Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology And Its Applications
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 Biology Biology
What is transgenic organism ?
Write two applications of biotechnology.
1. Treatment of diseases.
2. Production of genetically modified plants and animals.
What are probes ?
What are transgenic animals ?
Name two diseases that can be treated by producing biological compound in transgenic animal.
1. Emphysema.
2. Cystic fibrosis.
What is the utility of Bt-Toxin gene ?
How is inactive Bt-toxin converted into active form ?
How Bt toxin causes death of insect ?
List the specific insects killed by (i) cryIAc and (ii) cryIAb.
What is unique about transgenic animals ?
What is silencing of mRNA ?
Sponsor Area
Name the transgenic cow which produces human protein enriched milk. Give specific contents of milk.
(ii) The milk was enriched with human alpha-lactalbumin.
What is unique about Indian Basmati unique ?
(i) Aroma and
(ii) Flavour.
What is complementary DNA (cDNA) ?
Name two genetically engineered microbes.
(ii) Aspergilus niger a fungus.
What is the application of genetically engineered bacterium namely Pseudomonas putida ?
How did the first transgenic cows Rosie differ from other cows with respect to the quality of milk ?
List three critical research areas of biotechnology.
1. Providing the best catalyst in the form of improved organism usually a microbe or pure enzyme.
2. Creating optimal conditions through engineering for a catalyst to act, and
3. Downstream processing technologies to purify the protein/organic compound.
Give the few characteristics of GMOs.
(1) Their genes are altered by manipulation.
(2) They have incresed resistance to pests and can tolerate abiotic stresses more efficiently.
(3) They have high nutritional value.
(4) They may produce biological products which help in curing diseases.
List a few transgenic organisms and their potential application.
|
Transgenic |
Useful applications |
|
1.Bt Cotton 4.Cattles (cow, sheep, goat). |
2.Increased shelf-life (delayed ripening) and better nutrient quality. 3. Rich in Vitamin-A 4.Therapeutic human proteins in their milk |
What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produce it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
They are produced by bacteria called Bacillus thuringiensis. The toxic protein is present in active form in bacteria which when ingested by an insect leads to the activation of protein and subsequent death of insect.
Man has benefited from this protein by incorporating the Bt-toxin gene that produces the Cry protein in several crop plants like cotton. The incorporation of gene in plants makes them insect resistant and thus help in good yield and productivity.
Mention any six fields of application of biotechnology for human welfare.
(i) Therapeutics (ii) Genetically modified crops
(iii) Molecular diagnostics (iv) Processed food items.
(v) Bioremediation (vi) Gene therapy.
(vii) Vaccine production.
List two uses of cloned genes in molecular diagnostics.
1. Cloned genes can be used as probes to detect the mutated gene responsible for the disease from a pool of molecules.
2. Cloned gene can be used to detect antibodies or antigens in infections. Like in ELISA which is based on antibody-antigen interaction.
How is ELISA test carried out ?
Steps of ELISA
1. A micro titer plate is coated with antigen.
2. Primary antibody specific to antigen for diagnosis is added to the plate. The antibody interacts with the antigen. then the plate is washed to remove any extra free antibody.
3. Secondary antibody which has a tag is then added to the well. The secondary antibody attaches to the primary antibody. The plate is washed to remove free secondary antibody.
4.Chromagen is added which produces color and aids in detection.
Name two of common pharmaceutically important products obtained through genetic engineering.
1. Human insulin.
2. Vaccines .
How insulin is synthesised in human (or mammals) . Give a suitable diagram?
Synthesis of insulin in humans-:
i. Insulin is synthesised as an inactive form pro-insulin which contains an extra stretch called the C peptide.
ii.This pro-insulin is cleaved.
iii. C-peptide is removed and
iv. The two chains A and B are joined by disulfide bridges to form mature insulin.
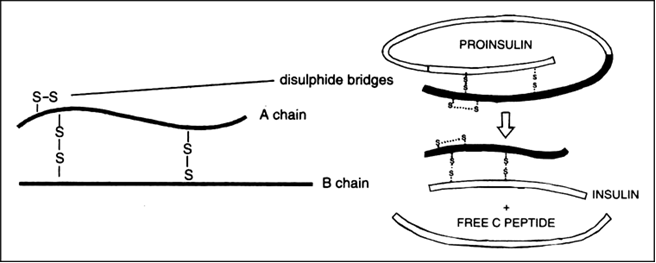
Fig.- Proinsulin which contain C-peptide is cleaved and C-peptide is removed and the Two chains A and B are joined to by disulfide bridges to form insulin.
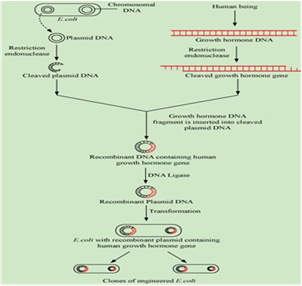
How is E.coli used to produce human insulin?
E.coli can be used to produce human insulin in the following way.
1. Gene encoding for the production of insulin in humans is isolated. Like the gene for two insulin chain A and B are isolated.
2. The desired genes are introduced in plasmids of two E.coli.
3. Since the plasmid is self replicating the introduced gene is expressed and the two chains A and B are formed separately.
4. These chains are extracted
5. They are joined by creating disulfide bonds to form insulin.
What is gene library ?
Define probes.
Why is the use of probes considered better than conventional diagnostic tools for disease diagnosis ?
1. They are highly specific, relatively rapid and much simpler.
2. They fascilitate detection because they have a tagged radioactive molecule.
3. They help in detecting even a single mutation in gene.
Why mice are considered most suitable animals for transgenic production ?
i. Short life cycle and reproductive cycle.
ii. Large number of off springs.
iii. Allow genetic manipulation.
iv. Closely related to humans.
v. Their genome is sequenced so manipulations are easy.
Sponsor Area
Write the advantages of recombinant therapeutics.
How many of them have been approved world over for human use and how many are available in Indian market ?
(a) Recombinant therapeutics are very effective and more potent.
(b) The recombinant therapeutics are safe and do not induce unwanted immunological responses like similar products of non-human origin.
About 30 recombinant therapeutics have been approved world over.
12 of them are being marketed in India.
What are ethical issues with genetic engineering?
1. Use of animals in research causes greater suffering to them.
2. Grant of patents to companies benefits them but the farmers are at loss.
3. Biopiracy
Explain the social, economical and environmental advantage of genetic engineering techniques.
1.Social - Since the transgenic crops show high productivity and nutitional value it can solve social issues like hunger and poor nutrition.
2. Economic- The transgenic crops have a high yield and vaccines produced by genetic engineering can prove economical and highly useful.
3. Environmental - Genetically engineered microbes are used to clear oil spills and also increase the fertility of soil.
Write a short note on :
(a) Production of human growth hormone by E. coli.
(b) Animals as organ donors for humans.
(b) Animals as organ donors for human. Organ transplantation from animal to humans is called as xenotransplantation. Usually baboons are used for transplantation as they are closely related to humans and chances of rejection are less.
Explain the following terms in one or two sentences : intellectual property rights, humulin and biofortified foods.
(ii) Humulin. It is the human insulin made using E.coli and recombinant DNA technology
(iii) Biofortified foods. They are food rich in nutritional values produced using genetic engineering.
What are transgenic bacteria ? Illustrate using any one example.
Example. Transgenic bacteria like E.coli which produces insulin. This bacteria is genetically manipulated by introducing two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin in plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains. Chains A and B produced separately are extracted and combined by disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
What are Cry proteins ?
Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based
on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Find out from internet what is golden Rice.
Does our blood have proteases and nucleases ?
Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Orally active protein pharmaceuticals are biologically active protein or peptides administered orally for the treatment of various diseases.
Orally active proteins pharmaceuticals are made by encapsulating the protein or peptide in liposomes or formulations. The encapsulation fascilitates their delivery.
The major problem encountered with orally active protein is that they are degraded by the proteases present in the stomach and thus their effect is nullified.
Explain the following terms briefly
(a) Single cell proteins (b) Biopatent (c) Bioethics (d) Biopiracy (e) Genetically modified food.
(b) Biopatent. is a patent right granted for a invention in the field of biology by a Government to an inventor to prevent others to make commercial use of their invention.
(c) Bioethics. Bioethics is the study of ethical issues that come up with the advances in the field of biology
(d) Biopiracy. Exploitation of biological resource by others without proper permission and without providing compensation from the people or country concerned.
(e) Genetically Modified Food. The food produce by genetically modified crops is called genetically modified food (GM food).
Briefly explain why are Transgenic animals produced ?
(i) Transgenic animals are designed to allow the study the regulation and functioning of gene.
(ii) Transgenic animals are designed to understand the development of diseases and their detection.
(iii) Transgenic animals are used to produce useful biological compounds .
