Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products And Their Elimination
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 11 Political+science Biology
What is Bowman's capsule?
What is glomerulonephritis ?
What is uremia ?
What is renin?
What do you understand by uricotelic animals?
What stimulates secretion of renin ?
The fall in the glorular filtration rate (GFR) or the fall in the glomerular pressure or blood flow results in secretion of renin from the JG cells.
What is the function of angiotensin II?
What is the colour and the pH of urine?
Why in winter there is increase in urination ?
During winter, the surrounding temperature will be very low. There is no sweating, there are no evaporation losses. To keep the body temperature constant, the blood capillaries in the skin are constricted and the blood pressure is increased. In order to maintain the blood pressure normal, the excess water along with the wastes is excreted mostly in the form of urine resulting in frequent urination in winter.
What are diuretic substances. Give examples ?
Sponsor Area
Give the term for the following
i. Hairpin shaped loop
ii Straight tube into which many DCT of nephrons open.
iii. Conical masses projecting into the calyces.
iv. Renal columns between the medullary pyramids
ii. Collecting duct.
iii.Medullary pyramids.
iv. Columns of Bertinin
Why water is not reabsorbed in ascending limb or PCT ?
Name the excretory organ in the following:
i. Platyhelminthes, annelids. rotifers.
ii. Earthworms.
iii. Insects
iv. Crustaceans.
i. Protonephridia in Platyhelminthes, annelids, rotifers
ii. Nephridia in earthworms.
iii. Malphigian tubules in insects.
iv. Green glands in crustaceans.
What is ureotelic animals ?
Give examples of ammonotelic organisms?
Where does the conditional reabsorption of Na+ and water take place?
What are the different types of Nephrons ?
i. Cortical nephrons - These nephrons have a very short loop of Henle which extends only a little into the medulla.
ii. Juxtamedullary nephrons- These nephrons have a long loop of Henle that runs deep into the medulla.
Why urea is preferred as excretory product in mammals to ammonia ?
However urea is leass toxic and does not need much water for excretion. Thus urea is preffered over ammonia as an excretory product.
In which part of the tubule are the essential nutients, major percentage of electrolytes and water absorbed?
Define Glomerular filtration rate?
What activates the JG cells to release renin?
Which substances are reabsorbed actively?
Why is tubular secretion important?
What are osmolytes ?
Sponsor Area
Name the three layers of through which the filtration of bood takes place. ?
i. The endothelium of glomerular blood vessels
iiThe epithelium of Bowman's capsule
iii. The basement membrane
Name two hormones which regulate functioning by feed back mechanism in kidneys.
Indicate whether the following statements are true or false.
A.
Micturition is carried out by a reflex.B.
ADH helps in water elimination, making the urine hypotonic.C.
Protein-free fluid is filtered from blood plasma into the Bowman's capsule.D.
Henle’s loop plays an important role in concentrating the urine.E.
Glucose is actively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.B. FALSE
C. TRUE
D. TRUE
E. TRUE
Match the items of column I with those of column II
| A. Ammonotelism | (i) Birds |
| B. Bowman's capsule | (ii) Water reabsorption |
| C. Micturition | (iii) Bony fish |
| D. Uricotelism | (iv) Urinary bladder |
| E. ADH | (v) Renal tubule |
A. Ammonotelism | (i) Bony fish |
B. Bowman's capsule | (ii) Renal tubule |
C. Micturition | (iii) Urinary bladder |
D. Uricotelism | (iv) Birds |
E. ADH | (v) Water reabsorption |
Fill in the gaps
Ascending limb of Henle’s loop is.............to water whereas the descending limb is.............to it.
Fill in the gaps:
Dialysis fluid contains all the constituents as in plasma except...........
Define the term excretion .
Excretion : It is the process by which the nitrogenous wastes is eliminated from the body.
Describe the various nitrogenous waste products.
Nitrogenous waste products : Ammonia , urea, uric acid are some nitrogenous waste products excreted by our body.
1. Ammonia : It is formed by the deamination of amino acids during the protein metabolism. Ammonia is highly toxic. It is highly soluble in water and needs a large amount of water for its excretion. The animals which excret ammonia are called ammonotelic organisms. For expmple bony fishes , aquatic amphibians and insects.
2. Urea : It is less toxic than ammonia. Most mammals, fishes and amphibians excrete their nitrogenous waste products in the form of urea. Process of excretion of urea is called ureotelism and such animals are called ureotelic. It needs less water for excretion, hence helps in the conservation of water. Animals like mammals, terrestrial amphibians and marine fishes excrete urea.
3. Uric acid : Reptiles and birds excrete uric acid and are called uricotelic. The uric acid is is excreted in the foprm of pellet and paste with minimum loss of water.
Describe the excretory organs in protozoans, sponges and coelentrates.
Sponges : Ammonia is the main excretory product in sponges. It diffuses from cells into the water filling the canals and surrounding the sponge. From the canal system, the waste matter is carried away by the outgoing current of water.
Coelentrates : Coelentrates have no excretory organs. They pass out metabolic waste by diffusion from all cells. They are ammonotelic i.e. their excretory product is ammonia. The waste water entering coelentron leaves when its water is renewed.
Briefly explain the following:
i. Flame cells.
ii. Nephridia.
ii. Nephridia - are tubular excretory strauctures found in earthworms and other annelids. These help to remove the nitrogenous wastes and maintain fluid and ionic balance.
Describe the structure of a nephron.
A nephron is the functional unit of the kidney.
Each nephron compreises of two parts – the glomerulus and the renal tubule.
The different parts of a nephrons are :
Glomerulus - is a tuft of capillaries formed by the afferent arteriole – a fine branch of renal
artery. Blood from the glomerulus is carried
away by an efferent arteriole.
Renal tubule - The renal tubule begins with a double walled cup-like structure called Bowman’s capsule, which encloses the glomerulus.
Malphigian body - The Glomerulus alongwith Bowman’s capsule, is called the malpighian body or renal corpuscle.
PCT - The tubule continues further to form a highly coiled network – proximal convoluted tubule
Loop Of Henle - A hairpin shaped Henle’s loop forms the next part of the tubule which has a
descending and an ascending limb.
DCT - The ascending limb continues as another highly coiled tubular region called distal
convoluted tubule (DCT).
Collecting Duct - The DCTs of many nephrons open into a straight tube called collecting duct, many of which converge and open into the renal pelvis through medullary pyramids in the calyces.
The Malpighian corpuscle, PCT and DCT
of the nephron are situated in the cortical
region of the kidney whereas the loop of Henle
dips into the medulla.
Peritubular capillaries - The efferent arteriole emerging from the glomerulus forms a fine
capillary network around the renal tubule called the peritubular capillaries.
Vasa recta - A minute vessel of this network runs parallel to the Henle’s loop forming a ‘U’ shaped vasa recta.
Describe the structure of Nephron.
Nephron : A nephron is a structural and functional unit of kidney. It is differentiated into four regions Bowman's capusle, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule (DCT). 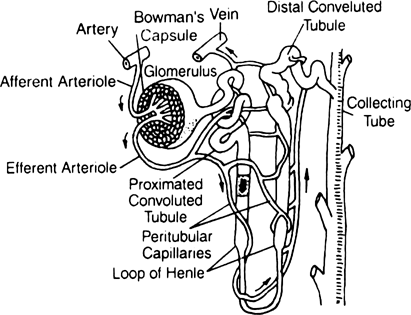
Fig. Uriniferous tubule
(i) Bowman's capsule : It is a double walled cup containing bunch of parallel capillaries called glomerulus. The glomerulus rests on basement membrane. It is a continuous layer. The Bowman's capsule and glomerulus together are called renal corpuscle or malpighian body. The endothelial cells lining the glomerulus have pores between them. The cells of inner wall of Bowman's capsule are called podocytes have gaps called slit pores 25nm wide between them.
The glomerulus is supplied by an afferent arteriole and is drained by a relatively narrow efferent arteriole. The latter forms peritubular capillary network around the rest of nephron.
(ii) Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) : It starts from the neck of the Bowman's capsule.
(iii) Loop of Henle : It is a U-shaped segment of the nephron located in the renal medulla. It consists of two straight parallel limbs.
