Biology Chapter 7 Evolution
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 राजनीतिक विज�ञान Biology
What conditions were created by Miller in his experiment?
Arrange the following substances in a proper sequence with regard to the formation of chemical constituents at the time of origin of life :
Sugar, methane, nucleic acid and amino acid.
What is the phenomenon called when the original drifted population becomes founders?
What are the two key concepts of Darwinian Theory of Evolution
Mention the type of nutrition in the cells originated first during the origin of life.
Which group of organisms were responsible for appearance of free oxygen in the atmosphere of the primitive earth ?
What is meant by the term fossil ?
Fossils are remains of hard parts of life-forms found in rocks. Fossils are the remains or impression of a prehistoric plant or animal embedded in rock and preserved in petrified form.
Name the different eras of geologic time scale.
(a) Coenozoic (b) Mesozoic (c) Palaeozoic
Consider a thorn in Bougainvillea and a tendril in cucurbita. Are these two organs homologous or analogous ? Give reason.
Give two examples that represent adaptive radiation.
Darwin's finches and Australian marsupials.
Evolution is a discontinuous process. Is it correct ?
Sponsor Area
Give the three key factors of the modern concept of evolution.
What are the five factors which influence Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Five factors that affect Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
are:
(i) gene migration or gene flow,
(ii)genetic drift,
(iii)mutation,
(iv)genetic recombination and
(v) natural selection.
Which other scientist postulated the same theory that Darwin held and at approximately the same time.
Define adaptve radiation.
The process of evolution of different
species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography (habitats) is called adaptive radiation.
Define gene migration.
When migration of a section of population to another place and population occurs, gene frequencies change in the original as well as in the new population and this process is called gene migration.
What is genetic drift ?
Name three types of natural selection.
(1) Stabilizing selection.
(2) Directional selection.
(3) Disruptive selection.
Name the age and give the year during which the modern man arose ?
Modern Homo sapiens arose during ice age between 75,000-10,000
years ago .
Attempt giving a clear definition of the term species.
Why was the theories of spontaneous generation not accepted ?
Spontaneous theory stated that life came from decaying and rotting matter like mud, straw etc. It was not accepted because Louis Pasteur demonstrated with the help of experiments that life always came from pre-existing life.
State the three connotations of the theory of special creation.
(i) All living organisms were created as such.
(ii) The diversity has remained the same since creattion and will continue to remain the same.
(iii) The earth is 4000 years old.
Briefly explain theory of biogenesis.
Write the composition of primitive earth’s atmosphere according to the Big Bang theory..
What are coacervates ?
List characteristics of coacervates.
1. Molecular aggregates.
2. Bounded by a membrane.
3. Grow by absorbing materials.
4. They divide by budding.
Why is nascent oxygen supported to be toxic to aerobic life forms?
Sponsor Area
Write the contribution of Urey and Miller.
Give a brief account on Darwin's Finches
While creation and presence of variation is directionless, natural selection is directional as it is in the context of adaptation. Comment.
Whereas the natural selection according to Darwin is a slow gradual process in which the nature selects for fitness and leads to speciation in the long run. In natural selection , the variations for better adaptation which are heritable and which make resource utilisation better for a few species will enable only those to reproduce and leave more progeny. Hence over a period of time, the favored species will become more common and the othespecies will be less common or lost. Thus natural selection is directional in context to adaptation.
State and explain any three factors affecting allele frequency in populations.
i. Genetic migration or Genetic drift. - When a section of population migrates to some other region then there is change in the gene frequencies and new allele or gene are added to the population.
ii. Mutation Mutation leads to the formation of new species and hence change in allelic frequencies.
iii. Natural selection - is the process in which heritable variations that enable better survival are chosen and the organism is enable to produce and leave more number of progeny.
Find out through internet and popular science articles whether animals other than man has self-consciousness.
What is convergent evolution ?
What are homologous organs ? Give examples.
Examples of homologous organs.
1. The wings of bird and bat, flipper (fin) of whale, structure of human forearm have common ancestory but perform different function.
2. In plants, the homologous organs may be a thorn of Bougainvillea or a tendril of cucurbita both arising in axillary position are examples of homologous organs.
What are analogous organs ? Give one example from plants and another from animals.
Examples. 1. Wings of birds and insects.
2. Leaves of a plant and cladodes of Ruscus are also analogous organs.
What are vestigial organs ? Give examples.
Write significance of vestigial organs.
Describe one example of adaptive radiation
Define connecting link (in regard to evolution) and give its one example from vertebrates.
What is the significance of connecting links ?
What are fossils ?
What is radioactive -dating? State the principle behind the procedure.
It is based on the principle - Each radioactive element decays at its own nearly constant rate. Once this rate is known, geologists can estimate the length of time over which decay has been occurring by measuring the amount of radioactive parent element, the amount of stable daughter elements and the amount of radioactive substances left, thus giving the age of the different things like rocks.
What does natural selection lead to ?
i. Stabilisation- in which more and more individuals aquire the mean character value.
ii. Directional change - in which more and more individuals aquire character other than the mean character.
iii. Disruption in which more and more individuals aquire peripheral character value at both the ends of distribution.
Why is Archaeopteryx called a connecting link between reptiles and birds ?
Discuss geological time scale as evidence of evolution.
G. Araduiana developed the first geological time scale. In the geological time scale, the duration of earth's history has been divided as follows :
Era Periods -
Palaeozoic era has 6 Periods. They are : Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian.
Mesozoic era has 3 Periods. They are Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous.
Coenozoic era has 2 Periods. Tertiary and Quarternary.
Some of the periods are further divided into still smaller time spans called epochs. Tertiary period 5 epochs namely Palaeocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene and Pliocene.
Quarternary has 2 epochs called Pleistocene and Recent.
Can we call human evolution as adaptive radiation?
How does embryology support evolution doctrine ?
According to Ernest Heckel certain features of the embryonic stages are common in the vetebrates..The comparative study of the embryology of different animal groups shows striking structural similarities between them. For example the embryos of all vetebrates including humans develop a row of vestigial gill slit just behind the head but it is functional organ only in fish and not found in any other adult vertebrates.
(i) Give any two striking similarities in the structure of embryos of all the vertebrates.
What according to Lamarck was the driving force for evolution? Explain with an example.
What is biogeography ? How does the distribution of animals and plants support evolution ?
What is adaptive radiation ?
Name the various theories of evolution.
(i) Lamarck's theory of inheritance of acquired characters or Lamarckism.
(ii) Darwin's theory of Natural selection or Darwinism.
(iii) De Vries Mutation theory.
List the main points of Lamarck's theory.
1. Effect of environment.
2. Effect of use and disuse of organs.
3. The inheritance of acquired characters.
4. The origin of new species.
Give the main points of Darwin's Theory of Evolution.
1. Rapid multiplication.
2. Struggle for existence.
3. Variations.
4. Natural selection or survival of the fittest.
5. Inheritance of useful variations.
6. Origin of new species.
Explain antibiotic resistance observed in light of Darwinian selection theory.
When the bacteria are grown in culture that have a certain antibiotic, most of the bacteria are killed but some of them develop a mutation which provides resistance against the antibiotic . With time the bacterial population having antibiotic resistance will increase and outgrow the population of the non-resistant bacteria. Thus a new species that has antibiotic resistance will be selected against the original one.
Find out from newspapers and popular science articles any new fossil discoveries or controversies about evolution.
Describe De Vries Mutation theory.
According to this theory, new species arise suddenly showing abrupt deviations in characters from the normal forms. Thus evolution is not a slow and gradual process but a sudden discontinuous and process. He believed that mutation caused speciation and hence called it saltation (single step large mutation)
What is the main difference between Darwin's theory of natural selection and De Vries mutation theory ?
What is competition in nature ? How does it affect the plant and animal life ? Mention some examples.
As a result of struggle for existence, only the fittest survives while the weak ones die.
Due to change in the environment, an organism which survives, adapts itself to the changed environment. This brings variations in the organism.
The variations are the raw materials of evolution. By the inheritance of some of these variations in successive generations, new species are formed both in plants and animals, e.g. progeny of pea plant.
Where did Darwin err in his theory of the “Origin of Species” through natural selection ?
1. Survival of the fittest. Darwinism can explain the survival of fittest but is unable to account for arrival of the fittest. It is difficult to suppose that small variations could have formed organs like wings and mimicry colouration which are useful only in their fully developed state.
Certain organs can be helpful to the organism only in fully developed state and what about their presence in early stages.
2. Over specialization. Tusks of elephants and the antlers of some deer have overgrown their usefulness.
3. Vestigial organs. A number of vestigial organs persisting generation after generation has no explanation according to Darwinism.
4. Darwin did not differentiate between somatic and germinal variations.
List three mechanisms by which variant genotypes can be produced in nature.
(a)Mutation.
(b) Random fertilization.
(c) Hybridization.
Why is the frequency of sickle cell anaemia more in the malaria prone areas ?
What is industrial melanism ?
Or
Explain how natural selection has worked on population of peppered moth in industrial area of England.
However, with the replacement of coal and petroleum by gas and electricity the situation has changed. Thus the white moth has become abundant with a sharp decline in the number of black. The reason being the decrease in pollution and restoration of grey colour on the trees because of the growth of the lichens on the tree trunk.
Thus industrial melanism is an interesting example of evidence in favour of natural selection.
What observations is natural selection based on ?
i. Natural resources are limited.
ii. Populations are stable in size except for seasonal fluctuation.
iii. Members of a population vary in characteristics (infact no two individuals are alike) even though they look superficially similar.
iv. most of variations are inherited etc.
How is artificial selection different from natural selection ?
|
Artificial selection |
Natural selection |
|
1. It is selection by man. 2. Variants suited to human requirement are selected by man |
1. In it, the selection is through nature. 2. Variants adapted to the environment are able to thrive better. |
Sponsor Area
'Polyploidy can also lead to the formation of a new species very rapidly.” Explain.
The organisms having more than two sets of chromosomes (3n, 4n, 5n, 6n) are called polyploids. The polyploids are common among plants and rarely found in animals. . Polyploidy is means of rapid speciation. Polyploidy often leads to uneven distribution of chromoses among the daughter cells due to large number of chromosomes thus leading to genetic variation and occurence of new species. Polyploidy also results in a large number of combinations of genes paving way for speciation. The different types of wheat varieties have evolved through polyploidy. Original number of chromosomes in wheat (Triticum moncoccum) is 2N = 14. By polyploidy hexaploid varieties of wheat (Triticum aestivum) have been obtained (6N = 42).
How were mammals better than the other organisms?
Describe three mechanisms by which genetic variability can be produced in nature.
(ii) By mutations. Mutations are induced artificially by radiations or chemical mutagens. Thus creating variations and leading to the evolvement of a new species even.
(iii) Recombination- the process of recombination during the cell division results in the variation in the genes.
Discuss the role of variations in evolution.
Genetic variability is necessary for evolution. They are the raw materials of evolution.
The homology in haemoglobin of man and gorilla is 99 per cent. What explanation would you give for this finding ?
Differentiate apes and man.
|
Ape |
Man |
|
1. Cranium expanded, maximum brain size 750 cc. 2. Less erect posture. 3. Strong jaws and without well marked 4. Incisor and canine teeth large. 5. Limited use and no manufacture of tools. 6. Not able to speak. |
1. Cranium expanded, maximum brain size 2,250 cc. 2. Fully erect posture. 4. Incisor and canine teeth reduced.
5. Extensive use and manufacture of tools. 6. Able to use spoken and written language. |
List the chronological sequence of evolution of genus Homo.
H. erectus → H. sapiens Neanderthalensis → H. sapiens sapiens.
Give important characteristics of the skull of Australopithecus.
1. Theythey hunted with stone weapons.
2. They ate fruits and did not eat meat.
3. Long snout like that of nose.
4. Dentition resembles present day man.
5. Face is less projected.
6. Large sized brain in comparison with other animals of that period.
Name the man-like primates in the evolutionary history of man which started tool making?
What role fire played in the early evolutionary history of man ?
1. Fire protected man from cold weather.
2. Fire protected man from wild beasts.
3. The cooking habits also changed with the help of fire, the man started cooking food.
4. Making of tools was made possible with the heat of fire.
Try to trace the components of human evolution.
|
Human type |
Cranial cavity |
Skeletal features |
Dietary preference |
|
(i) Australopithecus (ii) Homo habilis (v) H.sapiens fossilis (vi) H. sapiens sapiens |
600 cm3 735 cm3(650 - 800 cm3) 1660 cm3 |
Prognathous, well developed -do- -do- - do- Flat forehead, no supraorbital ridges, chin present. |
Primarily fruit-feeder but also hunted with stones. Primarily herbivorous. Primarily a meateater. Primarily carnivorous. Primarily carnivorous Primarily omnivorous. |
Briefly state the major theories of origin of life. Which one of them has scientific basis ?
The major theories of origin of life are :
1. Special Creation (Proposed by Father Saurez). This theory of special creation attributes the origin of life to a supernatural or vitalistic events at a particular time in the past. In other words, this theory believes in the creation of life by God.
2. Spontaneous Generation : This theory discards the abiogenesis and believes in biogenetic origin of life i.e. life originates from pre-existing life-biogenesis.
3. Extra terrestrial or Cosmic Origin (Richter). This theory believes that life on earth came from some other planet.
4. Terrestrial Origin or Abiogenic Origin (Oparin and Haldane). This theory states that life originates on earth from collections of organic molecules that were produced early in the history of the earth. This theory of terrestrial origin has scientific basis.
State the hypothesis of Oparin and Haldane about the primeval earth condition. What do you understand by Haldane’s hot, dilute soup ? State its significance.
Significance of hot dilute soup. Thus conditions of reducing nature are unable to oxidize these organic compounds which form the basis of life.
Summarise Miller's simulation experiment for organic synthesis. Comment on its efficacy.
Miller's experiment. Miller (1953) sealed in a spark chamber a mixture of water, methane, ammonia, hydrogen gas. He made arrangement for boiling water. The tap in turn, was connected with the flask for boiling water. After 18 days, significant amount of simple major organic compounds such as amino acids such as glycine, alanine, and aspartic acid and peptide chains, began to appear. Simple sugars, urea, short chain fatty acids were also formed. In atmosphere, this spark is provided by U.V. light or other energy source.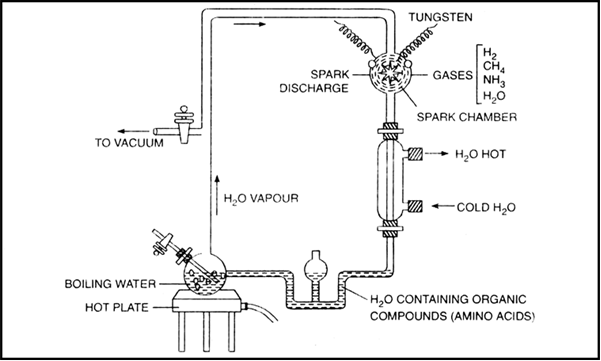
Stanley Miller's Experiment in the artificial production of organic compounds.