(iv) Transgenic animals are used to test the safety of vaccines.
State the ethical issues in using transgenic animals.
1.The transgeniv animals that are used as model are only produced to solve the purpose and usually suffer alot.
2. Crossing species or recombinant species is unnatural, immoral.
3. Transgenic animals can have unpredicatable results when such organisms are introduced into the ecosystem.
4. The use of non human gene in humans and human cloning is socially unacceptable.
Compare and Contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Advantages and Disadvatages of Genetically modified (GM) Crops.
| Advatages | Disadvantages |
| 1. GM crops are developed for pest resistance and thus the yield increases and there is less dependence on pesticides. | 1. GM crops that show pest resistance prove harmful for pollinators and hence pollination. |
| 2. GM crops are developed to increase the nutritional value in the crops. | 2. GM crops can lead to severe allergies in some and may not be as good in taste as the natural crop. |
| 3. They can be used to develop crops which are more tolerant to abiotic stresses | 3. The pollen of GM crops is also modified and can lead to the development of resistance and growth of super-weeds. Weeds prove harmful to the environment and crops. |
| 4. GM crops can be developed to have antibiotic properties | The intake of GM crops having antibiotic properties may lead to antibiotic resistance in some and less efficacy of antibiotic medications. |
| 5. GM crops can be modified to benefit humans. | 5. The patent provided for the development of GM crops has been creating problems because the companies are benefited while the farmers are at loss. |
What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Gene Therapy. It is defined as the introduction of a normal functional gene into cells which contain the defective gene with the objective of correcting a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo.
For example - Treatment of ADA deficiency by gene therapy. Adenosine deaminase is an enzyme crucial for funtioning of immune system. Gene therapy has been used to cure the deficiency of ADA enzyme
1. By growing the lymphocyte from blood cells of patient in culture outside the body.
2. A funtional ADA gene is introduced in the cultured lymphocyte using retrovirus.
3.The transformed lymphocytes are then returned to the patient.
4. Thus the cells now contain funtional gene for the enzyme and deficiency is cured.
How was the milk of the first transgenic cow Rosie different from the non transgenic cows?
(i) It was enriched with human alpha lactalbumin protein that is absent in milk of normal cow.
(ii) It was nutritionally more balanced product for human babies as compared to the milk of normal cows.
How is transgenic tobacoo plant protected against Meloidegyne incognita ? Explain the process ?
1. The specific genes from the parasite are introduced into the plant using Agrobacterium as the vector.
2. The introduced gene produces both sense/coding RNA and antisense RNA .
3. The two RNA being complementary anneal and become double stranded RNA.
4. This ds RNA initiates RNAi and silences the mRNA of the nematode.
5. As a result, the parasite cannot live in the transgenic host and the transgenic plant is protected from the pest.
Describe the responsibility of GEAC, set up by the Indian Government.
(i) It makes decisions regarding the validity of GM research.
(ii) It also ensure the safety of introducing GM-organism for public services.
Why insulin is being extracted from bacteria rather than animal source ?
Or
Name the source from whice insulin was extracted earlier.
Insulin was earlier extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cows and pigs
Biopiracy is related to which of the following ? - Transgenic animals
- Genetics
- Bioresources and their misuse.
- All of the above
C.
Bioresources and their misuse. What are transgenic plants ? - Plants which have no extra or foreign gene.
- Plants containing specially introduced genes and hence showing tolerance to certain herbicides
- A crop plant which is destroyed by herbicides
- A plant susceptible to insect pests
B.
Plants containing specially introduced genes and hence showing tolerance to certain herbicides The biological activity of cell on cryopreservation : - Essentially ceases
- Is normal
- Doubles
- All of the above
A.
Essentially ceases An example of gene therapy is : - production of injectable Hepatitis B vaccine
- production of vaccines in food crops like potatoes which can be eaten
- introduction of gene for adenosine deaminase in persons suffering from ADA deficiency.
- production of test tube babies by artificial insemination and implantation of fertilized eggs.
C.
introduction of gene for adenosine deaminase in persons suffering from ADA deficiency. Cultivation of Bt cotton has been much in the news. The prefix Bt means : - Barium treated
- Bigger thread
- Biotechnology
- Bacillus thuringiensis
D.
Bacillus thuringiensis The protein encoded in which gene control boll worm. - CryIAc
- CryIIAb
- Both (A) and (B)
- CryIIAb
C.
Both (A) and (B)Mention the type of host cells suitable for the gene guns to introduce an alien DNA.
Plant cells are considered suitable for the gene guns to introduce an alien DNA.
State how Agrobacterium tumifaciens has been made a useful cloning vector to transfer DNA to plant cells.
Agrobacterium is a pathogen that affects several dicots and delivers a piece of DNA known as ‘T-DNA’ to transform normal cells to tumor cells. This potential of Agrobacterium has been used to transfer desired gene into the plant. The desired gene is inserted in the T-DNA region and the bacterium is allowed to infect the plant. In this way, the desired changes are made in the plant.
How are 'sticky ends' formed on a DNA strand? Why are they so called?
Sticky ends are produced by restriction enzymes. These enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites but between the same two bases on the opposite strands. This leaves single-stranded portions at the ends. These overhanging stretches are called 'sticky ends'.
These are called sticky ends because they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. This stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.How did the process of RNA interference help to control the nematode from infecting the roots of tobacco plants?
RNA Interference (RNAi) is a gene-silencing process that is used for cellular defense in all eukaryotic organisms. RNAi has been used to control the nematode Meloidegyne incognitia that affects the roots of tobacco plants in the following way:
Using Agrobacterium vectors, nematode specific genes were introduced in the host plant. The genes were introduced in such a way that it produced both sense and anti-sense RNA in the host cells. The two RNA’s being complementary to each other form a double-stranded RNA dsRNA that initiates RNA interference and silences mRNA that is it inhibits mRNA expression. The nematode is not able to survive in the host which expresses specific interfering RNA and thus the plant is protected from the nematode.
Sponsor Area
What is Biopiracy?
Biopiracy is the use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper authorisation from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment.
Recombination DNA technology is of great importance in the field of medicine. With the help of a flow chart, show how this technology has been used in preparing genetically engineered human insulin.
Preparation of Human Insulin Using Recombinant DNA Technology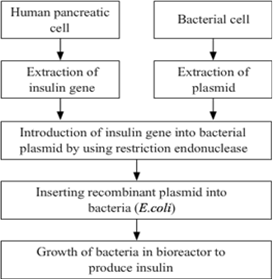
Following the collision of two trains a large number of passengers are killed. A majority of them are beyond recognition. Authorities want to hand over the dead to their relatives. Name a modern scientific method and write the procedure that would help in the identification of kinship.
DNA fingerprinting is the modern scientific method used for the identification of kinship. Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (VNTR) are satellite DNAs that show high degree of polymorphism. They are used as probes in DNA fingerprinting.
Procedure of DNA Fingerprinting:
i. Firstly, DNA from the individual and closest relative is isolated and cut with restriction endonucleases.
ii. Fragments are separated according to their size and molecular weight through gel electrophoresis of both the individual and the relative.
iii. Fragments separated through electrophoresis gel are blotted (immobilised) on a synthetic membrane such as nylon or nitrocellulose.
iv. Immobilised fragments are hybridized with a VNTR probe.
v. Hybridised DNA fragments can be detected by autoradiography. The autoradiograph of the individual and the relative is compared.
VNTRs vary in size, ranging from 0.1 to 20 kb. Hence, in the autoradiogram, a band of different sizes will be obtained. These bands are characteristics of an individual. They are different in each individual, except in the case of identical twins. The presence of similarities, between the individual and the relative helps to determine the kinship.
Hence the body of the individual can be handed over to their relatives.
Expand the following and mention one application of the following
(i) PCR (ii) ELISA
(i) PCR - Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is used to amplify the gene of interest.
(ii) ELISA - Enzyme linked Immuno-sorbent Assay. It is widely used as diagnostic test for AIDS.
(a) Mention the difference in the mode of action of exonuclease and endonuclease.
(b)How does restriction endonuclease function?The difference between the mode of action of endonuclease and exonuclease is that Exonuclease removes nucleotides from the ends of the DNA whereas Endonuclease makes cut at specific positions within the DNA.
(b) Restriction endonuclease functions by inspecting the entire length of the DNA sequence. When it finds the specific recognition sites it binds to the DNA molecule and cuts both the strands at specific palindromic sites in their sugar-phosphate backbone.
e.g. Eco R1 cuts the DNA at following pallindromic sequences.
|
5' G A A T T C 3'
3' C T T A A G 5'
|
(a) Why are transgenic animals so called?
(b) Explain the role of transgenic animals in
(i) Vaccine safety
(ii) Biological products with the help of an example each.
(a) Transgenic animals are so called because they have their DNA manipulated and thus they possess and express foreign gene.
