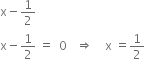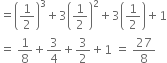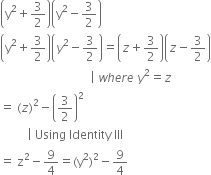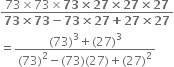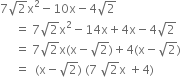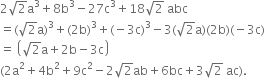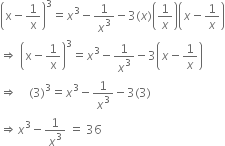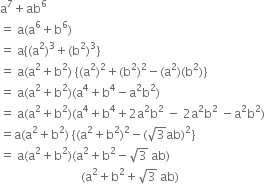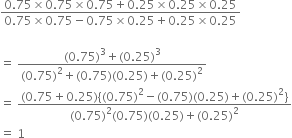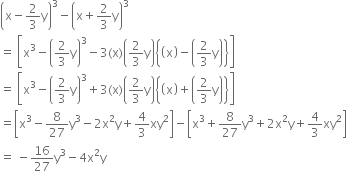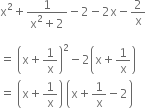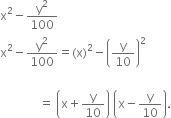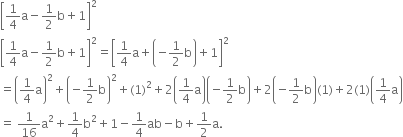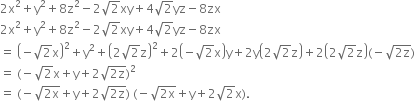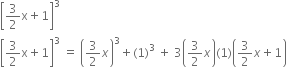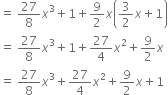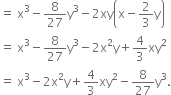Mathematics Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 9 About 2.html
Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
4x2 - 3x + 7
4x2 - 3x + 7
This expression is a polynomial in one variable x because in the expression there is only one variable (x) and all the indices of x are whole numbers.
Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
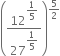
y2 + ![]()
y2 + ![]()
This expression is a polynomial in one variable y because in the expression there is only one variable (y) and all the indices of y are whole numbers.
Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
This expression is not a polynomial because in the term
Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
This expression is not a polynomial because in the term
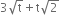
Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
x10+ y3 + t50
x10+ y3 + t50
This expression is not a polynomial in one variable because in the expression, three variables (x, y and t) occur.
Write the coefficients of x2 in each of the following:
2 + x2 + x
2 + x2 + x
Coefficient of x2 = 1.
Write the coefficients of x2 in each of the following:
2 - x2 + x3
2 - x2 + x3
Coefficient of x2 = - 1.
Sponsor Area
Give one example each of a binomial of degree 35, and of a monomial of degree 100.
One example of a binomial of degree 35 is 3x35- 4.
One example of a monomial of degree 100 is ![]()
Write the degrees of each of the following polynomials:
5x3 + 4x2 + 7x
5x3 + 4x2 + 7x
Term with the highest power of x = 5x3
Exponent of x in this term = 3
∴ Degree of this polynomial = 3.
Write the degrees of each of the following polynomials:
4 - y2
4 - y2
Term with the highest power of y = - y2
Exponent of y in this term = 2
∴ Degree of this polynomial = 2.
Write the degrees of each of the following polynomials:

Term with the highest power of t = 5t
Exponent of t in this term = 1
∴ Degree of this polynomial = 1.
Write the degrees of each of the following polynomials:
3
3
It is a non-zero constant. So the degree of this polynomial is zero.
Write the various coefficients in each of the following polynomials:
(i) x7 - 3x5 + 4 (ii) 5y2 - 3y + 2
(iii) x4 - 3x2 + 1 (iv) 1 - 2y + 3y6
(v) 7.
(i) 1, - 3, 4
(ii) 5, - 3, 2 (iii) 1, - 3, 1
(iv) 1, - 2, 3 (v) 7.
How many terms are there in each of the following polynomials? Write them for each polynomial.
(i) 3x2 - 5x + 7 (ii) t - 7t2 + 5 - t3
(iii) x4 - 3x2 + 2 (iv) 5 - 3y + 2y6
(v) 7 (vi) 3 - 2x.
(i) 3x2 - 5x + 7
Number of terms = 3
Terms: 3x2, - 5x, 7.
(ii) t - 7t + 5 - t3
Number of terms = 4
Terms: t, - 7t2, 5, - t3.
(iii) x4 - 3x2 + 2
Number of terms = 3
Terms: x4, - 3x2, 2.
(iv) 5 - 3y + 2y6
Number of terms = 3
Terms: 5, - 3y, 2y6.
(v) 7
Number of term = 1
Term: 7 (only).
(vi) 3 - 2x
Number of terms = 2
Terms: 3, - 2x.
Write the coefficient of x3 in each of the following polynomials:
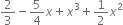
Solution not provided.
Ans. 1
Write the coefficient of x3 in each of the following polynomials:
1 + x2 + x4 - x - x3
Solution not provided.
Ans. - 1
Write the coefficient of x3 in each of the following polynomials:
2x3 - 7x + x2 + 3x4
Solution not provided.
Ans. 2
Write the coefficient of x3 in each of the following polynomials:
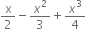
Solution not provided.
Ans. ![]()
Find the degree of each of the polynomials given below:
(i) x5 - x4 + 3 (ii) 2 - y2 - y3 + 2y8 (iii) 2.
Solution not provided.
Ans. (i) 5 (ii) 8 (iii) 0
Point out which of the following polynomials are monomials, binomials or trinomials?
(i) x3 + 2x - 3 (ii) x3 + 8
(iii) 4x + 3x (iv) 8
(v) 5x3 + 2x3 (vi) 7x2 - 5.
(i) trinomial (ii) binomial
(iii) binomial (iv) monomial
(v) monomial (vi) binomial.
Find the value of the polynomial 5x - 4x2 + 3 at
x = 0
Let f(x) = 5x - 4x2 + 3
(i) Value of f(x) at x = 0
= f(0) = 5(0) - 4(0)2 + 3
= 3
Sponsor Area
Find the value of the polynomial 5x - 4x2 + 3 at
x = - 1
Value of f(x) at x = - 1
= f(- 1) = 5(- 1) - 4(- 1)2 + 3
= - 5 - 4 + 3 = - 6
Find the value of the polynomial 5x - 4x2 + 3 at
x = 2.
Value of f(x) at x = 2
= f(2) = 5(2) - 4(2)2 + 3
= 10 - 16 + 3 = - 3.
Find p(0), p(1) and p(2) for each of the following polynomials:
p(y) = y2 - y + 1
p(y) = y2 - y + 1
∴ p(0) = (0)2 - (0) + 1 = 1,
p(1) = (1)2 - (1) + 1 = 1,
and, p(2) = (2)2 - (2) + 1 = 4 - 2 + 1 = 3.
Find p(0), p(1) and p(2) for each of the following polynomials:
p(t) = 2 + t + 2t2 - t3
p(t) = 2 + t + 2t2 - t3
∴ p(0) = 2 + 0 + 2(0)2 - (0)3 = 2,
p(1) = 2 + 1 + 2(1)2 - (1)3
= 2 + 1 + 2 - 1 = 4,
and, p(2) = 2 + 2 + 2(2)2 - (2)3
= 2 + 2 + 8 - 8 = 4.
Find p(0), p(1) and p(2) for each of the following polynomials:
p(x) = x3
p(x) = x3
∴ p(0) = (0)3 = 0,
p(1) = (1)3= 1,
and, p( 2) = (2)3 = 8.
Find p(0), p(1) and p(2) for each of the following polynomials:
p(x) = (x - 1)(x + 1).
p(x) = (x - 1)(x + 1)
∴ p(0) = (0 - 1)(0 + 1) = (- 1)(1) = - 1,
p(1) = (1 - 1)(1 + 1) = (0)(2) = 0,
and, p(2) = (2 - 1)(2 + 1) = (1)(3) = 3
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) = 3x + 1, x = 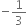
p(x) = 3x + 1, x = ![]()
![]()
![]() is a zero of p(x).
is a zero of p(x).