(iv) Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) : Like PCT, it is greatly twisted and lies in the renal cortex. DCT continues into a collecting tubule.
Collecting tubes or ducts : These are larger tubes, each receiving the collecting tubule of several nephrons. They join each other forming larger ducts of bellini. These open into calyces, which lead into the pelvis.
Describe briefly mechanism of urine formation in human kidney.
1. Ultrafiltration : It is the filtration which occurs under high blood pressure. The afferent arteriole supplies blood to glomerulus and efferent arteriole collects blood from glomerulus. The afferent arteriole has more breath than the capillaries of glomerulus. Therefore, the pressure in glomerulus is two and half times more than ordinary capillary bed. Thus smaller molecules of glucose, water, salts, ammonia etc. diffuse from glomerulus into Bowman's capusle. And this process is called ultrafiltration.
2. Selective reabsorption : It is the process by which useful materials are absorbed by the blood from glomerular filtrate. The tubular epithelial cells in different segments of nephron perform this either by active or passive mechanisms. For example, substances like glucose, amino acids, Na+, etc., in the filtrate are reabsorbed actively whereas the nitrogenous wastes are absorbed by passive transport. Reabsorption of water also occurs passively in the initial segments of the nephron
3. Selective secretion : The metabolic waste products like ammonia, creatine, H+ ions etc. present in the blood diffuse into distal convoluted tubule DCT. This process is called selective secretion. The tubular cells secrete substances like H+, K+ and ammonia into the filtrate. Tubular secretion helps in the maintenance of ionic and acid base balance of body fluids.
Describe control of ADH on urine output.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin hormone : Urine output is inversely proportional to ADH. It is secreted by hypothalamus and released through posterior lobe of pituitary gland.
If there is excess of water in body then ADH is secreted in less amount so that urine output is increased and if there is less amount of water in the body then ADH is secreted more, because osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect an increase in osmolarity of blood above a set point of 300 mosml–1, so that urine output is decreased. In this condition osmorecptor cells promote thirst. Drinking reduces osmolarity of blood. Those substances which increase urine output are called diuretics e.g. alcohol, tea, coffee and all type of non-alcoholic drinks etc. Control of ADH is a negative feed back circuit.
Give the functions of kidney.
Functions of kidney :
1. Excretion : Kidneys pass out metabolic waste products.
2. Regulation of pH value : Kidneys help in the removal of excess of acids from the blood and thus help in regulating pH value.
3. Osmoregulation : Kidneys help in the maintenance of the osmotic balance in the body.
4. Secretion of renin : The kidneys secrete renin which converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin. It stimulates the limbs of uriniferous tubules to absorb Na+ ions from blood.
5. Elimination of excess of salts : The kidneys elminate excess of salts from blood and thus help in regulating blood pressure.
6. Regulation of blood pressure : By controlling the fluid balance in the body, kidney nephron regulates blood pressure.
7. Homeostasis : As kidney removes various unwanted material from the blood, it helps in keeping the internal environment of the body constant.
8. Elimination of other substances : Kidney removes toxic substances like drugs, pigments etc. from the blood.
Discuss the composition of urine.
Composition of urine :
Nature : Urine is acidic in nature and its pH varies between 4.5 to 8.0.
Colour : Urine is pale yellow due to the presence of urochrome, a pigment.
Odour : Urine has a faint odour due to bad smelling urinod. On standing, urea changes to ammonia and produces a strong offensive pungent smell.
Quantity : A normal adult excretes about 1 to 1.8 litre of urine in 24 hours.
Chemical composition : An analysis of urine shows that urine contains 95% water, 5% nitrogenous metabolic waste products like urea, hippuric acid, creatinine etc. and non-nitrogenous waste products like oxalic acid, excess of vitamin etc.
Discuss the various abnormal constituents of urine.
Abnormal constituents of urine are :
1. Proteinuria : e.g. When albumin and globulin are present in urine.
2. Glycosuria : When glucose is present in urea.
3. Hematuria : It is the presence of blood in urine is called hematuria.
4. Ketouria : The presence of ketone bodies causes ketouria.
5. Albuminuria : Presence of albumin in urine is callcd albuminureu.
Describe the accessory excretory organs.
The skin, lungs, liver and large intestine in vertebrates are the accessory excretory organs.
1. Skin : Human skin possesses sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Sweat is an aqueous fluid containing sodium chloride, lactic acid, urea, amino acids and glucose. It serves mainly as a cooling process. Sweat contains 99.5% of water. The volume of sweat varies from negligible amount to 142 ml. a day depending upon activity and temperature. Sebum also contains excretory products like waxes, sterols and fatty acids. It also keeps skin oily.
2. Lungs : Lungs remove large volume of carbon dioxide produced in the body along with which some moisture is regularly excreted. Human living removes 182 ml. of C02/hr. and 400ml. of water per day in normal resting conditions volatile materials are also eliminated by lungs.
3. Liver : Liver is the principal organ for the excretion of cholesterol pigments (bilirubin and biliverdin) and inactivated products of steroids, hormones, some vitamins and many drugs.
Explain why :
(a) Skin functions as an accessory excretory organ.
Explain why :
(b) Mammalian can eliminate hypotonic urine and hypertonic urine according to body needs.
ADH (Aniti diuretic hormone) - is released when the there is loss of water, it facilitates water reabsorption from latter parts of the tubule, thereby producing hypertonic urine. An increase in body fluid volume can switch off the osmoreceptors and suppress the ADH release to complete the feedback.
Aldosterone - also causes reabsorption of water from the distal part of the tubule thus producing hypertonic urine. When the level of the aldosterone is low, water absorption is less and hence hypotonic urine is produced.
The counter current mechanism helps in the maintenace of the intestinal gradient. The intestinal gradient helps in easy passage of water from the collecting tubules thereby concentrating the urine.
Explain why :
(c) Micturition is reflex process but is under some control.
of urine.
The neural mechanisms causing it is called the micturition reflex.
The stretching of the urinary bladder activates the stretch receptors on the walls of the bladder. These receptors send signals to the central nervous system. The CNS passes the motor message to initiate the contraction of smooth muscles of the bladde and simultaneous relaxation of the urethral sphincter causing the release of the urine.
Explain why :
Mammals are ureotelic, but birds are obliged to be uricotelic.
Explain
Different parts of a nephron participate in different ways in the formation of urine.
i. Ultrafiltration occurs in Bowman's capsule.
ii. In proximal convoluted tubule, glucose and amino acids are absorbed. 25% of Na+ is absorbed in distal convoluted tubule.
iii. Absorption of water occurs in Loop of Henle.
iv. Collecting tube also secretes uric acid.
What is the function of osmoreceptors ?
Osmoreceptors in the body are activated by changes in blood volume, body fluid volume and ionic concentration.
These are present in hypothalamus. These send impulses to posterior lobe of pituitary gland to secrete ADH. The ADH (Anti diuretic hormone) increases the permeability of cells of distal convoluted part and collecting tube to absorb more water and produce hypertonic urine.Write a note on artificial kidney.
Artificial kidney or Haemodialysis : It is the artificial removal of the nitrogenous wastes from the body. It is used in those patients whose kidney tubules do not function properly so that the metabolic wastes start accumulating in the blood and they need to be eliminated frequently. It can be explained in following points.
1. In the process, the blood of the patient is pumped from one of the main arteries and cooled to 0°C.
2. It is then mixed with an anticoagulant heparin and passed through cellophane tube.
3. This cellophane tube is a semipermeable membrane which allows only small molecules like urea, uric acid, creatinine and mineral ions to pass out but the macromolecules like proteins are not able to pass through it.
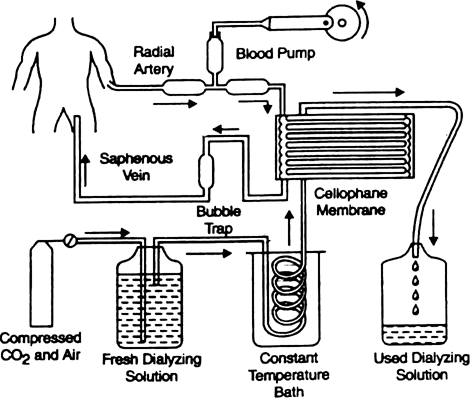
Fig. Diagram of Artificial Kidney
4. This cellophane tube is suspended in a salt solution which is isotonic with the blood plasma. Now, as the blood flows through this tube metabolic wastes are filtered out of the blood in the salt solution.