Using internet and discussing with your teacher, trace the evolutionary stages of any one animal say horse.
The major evolutionary trend of horses:
(i) General increase (with occasional decrease) in size.
(ii) Progressive loss of toes.
(iii) Lengthening of toes that are retained.
(iv) Lengthening of limbs in general.
(v) Enlargement of brain (especially cerebral hemisphere).
(vi) Increase in the height.
(vii) Increase in the complexity of molar teeth and an enlargement of the last two and, eventually, the last three premolars until they came to resemble molars.
Fig. Evolution of horse.
Evolution of horse. Top row shows change in form and size of the body.
Second row show reduction in lateral toes of hind and forelimbs.
The right figure in each set of two is of the forefoot, the left of the hindfoot.
Third row shows change in form and size of skull.
What is variation ? Name the basic processes that cause variation among organisms. Discuss the role of migration in evolution.
Causes of variation. Mutation, recombination, gene migration, genetic drift and natural selection.
Role of Migration. Few populations are isolated from the other populations of the same species, usually some migration takes place if the migrating individuals breed within the new population then immigrant will add new alleles to the local gene pool of host population and lead to variations.
Define genetic drift, founder effect and genetic bottleneck?
Genetic drift. Random change occurring in the allele frequency by chance alone are called genetic drift.
Founder effect. When a population gets separated from the existing population, it becomes the founder of new population. This is called the founder effect wmost of the the organisms of population died leaving behind few individuals of the population The remaining become the founder of new population which will produce only few genes by selection only i.e. by chance new population emerges and it is similar to a bottle in which only certain population is allowed to flow as in neck of bottle thus it is known as the bottleneck effect.
Fig. Bottleneck effect
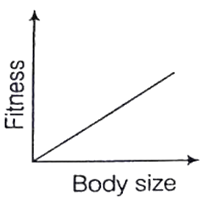
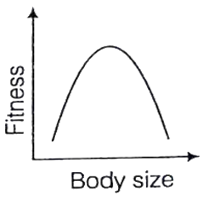
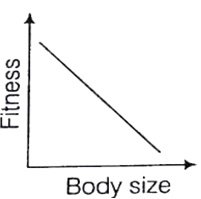
What is natural selection in modern terms ? Elucidate the three different effects of natural selection on variation.
If in a population both small and largest individuals contribute relatively fewer offspring to the next generation then those closer to the average size do, stabilizing selection is operating.
If centre of population contributes more, then equilibrium is maintained. While if extremes of population work, then two peaks in the distribution of a trait produced, while former is disruptive selection.
Describe present day concept of evolution.
(i) Mutations. These have been recognised as the ultimate source of biological changes and hence the raw material of evolution. The mutation in chromosomes may be due to changes in structure, number or gene.
(ii) Gene Recombination takes place during crossing over in meiosis. New combinations of genes produce new phenotypes.
(iii) Hybridisation is the intermingling of the genes of the members of closely related species.
(iv) Genetic drift is the elimination of the genes of some original characteristics of a species by extreme reduction due to different reasons.
In monoparental reproduction only chromosomal and gene mutation are sources of genetic variation.
(2) Natural Selection. If differential reproduction (i.e. some individuals produce abundant offspring, some only a few and some organisms none) continues for many generations, genes of the individuals which produce more offspring will become predominant in the gene pool of the population. Thus natural selection occurs through differential reproduction in successive generations.
(3)Migration of individuals from one to other population is an accessory factor for speciation (origin of new species).
(4) Isolation. The isolation plays a significant role in evolution. Isolation of a species population into different geographical zones may lead to formation of a new species.
State the advantages that the erect posture and large brain gave to the humans over other primates.
List a few modern day animals and from internet link to corresponding ancient fossil. Name both.
| Modern day animal | Ancient forssil |
| 1. Man | 1. Cro-magnon man |
| 2. Horse | 2.Eohippus |
| 3. Dog | 3.Leptocyon |
| 4. Giraffe | 4.Palaeotragus |
| 5.Camel | 5.Protylopus |
| 6. Elephant | 6.Mammoth |
| 7. Bat | 7. Archaeonycteris |
| 8. Whale | 8. Protocetus |
| 9. Birds | 9.Archeopterix |
| 10.Tetrapods | 10. Icthyostega |
As a student of biology, trace the evolutionary history of man.
1. The evolution of hominid occurred in Africa and Asia.
2. The evolution of man took place in Africa.
3. Ramapithecus and Dryopithecus lived in Africa and Asia were the forerunners of hominids.
4. Genus Australopithecus appeared in Africa about 5 million years ago.
5. The genus Homo appeared about 2 million years ago.
6. Homo habilis lived in Africa about 2 million years ago and was characterized by larger brain; could use tools.
7. Homo erectus appeared about 1.7 million years ago and believed to have migrated to Asia and Europe.
8. As a result of abrupt transition which occurred in Europe about 84000 years ago that Neanderthal man was wiped out and gave way to more efficient Cro-Magnon.
9. Homo sapiens were evolved about 10000 years ago.
Name any two vertebrate body parts that are homologous to human forelimbs.
(i) Wings of bats, (ii) Flippers of whale.
What is divergent evolution ? Explain taking an example of plants.
Example. Thorn of Bougainvillea or a tendril of Cucurbita both arising in axillary position. These modifications indicate the evolution of organ to suit different functions.
What is adaptive radiation ? Show how adaptive radiations gave rise to a variety of marsupials in Australia ?
It can be explained with an example of marsupial mammals present in Australia due to different geographical locality have similar habitat but have different species. A number of marsupials, each different from the other (Figure 7.6) evolved from an ancestral stock, but all within the Australian island continent. When more than one adaptive radiation appeared to have occurred in an isolated geographical area.
Give a brief summary od Darwin's theory of evolution and evidences in favor of it and its drawbacks.
Charles Darwin (1809-1882), a naturalist proposed a theory to explain the process of evolution. His theory was published in his famous book 'Origin of Species' published in 1858. His theory of natural selection is termed Darwinism.
Darwin's Theory of Evolution may be summed up as follows :
1. Rapid multiplication
2. Struggle for existence
3. Variations
4. Natural selection or survival of the fittest
5. Inheritance of useful variations
6. Origin of new species.
Evidences in favour of Darwin's theory.
Darwin's theory is supported by natural selection, phenomena of mimicry and protective colouration, and correlation between nectaries of flowers and proboscis of pollinating insects.
Draw backs - Darwin's theory fails to explain perpetuation of vestigial organs and over-specialization of organs.
Name the scientist who proved the spontaneous generation theory to be invalid.
Lichens are an indicator of pollution. Explain.
Mention the type of evolution that has brought the similarity as seen in potato tuber and sweet potato.
Why are wings of a butterfly and of a bat are called analogous ?
State the Hardy-Weinberg principle.
Hardy-Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a population are stable and is constant from generation to generation. The total number of genes and their alleles (Gene pool) in a population remains constant. This is called genetic equilibrium. The sum total of alleleic frequency is 1.
According to the law we get abinomial expression :
where
p and q are individual frequencies of allele A and a respectively.
p2 represents the frequency of the homozygous genotype AA,
q2 represents the frequency of the homozygous genotype aa, and
2pq represents the frequency of the heterozygous genotype Aa
According to Hardy–Weinberg’s principle, the allele frequency of a population remains constant. How do you interpret the change of frequency of alleles in a population ?
Lamarck's theory of evolution is also called :
-
Survival of the fittest
-
Special creation theory
-
Inheritance of acquired characters
-
None of these.
C.
Inheritance of acquired characters
Darwin's theory does not include :
-
Natural selection
-
Survival of the fittest
-
Evolution through inheritance
-
Struggle for existence.
C.
Evolution through inheritance
Darwin's theory states that :
-
Characters are acquired through inheritance
-
Nature selects species which can adapt
-
Species change morphologically with nature
-
Affect of environment on evolution.
B.
Nature selects species which can adaptSponsor Area
Hexaploid wheat developed through :
-
Hybridomas
-
Chromosome doubling
-
Hybridisation
-
Hybridisation and chromosome doubling
D.
Hybridisation and chromosome doubling
Which of the following is correct order of the evolutionary history of man ?
-
Peking man, Homo sapiens Neanderthal man, Cromagnon man
-
Peking man, Heidelberg man, Neanderthal man, Cromagnon man
-
Peking man, Heidelberg man, Neanderthal man, Cromagnon man
-
Peking man, Neanderthal man, Homosapiens, Heidelberg man.
C.
Peking man, Heidelberg man, Neanderthal man, Cromagnon man Homo sapien directly evolved from : - Peking man
- Java man
- Neanderthal
- Australopithecus
C.
Neanderthal Which ancestor of man for the first time began the bipedal locomotion ? - Cromagnon man
- Australopithecines
- Java-apeman
- Peking man
B.
Australopithecines
Advanced feature of man over ape is that :
-
man's hands are longer
-
man's hands are shorter
-
man's brain is smaller
-
man's spinal cord is curved
B.
man's hands are shorterDescribe one example of adaptive radiation.

Identify 'a' and 'b' in the figure given below representing proportionate number of major vertebrate taxa.
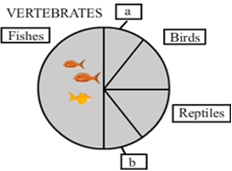
In the given figure,
a represents amphibians, and
b represents mammals
Explain Darwinian theory of evolution with the help of one suitable example. State the two key concept of the theory.
Darwinian theory of Evolution
According to Darwin, evolution took place by natural selection.
The number of life forms depends upon their life span and their ability to multiply.
Another aspect of natural selection is the survival of the fittest where nature selects the individuals, which are most fit to adapt to their environment.
An example of such a selection is the antibiotic resistance in bacteria. When a bacterial population was grown on an agar plate containing antibiotic penicillin, the colonies that were sensitive to penicillin died, whereas one or few bacterial colonies that were resistant to penicillin survived. This is because these bacteria had undergone chance mutation, which resulted in the evolution of a gene that made them resistant to penicillin drug. Hence, the resistant bacteria multiplied quickly as compared to the non-resistant (sensitive) bacteria, thereby increasing their number. Hence, the advantage of an individual over the other helps in the struggle for existence.
Darwin also observed that variations are inheritable and the species fit to survive the most leaves more offsprings. Hence, the population’s characteristics change, giving rise to the evolution of new life forms.
The two key concepts of the theory are:
(1) Branching descent: According to this concept, various species have come into existence from a common ancestor.
(2) Natural selection: According to this concept, nature selects the individuals, which are most fit to adapt to their environment.
State a reason for the increased population of dark coloured moths coinciding with the loss of lichens (on tree barks) during industrialization period in England.
Industrialization led to darkening of the tree trunks due to deposition of smoke and soot and increase in pollution. The dark colored moths were not attacked by the predators as they camouflaged against the dark bark of the trees while the white coloured moths were picked out by the predators. The lichen population also decreased due to the increase in pollution.
Explain adaptive radiation with the help of a suitable example.
The process of evolution that starts from a single point and radiates in different directions is called adaptive radiation. For example the evolution of marsupials of Australia, each different from one another evolved from a common ancestral stock is found within the Australian island. 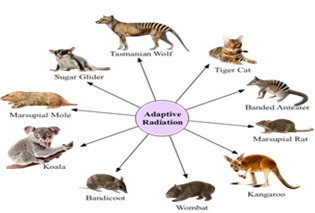
Identify the examples of convergent evolution from the following:
(i) Flippers of penguins and dolphins
(ii) Eyes of octopus and mammals
(iii) Vertebrate brainsThe examples of convergent evolution are:
(i) Flippers of penguins and dolphins
(iii) Eyes of octopus and mammals
With the help of any two suitable examples explain the effect of anthropogenic actions on organic evolution.
Two examples that explain the effect of anthropogenic actions on organic evolutions are:
(i) Industrial melanism: It was due to the industrialization. The smoke and soot coming out of industries caused the bark of the trees to become darker and so dark-coloured moths were selected over the white-coloured moths.
(ii) Excessive use of herbicides and pesticides has resulted in selection of resistant varieties in very short time span.
Write the similarity between the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat. What do you infer from the above with reference to evolution?
Wings of a butterfly and the wings of a bat are similar in function that is both are used for flying. These two are the result of convergent evolution.
State the theory of Biogenesis. How does Miller’s experiment support this theory?
The theory or law of biogenesis was proposed by Louis Pasteur. He proposed that all life originated from pre-existing life. These cells further originated from the organic compounds. So, ultimately life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g. RNA, protein, etc.) and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, i.e., formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents. In 1953, Urey and Miller conducted an experiment to prove this theory. They created the conditions of primeval earth − high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere containing CH4, NH3, etc at laboratory scale. They then stimulated electric discharge in a closed flask containing CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapour at 8000°C. They observed formation of amino acids. In similar experiments, others observed, formation of sugars, nitrogen bases, pigment and fats. These small organic molecules are the building blocks for proteins & other components. Hence, this experiment supported that life has come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules.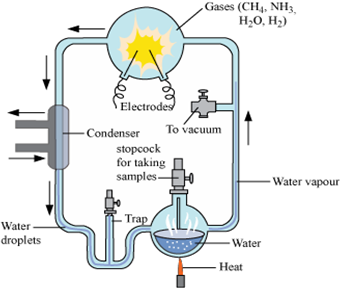
Explain the salient features of Hugo de Vries theory of mutation. How is Darwin theory of natural selection different from it? Explain.
(a) Name the primates that lived about 15 million years ago. List their characteristic features.
(b) (i) Where was the first man-like animal found?
(ii) Write the order in which Neanderthals, Homo habilis and Homo erectusappeared on earth.
State the brain capacity of each one of them.
(iii) When did modern Homo sapiens appear on this planet?
(a) Dryopithecus (ape-like) and Ramapithecus (man-like) were the two primates that lived 15 million years ago. These primates were hairy and their walk was similar to that of chimpanzees.
(b) (i) The first man-like animal was found in Africa.
(ii)
|
Year |
Evolution |
Brain capacity |
|
2 million years ago |
Homo habilis (Australopithecines) lived in East Africa |
650- 800 cc |
|
1.5 million years ago |
Homo erectus |
900 cc |
|
1,000 - 40,000 years ago |
Neanderthal man |
1400 cc |
(iii) Modern Homo sapiens first appeared primarily in east Africa about 75,000 to 10,000 years ago.