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) = 5x -  , x =
, x = 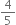
p(x) = 5x - ![]() , x =
, x = ![]()
![]()
![]() is not a zero of p(x).
is not a zero of p(x).
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) = x2 - 1, x = 1, - 1
p(x) = x2 - 1, x = 1, - 1
p(1) = (1)2 - 1 = 1 - 1 = 0
p(-1) = (-1)2 - 1 = 1 - 1 = 0
∴ 1, - 1 are zeroes of p(x).
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) = (x + 1)(x - 2), x = - 1, 2
p(x) = (x + 1)(x - 2), x = - 1, 2
p(- 1) = (-1 + 1)(- 1 - 2)
= (0)(- 3)
= 0
p(2) = (2 + 1)(2 - 2) = (3)(0) = 0
∴ -1, 2 are zeros of p(x).
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) = x2, x = 0
p(x) = x2, x = 0
p(0) = (0)2 = 0
∴ 0 is a zero of p(x).
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) =lx +m, 
p(x) =lx +m, ![]()
![]()
![]() is a zero of p(x).
is a zero of p(x).
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) = 3x2 - 1, 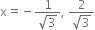
p(x) = 3x2 - 1, ![]()
![]()
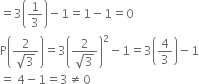
![]() is a zero of p(x) but
is a zero of p(x) but ![]() is not a zero of p(x).
is not a zero of p(x).
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
p(x) = 2x + 1, 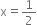
![]()
p(x) = 2x + 1, ![]()
![]()
![]() is not a zero of p(x).
is not a zero of p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
p(x) = x + 5
p(x) = x + 5
p(x) = 0
⇒ x + 5 = 0 ⇒ x = - 5
∴ - 5 is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
p(x) = x - 5
p(x) = x - 5
p(x) = 0
⇒ x - 5 = 0 ⇒ x = 5
∴ 5 is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
p(x) = 2x + 5
p(x) = 2x + 5
p(x) = 0![]()
![]() is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
p(x) = 3x - 2
p(x) = 3x - 2
p(x) = 0![]()
![]() is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
p(x) = 3x
p(x) = 3x
p(x) = 0
⇒ 3x = 0 ⇒ x = 0
∴ 0 is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
p(x) = ax, a ≠ 0
p(x) = ax, a ≠ 0
p(x) = 0
⇒ ax = 0 ⇒ x = 0 | ∵ a ≠ 0
∴ 0 is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
p(x)=cx + d, 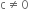 , c, d are real numbers
, c, d are real numbers
p(x)=cx + d, ![]() , c, d are real numbers
, c, d are real numbers
p(x) = 0![]()
![]() is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
is a zero of the polynomial p(x).
Find the zero of the polynomial px + q + r.
px + q + r = 0![]() px = - (q + r)
px = - (q + r)![]()
![]() is the required zero.
is the required zero.
If p(x) = 5x3 - 2x2 + 3x - 2, then find the values of p(1) and p(0). Also, find the value of p(-1).
p(x) = 5x3 - 2x2 + 3x - 2
∴ p(1) = 5(1)3 - 2(1)2 + 3(1) - 2
= 5 - 2 + 3 - 2 = 4
and p(0) = 5(0)3 - 2(0)2 + 3(0) - 2 = - 2
Also, p(- 1) = 5(- 1)3 - 2(- 1)2 + 3(- 1) - 2
= - 5 - 2 - 3 - 2 = - 12
Determine whether the indicated numbers are zeroes of the given polynomial?
g(x) = 3x2 - 2; 
We have
g(x) = 3x2 - 2![]()
![]() is not a zero of 8(x)
is not a zero of 8(x)![]()
![]() is not a zero of 8(x).
is not a zero of 8(x).
Determine whether the indicated numbers are zeroes of the given polynomial?
f(x) = x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6; x = 1, 3
We have
8(x) = 3x2 - 2
f(x) = x3 - 6x2
f(1) = (1)3 - 6(1)2 + 11 (1) - 6 = 0![]() x = 1 is a zero f f(x)
x = 1 is a zero f f(x)
f(3) = (3)3 - 6(3)2 + 11(3) - 6
= 27 - 54 + 33 - 6 = 0![]() x = 3 id s zero of f(x)
x = 3 id s zero of f(x)
If x = -2 is the root of the equation 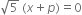 and is also the zero of the polynomial
and is also the zero of the polynomial 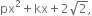 then find the value of k.
then find the value of k.

According to the question.
- p = - 2
Let f(x) = px2 + kx +
Then, f(x) = 2x2 + kx +
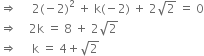
Find the value of each of the following polynomials at the indicated value of variables:
p(x) = 5x2 - 3x + 7 at x = 1
Solution not provided.
Ans = 9
Find the value of each of the following polynomials at the indicated value of variables:
q(y) = 3y3 - 4y +  at y = 2
at y = 2
Solution not provided.
Ans. ![]()
Find the value of each of the following polynomials at the indicated value of variables:
p(t) = 4t4 + 5t3 - t2 + 6 at t = a
Solution not provided.
Ans. 4a4 + 5a3 - a2 + 6.
Check whether - 2 and 2 are zeroes of the polynomial x + 2.
Solution not provided.
Ans. - 2 is a zero but 2 is not.
Verify whether 2 and 0 are zeroes of the polynomial x2 - 2x.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 2 and 0, both are zeros of the polynomial.
If -1 is a zero of the polynomial p(x) = ax3 - x2 + x + 4, find the value of a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 2
If  is a zero of the polynomial p(x) = 27x3 - ax2 - x + 3, then find the value of a.
is a zero of the polynomial p(x) = 27x3 - ax2 - x + 3, then find the value of a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 21
If 2 is a zero of polynomial 4y2 - 6y - k, find the value of k. Also, find the other zero.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 4; ![]()
Find the remainder when x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 is divided by
x + 1
Let p(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1
x + 1
x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = - 1
∴ Remainder
= p(- 1) = (- 1)3 + 3(- 1)2 + 3(- 1) + 1
= - 1 + 3 - 3 + 1 = 0.
Find the remainder when x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 is divided by
x
x
Remainder
= (0)3 + 3(0)2 + 3(0) + 1 = 1.
Sponsor Area
Find the remainder when x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 is divided by
x + 
x + ![]()
x + ![]() = 0 ⇒ x = -
= 0 ⇒ x = - ![]()
∴ Remainder = (- ![]() )3 + 3(-
)3 + 3(- ![]() )2 + 3(-
)2 + 3(- ![]() ) + 1
) + 1
= - ![]() 3 + 3
3 + 3![]() 2 - 3
2 - 3![]() + 1.
+ 1.
Find the remainder when x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 is divided by
5 + 2x
5 + 2x
5 +2x = 0 ![]() 2x = - 5
2x = - 5 ![]() x =
x = ![]()
![]() Remainder
Remainder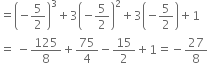
Find the remainder when x3 - ax2 + 6x - a is divided by x — a.
Let p(x) = x3 - ax2 + 6x - a
x - a = 0
⇒ x = a
∴ Remainder = (a)3 - a(a)2 + 6(a) - a
= a3 - a3 + 6a - a
= 5a.
Check whether 7 + 3x is a factor of 3x3 + 7x.
Let p(x) = 3x3 + 7x
7 + 3x = 0
The polynomial p(x) = kx3 + 9x2 + 4x - 8 when divided by x + 3 leaves a remainder - 20. Find the value of k.
Divisor = x + 3
x + 3 = 0 ⇒ x = - 3
∴ Zero of x + 3 is - 3
Remainder = -20 | Given
⇒ p(- 3) = -20
⇒ k(- 3)3 + 9(- 3)2 + 4(- 3) - 8 = - 20
⇒ - 27k + 81 - 12 - 8 = - 20
⇒ 27k = 81
⇒ k = 3.
