Physical Education Chapter 7 Test & Measurement In Sports
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 राजनीतिक विज�ञान Physical Education
What motor quality does a senior citizen lack,who finds difficulty in trying the shoe laces while sitting on a chair?
The senior citizen lacks lower body flexibility.
What is hypertrophy of muscles?
Muscles hypertrophy is a term for the growth and increase of the size of muscle cells.
Write a detail note on Harvard Step Test.
Harvard step test is a cardiovascular fitness test.It is also called aerobic fitness test.It was developed by Brouha and others in 1943.It is used to measure the cardiovascular fitness by checking the recovery rate.
Equipments required-A gym bench or box of 20 inches high for men and 16 inches for women,a stop watch and cadence tape.
Procedure-The athelete stand in front of the box.on the command 'go'the athelete steps up and down on the box at a rate of 30 steps per mintues.the heartbeat are counted for 30 seconds period.
Advantages-1.Minimum equipments are required for conducting this test.
2.It requires minimal cost
3.It is simple to set up and conduct.
Disadvantages-1.The height of the box remain same for tall individual and short individuals.
2.It will be easy for tall individuals and difficult for short individuals.
What is ‘Kraus-Weber-Test’ ? Explain the administration of Kraus-Weber test in detail.
This test consists of six items. These tests are supposed to measure the minimum muscular fitness of an individual. In fact, they measure the level of strength and flexibility of certain key muscle groups below which the functioning of the whole body as a healthy individual seems to be endangered. These tests are graded on a pass-fail basis. But partial movements on each test can be scored from 0 to 10.
The administration of these tests are as follows:
Test No.1: The subject lies down in supine position i.e., flat on his back and hands behind his neck. The examiner holds his feet to keep him on the ground. The subject is asked to perform one sit-up. If he performs one sit-up, he passes this test. If he cannot raise his shoulders from the table or ground, his score remains zero.
Test No.2: The lying position for this test remains same i.e., in supine position except that his knees are bent and ankles remain in touch with his buttocks. He is asked to perform one sit-up. If he is able to perform full sit-up, he passes this test. If he is unable to raise his shoulders from the table or ground, he gets zero.
Test No.3: The subject lies in supine position i.e., lies flat on his back with his hands behind the neck. He is asked to raise his feet 10 inches from the ground. His knees should be straight. The examiner counts to 10 seconds. He passes this test if he holds that position for ten seconds. Scoring from 0-10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the appropriate position.
Test No.4: The subject lies in prone position i.e., on his stomach with a pillow under his lower abdomen and his hands behind his neck. The examiner holds his feet down. The subject is asked to raise his chest, head and shoulders, while the examiner counts to 10 seconds. He passes this test if he is able to hold the exact position up to 10 seconds. Scoring from 0-10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the exact position.
Test No.5: The subject’s position remains the same, but the examiner holds his chest down. The subject is asked to raise his feet. His knees should be straight. The examiner counts to 10 seconds. Scoring from 0-10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the position.
Test No.6: It is also known as floor-touch test. It measures the flexibility of trunk. The subject stands erect, bare-footed, hands at sides and feet together. He is asked to lean down slowly to touch the floor with fingertips for 3 seconds. In this test bouncing or jerking is not allowed. The examiner holds his knees in order to prevent any bend, if it occurs. Scoring from 0-10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the position.
What test would you suggest to measure upper body strength for aged population ?
What do you mean by ‘Cardiac Output’ ?
Cardiac output:The amount of blood the heart pumps through the circulatry system in a minutes.
Discuss in detail about the AAPHER Motor Fitness test specifically mentioning the various items in this test battery and its administration.
AAPHER stands for American Alliance for Health, Physical Education and Recreation. Various AAHPER youth fitness test items included are as follows:
- Pull-ups (Boys) / Flexed – Arm Hang (Girls)
Pull-ups (Boys)
The bar is hung at a height where students can freely hang off the floor. With the overhand grip, the student should raise his body until his chin is over the bar and lower it again to the starting position with his arms fully extended. Swinging, Knee bend is not allowed. One point is scored each time the student completes a pull up.
Flexed – Arm Hang (Girls)
The height of bar should be adjusted to the standing height of the subject. The student grasp the bar with overhand grip. She then raises her body off the floor with the help of assistant to a position where the chin is above the bar. Now the subject holds the ‘hang’ position as long as possible. The stop watch is started when subject assumes starting position and stopped when the chin touches the bar.