(a) Select the homologous structures from the combinations given below :
(i) Forelimbs of whales and bats
(ii) Tuber of potato and sweet potato
(iii) Eyes of octopus and mammals
(iv) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita
(b) State the kind of evolution they represent.
(a) Homologous organs or structures are those that are similar in anatomy or structure and have a common origin, but perform different functions.
From the given options, following are homologous structures:
i. Forelimbs of whales and bats are similar in structure but perform different functions of swimming and flying, respectively.
ii. Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita are both modifications of a stem arising from axillary bud but perform different functions of protection (thorns) and climbing (tendrils), respectively.
(b) The evolution represented by homologous organs or structures is divergent evolution as they have a common origin but have diverged (became dissimilar) with time into different structures performing different functions.
What does the following equation represent? Explain
p2 + 2 pq + q2 = 1
The equation of p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 represents the genotypic frequencies of a population, when it is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
According to this law, the frequency of occurrence of alleles of a gene in a population remains constant through generations unless disturbances, such as mutations and non-random mating, are introduced.
Individual frequencies are represented as p and q such as in a diploid, where p and q represent the frequency of allele A and a respectively. The sum total of all allelic frequencies is 1.
The frequency of genotypes, AA is p2, that of aa is q2 and that of Aa is 2pq.
Hence, p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1, which is the expansion of (p + q)2.Since the origin of life on the earth, there were five episodes of mass extinction of species.
(i)How is the 'Sixth Extinction', presently in progress, different from the previous episodes?
(ii)Who is mainly responsible for the 'Sixth Extinction''?
(iii)List any four points that can help to overcome this disaster.
(i)The Sixth Extinction is different from the previous episodes of mass extinction in the following ways
a. The rates of extinction is faster and is estimated to be 100-1000 times faster than in the previous ones.
b.. It is due to the activities of human and not because of any natural calamity as compared to the previous episodes.
(ii).Human activities are mainly responsible for the Sixth extinction.
(iii) The points that can help to overcome this disaster are:
a Avoiding over exploitation of the ecosystem.b. Preventing habitat loss and fragmentation
c. Conservation / Preservation of species.
State the significance of Coelacanth in evolution.
Coelacanths are considered to be the missing link between fishes and the first four-limbed animals (amphibians) and were the ancestors of modern day frogs and salamanders.
How does industrial melanism support Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection? Explain.
Darwin's theory of natural selection is a process in which the organisms which have favourable variations in order to survive in the changed environment are selected by the nature to continue their generations and the rest fail to survive. Industrial melanism also showed the same case as was explained by Darwin’s theory of natural selection.
Industrial melanism - In England, it was noted that before industrial revolution, the number of white-winged moths was much more than that of dark melanised moth. However, after industrialisation, the number of dark moths increased. This happened because; the industrialization caused the tree trunks to become darker with deposits of soot and smoke. Hence, the dark moths increased as they escaped the predators as they were not easily visible while the white-winged ones were easily picked up. Thus, dark ones were selected by nature (natural selection) and light ones failed to survive.Write the probable differences in eating habits of Homo habilis and Homo erectus.
| Homo habilis | Homo erectus |
| Did not eat meat | Ate meat |
| Brain comparatively smaller. | Larger brain. |
How do homologous organs represent divergent evolution ? Explain with the help of a suitable example.
The organs with same structural design and origin but different functions are called. homologous organs
For example in plants the thorn and tendrils of Bougainuillea and Cucurbita represent homology. Both the thorn and the tendril have a common ancestor but have evolved to perform different function in different organism. Like the thorn has a protective function whereas the tendril provides support to the plant. Thus, it represents divergent evolution.
According to de-Vries what is saltation?
According to De Vries, Saltation is a single step large mutation which leads to speciation.
Describe the experiment that helped Louis Pasteur to dismiss the theory of spontaneous generation of life.
Louis Pasteur suggested that life propagated only from the pre-existing life forms. He conducted the swan-necked flask experiment and proved his point on the continuity of life.
His experiment was as follows:
• Two swan-necked flasks containing nutrient broth were used.
• The broth in both the flasks was boiled to kill any existing microbes and was made sterile.
• After sterilisation one of the flask necks was broken. The flasks were kept undisturbed for some time.
• After some time, the dust particles along with bacteria in the air entered the flask with the broken neck and got accumulated at the neck of the unbroken flask.
• The broth in the broken flask became cloudy, while the broth in the unbroken flask remained clear. Cloudiness of the broth indicated the presence of microbial life in the broken flask.
• Appearance of life, even after sterilisation, in the broken flask concluded that life in the flask arose only from pre-existing life; thus, and discarded the theory of spontaneous generation.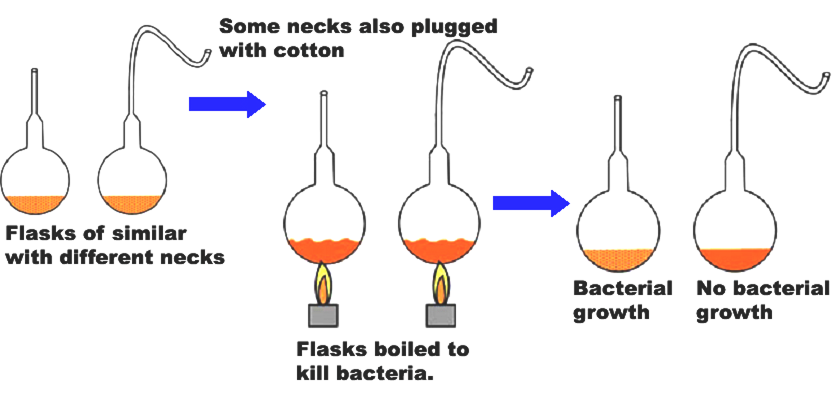
Name the common ancestor of the great apes and man.
Australopithecus were the common ancestor of the great apes and man
Branching descent and natural selection are the two key concepts of Darwinian Theory of Evolution. Explain each concept with the help of a suitable example.
Natural Selection is a process in which better-adapted organism’s or traits leads to better adaptation and survival while less adapted organisms get eliminated at successive stages. Selected organisms reproduce and produce stable population to sustain the changes. E.g peppered moth of England grew in number because of the natural selection of the peppered moth.
Branching descent is the process of development of a new species from a single common descendant. New species developed became geographically adapted to a new environment. This resulted into the the reproductive isolation and finaly to the development of a new species.
What role does an individual organism play as per Darwin’s theory of natural selection?
According to the Darwin’s theory of natural selection, the role of an individual organism is to pass on the necessary variations, changes or mutations that has been selected by the native, from present generation to the next.
p2+2pq+q2 Explain this algebraic equation on the basis of Hardy-Weinberg’s principle.
The equation p2 + 2pq + q2 , mathematically represents the Hardy-Weinberg’s principle. It is used to
calculate the genetic variation of a population at equilibrium.
Principle It states that allele frequencies in a population are stable and remain constant from generation to generation.
In this equation,
p – frequency of allele A
q – frequency of allele a
p2 – frequency of AA (homozygous) individuals in a population
q2 – frequency of aa (homozygous) individuals
2pq – frequency of Aa (heterozygous) individuals
Also, the sum total of all the allelic frequencies is equal to 1. If the p and q allele frequencies are known, then the frequencies of the three genotypes can be calculated using the Hardy-Weinberg equation.
This equation can be used to measure the differences in frequencies of observed genotype measured from the frequencies predicated by the equation. The disturbance in genetic equilibrium results in evolution, thus the presence of any difference indicates the exent of evolutionary change.
What are vestigial organs?
The organs which have no apparent utility in the present organisms but were functional in the ancestors are vestigial organs.
eg ; nictitating membrane as a remnant of third eyelid
Define root pressure.
It may be defined as the pressure under which water passes from the living cells of the root into the xylem. It is the pressure set up by the cortical cells of the root upon the liquid contents under fully turgid conditions forcing a quantity of it to flow into the xylem vessels and through them, upwards into the stem.
State three similarities between Australopithecus and aApes
2. Face was prognathous
3. Cranial capacity was between 450cc - 600cc
Give an account of the different types of natural selection.
Stabilizing Selection
When selective pressures select against the two extremes of a trait, the population experiences stabilizing selection. For example, plant height might be acted on by stabilizing selection. A plant that is too short may not be able to compete with other plants for sunlight. However, extremely tall plants may be more susceptible to wind damage. Combined, these two selection pressures select to maintain plants of medium height. The number of plants of medium height will increase while the numbers of short and tall plants will decrease.
Directional Selection
In directional selection, one extreme of the trait distribution experiences selection against it. The result is that the population's trait distribution shifts toward the other extreme. In the case of such selection, the mean of the population graph shifts. Using the familiar example of giraffe necks, there was a selection pressure against short necks, since individuals with short necks could not reach as many leaves on which to feed. As a result, the distribution of neck length shifted to favor individuals with long necks.
Disruptive Selection
In disruptive selection, selection pressures act against individuals in the middle of the trait distribution. The result is a bimodal, or two-peaked, curve in which the two extremes of the curve create their own smaller curves. For example, imagine a plant of extremely variable height that is pollinated by three different pollinators, one that was attracted to short plants, another that preferred plants of medium height and a third that visited only the tallest plants. If the pollinator that preferred plants of medium height disappeared from an area, medium height plants would be selected against and the population would tend toward both short and tall, but not medium height plants. Such a population, in which multiple distinct forms or morphs exist is said to be polymorphi
Define Neo-Darwinism
What are coacervates?
Give four anatomical differences between a dicot and monocot root.
DICOT ROOT
An inconspicuous pith or may be absent as well.
Mostly the number of xylem bundles are 4–6. So tetra or hexaxylic condition.
Pericycle (a thin parenchymatous circular layer inner to the endodermis) gives rise to lateral roots and secondary meristem (cambium & phellogen).
Cambium appears as a secondary meristem.
Secondary growth is seen cutting the secondary xylem towards the inner side and secondary phloem towards the outer side.
E.g. Root ot wheat.
MONOCOT ROOT
A very well developed parenchymatous central pith is present
Xylem shows polyarch condition. Exception= Allium cepa (onion).
Pericycle forms only lateral roots but no secondary meristem.
No cambium is present between xylem and phloem.
E.g. Zea mays
Both dicot and monocot roots have radial & exarch xylem.
Write the characteristics of Ramapithecus, Dryopithecus and Neanderthal man.
Characteristics of Ramapithecus : - * It evolved around 15 mya.
* More man-like, walked more erect, teeth like modern man. Characteristics of Dryopithecus : -
* It evolved around 25 mya. * Ape like, hairy arms and legs of same length, large brain, ate soft fruits and leaves, walked like gorillas and chimpanzees. Characteristics of Neanderthal Man : -
* It evolved around 1,00,000-40,000 year ago.
* Fossil found in east and central Asia, brain size 1400 cc used hides to protect body, buried their dead.
Write the names of the following :
(a) A 15 mya primate that was ape-like
(b) A 2 mya primate that lives in East African grasslands
(a) 15 mya, primates called Dryopithecus was more ape-like.
(b) 2 mya, Australopithecines lived in East African grasslands.
With the help of an algebraic equation, how did Hardy-Weinberg explain that in a given population the frequency of occurrence of alleles of a gene is supposed to remain the same through generations?
In a given population one can find out the frequency of occurrence of alleles of a gene or a locus. This frequency is supposed to remain fixed and even remain the same through generations. Hardy-Weinberg the principle stated it using algebraic equations.
This principle says that allele frequencies in a population are stable and is constant from generation to generation. The gene pool (total genes and their alleles in a population) remains a constant. this is called genetic equilibrium.
Sum total of all the allelic frequencies is 1. Individual frequencies, for example, can be named p, q, etc. In a diploid, p and q represent the frequency of allele A and allele a. The frequency of AA individuals in a population is simply p2. This is simply stated in another way, i.e., the probability that an allele A with a frequency of p appear on both the chromosomes of a diploid individual is simply the product of the probabilities,i.e., p2. Similarly of aa is q2, of Aa 2pq. Hence, p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1. This is a binomial expansion of (p + q)2.
When frequency measured, differs from expected values, the difference (direction) indicates the extent of evolutionary change. Disturbance in genetic equilibrium, or Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, i.e., change of frequency of alleles in a population would then be interpreted as resulting in evolution.
Differentiate between analogous and homologous structures.
| Analogous Organs | Homologous Organs |
| (i) Those organs which are structurally dissimilar but functionally similar are called analogous organs. | (i) Those organs, which are structurally similar but functional dissimilar are called homologous organs. |
| (ii)They lead to convergent evolution. | (ii) They lead to divergent evolution. |
| (iii) Eg. Wings of birds and insects. | Eg. Forelimbs of terrestrial vertebrates such as frog, lizard, bird, bat, horse, man. |
Select and write analogous structures from the list given below:
(i) Wings of butterfly and birds
(ii) Vertebrate hearts
(ii) Tendrils of bougainvillaea and Cucurbita
(iv) Tubers of sweet potato and potato
These are the analogous structure from the given list:
(i) Wings of butterfly and birds.
(ii) Tubers of sweet potato and potato.
Analogous structures are a result of
-
convergent evolution
-
shared ancestry
-
stabilising selection
-
divergent evolution
A.
convergent evolution
Analogous organs are those which are similar in function but do not have a common ancestor and thus they are a result of convergent evolution.
Which of the following structures is homologous to the wing of a bird?
-
Wing of a moth
-
Hind limb of a rabbit
-
Flipper of whale
-
Dorsal fin of a shark
C.
Flipper of whale
Wings of bird and flipper of whale are modified forelimbs of the two organisms so have same origin wings help in flying and flippers help in swimming but thus perform the different functions
Following are the two statements regarding the origin of life
I. The earliest organisms that appeared on the earth were non-green and presumably anaerobes.
II. The first autotrophic organisms were the chemoautotrophs that never released oxygen.
Of the above statement which one of the following options is correct?
-
II is correct but I is false
-
Both I and II are correct
-
Both I and II are false
-
I is correct but II is false
B.
Both I and II are correct
The first organisms were chemoautotrophic anaerobes.
The process by which organisms with different evolutionary history evolve similar to a common environmental challenge is called
-
natural selection
-
convergent evolution
-
non-random evolution
-
adaptive radiation
B.
convergent evolution
Convergent evolution occurs in an unrelated group of organisms. It is the development of similar functional structures but in related groups.
The process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography is called adaptive radiation. Natural selection is the basis of evolution.
The tendency of population to remain in genetic equilibrium may be disturbed by
-
random mating
-
lack of migration
-
lack of mutations
-
lack of random mating
D.
lack of random mating
According to Hardy-Weirberg principle, allele frequencies in a population are stable and is constant from generation to generation allele frequencies in a population will remain constant over generations only if the following condition are met
i) There is no mutation no gene flow and all mating is random
ii) All genotypes reproduce equally well (i.e., no natural selection,)But their conditions rarely met in nature.