(b) Role of transgenic animals in :
(i) Vaccine safety
Transgenic mice are being developed and used to test the safety of the vaccine before they are used on humans.
(ii) Biological products
Transgenic animals are developed and their genes are manipulated so that they produce certain biological products which are expensive to make. e.g. The first transgenic cow Rosie produced milk which had human alpha-lactalbumin.(a) State the role of DNA ligase in biotechnology.
(b) What happens when Meloidegyne incognitia consumes cells with RNAi gene?(a) DNA ligase is an enzyme which is used to join two DNA fragments.
(b) When Meloidogyne incognita (parasite) consumes cells with RNAi gene, the introduced RNAi gene forms both sense and anti-sense RNA and the two strands being complementary to each other form ds RNA, which cannot be transcribed. Thus, the mRNA of nematode is silenced and the parasite cannot survive there.Explain the work carried out by Cohen and Boyer that contributed immensely in biotechnology.
Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer conducted one of the first genetic engineering experiments. They invented the technique of DNA cloning. Cohen developed a method of removing plasmids from the cell and then reinserting them in other cells. Combining this process with that of DNA splicing enabled Boyer and Cohen to recombine segments of DNA in desired configurations and insert the DNA in bacterial cells, which could then act as manufacturing plants for specific proteins. Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer accomplished this in 1972.
Name the genes responsible for making Bt cotton plants resistant to bollworm attack. How do such plants attain resistance against bollworm attacks? Explain.
The Bt toxin is encoded by the cry gene. The cry I AC and cry II Ab control cotton bollworms, while the cry I-Ab controls corn borer. Bt gene produces Bt toxin. This toxin provides resistance to plants against lepidopteron, coleopterans and dipterans pests.
An example is Bt cotton, in which the gene from the bacterium that encodes for the toxin is incorporated. The activated Bt toxin binds to the surface of the midgut epithelium of the insects and causes swelling and cell lysis, which eventually leads to the death of the insects.
In the process of producing insect-resistant crops, specific Bt toxin genes are isolated from B.thuringiensis, and incorporated into the crops. Since these toxins are insect specific, they do not harm the crops or humans.Given below is the representation of amino acid composition not the relevant translated portion of β-chain of haemoglobin, related to the shape of human red blood cells. 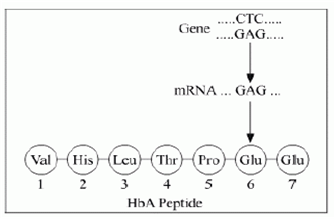
(a) Is this representation indicating a normal human or a sufferer from certain related genetic disease? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) What difference would be noticed in the phenotype of the normal and the sufferer related to this gene?
(c) Who are likely to suffer more from the defect related to the gene represented the males, the females or both males and females equally? And why?(a) This representation is of a normal person because in a normal person the mRNA contains the codon GAG at 6th position which codes for glutamic acid .
(b) In a sufferer, the codon GAG is replaced by GUG at the 6th position in the mRNA. Hence, during translation of the defective mRNA, Glutamic acid is replaced by Valine.
(c) The disease represented by the defect in the given gene is sickle-cell anaemia which is an autosomal recessive trait. This disease is transmitted to the progeny when both the parents are carriers for the disease (heterozygous). Since it is an autosomal recessive trait both males and females are equally at risk to develop the disease.
Draw a schematic sketch of pBR 322 plasmid and label the following in it:
(a) Any two restriction sites.
(b) Ori and rop genes.
(c) An antibiotic resistant gene.
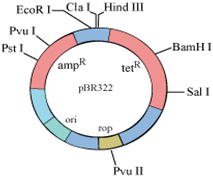
The Restriction sites mentioned in the figure are Hind III, EcoR I, BamH I, Sal I, Pvu II, Pst I, Cla I (any two can be considered)
Antibiotic resistant genes: ampR and tetR
How can bacterial DNA be released from the bacterial cell for biotechnology experiments?
Explain how a hereditary disease can be corrected. Give an example of first successful attempt made towards correction of such diseases.
Gene therapy can be used to correct hereditary diseases. It involves delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4-year old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. In this disease, the gene coding for enzyme ADA gets deleted leading to deficiency of ADA and problems in immune system. Gene therapy for ADA deficiency includes isolation of lymphocytes from patient’s blood, culturing them in-vitro, introduction of functional ADA cDNA and returning the cells to the patient’s body.
Why do children cured by enzyme-replacement therapy for adenosine deaminase deficiency need periodic treatment?
Explain the significance of satellite DNA in DNA fingerprinting technique.
Satellite DNA consists of highly repetitive and generally non-coding DNA. It is very significant in DNA fingerprinting for the following reasons:
i. It shows high degree of polymorphism which forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting
ii. Different tissues in the body show the same degree of polymorphism and thus are useful as an identification tool in the forensic application.
iii. They are inheritable from parents to offsprings and can be used for paternity testing.
Describe any three potential applications of genetically modified plants.
(i) Nutrient Enrichment and improved food- quality– Plants are genetically modified to contain more nutrients. For example- Golden rice is a variety of rice that is genetically engineered to produce beta-carotene, which is a precursor of vitamin A. Thus, consumption of this crop helps in the prevention of vitamin A deficiency diseases.
(ii) Insect/Pest Resistance – Plants are engineered to possess resistance against the insect or pest. GM crops, such as Bt cotton which were genetically modified to produce certain protein which acts as insecticides and kills certain insects such as lepidopterans and dipterans. Thus Bt cotton plants are resistant to insects.
(iii) Disease-free plants – Plants are genetically modified to become resistant against disease of bacteria, virus or fungus. For example Pusa swarnim a variety of brassica is resistant to disease caused by white rust.
How did an American Company. Eli Lilly use the knowledge of r-DNA technology to produce human insulin?
American Company Eli Lilly used the knowledge of r-DNA technology to produce human insulin in the following way.
1. Preparation of DNA corresponding to A and B chain separately2. Extraction of plasmid from bacteria
3. Insertion of DNA corresponding to A and B chain separately in plasmid
4. Transforming the bacteria with this recombinant plasmid
5. Expression of the desired product from this DNA .
6. Purification of A and B chain
7. Linking them with disulfide bonds so that they act as human insulin
State the role of C-peptide in human insulin.
C-peptide is the extra stretch of polypeptide which makes the insulin inactive (proinsulin).
How have transgenic animals proved to be beneficial in:
(a) Production of biological products
(b)Chemical safety testing.
(a) Transgenic animals can be used for the production biological products which are otherwise expensive to make. For example Rosie the transgenic cow produced human protein enriched milk. The milk contained human alpha-lactalbumin and thus was nutritionally more balanced for human babies than natural cow milk.
(b)Transgenic animals are made that carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals. They are then exposed to the toxic substances and the effects studied. Toxicity testing in such animals will allow us to obtain results in less time.
With advancements in genetics, molecular biology and tissue culture, new traits have been incorporated into crop plants. Explain the main steps in breeding a new genetic variety of a crop.
Plant breeding and improvement of crops is well supported by the governments and private companies. The major steps involved in the process are –
1. Collection of variability
2. Evaluation and selection of parents
3. Cross hybridisation among the selected parents
4. Selection and testing of superior recombinants
5. Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars
1. Collection of variability -Genetic variability is the primary requirement of breeding program, the wild character of plants is collected, preserved and characteristics for exploring natural genes called as germplasm collection.
2. Evaluation and selection of parents -The collected germplasm is then screened for the desirable character, followed by their multiplication and preparing for hybridization to obtain pure line.
3. Cross hybridisation among the selected parents
- Different characters are combined with two different parents e.g high quality protein gene is combined with disease resistant gene and developed a new cross hybrid.
4. Selection and testing of superior recombinants -The best combination is selected among the progeny; selection should be done very crucially with help of scientific community. The plant obtained in this step is superior to both parental plants. The plants are self-pollinated to obtain uniform generation, where character remains intact in the progeny.
5. Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars - Newly selected plant are evaluated (disease resistance, quality) by growing in research field and recognize management, irrigation requirement, followed by cultivation of the crop for 3 seasons under different climate. Then the plant is evaluated with present crop and defined useful or not.
(a) Mention the cause and the body system affected by ADA deficiency in humans.
(b) Name the vector used for transferring ADA-DNA into the recipient cells in humans. Name the recipient cells.(a) ADA (Adenosine deaminase) is an enzyme crucial for immune system. Its deficiency is caused due to the deletion of the gene coding for adenosine deaminase. Immune system is affected by ADA deficiency in humans.
(b) Retrovirus is used as a vector to introduce functional ADA cDNA into the lymphocytes cells (recipient cells).What are transgenic animals? Given an example
Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra (foreign) gene are known as transgenic animals.
For example - Transgenic cow like Rosie.
Explain enzyme-replacement therapy to treat adenosine deaminase deficiency. Mention two disadvantages of this procedure.