- Flexed – Leg Sit – ups
The student lies flat on the back with knees bent and feet on the floor. The angle of knees is 90 degree. Fingers are interlocked behind the neck with elbows touching the floor. The feet are held by a partner. The student then curls up to a sitting position and touches the elbows to the knees. This exercise is repeated as many times as possible in 60 seconds (1 minute).
- Shuttle Run
The student stands at one of the lines. On the signal ‘go’ he runs, takes the block one and returns to the starting line, and places the block behind that line, he then returns to the second block, which is carried across the starting line on the way back. Two trials are permitted.
- Standing Long Jump
The student stands behind the take-off line with feet several inches apart. He then jumps forward by bending knees and swinging arms backward. Three trials are permitted. Measurement is from the closest heel mark to the take-off line.
- 50 yard Dash
After a short warm-up, the student takes a position behind the starting line. On signal ‘go’ the student runs across the finish line. One trial is permitted.
- 600 yard Run – Walk
Students can run in a group of 10-12 students. When a group is running, the timer can call out times as each student crosses the finish line.
Your grandmother feels she has reduced her upper body flexibility and therefore she wants to test herself. Which test would you suggest her ?
Back scratch test for upper body flexibility
Explain the term hypertrophy of muscles.
Increase in size of the muscle fiber due to regular exercises or Hypertrophyis enlargement of heart due to regular exercises which is called “Athletic heart”
Explain the procedure for conducting Kraus-Weber test for measuring minimum muscular strength.
Kraus-Weber Test. This test consists of six items. It is commonly known as the Kraus-Weber Tests. These tests are supposed to measure the minimum muscular fitness of an individual. Infact, they measure a level of strength and flexibility of certain key muscle groups below which the functioning of whole body as a healthy individual seems to be endangered. These tests are graded on a pass-fail basis. But partial movements on each test can be scored from 0to 10. Six tests measures minimum muscular fitness of an individual Test No.1. The subject lies down in supine position i.e., flat on his back and hands behind his neck. The examiner holds his feet to keep him on the ground. The subject is asked to perform on sit- up. If he performs one sit- up, he passes this test. If he cannot raise his shoulders from the table or ground, his score remains zero. Test No.2. The lying position for this test remains same i.e., in supine position except that his knees are bent and ankles remains in touch with his buttocks. He is asked to perform one sit- up. If he is able to Physical Education Code No.75/1 6 perform full sit- up, he passes this test. If he is unable to raise his shoulders from the table or ground, he gets zero. Test No. 3. Subject lies in supine position i.e., lies flat on his back with his hands behind the neck. He is asked to raise his feet 10 inches from the ground. His knees should be straight. The examiner counts to 10 seconds. He passes this test if he holds that position for ten seconds. Scoring from 0- 10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the appropriate position. Test no. 4. Subject lies in prone position i.e., on his stomach with a pillow under his lower abdomen and his hands behind his neck. The examiner holds his feet down. The subject is asked to raise his chest, head and shoulders, while the examiner counts to 10 seconds. He passes the test if he is able to hold the exact position up to 10 seconds. Scoring from 0-10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the exact position. Test No. 5. The subject’s position remains the same, but the examiner holds his chest down. The subject is asked to raise his feet. His knees should be straight. The examiner counts to 10 seconds. Scoring from 0-10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the position. Test no 6. It is also known as floor- touch test. It measures the flexibility of trunk. The subject stands erect, bare footed, hands at sides and feet together. He is asked to lean down slowly to touch the floor with fingertips for 3 seconds. In this test bouncing or jerking is not allowed. The examiner holds his knees in order to prevent any bend, if it occurs. Scoring from 0-10 depends on the number of seconds he holds the position.
Explain in detail about any five advantages of correct posture.
Posture is the position you maintain while standing, sitting or lying down. You have good posture when your position creates the least amount of strain on supporting muscles and ligaments when you move or perform weight-bearing activity. It has many advantages. Some of them are :
- Better for Your Body : Good posture and back support are essential for avoiding back and neck pain. Good posture also prevents muscle aches and muscle fatigue. It keeps your bones and joints in proper alignment so you use your muscles more efficiendy, preventing strain and overuse.
