Physical Education Chapter 8 Physiology & Sports
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 राजनीतिक विज�ञान Physical Education
What is contusion?
A region of injured tissue or skin in which blood capillaries have been ruptured.
Define Friction and name its types.
The force that opposes the motion of an object is called Friction.
Two types of friction are-1.Static friction
2.Dynamic friction
a.Sliding friction
b.Rolling friction
What does the word'Coping strategies' mean,when talking about sports psychology?
In the field of psycology, coping refers to the thoughts and actions which we usually used to deal with a threatening situation.In fact psycological mechanism of coping are commonly called coping stratiges.
Explain in detail about the effects of regular exercise on Respiratory system.
Regular exercises have following effects on respiratory system:
(i) Increase in size of lungs and chest: When a person performs exercise regularly, he requires more amount of oxygen. He inhales more amount of air during exercise. Gradually in a long period, the size of his lungs and chest increases.
(ii) Increase in residual air volume: Residual air is that amount of air, which is left in the lungs after exhalation. If an individual performs regular exercise, his residual air capacity increases in comparison to an individual who does not perform regular exercise.
(iii) Strong will-power: Regular exercises increase will-power of the individual. As Pranayama, i.e. specific exercise for lungs, increases the will-power of the doer.
(iv) Unused alveolus become active: Regular exercise activates the unused alveolus, because much amount of oxygen, is required in vigorous and prolonged exercise of daily routine. The passive’ alveolus become active.
(v) Decrease in rate of respiration: Itis certain that when a beginner starts exercise, his rate of respiration increases. But when the same individual performs exercise daily, his rate of respiration decreases in comparison to the beginning stage at rest.
(vi) Avoids second wind: For a beginner, the stage of second wind is, indeed, a crucial stage. But for a regular exerciser, it is hardly felt. Sometimes, a well-experienced athlete does not feel it in his course of activity.
(vii) Increase in tidal air capacity: Tidal air is the amount of air that flows in and out of the lungs in each quiet respiratory movement. But tidal air capacity is the amount of air that can be breathed in and breathed out, over and above the tidal air by the deepest possible inspiration/expiration respectively.
(viii) Strengthens diaphragm and muscles: Regular exercise strengthens the diaphragm and the muscles of the chest.
(ix) Increase in endurance: If exercise is performed regularly and for a longer period, it increases endurance. An activity can be done for a longer period without taking any rest. Those who do not perform exercise, have less endurance. They cannot continue exercise for a long duration.
Explain the term “Realistic” in goal setting principles.
Realistic goals are achievable goals.
Maintaining physical activities for a longer period, brings desirous changes in circulatory system. Justify your answer by highlighting three benefits of exercise.
1. Cardiovascular system improves 2. Chemical composition of blood improves 3. New capillaries are formed 4. Reduction in cardiac problem 5. Decrease in blood viscosity (density) 6. Resting pulse increase 7. Return of normal pulse quickly 8. Faster adaptation to working load 9. Size of the heart increases.
Explain any two factors affecting wellness.
(i) Anatomical : An individual must be appropriate in body size, shape and structure essential for the performance. Sometime genetic impaired organs is responsible for weakness in structure which limit individual performance.
(ii) Physiological : Physiological system like muscular, respiratory, circulatory and nervous system must function effectively because if one is physiologically fit then only he can perform the specific movement of the game/sport.
(iii) Psychological factor or stress tension: Can become barrier in performance by contributing tension and anxiety which affects the fitness level of a person. One must be mentally tough/strong and prepared to perform better.
Define Cardiovascular endurance.
Cardiovascular Endurance; Cardiovascular endurance is the ability of heart to deliver blood, oxygen and nutrients present in it to the working muscles for a prolonged period. In other words, it can be said that it is the physical ability to maintain aerobic exercise for prolonged period of time.