5. The purified blood is mixed with antiheparin to restore its normal coaguability and is then pumped into the body through a vein.
Explain the process of haemodialysis
Haemodialysis is the artificial process by which urea is removed from the body of the patient.
i. Blood drained from an artery is
pumped into a dialysing unit after the addition of anticoagulant like heparin.
ii. The unit contains a coiled cellophane tube surrounded by a dialysing fluid having the same composition as that of plasma except the nitrogenous wastes.
iii. The porous cellophane membrance of the tube allows the passage of molecules based on concentration gradient. As nitrogenous wastes are absent in the dialysing fluid, these substances
freely move out, thereby clearing the blood.
iv. The cleared blood is pumped back to the body through a vein after adding anti-heparin to
it. This method is a boon for thousands of uremic patients all over the world.
Describe juxta glomerular feed back circuit to control kidney function.
Juxta glomerular Apparatus (JGA) has a complex regulatory role and it controls multihormonal Renin-Angiotensinogen System (RAAS). It responds to decrease in blood pressure in afferent arteriole of glomerulus. Afferent arteriole's cells release an enzyme called renin into blood stream.
Renin converts angiotensinogen present in plasma into angiotensin II peptide. Functions of Angiotensin II :
1. Angiotensin II is a hormone which increases B.P. by causing arterioles to contract.
2. Angiotensin II also increases blood volume in following two ways.
(a) It signals the PCT to absorb more H20 and more NaCl.
(b) It also stimulates adrenal cortex to release aldosterone which induces the DCT to absorb Na+ and water.
Therefore, B.P. and blood volume is increased and it completes the feed back circle.
ANF opposes RAAS, Explain.
ANF is released by walls of atria or auricles. ANF (Atrial Natiuretic Factor) is secreted in response to increase of B.P. or blood volume.
ANF checks the secretion of renin-angitensin mechanism, and thus inhibits reabsorption of NaCl by collecting duct and also stops release of aldosterone. ANF is a vasodilator whereas the Angiotensin II is a vasocontrictor.
What is a kidney stone ?
A kidney stone is formed by the precipitation of uric acid or oxalate.
Symptoms :
1. It blocks the kidney tubule.
2. It may pass into the ureter or urinary bladder and may grow, and cause severe pain or blockage.
3. When, the stone is in bladder, the patient experiences frequent and painful urination and may pass blood in urine.
What is kidney/renal failure ?
Kidney failure is the partial or total inability of kidneys to carry on excretory functions.
Symptoms :
(a) Kidney failure leads to uremia i.e. an excess of urea and other nitrogenous wastes in the blood.
(b) Salt-water imbalance.
Causes : Many factors can cause kidney failure. Among these prominent are
1. tubular injury
2. infection
3. bacterial toxins
4. glomerulonephritis.
5. fluid and electrolyte depletion
6. internal precipitation of calcium and urates
7. haemorrhage.
Discuss how kidney transplantation occurs.
Kidney transplantation is the transfer of a healthy kidney from one person into the body of a person who has little or no kidney function. A functioning kidney is used in transplantation from a donor, preferably a close relative, to minimise its chances of rejection by the immune system of the host.
First kidney transplant was performed by a Washington Surgeon, Dr. Charles Hufnagel. In India, first transplant was performed on a 35 yrs old Shaninughan at CMC, Vellore on December 1, 1971.
Give comparitive account of water balance in humans and desert kangaroo rats.
Human beings use less metabolic water. The human beings compensate water by drinking.
What is immunosuppression ?
Immunosuppression : It means to suppress the immune response of recipient to prevent transplant rejection.
This is done before or at time of kidney transplantation. The therapy is done with the help of drugs which destroy ‘T’ cells (which are responsible for providing immunity to the body. These T-cells produce antibodies against the foreign graft or transplant and result in the rejection of the transplant. Hence, the immune system of the patient is suprresed so that the transplant is not rejected.
Differentiate between the following :
(a) Ureters and urethra
|
Ureters |
Urethra |
|
These are 25-30 cm long.
These extend from the kidneys to bladder. These conduct only urine. These collect urine from kidneys and pass into urinary bladder. |
It is 4 cm long in female and 20 cm long in male. It is one. It extends from bladder to outside. It contains urine and seminal fluid in male. It collects urine from urinary bladder and pass it outside. |
Differentiate between the following :
(b) Proximal and Distal convoluted tubules
|
Proximal |
Distal convoluted tubule |
|
It has brush border epithlium. |
It has few short microvilli. |
| It connects the Bowman's capsule and Loop of henle | It connects loop of Hnle and collecting duct. |
| Diameter is larger | Diameter is smaller. |
|
Active absorption of whole of glucose, most of amino acids and vitamin C. It also reabsorbs 70% of Na, 75% K and large amount of Ca+2. Urea is also reabsorbed. |
Active absorption of some Na+, C1–ions and water. |
Differentiate between the following :
(c) Ascending limb and descending limb
|
Ascending limb |
Descending limb |
|
Thick Nephric filtrate becomes hypotonic. |
Thin Nephric fitrate becomes hypertonic. |
Distinguish between
(a) Ammonotelism, ureotelism and uricotelism
|
Ammonotelism |
Ureotelism |
Uricotelism |
|
Ammonotelism occurs in aquatic animals. |
Ureotelism occurs in terrestrial amphibians and some aquatic animals. |
Uricotelism occurs only in terrestrial animals. |
|
Ammonia is excreted |
Urea is the major excretory product |
Uric acid is the excretory product. |
|
Ammonia is very toxic |
Less toxic |
Least toxic. |
|
A lot of water is required for elimination of Ammonia. |
Comparatively less water is required for elimination of urea. |
Little water is required for elimination of uric acid. |
Sponsor Area
Distinguish between
Juxta medullary nephrons and cortical nephrons
|
Juxta Medullary Nephron |
Cortical Nephrons. |
|
Their glomeruli are present close to the inner margin of the cortex. |
Their glomeruli are located in the outer cortex. |
|
They have long loops of Henle. |
Their loops of Henle are relatively short. |
|
They are present deep in the medulla. |
They extend to a short distance into the medulla. |
|
They are associated with vasa rectae. |
Vasa rectae are absent. |
|
The juxta glomerular cells secrete renin. |
Cortical glomerular cells do not secrete renin. |
Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) is the amount of the filtrate formed by the kidneys per minute. GFR for a healthy individual is approximately 125 ml/minute. i.e. 180 litres per day.
Explain the autoregulatory mechanism of GFR.
The kidney regulates the glomerular filtration rate by an autoregulative mechanism carried out by the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
The Juxtaglomerular apparatus is a special sensitive microscopic structure formed by cellular modifications in the distal convoluted tubule and the afferent arteriole at the location of their contact.
When there is a fall in the glomerular filtration rate, it activates the juxtaglomerular cells to release renin. This stimulates the glomerular blood flow, thereby bringing the GFR back to normal. Renin brings the GFR back to normal by the activation of the renin-angiotensin mechanism
Give a brief account of the counter current mechanism.
The counter current mechanism operating inside the kidney is the main adaptation for the conservation of water. There are two counter current mechanisms inside the kidneys. They are Henle's loop and vasa rectae.
Henle's loop is a U-shaped part of the nephron. Blood flows in the two limbs of the tube in opposite directions and this gives rise to counter currents. The Vasa recta is an efferent arteriole, which forms a capillary network around the tubules inside the renal medulla. It runs parallel to Henley's loop and is U-shaped. Blood flows in opposite directions in the two limbs of vasa recta. As a result, blood entering the renal medulla in the descending limb comes in close contact with the outgoing blood in the ascending limb.
