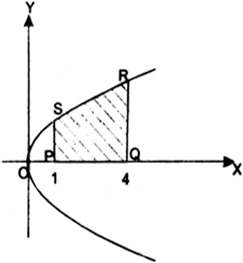
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y2 = x and the lines x = 1, x = 4 and the x-axis in the first quadrant.
The equation of curve is y2 = x
Required area = ![]()
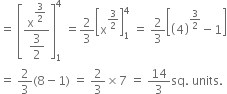
Sponsor Area
The equation of curve is y2 = x
Required area = ![]()
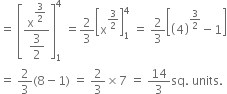

Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series