Mention any six factors affecting physical fitness, in brief
Six factors affecting physical fitness:
1. Stress and Tension. Stress and tension tend to have a negative effect on physical fitness. Stress and tension decrease the psychological power of an individual, which in turn, reduces the level of physical fitness.
2. Good Posture. Everyone appreciates the good posture of an individual. Good posture enhances the physical fitness. It is also the symbol of wellness. The person who does not have good posture, tends to have lower level of physical fitness.
3. Heredity. Heredity also plays a vital role in affecting the physical fitness. In fact, heredity decides the structure of a person. Slow twitch fibres (red fibres) and fast twitch fibres (white fibres) also depend on heredity. If the percentage of slow twitch fibre is more, the person will have more endurance, whereas if the percentage of fast twitch fibre is more, the person is likely to have more speed ..So, it can be said that heredity also affects the physical fitness
4. Environment. The environment, which includes climate, temperature, altitude, social and cultural factors, affects the physical fitness of a person. Research studies indicate that the persons who live in cold climate tend to have more physical fitness in comparison to those orAs who live in hot climate. There are many societies in the world in which stres~ is laid down upon physical fitness of individuals. So, as a whole, it can be said that environment plays a vital role in affecting the physical fitness of a person.
5. Standard of Living. Standard of liVing also affects the physical fitness of an individuaL It plays an indirect role in influencing the physical fitness It has been observed that the people who have low standard of living, are likely to have less phYSical fitness.
6. Balanced Diet. Balanced diet also influences the level of physical fitness. Balanced diet is not only helpful in maintaining the physical fitness but also it improves the level of physical fitness On the other hand. if balanced diet is not taken. it will have a negative effect on the level of physical fitness.
What is “Stroke Volume”?
Amount of blood pumped by left ventricle in per beat. At rest period - 50 to 70 ml/beat During Exercise – 110 to 130 ml/beat.
Participation in physical activity for a longer duration maintain functional fitness among aged population. Justify
i. Changes in Sensory Organs
ii. Changes in Skin iii. Changes in sleep
iv. Changes in bone density
v. Changes in Metabolism
vi. Changes in brain and nervous system/ brain ageing
vii. Heart and blood circulation
viii. Change in body composition.
ix. Slow down loss of muscle mass
x. Reduces age related diseases
xi. Improves muscular strength xii. Enhances lung capacity
xiii. Improves flexibility xiv. Decreases stress and tensions
What is flexibility?
Flexibility is the range of movement of a joint. The range of joints varies significantly from joint to joint & depends on the surrounding tendons, ligaments & muscle tissues.
What is ageing?
Ageing is a process of continuous & irreversible decline in the efficiency of various physiological functions.
What is stroke volume?
The amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle of the heart in one contraction.
Define oxygen intake?
It is the amount of oxygen, which can be taken by the lungs from the atmosphere.
Define physical fitness?
Physical fitness is considered a measure of the body’s ability to perform effectively & efficiently in work and leisure activities, to be healthy, resist hyperkinetic disease & emergency situations.
Sponsor Area
How much blood is pumped by the heart in one minute?
Blood pumped by the heart in one minute is given as
Cardiac output =‘heart rate x stroke volume’ =72 beats/min x 70 mL approximately
= 5 L approximately.
What is cardiac output?
The total volume of blood, pumped by heart per minute, cardiac output = heart rate Stroke volume
What is oxygen uptake?
The amount of oxygen, which can be absorbed and consumed by the working muscle from the blood.
What do you mean by physiology?
Physiology is the division of biology that deals with the functions and activities of living organisms & their parts as well as physical and chemical process i.e. Nutrition, movement & reproduction, which are the living activities.
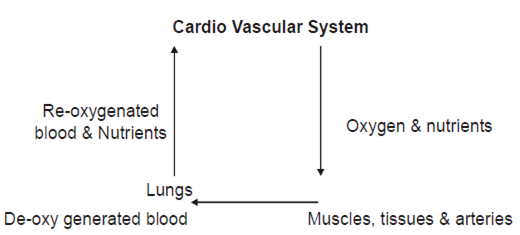
What is a cardio-vascular system?
