Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction In Organisms
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 राजनीतिक विज�ञान Biology
Testa and tegmen are present in : - (A) flower
- (B) ovary
- (C) seed
- (D) seed coat.
D.
(D) seed coat.
Vegetative type of reproduction means :
-
(A) plant portion is used as a means of propagation
-
(B) seed is used as a means of propagation
-
(C) flower is used as a means of propagation
-
(D) None of the above.
A.
(A) plant portion is used as a means of propagation
Micropropagation is based on :
-
(A) tissue culture
-
(B) hybridization
-
(C) microtomy
-
(D) genetic control.
A.
(A) tissue culture
Bryophyllum is vegetatively propagated by :
-
(A) Bulbil
-
(B) Leaf buds
-
(C) rhizome
-
(D) Offset.
B.
(B) Leaf buds
Which is having menstrual cycle ?
-
(A) Monkey
-
(B) Apes
-
(C) Human
-
(D) All of above.
D.
(D) All of above.
Which is male accessory duct ?
-
(A) Rate testis
-
(B) Vas effrentia
-
(C) Vas deferens
-
(D) All of above.
D.
(D) All of above.
Which of the following is having oestrous cycle ?
-
(A) Cow
-
(B) Rat
-
(C) Both (A) and (B)
-
(D) Monkey.
C.
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Which of the following is bisexual ?
-
(A) Earthworm
-
(B) Sponge
-
(C) Tapeworm
-
(D) All of above.
D.
(D) All of above.Frog is ................... while human female is ....................
Testes lie in ................... while ovaries lie in ....................
Sponsor Area
What is reproduction ?
Name artificial methods of vegetative propagation.
2. Grafting
3. Layering
4. Gootee.
5. Micropropagation.
Name various asexual reproductive structures.
In the whiptail lizards only the females are born generation after generation. There are no males. How is this possible ?
Define senescent phase.
The microscopic pollen grains of the past are obtained as fossils. Mention the characteristics of pollen grains that makes it happen
Why is reproduction essential for organisms ?
Why is the offspring formed by asexual reproduction referred to as clone ?
Offspring formed due to sexual reproduction have better chances of survival. Why? Is this statement always true?
It is not always true that sexual reproduction has an advatage over asexual reproduction. Sometimes when the organism has well established in a suitable environment asexual reproduction is more efficient because it requires less energy, no need to search for mate and is less time consuming.
How do lower organisms reproduce ?
What are the two main methods of reproduction ?
Name the organism in which following structures are formed during asexual reproduction.
(i) zoospore
(ii) conidia
(iii) buds
(iv)gemmules.
(ii) Penicillium
(iii) Hydra
(iv) Sponge.
Which type of division is involved in the asexual reproduction ?
What is sexual reproduction ?
Sponsor Area
Define zygote.
Name the three phases in the life span of an organism.
(2) Reproductive phase
(3) Senescence phase.
Why do internodal segments of sugarcane fail to propagate vegetatively even when they are in contact with damp soil ?
Define
(i) Juvenile phase
(ii) Reproductive phase
(iii) Senescent phase.
(i) Juvenile phase. The period of growth in life of organisms before they start reproducing sexually and attain a level of maturity is called juvenile phase. It is known as Vegetative phase in plants.
(ii) Reproductive phase. The period of active reproductive behaviour when the organisms show marked morphological and physiological changes is called reproductive behaviour. It is followed by senescence phase.
(iii) Senescence phase. The period when the reproductive phase ends and concomitant changes occur in the body such as slowing of metabolism is called senescence phase. It is the last phase when the organism grows old and it is followed by death.Explain the process of budding in yeast.

Budding in Saccharomyces.
Differentiate between a zoospore and a zygote.
Or
What is zoospore ?
|
Zoospore |
Zygote |
|
1.It is an asexual spore produced by the some algae and fungi species. 2.It is haploid or diploid in nature. |
1. It is a cell produced by sexual reproduction by the fusion of male and female gametes. 2. It is diploid in nature. 3. It is motile or non motile and non flagellated
|
Zoospores are asexual reproductive structures formed by some fungi or algae species for reproduction. They are microscopic motile species bearing flagella. They may be haploid or diploid in nature.
How does Bryophyllum plant propagate ?
Or
Why do the new plants grow on Bryophyllum leaf ?

Leaf of Bryophyllum with young plants.
Define external fertilization. Mention its disadvantages.
Disadvantages of external fertilization are :
(1) A large number of gametes are produced to ensure fertilization thus there is wastage.
(2) The offsprings formed are extremely vulnerable to predators and are risk upto adulthood.
(3) The gametes and zygotes face a greater risk of dessication.
Higher organisms have resorted to sexual reproduction inspite of its complexity. Why ?
1. The fusion of gametes and genetic recombination, causes variations in the offsprings thus, also forms the raw material for evolution.
2. The offsprings adapt more comfortably and quickly to the changes in environmental conditions and the survival rate is high.
3. Any mutation or disease present in the parents may not appear in the progeny due to variation in genes.
4. Sexual reproduction plays an important role in the origin of new species.
What is a bisexual flower ? Collect five bisexual flowers from your neighbourhood and with the help of your teacher find out their common and scientific names.
Scientific Names of flowers
Common Name Scientific Name
1. Rose - Rosa indica
2. Sun flower - Helianthus annus
3. Petunia - Petunia alba
4. Hibiscus - Rosa sinensis
5. Pea - Pisum sativum.
What are oviparous and viviparous animals ? Give one example of each.
Viviparous animals. The animals which give birth to young ones and fertilization and development are internal nutrition is obtained from mother. Examples. Rat, Rabbit, Human.
What is life span ?
Write the approximate average life span of following organisms :
May fly, wheat, monkey, dog, cat, horse, elephant, eagle, man, parrot, tortoise, Banyan tree and sequoia tree. Name the oldest tree.
Monkey — 26 years ; Dog — 13-15 years ;
Cat — 12-15 years ; Horse —25-30 years :
Elephant — 65 years ; Eagle — 20 years ;
Man — 85 years : Parrot — 80-100 years;
Tortoise — 150 years ; Banyan tree — 200 years ;
Sequoia tree — 3000 - 4000 years.
Oldest living tree is the Bristle Cone Pine in the White Mountains (California), with an age of 5,065 years.
Distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction. Why is vegetative reproduction also considered as a type of asexual reproduction ?
Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
1. The process involves only one cell or one parent. 2. The whole body of the parent may act as reproductive unit or it can be single cell or a bud. 3. The offsprings are genetically similar to parent. 4. Only mitotic division takes place. 5. No formation of sex organs. 6. No evolutionary significance. | 1. This process involves two cells or gametes belonging to either the same or different parents. 2. The reproductive unit is called gamete which is unicellular and haploid. 3. The offsprings differ from parents. 4. Meiosis and mitosis both take place. 5. Formation of sex organs is essential. 6. It introduces variation hence of evolutionary significance. |
(ii) Vegetative reproduction is also considered as a type of asexual reproduction because it does not involve fusion of male and female gametes and require only one parent. New plants are produced by vegetative parts of plants without the formation of seeds or spores .
List the different ways of asexual reproduction.
(a) Fission (Binary and Multiple fissions)
(b) Budding
(c) Fragmentation
(d) Gemmulation
(e) Vegetative propagation and
(f) Sporulation.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction.
1. It involves a single parent and their is no need to search for mate.
2. Reproduction is rapid and may produce large number of young ones.
3. It requires less time and energy.
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction
1. Their is no genetic variation.
2. If the parent has and disease the offspring also has it, because it is identical to its parent.
3. The offspring is not fit to adapt to the changing environment and chances of survival are less.
What is vegetative propagation ? Give two suitable examples.
Examples.
1. In Century plant (Agave sp.) flowers, buds develop into bulbils which drop to the ground and develop into new plants.
2. Potato tubers possess buds which grow into new plants.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction.
1.Fusion of two gametes, genetic recombination, interaction etc. take place which causes variations in the offsprings ,thus it also forms raw material for evolution.
2. The offsprings adapt more comfortably and quickly to the change in environmental conditions and have better chances of survival.
Disadvantages of sexual reproduction.
1.Usually two parents of opposite sexes are required (except in hermaphrodite).
2. It consumes more time and energy.
Describe the fission in yeast.
Show the different kinds of asexual reproductive structures.
Different kinds of asexual structures are represented below:
Fig. Different kinds of asexual structures.
A. Zoosporangium producing motile zoospores
B. Conidiophore of Penicillium bearing conidia;
C. Buds in Hydra D. Gemmules in sponges
D. Gemmules in sponges.
Describe fission in animals as mode of reproduction.
(i) Binary fission. It is the simplest method of asexual reproduction generally found in unicellular organisms like Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena etc. Binary means two and fission means breaking, thus this process involves the division of animal body into two parts.
After attaining an optimum size the adult undergoes division. It is completed in two steps. First the nuclear division followed by cleavage of cytoplasm into two parts each having a daughter nucleus. Amoeba and Paramecium divide in transverse plane and Euglena in longitudinal plane.
Binary Fission in Amoeba
(ii) Multiple fission. It is a type of asexual reproduction in which nucleus undergoes repeated divisions before the cytoplasm breaks to form a number of uninucleate daughter cells. Each body thus formed grows into a new individual. Multiple fission occurs in Amoeba and Plasmodium during the formation of merozoites (schizogony), sporozoites (sporogony) and male gametes (Gamogony). It is also quite common in Amoeba and other acellular organisms.

Spore formation in Amoeba.
Write a note on budding with the help of suitable diagram.
Budding. It is a common method of reproduction in Sponges and Hydra. In this process, the new individual develops from a small outgrowth on the surface of parent. The exogenous bud gets its nourishment from the parent till it gets the maturity. Then it breaks off from the parent body and develops into new individuals. Sometimes, the buds do not separate off and form parent.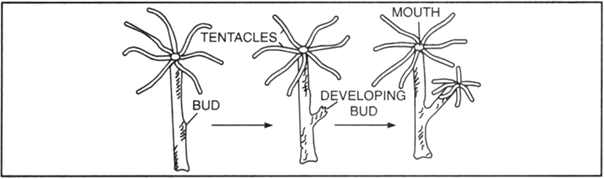
Fig. Budding in Hydra.
Differentiate fission and budding.
|
Fission |
Budding |
|
1. Fission is a division of an organism into two (binary fission) or more than two (multiple fission) new organisms. 2. There is no proliferation of any vegetative cells. |
1. Budding involves the enlargement of a vegetative part of body to form a bud which detaches from the parent body and forms a new organism. 2. There is proliferation of vegetative cells. |
Differentiate binary fission and multiple fission.
|
Binary fission |
Multiple fission |
|
1. It involves the division of parent into two equal-sized daughter individuals.
|
1. It involves the simultaneous division of parent into many small daughter individuals. 3. It occurs in many protozoans such as Plasmodium. |
What is Gemmulation ?

Gemmule of Spongilla.
List the features of sexual reproduction.
(1) Gametogenesis( by meiosis) -Development of male and female gametes which are haploid in nature .
(2) Fertilization- Fusion of the two gametes (haploid cells) to form zygote (diploid cell).