The osmolarity increases from 300 mOsmolL -1 in the cortex to 1200 mOsmolL -1 in the inner medulla by counter current mechanism. It helps in maintaining the concentration gradient, which in turn helps in easy movement of water from collecting tubules. The gradient is a result of the movement of NaCl and urea.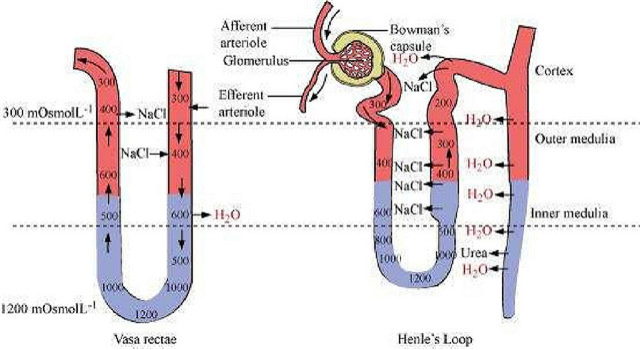
Describe the role of liver, lungs and skin in excretion.
Organs like lungs , liver and skin also play a role in excretion.
Lungs - Lungs remove large amounts of carbon dioxide and significant amount of water everyday.
Liver - The liver helps in the excretion of cholesterol, steroid hormones, vitamins, drugs, and other waste materials through bile. Urea is formed in the liver by the ornithine cycle. Ammonia - a toxic substance - is quickly changed into urea in the liver and thence eliminated from the body. Liver also changes the decomposed haemoglobin pigment into bile pigments called bilirubin and biliverdin.
Skin - Skin plays a major role in excretion of water, NaCl and small amounts of urea, lactic acid, etc. The sebaceous glands in the skin help eliminating substances like sterol, hydrocarbons, and waxes through sebum.
Explain micturition.
Micturition is the process of the discharge of urine from the urinary bladder.
The urinary bladder stores urine temporarily. the streching of the urinary bladder initiates a signal from the stretch receptore to the Central nervous system. The CNS then passes on the signal to initiate the contraction of smooth muscles of the bladder and simultaneous relaxation of the urethral spincter resulting in the release of the urine.
Usually an adult human excretes on an average 1 to 1.5 litres of the urine per day.
What is meant by the term osmoregulation?
Osmoregulation is the maintenance of the ionic and tconcentration and amount of water and salts in the body of the organism. It is the regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content and the concentration of salts and ions.
Terrestrial animals are generally either ureotelic or uricotelic, not ammonotelic, why?
Teresstrial animals live in drier conditions as compared to others. They always are in the grave dangers of excessive loss of water.
Excretion of urea and uric acid requires less amount of water as compared to the excretion of ammonia which requires a large amount of water. In order to avoid water loss they are ureotelic or uricotelic and not ammonotelic.
What is the significance of juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in kidney function?
The juxta glomerulus apparatus is plays a major role in the regulation of the rate of the glomerular filtrate. It is a special sensitive region formed by the cellular modifications in the distal covuluted tubule and afferent arteriole at the location of their contact.
The JGA plays a complex reulatory role. It regulates the complex mechanism called the renin-angiostensin mechanism. The JG cells are activated when there is a fall in the glomerular blood flow or GFR. On actibations these cells release renin which converts the inactive angiotensin to angiotensin- I and further to angiotensin-II.
Angiotensin-II is a powerful vasocontrictor and thus increase the glomerular blood pressure thereby the GFR. It also activates the adrenal cortex to release the hormone aldosterone.
Aldosterone directs the reabsorption the Na+ and water from the distal parts of the tubule. The reabsorption leads to increase in the blood pressure anf the GFR.
Name the following:
(b) Cortical portions projecting between the medullary pyramids in the human kidney
Fill in the gaps:
(a) Ascending limb of Henle's loop is ____________to water whereas the descending limb is___________to it.
impermeable
,permeable
In mammals, which blood vessel would normally carry largest amount of urea?
-
Dorsal aorta
-
Hepatic vein
-
Hepatic portal vein
-
Renal vein
B.
Hepatic vein
Urea is synthesised in the liver. So, maximum amount of urea of urea is present in hepatic vein and minimum in Renal vein.
The figure shows a human urinary system with structure labelled A to D. Select option, which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and of function.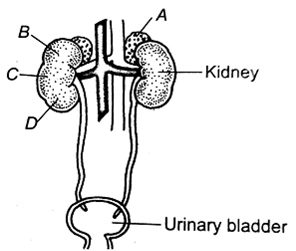
-
A - adrenal gland - located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete catecholamines, which stimulate glycogen breakdown
-
B- pelvis -board funnel-shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle
-
C - mediulla-inner zone of kidney and contains complete nephrons.
-
D - cortex -outer part of kidney and do not contain any part of nephrons
A.
A - adrenal gland - located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete catecholamines, which stimulate glycogen breakdown
A - adrenal gland, B - Renal pelvis, C - Medulla, D - cortex.
The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70-80 percent from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron?
-
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
-
Distal convoluted tubule
-
Proximal convoluted tubule
-
Descending limb of loop of Henle
C.
Proximal convoluted tubule
From the Bowman's capsule, the glomerular filtrate enters the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). PCT is surrounded by a network of peritubular capillaries and is the seat of reabsorption. About 75% of glomerular filtrate is normally reabsorbed in PCT before reaching the loop of Henle. The reabsorbed materials include glucose, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, sodium, potassium, chlorides, phosphates, bicarbonates, most of water and some urea etc.
Which of the following causes an increase in sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule?
-
Increase in aldosterone levels
-
Increase in antidiuretic hormone levels
-
Decrease in aldosterone levels
-
Decrease in antidiuretic hormone levels
A.
Increase in aldosterone levels
The increase in aldosterone levels cause and increase in sodium reabsorption is DCT. It is secreted by outer, layer of adrenal gland when aldosterone is present in the blood, all the Na+ in the filtrate is reabsorbed. Retaining Na+ raises the osmotic pressure of the blood and reduces the water loss from the body.
Which one of the following options gives the correct categorisation of six animals according to the type of nitrogenous wastes (A, B, C), they give out?
-
A
AmmonotelicB
UreotelicC
UricotelicPigeon, Humans Aquatic Amphibia, Lizards Cockroach, Frog -
A
AmmonotelicB
UreotelicC
UricotelicFrog, Lizards Aquatic Amphibia, Humans Cockroach, Pigeon -
A
AmmonotelicB
UreotelicC
UricotelicAquatic Amphibia Frog, Humans Pigeon, Lizards, Cockroach -
A
AmmonotelicB
UreotelicC
UricotelicAquatic Amphibia Cockroach, Humans Frog, Pigeon, Lizards
C.
| A Ammonotelic |
B Ureotelic |
C Uricotelic |
| Aquatic Amphibia | Frog, Humans | Pigeon, Lizards, Cockroach |
On the basis of nitrogenous metabolic waste the animal are of four types:
(i) Ammonotelic: Excreted ammonia, e.g., aquatic animals, bony fishes, frog, toad and crocodile, etc.
(ii) Aminotelic Excreted amino acid, e.g., Mollusca and echinoderms.
(iii) Ureotelic Excreted urea, e.g., frog, toad and mammals.
(iv) Uricotelic Excreted uric acid, e.g., insects, land reptiles and birds.
A fall in glomeruclar filtration rat (GFR) activates
-
Juxtra glomerular cells to release renin
-
Adrenal cortex to release aldosterone
-
Adrenal medulla to release adrenaline
-
Posterior pituitary ot release vasopressin
A.
Juxtra glomerular cells to release renin
Juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of macula densa and juxtaglomerular cells. The apparatus becomes active when there is decrease in renal blood pressure or decrease in glomerular filtration rate. There is increased absorption of NaCl in ascending limb or loop of Henle. The decreased NaCl content of filtrate activates cells of macula densa to increase secretion of renin from juxta glomerular cells. Renin convert angiotensinogen to angiotensin peptides.
Which one of the following characteristics is common both in humans and adult frogs?
-
Four chambered heart
-
Internal fertilisation
-
Nucleated RBCs
-
Ureotelic mode of excretion
D.
Ureotelic mode of excretion
Most animals convert toxic ammonia into less toxic urea and excreted it, e.g., adult frog and man.
Four-chambered heart is present in human but two-chambered in frog.
