Science Chapter 2 Micro-Organisms : Friends And Foe
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 8 Social+science
Match the following option.
| A. Mushroom | (i) Bacteria |
| B. Curd | (ii) Edible fungi |
| C. Streptococci | (iii) lactobacillus |
| D. Pickling | (iv) Yeast |
| E. Pasteurization | (v) Method of food preservation |
| F. Idli | (vi) Milk |
A. Mushroom | (i) Edible fungi |
B. Curd | (ii) lactobacillus |
C. Streptococci | (iii) Bacteria |
D. Pickling | (iv) Method of food preservation |
E. Pasteurization | (v) Milk |
F. Idli | (vi) Yeast |
Blue green algae fix _______ directly from air to enhance fertility of soil.
atmospheric nitrogen
Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is
female Anopheles mosquito
cockroach
housefly
butterfly
A.
female Anopheles mosquito
The bread or idli dough rises because of
heat
grinding
growth of yeast cells
kneading
C.
growth of yeast cells
Match the following option.
| A. Bacteria | (i) Setting of curd |
| B. Rhizobium | (ii) Causing Cholera |
| C. Lactobacillus | (iii) Nitrogen fixation |
| D. Yeast | (iv) Causes Malaria |
| E. A protozoan | (v) Baking of bread |
| F. A virus | (vi) Causing AIDS |
A. Bacteria | (i) Nitrogen fixation |
B. Rhizobium | (ii) Setting of curd |
C. Lactobacillus | (iii) Nitrogen fixation |
D. Yeast | (iv) Baking of bread |
E. A protozoan | (v) Causes Malaria |
F. A virus | (vi) Causing AIDS |
Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Microorganisms are very small in size and cannot be seen with naked eyes. A microscope has to be used to see these organisms.
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Microorganisms can mainly be divided into five groups :
(i) Bacteria
(ii) Fungi
(iii) Protozoa
(iv) Algae
(v) Virus
Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Bacteria like Rhizobium and Blue green algae can fix atmospheric nitrogen in soil.
Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Microorganisms are very useful to us. They help us in following ways :
(i) Microorganisms help us in food industry. They are used for curdling of milk, preparation of bread, cake, etc.
(ii) Microorganisms are used to produce alcohol at large scale on a commercial basis.
(iii) They are used to produce antibiotics.
(iv) They can act as decomposers and increase the fertility of the soil.
(v) They are also used as preservatives for food items.
(vi) They are used for the production of vinegar.
(vii) Microorganisms are used to prepare vaccines for various disease.
(viii) They fix the atmospheric nitrogen.
(ix) They are used for the production of cheeze.
(x) Microorganisms prepare manures by decomposing dead bodies of plants and animals.
Write a short paragraph on the harms caused by microorganisms.
Microorganisms can prove very harmful to us, as they cause a number of human, animal and plant diseases. Diseases in humans like common cold, tuberculosis, measles, chicken pox, polio, cholera, typhoid, hepatitis B, malaria, etc. are caused by microorganisms. Some serious diseases like Anthrax is also caused in animals by the microbes. Microbes also cause diseases of plants like blights in potatoes, sugarcanes, oranges etc. They also reduce the yield. Besides causing diseses these microorganisms lead to spoilage of food and even cause food poisoning. Microbes also spoil clothings and products.
Sponsor Area
What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Antibiotics are medicines derived from microorganisms. They stop the growth of harmful or disease causing microbes. Antibiotics are made from fungi and bacteria. Alexander Fleming discovered the antibiotic called Penicillin in 1929. Streptomycin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin etc are some commonly used antibiotics.
Precautions that must be taken while taking antibiotics are
i. Antibiotics should only be taken when advised by a qualified physician and one must finish the course prescribed by the doctor.
ii. Antibiotics should only be taken when needed and in the right dose, otherwise, they become less effective for future use.
iii. Taking atibiotics unnecessarily may kill the beneficial bacteria in the body.
What are micro-organisms?
The organisms which cannot be seen with our naked eyes are called micro-organisms.
What do you mean by viruses?
Very tiny microscopic organisms which reproduce only inside the cells of host organisms like bacterium, plant or animal, are called viruses.
How are viruses different from other micro-organisms?