Enzyme replacement therapy
In enzyme replacement therapy functional ADA is given to the patient by injection
1) Lymphocyte from the blood of the patient are given in a culture outside the body
2) A functional ADA cDNA ( using a retroviral vector ) is introduced into the lymphocyte , which are Returned to the patient.
3) These cells are not immortal , the plant require them periodic infusion. 4) If the gene isolate from marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into the cells at early embryonic stage, it could be permanent cure.
TWO DISADVANTAGES OF THIS PROCEDURE
i.These cells do not always remain alive.
ii. Patient required periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocyte.
(a) Why must a cell be made 'competent' in biotechnology experiments ? How does
calcium ion help in doing so ?
(b) State the role of 'biolistic gun' in biotechnology experiments.
(A) It is necessary to make cell competent in order to enhance the efficiency of cell to take up foreign DNA easily.
When the cell is treated with a specific solution of divalent cation calcium. It increases the efficiency of the cell to take up the foreign DNA through the pores in the cell wall.
(B) Biolistics and Gene gun is one of the methods to transfer the foreign DNA into the host.
In this method the suitable plant cells are bombarded with high-velocity micro-particles
of gold & tungsten coated with DNA.
What is a GMO? List any five possible advantages of a GMO is a farmer.
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is a living organism whose genes have been altered by biotechnological manipulation.
i. GMO are free from the diseases, resistant to pest or insects and thus reduce the dependency on chemical fertilisers or pesticides.
ii. GMO crops are more tolerant to abiotic stress, which can be in the form of cold, drought, heat or salt.
iii. The crops have a high yield and high nutritional value.
iv. It reduces post-harvest losses.
v. It increases the efficiency of mineral usage by plants and prevents early exhaustion of soil.
How has RNAi technique helped to prevent the infestation of roots in tobacco plants by a nematode Meloidegyne incognita?
The introduction of DNA using the Agrobacterium vectors into the host plant produced both sense and anti-sense RNA in the host cells. The RNAi (RNA interference method was initiated as the two RNA's were complementary to each other and formed double-stranded RNA. The dsRNA silenced the specific mRNAof the nematode and thus the parasite could not survive in the transgenic host plant. The plant was therefore protected from the parasite.
Biotechnologists refer to Agrobacterium tumifaciens as a natural genetic engineer of plants. Give reasons to support the statement.
Agrobacterium tumafaciens is known as a natural genetic engineer of a plant because it has the natural ability to integrates its plasmid genes into the plant genomes. It can deliver a piece of T-DNA in the plant genome.
How is “Rosie‟ considered different from a normal cow ? Explain.
Rosie was a transgenic cow. It was considered different from a normal cow as it produced human protein enriched milk. The milk contained 'human alpha-lactalbumin' and was nutritionally a more balanced product for human babies than the normal cow milk.
State the use of Biodiversity in modern agriculture.
Biodiversity is very instrumental in development of agriculture –
1. It helps in the conservation and promotes farming of all wild and native variety of plants.
2. Agricultural biodiversity is the base of our agricultural food chain, development and safeguard of live-stocks etc. For ensuring food security to all peoples.
3. It promotes sustainable management of agricultural resources.
Scientists have succeeded in recovering healthy sugarcane plants from a diseased one.
1. Name the part of the plant used as explant by the scientists.
2. Describe the procedure the scientists followed to recover the healthy plants.
3. Name this technology used for crop improvement.
1. Shoot tips or meristem of the plant
2. The virus free healthy sugarcane plants are obtained through the Meristem culture of the diseased plants. The meristematic tissues are free from viruses and are used as an explant for micropropagation.
Steps in Meristem Culture
i. The shoot tip explants are grown in a nutrient medium in either a test tube a Petri dish under aseptic conditions.
ii. The nutrient medium consists of a carbon source, inorganic salts, vitamins, amino acids and growth regulators like auxin and cytokinin in proper define ratio.
iii. The plantlets obtained are transferred to the nurseries and then sent to the fields.
3. Micropropagation is the technology used for the crop improvement.
How does the application of the fungal genus, Glomus, to the agricultural farm increase the farm output?
The application of Glomus to agricultural field increases the farm output by increasing the nutrient availability to the crops. Glomus develops symbiotic association with the roots of plants, called mycorrhiza. It absorbs phosphorus from the soil and passes it to the plants it associates with. In return, it derives sugars from the host plant cells for its survival.
Thus, it acts as a biofertiliser. This association has other advantages also, like
(i) Resistance to root borne pathogens
(ii) Tolerance to salinity and drought
(iii) Increase in plant growth and development
Write the steps you would suggest to be undertaken to obtain a foreign-gene-product.
To obtain a foreign-gene product, following steps should be undertaken:
(i) Identification of DNA with desirable genes.
(ii) Introduction of the identified DNA into suitable host to form recombinant DNA (rDNA).
(iii) Maintenance of introduced DNA in particular host and gene cloning.
(iv) Transfer of the DNA (gene transfer) to its progeny.
(v) Selection of the recombinants from non-recombinants.
(vi) Expression of gene of interest by culturing recombinant cells.
(vii) Culturing of cells in bioreactors for large scale production of desired gene product.
Why do lepidopterans die when they feed on Bt cotton plant? Explain how does it happen.
Bt cotton plants are the transgenic plants that express a Bacillus thuringiensis gene called cry gene. This gene, encodes for protein crystals having insecticidal properties against insects of group Lepidoptera, Diptera and Coleoptera. Inside the bacterium, these proteins remain inactive and does not harm the bacteria. However, these inactive crystals can get activated in the alkaline pH of the gut of insects upon ingestion. After activation, these crystals can bind to the receptors present on the membranes of gut epithelial cells. Due to this binding, the membrane swells and pores are created on them. These pores lead to bursting of cell. Hence, soon the lepidopteran die due to starvation.
What are Cry genes ? In which organism are they present ?
Cry genes codes for a toxin which is poisonous to some insects thus giving resistant to the plants. They are present in bacterium Bacillus thuriengiensis.
Explain the various steps involved in the production of artificial insulin.
* Insulin contains two short polypeptide chains: chain A and chain B linked together by disulphide bridges.
* In mammals insulin is synthesised as a pro-hormone. It contains an extra stretch called C-peptide.
* C-peptide is absent in the mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin.
* Production of insulin by rDNA techniques was achieved by an American company, Eli Lilly in 1983. It prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B, chains of human insulin and introduced them in plasmids of E. coli for production. The A and B chains produced were separated, extracted and combined, by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
Mention the chemical change that proinsulin undergoes, to be able to act as mature insulin.
The proinsulin is cleaved to remove extra stretch called the C-peptide to form mature insulin having only A-chain and B-chain joined by a disulphide bond.
Which of the following is not required for any of the techniques of DNA fingerprinting available at present?
-
Zinc finger analysis
-
Restriction enzymes
-
DNA-DNA hybridization
-
Polymerase chain reaction
A.
Zinc finger analysis
Zinc finger is a small structural motif that is characterised by the co-ordination of one or more Zn ions in order t stabilise the folds.
Which part of the tobacco plant is infected by Meloidogyne incognitia?
-
Leaf
-
Stem
-
Root
-
Flower
C.
Root
The nematode inects the roots of the tobacco plant and result in root know disease.
Golden rice is a genetically modified crop plant where the incorporated gene i's meant for
-
Vitamin B
-
Vitamin C
-
Omega 3
-
Vitamin A
D.
Vitamin A
Golden rice is a variety of rice produced through genetic engineering to biosynthesize 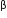 -carotene, a precursor of vitamin-A, in the edible parts of rice.
-carotene, a precursor of vitamin-A, in the edible parts of rice.
A pleiotropic gene
-
is expressed only in primitive plants.
-
is a gene evolved during Pliocene
-
controls a trait only in combination with another gene
-
controls multiple traits in an individual
D.
controls multiple traits in an individual
Pleiotropic gene is a gene that controls multiple traits is an individual. It is also called polyphenic gene, e.g., phenylketonuria causing multiple adverse effects due to the mutation in a single gene coding for enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase.
Sponsor Area
Green revolution in India occurred during
-
1960's
-
1970's
-
1980's
-
1950's
A.
1960's
Green revolution is the rapid increase in agricultural production (especially wheat and rice) during 1960-70. It has been achieved through introduction of high yielding varieties, increased irrigation facilities, fertilizer application, pesticides and agriculture management, Dr. MS Swaminathan is known as Fathe of Green Revolution in India.
Tobacco plants resistant to a nematode have been developed by the introduction of DNA that produced (in the host cells).
-
Both sense and anti-sense RNA
-
A particular hormone
-
An antifeedant
-
A toxic protein
A.