(3) Embryogenesis- Mitotic divisions and cell differentiation of zygote to form embryo. mitosis helps in increasing the cell number and differentiation helps to form specialized tissues and organs.
(4) Development - Growth of embryo to form new individual.
List the pre-fertilization events.
What is gametogenesis? Name and sketch the kind of gametes.
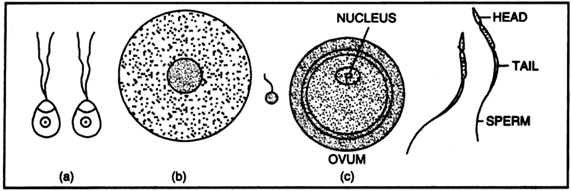
Types of gametes: (a) isogametes of Cladophora (b) heterogametes of Fucus (alga) and (c) human beings
What kind of cell division occurs during gamete formation ?
Differentiate between gametogenesis and embryogenesis.
|
Gametogenesis |
Embryogenesis |
|
1. The process of development of haploid gametes in the reproductive organs is called gametogenesis. It is of two types Spermatogenesis (male) and oogenesis(female). 2. It involves mitosis and meiosis. |
1. The process of development of the embryo from the zygote is called embryogenesis. 2. It involves mitosis only. |
Identify each part and write whether it is haploid (n) or diploid (2n).
(a) Ovary (b) Anther (c) Egg (d) Pollen (e) Male gamete (f) Zygote.
(a) Ovary → diploid (2n)
(b) Anther → diploid (2n)
(c) Egg → haploid (n)
(d) Pollen → haploid (n)
(e) Male gamete → haploid (n)
(f) Zygote → diploid (2n)
Explain the significance of fertilization.
1. The fusion of male and female pronuclei in fertilization restores the diploid number of chromosomes.
2. Fertilization initiates cleavage or segmentation.
3. The combination of the chromatin material from two different parents form the physical basis of biparental inheritance and variation.
What do you understand by vegetative methods of reproduction ? Explain with examples
It is of two types :
A. Natural Vegetative propagation
1. Vegetative propagation by stem. e.g. grasses, turmeric, onion, colocasia, potato, gladiolus and crocus.
2. Vegetative propagation by roots. e.g., Tuberous roots of sweet potato, asparagus, tapioca, dahlia and yams (Dioscorea).
3. Vegetative propagation by leaves e.g. Bryophyllum, Begonia, Lilium.
4. Vegetative propagation from reproductive organs. Flower buds of century plant (Agave sp.) develop into bulbils.
B. Artificial vegetative propagation.
1. Cutting e.g. leaf cutting in Bryophyllum.
2. Layering e.g. Jasmine.
3. Grafting e.g. Rose, Mango.
4. Micro-propagation.
5. Gootee e.g. lemon, orange, guava, litchi
Describe the importance of vegetative propagation.
(1) Plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically similar and constitute a uniform population called as clone.
(2) Plants that have reduced power of sexual reproduction, long dormant period of seed, poor viability can be multiplied by vegetative methods.
(3) Some fruit trees like banana, pineapple that do not produce viable seeds and dub grass which produces small quantity of seeds can be propagated by vegetative methods.
(4) It is a rapid and easier method of propagation.
(5) Good characters can be preserved by vegetative propagation.
(6) Vegetative Propagation can be used to develop Virus Free plants.
(7) Grafting helps in getting an economically important plant having useful characteristic of two different individuals in short time in a single plant.
Which is a better mode of reproduction: sexual or asexual? Why?
Explain why meiosis and gametogenesis are always interlinked?
Gametogenesis is the process of gamete production while meiosis is the process of reduction division in which the chromosome number is reduced to half. In order to produce gamete which are haploid in nature the cells have to undergo meiosis. The chromosome number is reduced to half in the two successive meiotic cycles. Thus, meiosis and gametogenesis are always interlinked.
Describe the post-fertilisation changes in a flower.
After fertilization the zygote is formed. The zygote then undergoes many division by the process of mitosis, to form an embryo by a process called embryogenesis. The ovule of the flower develops into a seed which along with the embryo is covered by a protective seed coat. The sepals, petals and stamens of the flower wither and fall off. The ovary forms the fruit which is covered by a protective thick wall called pericarp. The seeds germinate on meeting favourable conditions.
Examine a few flowers of any cucurbit plant and try to identify the staminate and pistillate flowers. Do you know any other plant that bears unisexual flowers?
Cucurbits are unisexual plants. The staminate or male flowers are bright, yellow coloured. The staminate flowers bear bright, yellow coloured petals bearing stamens. Whereas, the pistillate flowers have pistil. Other examples of unisexual flowers are papaya, cucumber, etc.
Why are offspring of oviparous animals at a greater risk as compared to offspring of viviparous animals?
Oviparous animals lay eggs outside of their body. Thus, the eggs have to face the harsh environmental conditions like excessive heat or cold, predators, water scarcity etc. On the other hand, in viviparous animals, the development of the egg takes place inside the body of the female. The egg is well protected from the unfavourable conditions. Hence, the offspring of an egg-laying or oviparous animal is at greater risk as compared to the offspring of a viviparous animal, which gives birth to its young ones.
Give an example of an organism that enters 'diapause' and why.
Zooplankton under unfavorable enters ‘diapause’ which is a state of suspended development.
Sponsor Area
Why do algae and fungi shift to sexual mode of reproduction just before the onset of adverse conditions?
Organisms such as fungi and algae switch to sexual mode of reproduction during adverse conditions because sexual reproduction brings variation into the individuals, some of which might help the individuals to adapt to the changed conditions and survive. This ensures the continuity of species.
Differentiate between male and female heterogamety.
|
Male Heterogamety |
Female Heterogamety |
|
Males produce two different types of gametes. |
Female produce two different types of gametes. |
|
It is found in humans |
It is found in birds. |
Double fertilization is reported in plants of both, castor and groundnut. However, the mature seeds of groundnut are non-albuminous and castor are albuminous. Explain the Post fertilization events that are responsible for it.
Double fertilization occurs in plants of both castor and groundnut but the mature seeds of groundnut are non-albuminous and castor are albuminous. The post fertilization events that are responsible for it are:
The primary endosperm nucleus divides repeatedly to give rise to a free nuclei and the stage of endosperm development is called free nuclear endosperm. The cell wall forms after giving rise to a cellular endosperm.
If the endosperm is fully consumed by the growing embryo then non-albuminous seeds are formed as in groundnut. If the endosperm is retained then it forms albuminous seeds as is the case with castor plant.
A flower of tomato plant following the process of sexual reproduction produces 240 viable seeds.
Answer the following questions giving reasons:
(a) What is the minimum number of pollen grains that must have been involved in the pollination of its pistil?
(b) What would have been the minimum number of ovules present in the ovary?
(c) How many megaspore mother cells were involved?
(d) What is the minimum number of microspore mother cells involved in the above case?
(e) How many male gametes were involved in this case?
The number of viable seeds produced by the tomato plant through sexual reproduction = 240
(a) The minimum number of pollen grains that must have been involved in the pollination of its pistil are 240 because each pollen grain contains two male gametes. Out of these two gametes, one fuses with polar nuclei and forms endosperm, while, the other male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form the zygote that eventually give rise to seeds. Therefore, in order to obtain 240 seeds, number of pollen grains needed would be 240.
(b) The minimum number of ovules involved in this process would be 240, as the number of viable seeds is 240. After fertilisation, the ovary turns into fruit and the ovules turn into seeds. Therefore, the number of ovules corresponds to the number of seeds formed.
(c) During the process of gametogenesis, 240 megaspore mother cells are involved as only one megaspore of the tetrad becomes functional and develops further and the rest three megaspores get degenerated.
(d) In the above case, 60 microspore mother cells must have undergone reduction division prior to dehiscence of anther, as each microspore mother cell would give rise to 4 microspores. Since 1 microspore mother cell would produce 4 microspores, therefore, to obtain 240 microspores, there must be 60 microspore mother cells.
(e) The number of male gametes involved in seed formation would be 240 as each male gamete will fuse with one egg nuclei to form zygote, which will further give rise to the seed.
An anther with malfunctioning tapetum often fails to produce viable male gametophytes. Give any one reason.
Tapetum nourishes the developing pollen grain so in case of a malfunctioning tapetum the pollen grain will not get any nourishment and lose its viability.
Geitonogamous flowering plants are genetically autogamous but functionally cross-pollinated. Justify.
In geitonogamy the pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of another flower on the same plant, thus functionally it involves cross-pollination. Since the pollen grains come from the plant it is genetically similar to autogamy.
(a) State the difference between meiocyte and gamete with respect to chromosome number.
(b) Why is a whiptail lizard referred to as parthenogenetic?(a) The gamete contains haploid set of chromosomes while the meiocyte contains a diploid set.
(b) Whiptail lizard is parthenogenetic because in this animal, an unfertilized egg develops into a new individual. This process of reproduction without fertilization is called parthenogenesis.
Name the type of cell division that takes place in the zygote of an organism exhibiting haplontic life cycle.
The type of cell division occurring in the zygote of an organism exhibiting haplontic life cycle is meiosis.
Why do moss plants produce very large number of male gametes? Provide one reason. What are these gametes called?
Mosses are bryophytes and they need water for fertilisation. During the transfer of male gametes, many of them are destroyed or lost. Thus, moss plants produce very large number of male gametes to compensate for the loss during transport.
These male gametes are called antherozoids.
Explain the significance of meiocytes in a diploid organism.
Meiocytes are specialised cells present in sexually reproductive organisms. They undergo meiotic division to produce male and female gametes that carry only one set of chromosomes and thus help in maintaining the chromosomal number of the organism.
Name the phase all organisms have to pass through before they can reproduce sexually.
The phase that all organisms have to pass through before they can reproduce sexually is Juvenile phase. It is known as Vegetative phase in plants.
Name the enzyme produced by Streptococcus bacterium. Explain its importance in medical sciences.
Streptokinase enzyme is produced by the bacterium Streptococcus.
It is used as a ‘clot buster’ which removes clots from the blood vessels of patients who have undergone myocardial infarction.
A. State the consequence if the electrostatic precipitator of a thermal plant fails to function.
B. Mention any four methods by which the vehicular air pollution can be controlled.
A. The thermal plants release particulate matter, which is considered very harmful for the human health. The electrostatic precipitator helps in the removal of particulate matter and can remove over 99 per cent of it present in the exhaust of the thermal power plant.
It has electrode wires that are maintained at several thousand volts. These produce a corona that releases electrons. The electron attach to the dust particles giving them a negative charge. The collecting plates of the precipitator are grounded and thus attract the charged dust particles. The scrubber removes gases like sulphur dioxide.
Four important methods that can be implemented to reduce pollution
1. Use of lead-free petrol .
2. Catalytic converter such as platinum-palladium and rhodium should be used for decreasing emission of poisonous gases.
3. Use of CNG.
4 . Reducing the sulphur and aromatic content in petrol and diesel fuels.
Give a scientific term:
The development of an embryo without the occurence of fertilization.
Parthenogenesis
Differentiate between Parthenocarpy and Parthenogenesis. Give one example of each.