Viruses can only reproduce inside a host cell. They are regarded as being the dividing line between the living and the nonliving.
Name two diseases caused by protozoans.
Dysentery and Malaria are the two diseases caused by protozoans.
Mention two diseases caused by bacteria.
Typhoid and cholera are diseases caused by bacterial.
Name two single celled microorganisms.
Single celled microorganisms are :
(i) Bacteria
(ii) Some algae.
Name two multi cellular microorganisms.
Multicellular microorganisms are
(i) Fungi
(ii) Algae
Mention two groups of microorganisms which live in colonies.
Two groups of microorganisms which live in colonies are:
(i) Bacteria
(ii) Fungi
Under which group of microorganisms does amoeba fall?
Amoeba falls in the protozoa group of micro-organisms.
Define 'fermentation'.
The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is known as fermentation. The conversion is brought about by yeast
What are antibiotics?
The medicines which kill or stop the growth of the disease causing micro-organisms are called antibiotics.
What do you mean by antibodies?
Antibodies are the substances made by our body to fight the invader, when a disease carrying microbe enters into the body. It protects our body from the disease causing microbes and body also remembers how to fight, if the pathogen enters again
.
Define 'vaccine'.
Vaccine is a preparation of a weakened or dead microbe that upon administration to an individual, stimulates the production of antibodies against the pathogen. The antibodies remain in the body and protect us from the disease causing microbes.
What do you mean by vaccination?
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to stimulate an individual's immune system to develop antibodies against the disease or pathogen.
Why antibiotics have no effect on viruses?
Antibiotics have no effect on viruses because viruses do not have a metabolism of their own. The antibiotics act by hampering the metabolism of the micro-organism rendering them harmless or killing them. Since the viruses have no metabolism of their own and rely on the host enzyme and machinery thus antibiotics have no effect on them.
What do you mean by nitrogen fixation?
The process by which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into nitrates which can be utilized by plants by the action of micro-organisms is called nitrogen fixation.
Sponsor Area
What do you mean by food preservation?
The method to prevent food material from spoilage is called food preservation.
What are food preservatives?
The substances which are used to check the growth of micro-organisms and prevent the spoilage of food, are called food preservatives. Substances like sugar, salt, oil or vinegar or other chemicals are used for this purpose.
What is meant by chemical preservation of food? Name one chemical preservative.
The method of food preservation by using certain chemical substances is called chemical preservation. Sodium benzoate is used as a preservative.
Name any two common preservatives which are available in kitchen.
Two common preservatives which are available in kitchen are:
(i) Salt
(ii) Oil
What do you mean by symbiotic relationship?
The relationship between two organisms in which both the organisms are benefitted is called symbiotic relationship. For example - Rhizobium and roots of legume plants.
Where can you locate the microorganisms?
Microorganisms thrive in almost all kinds of environments. They are present in air, water, soil and even inside the body of animals and plants. They can be found in extreme environmental conditions like extreme hot, cold or rainy climate. They may be present in hot springs, ice cold water, waters with high salt contents and organic matter, desert soil or even marshy land.
What are the major group of the microorganisms?
Major groups of microorganisms are :
(i) Bacteria : They are single celled microorganisms.
(ii) Fungi : They are long thread like unicellular as well as multicellular microorganisms.
(iii) Algae : Aquatic, photosynthetic organisms commonly called sea weeds.
(iv) Protozoan : They are unicellular organisms.
(v) Virus: They are non-cellular microbes which only get active inside a living cell.
What are viruses? Name some common diseases in human caused by virus.
Viruses are the microorganisms that have the characteristics of both the living and non-living things. They reproduce only inside the cells of host organism, which may be a bacterium plant or animal. Some diseases like cold, influenza, polio and chicken pox are caused by viruses.
How do micro-organisms survive under adverse conditions?
Under unfavourable conditions of temperature and water, they generally form a hard and tough covering called cyst or spore. This covering protects them from the harsh conditions. The covering is shed when favourable conditions appear.
Describe the role of blue-green algae in fertility of soil.
Blue-green algae can fix atmospheric nitrogen. They fix the atmospheric nitrogen in form of nitrates which can be absorbed by the plants
Mention important uses of fungi.
Importance of fungi are :
(i) Some fungi are eaten raw as food such as mushrooms.