Nucleated RBCs are found in frog but not in human.
Fertilization is internal in human but external in frog.
Removal of proximal convoluted tubule from the nephron will result in
-
more diluted urine
-
more concentrated urine
-
no change in quality and quantity of urine
-
no urine formation
A.
more diluted urine
The removal of proximal convoluted tubule from the nephron results in lack of reabsorption of high threshold substance from renal tubules and obligatory reabsorption of water is also affected leading to more diluted urine. Since, proximal convoluted tubule is mainly associated with reabsorption of much water by osmosis, reabsorption of glucose and amino acids by secondary active transport and other salts and ions as Na+, K+, vitamins act by primary active transport.
Sliding filament theory can be best explained as
-
When myofilaments slide pass each other actin filaments shorten while mysoin filament do not shorten
-
Actin and Myosin filaments shorten and slide pass each other
-
Actin and Myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide pass each other
-
When myofilaments slide pass each other, Myosin filaments shorten while Actin filaments do not shorten
C.
Actin and Myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide pass each other
Sliding filament theory is explained as actin and myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide pass each other.
Two groups of workers, i.e. Andrew Huxley and Ralph Niedegerke (1954) and Hugh Huxley and Iean Hanson (1954) proposed the sliding filament theory. It has essential feature as follows:
(i) During musocle contraction the thin myofilaments show sliding inward towards H-zone.
(ii) The sarcomere shortens, without changing the length of thin and thick myofilaments.
(iii) The cross bridge of thick myofilaments connect with portions of thin myofilaments. These cross bridges move on the surface of the thin and thick myofilaments over each other.
(iv) The lengths of thick and thin myofilaments don't change thin filament (actin) during muscle contraction. 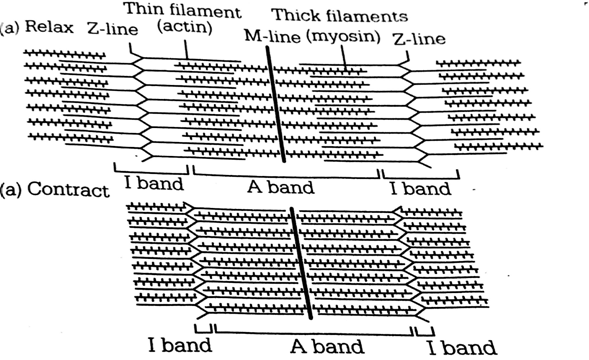
Which of the following does not favour the formation of large quantities of dilute urine?
-
Alcohol
-
Caffeine
-
Renin
-
Atrial-natriuretic factor
C.
Renin
Renin secreted by JGA regulates the glomerular filtration rate by inducing multihormonal system i.e. RAAS (Renin Angiotensin - Aldosterone System). Activation of this system increase the reabsorption rate of sodium (Na+) and water, making the urine more concentrated.
Alcohol decreases vasopressin level which lowers reabsorption of water thus making urine more dilute. ANF causes vasodilation and acts as check on RAAS
Which one of the following correctly explains the function of a specific part of a human nephron?
-
Henle's loop - most reabsorption of the major substances from the glomerular filtrate
-
Distal convoluted - reabsorption of ion into the surrounding blood capillaries
-
Afferent arteriole - carries the blood away from the glomerulus towards renal vein
-
Podocvytes - create minute spaces (slit pores) for the filtration of blood into the Bowman's capsule
D.
Podocvytes - create minute spaces (slit pores) for the filtration of blood into the Bowman's capsule
Podocytes or cvisceral epithelial cells are the cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around the capillaries of glomerules. They create minute pores (slit pores) for the filtration of blood into the Bowman's capsule.
Which one of the following is not a part of a renal pyramid?
-
Convoluted tubules
-
Collecting ducts
-
Loops Henle
-
Peritubular capillaries
A.
Convoluted tubules
The convoluted tubule is the highly convoluted segments of the nephron in the renal labyrinth of the kidney. It is made up of the proximal tubule leading from the Bowmans capsule to the descending limb of Henle's loop and the distal tubule leading from the ascending limb of Henle's loop to a collecting tubule.
When a neurone is a resting state, ie, not conducting any impulse, the axonal membrane is
-
equally permeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
-
impermeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
-
comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions
-
comparatively more permeable to Na+ ions and nearly impermeable to K+ ions
C.
comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions
Neurones are excitable cells because their membrane is in a polarised state. Different types of selectively permeable channels are present on the neural membrane. When a neurone is not conduction any impulse, i.e. resting, the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to potassium ion (K+) and nearly impermeable to sodium ion (Na+)
Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to kidney function regulation?
-
Exposure to cold temperature stimulates ADH release
-
An increase in glomerular blood flow stimulates formation of angiotensin II
-
During summer when body loses lot of water by evaporation, the release of ADH is suppressed
-
When someone drinks lot of water ADH release is supposed
D.
When someone drinks lot of water ADH release is supposed
When someone drinks a lot of water which is not required by the body, the osmolarity of the blood will decrease. The decrease in osmolarity will inhibit the release of ADH.
Which one of the following statements in regard to the excretion by the human kidneys is correct?
-
Descending limb of Loop of Henle is impermeable to water
-
Distal convoluted tubule is incapable of reabsorbing HCO3
-
Nearly 99 percent of the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed by the renal tubules
-
Ascending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to electrolytes
C.
Nearly 99 percent of the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed by the renal tubules
The plasma fluid that filters out from glomerular capillaries into Bowman's capsule of the nephron is called glomerular filtrate. A comparison of the volume of the filtrate formed per day (180 L /day) with that of the urine release (1.5 L), suggested that nearly 99 percent of the filtrate has to be reabsorbed by the renal tubules. This process is called reabsorption
The principal nitrogenous exceretory compound in humans is synthesised
-
in kidneys but eliminated mostly through the liver
-
in kidneys as well as eliminated by kidneys
-
In liver and also eliminated by the same through bile
-
in the liver, but eliminated mostly through the kidneys
D.
in the liver, but eliminated mostly through the kidneys
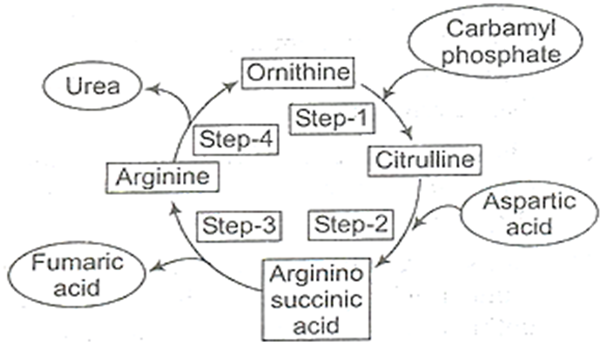
In humans, the principal nitrogenous excretory compound (i.e, urea) is synthesised in the liver by ornithine cycle. In liver, one molecule of CO2 is activated by biotin and combines with two molecules of NH3 in the presence of carbamyl phosphate synthetase enzyme and 2ATP to form carbonyl phosphate reacts with ornithine and forms citrulline. Citrulline combines with another molecule of ammonia and forms arginine that is broken into urea and ornithine in the presence of an enzyme arginase and water. 
Urea is eliminated mostly through kidney as a nitrogenous excretory product.
Consider the following four statement (1-4) regarding kidney transplant and select the two correct ones out of these
1) Even if a kidney transplant is proper the recipient may need to take immuno- suppressants for a long time
2)The cell-mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection
3) The B-lymphocytes are responsible for rejection of the graft
4) The acceptance of rejection of a kidney transplant depends on specific interferons
The two correct statements are
-
(2) and (3)
-
(3) and (4)
-
(1) and (3)
-
(1) and (2)
D.
(1) and (2)
To prevent graft (Kidney transplant) rejection, the principle is to use chemicals, which inhibit the enitre activity of the immune system. when this occurs graft rejection is delayed. It has been show that immunosuppression may make the patients more preeen to develop cancers.One way of overcoming the problems of radiatin and immunosuppression is to suppress only the cells responsible for rejection, normally the killer T- cells .In this way, the rest of the patients immune system would continue to function normally. The most promising approach is to treat the patient with monoclonal antibodies that recognize and destroy the killer T-cells. A monoclonal antibody has been developed, which is very effective at preventing rejection of transplanted kidneys.