In this system heart and lungs send oxygen to various muscles, tissues & arteries and at the same time returns the deoxygenated blood to the lungs to be re-oxygenated and return the fuel to the active tissues of the different parts of the body.
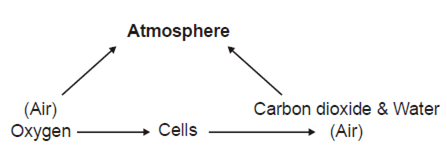
What is Respiration?
The process of Oxygen supplied to the cells and the transport of carbon dioxide from the cells is called respiration.
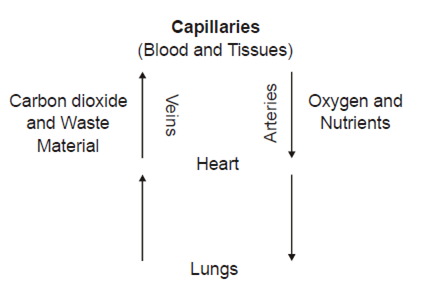
Define Blood Vessels?
Blood vessels are, tube-like structures in the body, in which, blood flows from heart to cell and vice-versa. Three types of blood cells arteries, veins & capillaries.
What do you mean by circulatory system?
The body system, which specialized function for transporting Air, Nutrients, Waste Material, Harmons and Enzymes. It consists of Heart, Blood vessels & glands.
What is ‘Trachea?
The trachea is a hollow wind pipe, which permanently kept and is lined with ciliated epithelium tissues.
What is the Tidal Volume?
It is the volume of Air, Ventilated with one normal inhalation during ordinary respiration.
what is vital capacity?
It is the volume of air, that can be expelled by the most forceful expiration after the deepest inspiration.
What is VO2 max (maximum oxygen uptake)
It is the maximum amount of oxygen, utilized by the body in one minute.
Explain Aerobic capacity?
It means to perform an activity with the maximum use of oxygen to produce energy for that activity.
Define total Lung volume?
It is the volume of Air, which, the lungs can accommodate after a deep inspiration.
Explain Muscle Fibre?
The muscles tissue consists of the specialized contractile cell. The type of muscle fibre in the body.
1) Fast twitch fibres - White fibres
2) Slow twitch fibres - Red fibres
What is myoglobin?
The myoglobin is a typical protein present in muscle fibre to store oxygen which produces energy in emergencies.
Define Anaerobic Capacity?
It means performing the activity without the use of oxygen to produce energy for that activity within the body and its resultant products are:-
- Lactic Acid
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
Differentiate between Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism?
| Aerobic Metabolism | Anaerobic Metabolism |
| Aerobic metabolism means the body can convert nutrients into energy with oxygen and it's waste products are Carbon dioxide and water. | Anaerobic Metabolism means the body can convert nutrients into energy with oxygen and it's waste products are Lactic Acid, Water and carbon dioxide. |
| Aerobic Metabolism occurs in the endurance activities. | Anaerobic Metabolism occurs in speed activities. |
What are the capillaries?
Capillaries are the smallest and thinnest vessels in the circulation system. The wall of capillaries made up of only one layer of cells. The interchange of gases and substance between the blood and the tissues take place here.
Write the immediate effects of exercise on the Cardio-Vascular system?
- Increase in heart rate: When an individual starts exercise, his heart rate increases as per the intensity and duration of exercise.
- Increase in stroke volume :Stroke volume increases proportionally with exercise intensity. It is measured in ml/beat.
- Increase in cardiac output: Cardiac output increases proportionally with the intensity of exercise’s is measured in ltr/ minute.
- Increases in blood flow :Cardio-vascular can be distribute more blood to those tissues which have more demand and less blood & those tissues which have less demand for oxygen. The blood is moved away from the main organs such as liver, intestine and kidney, in fact, it is redirected to the skin to enhance heat loss.