(ii) Yeast being rich in amino acids and proteins are an important source of food for man and his farm animals.
(iii) Yeast is also used in the preparation of products like wine and bears from fruit juices or barley. It brings about fermentation of sugars into alcohols and carbon dioxide.
To which category of microorganisms do the following belong?
| A. Amoeba | (i) Algae |
| B. Lactobacillus | (ii) Protozoa |
| C. Chlamydomonas | (iii) Bacteria |
| D. Pencillium | (iv) Fungi |
| E. Yeast | (v) Fungi |
| F. HIV | (vi) Virus |
A. Amoeba | (i) Protozoa |
B. Lactobacillus | (ii) Bacteria |
C. Chlamydomonas | (iii) Algae |
D. Pencillium | (iv) Fungi |
E. Yeast | (v) Fungi |
F. HIV | (vi) Virus |
Write the useful effects of the Algae and protozoa.
Useful effects of algae and protozoa are :
Algae is used as food, fertilizers and in laboratories. It is also used in medicines and cosmetics.
Protozoa help in decomposition and in treatment of waste materials and sewage.
Write the harmful effects of fungi and algae.
Some fungi causes diseases and food spoilage. Smuts and rusts are fungi that damage the crops. Ring-worm and athletes foot diseases are caused by fungi. Amanite mushrooms contain poisonous substance. Moulds that appear on bread lead to its spoilage.
Algae are great nuisance as they spoil the drinking water by degrading its quality. Excess growth of algae also blocks the movement of water in channels.
What is the role of yeast in baking industry?
Yeast plays an important role in the baking industry. Yeast produces carbon dioxide during respiration, this carbo-dioxide gas is responsible for the rising of the dough. This is the basis of yeast in the baking industry for making breads, pastries and cakes.
How do microorganisms spoil food?
Microorganisms grow on the food materials and multiply. They release toxins in the food and making them unfit for consumption. They break down the food molecules into amines and change the taste, texture and external appearance of food. They also release certain toxins and make the food poisonous.
The mosquito P is a carrier of virus and spreads a disease Q. Another mosquito R is the carrier of protozoan S and spreads a disease called T.
(a) Name (i) mosquito P and (ii) disease Q
(b) Name (i) Mosquito R, (ii) Protozoan (S) and (iii) disease T.
(c) What is the sex of mosquito P ?
(d) What is the sex of mosquito R ?
(a) (i) Aedes mosquito, (ii) Dengue.
(b) (i) Anopheles mosquito, (ii) Plasmodium, (iii) Malaria.
(c) Female.
(d) Female.
What is the economic importance of bacteria in agriculture?
The economic importance of bacteria in agriculture
(i) Nitrogen fixing bacteria, Rhizobium are present in the roots nodules of legumes such as gram and pea. These bacteria fix free nitrogen into nitrates and increase the fertility of the soil.
(ii) Bacteria act as decomposers and help in decomposing the dead plant and animals remains, adding nutrients to the soil. They help in the formation of manure which is used to increase the crop yield.
What are the basic features of Protozoa?
Protozoans are single celled animals. Some may be in the form of small clusters of cells or colonies. They live in ponds, rivers, lakes and sea. Some live as parasites in man and other animals. For example - amoeba. 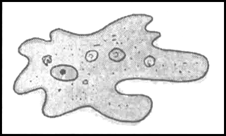
Explain how does a vaccine work?
The vaccine contains dead or weakened pathogens. When vaccine is administered, it stimulated the production of antibodies in the individuals body, against the pathogen. Antibodies stay in the body of the individual and protect them from the pathogen.
Differentate between yeasts and moulds.
|
Yeast |
Mould |
|
1. They are unicellular. 2. Very common. Can be found on fruit and berries, in the stomachs of mammals and on skin, among other places. 3. Yeasts are both aerobic as well as anaerobic. |
1. They are multicellular. 2. They are found in damp, dark areas. 3. Moulds are aerobic. |
What is pasteurization of milk?
Pasteurization is the process in which milk is heated to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. This process was discovered by Louis Pasteur. Pasteurized milk can be consumed without boiling as it is free from harmful microbes.
