dioxide (air), it deteriorates giving off chlorine and calcium carbonate,
CaOCl2(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + Cl2(g).
(v) Action of dilute acids: With dilute acids, it liberates the whole of its chlorine,
CaOCl2(s) + H2SO4(ag) → CaSO4(s) + H2O (l) + CI2(g)
CaOCl2(s) + 2HCl(ag) → CaCl2(s) + H2O(l) + Cl2(g).
The chlorine so obtained is known as available chlorine. The value of bleaching powder
in the market is proportional to the quantity of available chlorine liberated by excess of dilute acids. Higher the amount of chlorine liberated, higher is its price.
The bleaching powder in the presence of insufficient dilute acids acts as a bleaching agent due to the liberation of nascent oxygen. Hypochlorous acid is first formed which decomposes to give hydrochloric acid and nascent oxygen. Thus even with a small quantity of the acid, it acts as an oxidising agent and bleaching agent.
2CaOCl2(s) +H2SO4 →CaCl2(s) +CaSO4(s) +2HClO(aq)[Hypochlorous acid]
HClO →HCl +[O] nascent oxygen
(vi) Effect on long standing: Upon long standing, the following reaction takes place.
6CaOCl2 → 5CaCl2 + Ca(CO3)2
Thus, the quantity of available chlorine decreases.
Mention the important uses of bleaching powder.
Important uses of bleachng powder:
(i) Used for disinfecting drinking water.
(ii) Used in manufacture of chloroform.
(iii) Used for bleaching cotton and wood pulp in textiles etc.
(iv) Used for making wool unshrinkable.
Why does bleaching powder smell strongly of chlorine?
Bleaching powder smells strongly of chlorine because it slowly reacts with carbon dioxide of air to evolve chlorine gas.
CaOCl2(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + Cl2(g).
Why are commercial samples of bleaching powder not completely soluble in water?
What happens when:
(a) Quick lime is added to water?
(b) Carbon dioxide gas is passed through slaked lime?
(c) Chlorine gas is passed through dry slaked lime?
(b) Upon passing carbon dioxide gas through slaked lime, calcium carbonate is formed,
Ca(OH)2 + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
(c) When chlorine is passed through slaked lime, bleaching powder is formed.
Ca(OH)2(s) + Cl2(g) → CaOCl2(s) + H2O(l)
Identify the compounds which are used as disinfectants and germicides :
(a) CuSO4 · 5H2O (b) Na2CO3 · 10H2O
(c) CaOCl2 (d) CaSO4 · 2H2O
(c) CaOCl2.
Discuss the process of bleaching of cloth by bleaching powder.
Bleaching process. The article cloth to be bleached is taken through the following steps successively:
(i) It is dipped into a tank containing bleaching powder in water. The article gets covered with bleaching powder.
(ii) It is then passed through a tank containing very dilute hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid. Bleaching powder on the cloth reacts with dilute acid. Hypochlorous acid (HCIO) formed is unstable and decomposes to give hydrochloric acid and oxygen atom which bleaches the article.
2CaOCl2 +H2SO4 →CaCl2 +CaSO4 +2HClO
(Hypochlorous acid)
HClO → HCl +[O] nascent oxygen
(iii) It is then passed through a tank containing antichlor such as sodium thiosulphate or sodium bisulphite. It reacts with chlorine to change it into chloride ion and makes chlorine ineffective to act as an oxidising agent and the bleached article is not affected.
Na2S2O3 +5Cl2 +4H2O→2Na2SO4 +8HCl +2NaCl
(iv) It is then passed through a tank containing water to free it from hydrochloric acid and salts formed.
What is antichlor? Why do you use antichlor after treating the clothes with bleaching powder?
Antichlor is a substance used to remove excess of chlorine from a material/cloth. Examples are sodium bisulphite and sodium thiosulphate.
After the clothes are treated with bleaching powder and acid solutions, some chlorine remains sticking to the fibre which may injure it if not removed quickly after bleaching is over. Chlorine is removed by reaction with sodium bisulphite as given below:
NaHSO3 + Cl + H2O → NaHSO4 + 2HCl
Give your remark on: “Commercial bleaching powder is sold on the basis of its available chlorine.”
With dilute acids, bleaching powder gives up whole of its chlorine,
CaOCl2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + H2O + Cl2
The chlorine so formed is called available-chlorine and a good sample of bleaching powder contains 35—40% chlorine. The value of bleaching powder in the market is proportional to the quantity of available chlorine. Greater the amount of chlorine liberated higher is its price.
What is plaster of Paris? How is it prepared? Give its important uses.
This is prepared by heating gypsum to 120–130°C.
Uses of plaster of Paris:
(i) It is used in making chalks and fire proof materials.