- Future Health : Proper posture reduces abnormal wear and tear on joint surfaces, which can lead to arthritis. It also reduces stress on ligaments that connect spinal joints. Good posture helps you avoid developing an abnormal permanent position, which can cause spinal disk problems and constricted blood vessels and nerves. Good posture also protects spinal joints from injury and deformity.
- Breathe Right: Good posture helps to open the airways and ensure proper breathing. Proper breathing allows enhanc-ed oxygen flow in the cardiopulmonary system. The blood then carries sufficient oxygen to the nervous system, organs and other tissues, so they function effectively.
- Looking Good : Maintaining good posture does wonders * for your appearance. Proper posture can help you make a good
first impression, and appear more attractive and-confident. - Good posture : Good posture prevents fatigue because muscles are being used more efficiently, allowing the body to use less energy.
Recreational activities as means for fitness development.Justify
(a) It is an activity for pleasure and satisfaction to an individual. It refreshes one's mind and body after work.
(b) Recreational activities reduce the monotony and make a person alert.
(c) Absence of these activities can lead to laziness; boredom, stress or tension.
(d) Recreation through sports provides an opportunity for socialization, stimulation, co-operation which leads to some kind of strength and confidence in an individual.
(e) Recreational activities are very good for health. These stimulate your functioning and sense organs.
Explain the Rockport test.
Rock Port:
i) Purpose –To measure cardiovascular fitness
ii) Equipment required- Stop watch, weighing scale, Track
iii) Procedure- Measure Body weight, run one mile, timing taken, measure heart rate
iv) Calculation- Using this data cardiovascular endurance is calculated
What do you mean by correct posture? Explain the standing and sitting postures. What are the causes of bad posture?
Correct posture means the balancing of body in accurate and proper manner while sitting ,standing, reading,writing or during any other action of body.
Explanation of sitting and standing posture.
Standing-Heals together, toes apart, body erect. Knee straight, chin inside, chest forward, belly backward, body weight equally on both feet. Sitting-Hips as far back as possible on the chair, legs rest on the floor, thigh horizontal head, spinal column, shoulder and hips should be in straight line and erect.
Causes of bad posture (Explain any two)
i) Improper diet
ii) Heredity
iii) Accident
iv) Disease
v) Obesity
vi) Due to improper exercise
vii) Nature of job
viii) Fatigue
ix) wearing tight clothes
x) Unsuitable furniture
xi) Muscle weakness
xii) unawareness of correct footwear /Improper footwear.
Suggest any two free hand exercises for correcting round shoulder?
1. Keep your tips of fingers on your shoulder and encircle your elbow clockwise and anticlockwise direction for same number of times.
2. Pull the shoulders backward and see upward.
3. Chakra Asana, Dhanur Asana, Bhujang Asana
4. .Hold the hanging position on Horizontal Bar for sometime
Explain the procedure for Eight Foot Up and Go Test?
Procedure: Place the chair next to a wall & mark 8 feet in front of the chair. The subject starts by fully seated, hand resting on knees & feet flat on ground. On command ‘Go’ timing is started & the subject stands & walks as quickly as possible around the cone. Back to initial position and sit on to chair. A Person sit down Stop time. Perform two trials.
How the Cardiovascular fitness is measured with the help of “ Harvard Step Test ” ? Write in details about its administrative procedure.
After completion of administrative procedure of test the data will be put up in the formula for calculation of scores Fitness Index Score= 100 X test duration in seconds 2 X sum of heart beats in recovery periods After above calculation fitness rating will be measured.
PROCEDURE- The Athlete stands in front of the bench or box(Height of the bench between 18” to 20”). On the command ‘Go’ the athlete step up and down on the bench or box at a rate of 30 steps per minutes ( One second up and one second down ) for 5 minute (150 steps). Stopwatch is also started simultaneously at the start of stepping after that the athlete sit down immediately after completion of the test ie: after 5 minutes. The total number of heart beats are counted between 1 to 1.5 minutes after completion of the last step. The heart beats are counted for 30 seconds period. Again heart beats are noted for 30 seconds after the finish of the test. After that 3rd time the heart beats are noted after 3 minutes of completion of the test for 30 seconds period. The same foot must start the step up each time and an erect posture must be assumed on the bench.
Sponsor Area
What is a test?
A test is a tool, a question set of question an examination which is used to measure a particular characteristic of an individual or a group of individuals.