What are the major differences between Algae and Fungi?
|
Algae |
Fungi |
|
1. Autotrophic 2. Have chlorophyll 3. Cell wall made up of cellulose. |
1. Heterotrophic. 2. Do not have chlorophyll 3. Cell wall made up of chitin |
What do you understand by microorganisms ? Describe their different forms.
Organisms present around us which cannot be seen with naked eyes are called microorganisms. They are present in soil, water and air.
Microorganisms can be divided into five groups:
(i) Bacteria are the non-green single celled microscopic organisms. They have a rigid cell wall. It has a nuclear material. They are the simple most common form of life on earth. They have different shapes and sizes.
(ii) Algae are aquatic, photosynthetic organisms. In simple terms they are called sea weeds. They range in size, colour. Algae are of green, blue, red and blue-green colours.
(iii) Fungi are both unicellular and multicellular. Moulds, mushrooms etc. are fungi.
(iv) Protozoa are one called living things. They range from 2 to 200 microns. Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena and Plasmodium etc. are protozoas.
(v) Viruses are the non-cellular microbes. They are smaller than bacteria and multiply only inside a living cell.
Explain the Nitrogen cycle.
Nitrogen Cycle : Nitrogen is one of the most essential constituent of living beings. This is because nitrogen is part of chlorophyll, nucleic acids and vitamins. Plants and animals cannot directly consume the nitrogen present in the atmosphere. This work is done by the algae and bacteria . They fix the atmospheric nitrogen and converts it into nitrite and nitrate. The roots of the plants consume these nitrites and nitrates from the soil. The nitrogen is used to synthesis amino acid, proteins, etc. in the plants. This in turn is consumed by animals feeding on these plants. The dead bodies of these animals are worked upon by the bacteria and fungi present in soil and lead to their decomposition. They convert the compounds of nitrogen back into nitrates and nitrites. These are further converted into nitrogen gas and released in atmosphere by certain specialized bacteria thus balancing the percentage of nitrogen in atmosphere.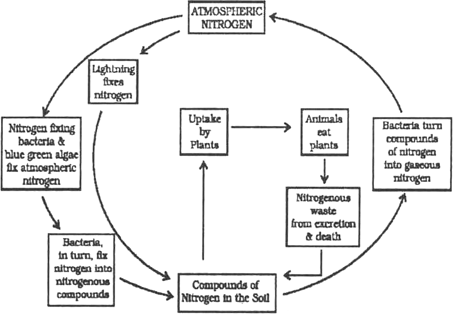
What are food preservatives? Explain some common food preservatives.
The chemical substances which are used to check or stop the growth of harmful micro-organisms in food and prevent the spoiling of food are called food preservatives .
Some common food preservatives are :
(i) Salt: Common salt is used to preserve meat, fish, amla, raw mangoes and tamarind etc.
(ii) Sugar : Jams, jellies and squashes are preserved by sugar. Sugar reduces the moisture contents which inhibits the growth of bacteria which spoil food.
(iii) Oil : Edible oils are used as preservatives in vegetables and pickles.
(iv) Vinegar: It is used to preserve fruits, vegetables, fish, meat and pickles.
How can we detect the spoilage in food?
Following indications help us an detecting the spoilage in food :
(a) Odour : When food gives out smell, it is the indication that the bacteria has spoiled the food.
(b) Discolouration : Growth of microbes on food results in discolouration of food. Black moulds on breads, blue green moulds.
(c) Souring : Sometimes the cooked food starts tasting sour. It is due to the production of acids by the action of certain bacteria.
(d) Sliminess : Sometimes the food becomes slimy. It is also due to action of certain bacteria.
(e) Gas formation : Due to action of bacteria gases like carbon dioxide are produced. They also spoil the food by making it swell or become spongy.
What are carriers of disease causing microbes? Explain with the help of two examples.
Disease causing microbes are some insects and animals which carry the disease causing micro-organisms like housefly, mosquitoes. Such insects and animals are called carriers of disease causing microbes.
Examples:-
(i) Housefly : The housefly is a carrier of micro-organisms. They sit on the garbage and animal excreta. The pathogens stick to their bodies, when these flies sit on uncovered food, they may transfer the pathogens.
(ii) Female Anopheles Mosquito : It is the carrier of the parasite of malaria.
(iii) Female Aedes mosquito acts as carrier of dengue virus.