In most plants, flowers need to be pollinated and fertilized to produce fruits. However, some plants can produce fruits before fertilization or without fertilization. Parthenocarpy is the process which produces fruits from unfertilized ovules in plants. Unfertilized ovules develop into fruits prior to fertilization. These fruits do not contain seeds.
Parthenogenesis is a type of reproduction commonly shown in organisms mainly by some invertebrates and lower plants. It can be described as a process in which unfertilized ovum develops into an individual (virgin birth) without fertilization. Therefore, it can be considered as a method of asexual reproduction.
It is seen in organisms like rotifers, honeybees and even some lizards and birds (turkey). The key difference between parthenogenesis and parthenocarpy is, parthenogenesis is shown by animals and plants while pathenocarpy is shown only by plants.
Assertion: A middle aged woman is reported to have small breasts and undersized uterus.
Reason: Her genotypic analysis shows XO condition of allosomes.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Females having 45 chromosomes (2A + XO) are affected with Turner's syndrome. Individuals having Turner's syndrome have female sexual differentiation but ovaries are rudimentary. Other associated phenotypes of this condition are short stature, webbed-neck, broad chest, lack of secondary sexual characteristics and sterility. Thus, any imbalance in the copies of the sex chromosomes may disrupt the genetic information necessary for normal sexual development.
Which of the following statements is correct ?
1. Common cold- Droplet Infection.
2. Typhoid - Contaminated food & water.
3. AIDS- Shaking hands.
4. Ringworm - Using infected towels.
1 and 2
3 and 4
1 and 3
1,2 and 4
D.
1,2 and 4
Common cold can take place from one person to other as it is a communicable in nature. A healthy person can get infected by being in close vicinity of infected person when he/she sneezes, coughs, as the droplets generated by sneeze and cough contain infecting agents. Typhoid occurs by the intake of contaminated water & food. While ringworm is one of the skin disease which can transfer from one person to other by the use of infected towel & handkerchief. AIDS (Acquired lmmuno deficiency) does not occur or transfer by shaking hands.
Which of the following statements is correct
Catalytic converter can separate particulate matter of diameter less than 2.5 micrometers.
Histones are acidic in nature that forms core for DNA packaging.
Lactobacillus is not present in dough used in idli formation.
Template with polarity 5' 3' has continuous DNA replication.
B.
Histones are acidic in nature that forms core for DNA packaging.
According to Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), particulate size 2.5 micrometers or less in diameter (PM 2.5) are responsible for causing the greatest harm to human health. These fine particulates can be inhaled deep into the lungs and can cause breathing and respiratory symptoms, such as irritation, inflammations and damage to the lungs and premature deaths.
Which of the following statements is correct
Lion and leopard show convergent evolution.
Cryptic camouflage is seen in Biston betularia
Natural selection is responsible for extinction of dinosaurs.
Homo habilis and Homo erectus are closely related.
B.
Cryptic camouflage is seen in Biston betularia
The peppered moth (Biston betularia) is a temperate species of night-flying moth. Peppered moth evolution is often used by educators as an example of natural selection. Peppered moths are cryptically camouflaged against their backgrounds when they rest on the tree trunk.
Monoecious plant of Chara shows occurrence of
-
antheridiophore and archengoniophore on the same point
-
stamen and carpel on the same plant
-
upper antheridium and lower oogonium on the same plant
-
upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
D.
upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
Monoecious or homothallic, a condition in Chara (green algae) is used to denote upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant. The organisms, which possess both the reproductive organs are bisexual. Unisexual condition represents both male or female organs in the same organism.
Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
-
Mode of reproduction Example
Offset Water hyacinth
-
Mode of reproduction Example
Rhizome Banana -
Mode of reproduction Example
Binary fission Sargassum -
Mode of reproduction Example
Conidia Penicillium
C.
Mode of reproduction ExampleBinary fission Sargassum
The plant body Sargassum is a diploid sporophyte. It does not multiply asexually by means of spores. Instead it reproduce by vegetative means, i.e. fragmentation which is the only known method of vegetative reproduction in the free floating species of Sargassum.
In vitro clonal propagation in plants is characterised by
-
PCR and RAPD
-
Northern blotting
-
Electrophoresis and HPLC
-
Microscopy
A.
PCR and RAPD
RAPD stand for Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA. It is a type of PCR reaction, but the segments of DNA that are amplified are random. Often, PCR is used to amplify a known DNA sequence.
Male gametes are flagellated in
-
Polysiphonia
-
Anabaena
-
Ectocarpus
-
Spirogyra
C.
Ectocarpus
Male gametes are flagellated in Ectocarpus belonging to Phaeophyceae. The flagella of male and gamete plays an important role in establishing initial sexual contact with the female gamete. However, in Ectocarpus the female gamete too is flagellated but is different in structure.
In Polysiphonia (Rhodophyceae) flagellated gametes are not observed, in Anabaena sexual reproduction through gametes is absent while in Spirogya sexual reproduction takes place by conjugation wherein male gamete passes through a tube to the adjacent filament. The male gametes here are non-flagellated and show amoeboid movement.
Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of sexually reproducing organism?
-
Transduction
-
Chromosomal aberrations
-
Genetic drift
-
Recombination
D.
Recombination
Recombination is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism. It involves the exchange of genetic material either between multiple chromosomes or between different regions of the same chromosome. This mechanism is generally mediated by homologous chromosomes, during meiosis, i.e, formation of gametes or germ cells.
Which one of the following matches is correct?
-
Phytophthora Aseptate mycelium Basidiomycetes -
Alternaria Sexual reproduction Deuteromycetes -
Mucor Reproduction by conjugation Asocmycetes -
Agaricus Parasitic fungus Basidiomycetes
B.
| Alternaria | Sexual reproduction | Deuteromycetes |
(i) Phytophthora belongs to Phycomycetes (algal fungi). They contain either unicellular thallus or non-separate coenocytic mycelium. They are mostly plant damaging Oomycetes (water molds).
(ii) Alternaria is Deuteromycetes (fungi imperfecti), which lacks sexual reproduction.
(iii) Mucor also belong to Phycomycetes. They have mycelium which is coenocytic (multinucleate) and profusely branched. They reproduce vegetatively via conjugation.
(iv) Agaricus belongs to Basidiomycetes (where karyogamy and meiosis occur). They contain well-developed filaments, branched and septate mycelium. They are saprophytic but parasitic.
So, hence (b) option is correctly matched.
What will you look for to identify the sex of the following?
-
male frog - a copulatory pad on the first digit of the hind limb
-
Female cock - anal cerci
-
Male shark - claspers borne on pelvic fins
-
Female Ascaris - sharply curved posterior end
C.
Male shark - claspers borne on pelvic fins
A clasper is a male anatomical structure found in some groups of animals, and used in mating. Male cartilaginous fish like shark hacve claspers formed from the posterior portion of their pelvic fin which serves as intromittent organs used to channel semane into the female's cloaca during mating.
Archegoniophore is present in
-
Chara
-
Adiantum
-
Funaria
-
Marchantia
D.
Marchantia
In Marchantia, a bryophyte, the archegonia (female sex organs) are borne on special branches called archegoniophore or female receptacles. Each archegoniophore has rows of archegonia protected by involucre or perichaetium.
What is common between vegetative reproduction and apomixis?
-
Both are applicable to only dicot plants
-
Both bypass the flowering phase
-
Both occur round the year
-
Both produces progeny identical to the parent
D.
Both produces progeny identical to the parent
Both vegetative and apomixis are an asexual reproduction. The progeny produced are genetically similar to a parent and are called clone.
Examine the figure below and select the right option giving all the four part (A, B,C and D) correctly identified.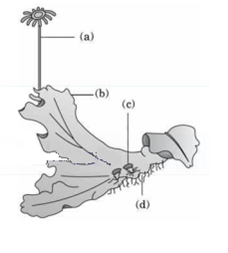
-
A
B
C
D
Archegoni Ophore
Female thallus
Gemma cup
Rhizoids
-
A
B
C
D
Archegoni
Female thallus Bud Foot -
A
B
C
D
Seta
Sporophyte Protonema Rhizods -
A
B
C
D
Antheridiophore
Male thallus Globule Roots
A.
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Archegoni Ophore |
Female thallus |
Gemma cup |
Rhizoids |
Marchantia, a liverwort, is dioecious. The female thallus bears female sex organs called archegonia on special branches called archegoniophores. The plant's body is anchored by unicellular rhizoids.
Keel is characteristic of the flowers of
-
gulmohur
-
cassia
-
Calatropis
-
Bean
D.
Bean
The bean or legume family is one of the most common plant families. Flowers in bean family typically have their two bottom petals grown together along one side forming a structure a bit like a narrow but deep scoop. This special Bean- family kind of two -in-one petal is called the keel, like the keel of a boat. Bean blossoms with the configuration are said to be papilionaceous.
Which one of the following plants is monoecious?
-
Marchantia
-
Pinus
-
Cycas
-
Papaya
B.
Pinus
Pinus is monoecious, which bear male cone as well as a female cone on the same tree on separate branches.
Marchantia Cyas and papaya are dioecious plants
In cloning of cattle a fertillized egg is taken out of the mother’s womb and
-
the egg is divided into 4 pairs of cells which are implanted into the womb of other cows
-
in the eight cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cow
-
in the eight cell stage the individual cells are separated under electrical field for further development in culture media
-
from this upto eight identical twins can be produced
B.
in the eight cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cow
In cloning of cattle a fertilized egg divides in 2, then in 4 and then in 8. This embryo is carefully removed from the womb. The embryonic cells are then separated using enzyme. Each isolated cell is kept in a nutrient medium and later implanted in the womb of a different 'host mother' cow.
How many different kinds of gametes will be produced by a plant having the genotype AABbCC?
-
Three
-
Four
-
Nine
-
Two
D.
Two
The types of gametes produced by a plant depend upon the number of hetrozygous pair.
Number of types of gametes = Zn
n = number of heterozygous pair
21 = 2
The gametes are - ABC and AbC.
Which among the following is not a prokaryote?
Saccharomyces
Mycobacterium
Oscillatoria
Nostoc
A.
Saccharomyces
- Saccharomyces i.e. yeast is a eukaryote (unicellular fungi)
- Mycobacterium – a bacterium
- Oscillatoria and Nostoc are cyanobacteria
Parthenogenesis is a term of
Budding
Asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Regeneration
C.
Sexual reproduction
Parthenogenesis is a form of sexual reproduction n which the ovum develops into a new individual without fertilisation.
Select the correct statement regarding reproduction
Mating in dogs is synchronised with lunar cycle.
Salamanders always have internal fertilisation.
In Trygon, the male introduces sperms into female through a modified pelvic fin.
Catla has internal fertilisation
C.
In Trygon, the male introduces sperms into female through a modified pelvic fin.
Mating in dogs is not synchronised with lunar cycle. Six of the nine families of Salamanders have internal fertilisation. Catla has external fertilisation.
Which of the following is a cloning vector?
DNA of Salmonella typhimurium
Ti plasmid
Amp' and Tet' loci
Ori minus pBR322
B.