Given below are four statements (A-D) regarding human blood circulatory system
-
Arteries are thick -walled and have narrow lumen as compared to veins
-
Angina is acute chest pain when the blood circulation to the brain reduced.
-
Persons with blood group-AB can donate blood to any person with any blood group under ABO system
-
Calcium ions play a very important role in blood clotting
A.
Arteries are thick -walled and have narrow lumen as compared to veins
Arteries are the blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart. In comparison to veins, arteries have a narrow lumen and more muscular thick walls to bear the pressure of pumping action of the heart.
Angina is constricting chest pain caused due to reduced blood supply to the heart wall.
Persons with blood group- AB are universal acceptor, while those with blood group -O are a universal donor.
What will happen if the stretch receptors of the urinary bladder wall are totally removed?
-
Urine will not collect in the bladder
-
Micturition will continue
-
Urine will continue to collect normally in the bladder
-
There will be no micturition
C.
Urine will continue to collect normally in the bladder
The urinary bladder is a pear-shaped, hollow muscular organ situated in the pelvic cavity, which is made up of smooth and involuntary muscles. The lumen of the urinary bladder is line by transition epithelium, which has great power of stretching. If stretch receptors of urinary bladder wall are totally removed, the urine will continue to collect normally in the bladder.
Which type of white blood cells are concerned with the release of histamine and the natural anticoagulant heparin?
-
Neutrophils
-
Basophils
-
Eosinophils
-
Monocytes
B.
Basophils
The basophils are probably like mast cells connective tissue. They release heparin, histamine and serotonin. Their nucleus is usually three-lobed and their granules take basic stain strongly.
Monocytes are largest of all types of leucocytes.Their nucleus is bean-shaped.They are motile and phagocytic in nature. They engulf bacteria and cellular debris.Generally, they will change into macrophages after entering tissue spaces.
A person who is on a longer hunger strike and is surviving only on water, will have
-
more sodium in his urine
-
less amino acids in his urine
-
more glucose in his blood
-
less urea in his urine
A.
more sodium in his urine
The normal concentration of sodium in the blood plasma is 150 mEq/L. If this level drops below 120 mEq/L, the result may be lethargy, coma or death. Unlike deficiencies of other important fluid constituents, the most common cause of this drop in sodium concentration is not a nutritional deficit of sodium, but rather an excess of water.
Angiotensinogen is a protein produced and secreted by
-
macula densa cells
-
endothelial cells (cells lining the blood vessels)
-
liver cells
-
juxtaglomerular (JG) cells
C.
liver cells
Angiotensinogen is a plasma protein produced and secreted by the liver cells. Renin secreted from juxtaglomerular cells and acts enzymaticaly on angiotensinogen to release 10 amino acid peptide angiotensin I.
Macula densa is actually a plaque in wall at the end of thick assending limb of nephrons.
Which of the following statements is correct?
-
The ascending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water
-
The descending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water
-
The ascending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water
A.
The ascending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water
Descending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water but impermeable to electrolytes while ascending limb is impermeable to water but permeable to electrolytes.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| Function | Part of the Excretory system | ||
| a | Ultrafiltration | i | Henle's loop |
| b | Concentration of urine | ii | Ureter |
| c | Transport of urine | iii | Urinary bladder |
| d | Storage of urine | iv | Malpighian corpuscle |
| v | Proximal convoluted tubule | ||
a b c d iv v ii iii a b c d iv i ii iii a b c d v iv i iii a b c d v iv i ii
B.
| a | b | c | d |
| iv | i | ii | iii |
- Ultrafiltration refers to filtration of very fine particles having molecular weight less than 68,000 daltons through malpighian corpuscle.
- Concentration of urine refers to water absorption from glomerular filtrate as a result of hyperosmolarity in the medulla created by counter-current mechanism in Henle's loop.
- Urine is carried from kidney to bladder through ureter.
- Urinary bladder is concerned with storage of urine.
A hormone, secreted by the endocrinal cells of duodenal mucosa which influences the releases of pancreatic juice is
relaxin
cholecystokinin
Secretin
Progesterone
B.
cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin Pancreozymin (CCK-PZ) is the hormone secreted from mucosa of the small intestine. It stimulates the pancreas to release enzymatic (Pancreatic) juice and gallbladder to eject bile.
The ornithine cycle removes two waste products from the blood in the liver. These products are
CO2 and urea
ammonia and urea
CO2 and ammonia
ammonia and uric acid
B.
ammonia and urea
Omithine cycles remove both ammonia and urea from the blood. It converts ammonia into urea (in the liver) and transports it to kidneys by the blood. Hence, it plays a key role in the detoxification of our blood. This cycle occurs in the liver.
Urea synthesis occurs in
kidney
Liver
Brain
Muscles
B.
Liver
The formation of urea from NH3, and CO2 Occurs in the liver. Through Ornithine cycle or Krebs Hansleit cycle. All the steps of this cycle are enzymatic and can be visualized as follows.
Sponsor Area
Which is common to kidney and skeleton in mammals?
Cortex
Medulla
Pelvis
Radius
C.
Pelvis
The term 'pelvis' is common to both kidney and skeleton in mammals. In relation to the kidney, it can be described as a chamber in the kidney into which the urine drains from renal tubules before passing to the ureter. For skeleton, it is related with a pelvic girdle or hip girdle.
Which is regarded as the urinary bladder of the embryo?
Amnion
Allantois
Chorion
Yolk sac
B.
Allantois
Allantois is an extraembryonic membrane developed as an outgrowth from hindgut. In the eggs of reptiles and birds, it functions as a urinary bladder and stores the waste excretory products. It also provides oxygen (in reptiles, birds and mammals) and food (in mammals) to the embryo.
Pyloric sphincter guards the opening between
Stomach and Duodenum
Cardia and Fundus
Oesophagus and Stomach
Fundus and Pylorus
A.
Stomach and Duodenum
Pyloric sphincter guards are the opening between the pylorus of a stomach and the duodenum of the small intestine. It periodically permits partially digested food to leave the stomach and enter the duodenum.
Uric acid is the excretory waste of
Adult amphibians
Birds
Amphibians Larvae
Mammals
B.
Birds
Birds are uricotelic organisms which excrete uric acid to reduce their weight.
A condition of failure of kidney to form urine is called
Deamination
Entropy
Anuria
None of these
C.
Anuria
The terms anuria, oligonuria, polynuria and dysuria are used for the absence of urine, scanty urine, large amounts of urine, and painful urination respectively. Deamination is the removal of amino (NH) group frequently from an amino acid by transaminase enzymes.
Solenocytes are the main excretory structures in
Annelids
Molluscs
Echinodermates
Platyhelminthes
D.
Platyhelminthes
Solenocytes (also called flame cells) are meant for excretion and osmoregulation in Platyhelminthes. Annelids have metanephridia for excretion, Molluscs have kidneys (although different from vertebrate kidneys) for excretion. In echinodermates, no special excretory organs are found for excretion. In them, excretion takes place through diffusion or osmosis or through active transport.
The canal system is a characteristic feature of
Echinoderms
Helminths
Coelenterates
Sponges
B.
Helminths
Sponges possess an extensive system of interconnected cavities called canal system, which typically consists of in current canals, radial canals, excurrent canals and spongocoel. The system is useful for nutrition, respiration and excretion.
The net pressure gradient that causes the fluid to filter out of the glomeruli into the capsule is
20 mm Hg
75 mm Hg
30 mm Hg
50 mm Hg
A.
20 mm Hg
Kidneys help in the formation of urine, from the blood flowing through glomerular capillaries. About 20% of plasma fluid filters out into the Bowman's capsule through a thin glomeular- capsular membrane due to a net or effective filtration of about 10 to 15 mm Hg.
Which leaves the liver and moves towards kidney
Ammonia
Urea
Glycogen
Bile
B.
Urea
Urea is the main nitrogenous excretory product of ureotelic animals. It is produced by liver cells from deaminated excess amino acid via urea cycle or Omithine cycle. Urea is released outside the body in the form of urine through the kidneys.