The polynomial p(x) = x4 - 2x3 + 3x2 - ax + 3a - 7. When divided by (x + 1) leaves the remainder 19. Find the value of a. Also find the remainder, when p(x) is divided by x + 2.
p(x) = x4 - 2x3 + 3x2 - ax + 3a - 7
By remainder theorem.
p(- 1) = 19 | x + 1 = 0 ![]() x = -1
x = -1![]() (- 1)4 - 2 (- 1)3 + 3 (- 1)2 - a(- 1) + 3a - 7 = 19
(- 1)4 - 2 (- 1)3 + 3 (- 1)2 - a(- 1) + 3a - 7 = 19![]() 4a = 20
4a = 20![]()
Also, the remainder when p(x) is divided by x + 2
= p(-2)
= (-2)4 - 2 (-2)3 + 3(-2)2
- a(-2) + 3a - 7
= 16 + 16 + 12 + 2a + 3a - 7
= 5a + 37
= 5(5) + 37
= 25 + 37
= 62
The polynomials ax3 - 3x2 + 4 and 2x3 - 5x + a when divided by (x - 2) leave the remainders p and q respectively. If p - 2q = 4, find the value of a.
Let f(x) = ax3 - 3x2 + 4
and g(x) = 2x3 - 5x + a
By remainder theorem,
f(2) = p ...(1) | x - 2 = 0 ⇒ x = 2
and g(2) = q ...(2) | x - 2 = 0 ⇒ x = 2
(1) gives
a(2)3 - 3(2)2 + 4 = p
⇒ 8a - 8 = p ...(3)
(2) gives
2(2)3 - 5(2) + a = q
⇒ 6 + a = q ...(4)
According to the question,
p - 2q = 4
⇒ (8a - 8) - 2 (6 + a) = 4
⇒ 8a - 8 - 12 - 2a = 4
⇒ 6a = 24
⇒ a = 4
The polynomials ax3 + 3x2 - 3 and 2x3 - 5x + a when divided by x - 4 leaves the remainders p and q respectively. Find the value of a, if 2p = q.
Let f(x) = ax3 + 3x2 - 3
and g(x) = 2x3 - 5x + a
By remainder theorem,
f(4) = p ...(1) | x - 4 = 0 ⇒ x = 4
and g (4) = q ...(2) | x - 4 = 0 ⇒ x = 4
(1) gives
a(4)3 + 3(4)2 - 3 = p
⇒ 64a + 48 - 3 = p
⇒ 64a + 45 = p ...(3)
(2) gives
2(4)3 - 5(4) + a = q
⇒ 128 - 20 + a = q
⇒ 108 + a = q ...(4)
According to the question,
2p = q![]() 2(64a + 45) = 108 + a
2(64a + 45) = 108 + a![]() 128a + 90 = 108 + a
128a + 90 = 108 + a![]() 128a - a = 108 - 90
128a - a = 108 - 90![]() 127a = 18
127a = 18
![]()
Divide p(x) by g(x) using long division method, where p(x) = x + 3x2 - 1 and g(x) = 1 + x.
Solution not provided.
Ans. Quotient = 3x - 2
Remainder = 1
Using long division method divide the polynomial 3x4 - 4x3 - 3x - 1 by x - 1.
Solution not provided.
Ans. Quotient = 3x3 - x2 - x - 4
Remainder = - 5
Using long division method, find the remainder obtained on dividing p(x) = x2 + 1 by x + 1.
Solution not provided.
Ans. Quotient = x2 - x + 1
Remainder = 0
Find the remainder obtained when x4 + 3x3 - 2x2 + x + 1 is divided by x - 1.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 2
Check whether the polynomial q(t) = 4t3 + 4t2 - t -1 is a multiple of 2t + 1.
Solution not provided.
Ans. Yes
If the polynomial p(x) = x4 - 2x3 + 3x2 - ax + 8 is divided by (x - 2), it leaves a remainder 10. Find the value of a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 10
The polynomials kx3 + 3x2 - 8 and 3x3 - 5x + 8 are divided by x + 2. If the remainder in each case in the same, find the value of k.
Solution not provided.
Ans. ![]()
If f(x) = x4- 2x3 + 3x2 - ax + b is divided by (x - 1) and (x + 1), it leaves the remainder 5 and 19 respectively. Find ‘a’ and ‘b’.
Solution not provided.
Ans. a = 5, b = 8
Find the remainders when 3x3- 4x2 + 7x - 5 is divided by (x - 3) and (x + 3).
Solution not provided.
Ans. 61, - 143
If p(x) =x3 - ax2 + bx + 3 leaves a rer.idinder -19 when divided by (x + 2) and a remainder 17 when divided by (x - 2), prove that a + b = 6.
Solution not provided.
Ans. a = 1, b = 5
If remainder is same when polynomial p(x) = x3 + 8x2 + 17x + ax is divided by (x + 2) and (x + 1), find the value of a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 0
The polynomials ax3 + 3x2 - 13 and 2x3 - 5x + a are divided by x - 2. The remainder in each case is the same. Find the value of a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. ![]()
If the polynomial p(x) = x4 - 2x3 + 3x2 - ax + 8 is divided by (x - 2), it leaves a remainder 10. Find the value of a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 5
The polynomials ax3+ 3x2 - 3 and 2x3 - 5x + a when divided by x - 4 leave the same remainder in each case. Find the value of a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 1
Determine which of the following polynomials has (x + 1) a factor:
x3 + x2 + x + 1
x3 + x2 + x + 1
The zero of x + 1 is - 1.
p(-1) = ( - 1)3 + ( - 1)2 + (- 1) + 1
= - 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 0
∴ By factor theorem, x + 1 is a factor of x3 + x2 + x + 1.
Determine which of the following polynomials has (x + 1) a factor:
x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
Let p(x) = x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
The zero of x + 1 is - 1.
p(- 1) = (- 1)4 + (- 1)3 + (- 1)2 + (- 1) + 1
= 1 - 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 1 ≠ 0
∴ By factor theorem, x + 1 is not a factor of x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1.
Determine which of the following polynomials has (x + 1) a factor:
x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
Let p(x) = x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
The zero of x + 1 is - 1.
P(- 1) = (- 1)4 + 3(- 1)3 + 3(- 1)2 + (- 1) + 1
= 1 - 3 + 3 - 1 + 1 = 1 ≠ 0
∴ By factor theorem, x + 1 is not a factor of x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1.
Determine which of the following polynomials has (x + 1) a factor:
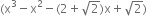
∴ By factor theorem, x + 1 is not a factor of
Use the factor theorem to determine whether g(x) is a factor ofp(x) in each of the following cases:
p(x) = 2x3 + x2 - 2x - 1, g(x) = x + 1
p(x) = 2x3 + x2 - 2x - 1, g(x) = x + 1
g(x) = 0
⇒ x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = - 1
∴ Zero of g(x) is - 1.
Now, p(- 1)
= 2(- 1)3 + (- 1)2 - 2(- 1) - 1
= - 2 + 1 + 2 - 1 = 0
∴ By factor theorem, g(x) is a factor of p(x).
Use the factor theorem to determine whether g(x) is a factor ofp(x) in each of the following cases:
p(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1,g(x) = x + 2
p(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1,g(x) = x + 2
g(x) = 0
⇒ x + 2 = 0 ⇒ x = -2
∴ Zero of g(x) is - 2.
Now, p(- 2)
= (- 2)3 + 3(- 2)2 + 3(- 2) + 1
= - 8 + 12 - 6 + 1 = - 1 ≠ 0
∴ By factor theorem, g(x) is not a factor of p(x).
Use the factor theorem to determine whether g(x) is a factor ofp(x) in each of the following cases:
p(x) = x3 - 4x2 + x + 6, g(x) = x - 3
p(x) = x3 - 4x2 + x + 6, g(x) = x - 3
g(x) = 0
⇒ x - 3 = 0 ⇒ x = 3
∴ Zero of g(x) is 3.