Ti plasmid
The DNA used as a carrier for transferring a fragment of foreign DNA into a suitable host is called vehicle DNA or cloning vector. The Ti plasmid is present in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is a Gram negative soil bacterium that infects a wide range of plants and causes tumorous growth especially at the root or stem junction (crown gall).
Ti plasmid can be used as a DNA vector by replacing the tumour inducing genes with the gene of interest and a marker gene to enable selection of transformed cells.
Starting from the maximum, arrange the following male reproductive accessory organs in the correct order, based on the amount of secretion poured into urethra.
(i) Prostrate gland
(ii) Seminal vesicle
(iii) Bulbourethral gland
(i) > (ii) > (iii)
(iii) > (ii) > (i)
(ii) > (iii) > (i)
(ii) > (i) > (iii)
D.
(ii) > (i) > (iii)
Seminal vesicles produce an alkaline secretion which forms 60% of the volume of semen. Its secretion include fructose, prostaglandins, citrate, inositol and clotting proteins.
Prostate gland produces a milky and slightly alkaline secretion whch forms 25% of the volume of semen. It consists of Calcium, Phosphate, Bicarbonate, enzyme prefibrolysin, clotting enzymes and prostaglandins.
Bulbourethral glands or Cowper's glands also secrete an alkaline fluid which neutralizes acids from urine in the urethra. Its secretion is the least but is of great importance.
Which of the following contraceptive devices make uterus unsuitable for implantation?
Progestasert
CuT
Lippe's loop
Multiload
A.
Progestasert
Progestasert is a hormone releasing IUCD which makes the uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile to the sperms.
Lippe's loop is non- medicated IUCD.
CuT and Multiload are copper releasing IUCDs, which suppress motility and fertilizing capacity of sperms.
In Miller's experiment, he used a mixture of CH4, NH3, H2 and water vapour in a closed flask to mimic early earth conditions. What was the temperature at which this flask was kept?
800C
1200
200C
400C
A.
800C
Initially, Oparin and Haldane proposed that first form of life could have come from pre- existing non- living organic molecules. The conditions were high temperature, volcanic eruption , storms, reducing atmosphere consisting of CH4, NH3 etc. Later in 1953, Miller created similar conditions in a laboratory and created an electric discharge in a closed flask containing CH4, H2 and NH3 and water vapour at 800C.
Sponsor Area
Sexual stage (gametocytes) of Plasmodium occurs in
Salivary glands of mosquito
Human RBC
Intestine of mosquito
Human liver
B.
Human RBC
Inside human RBCs, merozoites stop moving with erythrocytic cycle to increase in size and become rounded gametocytes. Male gametophytes or microgametocytes are smaller and contain a large diffused nucleus. Female gametophytes or mega gametophytes are larger with a small compact peripheral nucleus. They do not divide but give rise to gametes in insects.
Sporopollenin is a constituent of pollen exine. It can be degraded by the action of
enzymes
high temperature
strong acids
cannot be degraded
D.
cannot be degraded
Exine is the outer layer of pollen grain. It is thick and smooth and culticularised. Sporopollenin is the cutin. It protects the pollen grains as microfossils. It is not degraded by enzyme. It is not affected by high temperature, strong acid or alkali. It is resistant to chemical and biological decomposition.
The pollen grains of rice and wheat lose their viability inminutes of their release
30
10
60
90
A.
30
Pollen viability is the period for which pollen grains retain the ability to germinate. It is little in flowers which are pollinated in bud condition. Eg, it is 30 minutes in rice and wheat. It depends upon environmental conditions of temperature and humidity.
After doble fertilization, a mature ovule has
1 diploid and 1 haploid cell
1 diploid and 1 triploid cell
2 haploid and 1 triploid cell
1 haploid and 1 triploid cell
B.
1 diploid and 1 triploid cell
Double fertilization is the fusion of two male gametes with a female gametophyte. It is found only in Angiosperms.
In angiosperms, the pollen tube bursts open in one of the two synergids to release the two male gametes. One male gamete fuses with the egg to form a diploid zygote and is known as generative fertilization. The second male gamete descends down and fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus of the central cell to form a triploid primary endosperm cell and is known as vegetative fertilization.
After double fertilization, mature angiospermous ovule contains one diploid cell (zygote) and one triploid cell (endosperm).
Genetically modified (GM) crops can be produced by
recombinant DNA technology
somatic hybridization
cross breeding
micropropogation
A.
recombinant DNA technology
Genetically modified (GM) crops or transgenic plants are the plants in which a foreign gene has been introduced and integrated into the host DNA via RDT (Recombinant DNA Technology). It results in the production of desirable traits like disease resistance, insect resistance, herbicide resistance etc.
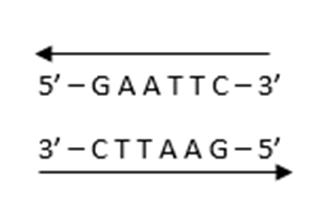
Which of the following is a palindromic sequence?
5' - CGTATG - 3'
3' - GCATAC - 5'
5' - CGAATG - 3'
3' - CGAATG - 5'
5' - GAATTC - 3'
3' - CTTAAG - 5'
5' - GACTAC - 3'
3' - TACGAC - 5'
C.
5' - GAATTC - 3'
3' - CTTAAG - 5'
A palindromic sequence is a sequence made up of nucleic acids within double helix of DNA and/ or RNA that is same when read from 5' to 3' on one strand and 5' to 3' on the other. Eg,
Which of the following is true for a recessive disease in Family A and B?
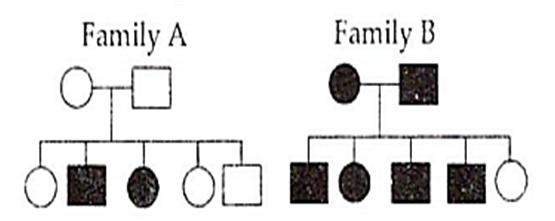
In family A, both the parents are homozygous recessive
In family B, both the parents are heterozygous dominant.
In family B, both the parents are heterozygous recessive
In family A, both the parents are heterozygous recessive.
D.
In family A, both the parents are heterozygous recessive.
In family A, if both the parents are homozygous recessive, then both should be diseased and should have 100% diseased progeny.
In family B, if both the parents are homozygous dominant, they would not have got the recessive disease in first place.
In family B, if both are heterozygous recessive, then also, they would not have got the disease, neither 80% of progeny would be diseased.
The 'cells of Rauber' are
secretory cells of endometrium in uterus
inner cell mass of blastocoel
outer cells of trophoblast in contact with uterine wall
cells of trophoblast, in contact with inner cell mass of blastocyst.
D.
cells of trophoblast, in contact with inner cell mass of blastocyst.
The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast and an inner group of cells attached to trophoblast called the inner cell mass. Inner cell mass looks like a small knob at one pole which gives rise to the embryo and is called the embryonal knob. The trophoblast does not take part in the formation of the embryo proper. It remains external to the embryo and gives rise to the extraembryonic membranes, namely, chorion and amnion, for the protection and nourishment of the embryo. The trophoblast cells in contact with the embryonal knob are known as cells of Rauber.
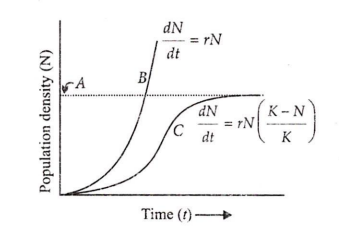
Which is correctly labelled with respect to the given diagram
B: Logistic curve
C: Carrying capacity
C: Exponential curve
A: Carrying capacity
D.
A: Carrying capacity
The given figure shows population growth curve, in which A is carrying capacity, B is exponential growth curve and C is logistic growth curve
Choose the correct statement.
hPL plays a major role in parturition.
Foetus shows movements first time in the 7th month of pregnancy.
Signal for parturition comes from fully developed foetus and placenta.
Embryo's heart is formed by the 2nd month of pregnancy.
C.
Signal for parturition comes from fully developed foetus and placenta.
Parturition is induced from the fully developed foetus and the placenta. Parturition involves foetal ejection reflex which are mild contractions of the placenta. This reflex triggers release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary which acts on the uterine muscles and causes stronger uterine contractions and that further stimulates secretion of oxytocin. This stimulatory reflex between uterine muscle contraction and oxytocin secretion continues resulting in stronger contractions and eventually leading into expulsion of the baby out of the uterus.
Which one has the largest species variety in India
Wheat
Maize
Rice
Potato
C.
Rice
India produces the largest variety of rice.
Cattle ranches are known to causes acute green house effect. This is due to
mechanized milking practices
methanogenic bacteria in rumen
decomposition of left over fodder
decomposition of organic remains in faeces.
B.
methanogenic bacteria in rumen
Cattle ranching refers to practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle or sheep for meat and wool, etc. The area of landscape meant primarily for cattle ranching is called a ranch. The practice has lead to accelerated deforestation and contributed to increased methane gas concentration in atmosphere. Whatever cattle eat; is subjected to the action of methanogens (bacteria) harbouring the stomach (rumen) of cattle. The action of these bacteria on food material produces methane gas which is released through cattle fart into the earth's atmosphere where it absorbs heat just like carbon dioxide, contributing to global warming.
Select the option having all the correct characteristics.
Structure Percentage Function

Structure Percentage Function

Structure Percentage Function

Structure Percentage Function

B.
Structure Percentage Function

D.
Structure Percentage Function

The structure in option (b) is of a basophil. Basophils are granular WBCs and are the least (0.5- 1 per cent) of the total WBCs. They secrete histamine, serotonin, heparin, etc. and are involved in inflammatory reactions.
Plants with inferior ovary usually bear
pseudocarps
berries
aggregate fruits
seedless fruits
A.
pseudocarps
An accessory fruit (sometimes called false fruit, spurious fruit, pseudofruit, or pseudocarp) is a fruit in which some of the flesh is derived not from the ovary but from some adjacent tissue exterior to the carpel.
The extinct human ancestor, who ate only fruits and hunted with stone weapons was
Ramapithecus
Australopithecus
Dryopithecus
Homo erectus.
B.
Australopithecus
Australopithecus apparently evolved in eastern Africa around four million years ago before spreading throughout the continent and eventually becoming extinct two million years ago. Australopithecus is not literally extinct (in the sense of having no living descendants) as the Kenyanthropus, Paranthropus and Homo genera probably emerged as sister of a late Australopithecus species such as A. Africanus and/or A. Sediba.
Beads on string like structures of A are seen in B, which further condense to form chromosomes in C stage of cell division
A B C
Chromonema Chromatin Metaphase
A B C
Chromatin Chromatid Metaphase
A B C
Chromonema Chromosome Anaphase
A B C
Chromonema Chromatid Anaphase.
A.
A B C
Chromonema Chromatin Metaphase
The 'beads-on-a-string' structure is seen in electron microscope of isolated metaphase chromosomes. The chromonema form the gene bearing portions of the chromosome. Basically chromonema is made up of nucleosome chains. Nucleosome chain gives a beads on string appearance under electron microscope. Nucleosome is the fundamental packaging unit in eukaryotic chromosomes.