- Increase in blood pressure: During the exercise, systolic blood pressure can increase while diastolic blood pressure usually remains unchanged even during the intensive exercise.
Differentiate between slow twist fibre and fast twist fibre?
Difference between slow twitch fibre and fast twitch fibre:
| Slow twitch fibre (red fibres) | Fast twitch fibre (white fibres) |
| The red fibres of muscles are mainly responsible for the endurance activities. | The white fibres of muscle are responsible for strength and speed activities. |
| The red fibres are produced energy but the nutrients in the presence of oxygen only. | The white fibres are produced energy by the nutrients without the presence of oxygen. |
Write the effects of exercise in the muscular system?
Effects of exercise in a muscular system:
- Increase in Muscle Mass: Through the regular exercise, the cells of the muscle are enlarged, which change the size and shape of the muscle.
- Control extra fat: Regular exercise controls extra fat of the body. Exercise burns the calories, which is taken in the form of fat. This increases the lean mass in the body.
- Delays fatigue: Regular exercise delays fatigue. This fatigue is mainly due to formation of carbon dioxide, lactic acid and acid phosphate. The accumulation of carbon dioxide, acid phosphate, lactic acid become less in a person who perfroms regular exercise.
- Posture: Regular exercise helps in improving posture by improving postural deformities.
- Strength and speed - Regular exercise improve the strength and speed of muscle cells. This is partially due to the hypertrophy of muscles and partially due to increase in the capacity of giving and receiving stimulus.
Sponsor Area
Describe the effects of exercise on the respiratory system?
The effect of exercise on the respiratory system is closely linked with the effect of exercise on the circulatory and muscular system.
This means that the effect produced on the respiratory system by training are improved lung capacity and gas exchange.
- Improved tidal volume and vital capacity of lungs.
- Improved aerobic and anaerobic capacity.
- Avoid second wind.
- Increased willpower.
- Unused alveoles become active during regular exercise activity because much amount of oxygen is required in the vigorous and prolonged exercise of the daily routine. The passive alveoles becomes active.
Elucidate physiological changes due to Ageing?
The physiological changes, which take place mentioned below.
- Change in Nervous System:- During ageing, reaction time and movement time slows done with an increase in age. The brain waits, the size of its network and its blood flow decreases with age.
- Change in Gastro-Intestinal System: With the increase in age, there is a reduction in the production of Hydrochloric Acid, Digestive Enzymes and Saliva. These changes may result In delayed emptying the stomach, impaired swallowing. The breakdown and absorption of food may also be impaired. The liver becomes less efficient in metabolizing drugs and repairing damaged liver cells.
- Change in Urinal System: As we age, the mass of the kidney decreases, which leads to a reduction in blood filtration by the kidneys. The capacity of the bladders decreases and there is an increase in residual urine. This increases the chance of urinal infections.
- The change in senses: With the advance in age, the senses such as vision, hearing, taste, smell and touch may become less active. Vision and hearing are the most affected by ageing. The taste buds are reduced with age so they lose interest in food.
- Change in Respiratory System: With the age, pulmonary function is impaired with advancing age. The airways and lung tissues become less elastic and less efficient. There is decreased oxygen uptake and oxygen exchange.
- Change in fitness: The elasticity of tendons, ligaments and joint capsules decrease with Ageing. The range of the movement is restricted and muscle mass decreased as the age increases. This leads to decrease Flexibility, Endurance, Strength, the speed with shortness of Breath, Blood flow, Enzymes etc.
Explain the effect of exercise on the Circulatory system?
Increase in heart size: Regular exercises develop the muscles of the heart. It increases the size of the heart along with the strengthening of heart. The heart becomes efficient in doing its job.