Now, p( 3)
= (3)3 - 4(3)2 + 3 + 6
= 27 - 36 + 3 + 6 = 0
∴ By factor theorem, g(x) is a factor of p{x).
Find the value of k, if x - 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
p(x) = x2 + x + k
p(x) = x2 + x + k
If x - 1 is a factor of p(x), then p(1) = 0
| By Factor Theorem![]() (1)2 + (1) + k = 0
(1)2 + (1) + k = 0![]() 1 + 1 + k = 0
1 + 1 + k = 0![]() 2 + k = 0
2 + k = 0![]() k = - 2.
k = - 2.
Find the value of k, if x - 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
p(x) = 2x2 + kx + 
p(x) = 2x2 + kx + ![]()
If x - 1 is a factor of p(x), then p(1) = 0
| By Factor Theorem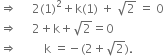
Find the value of k, if x - 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
p(x) = kx2 - 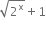
p(x) = kx2 - ![]()
If x - 1 is a factor of p(x), then p(1) = 0
| By Factor Theorem
![]() k(1)2 -
k(1)2 -  + 1 = 0
+ 1 = 0
![]()
Find the value of k, if x - 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
p(x)=kx2 - 3x + k
p(x)=kx2 - 3x + k
If x - 1 is a factor of p(x) then p(1) = 0
| By Factor Theorem![]() k(1)2 - 3(1) + k = 0
k(1)2 - 3(1) + k = 0![]() k - 3 + k = 0
k - 3 + k = 0![]() 2k = 3
2k = 3![]() k =
k = ![]()
Factorise
12x2 - 7x + 1
12x2 - 7x+ 1
12x2 - 7x + 1 = 12x2 - 4x - 3x + 1
= 4x(3x - 1) - 1(3x - 1)
= (3x - 1) (4x - 1)
Factorise
2x2 + 7x + 3
2x2 + 7x + 3
2a2 + 7x + 3 = 2x2 + 6x + x + 3
= 2x(x + 3) + 1(x + 3)
= (x + 3) (2x + 1)
Factorise
6x2 + 5x - 6
6x2 + 5x - 6
6x2 + 5x - 6 = 6x2 + 9x - 4x - 6
= 3x(2x + 3) - 2(2x + 3)
= (2x + 3) (3x-2)
Factorise
3x2 - x - 4
3x2 - x - 4
3x2 - x - 4 = 3x2 - 4x + 3x - 4
= x(3x - 4) + 1(3x - 4)
= (3x - 4)(x + 1)
Factorise
x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
Let p(x) = x3 - x2 - x + 2
By trial, we find that
p(1) = (1)3 - 2(1)2 - (1) + 2
= 1 - 2 - 1 + 2 = 0
∴ By Factor Theorem, (x - 1) is a factor of p(x).
Now,
x3 - 2x2 - x + 2 = x2(x - 1) - x(x - 1) - 2(x - 1)
= (x - 1)(x2 - x - 2)
= (x - 1)(x2 - 2x + x - 2)
= (x - 1){x(x - 2) + 1(x - 2)}
= (x - 1)(x - 2)(x + 1).
Factorise
x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
Let p(x) = x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
By trial, we find that
p(- 1) = (- 1)3 - 3(- 1)2- 9(- 1) -5
= - 1 - 3 + 9 - 5 = 0
∴ By Factor Theorem, x - (- 1), i.e., (x + 1) is a factor of p(x).
Now,
x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
= x2(x + 1) - 4x(x + 1) - 5(x + 1)
= (x + 1)(x2- 4x - 5)
= (x + 1)(x2 - 5x + x - 5)
= (x+ 1){x(x - 5) + 1 (x - 5)}
= (x + 1)(x - 5)(x + 1).
Sponsor Area
Factorise
x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
Let p(x) = x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
By trial, we find that
p(- 1) = (- 1)3 + 13(- 1)2 + 32(- 1) + 20
= - 1 + 13 - 32 + 20 = 0
∴ By Factor Theorem, x - (- 1), i.e., (x + 1) is a factor of p(x).
Now,
x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
= x2(x + 1) + 12x(x + 1) + 20(x + 1)
= (x + 1)(x2+ 12x + 20)
= (x + 1)(x2 + 2x + 10x + 20)
= (x + 1) {x(x + 2) + 10(x + 2)}
= (x + 1)(x + 2)(x + 10).
Factorise
2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
Let p(y) = 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
By trial, we find that
p(1) = 2(1)3 + (1)2 - 2(1) - 1
= 2 + 1 - 2 - 1 = 0
∴ By Factor Theorem, (y - 1) is a factor of p(y).
Now,
2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
= 2y2(y - 1) + 3y(y - 1) + 1(y - 1)
= (y - 1)(2y2 + 3y + 1)
= (y - 1)(2y2 + 2y + y+ 1)
= (y - 1){2y(y + 1) + 1(y + 1)}
= (y - 1)(y + 1) (2y + 1).
Use Factor Theorem to verify that x + a is a factor of xn + an for any odd positive integer n.
Let p(x) = xn + an
The zero of x + a is - a. | x + a = 0 ⇒ x = - a
Now,
p(- a) = (- a)n + an = (- 1)nan + an
= (- 1)an + an
![]() n is an odd positive interger
n is an odd positive interger![]() (-1)n = - 1
(-1)n = - 1
= - an + an = 0
∴ By Factor Theorem, x + a is a factor of xn + an for any odd positive integer n.
Determine the value of ‘b’ for which the polynomial 5x3 - x2 + 4x + b is divisible by 1 - 5x.
Let p(x) = 5x3 - x2 + 4x + b
1 - 5x = 0![]()
![]() The zero of 1 - 5x is
The zero of 1 - 5x is ![]()
If p(x) is divisivle by 1 - 5x, then ![]()
| By Factor Theorem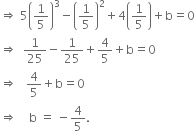
Find the values of a and b so that (x + 1) and (x - 1) are factors of x4 + ax3 - 3x2 + 2x + b.
Let p (x) = x4 + ax3 - 3x2 + 2x + b
If (x + 1) and (x - 1) are factors of p(x), then by factor theorem,
p(-1) = 0 ...(1) | x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1
and p(1) = 0 ...(2) | x - 1 = 0 ⇒ x = 1
Now,
P(-1) = 0
⇒ (-1)4 + a(-1)3 - 3(-1)2 + 2 (-1) + b = 0
⇒ 1 - a - 3 - 2 + b = 0
⇒ -a + b = 4 ...(3)
and p(1) = 0
⇒ (1)4 + a(1)3 - 3(1)2 + 2 (1) + b = 0
⇒ 1 + a - 3 + 2 + b = 0
⇒ a + b = 0 ...(4)
Solving (3) and (4), we get
a = -2,b = 2
For what value of a the polynomial 2x3 + ax2 + 11x + a + 3 is exactly divisible by 2x - 1?
Let p(x) = 2x3 + ax2 + 11x + a + 3
If p(x) is exactly divisible by 2x - 1, then by factor theorem,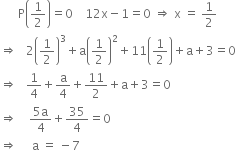
Hence, the required polynomial is
2x3 - 7x2 + 11x - 7 + 3
or 2x3 - 7x2 + 11x - 4
Without actual division prove that x4 + 2x3 - 2x2 + 2x - 3 is exactly divisible by x2 + 2x - 3.
x2 + 2x - 3
= x2 + 3x - x - 3
= x(x + 3) - 1 (x + 3)
= (x + 3) (x - 1)
Let p(x) = x4 + 2x3 - 2x2 + 2x - 3
We see that
p(-3) = (-3)4 + 2(-3)3 - 2(-3)2 + 2(-3) - 3
= 81 - 54 - 18 - 6 - 3
= 0
Hence by converse of factor theorem, (x + 3) is a factor of p(x).
Also, we see that
p(1) = (1)4 + 2(1)3 - 2(1)2 + 2(1) - 3
= 0
Hence by converse of factor theorem, (x - 1) is a factor of p(x).