RNA interference is essential for the
cell proliferation
cell defence
cell differentiation
micropropagation
B.
cell defence
RNAi is a regulatory mechanism for an estimated 30% of all protein-coding genes(in mammals). It helps to protect cells against certain viruses by targeting viral RNA for destruction. It helps to silence potentially disruptive transposons in the genome by destroying RNA copies arising from transposon replication. RNAi is a precise and efficient tool for knockout of specific genes when studying gene function in experimental organisms. It also has potential for new forms of targeted gene therapy.
Assertion: There are 34 biodiversity hotspots in the world.
Reason: High level of species richness is a criteria for selection of a biodiversity hotspot.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Hotspots are areas with high density of biodiversity or megadiversity which are also the most threatened ones. Ecologically hotspots are determined by four factors.
(i) Number of species/species diversity.
(ii) Degree of endemism
(iii) Degree of threat to habitat due to itsdegradation and fragmentation.
(iv) Degree of exploitation.
Myers (1988) initially identified 12 hot spots. Today the number of hotspots identified by ecologists is 34 covering an area less than 2% of land surface with about 20% of human population living there
Assertion: Inbreeding increases homozygosity, thus exposes harmful recessive genes, which are eliminated by selection.
Reason: Continued inbreeding reduces fertility and productivity.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
When the offsprings are produced by self fertilization or breeding between closely related parents it is called inbreeding. Inbreeding results in increase in homozygosity. The most revealing impact of inbreeding is the loss of vigour and physiological efficiency of the organisms characterized by reduction in size. A number of lethal and defective characters appear in the population which has undergone inbreeding (selfing). This loss of fitness in the progenies or decline in character expression with decreased heterozygosity arising from self mating is known as inbreeding depression or inbreeding decline. Continued inbreeding reduces fertility and even productivity. But the inbreeding progeny with lethal and harmful recessive genes being homozygous express these traits which otherwise remain hidden in heterozygous individuals. Natural selection works upon these individuals and eliminate them. Gradually, such genes get eliminated from the population.
Assertion: Some marine animals find it difficult to live in fresh water and vice versa.
Reason: Some animals can tolerate a narrow salinity range, while others can tolerate a wide salinity range.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
For aquatic organism salt concentration (measured as salinity in parts per thousand) is a major factor for their survival. Salinity of different aquatic habitats varies greatly. It is less than 5 per thousand parts, in inland waters, 30-35 per thousand parts in the sea and more than 100 per thousand parts in some hypersaline lagoons. Many fresh water animals cannot live for long in sea water and vice versa because of the osmotic problems they would face due to the change in relative tonicity of the surrounding water with cytoplasm. It may result into endosmosis or exosmosis according to the conditions. The tolerance of organisms to the salinity range varies. Some organisms are tolerant of a wide range of salinities and are called euryhaline e.g. salmon, while some can tolerate only a narrow range of salinity i.e., stenohaline e.g., shark
Assertion: Hbs Hbs denotes the homozygous condition for sickle-cell anaemia.
Reason: It occurs due to substitution of glutamic acid by valine at the 6 position of (B-chain of Hb.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Sickle cell anaemia is an autosomal hereditary disorder in which the erythrocytes become sickle shaped. The disorder or disease is caused by the formation of an abnormal haemoglobin called haemoglobin-s denoted as Hbs. Thus, the genotype of an individual homozygous for sickle cell anaemia is written as Hbs Hbs.
Assertion: In a terrestrial ecosystem, detritus food chain is the major conduit for energy flow.
Reason: Solar energy is the direct source for energy supply in a detritus food chain.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
There are two types of food chains: grazing food chain and detritus food chain.
Detritus food chains are those which start from the dead bodies of animals or fallen leaves etc.
In terrestrial ecosystems, detritus food chain is the major conduit of energy flow, while in aquatic ecosystems, grazing food chain is the major conduit of energy flow. As the detritus food chains depend upon the dead organic matter hence, these are not directly dependent upon solar energy.
Assertion: Filarial worm is transmitted to humans by Culex mosquito.
Reason: Culex prefers to breed in fresh water.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
Wuchereria (W.bancrofti & W.malayi), the filarial worms cause a slowly developing chronic inflammation of the organs in which they live for many years, usually the lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs, and the disease is called filariasis. The pathogen spread from one human being to another through mosquitoes like Culex and to a Jess extent by Anopheles and Aedes. The parasite resides in lymph vessels, connective tissues and mesentery. It is manifestated by lymphoedema accompanied by thickening of subcutaneous tissues and skin so that there is permanent swelling mostly of feet, legs, thighs, scrotal sacs, breast etc. In Culex and other mosquitoes females are blood sucking while males suck juices of flowers and fruits. Female Culex carries filarial worm from one person to another. It prefers to breed in dirty water near human. habitation.
Assertion: AIDS is caused by the HIV, a retro-virus.
Reason: Retroviruses have RNA genome.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Retrovirus is an RNA-containing virus that converts its RNA into DNA by means of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This enables it to become integrated into its host's DNA. Some retroviruses can cause cancer in animals they contain oncogenes (cancer-causing genes), which are activated when the virus enters its host cell and starts to replicate. The special properties of retroviruses make them useful as vectors for inserting genetic material into eukaryotic cells. The best-known retrovirus is HIV, responsible for AIDS in humans.
Assertion: A male is found to be lacking facial hair and pubic hair.
Reason: It is a case of hyposecretion of testosterone from Leydig's cells of testes.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Leydig's cells or interstitial cells of testes are large, polygonal cells that lie in the connective tissue present between the seminiferous tubules. They secrete androgens, the male sex hormones e.g., testosterone into the blood. Androgens control male sexual characteristics including facial and pubic hairs.
Assertion: Extra oxygen consumption in human, body is known as oxygen debt.
Reason: The extra oxygen is required by the body to oxidise the accumulated lactic acid produced during strenuous exercise.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
During strenuous exercise, the muscle does not get sufficient oxygen to meet its energy needs immediately. So, it contracts anaerobically and accumulates lactic acid. During recovery, the oxygen consumption of the muscle far exceeds than that in the resting state. The extra oxygen consumed during recovery is called oxygen debt of the muscle.
Which of the following is not true for inbreeding?
It causes inbreeding depression after a few generations
It always increases the productivity.
It is used to produce a pure line.
It leads to homozygosity
B.
It always increases the productivity.
Inbreeding leads to increase in homozygosity. In recessive alleles, it may cause expression of harmful effects. It may also lead to loss of fitness in progenies, thus decrease productivity in some cases.
Chromatin is made up of
DNA and protein
DNA and histone
DNA, RNA, protein
RNA, histone and oil bodies
C.
DNA, RNA, protein
Nucleus contains nucleoli and chromatin network. Chromatin contains DNA and some basic proteins called histones, some nonhistone proteins and also RNA.
A large quantity of urban sewage is drained to nearby village river. Which among the given conditions would happen after mixing of sewage into the river?
(i) Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of receiving water body increases.
(ii) Dissolved oxygen of receiving water body decreases.
(iii) It will not cause mortality among fishes and other aquatic creatures.
(iv) It will lead to nutrient enrichment of receiving water body.
(i), (ii) and (iii)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
(ii) and (iii)
(iii) and (iv)
B.
(i), (ii) and (iv)
Sewage having biodegradable organic matter is released into water body, micro- organisms involved in biodegradation consumes lot of oxygen to decompose the sewage. This results in a sharp decline in dissolved oxygen downstream from the point of sewage discharge and hence increases biological oxygen demand (BOD).
Presence of large amount of nutrients in water causes excessive growth of planktonic algae known as algal bloom. It causes deterioration of water quality and fish mortality.
Which of the following is a secondary pollutant?
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogen oxides
Peroxyacyl nitrates
All of these
C.
Peroxyacyl nitrates
Secondary air pollutants are photochemically produced from primary pollutants and are thus called photochemical oxidants. Ozone, peroxyacyl nitrates, aldehydes and phenols are produced due to photochemical reactions between nitrogen oxides and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Assertion: In a regular medical examination of a small population, a 35 years old lady was found to have higher levels of oestrogens, progesterone in her blood.
Reason : The lady is 12 weeks pregnant.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) hormone is secreted by the trophoblast cells and is assayed during pregnancy test. It helps in maintaining the mother's corpus luteum. Corpus luteum prevents menstruation and ovulations by secreting oestrogens and progesterones.
Around 10th week of pregnancy, hCG secretion is declined by placenta, menstruation stops and the amount of estrogens and progesterone exceeds the amount secreted by ovaries. High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibits the level of FSH and LH and prevents ovulation. It also maintains the uterus and prepare it for labor and delivery.
Assertion: While working on Staphylococci, Alexander Fleming observed that Penicillin nolatum inhibits the growth of the bacteria.
Reason : This inhibiting chemical was commercially extracted and its full potential was established by Alexander Fleming.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
Alexander Fleming while working on Staphylococci bacteria, once observed a mould growing in one of his unwashed culture plates around which Staphylococci could not grow. He found out that it was due to a chemical produced by the mould and he named it Penicillin after the mould Penicillium notatum. However, its full potential as an effective antibiotic was established much later by Ernest Chain and Howard Florey.
Assertion : Saccharomyces cerevisiae produces acetic acid.
Reason : Trichoderma polysporum produces blood cholestrol lowering agent.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
D.
If both assertion and reason are false.
Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is used for commercial production of ethanol. A bioactive molecule, cyclosporin A which is used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ-transplant patients, is produced by the fungus Trichoderma polysporum.
Assertion : Rice field is an ecosystem for plants and animals.
Reason : Gut of human/animals is an ecosystem for flora and fauna.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
The human digestive system consist of about trillions of micro- organisms colonising the gut. Therefore, it is said to be rich in flora and fauna. The micro-orgnaisms perform various functions such as-
- fermenting unused energy substrates
- training the immune system
- preventing growth of pathogenic bacteria
- regulating the development of gut producing vitamins for the host.
Fish culture is done in combination with a rice crop, so that they are grown in the water. Therefore, it is an ecosystem inhabitaing plants and animals.
Assertion :Now-a-days, the biodiversity is declining with an accelerated rate.
Reason : Exotic species are considered to be a major cause of extinction of species.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
There are four major causes of species extinction due to human interference.
- habitat loss and fragmentation
- over- exploitation
- alien species invasions
- co- extinctions
The exotic species are considered to be second major cause of extinction of species (the first being habitat destruction).
Assertion : Periodic abstinence is a natural method where couples abstain from coitus.
Reason : Coitus from day 5-10 should be avoided because this is the time of ovulation.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
Periodic abstinence is a natural method of birth control in which the couples avoid or abstain from coitus (copulation or intercourse) from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle because ovulation occurs during this period. The chances of fertilization are very high during this period, therefore, it is called the fertile period.
Assertion : Only a boy child could be born with a substitution of glutamic acid by valine on 6 codon of beta-chain of haemoglobin.
Reason : The gene for the above mutation is found on Y-chromosome.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are hue but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
D.
If both assertion and reason are false.
Sickle cell anaemia is an autosomal recessive hereditary disorder in which the erythrocytes become sickle-shaped under oxygen deficiency as during strenuous exercise and at high altitudes. The disease is caused by the formation of an abnormal haemoglobin called haemoglobin- S. It differs from normal haemoglobin in only one amino acid- 6th amino acid of - chain. Glutamic acid is replaced by valine due to substitution of T by A in the second position of the triplet codon (CTC) which is changed to CAC in the - haemoglobin gene on chromosome 11.
