At any point (x, y) of a curve, the slope of the tangent is twice the slope of the line segment joining the point of contact to the point (– 4, – 3). Find the equation of the curve given that it passes through ( 2, 1).
Now
From the given condition,
Separating the variables, we get,
Integrating,
Since curve passe through (-2, 1)
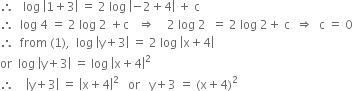
which is required equation of curve.