From above, we see that
(x + 3) (x - 1), i.e., x2 + 2x - 3 is a factor of p(x)
⇒ p(x) is exactly divisible by (x2 + 2x - 3).
Determine whether (3x — 2) is a factor of 3x3 + x2 - 20x + 12?
Let p(x) = 3x3 + x2 - 20x + 12
We see that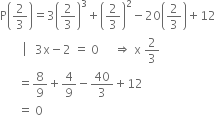
Hence by converse of factor theorem, (3x - 2) is a factor of p(x).
Factorise: x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6.
Let p(x) = x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6
By trial, we find that
p(1) = (1)3 - 6(1)2 + 11(1) - 6 = 0
∴ By converse of factor theorem, (x - 1) is a factor of p(x).
Now, x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6
= x2 (x - 1)- 5x (x - 1) + 6 (x - 1)
= (x - 1) (x2 - 5x + 6)
= (x - 1) {x2 - 2x - 3x + 6}
= (x - 1) {x(x - 2)-3 (x - 2)}
= (x - 1)(x - 2)(x - 3)
If both (x - 2) and  are factors of px2 + 5x + r, show that p = r.
are factors of px2 + 5x + r, show that p = r.
Let f(x) = px2 + 5 x + r
If (x - 2) is a factor of f (x), then by factor theorem
f(2) = 0 | x - 2 = 0 ⇒ x = 2
⇒ p(2)2 + 5(2) + r = 0
⇒ 4p + r + 10 = 0 ...(1)
If ![]() is a factor of f (x), then by factor theorem,
is a factor of f (x), then by factor theorem,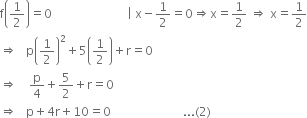
Subtracting (2) from (1), we get
3p - 3r = 0
⇒ p = r
Using factor theorem, factorise the polynomial x4 + x3 - 7x2 - x + 6.
Let f(x) = x4 + x3 - 7x2 - x + 6
By trial, f(1) = 0 and f(2) = 0
So by factor theorem, (x - 1) and (x - 2) are factors of f(x).
(x - 1) (x - 2) = x2 - 3x + 2
Now, f(x) = x2 (x2 - 3x + 2)+ 4x (x2 - 3x + 2) + 3 (x2 - 3x + 2)
= (x2 - 3x + 2) (x2 + 4x + 3)
= (x - 1) (x - 2) (x + 1) (x + 3)
Examine whether x + 2 is a factor of x3 + 3x2 + 5x + 6 and 2x + 4.
Solution not provided.
Ans. Yes
Find the value of k if x - 1 is a factor of 4x3 + 3x2 - 4x + k.
Solution not provided.
Ans. - 3
Factorise 6x2 + 17x + 5 by splitting the middle term.
Solution not provided.
Ans. (3x + 1) (2x + 5)
Factorise y2 - 5y + 6 by using the Factor Theorem.
Solution not provided.
Ans. (y - 2) (y - 3)
Find the value of a if (a: + a) is a factor of x4 - a2 x2 + 3x - a.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 0
Show that (x - 2) is a factor of the polynomial f(x) = 2x3 - 3x3 - 17x + 30 and hence factorize f(x).
Solution not provided.
Ans. (x - 2) (x + 3) (2x - 5)
Check whether polynomial p(s) = 3s3 + s2 - 20s + 12 is a multiple of 3s - 2.
Solution not provided.
Ans. Yes
Check whether (p + 1) is a factor of (p100 - 1) and (p100 - 1).
Solution not provided.
Ans. Yes, No
Find if remainder obtained on dividing polynomial p(y) = y3 + ay2 + 5y - 25 by (y + a) is a factor of polynomial f(a) = a2 -5a + 25.
Solution not provided.
Ans. No
If (2x - 3) is a factor of 2x4 - 3x2 + 15x - 15k, find the value of 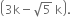
Solution not provided.
Ans. ![]()
Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(i) (x + 4)(x + 10)
x + 4)(x + 10)
(x + 4)(x + 10) = x2 + (4 + 10)x + (4)(10)
| Using Identity IV
= x2 + 14x + 40.
Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(x + 8)(x - 10)
x + 8)(x - 10)
(x + 8)(x - 10) = (x + 8){x + (- 10)}
= x2 + {8 + (- 10)}x + (8)(- 10)
| Using Identity IV
= x2 - 2x - 80.
Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(3x + 4)(3x - 5)
(3x + 4)(3x - 5)
(3x + 4)(3x - 5) = (3x + 4) {3x + (- 5)}
= (3x)2 + (4 + (- 5)} (3x) + (4)(- 5)
| Using Identity IV
= 9x2 - 3x - 20.
Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(3 - 2x)(3 + 2x)
3 - 2x)(3 + 2x)
(3x - 2x)(3 + 2x) = (3)2 - (2x)2
| Using Identity III
= 9 - 4x2.
Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
103 × 107
103 × 107
103 × 107 = (100 + 3) × (100 + 7)
= (100)2 + (3 + 7) (100 + (3)(7))
| Using Identity IV
= 10000 + 1000 + 21 = 11021.
Aliter
103 × 107 = (105 - 2) × (105 + 2)
= (105)2 - (2)2
| Using Identity III
= (100 + 5)2 - 4
= (100)2 + 2(100)(5) + (5)2 - 4
| Using Identity I
= 10000 + 1000 + 25 - 4 = 11021.
Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
95 × 96
95 × 96
95 × 94 = (90 + 5) × (90 + 6)
= (90)2 + (5 + 6)(90) + (5)(6)
| Using Identity IV
= 8100 + 990 + 30 = 9120.
Aliter
95 × 96 = (100 - 5) × (100 - 4)
= {100 + (- 5)} (100 + (- 4)}
= (100)2 + {(- 5) + (- 4)}(100)
+ (- 5)(- 4) | Using Identity IV
= 10000 - 900 + 20
= 9120.
Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
104 × 96.
104 × 96
104 × 96 = (100 + 4) × (100 - 4)
= (100)2 - (4)2 | Using Identity III
= 10000 - 16 = 9984.
Evaluate using suitable identify: (999)3.
(999)3
= (1000 - 1)3
= (1000)3 - (1)3 - 3(1000)(1) (1000 - 1)
= 1000 000 000 - 1 - 3000 × 999
= 1000 000 000 - 1 - 2997000
= 997002999
Multiply 9x2 + 25y2 + 15xy + 12x -20y + 16 by 3x - 5y - 4 using suitable identity.
(3x - 5y - 4) (9x2 + 25y2 + 15xy + 12x - 20y + 16)
= {(3x) + (-5y) + (-4)} {(3x)2 + (-5y)2 + (-4)2 - (3x) (-5y) - (-5y) (-4) - (-4) (3x)}
= (3x)3 + (-5y)3 + (-4)3 - 3 (3x) (-5y) (-4)
= 27x3 - 125y3 - 64 - 180cy.
15. Factorise:
a2 + b2 - 2 (ab - ac + bc)
a2 + b2 - 2(ab - ac + bc)
= a2 + b2 - 2ab + 2ac - 2bc
= (a - b)2 + 2c(a - b)
= (a - b) (a - b + 2c).
Factorise: (ax + by)2 + (ay - bx)2
(ax + by)2 + (ay - bx)2
= a2x2 + b2y2 + 2abxy + a2y2 + b2x2 - 2abxy
= a2 (x2 + y2) + b2 (x2 + y2)
= (x2 + y2) (a2 + b2).
Find the value of x3 - 8y3 - 36xy - 216 when x = 2y + 6.
We have x = 2y + 6
⇒ x + (-2y) + (-6) = 0
∴ x3 + (-2y)3 + (-6)3 = 3x (-2y) (-6)
⇒ x3 - 8y3 - 216 = 36xy
∴ x3 - 8y3 - 36xy - 216 = 0
Factorise:
(x - 3y)3 + (3y - 7z + (7z - x)3
We have
(x - 3y) + (3y - 7z) + (7z - x) = 0
∴ (x - 3y)3 + (3y - 7z)3 + (7z - x)3
= 3(x - 3y) (3y - 7z) (7z - x)
If a + b + c = 7 and ab + be + ca = 20, find the value of a2 + b2 + c2.