What does 'T' stands for in DPT vaccine?
Tuberculosis
Typhoid
Trachoma
Tetanus
D.
Tetanus
DPT vaccine is a combined vaccine against diphtheria, whooping cough (pertussis), and tetanus now replaced by the DTaP/ IPY/ Hib and DTaP/ IPV vaccines.
Which of the following has highest diversity in India?
Mango
Dolphin
Tiger
Orchids
A.
Mango
A single species might show high diversity at the genetic level over its distributional range. India has more than 50,000 genetically different strains of rice, and 1,000 varieties of mango.
Which of the following disorders are caused due to recessive autosomal mutations?
Turner"s syndrome and sickle cell anaemia
Edward's syndrome and Down's syndrome
Cystic fibrosis and phenylketonuria
Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's chorea
C.
Cystic fibrosis and phenylketonuria
Gene related human disorders are determined by mutations in single gene. The pattern of inheritance of Mendelian disorders can be traced in a family by Pedigree analysis.
Cystic Fibrosis is an abnormal recessive disorder of infants, children and young adults. It occurs due to an abnormal recessive autosomal allele present on chromosome 7. Presence of fibrous cysts in pancreas. It produces a defective glycoprotein that causes formation of thick mucus in skin, lungs, pancreas and other secretory organs.
Phenylketonuria is an inborn, autosomal, recessive metabolic disorder in which homozygous recessive individual lacks the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase needed to change phenylalanine to tyrosine in liver. Lack of this enzyme is due to the abnormal autosomal recessive gene on chromosome 12.
Which one is correct?
Salmonella typhi and Haemophilus influenzae cause pneumonia
Widal test is done for malaria
Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebiasis
Wuchereria causes enterobiasis
C.
Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebiasis
Entamoeba histolytica is a protozoan parasite in the large intestine of human which causes amoebiasis (amoebic dysentery).
Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are responsible for the disease pneumonia in humans which infects the alveoli (air filled sacs) of the lungs.
Plasmodium, a tiny protozoan is responsible for malaria. Typhoid fever could be confirmed by Widal test.
Wuchereria (W. bancrofti and W. malayi), the filarial worms cause a slowly developing chronic inflammation of the organs in which they live for many years, usually the lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs and the disease is called elephantiasis or filariasis.
What is the Greek word for ecology?
Ethology
Oekologie
Synecology
Hexicology
B.
Oekologie
The term ecology was coined by combining two Greek words, oikos- 'house' or 'dwelling place' and logos - 'the study of' to denote such relationships between the organisms and their environment. Thus, literally ecology is the study of organisms 'at home'.
Which of the following is correct regarding genetic code?
UUU is the initiation codon which also codes for phenylalanine.
There are 64 triplet codons and only 20 amino acids
Three random nitrogen bases specify the placement of one amino acid
UAA is the nonsense codon which also codes for methionine
B.
There are 64 triplet codons and only 20 amino acids
There are 64-triplet codons that code for 20 amino acids. This is due to the degeneracy of code as some amino acids are influenced by more than one codon. Only tryptophan and methionine are specified by single codons. All other amino acids are specified by two (e.g., phenylalanine UUU, UUC) to six (e.g., arginine CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG AGA, AGG) codons.
The given figure shows L.S of the seed of maize. What do A, B, C and D represent?

A : endosperm, B : scutellum, C : plumule, D : coleoptile
A : scutellum, B : pericarp, C : radicle, D : coleoptile
A : endosperm, B : scutellum, C : radicle, D : coleorrhiza
A : scutellum, B : pericarp, C : plumule, D : coleorrhiza
C.
A : endosperm, B : scutellum, C : radicle, D : coleorrhiza
Endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch.
Scutellum is a small structure shaped like a shield. It is also a modified cotyledon in the embryo of a grass seed.
Radicle is the part of a plant embryo that develops into the primary root.
Coleorhiza is a sheath protecting the root of a germinating grass or cereal grain.
Select the correct statement.
Acetobacter aceti produces citric acid
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used as clot buster
Penicillium notatum restrict the growth of Staphylococci
Methanogens are found in aerobic conditions
C.
Penicillium notatum restrict the growth of Staphylococci
Penicillium notatum restricts the growth of Staphylococci.
Acetobacter acetii produces acetic acid.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for commercial production of ethanol.
Streptococcus produces streptokinase which is modified by genetic engineering to be used as a clot buster for removing clots from the blood vessels of patients.
Bacteria which produce methane are collectively called methanogens and one such common bacterium is Methanobacterium. These are commonly found in anaerobic sludge during sewage treatment.
Which of the following diseases is also called Christmas disease?
Sickle-cell anaemia
Haemoglobinuria
Myocardial infarction
Haemophilia- B
D.
Haemophilia- B
Haemophilia B is due to deficiency of factor IX. Also known as Christmas factor. The patient may experience prolonged bleeding following any injury or wound, and in severe cases there is spontaneous bleeding into muscles and joints.
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited form of anemia. It is a condition in which there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen throughout your body.
Haemoglobinuria is a condition in which the oxygen transport protein hemoglobin is found in abnormally high concentrations in the urine.
Myocardial infarction or heart attack occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to a part of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle.
Which of the following is correct?
All fungi are filamentous.
Transfer of DNA from one bacteria to another bacteria cannot take place
Virus cannot have both DNA and RNA
Protists reproduce asexually only
C.
Virus cannot have both DNA and RNA
Virus is a nucleoprotein entity which is able to utilize the synthetic machinery of a living cell of another organism for its multiplication which does not involve growth and division.The nucleic acid is either DNA or RNA but never both. DNA containing viruses are called deoxyviruses while RNA containing viruses are termed as riboviruses.
CD-4 receptor is associated with
AIDS
Cancer
Malaria
Pneumonia
A.
AIDS
AIDS or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome is a serious disease caused by a retrovirus HIV or Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It results in the depletion of number of T- lymphocytes and renders the patient susceptible to opportunistic infection ie, infection caused by non- pathogens.
What do A, B, C and D represent?

A- Infundibulum; B- Fertilization; C- Myometrium; D- Morula
A- Infundibulum; B- Fertilization; C- Endometrium; D- Blastocyst
A- Isthmus; B- Fertilization; C- Myometrium; D- Blastocyst
A- Isthmus; B- Fertilization; C- Endometrium; D- Morula
B.
A- Infundibulum; B- Fertilization; C- Endometrium; D- Blastocyst
Infundibulum is funnel shaped and is closer to the ovary. Its edges possess finger like projections called fimbriae that helps in collection of the ovum after ovulation.
Fertilization is the fusion of haploid gametes, egg and sperm to form the diploid zygote.
Endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus.
Blastocyst is a structure formed when embryo reaches the uterine cavity after 5 to 6 days of fertilization.
Which animal has the longest gestation period?
Shark
Walrus
Elephant
Dog
C.
Elephant
Gestation period is the fetal development period from the time of conception until birth.
Elephant has the longest gestation period among the given animals. It is of about 624- 641 days.
What is a plasmid?
Bacterial, linear, dsDNA
Extrachromosomal linear RNA
Extrachromosomal circular dsDNA
Autonomously replicating circular RNA
C.
Extrachromosomal circular dsDNA
Plasmid is a structure present in bacterial cells that consists of DNA whichis self- replicating. It is an extra- chromosomal circular double stranded DNA that provides genetic information for various cell activities. For eg, resistance to antibiotic drugs. They are widely used as vectors to produce recombinant DNA for gene cloning.
The concept of chemical evolution is based on
interaction of water, air and clay under intense heat
effect of solar radiation on chemicals
possible origin of life by combination of chemicals under suitable environmental conditions
crystallization of chemicals
C.
possible origin of life by combination of chemicals under suitable environmental conditions
Concept of chemical evolution refers to origin of life from non living matter. First inorganic compounds and then organic compounds were formed in accordance with ever changing environmental conditions.
Which of the following is a correct match between crop, variety and resistance to diseases?
Crop Variety Resistance to diseases Wheat Himgiri White rust Brassica Pusa sadabahar Black rot Cowpea Pusa komal Bacterial blight Chilli Pusa swarnim Chilly mosaic virus
C.
| Cowpea | Pusa komal | Bacterial blight |
| Crop | Variety | Resistance to diseases |
| Wheat | Himgiri | Leaf and stripe rust, hill bunt |
| Brassica | Pusa swarnim | White rust |
| Cowpea | Pusa komal | Bacterial blight |
| Chilli | Pusa sadabahar | Chilly mosaic virus |
Recombinant DNA technology involves several steps in which initial step is of isolation of the DNA. Which enzymes are used in the process for the breakdown of fungal cell, plant cell and bacterial cell respectively?
Lysozyme, lipases, trypsin
Chitinase, cellulase, lysozyme
Chitinase, cellulase, trypsin
Trypsin, lipases, cellulase
B.
Chitinase, cellulase, lysozyme
Process of RDT or Recombinant DNA Technology involves isolation of DNA of a desired DNA fragment. The DNA should be in pure form, free form other macro- molecules.
The bacterial cell or plant or an animal tissue is treated with enzyme lysozyme or cellulase or chitinase (fungal) enzyme respectively in order to break the cell to release DNA. RNA can be removed by treated the cell with ribonuclease and proteins can be removed by treatment with protease.
Which of the following is correct regarding HIV, hepatitis B, gonorrhoea, trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is a STD whereas other are not
Gonorrhoea is a viral disease whereas others are bacterial
HIV is a pathogen whereas others are diseases
Hepatitis B is eradicated completely whereas others are not
C.
HIV is a pathogen whereas others are diseases
HIV or Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a lentivirus that causes HIV infection and leads to AIDS.
Hepatitis B is an infection of liver. It causes scarring of the organ, liver failure and cancer.
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria called Neisseria gonorrhoeae or gonococcus.
Trichomoniasis is also a sexually transmitted disease. It is caused by infection with a protozoan paraite called Trichomonas vaginalis.
Assertion : Interferons are antiviral proteins.
Reason : Interferons are secreted by virus infected cells.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Interferons or IFNs are a group of soluble glycoproteins that are produced and released from cells in response to virus infection. In humans, there are three types of interferons:
1. - interferons
2. - interferons
3. - interferons
Assertion : Inbreeding produces pureline.
Reason : It causes homozygosity.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Inbreeding refers to the mating of closely related individuals within the same breed for 4 - 6 generations. Superior males and superior females of the same breed are identified and mated in pairs. The progeny obtained from such matings are evaluated and superior males and females among them are identified for further mating. Inbreeding increases homozygosity. Thus inbreeding is necessary if we want to evolve a pureline in any animal.
Assertion : Parturition is induced by neural signal in maternal pituitary.
Reason : At the end of gestation period, the maternal pituitary release prolactin which causes uterine contractions.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
D.