The decrease in cholesterol level: Regular exercise reduces the level of cholesterol in Our blood. The level of cholesterol in our blood is directly linked with blood pressure. Exercise decreases the level of low-density protein and increases the level of high-density lips protein. It means that exercise decreases the LDL (bad cholesterol) and increase HDL (good cholesterol)
Faster adaptation to workload: Due to the regular exercise, the heart can adapt to working load quickly i.e. quick adjustment of the heart according to body needs.
Increase in no. and efficiency of capillaries: With the regular exercise, efficiency and no. of capillaries is increased with the increase of Muscle mass. The unused and new capillaries become efficient and nourish the various cells efficient and nourish the various cells effectively.
Improve the working capacity of the cardiovascular system: Regular exercise Improve cardio-vascular system thus the blood travels faster through the blood vessels and increased circulation of blood makes healing faster.
Discuss how physiological factors determine flexibility?
- Muscle strength: The muscle should have a minimum level of strength to make the movement, especially against the gravity or external force.
- Joint structure: There are different types of joint in the human body, some of the joints intrinsically have a greater range of motion than others for example. The ball & socket joint of the shoulder has the greatest range of motion in comparison to the knee joint.
- Internal environment:- Internal environment of athlete influences the flexibility. For example-warm bath increases body temperature and flexibility whereas 10 minutes outside stay in 100c temperature reduces the body temperature and flexibility.
- Injury: Injuries to connecting tissues and muscles can lead to thickening or fibronectin on the effected area. Fibrous tissues are less elastic and can lead to limb shortening and lead to reduce flexibility.
- Age and gender: Flexibility decreases with the advancement of age. However, it is trainable. It can be enhanced with the help of training as strength and endurance are enhanced. Gender also determine the flexibility. Females tend to be more flexible than male.
- Active and sedentary lifestyle: Regular activities enhance the flexibility, whereas inactive individual loses flexibility due to the soft tissues and joints shrinking and losing extensibility.
- Heredity: Bony structures of joints and structure length and flexibilities of the joint capsules and surrounding ligaments are genetical and cannot be altered by stretching programs.
Elaborate the Role of Regular Exercise on Ageing Process?
Reduces the risk of Age-Related Dieses: Regular exercise reduces the risk of a number of health problems, many aged persons face. Such health problems are:
Reduces the risk of Age-Related Dieses: Regular exercise reduces the risk of a number of health problems, many aged persons face. Such health problems are cholesterol, increase good cholesterol, decreases blood pressure and blood vessels stiffness.
- Increase in muscular strength: the Ageing process does not hinder the individual ability to enhance the muscle strength. Regular exercise increases the strength of the muscles. As a matter of fact, exercise increases the size of muscle which ultimately increases muscular strength.
- Reduce the loss of muscle mass: Muscle mass decreases with advancing age. Ageing has a negative effect on metabolism. Regular exercise reduces the loss of lean body mass and drops in the metabolic rate. Regular exercise also reduces the accumulation of fats.
- Enhances the capacity of lungs and hearts: Regular exercise enhance the working capacity of lungs and heart, it reduces the loss of electricity of the muscle fibres of lungs and heart. It also plays a key role in keeping the lungs strong and increase oxygen update and oxygen exchange.
- Maintaining the bone density: The bone density decreases with age. It usually leads to fracture and osteoporosis. Physical exercise helps to maintain bone mass and stimulate bone growth. The ageing persons can increase their bone density with the help of regular exercise.
- Slow down the brain due to ageing: The regular exercise reduces the risk of mild cognitive new nerve cells and builds new capillaries to supply the brain with more oxygen.
- Improve mental health and mood: Regular physical activities can help to keep thinking learning and judgement skills sharpen. Aerobic and muscle strengthening activities can also reduce the risk of depression and may help to sleep better.
Discuss the physiological factors, determine the strength as a component of physical fitness?
- Muscle size: Muscle strength directly depends on the cross-sectional area of muscle. It is well known that bigger and larger muscle can produce more force. The force produced by the same size of muscles in males and females is approximately the same but males are found to be stronger because they have larger and bigger muscles in comparison to females.