We know that
(a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2 (ab +bc + ca)
⇒ (7)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(20)
⇒ a2 + b2 + c2 = 9
If p = 2 - a, then prove that a3 + 6ap + p3 - 8 = 0.
p = 2 - a
⇒ p + a - 2 = 0
∴ p3 + a3 + (- 2)3 = 3 (p) (a) (- 2)
| Using Identity VI
⇒ p3 + a3 - 8 = - 6ap
⇒ a3 + 6ap +p3 - 8 = 0
Simplify: (x + y)3 - (x - y)3 - 6y(x2 - y2)
Let x + y = a, x - y = b
Then, ab = (x + y) (x - y) = x2 - y2
and a - b = (x + y) - (x - y) = 2y
Now, (x + y)3 - (x - y)3 - 6y (x2 - y2)
= (x + y)3 - (x - y)3 - 3(2y) (x2 - y2)
= a3 - b3 - 3(a - b) ab
= (a - b)3 | Using Identity VII
= {(x + y) - (x - y)}3
= (2y)3 = 8y3
If x2 + px + q = (x + a)(x + b), then factorise x2 + pxy + qy2.
x2 + px + q = (x + a)(x + b)
⇒ x2+ px + q = x2 + ax + bx + ab
⇒ x2+ px + q = x2 + (a + b)x + ab
Comparing the coefficients, we get
a + b = p ...(1)
ab = q ...(2)
∴ x2 + pxy + qy2 = x2 + (a + b)xy + aby2
| Using (1) and (2)
= x2 + axy + bxy + aby2
= x(x + ay) + by(x + ay)
= (x + ay)(x + by).
Prove that: (a + b)3 + (b + c)3 + (c + a)3 - 3(a + b)(b + c)(c + a) = 2(a3 + b3+ c3 - 3abc).
L.H.S. = (a + b)3 + (b + c)3 + (c + a)3 - 3(a + b)(b + c)(c + a)
= {(a + b) + (b + c) + (c + a)} [(a + b)2 + (b + c)2 + (c + a)2 - (a + b)(b + c) - (b + c)(c + a) - (c + a)(a + b)]
| Using Identity VIII
= 2(a + b + c) [a2 + 2ab + b2 + b2 + 2bc + c2 + c2 + 2ca + c2 - ab - ac - b2 - bc - bc - ba - c2 - ca - ca - cb - a2 - ab]
| Using Identity I
= 2(a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 - ab - be - ca)
= 2(a3 + b3 + c3 - 3abc).
| Using Identity VIII
Evaluate using suitable identify: (999)3.
(999)3
= (1000 - 1)3
= (1000)3 - (1)3 - 3(1000)(1) (1000 - 1)
= 1000 000 000 - 1 - 3000 × 999
= 1000 000 000 - 1 - 2997000
= 997002999
Multiply 9x2 + 25y2 + 15xy + 12x -20y + 16 by 3x - 5y - 4 using suitable identity.
(3x - 5y - 4) (9x2 + 25y2 + 15xy + 12x - 20y + 16)
= {(3x) + (-5y) + (-4)} {(3x)2 + (-5y)2 + (-4)2 - (3x) (-5y) - (-5y) (-4) - (-4) (3x)}
= (3x)3 + (-5y)3 + (-4)3 - 3 (3x) (-5y) (-4)
= 27x3 - 125y3 - 64 - 180cy.
Show that if a + b is not zero, then the equation a(x - a) = 2ab - b(x - b) has a solution x = a + b.
a(x - a) = 2ab - b(x - b)
⇒ ax - a2 = 2ab - bx + b2
⇒ ax + bx = a2 + 2ab + b2
∴ x(a + b) = (a + b)2 | Using Identity I
∴ x = a + b
| Cancelling (a + b) from both sides as (a + b) ≠ 0
Hence the given equation has a solution x = a + b.
Show that if 2(a2 + b2) = (a + b)2, then a = b.
2(a2 + b2) = (a + b)2
⇒ 2a2 + 2b2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
⇒ a2 + b2 - 2ab = 0
⇒ (a - b)2 = 0
⇒ a - b = 0
⇒ a = b.
Factorise each of the following:
a4 - b4 (b)a4 - 16b4
a4 - b4
a4 - b4 = (a2)2 - (b2)2 = (a2 + b2) (a2 - b2)
| Using Identity III
= (a2 + b2)(a + b)(a - b)
| Using Identity III
Factorise each of the following:
a4 - 16b4
a4 - 16b4
a4 - 16b4 = (a2)2 - (4b2)2 = (a2 - 4b2)(a2 + 4b2)
| Using Identity III
= {(a)2 - (2b)2}(a2 + 4b2)
= (a + 2b)(a - 2b)(a2 + 4b2)
| Using Identity III
Factorise each of the following:
a2 - (b - c)2
a2 - (b - c)2
a2 - (b - c)2 = {a + (b - c)}{a - (b - c)}
| Using Identity III
= (a + b - c)(a - b + c)
x2 + 7xy + 12y2
x2 + 7xy + 12y2 = x2 + 3xy + 4xy + 12y2
= x(x + 3y) + 4y(x + 3y)
= (x + 3y)(x + 4y)
Factorise each of the following:
x2 + 2ax - b2 - 2ab
x2 + 2ax - b2 - 2ab
x2 + 2ax - b2 - 2ab = (x2 - b2) + (2ax - 2ab)
= (x- b)(x + b) + 2a(x - b)
| Using Identity III
= (x - b)(x + b + 2a)
Factorise each of the following:
(x2 + x)2 + 4(x2 + x) - 12
(x2 + x)2 + 4(x2 + x) - 12
(x2 + x)2 + 4(x2 + x) - 12 = y2 + 4y - 12
| where y = x2 + x
= y2 + 6y - 2y - 12
= y(y + 6) - 2(y + 6)
= (y + 6)(y - 2)
= (x2 + x + 6)(x2 + x - 2)
| ∵ = x2 + x
= (x2 + x + 6)(x2 + 2x - x - 2)
= (x2 + x + 6)[x(x + 2) - 1(x + 2)]
= (x2 + x + 6)(x + 2)(x - 1).