Both sense and anti-sense RNA
Antisense RNA can be produced by inverting a cDNA copy of an mRNA with respect to the promoter in an expression vector. This yields a full length complementary copy of mRNA sequence. Antisense RNA molecule are thought to interact with mRNA molecule by base pairing to form double stranded RNA.
The first clinical gene therapy was given for treating
-
diabetes mellitus
-
chicken pox
-
rheumatoid arthritis
-
adenosine deaminase deficiency
D.
adenosine deaminase deficiency
Gene therapy is the treatment of disease by the transfer and extension of genetic material in the patient's cell in order to restore normal cellular functions. The first clinical gene therapy was given for treating adenosine deaminase deficiency.
In Bt cotton, the Bt toxin present in plant tissue as pro-toxin is converted into active toxin due to
-
alkaline pH of the insect gut
-
acidic pH of the insect gut
-
action of gut microorganisms
-
Presence of conversion factors in insect gut
A.
alkaline pH of the insect gut
The Bt toxin is an inactive protoxin, which is activated due to the alkaline pH in the insect gut.
Bt toxin dissolve in high pH of insect gut and become active. The toxins then attack the gut cells of the insect, punching holes in the lining.
(i) Insect eats Bt crystals and spores.
(ii) The toxin binds to specific receptors in the gut and the insects stops eating.
(iii) The crystals cause the gut wall to break down allowing spores and normal gut bacteria to enter the body.
(iv) The insect dies as spores and gut bacteria proliferate in the body.
The crops engineered for glyphosate are resistant/ tolerant to
-
fungi
-
bacteria
-
insects
-
herbicides
D.
herbicides
Glyphosate (N-phosphonomethyl glycine) is systemic broad spectrum herbicide used to kill weeds especially broad leaves and grasses. It is used to engineer new crop for having herbicides tolerance (resistant).
Read the following four statements (I - IV) about certain mistakes in two of them
I .The first transgenic buffalo, Rosie produced mile which was human alpha - lactal bumin enriched
II. Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from another macro -molecules.
III. downstream processing is one of the steps of R-DNA technology.
IV. Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of R - DNA into the host.
Which are the two statements having mistakes?
-
Statement (II) and (III)
-
Statements (III) and (IV)
-
Statements (I) and (III)
-
Statements (I) and (II)
D.
Statements (I) and (II)
Transgenic Rosiae is actually Cow. It is first transgenic cow produced in 1997.
Restriction enzymes cut the DNA at a specific site. The separation of DNA is performed by gel electrophoresis
Some of the characteristics of Bt cotton are
-
long fibre and resistance of aphids
-
medium yield, long fibre and resistance to beetle pests
-
high yield and production of toxic protein crystals which kill dipteran pests
-
high yield and resistance to bolloworms
D.
high yield and resistance to bolloworms
Bacillus thuringiensis forms crystals containing a toxic insecticidal protein. Bt toxin protein exists as an inactive toxin, it is converted into an active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of the gut, which solubilises the crystals. The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and creates pores the cause cell swelling and lysis and eventually cause the death of the insect. Specific Bt toxin genes were isolated from B. thruingiensis and incorporated into the several plants such as cotton. The toxin is coded by the gene name cry. There is a number of them, eg, the proteins encoded by the genes cry IAc a cry II Ab control the cotton bollworms, that of cry IAB control corn borers.
Which one of the following proved effective for biological control of nematodal diseases in plants?
-
Pisolithus tinctorius
-
Pseudomonas cepacin
-
Gliocladium virens
-
Paceilomyces Lilacinus
D.
Paceilomyces Lilacinus
Paexcilomyces Lilacinus is proved effective for biological control of nematodal disease in plants. it is easily produced in vitro, Rhizosphere competent, attack the eggs of several nematodes species and treatment of plant matter, eg, seed tuber, can be effective.
Farmers in a particular region were concerned that pre-mature yellowing of leaves of a pulse crop might cause decrease in the yield. Which treatment could be most beneficial to obtain maximum seed yield?
-
Frequent irrigation of the crop
-
Treatment of the plants with cytokinins alongwith a small dose of nitrogenous fertilizer
-
Removal of all yellow leaves and spraying the remaining green leaves with 2,4,5- trichlorophenoxy acetic acid
-
Application of iron and magnesium to promote synthesis of chlorophyll
D.
Application of iron and magnesium to promote synthesis of chlorophyll
If a pulse crop possesses premature yellowing of leaves and decrease in yield and application of magnesium and iron to promote synthesis of chlorophyll may become most beneficial to overcome the problem and to obtain maximum seed yield.
Magnesium is an important part of ring structure of chlorophyll molecule and its deficiency causes chlorosis and premature leaf abscission.
In iron deficiency also, the leaves become chlorotic because iron is required for the synthesis of some of the chlorophyll protein complexes in the chloroplast.
Microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering are
-
Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
-
Vibrio cholerae and a tailed bacteriophage
-
Diplococcus sp. and Pseudomonas sp
-
Crown gall bacterium and Caenorhabditis elegans
A.
Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens are the microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering.
E. coli is a motile, gram negative, rod shaped bacterium which is a normal inhabitant of human colon. It is most extensively used in bacterial genetics and molecular biology.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil bacterium. It has Ti plasmid (Tumour inducing plasmid) and it can be used for the transfer of a desired gene in dicot plants.
Female cone of Pinus is a
Modified needles
Modified long shoot
Modified dwarf shoot
Modified scale
D.
Modified scale
The female cone of Pinus is formed by the aggregation of megasporophylls, which bear ovules. Each megasporophyll consists of a lower bract scale and a larger upper ovuliterous scale.
Which statement is correct for bacterial transduction?
Transfer of some genes from one bacteria to another bacteria through virus
Transfer of genes from one bacteria to another bacteria by conjugation.
Bacteria obtain DNA directly
Bacteria obtain DNA from other external sources
A.
Transfer of some genes from one bacteria to another bacteria through virus
Transduction involves the picking up of DNA by bacteriophage from one bacterial cell and carrying it to another where the DNA fragment may get incorporated into the bacterial host's genome.
Which of the following is not true for a species?
Members of a species can interbreed
Variations occur among members of species
Each species is reproductively isolated from every other species
Gene flow does not occur between the populations of a species
D.
Gene flow does not occur between the populations of a species
Gene flow means the spread of genes through the population as affected by movements of individuals and other propagules, e.g., spores seeds, etc.
One gene- one enzyme hypothesis of Beadle and Tatum was experimentally proved on
Saccharomyces
Neurospora crassa
Lathyrus odoratus
Claviceps
B.
Neurospora crassa
One gene- one enzyme theory was given by Beadle and Tatum in 1958, while they were working on red mould or Neurospora crassa (Ascomycetes fungus), which is also called Drosophila of plant kingdom.
Genes for cytoplasmic male sterility in plants are generally located in
mitochondrial genome
cytosol
chloroplast genome
nuclear genome
A.
mitochondrial genome
Mitochondria are the eukaryotic cell organelles. These originate from pre-existing mitochondria only. Also known as semi autonomous organelles because they consists of a circular, double stranded DNA molecule, RNA and 70 S type of ribosome. The genes, located outside of nucleus (i.e., within the cytoplasm) also governes some traits and are referred as plasmogenes or cytoplasmic genes. Cytoplasmic male sterility (i.e., dominance of female cytoplasmic genes over male) is due to plasmogenes located in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) strains have been used for designing novel
bio- metallurgical technique
bio- mineralization processes
bio- insecticidal plants
biofertilizers
C.
bio- insecticidal plants
Bioinsecticides are those biological agents, which are used to control harmful insects. A bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis is used for this purpose. Spores of this bacterium produce the insecticidal cry-protein. Therefore, spores, of this bacterium kill larvae of certain insects. The commercial preparations of B. thuringiensis contain a mixture of spores, cry-protein and an inert carrier.
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched
Central dogma- Codon
Okazaki fragments - Splicing
RNA polymerase -RNA primer
Restriction enzymes - Genetic engineering
D.
Restriction enzymes - Genetic engineering
Restriction enzyme recognises specific nucleotide sequences in DNA and then makes a double-stranded cleavage of DNA molecule. Restriction enzymes are called genetic scissors as they slice off genes and is recently being used in gene therapy technique. They are key tool of genetic engineering. Central dogma is related with protein synthesis. Okazaki fragments are found during DNA synthesis and RNA polymerase is used in synthesis of RNA.
Restriction enzymes are used in genetic engineering, because they
can degrade harmful proteins
can join different DNA fragments
can cut DNA at specific base sequence
are nucleases that cut DNA at variable sites
C.
can cut DNA at specific base sequence
Restriction enzyme are also known as molecular knifes or molecular scissors. They are isolated from bacteria. They recognize specific base sequence in DNA and cleave both strands of it.