- Body weight: There is a positive correlation between the body weight and strength individuals with than heavier body weight are stronger than the individual with the lighter weight.
- Muscle composition: The muscle composition is genetically determined and can not be changed by any type of training.
- Nerve impulses: The nervous system also plays a role in muscle strength. The brain and nervous system have the power to activate more motor units when they need to generate a larger amount of force. Through the strength training, the body learns to recruit more motor units and increase these units.
- Age and gender: Age and gender is a factor which effects the muscle strength. Muscle strength decline with the age but it is primarily due to a decrease in muscle cross-sectional area and a decline in the number of contractile tissues within the muscle fibres. Regular strength training limits loss of muscle strength with ageing. Men have greater absolute muscle strength than women.
Describe the physiological factors which determine the speed as a component of physical fitness?
Speed is determined to a great extent by the genetic factors. The study of physiological Factors helps to select the activity for an individual.
- The mobility of the Nervous System: The rapid contraction and relaxation of muscles are made possible by the rapid excitation and inhibition of the concerned motor centres. The nervous system can maintain this rapid excitation and inhibition for only for a few seconds. After which the excitation and inhibition for only for a few seconds. After which the excitation spread to the neighbouring centres causing tension in the entire body. This results in a decrease in speed. The mobility of the nervous can be trained only to a very limited extent.
- Muscle composition: The muscle, which has more percentage of fast twitch fibre, contract with more speed in comparison to the muscle which has lower percentage be slow twitch fibre. The muscle position is genetical and cannot be changed by training.
- Explosive strength: For very quick and explosive movements, explosive strength is indispensable. It depends upon metabolic composition, muscle size & muscle coordination. The explosive strength of the muscles can be improved through training.
Explain the physiological factors determine endurance as a component of physical fitness?
Endurance is a very significant component of physical fitness, which is determined by the following physiological factors.
- Aerobic capacity: To perform an activity continuously energy is required by the muscles which can be supplied in the presence of oxygen. Therefore the ability or organism to maintain the adequate supply to oxygen to the working muscles for energy liberation is important for endurance performance. The aerobic capacity depends upon:
- Oxygen intake: The oxygen intake depends on the vital capacity which further depends on lungs size, no of active alveoli, respiratory muscle and the size of the chest cavity.
- Oxygen transport: The oxygen transport depends on the amount of oxygen, which the blood has absorbed from the lungs and the ability of th circulatory system to carry this quickly to the working muscles. The amount of oxygen absorbed into the blood depends on the speed of blood flow through the lungs and on the blood haemoglobin. The concentration of blood haemoglobin can be enhanced by training. The transportation of oxygenated blood depends on the capacity of the heart. This capacity can be improved by training.
- Oxygen uptake:- This depends on the rate of defusion, which determines the speed of blood flow, temperature & partial pressure of oxygen in the blood and of carbon dioxide in the muscles. The speed and amount of oxygen consumption depend on the no. size & metabolic capacity of mitochondria and fortunately can be improved to some extent through training.
- Energy reserves: The aerobic capacity depends on the muscle glycogen & sugar level in the blood. This can be enhanced by the training.
- Anaerobic capacity: The working capacity of muscle in absence of oxygen is called anaerobic capacity more or less Anaerobic capacity is required in all kind of endurance activities. Anaerobic capacity depends on the following factors.
- Phosphagen store: Means stronger of ATP and CP for producing energy.
- Buffer capacity: Means total storage of Alkali reserve in the body to fight against the effect of lactic acid is called buffer capacity.
- Lactic Acid Tolerance: The ability to tolerate the higher concentration of lactic Acid is a significant factor in determining anaerobic capacity.
- Movement Economy: Energy may be saved if the movements are correct so the economical movements are necessary for endurance performance
- Muscle composition: The slow twitch fibres of muscles are best for endurance activities.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