According to Darwin, the organic evolution is due to
-
intraspecific competition
-
interspecific competition
-
competition within closely related species
-
reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species
B.
interspecific competition
Darwin stated that the organic evolution is due to interspecific competition. it is the competition between members of different species. Intraspecific competition occurs amongst members of the same species for obtaining optimum amounts of their food, shelter, mate, water, light, species etc. Closely species compete cannot cause evolution. Reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species is due to strugle for existance.
Select the wrong statement:
-
the viroids were discovered by D.J. Ivanowski
-
W.M. Stanley showed that viruses could be crystallized
-
The term 'contagium vivum fluidum' was conined by M.W. Beijerinek
-
Mosaic disease in tobacco and AIDS in human being are caused by viruses
A.
the viroids were discovered by D.J. Ivanowski
All statements are correct except the statement (a), which can be corrected as Viroids were discovered by TO Diener in 1971 as a new infectious agent that was smaller than virus.
The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are:
-
homologous structures and represent divergent evolution
-
analogous structures and represent convergent evolution
-
phylogenetic structures and represent divergent evolution
-
homologous structures and represent convergent evolution
B.
analogous structures and represent convergent evolution
The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are analogous structures and represent convergent evolution.
Analogous organs have the same function and are superficially alike only. However their fundamental structures are quite different in morphology, anatomy and embryonic origin.
Analogy is an example of convergent evolution.
Industrial melanism is an example of
-
Neo Darwinism
-
Natural selection
-
Mutation
-
Neo Lamarckism
B.
Natural selection
Within a period of years in industrial or polluted areas, the dark species has almost replaced the light species. This is called industrial melanism because of its association with the sooty atmosphere of industry. It is an example of natural selection.
Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as
-
Adaptive radiation
-
Natural selection
-
Migration
-
divergent evolution
A.
Adaptive radiation
The diversification of an ancestral group into two or more species in different habitats is called divergent evolution. When this involves large number of species to occupy different ritches, this is called adaptive radiation. Adaptive radiation is the process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a species of animals or plants and literally radiating to other areas of geography (habitats). Darwin's finches represent one of best examples of this phenomenon. Australian marsupials are another example of adaptive radiation.
Which is the right option for Convergent and Divergent Evolution
Convergent Evolution Divergent Evolution Eyes of Octopus and mammals Bones of forelimbs of vertebrates Convergent Evolution Divergent Evolution Thorns of Bougainvillia and tendrils of Cucurbita Wings of butterflies and birds Convergent Evolution Divergent Evolution Bones of forelimbs of vertebrates Wings of butterfly and birds Convergent Evolution Divergent Evolution Thorns of Bougainvillia and tendrils of Cucurbita Eyes of Octopus and mammals
A.
| Convergent Evolution | Divergent Evolution |
| Eyes of Octopus and mammals | Bones of forelimbs of vertebrates |
Convergent evolution involves the independent development of similar structures in organisms that are not directly related. It is represented by analogous organs. e.g., eyes of Octopus and mammals evolution, same basic organ becomes adapted by specialisation to perform different functions. It is represented by homologous organs, e.g., fore limbs of vertebrates (like seal's flipper, bat's wing, cat's paw horse's front leg and human hand), thorns of Bougainvillia and tendrils of Cucurbita.
What was the most significant trend in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors?
-
Shortening of jaws
-
Binocular vision
-
Increasing cranial capacity
-
Upright posture
C.
Increasing cranial capacity
Modern man (Homo sapiens) is most evolved. The most significant trend in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors is the gradual increase in the cranial capacity. Cranial capacity of modern man is an average of 1450 cc.
The extinct human who lived 1,00,000 to 40,000 years ago, in Europe, Asia and parts of Africa, with short stature, heavy eye brows, retreating for heads, large jaws with heavy teeth, stocky bodies, a lumbering gait and stooped posture was
-
Homo habilis
-
Neanderthal human
-
Cro-magnon humans
-
Ramapithecus
B.
Neanderthal human
Neanderthal man with a brain size of 1400cc lived in near East and Central Asia, Europe and North Africa between 100000 to 40000 years back. It had slightly prognathus face sloping forehead eye brow ridges, smaller or no chin, large receding jaws, thick-boned skul and high domed head. They used hides to protect their body and buried their dead.
If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence as ATCTG, what would be the complentary RNA strand sequence?
-
TTAGU
-
UAGAC
-
AACTG
-
ATCGU
B.
UAGAC
If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence as ATCTG, the complementary sequence of mRNA will be UAGAC.
In a population of 1000 individuals 360 belongs to genotype AA, 480 to Aa and the remaining 160 to aa. Based on this data, the frequency of allele A in the population is
-
0.4
-
0.5
-
0.6
-
0.7
C.
0.6
According to Hardy - Weinberg principle
(p+q)2 = p2 +2pq + q2 = 1
Where, p = the frequency of allele 'A'
q= the frequency of allele 'a'
p2 = the frequency of individual 'AA'
q2 = the frequency of individual 'aa'
2pq = the frequency of individual Aa
(AA)p2 = 360 out of 1000 individual
or
p2 = 36 out of 100
q2 = 160 out of 1000 or q2 = 16 out of 100.
So, q = 0.161/2 = 0.4
As p+q = 1
so, p is 0.6
Forelimbs of cat, lizard used in walking forelimbs of whale used in swimming and forelimbs of bats used in flying are an example of
-
analogous organs
-
adaptive radiation
-
homologous organs
-
convergent evolution
C.
homologous organs
Homologous organs, are those organs which have a common fundamental anatomical plan and similar embryonic origin but perform varied functions. Forelimbs of cat, lizard used in walking, forelimbs of bats used in flying are the example for homologous organs. All are the modified forelimbs, with the same type of bones. They have become different due to the adaptions to the different habitat.
Which one of the following are analogous structures?
-
Wings of bat and wings of pigeon
-
Gills of prawn and lungs of man
-
Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita
-
Flippers of dolphin and legs of horse
B.
Gills of prawn and lungs of man
Analogous organs are the structures of different species having similar or corresponding functions but different structure. They do not belong to the same evolutionary origins.
Wings of bat are skin folds stretched mainly between elongated fingers but the wing of birds are a feather covering all along the arm. They look similar because they have a common use for flying but their origin is not common.
Which of the following had the smallest brain capacity?
-
Homo erectus
-
Homo sapiens
-
Homo neanderthalensis
-
Homo habilis
D.
Homo habilis
Homo habilis had the smallest brain capacity. Homo habilis also called the 'tool maker' or 'hand man' had a brain capacity of 700 cc.
Homo erectus had a brain or cranial capacity of 800-1300 cc.
Homo sapiens or modern man showed a slight reduction in brain/cranial capacity, i.e. 1300-1600 cc will be an average of 1450 cc.
A population will not exist in Handy - Weinberg equilibrium if
-
individuals mate selectively
-
there are no mutations
-
there is no migration
-
the population is large
A.
individuals mate selectively
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium exists in population only when following conditions are present.
No mutation
No gene flow
No genetic drift
No genetic recombination
No natural selection pressure.
If the individuals in the population mate selectively, it will had to mutation thus shifting the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
What was the most significant trend in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens) from his ancestors?
-
shortening of jaws
-
Binocular vision
-
Increasing brain capacity
-
Upright posture
C.
Increasing brain capacity
The first human- like being was the hominid, called Homo habilis. The brain capacities were between 650 - 800 cc. They probably did not eat meat. Fossils discovered in Java in 1891 revealed the next stage, i.e, Homo erectus. Homo erectus had a large brain and probably ate meat. The Neanderthal man with a brain size of 1400 cc lived in near east and central Asia between 1,00,000-40,000 year back. They used hides to protect their body and buried their dead. Homo sapiens arose in Africa and moved across continents and developed into distinct races. During ice age between 75,000 - 10,000 years back modern HOmo sapiens arose
Darwin's finches are a good example of
-
industrial melanism
-
connecting link
-
adaptive radiation
-
convergent evolution
C.
adaptive radiation
Darwin's finches are a good example of adaptive radiation. It is an evolutionary process starting from a point in the geographical area, giving rise to new species depending upon habitat. Main Darwin finch was in South America, some flew to Galapagos islands and some variations got selected and gave rise to new species.
Given below are four statements (A-D) each with one or two blanks. Select the option which correctly fills up the blanks in two statements.
A) Wings of butterfly and birds look alike and are the results of ...... (i) .... evolution.
B) Miller showed that CH4, H2, NH3, and .....(i) ....., when exposed to electric discharge in a flask resulted in the information of ......(ii) .....
C) The vermiform appendix is a ..... (i) ..... organ and a ......(ii) ..... evidence of evolution.
D) according to Darwin evolution took place due to ....(i) ...... and .....(ii) .... of the fittest.
-
(D)-(i) small variations, (ii) survival, (A)-(i) convergent
-
(A)- (i) convergent, (B)-(i) oxygen,(ii) nucleosides
-
(B)-(i) water vapour, (ii) amino acids (C)-(i) rudimentary, (ii) anatomical
-
(C)- (i) vestigal, (ii) anatomical (D)-(i) mutations, (ii) multiplication
A.
(D)-(i) small variations, (ii) survival, (A)-(i) convergent
Wings of butterfly and birds look alike and are the result of convergent evolution. Miller showed that CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapour, when exposed to electric discharge in a flask resulted in the formation of amino acids.
the vermiform appendix is a vestigial organ and an anatomical evidence of evolution.
According to Darwin, evolution took place due to small variations and survival of the fittest hence, option (a) is correct.
The most apparent change during the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens is traced in
-
loss of body hair
-
walking upright
-
shortening of the jaws
-
the remarkable increase in the brain size
D.
the remarkable increase in the brain size
Rounding and enlargement of cranium, ie, gradual increase in the brain size is the most apparent change during the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens
In the case of peppered moth (Biston betularia), the black-coloured form became dominant over the light-coloured form in England during the industrial revolution. This is an example of
-
natural selection whereby the darker forms were selected
-
the appearance of the darker coloured individuals due to very poor sunlight
-
protective mimicry
-
inheritance of darker environment
A.
natural selection whereby the darker forms were selected
The given case in an example of natural selection. As a result of the struggle for existence only those organisms could survive, which have favourable variations to adapt environmental conditions on with so many variations in populations of species the struggle for existence results in survival of the fittest. The survival of the fittest is the result of selection and proliferation of only those organisms, which were most suitably adapted the environment and most successful in mating, ie, natural selection.
Darwin's finches are an excellent example of
-
adaptive radiation
-
seasonal migration
-
brood parasitism
-
connecting links
A.
adaptive radiation
Adaptive radiation represents the evolution of new forms is several directions from the common anxcestral type. In 1831 Darwin got an opportunity to travel by H M S beagle for a voyage of world exploration. Beagle sailed to the Galapagos Islands, here Darwin found a living laboratory of evolution. The common birds of Galapagos Islands, the finches were markedly different from the finches of the main land. The closely related species of finches has beaks of different shapes and sizes and adapted for feeding on completely different diet showing adaptive radiation.
The transitional fossil forms, which show the characteristic of two different groups of living animals is called connecting links, eg, Archaeopteryx, Seymouria etc.
Which one of the following is incorrect about the characteristics of protobionts (coacervates and microspheres) as envisaged in the abiogenic origin of life?
-
They were able to reproduce
-
They could separate combinations of molecules from the surroundings
-
They were partially isolated from the surroundings
-
They could maintain an internal environment
D.
They could maintain an internal environment
Homoeostasis is keeping the internal environment of the body constant. It is necessary for normal life processes. Microspheres are molecular aggregates of proteinoids. Oparin and Sydney Fox held that large organic molecules synthesized abiotically on primitive earth formed large colloidal aggregates due to the intermolecular attraction. These colloidal particles were called coacervates. Oparin called giant nucleoprotein poid molecules as protobionts. These reproduce either by budding a binary fission but do not exhibit homoeostasis.
One of the important consequences of geographical isolation is
-
no change in the isolated fauna
-
preventing speciation
-
speciation through reproductive isolation
-
random creation of new species
D.
random creation of new species
Speciation is the formation of new species and the development of species diversity occurs when gene flow within the common pool is interrupted by an isolating mechanism. The isolation can occur through geographical separation of population, known as allopatric speciation.
Among the human ancestors the brain size was more that 1000 CC in
-
Homo neander-thalensis
-
Homo erectus
-
Ramapithecus
-
Homo habilis
A.
Homo neander-thalensis
The cranial capacity of Homo neanderthalensis was about 1450 CC, roughly equal to that of Modern Man.
The concept of chemical evolution is based on
-
cyrstallization of chemicals
-
interaction of water, air and clay under intense heat
-
effect of solar radiation on chemicals
-
possible origin of life by combination of chemicals under suitable environmental conditions
D.
possible origin of life by combination of chemicals under suitable environmental conditions
The concept of chemical evolution is based on possible origin of life by combination of chemicals under suitable environmental conditions.
Industrial melanism as observed in peppered moth proves that
-
The true black melanic forms arise by a recurring random mutation.
-
The melanic form of the moth has no selective advantage over lighter form in industrial area
-
The lighter-form moth has no selective advantage either in polluted industrial area or non-polluted area
-
Melanism is a pollution-generated feature
A.
The true black melanic forms arise by a recurring random mutation.
Industrial melanism is a term used to describe the evolutionary process in which darker individuals come to predominate over lighter individuals since the industrial revolution as a result of natural selection. In 1848 a black form of the moth was recorded in Manchester and by 1895, 98% of the peppered moth population in Manchester was black. This black 'melanic' form arose by a recurring random mutation, but its phenotypic appearance had a strong selective advantage in industrial areas.
About 98 percent of the mass of every living organism is composed of just six elements including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and
-
phosphorus and sulphur
-
sulphur and magnesium
-
magnesium and sodium
-
calcium and phosphorus
A.
phosphorus and sulphur
About 98% of the mass of every living organisms including bacterium and human beings is composed of just six elements i.e., Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P) and Sulphur (S).
The finches of Galapagos islands provide an evidence in favour of
-
special creation
-
evolution due to mutation
-
retrogressive evolution
-
biogeographical evolution
D.
biogeographical evolution
Darwin's finches of Galapagos islands had common ancestors lateron whose beaks modified according to their feed habit. These provide evidence of geographical distribution.
Which one of the following statement is correct?
-
Stem cells are specialize cells
-
There is no evidence of the existence of gills during embryogensis of mammals
-
All plant and animal cells are totipotent
-
Ontogeny repeats phylogeny
D.