Major nitrogenous waste product in ureotelic animals like rabbit and other mammals is
uric acid
urea
ammonia
amino acids
A.
uric acid
Urea is the main nitrogenous excretory product of ureotelic animals. It is produced by liver cells from deaminated excess amino acid via urea cycle or Omithine cycle. Urea is released outside the body in the form of urine through the kidneys.
Urine is concentrated in
kidney
deamination
arginine
Omithine
A.
kidney
Urine formation takes place in kidney. It includes glomerular filtration (ultrafiltration), selective reabsorption and tubular secretion. Urine is stored temporarily in urinary bladder.
Blood leaving liver and going towards heart is rich in
bile
urea
ammonia
oxygen
B.
urea
As urea formation takes place in liver through Ornithine cycle, the blood leaving liver and going towards heart has high amount of urea.
Bowman's capsule is found in
glomerulus
uriniferous tubule
nephron
Malpighian capsule
D.
Malpighian capsule
Human kidney possesses about one million nephrons. Each nephron in made up of two main parts i.e., Malpighian body and renal tubule.
Malpighian body comprises a cup shaped Bowman's capsule and a meshwork of blood capillaries, the glomerulus.
A person is undergoing prolonged fasting. His urine will be found to contain abnormal quantities of
fats
ketones
amino acids
glucose
B.
ketones
If a person is undergoing prolonged fasting, his urine will be found to contain abnormal quantities of ketones. During fasting, energy is obtained by the oxidation of reserved fats. As a result of fatty acid oxidation large amount of ketone bodies are produced such as acetoacetate, -hydroxybutyrate and acetone.
ADH controls water permeability of
collecting tube
proximal convoluted tubules
distal convoluted tubules
all of the above
C.
distal convoluted tubules
The vasopressin hormone, secreted by neurohypophysis of pituitary gland promotes the reabsorption of water from the distal convoluted tubules of nephrons, reducing excretion of water in urine (diuresis). Hence, it is called Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH). Its release in blood is controlled by an 'osmoregulatory centre' located in hypothalamus. Hyposecretion of ADH causes diabetes incipidus.
Which of the following amino acids are present in ornithine cycle
Valine and cystine
Arginine and citrulline
Glycine and methionine
None of these
B.
Arginine and citrulline
Ornithine cycle takes place in liver. The amino acid arginine and citrulline are formed during this cycle. Therefore it is referred as ornithine, arginine cycle and also Kreb-Henseleit cycle. The products of this cycle are urea and ornithine. The substances excreted through this cycle are CO2 and NH2
Haemodialysis helps in patient having
uremia
anaemia
diabetes
goitre
A.
uremia
Haemodialysis helps the patient suffering from uremia. In this condition, the excretory products (i.e., urea) go on accumulating in blood. This happens due to kidney, failure. In haemodialysis, the patients blood is passed through disposable dialyser and is then returned to body by the intravenous route.
X- rays are used in
ECG
EEG
CT- scan
Endoscopy
C.
CT- scan
X-rays are used in CT-scan (computed tomographic scanning). It uses X-rays but employs a computer for reconstructing the image instead of directly recording it on a photographic film. This technique is used in the diagnosis of diseases of brain, spinal cord, chest, etc. It is also useful in detecting tumors.
ECG or Electrocardiogram is a medical test that detects cardiac (heart) abnormalities by measuring the electrical activity generated by the heart as it contracts.
EEg or Electroencephalogram is a non- invasive test that records electrical patterns in your brain. It is used to help diagnose conditions such as seizures, epilepsy, head injuries, dizziness etc.
Endoscopy helps in identifying inflammation, ulcers and tumors. It is more accurate than X- rays for detecting abnormal growths such as cancer and for examining the inside of the upper digestive system.
In living beings ammonia is converted into urea through
ornithine cycle
citrulline cycle
fumarine cycle
arginine cycle
A.
ornithine cycle
Ornithine combines with one molecule of NH3 and CO2 to produce citrulline. Citrulline combines with another molecule of NH3 to form arginine. Arginine is broken down into urea and ornithine which repeats the cycle.
Which part of the nephron is impermeable to water
Proximal convoluted tubule
Distal convoluted tubule
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
Descending limb of loop of Henle
C.
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
Ascending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water. Here water is not reabsorbed, rather sodium, potassium, magnesium and chloride are reabsorbed and therefore the filtrate becomes hypotonic to blood plasma.
The ornithine cycle removes two waste products from the blood in liver. These products are
CO2 and urea
ammonia and urea
CO2 and ammonia
ammonia and uric acid
C.
CO2 and ammonia
During ornithine cycle in liver cell, ammonia and CO2 are combined to form urea which is released into the blood.
Refer the given figure of nephron.
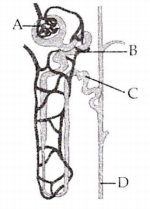
Identify A, B, C and D and select the correct option regarding them
A-Glomerulus -a tuft of capillaries formed by afferent arteriole.
B-PCT-reabsorption of HCO3 and selective secretion of H and K+ occurs here.
C-DCT-almost all glucose, amino acids, water, Na, K and uric acid are absorbed here.
D-collecting duct-extends from the cortex of the kidney to the inner parts of medulla. Large amount of water is secreted in this region.
A.
A-Glomerulus -a tuft of capillaries formed by afferent arteriole.
PCT-The PCT regulates pH of the filtrates by exchanging hydrogen ions in the interstitium for bicarbonate ions in the filtrate. It is also responsible for secreting organic acids such as creatinine and other bases into the filtrate
DCT-It is a duct of the renal tubule located in the kidney's cortex that reabsorbs calcium, sodium, and chloride and regulates the pH of urine by secreting protons and absorbing bicarbonate.
Collecting duct-The collecting duct system is the final component of the kidney to influence the body's electrolyte and fluid balance.
Assertion : Secreting hypotonic urine is effective in reducing urinary loss of water.
Reason : Hypotonic urine is more concentrated and higher in osmotic pressure than the blood.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
D.
If both assertion and reason are false
When there is a threat of excessive water loss from the body of the animal, then the urine excreted needs to be hypertonic and not hypotonic. This is due to the reason as excessive water loss from the body possess the threat of a rise in osmoconcentration of the blood. Since hypertonic urine is more concentrated and higher in osmotic pressure than the blood, therefore it helps in reducing the loss of water with urine.
Mammals and birds can excrete hypertonic urine which is more concentrated than their blood. For this, an isotonic glomerular filtrate is first filtered into the Bowman's capsules of nephrons in kidneys. The tubules then reabsorb a large volume of water from the glomerular filtrate not accompanied by the reabsorption of proportionate amounts of solutes. This leaves the urine more concentrated than the blood which is very effective in reducing the urinary loss of water.
Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to salt water balance inside the body of living organisms?
when water is not available camels do not produce urine but store urea in tissues.
Salmon fish excretes lot of stored salt through gill membrane when in fresh water
Paramecium discharges concentrated salt solution by contractile vacuoles
The body fluids of fresh water animals are generally hypotonic to surrounding water
A.
when water is not available camels do not produce urine but store urea in tissues.
The balance of water and salt is essential in order to maintain the health of an animal or humans.
Camels, excrete highly concentrated urine to conserve water. They do not sweat till body temperature rises about 55€-60C. Camel can also tolerate desiccation upto 40% cellular content.
A person passes much urine and drinks much water but his blood glucose level is normal. This condition may be the result of:
a reduction in insulin secretion from pancreas
a reduction in vasopressin secretion from posterior pituitary
a fall in the glucose concentration in urine
an increase in secretion of glucagon
B.
a reduction in vasopressin secretion from posterior pituitary
Vasopressin or ADH secreted from posterior pituitary stimulates reabsorption of water by the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting renal tubules and thus regulates urine volume. It has no such important effect on glucose metabolism. Therefore, a person whose blood glucose level is normal, but passes much urine and drinks much water has a reduction in vasopressin secretion which ultimately leads to diabetes insipidus.
The amount of liquid filtered by glomeruli of kidney in 24 hours period is
170 L
100 L
200-250 cc
500-1000 cc
A.