What is measurement?
According to R.N. Patel “Measurement is an act or process that involves the assignment of numerical values to whatever is being tested. So it involves the quantity of something.”
What do you understand by muscular strength?
It is defined as the amount of force the muscle or a group of muscles can exert against resistance for short duration as in anaerobic activities and aerobic activities.
What is the Kraus-Weber test?
Kraus-Weber Test: Kraus-Weber test is composed of six items. It is supposed to measure the minimum muscular fitness of an individual.
What is motor fitness?
Motor fitness is a “person’s ability to perform physical activities”.
What do you understand by cardiovascular fitness?
Cardiovascular fitness is the ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen-rich blood to the working muscle tissues and the ability of the muscles to use oxygen to produce energy for movement.
What do you understand by the Harvard step test?
It is a cardiovascular fitness test. It is good for measurement of fitness and the ability to recover after a strenuous exercise.
What is Rockport one mile test?
It is cardiorespiratory test used to determine VO2 max.(volume of oxygen) VO2 max is the maximum capacity of the person’s body to move and use oxygen during exercise.
What do you understand by flexibility?
Flexibility is the range of motion in a joint muscle or group of joints, muscular, or, the ability to move joints effectively. Flexibility is related to muscle strength.
What do you understand by senior citizen fitness test?
Senior citizen fitness test are easy to understand and effective tests to measure aerobic fitness, strength and flexibility using the minimum and inexpensive equipment.
Why measurement is necessary?
It is a tool which provides information regarding the individual’s ability, knowledge, performance and achievement.
By which test the one can measure abdominal strength?
Kraus-Weber test Abdominal pulse and minus psoas muscle.
Write the slaughter & Lohman children skin foid formulae to calculate the fat percentage in boys & girls.
Slaughter– lohman children skin fold formula
fat % (boys) = 0.735 + (sum of skin fold) + 1.0
fat % (girls) = 0.610 + (sum of skin fold ) + 5.0
To calculate the fitness index of an individual?
Fitness index can be calculated as,
Fitness index = Duration of activities (in seconds)x100 / 5.5 x pulse count after rest (1-1.5 min.)
Calculate body fat % of a boy aged 16 years whose measurement of skinfold triceps 14 mm and calf is 11 mm. By using Slaughter & Lohman's formula?
Slaughter Lohman's fat% of formula = (0.735 x (sum of skinfold) + 1.0
= 0.735 x (14 + 11) + 10
= (0.735 x 25) + 1.0
= 18.375 + 1.0
= 19.375
Explain the Rock port one-mile test’s Administration?
It is also known as Rock port fitness walking test. Its objective is to check or observe the development of the individual VO2 max, (maximum volume of oxygen.)
Administration of Rockport Fitness Walking Test :
The athlete is asked to start the mile-long walk and complete it as quickly as possible. The athlete has to bear in mind that She/he does not start running or jogging in an effort to complete the test. Once the athlete has completed walking the mile, the time taken to do so is recorded in minutes and hundreds of seconds and the heart rate is recorded as beats per minute. After the time and heart rate are recorded, the following variables are also recorded :
Age in years
Gender (women are given a value of 0 and men a value of 1)
Time to complete the one-mile walk (in minutes and hundreds of seconds.)
Heart rate in beats per minute (recorded immediately after stopping)
The following formula is used to calculate the score for this
test:
VO2 max = 132.853 – (0.0769 × Weight) – (0.3877 × Age) +(6.315 × Gender) – (3.2649 × Time) – (0.1565 × Heart rate)
Discuss the Back Scratch test for upper body flexibility.
Back Scratch Test :
Purpose: To assess the upper body (shoulder) flexibility, which is important in performing various jobs such as combing one’s hair, putting on overhead garments and reaching for a seat belt etc.
Equipment Required: A ruler.
Procedure:- This test is performed in a standing position. Keep one hand behind the head and back over the shoulder and reach as far as the possible down middle of the back. Palm should touch to the body and the fingers should be downwards.
Then carry another arm behind back palm facing outward and fingers upward and reach up as far as possible trying to touch or overlap the middle fingers of both hands.
Fingers should be aligned. Measure the distance between the tips of the fingers. If the fingertips touch then the score is zero. If they do not touch measure the distance between the fingertips (–ve score).