Ontogeny repeats phylogeny
Recapitulation theory or Biogenetic law states that ontogeny (development of embryo) is recapitulation of phylogeny (ancestral sequence)
What is common to whale, seal and shark?
-
Seasonal migration
-
Thick subcutaneous fat
-
Convergent evolution
-
Homeothermy
C.
Convergent evolution
Distantly related animals (as whale, seal and shark) inhabiting similar habitats often develop similarly morphological features that make them look similar. This is termed adaptive convergence or convergent evolution.
Adaptive radiation refers to
-
adaptations due to geographical isolation
-
evolution of different species from a common ancestor
-
migration of members of a species to different geographical areas
-
power of adaptation in an individual to a variety of environments
B.
evolution of different species from a common ancestor
Adaptive radiation is the development of different functional structures from a common ancestral form.
When two species of different genealogy come to resemble each other as a result of adaptation, the phenomenon is termed
-
divergent evolution
-
microevolution
-
co-evolution
-
convergent evolution
D.
convergent evolution
In convergent evolution lineages show similar morphology under the influence of similar environmental factors.
Which one of the following amino acids was not found to be synthesized in Miller's experiment?
-
Glycine
-
Aspartic acid
-
Glutamic acid
-
Alanine
C.
Glutamic acid
Miller and Urey were the two scientists who recreated the conditions of primitive earth in laboratory and abiotically synthesized amino acids and bases. They synthesized glycine, aspartic acid and alanine in abundance quantities while glutamic acid is not synthesized in their experiment.
An important evidence in favour of organic evolution is the occurrence of
-
homologous and vestigial organs
-
analogous and vestigial organs
-
homologous organs only
-
homologous and analogous organs
A.
homologous and vestigial organs
An important evidence in favour of organic evolution is the occurrence of homologous and vestigial organs. Homologous organs are those which have the common origin and are built on the same fundamental pattern but they perform different functions and have different appearances e.g., whale's flipper, bat's wings, cat's paw, horse's front leg, bird's wing, ox's front leg and human hand.
Vestigial organs in animals are those having no function now, in them, but had important functions in their ancestors.
Analogous organs are quite different in fundamental structure and embryonic origin but perform the same function. The study of analogous organs illustrates the occurrence of convergent evolution.
Jurassic period of the Mesozoic era is characterised by
-
gymnosperms are dominant plants and first birds appear
-
radiation of reptiles and origin of mammal like reptiles
-
dinosaurs become extinct and angiosperms appear
-
flowering plants and first dinosaurs appear
A.
gymnosperms are dominant plants and first birds appear
Jurassic period is the second geological period of Mesozoic era. In this period, the gymnosperms were dominant and the plants included ferns, cycads, Ginkgo, rushes and conifers. Among animals, important invertebrates included ammonites, corals, brachiopods, bivalves and echinoids. Reptiles dominated the vertebrates and the first flying reptiles the pterosaurs appeared.
The first primitive bird, Archaeopteryx, also made its appearance.
A woman has an X-linked condition on one of her X chromosomes. This chromosome can be inherited by
Only daughters
Only sons
Both sons and daughters
Only grandchildren
C.
Both sons and daughters
(i) Woman is a carrier
(ii) Both son & daughter inherit X–chromosome
(iii) Although only son be the diseased\
According to Hugo de Vries, the mechanism of evolution is
Multiple step mutations
Saltation
Minor mutations
Phenotypic variations
B.
Saltation
As per mutation theory given by Hugo de Vries, the evolution is a discontinuous phenomenon or saltatory phenomenon.
Among the following sets of examples for divergent evolution, select the incorrect option :
Forelimbs of man, bat and cheetah
Heart of bat, man and cheetah
Eye of octopus, bat and man
Brain of bat, man and cheetah
C.
Eye of octopus, bat and man
Divergent evolution demonstrates how species can have common (homologous) anatomical structures.Divergent evolution occurs in the same structure, example - forelimbs, heart, brain of vertebrates which have developed along different directions due to adaptation to different needs whereas eye of octopus, bat and man are examples of analogous organs showing convergent evolution.
The similarity of bone structure in the forelimbs of many vertebrates is an example of
Homology
Analogy
Adaptive radiation
Convergent evolution
A.
Homology
In different vertebrates, bones of forelimbs are similar but their forelimbs are adapted in a different way as per their adaptation.
Bird and bat wings are analogous, as forelimb is homologous.
The appearance of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is an example of
adaptive radiation
transduction
Pre-existing variation
divergent evolution in the population
C.
Pre-existing variation
Post-mitotic gap phase is characterised by all except the synthesis of histone proteins. Histone proteins are synthesised in S-phase. S-phase is called invisible phase of the cell cycle as replicated chromosomes are not visible at this stage.
Which one of the following graphs correctly describes disruptive selection? When studying fitness level associated with body size?
D.
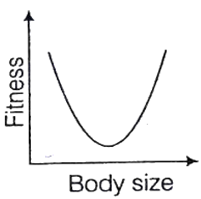
Disruptive selection occurs when an environmental change may produce selection pressure that favours two extreme characteristics. Selection acts on the phenotype, physical biochemical and behavioural traits oft he an organism. It indirectly adapts of population to its environment by selecting and maintaining favourable genotypes in their given pool
Ancestor of man who first stood erect was
Australopithecus
Cro-magnon
Java-ape man
Peaking man
A.
Australopithecus
Australopithecus is considered as connecting link between ape and man. They were the ancestors of the man who first stood erect. Their cranial capacity was 300-500 cc.
Origin of life occurred in
Precambrian
Coenozoic
Palaeozoic
Mesozoic
D.
Mesozoic
The first living form is named as protocell or eobiont or protobiont, which evolved into the prokaryotic cell. These were originated about 3900-3500 million years ago, during the Precambrian era.
The most recent and direct pre-historic ancestor is
Cro-magnon
Neanderthal
Pre-neaderthal
None of these
A.
Cro-magnon
The Cro-magnon man (Home sapiens fossils) is the most recent and direct prehistoric ancestor of the present man. It arose about 3,40,000 years ago.
Darwins finches represent
Morphological variations
Geographical isolations
Climate variations
Reproductive isolation
B.
Geographical isolations
There are thirteen types of finches described by Darwin, they are geographically isolated and found in Galapagos islands of South Pacific.
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is known to be affected by gene flow, genetic drift, mutation, genetic recombination and
Evolution
Limiting factors
Saltation
Natural selection
D.
Natural selection
Hardy-Weinberg law states that the genes and the genotypic frequencies in the Mendelian populations remain constant generations after generations of there is no selection, mutation, migration or random drift.
Which one of the following in birds indicates their reptilian ancestry?
Scales on their hindlimbs
Four-chambered heart
Two special chambers crop and gizzards in their digestive tract
Egg with a calcareous shell
D.
Egg with a calcareous shell
The birds have evolved from reptiles. Both birds and reptiles lay eggs which are large and telo lecithal with thick hard calcareous shell le.cleiodic eggs.
Darwinism explains all the following except
Within each species, there are variations
Organisms tend to produce more number of offspring that can survive
Offspring with better traits that overcome competition are best suited for the environment
Variations are inherited from parents to offspring through genes
D.
Variations are inherited from parents to offspring through genes
Variation is one of the main postulates of Darwinism. Darwin recognised two types of variations-continuous and dis-continuous variation but he could not explain the inheritance of variations.
Theory of pangenesis was given by
Darwin
Lamarck
Hugo de Vries
Oparin
A.
Darwin
Darwin proposed the theory of pangenesis to explain the inheritance of characteristics from parents to offsprings. According to this theory, every somatic cell produces gemmules and the actual germ cells are the sites of a collection of gemmules coming from different somatic
cells.
The best description on natural selection is
The reproductive success of the members of a population best adapted to an environment
It acts when the resources are unlimited
A change in the proportion of variations within a population
It follows Hardy-Weinberg principle
A.
The reproductive success of the members of a population best adapted to an environment
Natural selection is show by the reproductive success of the members of a population best adapted to the environment. The organisms which adapt useful variation successfully survive in changing the environment and reproduce.
Golden ages of reptiles and fishes are respectively
Mesozoic and Devonian
Jurassic and Permian
Triassic and Silurian
Palaeozoic and Mesozoic
A.
Mesozoic and Devonian
Mesozoic period was golden age for reptiles. In this period reptiles were dominant species, like dinosaurs. Devonian period was golden age for fishes due to their abundance and diversity.
Which one of the following human ancestors is known as tool maker?
Homo erectus
Java man
Homo habilis
Heidelberg man
C.
Homo habilis
Homo habilis was also known as toolmaker because it was the first human who made weapons and tools from rocks.
The term ‘prebiotic’ soup’ for organic water containing mixture of simple organic compounds was given by
Richter
Haldane
Arrhenius
Miller
B.
Haldane
The term 'prebiotic soup' is used by Haldane for organic water containing a mixture of simple organic compounds during the early stage of origin of life.
Which of the following is the most primitive ancestor of man?
Ramapithecus
Homo habilis
Australopithecus
Homo sapiens neanderthalensis
A.
Ramapithecus
Ramapithecus was the most primitive hominid. It is fossils were obtained from Asia and Africa. Its features suggested that they were the beginning of the linkages leading to human.
During which geological period of evolution did the greatest diversification of life occurred on the earth?
Permian
Jurassic
Cambrian
Ordovician
C.
Cambrian
The Cambrian explosion in the Cambrian period marks the occurrence of greatest diversification on the earth.
Most major phyla appeared (indicated by fossil study) divergence of modern Metazoan phyla occurred and major diversification of other organisms.
Before this period, most organisms were simple however, this changed after Cambrian period, the diversification rate accelerated and the diversity of life began to resemble that of today.
About how long ago was the earth formed
3 billion years ago
10 billion years ago
4.6 billion years ago
20 billion years ago
C.
4.6 billion years ago
On the basis of geological, chemical and physical data, the scientist has come to the conclusion that the solar system came into being about 4.57 billion years ago.
Total number of bones in the hindlimb of a man is
14
21
24
30
D.
30
1 femur + 1 fibula + 1 tibia + 1 patella+ 7 tarsals > + 5 metatarsals + 14 phalanges make one hindlimb of man.
The diversity in the type of beaks of finches adapted to different feeding habits on the Galapagos islands, as observed by Darwin, provides evidence for
Origin of species by natural selection
Intraspecific Variations
Intraspecific competition
Interspecific competition
A.
Origin of species by natural selection
Bird of Galapagos islands (Darwin's Finches) is believed to have evolved from ancestors on the South American mainland as a result of natural selection due to the different feeding niches available to them.
Age of fishes is also known as
Permian Era
Silurian Era
Devonian Era
Ordovician Era
C.
Devonian Era
The Devonian Perioid is known as 'the age of fishes'. It is famous for the thousands of species of fish that developed in Devonian sea. The Devonian Period of Palacozonic Era lasted from 417 million years ago to 354 million years ago.
Human ancestors who left cave paintings were
Neanderthal man
Cro- magnon man
Java ape man
Peking man
B.
Cro- magnon man
| Human ancestor | Characteristic feature |
| Neanderthal man | Believe in 'Immortality of soul', Make tools of bones, stones, quartz. |
| Cro- magnon mam | Cave painting, highest cranial capacity |
| Java ape man | Make use of fire |
| Peking man | Use nonsyllabic and non-articulate language. |
Pneumatic bones are expected to be found in
house lizard
flying fish
pigeon
tadpole of frog
C.
pigeon
Bones of Aves (eg, pigeon) are pneumatic. Pneumatic bones contain air cavities to reduce weight, which help in aerial mode of life.
Which of the following is not a vestigial structure in Homo sapiens ?
Third molar
Epiglottis
Plica semilunaris
Pyrimidalis muscle
B.
Epiglottis
Vestigial organs are degenerate, non- functional and rudimentary organs correspond to fully developed and functional organs of related organism. Wisdom teeth (third molar) , Plica semilunaris and Pyrimidalis muscles are vestigial organs.
Epiglottis is not a vestigial organ in man. It is the structure that prevents the entry of food into respiratory tract during swallowing in man.
The presence of diversity at the junction of territories to two different habitats is known as
bottleneck effect
edge effect
junction effect
Pasteur effect
B.
edge effect
Edge effect are changes in population or community structures that occur at the boundary of two or more habitats.
Bottleneck effect can be defined as the yearly or seasonal phenomenon in which size of a population is reduced severely.
Pasteur effect is defined as the reduction in the amount of breakdown of respiratory substrate and evolution of carbon dioxide when an anaerobically respiring material is brought in oxygen containing environment.
Which of the following provides most evident proof of evolution?
Fossils
Morphology
Embryo
Vestigial organs
A.
Fossils
Fossils provide the direct evidences of organic evolution. It may be entire organisms buried in sediment or snow or a small part or impressions of ancient organisms on leaf or stem.
Morphology is the study of form and structure in organisms. Study of homologous and analogous organs provide evidence of evolution.
Embryology provides evidence of organic evolution which is based on basic laws of principles of embryonic development.
Vestigial organs are degenerate, non- functional and rudimentary organs. These provide evidences for organic evolution.
Which of the following is not vestigial in man?
Tail vertebrae
Nails
Nicitating membrane
Vermiform appendix
B.
Nails
Vestigial organs can be defined as the imperfectly developed, non- functional organs which when compared to ancestral forms were fully developed and functional.
Eg, nicitating membrane, tail vertebrae, vermiform appendix.
Pneumatic bones are expected to be found in
house lizard
flying fish
pigeon
tadpole of frog
C.
pigeon
Bones of Aves (eg, pigeon) are pneumatic. Pneumatic bones contain air cavities to reduce weight. These help in aerial mode of life.
Presence of tail in a child is an example of
atavism
divergent evolution
convergent evolution
mutation
A.
atavism
Atavism is the phenomenon of appearance of ancestral character (not parental) in young ones after many generations, eg, presence of tail in a child.
Mesozoic era is Golden period of
reptiles
Mollusca
fishes
amphibians
A.
reptiles
The Mesozoic era is known as 'Golden age of reptiles'.
Organs which differ in origin but perform similar functions
analogous
homologous
vestigial
all of these
A.
analogous
The oragns which have similar function but are different in their structure and origin are called analogous organs. The organs which have same fundamental structure and origin but function may be similar or different, are called homologous organs. The organs which are present in reduced form and do not correspond to the fully developed functional organs to related animals are called vestigial organs
Which one of the following phenomena supports Darwin's concept of natural selection in organic evolution?
Development of transgenic animals
Production of 'Dolly' the sheep by cloning
Prevalence of pesticide resistant insects
Development of organs from 'stem cells' for
organ transplantation
C.