If both assertion and reason are false
Parturition is the process of delivery of the foetus. It is induced by a complex neuroendocrine mechanism. The signals for parturition originates from the foetus and the placenta which induces mild uterine contractions called foetal ejection reflex. It triggers release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary. Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscle and causes stronger uterine contractions, which in turn stimulates further secretion of oxytocin. The stimulatory reflex between the uterine contraction and oxytocin secretion continues resulting in stronger and stronger contractions. This leads to expulsion of the baby out of the uterus through the birth canal.
Assertion : Commelina shows cleistogamy.
Reason : This reduces chances of inbreeding.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Commenlia produce two types of flowers-
(i) Chasmogamous: These flowers are similar to flowers of other species with exposed anthers and stigma.
(ii) Cleistogamous: These flowers do not open at all. In these flowers, anther and stigmalie close to each other. When anther dehisce in the flower buds, pollen grains come in contact with the stigma to effect pollination. Thus, cleistogamous are invariably autogamous as there is no chance of cross- pollen landing on the stigma.
What is the source of EcoRI
Escherichia coli R I
Escherichia coli R I 13
Escherichia coli R Y 13
Escherichia coli RX 13
C.
Escherichia coli R Y 13
Eco R I is type II restriction endonuclease enzyme extracted from Eco R Y 13 bacteria. It can recognize and cleave 5'-GAATTC-3' palindromic sequence and is widely used in biotechnology experiments.
Assertion : Antirrhinum is a good example to understand incomplete dominance.
Reason : Heterozygotes show characteristics of both the alleles.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Incomplete dominace is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele of a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele.
Eg, Inheritance of flower colour in Antirrhinum.
There are two types of flower colour in pure state, red and white. When the two types of plants are crossed, the hybrid or plants of F1 generation have pink flowers. The pink colour apparently appears due to mixing of red and white colours.
Parent generation- RR (Red) rr (White)
Gametes- R r
F1 generation- Rr (Pink)
F2 generation- Rr Rr
Gametes- RR (Red) : Rr (Pink) : Rr (Pink) : rr (White)
Phenotypic ratio- Red : Pink : White
1 : 2 : 1
Genotypic ratio- RR : Rr : rr
1 : 2 : 1
First clinical gene therapy was given in 1992 to a 4 years old girl for
adenine deficiency
growth deficiency
adenosine deaminase deficiency
adenosine deficiency
C.
adenosine deaminase deficiency
Gene therapy is a procedure of introducing copies of a healthy gene to replace defective gene responsible for disease development. The first clinical gene transfer took place on 22nd May 1992 for correction of adenosine deaminase (ADA) enzyme deficiency.
Assertion : Presence of large amounts of nutrients in water body causes excessive growth of planktonic algae.
Reason : It is due to biomagnification.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Presence of large amounts of nutrients in water causes excessive growth of planktonic algae or free- floating algae. It is known as algal bloom as it imparts a unique colour to the water bodies. Algal bloom cause deterioration of the quality of water and fish mortality.
Biomagnification is the process by which a compound such as pollutant or pesticide increases its concentration in the tissues of organisms as it travels up the food chain.
What are labelled phases A, B and C in given sigmoidal growth curve.

A B C stationery Log Lag A B C Lag stationery Log A B C Log Lag stationery A B C Lag Log stationery
D.
| A | B | C |
| Lag | Log | stationery |
When a graph is plotted taking into consideration time on one hand and growth rate on the other hand, a 'S' shaped curve is obtained. It is called "grand period of growth". This total growth period is divided into three stages.
(1) Initial lag phase
(2) Middle log phase
(3) Final stationary phase
Monarch butterfly escapes from predators by
foul smell
bitter taste
colour combination
rough skin
B.
bitter taste
Monarch butterfly escapes from predators because of its bitter taste. Viceroy butterfly (Basilarchia archippus) mimics monarch butterfly to escape from predators.
What is the characteristic of tapetum
It does not store food.
It is multi-nucleated.
It is multi-layered structure.
It nourishes the megaspore
B.
It is multi-nucleated.
Tapetum is the innermost one cell thick layer of microsporangium wall. The cells of this layer are radially enlarged and store food. The cells are multinucleated and provide nourishment to developing microspores or pollen grains.
In vehicles, catalytic converters are used
to increase mileage of vehicles
to convert CO2 into carbonates
to increase the efficiency of lead mixed petrol
to convert CO to CO2
D.
to convert CO to CO2
Catalytic converters have platinumpalladium and rhodium metals as catalyst. It converts more harmful carbon monoxide and unburnt hydrocarbons into less harmful carbon dioxide and water.
Assertion : DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in specific regions in DNA sequence.
Reason : DNA fingerprinting is the basis of paternity testing.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in some specific regions in DNA sequence called as repetitive DNA, as there is a small stretch of DNA which is repeated many times. These do not code for any proteins, but they form a large portion of human genome. These sequence show high degree of polymorphism and form the basis of DNA fingerprinting. As the polymorphisms are inheritable from parents to children, DNA fingerprinting is the basis of paternity testing in case of disputes.
Assertion : All pathogens are parasites but all parasites are not pathogens.
Reason : Majority of the parasites confer benefits to the host.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Parasitism is a relationship between two living organisms of different species in which one organism called parasite obtains its food directly from another living organism called host. Majority of the parasites harm the host; they may reduce the survival, growth and reproduction of the host and reduce its population density. Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms which get benefit by causing harm to host organism. Pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoans, helminths, insects etc., reproduce or multiply inside the host organism and therefore, they get the opportunity to complete the life cycle and spread their population.
Which of the following is best method of germplasm conservation
Herbarium
Botanical garden
Seed bank
Zoological park
C.
Seed bank
Endangered plants may be preserved in part through seed bank or germplasm bank. The term seed bank sometimes refers to a cryogenic laboratory facility in which the seeds of certain species can be preserved for up to a century or more without losing their fertility. It can also be used to refer to a special type of arboretum where seeds are harvested and the crop is rotated. For plants that cannot be preserved in seed banks, the only other option for preserving germplasm is in vitro storage, where cuttings of plants are kept under strict conditions in glass tubes and vessels.
Which one of the following options is a correct match of phenomenon and its explanation
Reverse Transcription PCR - Many copies of a DNA sequence.
Central dogma - RNA > DNA > Protein > RNA.
RNA silencing - Use of ds-RNA to stop the expression of ss-RNA.
Transcription- Process of formation of RNA & proteins.
A.
Reverse Transcription PCR - Many copies of a DNA sequence.
Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) is a variant of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), a laboratory technique commonly used in molecular biology to generate many copies of a DNA sequence, a process termed 'amplification'. In RT-PCR, however, an RNA strand is first reverse transcribed into its DNA complement (complementary DNA, or cDNA) using the enzyme reverse transcriptase, and the resulting cDNA is amplified using traditional PCR or Real-Time PCR.
Which of the following is correct
Henking discovered the small Y-chromosome.
Drosophila also shows XX-XY sex determination like human.
Birds have ZZ-ZW sex determination, where females are ZZ & males are ZW.
Grasshoppers show XX-XY sex determination
B.
Drosophila also shows XX-XY sex determination like human.
Hermann Henking discovered the X chromosome while studying insects in the early 1890s.
The sex chromosomes in birds are opposite of that in humans. Human males areheterogametic (XY), females are homogametic (XX), in birds males are homogametic (ZZ) and females are heterogametic (ZW). The 'W' is the sex determining chromosome just as the Y in humans. A bird with a W is always a female.
In grasshoppers, there is no Y chromosome, so a grasshopper with one X chromosome (symbolized as XO) is normally a male, while a grasshopper with two X chromosomes (XX) is normally a female.
Which of the following statements is correct
Monkey, apes and humans exhibit estrous cycle.
Urine is pale yellow and slightly alkaline.
Lots of enzymes are present in bile juice.
Ovulation in humans is spontaneous.
D.
Ovulation in humans is spontaneous.
Great apes, humans goes through a menstrual cycle while monkey goes through estrous cycle.Urine is light yellow colored watery fluid which is slightly acidic. Bile juice does not contain any digestive enzymes.
Which of the following evidences does not favour the Lamarckian concept of inheritance of acquired characters
Absence of limbs in snakes
Melanization in peppered moth
Presence of webbed toes in aquatic birds
Lack of pigment in cave-dwelling animals
B.
Melanization in peppered moth
Industrial melanism is an adaptation where the moths living in the industrial areas developed melanin pigments to match their body to the sootcovered surroundings. The phenomenon provides an excellent example of operation of selection in natural conditions.
Industrial melanism, therefore, presents an excellent example of natural selection (proposed by Darwin), but it is not the example of acquired characters proposed by Lamarck. In caves, due to absence of light, the body of the animal lacks pigmentation. e.g. Proteus anguinus
Assertion: Amount of organic biodegradable compounds present in water is measured by the BOD of that water.
Reason: During biodegradation of biodegradable organic compounds, oxygen is released by bacteria
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Organic biodegradable (i.e. they can be degraded by decomposers) pollutants in water are measured by BOD. BOD( biological oxygen demand) is the oxygen demanded or required by bacteria and other decomposers to oxidise pollutants.
In assisted reproductive technology where gametes have been fertilized in vitro, which of the following is practicable for embryo transplantation in Fallopian tube
Only embryo up to 8 blastomeres if zygote is not transplanted.
Only zygote is transplanted not embryo
Either embryo or zygote with 8 blastomere phase transplanted
Morulla with 8-24 celled stage is transplanted in Fallopian tube.
A.
Only embryo up to 8 blastomeres if zygote is not transplanted.
In in vitro fertilization (IVF-fertilization outside the body in almost similar conditions as that in the body) followed by embryo transfer (ET), ova from the wife/donor (female) and sperms from the husband/donor (male) are collected and are induced to form zygote under simulated conditions in the laboratory. The zygote or early embryos (with upto 8 blastomeres) could then be transferred into the Fallopian tube (ZIFT-Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer) and embryos with more than 8
Which of the following features can be said to be a true defining feature of living beings without any exception
They can digest their food.
All of them can reproduce.
They can regenerate.
They can respond to external stimuli.
D.
They can respond to external stimuli.
All organisms, from the prokaryotes to the most complex eukaryotes can sense and respond to environmental cues eg. Photoperiod affects reproduction in seasonal breeders, both· plants and animals. Consciousness therefore, becomes the defining property of living organisms.
Assertion: In some species of asteraceae and poaceae seeds are formed without fertilization.
Reason: Formation of fruit without fertilization is called parthenocarpy.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Formation of seeds without fertilization is called apomixis. It leads to clonal reproduction in which all offsprings are by and large genetically identical to the parent. The egg contains a full complement of genes and does not need to fuse with a sperm to produce a zygote. Apomixis provides for the perpetuation of traits favourable to individual survival but eliminates the longer-term evolutionary advantage of biparental inheritance. In Asteraceae, various genera and individual species of the order asterales are known to reproduce by apomixis (the setting of seeds without fertilization), either completely or in addition to normal sexual means.
In poaceae about 35 genera produce seeds without fertilization. On the other hand, parthenocarpy is development of fruits without fertilization. The fruit resembles a normally produced fruit but is seedless, e.g. pineapple, banana, cucumber, grape, orange, grapefruit etc.
Assertion: Algal blooms are formed in nutrientless water.