The Triticale is an intergeneric hybrid between
wheat and maize
maize and rye
wheat and rye
bajra and wheat
C.
wheat and rye
The Triticale is the first man made cereal. It is formed by a cross between wheat (Triticum) and rye (Secale cerale) followed by allopolyploidy (multiplication of non- homologous chromosomes).
Triticum sp Secale cerale
Diploid
Allopolyploidy
Triticale
Micro-organism which act as a vehicle for foreign gene transfer in higher plants
Agrobacterium
E. coli
T.M.V.
Bacillus anihracis
A.
Agrobacterium
The bacterium-Agrobacterium acts as a vehicle for transfer of DNA or genes from one organism to another organism because it infects all dicot plants.
Which one of the following methods is commonly used to maintain the genetic traits of a given plant
By propagating through seed germination
By propagating through vegetative multiplication
By generating hybrids through intergeneric pollination
By treating the seeds with gamma radiations
B.
By propagating through vegetative multiplication
The propagation through vegetative multiplication is used to maintain the genetic traits of a given plant. It gives rise to genetically uniform population or clone. In case of plants propagated through seeds, variations creep in due to chance segregation and recombination of genes during meiosis and their chance combination during fertilisation.
Which one of the following is a correct statement
"Bt" in "Bt-cotton" indicates that it is a genetically modified organism produced through biotechnology.
Classical plant breeding involves fusion of two somatic cells carrying desired genes.
The anticoagulant hirudin is being produced from transgenic Brassica napus seeds.
Golden rice is a transgenic variety of rice rich in vitamin E.
C.
The anticoagulant hirudin is being produced from transgenic Brassica napus seeds.
Transgenic Brassica napus seeds are being used to produce the anticoagulant hirudin. Bt in "Bt Cotton" stands for Bacillus thuringiensis. This is naturally occurring soil bacterium. Classical plant breeding involves crossing or hybridisation of pure lines, followed by artificial selection to produce plants with desirable traits whereas somatic hybridisation involves fusion of protoplast of two cells. Golden rice is a transgenic variety of rice rich in carotene (provitamin A- inactive state of vitamin A).
Assertion: Flavr-Savr tomato was the first transgenic commercial crop that entered the market.
Reason: Roundup variety of soybean was prepared through breeding.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
The Flavr-Savr tomato, was the first genetically modified fruit/vegetable to reach the market in USA. Roundup ready soybean is a genetically modified herbicide tolerant cultivar.
Which of the following is the correct scientific name of wheat derived by binominal nomenclature?
Triticum Vulgare
Triticum aestivum
Oryza sativa
Zea mays
B.
Triticum aestivum
Triticum aestivum is the scientific name of Bread wheat commonly used at home. It is an annual grass that can grow up to 150 cm tall, usually producing 2- 5 tillers. It is one of the most important human food crops, providing a staple food for billions of people.
The genetic material in tobacco mosaic virus is
ss DNA
ss RNA
ds RNA
ds DNA
B.
ss RNA
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) is a positive sense single stranded RNA virus, that infects a wide range of plants. It contains single stranded RNA (ss RNA) as genetic material.
Which organism is used to transfer T-DNA
Streptomyces hygroscopicus
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Salmonella typhi
Escherichia coli
B.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Ti plasmid (tumour inducing) from the soil bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is effectively used as vector for gene transfer to plant cells. The part of Ti plasmid transferred into plant cell DNA, is called the T-DNA. This T-DNA with desired DNA spliced into it, is inserted into the chromosome of the host plant where it produces copies of itself, by migrating from one chromosomal position to another at random.
Which of the following represents the action of insulin?
Increases blood glucose level by stimulating glucagon production
Decreases blood glucose level by forming glycogen
Increases blood glucose level by promoting cellular uptake of glucose
Increases blood glucose level by hydrolysis of glycogen
B.
Decreases blood glucose level by forming glycogen
Insulin decreases the level of glucose in the blood. It acts by stimulating liver cells and muscle cells to take up glucose from the blood and convert it into glycogen. When the blood sugar level drops, the secretion of insulin is suppressed. When the blood sugar level increases, the secretion of insulin is stimulated.
Assertion: GM foods are facing widespread resistance by the people.
Reason: GM foods have mutated genes which cause infections and allergies.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
The GM crops are fast becoming a part of agriculture throughout the world because of their contribution to the increased crop productivity and to global food, feed and fiber security, besides their use in health-care and industry.
However, GM foods are facing widespread resistance by the people from all over the world. It is because transgenes in commercial crops can endanger native species. For example, the gene for Bt toxin expressed in pollen might endanger pollinators like honeybees. These crops cause problems in human health by supplying allergens and transfer of antibiotic resistance markers. The GM crops may change the fundamental vegetable nature of plants as the genes from animals (e.g., fish or mouse) are being introduced into crop plants. GM foods also have a bad effect on environment and biodiversity.
The number of chromosomes present in the cells of the bread wheat, Triticum aestivum suggests that it is
hexaploid
diploid
tetraploid
pentaploid
A.
hexaploid
Bread wheat is an allohexaploid, an allopolyploid, with six sets of chromosomes.
Assertion : The technique of micropropogation has been used to introduce variations in the offspring.
Reason : It is not possible to generate virus free plants by micropropogation.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
D.
If both assertion and reason are false
Micropropagation is used for rapid vegetative multiplication of plants. As the size of the propagule is minute, thus the technique is named micropropagation. Each, such plant, will be genetically identical to the parent plant. Generally, apical or axillary meristems are free from viruses. Hence, can be used as explants in tissue culture to produce virus free plants.
Somaclones are prepared by
callus culture
sexual reproduction
micropropagation
somatic hybridisation
C.
micropropagation
Somaclones are genetically identical (Clones) plants developed from any part of a plant by tissue culture/micropropagation. This type of micropropagation is also called somaclonal propagation.
What is true about Bt toxin
Bt protein exists as active toxin in the Bacillus.
The activated toxin enters the ovaries of the pest to sterilise it and thus prevent its multiplication.
The concerned Bacillus has antitoxins.
The inactive protoxin gets converted into active form in the insect gut
D.
The inactive protoxin gets converted into active form in the insect gut
Some strains of Bacillus thuringiensis produce proteins that kill certain insects like lepidopterans and coleopterans, etc. Bacillus thuringiensis forms some protein crystals. These crystals contain a toxic insecticidal protein. Bt toxin proteins exist as inactive protoxins, but once an insect ingests the inactive toxin it is converted to active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of the alimentary canal that solublizes the crystals
Wine and beer are produced directly by fermentation whereas brandy and whisky require both fermentation and distillation. This is because
fermentation is inhibited at an alcohol level of 10-18%
distillation prolongs storage
distillation improves quality
distillation purifies the beverage.
D.
distillation purifies the beverage.
Beverages like beer, wine are fermented but not distilled. They have relatively low alcohol content typically less than 100%. Hard liquor like brandy and whisky are produced by both fermentation and distillation. Distillation process purifies them and removes diluting components like water and increases the alcohol content.
Assertion: GM crops can affect human health by causing allergic reactions.
Reason: Transgenes in commercial crops can endanger native species e.g., the Bt toxin gene expressed in pollen might endanger pollinators like honeybees.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
The transgenic food may cause toxicity or produce allergies. The enzyme produced by the antibiotic resistance can cause allergies, because it is a foreign protein. The introduction of transgenic plants into agriculture is creating some issues. One of them is the potential risk of transgene in commercial crops endangering native or nontarget species. For example the gene for Bt toxin expressed in pollen might endanger pollinators like honeybees.
The first bioherbicide developed in 1981 was based on
Phytophthora palmivora
Phytophthora infestans
Bacillus thuringiensis
Azadirachta indica
A.
Phytophthora palmivora
The first bioherbicide is devine, which is a mycoherbicide, based on fungus Phytophthora palmivora. It is being used since 1981 to control Morrenia odorata (milkweed vines) in Citrus orchards.
One of the major difficulties in the biological control of insect pest is that
the predator develops a preference to other diets and may itself become a pest
the predator does not always survive when transferred to a new environment
the method is less effective as compared with the use of insecticides
the practical difficulty of introducing the predator to specific areas.
A.
the predator develops a preference to other diets and may itself become a pest
In transgenics, expression of transgene in target tissue is determined by
enhancer
transgene
promoter
reporter.
D.
reporter.
The plants, in which a functional foreign gene has been incorporated by any biotechnological methods that generally is not present in plant, are called transgenic plants. When plant cell are transformed by any of the transformation methods it is necessary to isolate the transformed cells/tissue. There are certain selectable marker genes present in vectors that facilitate the selection process. In transformed cells the selectable marker genes or are introduced through vector. There is a number of marker genes which are commonly described as reporter genes screenable genes. Some of the reporter genes which are most commonly used in plant transformation arc : cat, gus, lux, nptll., etc.
In the following table identify the correct matching of the crop, its disease and the corresponding pathogen.