Prevalence of pesticide resistant insects
According to Darwin's concept of natural selection, the organisms which are provided with favourable variations would survive because, they are the fittest to face their surrounding while the organisms, which are unfit for surrounding variations are destroyed. Prevalence of pesticide resistant insects is due to adaptability of these insects for the changes in environment (due to use of pesticides).
Which one of the following experiments suggests that simplest living organisms could not have originated spontaneously from non-living matter?
Microbes did not appear in stored meat
Larvae could appear in decaying organic matter
Microbes appeared from unsterilized organic matter
Meat was not spoiled, when heated and kept sealed in a vessel
D.
Meat was not spoiled, when heated and kept sealed in a vessel
Pasteur performed experiments in which he took sterilized (by boiling) yeast and sugar solution in a long necked, then he bent the neck of the flask like a neck of swan. After one month he observed that no life appeared in flask solution because the curved flask neck acts as a filter. He later on broken down the neck and observed the solution. He found that many micro-organisms were originated in solution.
Example of analogous organs is :
wings of bird and insect
forelimbs of horse and man
teeth of elephant and man
none of the above
A.
wings of bird and insect
Wings of bird and insects are analogous organs
During starvation what will be sequence of ending of food stuffs ?
Carbohydrates - Fat- Protein
Carbohydrate - Protein - Fat
Fat - Protein - Carbohydrate
Fat - Carbohydrate- Protein
A.
Carbohydrates - Fat- Protein
During starvation cells use glucose present in blood. After depletion of glucose from blood, glycogen are released from liver(stored glycogen are enough to carry out the normal daily activity of a day) and broken down into glucose to be used as ATP source. After glycogen consumption, the body switches to fat as energy source. In extreme conditions when body runs out from stored glucose/glycogen and fats to uses protein as energy source.
Which of the following as a living fossil
Pinus
Gnetum
Ginkgo
Riccia
C.
Ginkgo
Linkgo, a member of order linkgoales, is called living fossil because all the others except Ginko biloba are now extinct.
Which one is not correct?
Human - Ureotelic
Birds - Uricotelic
Lizards - Uricotelic
Whale - Ammonotelic
D.
Whale - Ammonotelic
The animals that excrete nitrogen in the form of urea are called ureotelic. Ureotelic animals include man and all other mammals and aquatic mammals like whales. So, whale is ureotelic and not ammonotelic.
Which one of the following is vestigeal organ of human
Hair
Intestine
Wisdom teeth
Muscle of glottis
C.
Wisdom teeth
Vestigeal organs are present in reduced form and are of no use to the animal in which they are present. Man has 180 vestigeal organs. e.g., nictitating membrane, vermiform appendix, wisdom tooth, muscle of pinna and forhead, mammary glands in male etc.
Stanley Miller performed an experiment to prove the origin of life. They took gases NH3 and H2 along with
N2 and H2O
H2O and CH4
CH4 and N2
CO2 and NH3
B.
H2O and CH4
Stanley Miller using CH2 :NH3 :H2 gases in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1 and water vapours synthesised many simple organic compounds including amino acids, glycine, alanine and aspartic acid. According to him, life originated from NH3, CH2, H2 and H20.
The first animal domesticated by primitive man was
dog
horse
cat
cow
A.
dog
Dog was the first animal to be domesticated by man.
The correct sequence for the formation of chemicals on the primitive earth is
NH3, protein, carbohydrate and nucleic acid
NH3, water, nucleic acids and proteins
NH3, nucleic acids, protein and carbohydrate
protein, carbohydrate, water and nucleic acids
B.
NH3, water, nucleic acids and proteins
As the earth cooled, free atoms in the atmosphere formed inorganic molecules (including H2O and NH3) which interacted to form sugars and then proteins and nucleic acids.
Which of the following evidences does not favour the Lamarckian concept of inheritance of acquired characters
Absence of limbs in snakes
Melanisation in peppered moth
Presence of webbed toes in aquatic birds
Lack of pigment in cave-dwelling animals
B.
Melanisation in peppered moth
Industrial melanism is an adaptation where the moths living in the industrial areas developed melanin pigments to match their body to the soot-covered surroundings. The phenomenon provides an excellent example of operation ofselection in natural conditions. Industrial melanism, therefore, presents an excellent example ofnatural selection (proposed by Darwin), but it is not the example of acquired characters proposed by Lamarck.
In caves, due to absence of light, the body of the animal lacks pigmentation, e.g., Proteus anguinus. In pythons and related snakes rudimentary pelvic girdle and traces of hindlimb are present. They form small clawed projections externally, but internally there are vestiges of an ilium, femur, tibia and a claw. In aquatic birds and flying frog, the feet are webbed which sustain it in the prolonged leaps to which it is adapted
Keystone species deserve protection because these
are capable of surviving in harsh environmental conditions
indicate presence of certain minerals in the soil
have become rare due to overexploitation
play an important role in supporting other species.
D.
play an important role in supporting other species.
Keystone species are species which have significant and disproportionately large influence on the community. Removal or decrease in their number causes disruption in structure and function of community. For example in intertidal regions starfish feeds on mussels. Removal of starfish leads to dominance of mussels that excludes algae and browsing species. In tropical rain forests, fig trees function as keystone species as they provide fruits to a number of animals during the period of food scarcity.
Assertion: Chimpanzee is the closest relative of the present day humans.
Reason: The banding pattern in some autosomes of man and chimpanzee is remarkably similar.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
I has been observed that the banding pattern of some human chromosomes is very similar to the banding pattern of the corresponding chromosomes in apes. It shows common origin of man and chimpanzee and their close relatedness.
Assertion: Analogous organs are a result of divergent evolution.
Reason: Eye of octopus and of mammals depict divergent evolution.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
D.
If both assertion and reason are false.
The organs which have similar functions but are different in their structural details and origin are called analogous organs. The analogous structures are the result of convergent evolution. Eyes of octopus and of mammals show different patterns of structure. Yet they perform similar functions, so they depict convergent evolution.
The correct sequence ofstages in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens), is
Homo erectus, Australopithecus, neanderthal man, cro-magnon man, modern man
Australopithecus, Homo erectus, neanderthal man, cro-magnon man, modern man
Neanderthal man, Australopithecus, cromagnon man, Homo erectus, modern man
Australopithecus, Neanderthal man, cromagnon man, Homo erectus, modern man
B.
Australopithecus, Homo erectus, neanderthal man, cro-magnon man, modern man
Australopithecus evolved around 4 million years ago in Eastern Africa.
Homo erectus evolved around 1.8 million years ago and lived throughout Pleistocene geological epoch.
Neanderthal man lived around 40,000 years ago. These are an extinct species of archaic humans in the genus Homo.
Cro- magnon man were found in the year 1868.
Modern man or Homo sapiens are found from the last 200,000 years.
Which one ofthe following is reptilian ancestor of birds
Hesperornis
Archaeopteryx
Ichthyornis
Lycaenops
B.
Archaeopteryx
D.
Lycaenops
The first fossil birds found in the rocks of Jurassic period belonged to genera Archaeopteryx and Archaeornis. These are considered as reptilian ancestors of birds. It was about the size of a crow and possessed feathers and wings but had a long reptilian tail very much unlike the modern birds and a toothed beak. Fossils ofHesperornis, an aquatic diving bird, and Ichthyornis, a powerful flying bird, have been found from Cretaceous.
Assertion: Darwin's finches are a classical example of natural selection.
Reason: Darwin explained that the difference in size and shape of the beaks of the species was a result ofthe adaptation ofthe species to different food habits.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Darwin's finches represent an excellent example of adaptive radiation. Darwin's finches showed wide variations in beak shape and size from island to island. Darwin deduced that these variations made the finches better adapted to take advantage of the food in their particular local environment - thin, sharp beaks prevailing where the birds' main food was insects and grubs, and large claw shaped beaks where their diet was buds, fruits and nuts.
Assertion : Hardy-Weinberg principle states that in the absence of disturbing influences, gene frequencies of large populations of sexually reproducing organisms do not change, provided that matings, occur at random.
Reason : The disturbing influences include mutation, gene flow, genetic drift, genetic recombination and natural selection.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
According to Hardy-Weinberg principle gene frequencies will remain constant if there is no mutation, no gene flow, no genetic drift, no genetic recombination, no natural selection pressure and mating occurs at random.
Select the correct sequence for Homo erectus
Erectus homo primata chordata animalia
Homo erectus primata animalia chordata
Homo erectus primata chordata animalia
Erectus homo animalia primatachordata
A.
Erectus homo primata chordata animalia
Taxonomical hierarchy shows arrangement in ascending order.
Species Genus Family Order Division Kingdom
Assertion: Interspecific competition is the only potent force in organic evolution.
Reason: Unexceptionally two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
D.
If both assertion and reason are false.
Darwin was convinced that interspecific competition is a potent force in organic evolution. It is generally believed that competition occurs when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting, but it is not entirely true. Totally unrelated species could also compete for the same resource. Gause's 'Competitive Exclusion Principle' states that two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and the competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventually. This may be true if resources are limiting, but not otherwise.
Delicate hair-like feathers which remain sparsely distributed over the body are
coverts
filoplumes
plumules
remiges
B.
filoplumes
Filoplumes are hair- like feathers with a few soft barbs near the tip. They are associated with contour feathers and may be sensory or decorative in function.
Coverts is a feather covering the base of a main flight or tail feather of a bird.
Plumules is a bird's down feather, numbers of which form an insulating layer under the contour feathers.
Remiges are long, stiff, aymmetrically shaped but symmetrically paired feathers on the wings or tails of a bird.
Homo erectus evolved during
pleistocene
miocene
pliocene
holocene
A.
pleistocene
Homo erectus appeared about 1.7 million years ago in middle pleistocene. H. erectus evolved from Homo habilis. He was about 1.5 - 1.8 metres tall.
Which of the following postulates is related with Neo-Darwinism?
Mutations are believed to help form new species
It incorporates isolation as an essential component of evolution.
It can explain the occurrence of unchanged forms over millions of years.
All of the above
D.
All of the above
Neo- Darwinian theory is also referred as Modern Synthetic theory of Evolution. It is a fusion of Mendelian genetics with Darwinian evolution.
By all of the following ways bacteria become resistant to antibiotic except
making enzymes that inactivate the drug
becoming impermeable to the drug
modifying the target of the drug
moving away from the drug
D.
moving away from the drug
Bacteria become resistant to antibiotic by either producing enzymes or forming impermeable capsule and modifying the target of the drug.
Two opposite forces operate in the growth and development of every population. One of them is related to the ability to reproduce at a given rate. The force opposite to it is called
fecundity
environmental resistances
biotic control
mortality.
B.
environmental resistances
The environmental factors which can check the growth of population size constitute the environmental resistance. These include predators, food, water, nesting sites, similar competitors, etc. All living things tend to reproduce until the point at which their environment becomes a limiting factor. No population, human or otherwise, can grow indefinitely; eventually, some biotic or abiotic variable will begin to limit population growth.
What is a keystone species
A species which makes up only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community, yet has a huge impact on the community's organization and survival.
A common species that has plenty of biomass, yet has a fairly low impact on the community's organization.
A rare species that has minimal impact on the biomass and on other species in the community.
A dominant a large proportion of the biomass and which affects many other species.
A.
A species which makes up only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community, yet has a huge impact on the community's organization and survival.
Keystone species are those species which has significant and disproportionately large influence on the community structure and characteristics. It has often considerably low abundance and biomass as compared to dominant species. Removal of such species causes serious disruption in structure and function of community.
Assertion : Bursa fabricii lies on the ventral side of the cloaca in birds.
Reason : Bursa fabricii is related with flight adaptation.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
D.
If both assertion and reason are false
In birds, the bursa of Fabricius is the site of Hematopoisis, a specialized organ that is necessary for B cell development in birds. Bursa is a small, glandular, blind pouch of lymphatic tissue present on the dorsal side of the cloaca. It is lined with endoderm, and opens into the proctodaeum.
In a young bird, bursa fabricii forms lymphocytes, and probably it produces antibodies and protects against local infection, but it atrophies in the adult before sexual maturity. It is also called cloacal thymus, because like thymus, it secretes lymphocytes. Thus, it is not related with flight adaptation, rather it helps in immunity.
Assertion : The primitive atmosphere was reducing one i.e. without oxygen.
Reason : In the primitive atmosphere, oxygen was involved in forming ozone layer.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
The lightest atoms of nitrogen, carbon etc. formed the primitive atmosphere. Hydrogen atoms were most numerous and most reactive in primitive atmosphere. Hydrogen atoms combined with all oxygen atoms to form water leaving no free oxygen. Thus primitive atmosphere was reducing atmosphere (without free oxygen) unlike the present oxidising atmosphere (with free oxygen). Formation of ozone layer is the consequence of modern oxidizing atmosphere having plenty of free oxygen. As more oxygen accumulated in the atmosphere (due to photosynthesis) ozone began to appear in the top layers.
Assertion : Jave Apeman, Peking man and Heidelberg man are the fossils of Homo erectus.
Reason : Homo erectus evolved from Homo habilis.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
The fossil of Java Apeman was discovered from pleistocene rocks in central Java. The fossil of Peking man was discovered from the lime stone caves of Choukoutien near Peking while that of Heidelberg man was discovered in mid pleistocene. All these three fossils come under the category of Homo erectus. Homo erectus appeared about 1.7 million years ago in middle pleistocene. It evolved from Homo habilis. Genral characteritics are as followed:
(i) Height 1.5-1.8 metres tall.
(ii) Erect posture.
(iii) Skull was flatter than that of modern man.
(iv) Protruding jaws, projecting brow ridges, small canines and large molar teeth.
(v) Made tools of stones and bones.
(vi) Hunted big game
(vii) Knew use of fire.
Nicotiana sylvestris flowers only during long days and N.tabacum flowers only during short days. If raised in the laboratory under different photoperiods, they can be induced to flower at the same time and can be cross-fertilized to produce self-fertile offspring. What is the best reason for considering N.sylvestris and N.tabacum to be separate species
They cannot interbreed in nature.
They are reproductively distinct.
They are physiologically distinct.
They are morphologically distinct.
D.
They are morphologically distinct.
Speciation can take place in two general ways. A single species may change over time into a new form that is different enough to be considered a new species. This process is known as anagenesis. More commonly, a species may become split into two groups that no longer share the same gene pool. This process is known as cladogenesis. There are several ways in which anagenesis and cladogenesis may take place. In all cases, reproductive isolation occurs.
'Homo sapiens' implies
human race
human beings
modern man
none of these
B.
human beings
Humans, or human beings are bipedal primates belonging to the mammalian species Homo sapiens in the family Hominidae (the great apes). It includes both archaric and modern humans, as well as the subspecies Homo sapeins neanderthalensis, also known as the Neanderthals. They first started appearing about 500,000 or fewer years ago. It is one of the several species grouped into the genus Homo, but it is the only one that is not extinct.