If they overlap measure by how much (+ive score). Practise two times and then test.
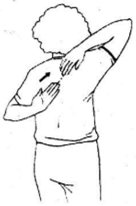
Explain the chair stand test for lower body strength?
Chair Stand Test: Purpose. The main purpose of this test is to measure the lower body strength, particularly legs strength which is usually required for various tasks such as climbing stairs, getting in and out of the vehicle, bathtub or chair.
Equipment Required: A chair with a straight back and a seat of at least 44 cm and a stopwatch.
Instructions for Participants.
- The participant should sit in the middle of the chair.
- She/He should keep his hands on the opposite shoulder crossed at the wrists.
- The feet should be flat on the floor.
- Her/His back should be erect.
- Repeat sit up and down for 30 seconds.
Procedure: Keep the chair against the wall. The participant sits in the middle of the seat. His/her feet should be shoulder width apart and flat on the floor.
The arms should be crossed at the wrists and held close to the chest. From the sitting position, the participant stands up completely then back down at the start of the signal.
This is repeated for 30 seconds. Count the total number of complete chair stands. In case the participant has completed a full stand from the sitting position when the time is finished the final stand is counted in the total.
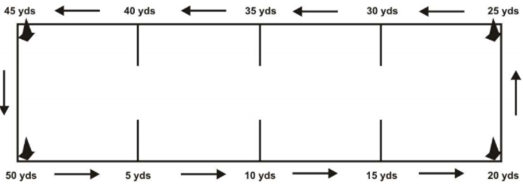
Write the test to measure the aerobic fitness of serious infirm?
Rikli & Jone’s Test- Senior citizen’s test.
6 Minutes Walk Test is used for aerobic fitness.
Purpose: This test measures aerobic fitness of senior citizens.
Equipment required: Measuring tap to mark out the track distances, stopwatch, chairs positioned for resting.
Procedure :
- The walking course is laid out in a 50 yard (45.72m) rectangular area (dimensions 45 × 5 yards), with cones placed at regular intervals to indicate distance walked.
- The aim of this test is to walk as quickly as possible for six minutes to cover as much distance as possible.
- Subjects are set their own pace (a preliminary trial is useful to practice pacing) and are able to stop for a rest if they desire.
Discuss the test item of Rikli & Jones to measure the upper body strength?
Arm Curl test of Rikli & Jones used to Testing upper body strength of senior citizen
Equipment: 5 lb Weight & an 8 lb weight, stopwatch & a straight-back chair with no arms.
Women will curl a 5 lb. weight in this test and men will curl an 8 lb. weight for their test. It is extremely important to the accuracy of the test that we use the appropriate weight for men & women in this test.
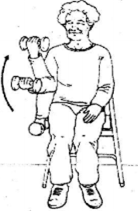
Procedure :
- Test assistant will tell to begin and will time for 30 seconds, using the stopwatch or a watch with a second hand.
- Do as many curls as can in the allotted30-second time period, moving in a controlled manner.
- Do a full curl, squeezing lower arm against upper arm at the top of each curl and returning to a straight arm each time. Keep upper arm still.
- Do not swing the Weight.
- If started raising the weight again and are over half way up when the time is over, count that curl!
- Scoring: The score is the total number of controlled arm curls performed in 30 seconds.
Which Test is used to measure the coordination and Agility of senior citizen? Write in detail?
Eight Foot up and Go Test:- Rekli & Jones Senior Citizen
Test: This test is a coordination and agility test for senior citizens.
Purpose: To assess speed, agility and balance while moving. These are important in performing various jobs which require quick manoeuvring, such as getting off a bus in time and to answer the phone etc.
Equipment Required: A chair with a straight back (about 44 cm high) a stopwatch, cone marker, measuring tape and an area without any hindrances.
Procedure: Keep a chair next to the wall and the marked, 8 feet in front of the chair. The participant starts completely seated, hands resting on the knees and feet flat on the ground.
On the command ‘Go’’ stopwatch is started and the participant stands and walks (no running at all) as quickly as possible to and around the cone and returns to the chair to sit down. Time is noted as She/he sits down on the chair. Two trials are given to the participant.

Discuss Chair Sit and Reach Test in briefly?
Chair Sit and Reach Test
Daily Benefits: Lower body flexibility is important for preventing lower back pain. It also plays a role in balance, posture, in fall prevention, or walking. Lower body flexibility is important for maintaining an active, independent lifestyle.