Observe the following figure carefully and identify it. Name a common disease caused by it.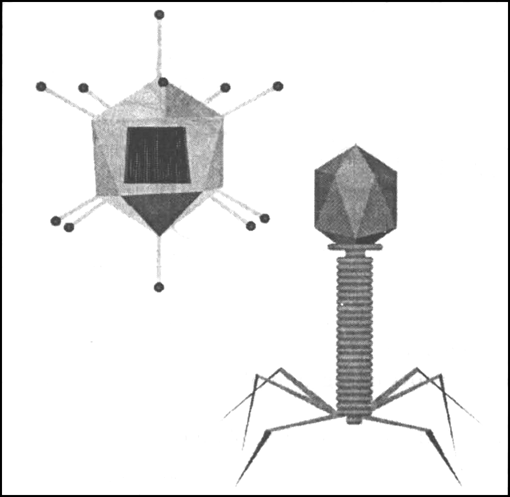
The given figure shows the virus.
The most common disease caused by the virus is Polio.
Draw a diagram to show
(i) Any two algae and name them
(ii) Two Protozoans and name them
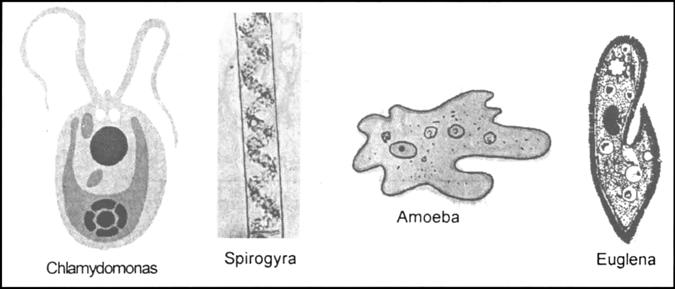
Chlamydomonas and spirogyra are examples of algae.
Draw a diagram of
(i) Bread mould (ii) Penicillium (iii) Aspergillus
(a) Name the group to which above said microorganisms belong.
(b) Name the antibiotic prepared by penicillium.
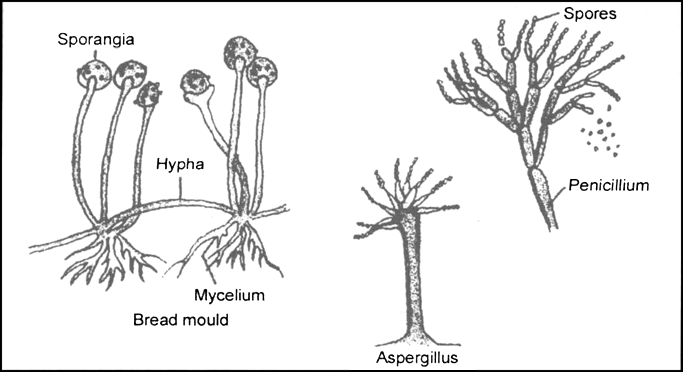
(a) Above said microorganisms belong to fungi group.
(b) The antibiotics is penicillin.
Draw a diagram of roots of legume plant with root nodules. Name the bacteria live in these roots.
The bacteria live in these roots is Rhizobium.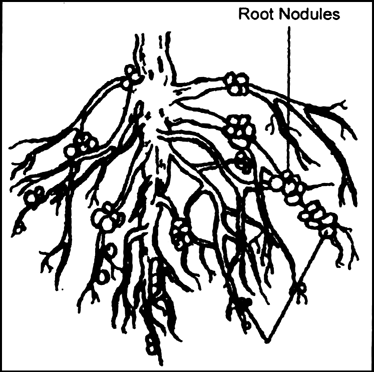
Sponsor Area
What is the ‘carrier’ of Dengue?
Male Aedes Mosquito
Female Aedes Mosquito
Male Anopheles Mosquito
Female Amopheles Mosquito
B.
Female Aedes Mosquito
Antibiotics are prepared by the microorganisms :
Bacteria and Virus
Virus and Fungus
Bacteria and Fungus
Protozoa and Fungus
C.
Bacteria and Fungus
Rhizobium bacteria
help in digestion
help in fixation of nitrogen
caused various disease
all of the above
B.
help in fixation of nitrogen
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