Wings of pigeon, mosquito and bat show
divergent evolution
atavism
convergent evolution
all of these
C.
convergent evolution
Wings of pigeon, mosquito and bat show convergent evolution. It is the evolutionary process whereby organisms not closely related, independently evolve similar traits to adapt to their environment.
Atavism is the regaining of same structures after a certain gap of few generations.
Divergent evolution is the process where member of a species become more different resulting into new species. Eg, humans bats and whales (pentadactyl limbs).
Assertion : The earliest fossil form in the phylogeny of horse is eohippus.
Reason : Eohippus lived during the early pliocene epoch.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
The evolution of Horses include- small, terriero sized Hydracotherium eohippus to the large modern horse, Equus eohippus, found in Eocene period.
Eohippus was the earliest known horse. It is also known as Hyracotherium. It was only 2 feet long and 8 to 9 inches high at the shoulder. It had 4 hoofed toes on front feet and 3 hoofed ant on each hind foot. It had long skull with 44 long crowned teeth.
This horse was a herbivore that mainly ate soft leaves and plant shoots. It lived early during Eocene Epoch ie, 50 million years ago.
Assertion: The earliest organisms that appeared on the Earth were non-green and presumably anaerobes.
Reason: The first autotrophic organisms were the chemoautotrophs that never released oxygen.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
The first living organisms originated among organic molecules and in oxygen free atmosphere. They presumably obtained energy by fermentation of some of these organic molecules. They were non-green and anaerobes (capable of respiring in absence of oxygen). They depended on the existing organic molecules for their nutrition, hence they were heterotrophs.
Then came autotrophs when the supply of existing organic molecules were exhausted. These organisms were capable of producing their own organic molecules by chemosynthesis. They synthesized food from inorganic molecules. Photoautotrophs were also anaerobic at first but later on oxygen releasing photosynthetic organism developed
If the Bengal Tiger becomes extinct
hyenas and wolves will become scars
the wild areas will be safe for man and domestic animals
its gene pool will be lost forever
the populations of beautiful animals like deers will get stabilized.
C.
its gene pool will be lost forever
A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survive bouts of intense selection. Meanwhile, low genetic diversity (see inbreeding and population bottlenecks) can cause reduced biological fitness and an increased chance of extinction, although as explained by genetic drift new genetic variants, that may cause an increase in the fitness of organisms, are more likely to fix in the population if it is rather small.
DNA is present in
chromosomes and dictyosomes
chloroplasts and lysosomes
mitochondria and chloroplasts
mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
C.
mitochondria and chloroplasts
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have striking similarities to bacteria cells. They have their own DNA, which is separate from the DNA found in the nucleus of the cell. And both organelles use their DNA to produce many proteins and enzymes required for their function.
Potato and sweet potato
have edible parts which are homologous organs
have edible parts which are analogous organs
have been introduced in India from the same place
are two species of the same genus.
B.
have edible parts which are analogous organs
Analogous organs are the opposite of homologous organs, which have similar functions but different origins. An example of an analogous trait would be the wings of insects, bats and birds that evolved independently in each lineage separately after diverging from an ancestor without wings.
Potato and sweet potato arc absolutely different in their origin as potato is modified underground stem (tuber), while sweet potato is tuberous root. It means both have edible parts, which are different organs.
Assertion : Human ancestors never used their tails and so the tail expressing gene has disappeared in them.
Reason : Lamarck's theory of evolution is popularly called theory continuity of germ plasm.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false
D.
If both Assertion and Reason are false
Humans did not shared ancestry with other primates. If they would have then, there should be some common ancestry should be seen.
For example, tails: this characteristic is still exhibited occssionally in atavism.
According to current evolutionary theory, the ancestors of humans lost their tails about 25 million years ago, when apes (tail-less primates) diverged from monkeys (tailed primates). Theory of the continuity of the germplasm was given by Weismann. He recognized that animals are made up of- body cells or somaplasm, which contain gamete-producing cells or germplasm. At each generation, the embryo that develops from the zygote not only sets aside some germplasm for the next generation but also produces the cells that will develop into the body, the soma, of the organism.
Assertion : Comparative biochemistry provides a strong evidence in favour of common ancestry of living beings.
Reason : Genetic code is universal
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false
B.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
Convincing evidence of common ancestry comes from the similarities in the biochemical composition, reactions and physiological activities of living beings, like metabolic process, enzymes. cytochrome C, insulin, haemoglobin, blood and lymph etc.
Genetic code is the sequence of DNA nucleotides that determines the amino acid sequence of the translated protein. It is read in triplets of bases called codons. It is applicable universally i.e. a codon specifies the same amino acid from a virus to a tree or human beings. The mRNA from chick oviduct introduced in E.coli produces an ovalbumen in the bacterium exactly similar to one formed in chick.
Assertion : Darwin's finches show a variety of beaks suited for eating large seeds, flying insects and cactus seeds.
Reason : Ancestral seed-eating stock of Darwin's finches radiated out from South American mainland to different geographical areas of the Galapagos Islands, where they found competitorfree new habitats.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
Darwin finches are an excellent example of the way in which the species gene pools have adapted in order for long term survival via their offspring. They were formed due to divergent evolution to avoid intcrspecific competition.
The common birds of Galapagos islands, were different from the finches of main land. The closely related species of finches had beak of different shapes and sizes, and adapted for feeding on completely different diets. Darwin also found that fossils of Galapagos islands are most similar to living species of South America. The food supply increases in arithmetic ratio but the population increases in geometric ratio. With the study of this theory it struck to Darwin that there is struggle for existence among plants and animals. This concept or competition among the living beings for their survival offered the basis for the theory of natural selection. Apparently a single ancestral group can give rise to several different varieties of species.
The early stage human embryo distinctly possesses
gills
gill slits
external ear (pinna)
eye brows
B.
gill slits
Both chick and human embryos go through a stage where they have slits and arches in their necks like the gill slits and gill arches of fish. These structures are not gills and do not develop into gills in chicks and humans, but the fact that they are so similar to gill structures in fish at this point in development supports the idea that chicks and humans share a common ancestor with fish. Thus, developmental characters, along with other lines of evidence, can be used for constructing phylogenies.
Assertion: Coaccrvates are believed to be the precursors of life.
Reason: Coaccrvates were self-duplicating aggregates of proteins surrounded by lipid molecules
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
C.
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
A coacervate is a spherical aggregation of lipid molecules making up a colliodal inclusion which is held together by hydrophobic forces. Coacervates measure 1 to 100 micrometers across, possess osmotic properties , and form spontaneously from certain weak organic solutions. Their name derives from the Latin coacervare, meaning to assemble together or cluster. It was suggested by Oparin that coacervates may have played a significant role in the evolution of cells.
Assertion: Animals adopt different strategies to survive in hostile environment.
Reason: Praying mantis is green in colour which merges with plant foliage
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Praying mantids are camouflaged. This means they have adapted the colors of their surroundings that help them blend in. Some also have body shapes that make them look like leaves or branches.
Assertion: Among the primates. chimpanzee is the closest relative of the present day humans.
Reason: The banding pattern in the autosome numbers 3 and 6 of man and chimpanzee is remarkably similar.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Carolus Linnaeus called humans as Homo sapiens or wise men and placed them along with apes and monkeys. There are certain similarities between human and chimpanzee. These are
(i) RNA content of diploid cells is similar
(ii) DNA matching shows that human similarity is 100 % with chimpanzee and
(iii) banding pattern of chromosomes shows very little difference in chromosomes 3 and 6 between humans and chimpanzee. Thus it can be concluded that among the primates, chimpanzee is the closest relative of the present day humans
Assertion: From evolutionary point of view, human gestation period is believed to be shortening.
Reason: One major evolutionary trend in humans has been the larger head undergoing relatively faster growth rate in the foetal stage.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
D.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
The head size is increasing (especially the frontal brain) hence growth rate needs to increase but surprisingly most of the brain growth occurs after birth till 2 years (when the anterior fontanellae close at 18 months) and some more till 30 years when finally the cranial sutures close. Thus an increase in brain/ skull size would required increase in gestation period, hence both assertion and reason are false
Assertion: Natural selection is the outcome of differences in survival and reproduction among individuals that show variation in one or more traits.
Reason: Adaptive forms of a given trait tend to become more common; less adaptive ones become less common or disappear.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Natural selection is a process that results in the adaptation of an organism to its environment by means of selectively reproducing changes in its genotype, or genetic constitution.
A force which acts against the achievement of highest possible level to population growth is known as
population pressure
saturation level
carrying capacity
environmental resistance
D.
environmental resistance
Environmental resistance factors are things that limit the growth of a population. They include biotic factors - like predators, disease, competition, and lack of food - as well as abiotic factors - like fire, flood, and drought. The biotic potential of a population is how well a species is able to survive
Assertion : Bats and whales are classified as mammals.
Reason : Bats and whales have four-chambered heart.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
B.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
Bats and whales are classified as mammals as they possess the essential mammalian characteristics like presence of milk gland or mammae, presence of pinnae, viviparous nature, hair on body, presence of diaphragm etc.
Though bats and whales have four chambered heart, it cannot be considered as the main characteristic of being mammals because it is also present in some reptiles (e.g. crocodile) and all birds.
Assertion : Organochlorine pesticides are organic compounds that have been chlorinated.
Reason : Fenitrothion is one of the organochlorine pesticides.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
C.
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
Organochlorinc pesticides arc organic compounds or hydrocarbons to which are added several atoms of chlorine through the process called chlorination. Rate of degradation of organochlorines is very low. E.g. DDT, BHC.
Fenitrothion is an organophosphate pesticide which is the organic ester of phosphoric acid and its derivatives. These pesticides arc very toxic but are not persistant. It is an inhibitor used as an insecticide. It is cheap and used worldwide.
Assertion : Holoblastic cleavage with almost equal-sized blastomeres is a characteristic of placental animals.
Reason : Eggs of most mammals, including humans, are of centrolecithal type.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
C.
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
In holoblastic cleavage, the cleavage furrows bisect the entire egg ie, entire egg divides by each cleavage furrow. Placental mammals have isolecithal or microlecithal egg, the holoblastic cleavage produces blastomeres of equal or approximately equal size.
Centrolecithal eggs are found in insects and in some hydrozoa. In these yolk is concentrated at the centre of egg and the cytoplasm is present surrounding it. Meroblastic cleavage occurs in them.
Assertion : All birds, except the ones like koel (cuckoo) build nests for retiring and taking rest during night time (day time for nocutrnal).
Reason : Koel lays its eggs in the nests of tailor bird.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
C.
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
Koel or cuckoo need not build nests because they transfer their responsibilities to build nests, incubate eggs and nurture hatchlings to other birds specifically crows. Thus, they are called as brood parasites ie, they rely on others to raise their young ones. Being the brood parasite of the crow, the koel's breeding cycle synchronizes with that of crow. Both the koel's and crow's eggs are grey-green with rusty brown markings.
Tailor bird is a garden bird which makes its nest by sewing, it has no direct relation with koel and cuckoo. Also it is a songbird found across tropical Asia.
Assertion : Old age is not an illness. It is a continuation of life with decreasing capacity for adaptation.
Reason : Cessation of mitosis is a normal genetically programmed event.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
C.
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
Old age is the result of ageing or senescence which is defined as the progressive deterioration in structure and function of the body cells, tissues, organs and organ systems of the organism with their advancing age. Also, the immune system loses its ability to effectively deal with the antigens. This reduces the resistance as well as adaptation of the body.
Cessation of mitosis is not as such a genetically programmed event. During ageing, there is a decrease in multiplication of cells, though it differs in various tissues.
Prototherians are the connecting links between:
amphibians and aves
reptiles and mammals
fishes and amphibians
reptiles and amphibinas
B.
reptiles and mammals
Prototherians is the sub- class of Order Monotremata. These contains egg laying animals, which are the most ancestral forms in the class Mammalia. These are the connecting links between repltiles and mammals. Connecting links are those extinct organisms which possess the characters of two different groups of organisms.
The pioneers in the field of 'organic evolution' are:
Karl Landsteiner, Hugo de Vries, Malthus
Darwin, Hugo de Vries, Lamarck, Huxley
Lamarck, Karl Landsteiner, Malthus, Hugo de Vries
Darwin, Lamarck, Karl Landsteiner, Hugo de Vries
B.
Darwin, Hugo de Vries, Lamarck, Huxley
The theories in the field of 'organic evolution' were suggested by Darwin, Hugo de Vries, Lamarck and Huxley.
Darwin in 1859 explained the theory of natural selection and wrote a book 'The origin of species'.
Hugo de Vries, a Dutch botanist, propounded mutation theory in 1901.
Lamarck explained the theory of organic evolution on the basis of inheritance of acquired character and wrote a book Philosophic zoologique.
Huxley performed a number of experiments to remove the objections against Darwin's theory.
Darwin finches are related to which of the following evidences ?
Fossils
Embryology
Anatomy
Geographical distribution
D.
Geographical distribution
The study of geographical distribution and factors controlling the organism is called biogeography. Darwin studied the biogeography of shape and size of the beak of birds. These birds are now called Darwin's finches.
Allopatric speciation is due to :
geographical separation of population
hybridization between closely related species
migration of the members of a species from one to other population
both (b) and (c)
A.
geographical separation of population
Speciation is the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution. Allopatric speciation is due to the geographical separation of a population. It is related to the groups of similar organisms that could interbreed and are geographically separated.
Evolutionary convergence is characterized by:
development of characteristics by random mating
replacement of common characteristic in different related groups
development of dissimilar characteristics in closely related groups
development of a common set of characteristics in groups of different ancestry
D.
development of a common set of characteristics in groups of different ancestry
Evolutionary convergence is a phenomenon in different groups of animals come to resemble each other through similarity of habit or environment. It is the development of common set of characteristics in groups of different ancestry.
What is a key stone species ?
A rare species that has minimal impact on biomass and on other species in community
A dominant species that constitutes a large proportion of biomass, which affects many other species
A common species that has plenty of biomass, yet has a fairly low impact on the community's organization
A species which makes up only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community, yet has a huge impact on the community's organization and survival
D.
A species which makes up only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community, yet has a huge impact on the community's organization and survival
Key stone species is a apecies which makes up only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community, yet has a huge impact on the community's organization and survival.
Eg, Elephants damage trees by browsing the lower branches, stripping the bark and uprooting them. It prevents the forest from encroaching on the grasslands, where grazing beasts flourish.
In which of the following population, genetic drift operates?
Island
Smaller
Larger
Continental
B.
Smaller
Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population change over generations due to chance (sampling error). It occurs in all populations of non- infinite size but its effects are strongest in small populations.