Crop Disease Pathogen Citrus Canker Pseudomonas rubrilineans Potato Late blight Fusarium udum Brinjal Root-knot Meloidogyne incognita Pigeon pea Seed gall Phytophthora infestans
C.
| Brinjal | Root-knot | Meloidogyne incognita |
The root knot disease of brinjal is quite common in all vegetative growing areas especially when the climate is warm, with short winters. The disease is caused by root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. It devitalizes root tips, develop swelling over roots and reduces flow of I water and minerals to the aerial parts. As a result yield and quality of fruits are affected. Citrus canker is a common bacterial diseases of citrus tree, caused by Xanthomonas citri. Late blight is a disease of potato caused by fungus Phytophthora infestans having blight type symptoms. Wilt of pigeon pea is caused by Fusarium udum (fungi) where wilting of seedlings and adult plants occur
Which one of the following is a correct statement?
"Bt" in "Bt-cotton" indicates that it is a genetically modified organism produced through biotechnology
Somatic hybridization involves fusion of two complete plant cells carrying desired genes.
The anticoagulant hirudin is being produced from transgenic Brassica napus seeds.
"Flavr Savr" variety of tomato has enhanced the production of ethylene which improves its taste.
A.
"Bt" in "Bt-cotton" indicates that it is a genetically modified organism produced through biotechnology
Bt in Bt Cotton means Bacillus thuringiensis. It is a naturally occuring soil bacterium.
Somatic hybridization involves the fusion of protoplast of two cells.
Flavr Savr is genetically engineered tomotoes. They express delayed softening by insertion of an additional copy of PG endoiciding gene. PG or Poly Galactouronase enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of cell wall pectin.
Transgenic Brassica napus seeds are used to produce the anticoagulant hirudin.
In which one of the following combinations (a-d) of the number of chromosomes is the present day hexaploid wheat correctly represented
Combination Monosoic Haploid Nullisomic Trisomic (a) 21 28 42 43 (b) 7 28 40 42 (c) 21 7 42 43 (d) 41 21 40 43
D.
| (d) | 41 | 21 | 40 | 43 |
The present day wheat is hexaploid, known as triticale (2n = 42) with 3 genomes A, B and D i.e, AABBDD The 3 genomes are obtained from 3 different diploid species.
(i) Triticum aegilopoides -AA (2n = 14)
(ii) Aegilops speltoides - BB (2n = 14)
(iii) Aegilops squarossa - DD (2n = 14)
By crossing of first two diploids sps Triticum dicoccoides (2n = 28) i.e., tetraploid is produced AABB which on crossing with third species gives rise to Triticum aestivum (2n = 42) hexaploid (AABBDD). So its haploid set will have 21 chromosomes, monosomic (2n - I) will have 41 chromosomes, nullisomics (2n - 2) will have 40 chromosomes, and trisomic (2n + I) will have 43 chromosomes.
Hirudin is
a protein produced by Hordeum vulgare, which is rich in lysine
a toxic molecule isolated from Gossypium hirsutum, which reduces human fertility
a protein produced from transgenic Brassica napus, which prevents blood clotting
an antibiotic produced by a genetically engineered bacterium, Escherichia coli.
C.
a protein produced from transgenic Brassica napus, which prevents blood clotting
Transgenic plants are those plants in which a foreign gene has been introduced and stably integrated into the host DNA. A gene that is transferred using the tools of molecular biology is called transgene.
Brassica napas is one of the transgenic plant species. Recently transgenic plants have been explored for production of biologically active peptides and proteins having pharmaceutical applications including use as blood proteins, enzymes, growth, hormones etc. The protein hirudin present in leech, prevents blood clotting. The gene was chemically synthesized and introduced in Brassica napas and later on the seeds contained the protein.
In India, we find mangoes with different flavours, colours, fibre content, sugar content and even shelf-life. The large variation is on account of
species diversity
induced mutations
genetic diversity
hybridisation
C.
genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the diversity in the number and types of genes as well as chromosomes present in different species and the variations in the genes and their alleles in the same species. Variations in the genes of a species increase with the increase in size and environmental parameters of the habitat. It helps in speciation and evolution of new species.
Somaclonal variation is seen in
tissue culture grown plants
apomiets
polyploids
vegetatively propagated plants.
A.
tissue culture grown plants
Genetic variation present among plants cell is of a culture is called somaclonal variation. The term is also used for the genetic variation present in plants regenerated from a single culture. This variation has been used to develop sexual/useful variations.
Cultivation of Bt cotton has been much in the news. The prefix Bt means
"Barium-treated" cotton seeds
"Bigger thread" variety of cotton with better tensile strength
produced by "biotechnology" using restriction enzymes and ligases
carrying an endotoxin gene from Bacillus thuringienesis.
D.
carrying an endotoxin gene from Bacillus thuringienesis.
Some strains of Bacillus thuringiensis produce proteins that kill certain insects such as lepidopterans (tobacco budworm, armyworm), coleopterans (beetles) and dipterans (flies, mosquitoes). B. thuringiensis forms protein crystals during a particular phase of their growth. These crystals contain a toxic insecticidal protein.
An example of gene therapy is
production of injectable hepatitis B vaccine
production of vaccines in food crops like potatoes which can be eaten
introduction of gene for adenosine deaminase in persons suffering from Severe Combined Immuno-deficiency (SCID)
production of test tube babies by artificial insemination and implantation of fertilized eggs
C.
introduction of gene for adenosine deaminase in persons suffering from Severe Combined Immuno-deficiency (SCID)
On September 14, 1990 researchers at the U.S. National Institutes of Health performed the first (approved) gene therapy procedure on four-year old Ashanti DeSilva. Born with a rare genetic disease called severe combined immune deficiency (SCID), she lacked a healthy immune system, and was vulnerable to every passing germ. Children with this illness usually develop overwhelming infections and rarely survive to adulthood.
In this gene therapy procedure doctors removed white blood cells from the child's body, let the cells grow in the lab inserted the missing gene into the cells, and then infused the genetically modified blood cells back into the patient's blood stream. Laboratory test have shown that the therapy strengthened her immune system.
Somaclonal variation can be obtained by
application of colchicine
irradiation with gamma rays
tissue culture
hybridisation.
C.
tissue culture
Somaclonal variation is the variation seen in plants that have been produced by plant tissue culture. Chromosomal rearrangements are an important source of this variation. Somaclonal variation is not restricted to, but is particularly common in, plants regenerated from callus. The variations can be genotypic or phenotypic, which in the latter case can be either genetic or epigenetic in origin.
Tissue culture, a method of biological research in which fragments of tissue from an animal or plant are transferred to an artificial environment in which they can continue to survive and function. The cultured tissue may consist of a single cell, a population of cells, or a whole or part of an organ. Cells in culture may multiply; change size, form, or function; exhibit specialized activity (muscle cells, for example, may contract); or interact with other cells.
Assertion : Agrobacterium tumefaciens is popular in genetic engineering because this bacterium is associated with the roots of all cereal and pulse crops.
Reason : A gene incorporated in the bacterial chromosomal genome gets automatically transferred to the crop with which the bacterium is associated.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
D.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Agrobacterium tumefacines is a gram negative, non sporing, motile, rod shaped bacterium, closely related to Rhizobium. It is commonly found on and around root surfaces.
Rhizosphere seems to survive by using nutrients that leak from the root tissues. But it infects only through the wound-site either by naturally occurring or caused by transplanting of seedling and nursery stock. It is harmful to plants and useful to scientists for the same reason i.e, it transfers DNA into plant genomes found in soil worldwide.
A. tumefaciens cause crown gall disease of a wide range of dicot (broad leaved) plants especially members of rose family by transferring its own DNA into plant cells. But in laboratory, the ability to move all sorts of genes into plants has made the microbe the standard tool for investigating plant genetics and modifying crops.
Assertion: Cattle breeds can be improved by superovulation and embryo transplantation.
Reason: Superovulation in high milk-yielding cows is induced by hormonal injection.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
B.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
Embryo transfer is the process of placing embryos into the uterine cavity during an IVF procedure.
For superovulation donor cows of particularly fine pedigree are treated with hormones (mainly FSH and LH) to increase the number of eggs released at ovulation - multiple ovulation (MO). The cows are artificially inseminated using semen from a proven bull.
After 6-7 days the embryos are collected non-surgically, and then implanted into recipient cows whose oestrous cycle is at the correct receptive stage - usually as te result of hormonal manipulation
Long fibres of cotton seed are known as
coir
fuzz
lint
flax
C.
lint
Long fibres of cotton are called lint and small fibres are called fuzz. Lint are extractable while fuzz are non-extractable
Pests which only feed and oviposit on crop are called
major pests
minor pests
accidental pests
occasional pests
A.
major pests
The pests are the communities of life that are capable of causing damage to cultivated crops, fruits, vegetables, wood and forest wealth.