Expand the following:
(i) (x - 2y - 3z)2 (ii) 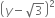
(i) (x - 2y - 3z)2
= (x)2 + (- 2y)2 + (- 3z)2 +2(x) (- 2y) +2(-2y)(-3z)+2(-3z)(x)
= x2 + 4y2 + 9z2 - 4xy + 12yz - 6zx
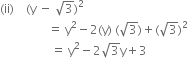
Factorise the following using appropriate identities:
9x2 + 6xy + y2
9x2 + 6xy + y2
9x2 + 6xy + y2 = (3x)2 + 2(3x)(y) + (y)2
= (3x + y)2 = (3x + y) (3x + y)
| Using Identity 1
Factorise the following using appropriate identities:
4y2 - 4y + 1
4y2 - 4y + 1
4y2 - 4y + 1 = (2y)2 - 2(2y)(1)+(1)2
= (2y - 1)2 = (2y - 1) (2y - 1)
| Using Identity II
Expand each of the following using suitable identities:
(x + 2y + 4z)2
(x + 2y + 4z)2
(x + 2y + 4z)2 = (x)2 + (2y)2 + (4z)2 + 2(x)(2y) + 2(2y)(4z) + 2(4z)(x)
| Using Identity V
= x2 + 4y2 + 16z2 + 4xy + 16yz + 8 zx
Expand each of the following using suitable identities:
(- 2x + 3y + 2z)2
(2x - y + z)2
(2x - y + z)2 = {2x + (- y) + z}2
= (2x)2 + (- y)2 + (z)2 + 2(2x)(- y) + 2(- y)(z) + 2(z)(2x)
| Using Identity V
= 4x2 + y2 + z2- 4xy -2yz + 4 zx
Expand each of the following using suitable identities:
(- 2x + 3y + 2z)2
(- 2x + 3y + 2z)2
(- 2x + 3y + 2 z)2 = {(- 2x) + 3y + 2z)}2
= (- 2x)2 + (3y)2 + (2z)2 + 2(- 2x)(3y) + 2(3y)(2z) + 2(2z)(-2x)
| Using Identity V
= 4x2 + 9y2 + 4z2 - 12xy + 12yz - 8zx
Expand each of the following using suitable identities:
(3a -7b - c)2
(3a -7b - c)1
(3a - 7b - c)2 = {3a + (- 7b) + (- c)}2
= (3a)2 + (- 7b)2 + (- c)2 + 2(3a)(- 7b) + 2(- 7b)(- c) + 2(- c)(3a)
= 9a2 + 49b2 + c2 - 42ab + 14bc - 6ca
Expand each of the following using suitable identities:
(- 2x + 5y - 3z)2
(- 2x + 5y - 3z)2 (-2x + 5y - 3z)2
={(-2x) + 5y + (- 3z)}2
= (- 2x)2 + (5y)2 + (- 3z)2 + 2(- 2x)(5y) + 2(5y)(- 3z) + 2(- 3z)(- 2x)
= 4x2 + 25y2 + 9z2 - 20xy - 30yz + 12zx
Factorise
4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy - 24yz - 16xz
4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy - 24yz - 16xz
4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy - 24yz - 16xz
= (2x)2 + (3y)2 + (- 4z)2 + 2(2x) (3y) + (3y) (- 4z) + (- 4z) (- 2x)
= {2x + 3y) + (- 4z)}2 = (2x + 3y - 4z)2
= (2x + 3y - 4z) (2x + 3y - 4z)
Write the following cubes in expanded form:
(2x + 1)3
(2x + 1)3
(2x + 1)3 = (2x)3 + (1)3 + 3(2x)(1)(2x + 1)
| Using Identity VI
= 8x3 + 1 + 6x(2x + 1)
= 8x3 + 1 + 12x2 + 6x
= 8x3+ 12x2 + 6x + 1
Write the following cubes in expanded form:
(2a - 3b)3
(2a - 3b)3
(2a - 3b)3 = (2a)3 - (3b)3 - 3(2a)(3b)(2a - 3b)
| Using Identity VII = 8a3 - 27b3 - 18ab(2a - 3b)
= 8a3 - 27b3 - 36a2b + 54ab2
Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(99)3
(99)3
(99)3 = (100 - 1)3
= (100)3 - (1)3 - 3(100)(1)(100 - 1)
| Using Identity VII
= 1000000 - 1 - 300(100 - 1)
= 1000000 - 1 - 30000 + 300
= 970299
Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(102)3
(102)3
(102)3 = (100 + 2)3
= (100)3 + (2)3 + 3(100)(2)(100 + 2)
| Using Identity VI
= 1000000 + 8 + 600(100 + 2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 60000 + 1200
=1061208
Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(998)3
(998)3
(998)3 = (1000 - 2)3
= (1000)3 - (2)2 - 3( 1000)(2)( 1000 - 2)
| Using Identity VII
= 1000000000 - 8 - 6000(1000 - 2)
= 1000000000 - 8 - 6000000 + 12000
= 994011992.
Factorise each of the following:
8a3 + b3 + 12a2b + 6ab2
8a3 + b3+ 12a2b + 6ab2
8a3 + b3+ 12a2b + 6ab2
= (2a)3 + (b)3 + 3(2a)(b) (2a + b)
= (2a + b)3 | Using Identity VI
= (2a + b)(2a + b)(2a + b)
Factorise each of the following:
8a3 - b3 - 12a2b + 6ab2
8a3 - b3 - 12a2b + 6ab2
8a3 - b3 - 12a2b + 6ab2
= (2a)3 - (b)3 - 3(2a)(b) (2a - b)
= (2a - b)3 | Using Identity VII
= (2a - b)(2a - b)(2a - b)
Factorise each of the following:
27 - 125a3 - 135a + 225a2
27 - 125a3 - 135a + 225a2
27 - 125a3 - 135a + 225a2
= (3)3 - (5a)3 - 3(3)(5a)(3 - 5a)
= (3 - 5a)3 | Using Identity VII
= (3 - 5a)(3 - 5a)(3 - 5a)
Factorise each of the following:
64a3 - 27b3 - 144a2* + 108ab2
64a3 - 27b3 - 144a2* + 108ab2
64a3 - 27b3 - 144a2b + 108ab2
= (4a)3 - (3b)3 - 3(4a)(3b) (4a - 3b)
= (4a - 3b)3 | Using Identity VII
= (4a - 3b)(4a - 3b)(4a - 3b)
Verify: x3 + y3 = (x + y)(x2 - xy + y2)
We know that
(x + y)3 = x3 + y3 + 3xy(x + y)
| Using Identity VI
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)3 - 3xy(x + y)
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y){(x + y)2 - 3xy)
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)(x2 + 2xy + y2 - 3xy)
| Using Identity I
⇒ x3 + y3 = (x + y)(x2 - xy + y2)
Verify: x3 - y3 = (x - y)(x2 + xy + y2).
We know that
(x - y)3 = x3 - y3 - 3xy(x - y)
| Using Identity VII
⇒ x3 - y3 = (x - y)3 + 3xy(x - y)
x3 - y3 = (x - y){(x - y)2 + 3xy}
⇒ x3 - y3 = (x - y)(x2 - 2xy + y2 + 3ry)
| Using Identity IV
⇒ x3 - y3 = (x - y)(x2 + xy + y2).
Factorise each of the following: 27y3 + 125z3
27y3 + 125z3
27y3 + 125z3 = (3y)3 + (5z)3
= (3y + 5z){(3y)2 - (3y)(5z) + (5z)2}
= (3y + 5z)(9y2 - 15yz + 25z2)
Factorise each of the following: 64m3 - 343n3.
64m3 - 343n3
64m3 - 343n3 = (4m)3 - (7n)3
= (4m - 7n){(4m)2 + (4m)(7n) + (7n)2}
= (4m - 7n)(16m2 + 28mn + 49n2).
Factorise: 27x3 + y3 + z3 - 9xyz.
27x3 + y3 + z3 - 9xyz
= (3x)3 + (y)3 + (z)3 - 3(3x)(y)(z)
= (3x + y + z){(3x)2 + (y)2 + (z)2 - (3x)(y) - (y)(z) - (z)(3x)}
| Using Identity VIII
= (3x + y + z)(9x2 + y2 + z2 - 3xy - yz - 3zx).
Verify that x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz = 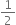 (x + y + z)[(x - y)2 + (y - z)2 + (z - x)2].
(x + y + z)[(x - y)2 + (y - z)2 + (z - x)2].
L.H.S. = x3 + y3 + z3 -3xyz
= (x + y + x) (x2 + y2 + z2 -xy - yz -zx)
| Using Identity VIII![]() (x+y+z){2x2 + 2y2 + z2 -xy -yz -zx)
(x+y+z){2x2 + 2y2 + z2 -xy -yz -zx)![]() (x+y+z){2x2 + 2y2 + 2z2 -2xy -2yz -2zx)
(x+y+z){2x2 + 2y2 + 2z2 -2xy -2yz -2zx)![]() (x + y + z) {x2 - 2xy + y2 ) (y2 -2yz + z2) + (z2 - 2zx + x2 )}
(x + y + z) {x2 - 2xy + y2 ) (y2 -2yz + z2) + (z2 - 2zx + x2 )}![]()
| Using Identity II
If x + y + z = 0, show that x3 + y3 + Z3 = 3xyz.
We know that
x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz
= (x + y + z)(x2 + y2 + z2 - xy - yz - zx)
| Using Identity VIII
= (0)(x2 + y2 + z2 - xy - yz - zx)
| ∵ x + y + z = 0
= 0
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 = 3xyz.
Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following:
(- 12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3
(28)3 + (- 15)3 + (- 13)3.