Lichens are important in the studies on atmospheric pollution because they
can grow in polluted atmosphere
can readily multiply in polluted atmosphere
efficiently purify the atmosphere
are very sensitive to pollutants like sulphur dioxide
D.
are very sensitive to pollutants like sulphur dioxide
Lichens are extremely sensitive to SO2 an could be regarded as indicator of SO2 pollution.
Which is the closest pet of human being ?
Cat
Cow
Dog
Buffalo
C.
Dog
Th closest pets of human being are dogs and cats. Dog is one of the earliest animals to be domesticated. Therefore, dogs are the closest pet of human beings.
The scientific name of Java man is
Homo habilis
Homo sapiens neandarthalensis
Homo erectus erects
Australopithecus bisei
C.
Homo erectus erects
Java man is the name given to fossils discovered in 1891 at Trinil Ngawai Regency on the banks of the Solo river in East Java in Indonesia. It was one of the first known specimens of Homo erectus. The scientific name Pithecanthropus erectus, a name derived from Greek and Latin roots meaning upright ape man.
What are poikilothermic animals?
The organisms whose body temperature fluctuates considerably with that of their environment are called poikilothermic or cold blooded animals, eg, fishes, amphibians.
Which is not applicable to the biological species concept
Hybridization
Natural population
Reproductive isolation
Gene pool
A.
Hybridization
The biological species concept gives an explanation of how species form (speciation). A biological species is a group of individuals that can breed together (panmixia). However, they cannot breed with other groups.
Which one of the following is the most primitive ancestor of man?
Homo habilis
Australopithecus
Ramapithecus punjabicus
Homo neanderthalensis
C.
Ramapithecus punjabicus
The sequence of human evolution is
Ramapithecus Australopithecus Homo habilis Homo erectus erectus Homo erectus pekinensis Homo sapiens neanderthalensis Homo sapiens fossilis Homo sapiens sapiens.
Which one of the following ancestors of man first time showed bipedal movement
Australopithecus
Cro-magnon
Java ape man
Peking mann
A.
Australopithecus
Australopithecus was the first ape man having fully bipedal locomotion. Its thighs and hips were adapted for erect standing, walking and running. This man lived from 4 to 1.5 million years ago in caves during Pleistocene period.
The important gas which was absent during the formation of Earth is
oxygen
hydrogen
nitrogen
carbon dioxide
A.
oxygen
The primitive atmosphere of Earth was devoid of oxygen gas. In primitive atmosphere, hydrogen atoms were most numerous and most reactive. They combined· with all available oxygen atoms and formed water, which is very important for life.
Homo erectus evolved during
Oligocene
Pliocene
Pleistocene
Miocene
C.
Pleistocene
Homo erectus lived from the end of Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene about 1.3 to 1.8 million years ago. This species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. It walked erect over long legs, height 1.5 - 1.79 mt, brain size (cranial capacity) 775 - 1225 cm, prognathus face with prominent brow ridges, no chin, massive jaws and larger teeth. Use of tools made up of bones and stones, fire, acheulean hand axes and some primitive type of speech had developed.
Mammals have originated from which of the following
Pisces
Amphibia
Reptilia
Aves
C.
Reptilia
Mammals evolved from the reptiles during Triassic period of Coenozoic era which is called the age of mammals.
Bursa fabricius is an important organ of birds. This organ is associated with
generation of basophil
production of uric acid
metabolism of fatty acids
generation of B-cell
D.
generation of B-cell
Bursa of fabricius is a thymus like lymphoid organ found in birds. It is the site of B-cell maturation as bone marrow is absent in birds. It plays a central role in the development of the antibody- producing B- lymphocyte lineage in birds.
Variation in gene frequencies within populations can occur by chance rather than by natural selection. This is referred to as
genetic flow
genetic drift
random mating
genetic load
B.
genetic drift
Genetic drift is a random change in allele frequencies over the generations. Gene flow or gene migration is the physical movement of alleles into and out of a population. The existence within the population of disadvantages alleles in heterozygous genotypes is known as genetic code.
The process by which organisms with different evolutionary history evolve similar phenotypic adaptations in response to a common environmental challenge, is called
natural selection
convergent evolution
non-random evolution
adaptive radiation
B.
convergent evolution
Convergent evolution occurs in unrelated group of organisms. It is the development of similar functional structures but in unrelated groups.
The process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography is called adaptive radiation. Natural selection is the basis of evolution.
The tendency of population to remain in genetic equilibrium may be disturbed by
random mating
lack of migration
lack of mutations
lack of random mating
D.
lack of random mating
According to Hardy-Weirberg principle, allele frequencies in a population are stable and is constant from generation to generation allele frequencies in a population will remain constant over generations only if the following condition are met
(i) There is no mutation no gene flow and all mating is random.
(ii) All genotypes reproduce equally well (i.e., no natural selection). But, all there conditions rarely met in nature.
According to Darwin, the organic evolution is due to
intraspecific competition
interspecific competition
competition within closely related species
reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species
B.
interspecific competition
Darwin stated that, the organic evolution is due to interspecific competition. It is the competition between members of different species.
lntraspecific competition occurs amongst members of the same species for obtaining optimum amounts of their food, shelter, mate, water, light, etc.
Closely related species if compete cannot cause evolution.
Reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species is due to struggle for existence.
The· eyes of Octopus and eyes of cat show different patterns of structure, yet they perform similar function. This is an example of
homologous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
homologous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution
analogous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
analogous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution
C.
analogous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
The analogous organs are not anatomically similar structures through they perform similar functions. Hence, analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution; different structures evolving for the same function and hence, having similarity. On the other hand, homologous organs developed along different direction due to adaptations to different needs. This is divergent evolution and the structures are homologous.
Industrial melanism is an
effect of industrial pollution
effect of mutation
evidence of survival of fittest
evidence of favour of natural selection
D.
evidence of favour of natural selection
Industrial melanism is an evidence of natural selection. It is the prevalence of dark-coloured varieties of animals (especially moths) in industrial areas where they are better camouflaged than paler or light forms. Hence, darker pigmented individuals have a higher chances of survival and is favoured by natural selection.
Archaeopteryx is a connecting link between
pisces and amphibians
amphibians and reptiles
reptiles and birds
birds and mammals
C.
reptiles and birds
Archaeopteryx is a connecting link between birds and reptiles. They possessed long tail, teeth in jaws, long neck with cervical vertebrae, all are reptilian characters. Like birds, it had wings and beak. It was warm blooded. Hence, it is considered as a connecting link between reptiles and birds.
Which of these gases was/were present in prebiotic atmosphere?
Ammonia
Methane
Oxygen
Hydrogen
A.
Ammonia
B.
Methane
D.
Hydrogen
Primitive atmosphere contained gases like CO2, CO, N, H2, NH3, etc. Water vapour and metallic carbites reacted to form CH4. There was no oxygen present at that time. With the addition of O2 in the atmosphere, it became oxidising in nature and CH4 and NH3 began to disappear as they got oxidised forming CO2 and N2 respectively.
The direct ancestor of the living modern man is
Homo erechis
Homo neanderthalensis
Homo sapiens fossils
Homo sapiens sapiens
C.
Homo sapiens fossils
The direct ancestor of living modern man is Cro- magnon man or Homo sapiens fossils. It is so called, because its fossils were discovered in 1868 from Cro-Magnon rocks of trance by Mac Gregor. They emerged around 34000 years ago in Holocene epoch and are regarded as the most recent ancestor's of modern man.
Consider the following statements given below.
I. First living form originated from semi-arid land.
II. Nucleic acid were the first sign of life and represented beginning of life.
III. It was strongly beleived that prokaryotes evolved to from eukaryotes.
Choose the correct option
I and II
II and III
Only III
I, II and III
C.
Only III
Out of all the three statements, only 3rd statement is correct.
First living form originated from primitive oceans. Nucleoproteins were the first sign of life and represented beginning of life.
Parapatric speciation takes place when
a small segment of the original population becomes isolated reproductively
a part of the population becomes geographically isolated from the main population
a very different daughter species bud off from a semi- isolated peripheral population of ancestral species
a population of a species enters a new habitat
D.
a population of a species enters a new habitat
Parapatric speciation separates adjacent population. It takes place when a population of a species enters a new niche or habitat. It occurs only at the edge of the parent species range. No physical, but gene flow does not occur due to the occupancy of new niche.
Evolution of horses occured in
Holocene epoch
Miocene epoch
Palaeocene epoch
Eocene epoch
D.
Eocene epoch
The history of the horse family, Equidae, began during the Eocene Epoch, which lasted from about 56 million to 33.9 million years ago. It was described by Othniel C Marsh in 1879.
Reproductive isolation mechanism prevent interbreeding of naturally sympatric population. Given below are categories of isolating mechanisms. Choose the correct name for isolation when potential mates occupy overlapping ranges but reproduce at different times of the year.
Ecological isolation
Behavioural isolation
Temporal isolation
Mechanical isolation
C.
Temporal isolation
Temporal isolation is an evolutionary mechanism that keeps individuals of different species from interbreeding, even if they live in the same environment. It prevents species from mating because they breed at different times. These differences can be time of day, season, or even different years. Both plants and animals may exhibit temporal isolation, even if species are closely related and live in the same habitat.
Darwin in the 'theory of natural selection' states that
characters acquired during the life of an individual are inherited by its offsprings
environment does not play any role in the evolution
natural selection acts on favourable variations, which appear among individuals of a species
heritable variations arises through changes in the gene complex of species
C.
natural selection acts on favourable variations, which appear among individuals of a species
In 1859, Darwin published 'the' origin of species. His views were published in his book Origin of Species by, natural selection. He stated that all living things on earth today are the descendants with modification of earlier species. He also proposed a mechanism natural selection to explain how evolution takes place. Darwin's theory of natural selection state that natural selection acts on favourable variation, which appears among individual of a species.
The most ancient member of the genus Homo belonged to which of the following species or sub-species?
Fossilis
Sapiens
Erectus
Habilis
D.
Habilis
Homo habilis species are considered as one of the earliest members of the genus Homo. The characteristic feature of this species includes a slightly larger brain case, i.e. it had cranial capacity about 700 cc and smalle face and teeth than Australopithecus.
Select the correct sequence of stages in the evolution of modern man (Homo sapiens)
Australopithecus, Homo habilis, Neanderthal, Cro-magnon man, Modern man
Homo habilis, Neanderthal, Australopithecus, Cro-magnon man, Modern man
Australopithecus, Neanderthal, Cro-magnon man, Homo habilis, Modern man
Neanderthal, Australopithecus, Cro-magnon man, Homo habilis, Modern man
A.
Australopithecus, Homo habilis, Neanderthal, Cro-magnon man, Modern man
The correct sequence is
Australopithecus Homo habilis Neanderthal man Cro-magnon man Modern man
The characteritics of the following are:-
Australopithecus: Herbivorous, fully erect, canines and incisors small.
Homo habilis: Carnivorous, canines small, earliest stone tools.
Neanderthal man: Omnivorous, cave dweller, used hides as cloth, buried the dead
Cro-magnon man: Omnivorous, strong jaws with teeth, cave dweller, paintings and carving in caves
Modern man: Omnivorous, backbone with 4 curves, most intelligent, speech, language, domesticates animals.
Which one of the given statement is not true for Archaeopteryx?
Each wing had three clawed digit
Hind feet with five digits
Long jointed lizard like tail
Thecodont teeth on both jaws
B.
Hind feet with five digits
Hind feets of Archaeopteryx had four digits. It is considered to be the first bird by many. It is actually intermediate between the birds that we see flying and the predatory dinosaur (connecting link between reptiles and birds).
Which of the following assumption is not belonging to Hardy-Weinberg principle?
The population size is very large
Random mating is occurring
Natural selection takes place
No mutation occurs
C.
Natural selection takes place
In Hardy-Weinberg principle, the natural selection is not occurring as they explained the natural selection as the cause of failure of equilibrium of allele.
Abundance of a species in a population, within habitat is called
niche density
absolute density
relative density
geographic density
A.
niche density
Niche density is the abundance of a species in a particular population within its habitat.
Absolute density is the number of organisms per unit area or volume.
Relative density is the density of one species as a percent of total plant density.
Which of the following is a mismatch?
Giraffe - Lamarck
Drosophila - Morgan
Galapagos island - Darwin's finches
Origin of species - Mendel
D.
Origin of species - Mendel
Origin of species is the publication of Darwin.
Mendel is known as the Father of Genetics.
Archaeopteryx is
a living fossil
a mammal
a connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda
a connecting link between reptiles and birds
D.
a connecting link between reptiles and birds
Archaeopteryx (lizard bird) is a prin itive fossil bird, which existed on earth about some 150 million years back. It is a connecting link between reptiles and birds.
It characteristic feature are wings, feather, prolonged beak (birds), teeth in beak, keetless-sternum, long tail with unfused vertebrae, pygostyle absent, separate digits of wings and claws on fingers (reptiles).
The cranial capacity of Peking man was about
900 cc
1660 cc
1075 cc
1450 cc
C.
1075 cc
Cranial capacity of Peking man was about 1075 cc.
Beak is toothed in
pelican
kiwi
ostrich
Archaeopteryx
D.
Archaeopteryx
The upper and lower jaws of birds prolonged and modified into beak. The beak is toothed in Archaeopteryx whereas rest of the birds lack teeth. The Archaeopteryx is an extinct primitive bird.
The earliest fossil form in phylogeny of horse is
Merychippus
Mesohippus
Eohippus
Equus
C.
Eohippus
Eohippus (dawn horse) is the earliest fossil form in phylogeny of horse. It appeared in the beginning of Eocene. It was small, browsing animal of size of fox-terrier.
Haeckel's biogenetic law or recapitulation theory states that
life history of an animal reflects evolutionary history of the same
progeny resembles parents
mutations are acquired characters
all organisms begin their life from zygote
A.
life history of an animal reflects evolutionary history of the same
Biogenetic law or Theory of recapitulation states that the development of the embryo of an animal briefs its ancestral history. It was proposed by Ernst Haeckel.
Cranial capacity of modern man is
450-650 cc
600-1000 cc
900-1100 cc
1200-1600 cc
D.
1200-1600 cc
The cranial capacity of modern man (Homo sapiens sapiens) is 1200-1600 cc.
Name the ship on which Darwin got opportunity for a voyage of world.
Titanic
Vikrant
Vectoria
Beagle
D.
Beagle
In 1831, Darwin got opportunity to travel by H.M.S. Beagle for voygae of world exploration, planned by British Adminastry. The voygae tested for 45 years..
Two or more species occupying same or ovarlapping areas are :
sympatric
sibling
sub species
allopatric
A.
sympatric
Sympatric species are the species having same or overlapping areas of geographical distribution.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area