Purpose: This test measures lower body flexibility. Equipment required: Ruler, straight back or folding chair, (about 17 inches/ 44 cm high)
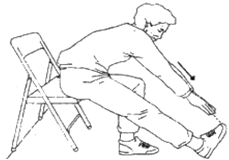
Procedure :
- The subject sits on the edge of a chair (placed against a wall for safety).
- One foot must remain flat on the floor. The other leg is extended forward with the knee straight, heel on the floor, and ankle bent at 90°.
- Place one hand on top of the other with tips of the middle fingers even. Instruct the subject to inhale, and then as they exhale, reach forward toward the toes by bending at the hip.
- Keep the back straight and head up. Avoid bouncing or quick movements, and never stretch to the point of pain. Keep the knee straight, and hold the reach for 2 seconds.
- The distance is measured between the tip of the fingertips and the toes.
- If the fingertips touch the toes then the score is zero. If they do not touch, measure the distance between the fingers and the toes (a negative score). If they overlap, measured by how much (a positive score).
- Perform two trials.
Sponsor Area
Explain General Motor Fitness Test?
General Motor Fitness Test :
Barrow’s Three-items General Motor Ability Test Motor abilities play a very vital role in achieving apex position in games and sports. Motor fitness involves speed, agility, power, coordination, strength and so on. These components of fitness are necessary for competing at top levels.
For measuring general motor fitness, the three-item test battery of Barrow is used. In this test, a battery of three items such as standing broad jump, zig-zag run and medicine ball throw is used to measure the general motor ability of an individual.
The details of administration of these tests are described below:
1. Standing Broad Jump (for measuring leg strength) Equipment and material: A mat of 5 × 12 feet and a measuring taps, if the mat is unmarked.
Procedure: A take-off line is marked on the ground. The subject stands just behind the take-off line with the feet several inches apart. The subject swings the arms and bends the knees to take a jump in the long jump pit. Three trials are given to the subject. The distance is measured from the take-off line to the heel or another part of the body that touches the ground nearest to the take-off line. All jumps are measured and the best one is recorded.

2. Zig-Zag Run (for measuring agility and speed) Equipment and material: Stopwatch, five obstacles and space enough to accommodate the 16 × 10 feet course.
Procedure: The subject begins from a standing start on the command to run. The subject runs the prescribed pattern stated to him as quickly as he can without gasping. Three complete circuits are run. The stopwatch is started when the command to run is given and stopped immediately when the subject crosses the finish line. The time is recorded to the nearest tenth of a second. Before running the zig& zag run, the subject should warm up properly. The subject should wear proper fitting shoes with good traction to avoid blisters and slipping. Demonstration of the pattern of the course should be given by the administrator before the beginning of the run.

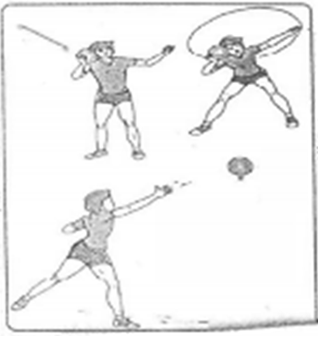
3. Medicine Ball Put (for measuring arm and shoulder strength)
Equipment and material: A medicine ball and measuring taps.
Procedure: The subject stands between two restraining lines which are 16 feet apart. In the case of girls, a medicine ball of 1 kg is provided, whereas in the case of boys a medicine ball of 3 kg is provided to be put. After that, he/she attempts to put the medicine ball out as far as possible without crossing the restraining line. He/she should hold the medicine ball at the junction of the neck and shoulder then the ball should be put straight down the course. Three trials are given to him/her. The best of three trials is recorded. The distance is computed to the nearest foot. A put in which the subject commits a foul is not scored. However, if all the trials are fouls, a subject he/she should try until he/she make a fair put.
The duration of a runner to run 30 seconds. The of heartbeats in 1-1/2, 2-2 & 3-3 minutes 85, 75 and 60 respectively of calculating physical fitness index for the runner?
According to the Harvard step test,
Physical fitness Index of runner
= 100 x Test duration (in sec) / 2 x no. of heartbeats during the process of regaining health
Total no. of heartbeats = 85+ 75 + 60 = 220
Physical Fitness index = 100 x 300 / 2 x 220 = 68.18
Describe the procedure of the components of the Kraus-Weber Test?