(ii) Used for making patient plasters used in surgery and for plastering fractured parts of the body.
(iii) Mixed with alum, it is used as a cement in ornamental casting and for making moulds in pottery work.
What happens when plaster of Paris is heated beyond 120°C?
Give the properties of plaster of Paris.
On heating gypsum at 373K, it loses water molecule and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate(CaSO4.1/2H2O).
Properties of plaster of Paris:
(i) It is a white powder.
(ii) Setting property: When wetted with water, this forms a solid plastic mass and heat is given out during this process and finally a hard porous mass results within 10-15 minutes. This involves two steps. Firstly, water is absorbed to form orthorhombic dihydrate and change to monoclinic, when the plaster hardens, thus setting takes place.
What is gypsum? What happens when gypsum is heated to 120°C?
What are the special properties of ‘plaster of Paris’ which make it useful in the hospitals?
is used as plaster of Paris but CaSO4 is used as a drying agent and cannot replace plaster of Paris. Explain.
Anhydrous calcium sulphate (CaSO4) takes up water readily and forms hydrated salt and so is used as a drying agent,
CaSO4 + 2H2O → CaSO4 · 2H2O
has a particular crystal structure which imparts property of setting and hardening on mixing with water. CaSO4 cannot replace plaster of paris because on mixing with water it does not acquire the property of setting and hardening.
Answer the following:
(a) Why is Plaster of Paris written as How is it possible to have half a water molecule attached to CaSO4?
(b) Why is Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate an essential ingredient in antacids?
(c) When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, three products are obtained. Why is the process called chlor-alkali?
(b) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a mild base. It neutralize acidic character but does not impart noticeable basic character.
(c) When sodium chloride is electrolysed, sodium is obtained at cathode which then reacts with water to give alkali and hydrogen. Thus alkali is the main product. On the other hand, chlorine is obtained at anode. So it is called chlor-alkali process.
What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2?
Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Name the sodium compound which is used for softening the hard water.
What will happen if. a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
A solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate on heating gives sodium carbonate and CO2 gas is evolved.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
What would be the pH of a salt of weak acid and strong base?
A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
(a) 1 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 10
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when:
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
(a) Zinc + dil sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
Zn + H2SO4→ ZnSO4 + H2
b) Magnesium ribbon +dil hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
Mg +2HCl → MgCl + H2
c) Aluminium powder + dil sulphuric acid → aluminium sulphate + hydrogen
2Al +3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 +3H2
d)dil. hydrochloric acid + Iron filings → iron chloride + hydrogen
2Fe +6HCl → 2FeCl3 +3H2
Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.

Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does ?
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9, respectively. Which solution is:
(a) neutral? (b) strongly alkaline? (c) strongly acidic?
(d) weakly acidic? (e) weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration.
| solution | pH | Character |
| A | 4 | weakly acidic |
| B | 1 | strongly acidic |
| C | 11 | strongly alkaline |
| D | 7 | neutral |
| E | 9 | weakly alkaline |
pH values in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration:
11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1.
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Metal +acid ---> salt + hydrogen gas
Fizzing will occur more vigorously in test A containing hydrochloric acid. This is because hydrochloric acid is stronger acid than acetic acid and reaction between magnesium ribbon and HCl is faster than between Mg and acetic acid.
Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
(a) The milkman adds a little baking soda to fresh milk to make it slightly alkaline so that it can be preserved for a longer time.
(b) Initially lactic acid formed is used up to neutralize the base i.e., baking soda and when more lactic acid is formed, the milk sets as curd.
Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
The reaction between an acid and a base to give salt and water is known as a neutralization reaction.
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
Examples:
i) HCl +NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Uses of baking soda:
(i) It is used in bakery.
(ii) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
Uses of washing soda:
(i) It is used in the manufacture of glass, soap and paper.
(ii) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
.................. gas is generally evolved when a metal is dropped into a dilute acid.
Bleaching powder is obtained by the action of chlorine on dry .................. .
Acetic acid is present in .................. while .................. is present in lemon.
citric acid
An oxide is acidic and has a pungent order. It could be Carbon monoxide
- Carbon dioxide
- Sodium oxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
Carbon monoxide
D.
Nitrogen dioxide Which of the following will give pH less than seven? - Blood
- Milk of magnesia
- Sodium hydroxide
- Gastric juice
D.
