A circus artist is climbing a 20 m long rope, which is tightly stretched and tied from the top of a vertical pole to the ground. Find the height of the pole, if the angle made by the rope with the ground level is 30° (see Fig. 9.11)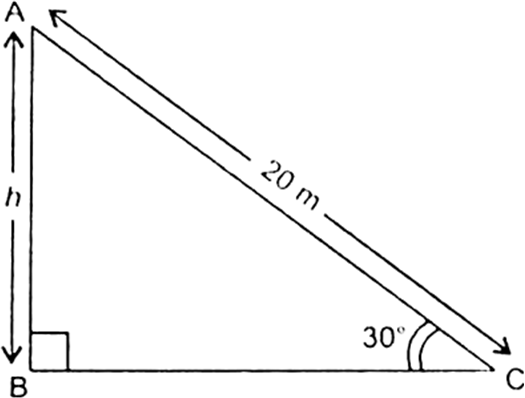
Fig. 9.11
Let AC be the rope whose length is 20 m, and AB be the vertical pole of height h m and the angle of elevation of A at point C on the ground is 30°.
Fig. 9.11
i.e., ∠ACB = 30°
In right triangle ABC, we have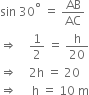
Hence, the height of the pole is 10 m.