In which stage of its life cycle, the silk moth begins to produce silk fibre?
3rd instar larva
4th instar larva
5th instar larva
Pupa
D.
Pupa
The caterpillar larva hatches from egg of silkmoth. The full grown caterpillar larva grows into pupa. Its salivary glands now secrete a sticky fluid through a narrow pore of its spinning apparatus called spinneret situated on hypopharynx. The sticky substance turns into the fine long and solid thread of silk.
Which one of the following is the American poultry breed
Australop
Assel
Minorica
Rhod Island Red
D.
Rhod Island Red
The Rhode Island Red is an American breed of domestic chicken. It was developed in the late nineteenth century in Massachusetts and Rhode Island by cross-breeding birds of Oriental origin such as the Malay with brown Leghorn birds from Italy
Transposons are
house-keeping genes
jumping genes
transporting genes
stationary genes
B.
jumping genes
Transposons are sequences of DNA that can move around to different positions within the genome of a single cell, a process called transposition. They are also known as jumping genes and can cause mutations. They were discovered by Barbara McClintock, for which she was awarded a Nobel prize in 1983.
Housekeeping genes are constitutive genes that are required for maintenance of basic cellular function and are expressed in all cells of an organism under normal and patho- physiological conditions.
First genetically modified plant commercially released in India is
golden rice
slow ripening tomato
Bt brinjal
Bt cotton
D.
Bt cotton
Bt cotton is the first genetically modified plant that is commercially released in India.
Cotton fibre is basically a type of
trichome
scale
dried seed coat
non glandular hair
A.
trichome
Cotton fibre is basically a type of trichome. Trichome is a small hair or outgrowth from the epidermis of a plant, typically unicellular and glandular.
Biolistic technique is used in
tissue culture process
gene transfer process
hybridization process
germplasm conservation process
B.
gene transfer process
Electroporation and biolistics are two physical methods for gene transfection. In biolistics DNA is coated on to the surface of tiny metal particles usually tungeston or gold, which is then shot into the cells.
Electroporation is a molecular biology technique in which an electrical field is applied to cells in order to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, allowing chemicals, drugs or DNA to be introduced into the cell.
Which one of the following bacterium is used for production of transgenic plants
Escherichia coli
Bacillus thuringiensis
Staphylococcus aureus
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
D.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Transgenic plants are the plants that have been genetically engineered, a breeding approach that uses recombinant DNA techniques to create plants with new characteritics.
Plant cells do not have endogeneous plasmids. The plasmid vectors used for plant cell transformation are mostly based on Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. These are plant pathogenic Gram ve soil bacteria which cause crown gall disease of dicot plants.
Basic principle of developing transgenic plants and animals is to introduce the gene of interest into the nucleus of
somatic cell
vegetative cell
germ cell
body cell
C.
germ cell
Transgenic organisms can be produced by incorporating the desired gene into the genome of the organism. For this purpose, the gene of interest is introduced into the nucleus of the germ cell of the organism.
Which of the following Bt crops is being grown in India by the farmers?
Maize
Cotton
Brinjal
Soyabean
B.
Cotton
Bt toxin is produced by a bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis. Examples of Bt crops are Bt cotton, Bt corn, rice, tomato, potato and soyabean, etc. In India Bt cotton is grown by farmers extensively.
Insect pest resistant Bt cotton plant was developed using
somaclonal variation
micropropagation
somatic hybridisation
Transgenic technology
D.
Transgenic technology
Bt cotton is a genetically modified variety of cotton producing an insecticide. It was developed by inserting Cry gene coding for Bt toxin into cotton plant genome by using transgenic technology causing cotton to produce this natural insecticide in its tissues. It was obtained from Bacillus thuringiensis. Techniques such as somaclonal variation, somatic hybridisation and micropropagation are the methods that rely as tissue culture techniques of producing plants by using different plant parts. They does not involve the gene level transfer.
Genetically improved crop varieties can be developed in laboratory by
somatic hybridisation
transgenic technology
cell suspension culture
somaclonal variation
A.
somatic hybridisation
B.
transgenic technology
D.
somaclonal variation
Cell suspension culture which is used for the multiplication of cells by providing them culture or by suspended them in a suitable medium.
Somatic hybridisation, transgenic technology and somaclonal variation are the methods which are used to produced genetically improved varieties in labs.
Which one of the following statements is wrong in relation to transgenic Bt cotton plant?
Crop yield loss due to the attack by Bacillus thuringiensis bacterium is reduced
Crop yield loss due to the attack by lepidopteran insect pests is reduced
The use of chemical insecticides in the cotton field is minimised
Better quality cotton is produced
A.
Crop yield loss due to the attack by Bacillus thuringiensis bacterium is reduced
Crop yield loss due to the attack by Bacillus thuringiensis bacterium is reduced.
Gene therapy has been successful in curing Codes genetic diseases in laboratory animals through
exposure to X-ray to rectify the defective gene
replacing the defective gene with a functional gene
oral delivery of genes
use of therapeutic medicines to rectify the defective gene
B.
replacing the defective gene with a functional gene
Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child or embryo. Here, genes are inserted into a person's cells and tissues to treat a disease. Correction of a genetic defect involves delivery of a normal (functional) gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene.
The replacement of a normal gene by its specifically mutated copy is
Gene cloning
Gynogenesis
Gene knockout
lnterparietal hybridisation
C.
Gene knockout
Gene knockout is the replacement of a normal gene by its specifically mutated copy.
A natural form of genetic engineering is exhibited by
Haemophilus influenzae
E.coli
Dolly
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
D.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is known as natural genetic engineer. It is known to infect broad leaved crops such as, tomato, soyabean and tobacco. It causes tumours called crown galls. The tumour formation is induced by its plasmid-Ti. The plasmid integrates a segment of its DNA called T-DNA into chromosomal DNA of its host plant cells. It then causes tumours. i.e., gene transfer occurs without human effort.
In which of the following, determination of order of bases in a DNA molecule takes place
Gene probing
Gene splicing
Gene mapping
Gene sequencing
D.
Gene sequencing
Gene sequencing is the process of determination of order of bases in a gene on DNA strand.
Gene splicing is the cutting of introns from DNA segments and addition of exons with each other.
Gene mapping is relative determination of position of genes on chromosome.
Gene probing is searching of a particular gene from a group or cluster of gene.
During 'gene cloning', which is called 'gene taxi' ?
Plasmid
Protozoa
Vaccine
Bacterium
A.
Plasmid
Gene taxi refers to a vector or a carrier which is used to transfer genes from one cell to another in a bacterial colony.
Plasmids are double stranded closed DNA molecule capable of self replication, which is present as extra chromosomal structures in the bacterial cells. They are commonly used as vectors to produce recombinant DNA for gene cloning.
Flavr savr variety of tomato is a
mutated form
somaclonal variety
transgenic crop
high yielding variety
C.
transgenic crop
Flavr savr variety of tomato is a transgenic crop. It is genetically engineered tomatoes, which express delayed softening by insertion of an additional copy of PG encoding gene. PG is polygal-acturonase enzyme, which is responsible for the break down of cell wall pectin.
In genetic engineering, which of the following is used?
Plasmid
Plastid
Mitochondria
ER
A.
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are widely used in Genetic engineering experiments as vectors which carry desired segment of DNA to the target organism.
Which one of the following bacteria has found extensive use in genetic engineering work in plants?
Bacillus coagulens
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Bacillus subtilis
E. coli
B.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen that causes a disease of plants called crown gall disease. The tumour like gall grows when A. tumefaciens inserts a plasmid (Ti plasmid), containing bacterial genetic information into the plant's chromosomal DNA. Therefore, this bacteria has been extensively used as a vector for gene transfer to plant cells.
Vaccines prepared by genetic engineering are safe to man because they are
least active form of virus
active form of virus
coat protein formed as antibody
All of the above
A.
least active form of virus
Vaccination is a technique to develop immunity without infection, ie, weakened or dead pathogens or part of pathogens infected into a person who required to made immune. This is the reason that vaccines prepared by genetic engineering are safe to man because they are least active form of virus.
The principal cereal crop of India/Asia is :
Sorghum
barley
wheat
rice
D.
rice
Rice is the principal cereal crop of India/ Asia.
Major coffee producing state of India is :
Tamil Nadu
Kerala
Karnataka
Andhra Pradesh
C.
Karnataka
Coffee is mainly grown in three Southern states Karnataka. Tamil Nadu and Kerala. 70% coffee is grown in Karnataka.
A student wants to study metaphasic behaviour of chromosomes in a living cell. The technique most suitable is :
phase contrast microscope
x-ray microscope
cell fractionation
scanning electron microscope
A.
phase contrast microscope
The phase contrast microscope is used in studying living or unstained cells and their activities like cytoplasmic movements and cell division etc.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area