Gastric juice Sodium carbonate is NOT used as: - ingredient in antacids
- as a cleansing agent
- for removing permanent hardness of water
- for manufacture of glass
A.
ingredient in antacids Tooth enamel contains: - calcium carbonate
- calcium sulphate
- calcium chloride
- calcium phosphate
D.
calcium phosphate On diluting a solution of pH 11, its pH: - increases
- decreases
- remains same
- can’t say
B.
decreases One of the components of baking powder is: - tartaric acid
- acetic acid
- oxalic acid
- citric acid
A.
tartaric acid Basic solutions contain: - H+ ions
- OH– ions
- both H+ and OH– ion
- Na+ ions
C.
both H+ and OH– ion Select the mineral acid among the following: - acetic acid
- citric acid
- hydrochloric acid
- lactic acid
C.
hydrochloric acidA student Prepared 20% sodium hydroxide solution in a beaker to study saponification reaction. Some observations related to this are given below :
(I) Sodium hydroxide solution turns red litmus blue
(II) Sodium hydroxide readily dissolves in water
(III) The beaker containing solution appears cold when touched from outside
(IV) The blue litmus paper turns red when dipped into the solution
The correct observations are :
-
I, II and IV
-
I, II and III
-
Only III and IV
-
Only I and II
D.
Only I and II
The correct option is D.
Sodium hydroxide being a base dissolves in water to form an alkaline solution which turns red litmus blue. A large amount of heat is dissipated, when sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water because the process is exothermic in nature. So, when touched from outside the beaker containing sodium hydroxide solution should be hot.
Hard water is not available for an experiment. Some salts are given below :
(I) Sodium chloride
(II) Sodium Sulphate
(III) Calcium chloride
(IV) Calcium Sulphate
(V) Potassium chloride
(VI) Magnesium Sulphate
Select from the following group of these salts, each member of which may be dissolved in water to make it hard.
-
I, II, V
-
I, III, V
-
III, IV, VI
-
II, IV, VI
C.
III, IV, VI
Correct option is C.
Hard water contains sulphates, chlorides and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium. So, calcium chloride, calcium sulphate and magnesium sulphate should be added in water to make it hard water.
When you add about 2 ml of acetic acid to a test tube containing an equal amount of distilled water and leave the test tube to settle after shaking its contents, what will you observe in the test tube after about 5 minutes?
-
A white precipitate settling at its bottom
-
A clear colorless solution
-
A layer of water over the layer of acetic acid.
-
A layer of acetic acid over the layer of water.
B.
A clear colorless solution
The correct option is B.
When acetic acid is mixed with distilled water, they form a clear solution because acetic acid is completely miscible with water.
A student adds a few drops of ethanoic acid to test tubes X, Y and Z containing aqueous solutions of sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate, respectively. If he now brings a burning splinter near the mouth of the test tubes immediately after adding ethanoic acid in each one of them, in which of the test tube or test tubes the flame will be extinguished?
-
X and Y
-
Y and Z
-
X and Z
-
Only Z
D.
Only Z
The correct option is D.
The chemical reaction involved is:
Test tube X:
CH3COOH +NaCl ---> No reaction
Test tube Y:
CH3COOH +NaOH ---> CH3COONa + H2O
Test tube Z:
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 ---> 2 CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
Thus, the flame will be extinguished when test tube Z is brought near a burning splinter. Carbon dioxide is evolved in this reaction and it does not support combustion.
A student takes about 6 ml of distilled water in each of the four test tubes P, Q, R and S. He then dissolves an equal amount of four different salts namely, sodium chloride in 'P', potassium chloride in ‘Q’, calcium chloride in ‘R’ and magnesium chloride in ‘S’. He then adds 10 drops of soap solution to each test tube and shakes its contents. The test tube in which scum (insoluble substance) is formed with soap is:
-
P and Q
-
Q and R
-
R and S
-
Q and S
A.
P and Q
C.
R and S
The correct option is C.
Scum is formed by reaction of soap with calcium and magnesium salts in water. Test tubes R and S contain calcium chloride and magnesium chloride, respectively. Therefore, scum will be formed in these two tubes.
Out of HCl and CH3COOH, which one is a weak acid and why? Describe an activity to support your answer.
HCl completely dissociates into ions in solution and CH3COOH gets partially dissociated into ions in solution. So, CH3COOH is a weak acid when compared to HCl.
This can be proved by the following activity:
- Two iron nails are fitted on a cork and are kept in a 100 mL beaker.
- The nails are then connected to the two terminals of a 6-volt battery through a bulb and a switch.
- Pour dilute HCl in the beaker and switch on the current.
- Repeat the same procedure replacing HCl with CH3COOH.
Observations: It will be observed that the bulb glows in the HCl solution and does not glow in the CH3COOH solution.