(- 12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3
(- 12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3 = 3(- 12)(7)(5)
| ∵ (- 12) + (7) + (5) = 0
= - 1260
Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following:
(28)3 + (- 15)3 + (- 13)3
(28)3 + (- 15)3 + (- 13)3
(28)3 + (- 15)3 + (- 13)3
= 3(28)(- 15)(- 13)
| ∵ (28) + (- 15) + (- 13) = 0
= 16380.
Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given:
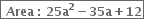
25a2 - 35a + 12
= 25a2 - 20a - 15a + 12
= 5a(5a - 4) - 3(5a - 4)
= (5a - 4)(5a - 3)
∴ The possible expressions for the length and breadth of the rectangle are 5a - 3 and 5a - 4.
Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given:
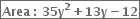
35y2 + 13y - 12
= 35y2 + 28y - 15y - 12
= 7y (5y + 4) - 3(5y + 4)
= (5y + 4)(7y - 3)
∴ The possible expressions for the length and breadth of the rectangle are 7y - 3 and 5y + 4.
What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below?![]()
3x3 - 12x
= 3x(x - 4)
∴ The possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboid are 3, x and x - 4.
What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below?![]()
12ky2 + 8ky - 20k
= 4k(3y2 + 2y - 5)
= 4k(3y2 + 5y - 3y - 5)
= 4k{y(3y + 5) - 1(3y +5)}
= 4k(3y + 5)(y - 1)
∴ The possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboid are 4k, 3y + 5 and y - 1.
Write (3a + 4b + 5c)2 in expanded form.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 9a2 + 16b2 + 25c2 + 24ab + 40bc + 30ac
Write the following cubes in the expanded form:
(3a + 4b)3
Solution not provided.
Ans. 27a3 + 64b3 + 108a2b + 144ab2
Write the following cubes in the expanded form:
(5p - 3q)3
Solution not provided.
Ans. 125p3 - 27q3 - 225p2q + 135pq2
Write the following cubes in the expanded form:
(i) (104)3 (ii) (999)3.
Solution not provided.
Ans. (i) 1124864 (ii) 997002999
Factorise: 8x3 + y3 + 27z3 - 18xyz.
Solution not provided.
Ans. (2x + y + 3z) (4x2 + y2 + 9z2 - 2xy - 3yz - 6xz)
Factorise: x6 - y6
Solution not provided.
Ans. (x - y) (x2 + xy + y2) (x + y) (x2 - xy + y2)
If x + y + z = 1, xy + yz + zx = -1 and xyz = -1, find the value of x3 + y3 + z3.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 1
Factorise: ax2 + y2 + z2 - 6xy + 2yz - 6zx. Hence find its value if x = 1, y = 2 and z = -1.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 4
The number 0 is called a
-
zero polynomial
-
binomial
-
trinomial
-
linear polynomial.
A.
zero polynomial
A polynomial having one term is called
-
monomial
-
binomial
-
trinomial
-
zero polynomial.
A.
monomial
A linear polynomial
-
has one and only one zero
-
may have no zero
-
may have one zero
-
may have more than one zero.
A.
has one and only one zero
The integral zero of the polynomial 3y3 + 8y2 -1 is
-
1
-
-1
-
0
-
does not exist
1
-1
0
does not exist
D.
does not exist
The value of (a - b)3 + (b - c)3 + (c - a)3 is
-
0
-
abc
-
3abc
-
3 (a - b) (b - c) (c - a)
0
abc
3abc
D.
3 (a - b) (b - c) (c - a)
a3 + b3 + c3 - 3abc =
-
(a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 - ab - be - ca)
-
(a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 - ab - be + ca)
-
(a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 - ab + be - ca)
-
(a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 + ab - be - ca)
A.
(a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 - ab - be - ca)
The algebraic expansion of (x + y - z)2 is
-
x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy + 2 yz + 2 zx
-
x2 + y1 + z2 + 2xy + 2yz - 2zx
-
x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy - 2yz - 2zx
-
x2 + y2 + z2 - 2xy - 2yz - 2zx
C.
x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy - 2yz - 2zx
The factors of x3 + 9x2 + 23x + 15 are
-
(x + 1)(x + 3)(x + 5)
-
(x + 1)(x + 3)(x - 5)
-
(x + 1) (x - 3) (x - 5)
-
(x - 1) (x - 3) (x - 5)
(x + 1)(x + 3)(x - 5)
A.
(x + 1)(x + 3)(x + 5)
The expanded form of (x + 2y + z)2 is
-
x2 + 4y2 + z2 + 4xy + 4yz + 2zx
-
x2 + 4y2 + z2 + 2xy + 2yz + zx
-
x2 + 4y2 + z2 + 4xy + 2yz + 4zx
-
x2 + 4y2 + z2 + 4xy + 4yz + 4zx
x2 + 4y2 + z2 + 4xy + 4yz + 2zx
A.
x2 + 4y2 + z2 + 4xy + 4yz + 2zx
The expanded form of (x - y - z)2 is
-
x2 + y2 + z2 - 2xy + 2yz - 2zx
-
x2 + y2 + z2 - xy + yz - zx
-
x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy - 2yz - 2zx
-
x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy + 2yz + 2zx
A.
x2 + y2 + z2 - 2xy + 2yz - 2zx
The factors of y2 - 5y + 6 are
-
(y - 2) (y - 3)
-
(y + 2) (y + 3)
-
(y - 2) (y + 3)
-
(y + 2) (y - 3)
A.
(y - 2) (y - 3)
The factors of bx2 + 17x + 5 are
-
3x + 1) (2x + 5)
-
(3x - 1) (2x - 5)
-
(3x + 1) (2x - 5)
-
(3x - 1) (2x + 5)
A.
3x + 1) (2x + 5)
4a2 + 9b2 + c2+ 12ab + 4ac + 6be is
-
(2a + 3b + c)2
-
(a + 2b + 3c)2
-
(2a + b + 3c)2
-
(3a + b + 2c)2
A.
(2a + 3b + c)2
The factor of (2a - b)3 + (b - 2c)3 + 8(c - a)3 is:
-
(2a - b)(b - 2c) (c - a)
-
3(2a - b)(b - 2c) (c - a)
-
6(2a - b)(b - 2c) (c - a)
-
2a × b × 2c
C.
6(2a - b)(b - 2c) (c - a)Factorise: a3 - b3 + 1 + 3ab
Solution not provided.
Ans. (a - b + 1) (a2 + b2 + 1 + ab + b - a)
Find the value of ‘a’ if (x - a) is a factor of x5 - a2x3 + 2x + a + 3, hence factorise x2- 2ar -3.
Solution not provided.
Ans. - 1; (x - 3) (x + 1)
Factorise: (x2 - 2x)2 - 11 (x2 - 2x) + 24
Solution not provided.
Ans. (x - 3) (x + 1) (x - 4) (x + 2)
Prove that 2x3 + 2y3 + 2z3 - 6xyz
= (x + y + z) [(x - y)2 + (y - z)2 + (z - x)2].
Solution not provided.
Ans. 1624
If x2 - 3x + 2 is a factor of x4 - ax2 + b, then find a and b.
Solution not provided.
Ans. a = 5, b = 4
The volume of a cube is given by the polynomial
p(x) = 8x3 - 36x2 + 54x - 27
Solution not provided.
Ans. 2x - 3
Using factor theorem, factorise the polynomial:
x4 + 3x3 + 2x2 - 3x - 3.
Solution not provided.
Ans. (x - 1) (x + 1) (x - 4) (x + 2)
The lateral surface area of a cube is 4 times the square of its edge, find the edge of a cube whose lateral surface area is given by:

Solution not provided.
Ans. ![]()
Divide the polynomial 3x4 - 4x3 - 3x - 1 by x - 1 and find its quotient and remainder.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 3x3 - x2 -x -4 ; - 5
If 3a - 2b + 5c = 5 and 6ab + 10bc - 15ac = 14, find the value of 27a3 + 125c3 + 90 abc -8b3.
Solution not provided.
Ans. 20
Find the value of (x - a)3 + (x - b)3 + (x - c)3 - 3(x - a) (x - b) (x - c) where a + b + c = 3x
Solution not provided.
Ans. 0
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area