Reason: Algal blooms in water turn it unfit for human consumption, but cause enormous growth of fish.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
D.
If both assertion and reason are false.
Algal blooms are a result of eutrophication. Eutrophication involves change in biological
productivity and nutrient content of a water body. They are harmful for both humans and aquatic
organisms. Eutrophication results in higher BOD and reduced dissolved oxygen in water body.
It causes death of fish and other aquatic animals.
Assertion: A mangrove tree growing in marshy place has pneumatophores.
Reason: Pneumatophores help in better anchorage to marshy soil.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Mangroves which form shallow littoral forests near sea shores areas are halophytes. Mangrove grow in physiologically dry environment (water is available in plenty but in the form of strong salt solution). These plants develop shallow rootings due to water logged environment where oxygen scarcity prevails. To ensure proper aeration in root system, plants produce respiratory roots or pneumatophores which are negatively geotropic peg-like projections above ground with numerous pores or lenticels for gaseous exchange:
Assertion: A geneticist crossed two plants, he got 50% tall and 50% dwarf progenies.
Reason: It follows Mendelian law as one of the parent plant might be heterozygous.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
It can be explained as follows

or 50% tall, 50% dwarf progeny
Assertion: Now-a-days amniocentesis is banned.
Reason: Amniocentesis gives the information of any abnormality in the foetus and many other complications regarding pregnancy can be detected.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Amniocentesis is a foetal sex determination and disorder test based on the chromosomal pattern in the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing embryo. The amniotic fluid contains cells from foetus skin and respiratory tract.
These cells are cultured and are used to determine chromosomal abnormalities (Down's syndrome, Klinefelter's syndrome, etc.) and metabolic disorders (phenylketonuria, sickle cell anaemia, etc.) of the foetus. But now-a-days instead of positive uses of amniocentesis it is being used for female foeticide. Sex of the foetus is determined using amniocentesis and then if it turns out to been a female one, foetus is aborted. That is why amniocentesis has been banned in India.
Assertion: A gene from Bacillus thuringiensis is incorporated in plant genome to increase their yield.
Reason: Bacillus thuringiensis has Bt toxin producing gene, which kills the larva of insects
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Bacillus thuringiensis is a bacterium found in soil worldwide. Several strains can infect and kill insects. Due to this property, through genetic engineering, gene coding for insecticide is incorporated into plant genome. Plant having this gene are insect resistant thus high yielding e.g. Bt cotton is usually resistant to bollworm disease of cotton. It is the first genetically modified crop of India. This produces its own insecticide, as it contain a gene from soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis.
Assertion: Blood group 'O' have anti-A & antiB antibodies.
Reason: It does not have any antigens.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
ABO blood groups are determined by the gene I (iso agglutinin). There are three alleles, IA, IB and IO of this gene. Proteins produced by the IA and IB alleles are called A antigen and B antigen. People with blood group A have the A antigen on the surface of their RBCs, and antibodies against antigen Bin their plasma. Persons with blood group B have B antigen on their RBCs, and antibodies against A antigen in their plasma. Individuals with AB blood group have both antigen A and antigen B on their RBCs, and no antibodies for either of the antigens in their plasma. Type O individuals are without A and B antigens on their RBCs, but have antibodies for both these antigens in their plasma.
Assertion: Corpus luteum is produced by Graafian follicle after ovulation.
Reason: It secretes estrogen which is necessary to maintain pregnancy.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
After ovulation, the empty Graafian follicle contains a blood clot which is called corpus haemorrhagic. Its granulosa cells continue to proliferate, develop yellow carotene pigment or lutein and get converted into lutein cells. This converts the ruptured follicle into yellow body called corpus luteum. It becomes a temporary endocrine gland secreting progesterone with small quantity of estrogen.
Assertion: Sporozoites of malarial parasite enter in the human body due to biting of freshly born female Anopheles mosquito, whose mother was a carrier of malarial parasite.
Reason: Male and female gametocytes of malarial parasites are formed in the human intestine
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
A healthy person acquires infection when a female Anopheles mosquito, containing infective stages of parasite (sporozoites) in its salivary glands, bites him for sucking his blood. The mosquito punctures the host's skin by its proboscis and first introduces some saliva into blood stream. Along with saliva, thousands of sporozoites contained therein are also inoculated. Sporozoites represent the infective forms of parasite.
Which form of reproduction is correctly matched?
Euglena transverse binary fission
Paramecium longitudinal binary fission
Amoeba multiple fission
Plasmodium binary fission
C.
Amoeba multiple fission
Reproduction is an essential feature of all living organisms. It is the process by which an individual multiplies in number by producing more individuals of its own type.
Amoeba proteus does not reproduce sexually. The reproduction is essentially asexually and takes place by various methods such as binary fission, multiple fission and sporulation. Binary fission is the most common mode of reproduction. It results in the division of the parent Amoeba into two daughter amoebea. Amoeba reproduces by multiple fission during adverse environmental conditions.
Euglena has longitudinal binary fission. Paramecium has transverse binary fission and Plasmodium has multiple fission.
Assertion: Many plants are propagated vegetatively even though they bear seeds.
Reason: Potatoes multiply by tubers and apple by cutting.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
The most common form of asexual reproduction in plants is called vegetative propagation. It is the formation of new plants from vegetative units (propagules) such as buds, tubers, rhizomes, roots, stem, leaf etc. Besides the natural methods of vegetative propagation, there are a number of techniques for artificial vegetative propagation of economically and aesthetically important plants. Potatoes are produced by tubers and not by seeds. Stem tubers are found in potato and artichoke. They have buds in the region of nodes or eyes for vegetative multiplication. Root cuttings are used in propagation of lemon, apple, orange, blackberry etc.
Noncleidoic eggs occur in
birds
fish
reptiles
platypus
A.
birds
Non Cleidoic egg - Egg membranes are soft in these eggs e.g. All viviparous animals and in oviparous animals which lays eggs in water.
Division in a bacterial cell is carried out through
multiple fission
binary fission
budding
plasmotomy
B.
binary fission
Division of bacterial cell is carried out by binary fission, in which, a single cell divides into two equal sized cells after developing a transverse cell wall.
Multiple fission is the division of the nucleus, simultaneously or successively into a number of daughter nuclei, followed by division of the cell body into an equal number of parts each containing a nucleus.
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site.
Plasmotomy is a type of asexual reproduction in which a multi- nucleate protozoan cell divides into two or more multi- nucleate daughter cells without the occurence of mitosis.
Which of the following two hormones are essential for induced breeding of fishes?
TSH and ACTH
Oestrogen and progesterone
FSH and LH
Vasopressin and oxytocin
C.
FSH and LH
Induced or artificial methods of breeding are used to obtain desirable eggs. In this ova from the desired female and sperms from the desired male are obtained by artificial mechanical process and the ova gets fertilized by the sperms and then fertilized eggs are collected. FSH and LH present in pituitary extract helps in induced breeding.
One micrometer is equal to
0.0001 mm
0.001 mm
0.01 mm
0.00001 mm
B.
0.001 mm
1 micrometre/ micron/ m/ = 0.001 mm
1 mm = 10-3 mm = 10 -6 m = 10-4 cm
Product of sexual reproduction generally generates
longer viability of seeds
prolonged dormancy
new genetic combination leading to variation
large biomass
C.
new genetic combination leading to variation
Sexual reproduction leads to new genetic combination leading to variation in new products. Longer viability of seeds, prolonged dormancy and large biomass are not related to sexual reproduction.
Which of the following processes was discovered by Lederberg and Tatum (1946)?
Transduction
Transformation
Asexual reproduction
Conjugation
D.
Conjugation
Bacterial conjugation is the phenomenon of transfer of genetic material between the bacterial cells with the help of conjugation bridge (tube) or cell to cell contact. This process was firstly discovered by Joshua Lederberg and Edward Tatum in 1946. During conjugation the donor cell provides a conjugative or mobilisable genetic element to the recipient cell.
The component of bacteria that retains the crystal violet stain during Gram staining is
O- antigen
lipopolysaccharide
peptidoglycan
cytoplasmic membrane
C.
peptidoglycan
Gram staining is the method of differentiating bacterial species into two large groups, i.e., Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria based on the physical properties of their cell walls.
In the process of Gram staining
- alcohol is used for decolourlisation process. It solubilises lipid but does not solubilise peptidoglycan layer.
As Gram positive bacteria has less lipid percentage as compared to peptidoglycan. Thus, peptidoglycan which does not get solubilised retain the Gram stain and Gram negative bacteria which has thinner peptidoglycan layer cannot retain the Gram stain.
Neoteny refers to
development of gonads
moulting
metamorphosis
retention of larval traits in the adult body
D.
retention of larval traits in the adult body
Neoteny refers to retention of some larval or immature character in adulthood. The development of the gonads is a part of the development of reproductive system and ultimately forms the testes in males and ovaries in females.
Moulting is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle. Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching.
Select the correct statements from the following regarding asexual reproduction.
I. It is slower than sexual reproduction.
II. It involve a single parent.
III. It produces progeny that are genetically identical with the parent.
IV. Clones are the progeny of asexual reproduction
I, II, III, IV
I, II, IV
I, II, III
II, III, IV
D.
II, III, IV
Statement II, III and IV are correct.
Asexual reproduction is a rapid mode of reproduction involving single parent. Since, no meiosis and gametic fusion occur, genetic variation is not observed in offspring. These are clones of their parent and are genetically identical. It is a uniparental phenomenon. The organisms increase their mass and maturity until at a critical point. They reproduce by simple division of their substance. Each successive organism has the same physio-chemical constitution as the parent.
Multiplication of genetically identical copies of a cultiver by asexual reproduction is known as
aclonal propagation
clonal propagation
vegetative propagation
polyclonal propagation
B.
clonal propagation
Clonal propagation is the process of vegetative propagation in which clones are multiplied by culture techniques. Vegetative propagation is the culture process in which callus is grown and differentiated.
How many ovum are developed in ovary of Hydra?
Two
Many
One
Three
C.
One
In Hydra generally one egg is present in ovary but sometimes in unfavourable condition two eggs are formed.
Gametes formation in animals is found in
ovaries
gonads
gall bladder
testes
B.
gonads
Gametogenesis is the process of forming gametes from diploid cells of the germ line. In animals, it takes place in gonads.
Hydra is
herbivorous
more developed
carnivorous
omnivorous
A.
herbivorous
Hydra are carnivorous and feed mainly on small crustaceans like water fleas (Daphnia) and small worms.
In rabbit, head of epididymis present at the head of the testis is called
vas deferens
cauda epididymis
gubernaculum
caput epididymis
D.
caput epididymis
In rabbit head of epididymic present at the head of the testis is called caput epididymis.
Epididymis differentiated into smaller posterictir enlarged part is called caud epididymis.
Gubernaculum is fibro muscular mesodermal tissue which helps in positioning the testes within the scrotal sac.
The most primitive cell like chemical aggregates capable of growth and division were
chemoautotrophs
eobionts
prokaryotes
microspheres
D.
microspheres
Microspheres are the most primitive cell like chemical aggregates. They resemble coccoid bacteria. These are molecular aggregates of proteinoids and capable of growth and division (binary fission or by budding).
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