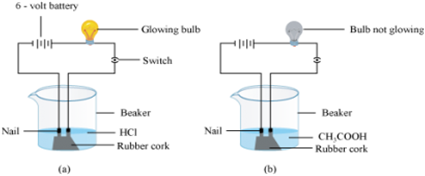
Inference:
HCl, being a strong acid dissociates into H+ and Cl− ions. These ions conduct electricity in the solution resulting in the glowing of the bulb. On the other hand, the CH3COOH is a weak acid. It does not dissociate into ions completely in solution. Therefore, it does not conduct electricity.
To show that zinc is a more active metal than copper, the correct procedure is to:
-
Add dilute nitric acid on strips of both the metals.
-
Observe transmission of heat through strips of zinc and copper.
-
Prepare a solution of zinc sulphate and hang a strip of copper into it.
-
Prepare a solution of copper sulphate and hang a strip of zinc into it.
D.
Prepare a solution of copper sulphate and hang a strip of zinc into it.
Acetic acid solution turns:
-
blue litmus red
-
red litmus blue
-
blue litmus colourless
-
red litmus colourless
A.
blue litmus red
Which of the following observations is true about dilute solution of acetic acid?
-
It smells like vinegar and turns red litmus blue
-
It smells like onion and turns blue litmus red
-
It smells like orange and turns red litmus blue
-
It smells like vinegar and turns blue litmus red
D.
It smells like vinegar and turns blue litmus red
The odor of vinegar is same as that of acetic acid. Also, being an acid (though weak) it turns blue litmus to red.
A student takes Na2CO3 powder in a test tube and pours some drops of acetic acid over it. He observes:
-
no reaction in the test tube
-
colourless gas with pungent smell
-
bubbles of a colourless and odourless gas
-
white fumes with smell of vinegar
C.
bubbles of a colourless and odourless gas
Acetic acid reacts with Na2CO3 to form sodium acetate, carbon dioxide and water. It is this colorless gas carbon dioxide gas which comes out as bubbles.
A student adds 4 mL of acetic acid to a test tube containing 4 mL of distilled water. He then shakes the test tube and leaves it to settle. After about 10 minutes he observes:
-
a layer of water over the layer of acetic acid
-
a layer of acetic acid over the layer of water
-
a precipitate settling at the bottom of the test tube
-
a clear colorless solution
D.
a clear colorless solution
Acetic acid forms a homogeneous solution with water.
A student prepared an aqueous solution of CuSO4 in beaker X and an aqueous solution of FeSO4 in beaker Y. He then dropped some iron pieces in beaker X and some zinc pieces in beaker Y. After about 10 hours he observed that the solutions in X and Y respectively appear:
-
blue and green
-
colorless and pale green
-
colourless and light blue
-
greenish and colourless
D.
greenish and colourless
Reaction in beaker X:
Fe + CuSO4 (blue) -> FeSO4 (green) + Cu
Reaction in beaker Y:
Zn + FeSO4 (green) -> ZnSO4 (colourless) +Fe
What do you observe when you drop a few drops of acetic to test tubes containing
(a) phenolphthalein
(b) distilled water
(c) universal indicator
(d) sodium hydrogen carbonate powder
Acetic acid is a weak acid. The following changes will occur when a few drops of acetic acid are added to the given solutions:
i. Phenolphthalein remains colourless, as acetic acid shows a change in colour in basic substances.
ii. Acetic acid dissolved in water
iii. Acetic acid turns the colour of the universal indicator to pale orange.
iv. When added to sodium hydrogen carbonate powder, acetic acid causes effervescence because of the evolution of carbon dioxide gas in the process. 
A student puts a drop of the reaction mixture of a saponification reaction first on a blue litmus paper and then on red litmus paper. He may observe that:
-
There is no change in the blue litmus paper and the red litmus paper turns white.
-
There is no change in the red litmus paper and the blue litmus paper turns red.
-
There is no change in the blue litmus paper and the red litmus paper turns blue.
-
No change in colour is observed in both the litmus papers.
C.
There is no change in the blue litmus paper and the red litmus paper turns blue.
What do we observe on pouring acetic acid on red and blue litmus papers?
-
Red litmus remains red and blue litmus turns red.
-
Red litmus turns blue and blue litmus remains blue.
-
Red litmus turns blue and blue litmus turns red.
-
Red litmus becomes colourless and blue litmus remains blue
A.
Red litmus remains red and blue litmus turns red.
Which one of the following are the correct observations about acetic acid.
-
It turns blue litmus red and smells like vinegar
-
It turns blue litmus red and smells like burning sulpur
-
It turns red litmus blue and smells like vinegar
-
It turns red litmus blue and has a fruity smell
A.
It turns blue litmus red and smells like vinegar
Vapour of acetic acid smell
-
Pungent like vinegar
-
Sweet like rose
-
Suffocating like sulphur dioxide
-
Odourless like water
A.
Pungent like vinegar
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area