Kraus-Weber Test
Dr Hans Kraus and Dr Sonja Weber developed the Kraus- Weber Minimum muscular strength Test in the 1950’s. The six-items medical fitness test measures the strength and flexibility of key postural (core) muscles. The test consists of five strength challenges and one general flexibility procedure.
Administration of the Kraus-Weber Test:
The following six tests of key muscle groups represent the minimal performance necessary for healthy living. Because this is a minimum test, you will need to be able to perform All six parts successfully.
Test-1
Purpose: To measure the flexibility of the lower back and hamstring muscles.
Procedure: The subject lies down in supine position i.e.flat on his back and hands behind his neck. The legs are straight. The examiner holds the feet to keep them on the ground. The subject is asked to perform one sit-up.

Test-2
Purpose: to assess the strength of the abdominal muscles.
Procedure: The subject lies down in a supine position flat on his back and hands behind his neck except that this time the knees are bent. The examiner holds the feet to keep them on the ground. The subject is required to perform one sit-up.

Test-3
Purpose: to assess the strength of the psoas and lower abdominal muscles.
Procedure: Subject lies in supine position i.e., flat on his back with his hands behind the neck. He is asked to raise his feet 25 cm (10 inches) from the ground. His legs should be straight, no bending at the knee.

Test-4
Purpose: to assess the strength of the upper back muscles.
Procedure: The subject lies in prone position i.e.face down on his stomach with a pillow under his lower abdomen and his hands behind his neck. The examiner holds his feet down. The subject is asked to raise his chest, head and shoulders, while the examiner counts to 10 seconds.

Test-5
Purpose: to assess the strength of the lower back muscles.
Procedure: The subject lies in prone position i.e.face down on his stomach with a pillow under this lower abdomen and his hands behind his neck. The examiner holds his chest down. The subject is asked to raise his feet, keeping his knees straight. The examiner counts to 10 seconds.

Test-6
Purpose: To measures the flexibility of the lower back and hamstring muscles.
Procedure: The subject stands erect, bare-footed, hands at sides and feet together. He is asked to lean down slowly to touch the floor with finger-tips for 10 seconds. Bouncing and jerking are not allowed. The examiner holds his knees in order to prevent any bending.

Explain the harvard Step Test in details?
Harvard Step Test: The Harvard step test is a test of aerobic fitness, developed by Brouha et al. (1943).
Objective: The objective of this test to monitor the development of the athlete’s cardiovascular system.
Required Resources:-
- Gym bench (45 cm high)
- Stopwatch
- Assistant
How to Conduct the test
- This test requires the athlete to step up and down off a 45 cm high gym bench for 5 minutes at a rate 30 steps/minute.
- The athlete warm-up for 10 minutes
- The assistant gives the command “Go” and starts the stopwatch.
The athlete steps up-up and down-down onto a standard gym bench once every two seconds for five minutes (150 steps) - The assistant stops the test after 5 minutes.
- The assistant measures the athlete’s heartbeat rate (bpm) one minute after finishing the test pulse 1
- The assistant measures the athlete’s rate (bpm) two minutes after finishing the test - Pulse-2
- The assistant measures the athlete's heart rate (bpm) three minutes after finishing the test pulse 3.
Explain the Administration of AAPHER Youth Fitness Test?
Motor Fitness Test AAHPER (American Alliance for Health, Physical Education and Recreation) Motor fitness refers to the capability of an athlete to perform effectively at their particular sports. The components of motor fitness are agility, balance, coordination, which entails speed and strength and finally reaction time.
The following items were included in AAPHER youth fitness test battery.
- Pull-ups for boys & flexed arm hand for girls.
- Flexed-let sit-ups
- Shuttle run
- Standing long jump
- 50 yards dash
- 600 yards run/walk
1: A. Pull-ups for boys, to measure arm and shoulder strength.
B. Flexed arm hang for girls, to measure arm and shoulder strength.
2. Flexed-leg sit-ups: To measure abdominal strength and endurance.
3. Shuttle run: To measure speed and agility
4. Standing long jump: To measure legs power.
5. 50 yards dash: To measure the speed
6. 600 Yards run: To measure the stamina and endurance.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