170 L
The volume of filtrate formed by both kidneys per minute is termed glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Approximately 20% of your cardiac output is filtered by your kidneys per minute under resting conditions. The work of the kidneys produces about 125 mL/min filtrate in men (range of 90 to 140 mL/min) and 105 mL/min filtrate in women (range of 80 to 125 mL/min). This amount equates to a volume of about 180 L/day in men and 150 L/day in women. However, 99% of this filtrate is returned to the circulation through reabsorption resulting in only about 1–2 liters of urine per day.
Average pH of human urine is :
6.0
9.0
3.0
7.0
A.
6.0
Average pH of human urine is 6.0. Normal urine is slightly acidic. The variations in urine pH are closely related to the diet. A high protein diet increases acidity, while a diet composed largely of vegetables increases aikalinity. The colour of the urine is due to pigment urochrome.
Cells present in the inner lining of kidneys are :
podocytes
choanocytes
pinocytes
nephrocyte
A.
podocytes
Podocytes are the cells of Bowman's capsule in kidney. They are less flattened cells, which line the concavity of the Bowman's capsule. They possesses foot-like projections the pedicels.
Choanocytes or collar cells are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body type sponges that contain a central flagellum, or undulipodia, surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a thin membrane.
Nephrocytes are the specialized cells, present in arthropods. Their main function is the accumulation or formation of waste or excretory products.
Pinocytes are the flat cells found on the outermost layer of a sponge.
Which of the following is impermeable to water?
Vertical limb of loop of Henle
Descending limb of loop of Henle
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
Both 'a' and 'b'
C.
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
Ascending limb of loop of Henle has two, characteristics.
(i) It actively pumps Na+ and Cl- into the surrounding tissue fluid in the medulla.
(ii) It is impermeable to water, and partialy permeable to urea. This is because in the thick ascending limb, there is active reabsorption of ions. As a result, these cells can make the interstitial fluid hyperosmotic relative to the fluid inside the tubule (the filtrate).
Ducts of Bellini are present in :
liver
kidney
intestine
medulla oblongata
B.
kidney
In the kidney, the collecting tubule which is a straight part of the distal convoluted tubule, opens into a wider collecting duct. The collecting ducts forms larger duct of Bellini. These open into the papillae which then pass into calyces and finally into renal pelvis.
Liquid, which collects in Bowman's capsule is
water and sulphates
water and glycogen
plasma minus blood protein
concentrated urine
C.
plasma minus blood protein
Bowman's capsule is a double layered cup-shaped structure. Its visceral layer surrounds the glomerulus. During urine formation, water and many dissolved substances from the blood are filtered into the lumen of Bowman's capsule. The glomerular filtrate contains a large amount of water and other dissolved substances such as urea, uric acid, amino acids, glucose, sodium, potassium etc. The glomerular filtrate and blood plasma are similar except that glomerular filtrate does not have proteins and fats.
Diabetes insipidus is caused due to the lack of
ADH
ACTH
insulin
glucagon
A.
ADH
Diabetes insipidus is caused by deficiency of ADH or vasopressin. It is characterized by excessive excretion of dilute urine.
Mention the location and function of juxtaglomerular apparatus.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is a microscopic structure in the kidney, which regulates the function of each nephron. It is named for its proximity to the glomerulus, it is found between the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle and the returning distal convoluted tubule of the same nephron.
It is important in regulating blood pressure, body fluid and electrolytes.
What is glycosuria?
Low amount of sugar in urine
Low amount of fat in urine
Average amount of carbohydrate in urine
High amount of sugar in urine
D.
High amount of sugar in urine
Glycosuria is the excretion of glucose into the urine. This is a rare condition in which the kidneys release glucose into the urine. Renal glycosuria can cause urine glucose levels to be high even if blood glucose levels are normal.
Volume of urine is regulated by
aldosterone
aldosterone and testosterone
ADH
aldosterone and ADH
D.
aldosterone and ADH
Urine volume and concentration is regulated through the same processes that regulate blood volume. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) produced by the posterior pituitary gland that increases the amount of water reabsorbed in the distal convulated tubule and collecting duct.
Name the condition when the concentration of ketone body increases in urine.
Acromegaly
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes insipidus
Cushing's disease
B.
Diabetes mellitus
Ketonuria is a medical condition in which ketone bodies are present in the urine. It is seen in conditions in which the body produces excess ketones as an alternative source of energy. It is seen during starvation or more commonly in type I Diabetes mellitus.
Write two functions of juxtaglomerular apparatus.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is a specialized structure formed by the distal convoluted tubule and the glomerular afferent arteriole. Functions:-
- These cells secrete the enzyme renin that modulates the blood pressure.
- Renin also helps stimulation of the beta- 1 adrenergic receptor.
In 24 hours, total glomerular filtrate formed in human kidney is
1.7 litres
7 litres
17 litres
170 litres
D.
170 litres
The blood pressure in glomerular capillaries become very high, so that there is continuous process of ultra-filtration. Glomerular filtrate contains a large amount of water and other dissolved substances such as urea, uric acid, creatinine, amino acids, glucose, sodium, potassium, vitamins etc. About 120 mL GP is produced per minute, ie, approx 170 L filtrate is produced in 24 hour.
The size of filtration slits of glomerulus
10 nm
15 nm
20 nm
25 nm
D.
25 nm
The average size of filtration slit or slit pore of glomerulus is 25 nm.
Figure shows human urinary systemwith structures labelled A to D. Select option, which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and/of functions

A - adrenal gland - located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete catecholamines, which stimulate glycogen breakdown
B - pelvis - broad funnel shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle
C - mediulla - inner zone of kidney and contains complete nephrons
D - cortex - outer part of kidney and do not contain any part of nephrons
A.
A - adrenal gland - located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete catecholamines, which stimulate glycogen breakdown
A - adrenal gland-
B - Renal pelvis - The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. In humans, the renal pelvis is the point where the two or three major calyces join together.
C - Medulla - The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the interlobar arteries.
D - Cortex - It contains the renal corpuscles and the renal tubules except for parts of the loop of Henle which descend into the renal medulla. It also contains blood vessels and cortical collecting ducts. The renal cortex is the part of the kidney where ultrafiltration occurs. Erythropoietin is produced in the renal cortex.
Which hormone is responsible for reabsorption of water in kidney?
ADH
STH
ACTH
GTH
A.
ADH
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) or vasopressin is the hormone responsible for reabsorption of water from kidney tubules resulting in concentrated urine. It helps in regulating the body's retention of water.
STH or somatotropin or somatotrophic hormone refers to the growth hormone produved naturally in animals.
ACTH or adrenocorticotropic hormone is a hormone produced in the anterior part of brain. It regulates the levels of the steroid hormone cortisol.
GTH or gonadotropic hormone are glycoprotein polypeptide hormones secreted by gonadotrope cells of the anterior pituitary of vertebrates. It regulates normal growth, sexual development and reproductive function.
Which one of the following animals is uricotelic?
Lizard
Camel
Toad
Rohu fish
A.
Lizard
Birds, lizards, snakes, terrestrial insects, snails excrete nitrogenous wastes as uric acid in the form of pellet or paste with a minimum loss of water and are called uricotelic animals.
Camels, toads, cartilaginous fish (rohu fish), some bony fish, adult amphibians and mammals excrete urea and are called ureotelic animals.
Which one of the following components of urine in a healthy human does not differ much in concentration from that of blood plasma?
NH4 +
K+
Na+
SO4 2-
D.
SO4 2-
SO4 2-, creatinine and other metabolic end products are the non-threshold substances which are not at all reabsorbed and are excreted in urine even under normal conditions. This is the reason these substances do not differ much in concentration from that of blood plasma.
Na+, K+, glucose and Ca2+ are the high-threshold substances, which are reabsorbed very extensively and do not appear in urine under normal conditions. These appear in urine only if their concentration in plasma is abnormally high or in renal diseases when reabsorption is affected. NH4 + is excreted in the form of urea.
Statement I. The renal fluid becomes increasingly concentrated, when it flows down in the descending limb of loop of Henle towards inner medulla, but its concentration decreases in the ascending limb, when it flows towards the cortex.
Statement II. The descending limb of the loop of Henle water is reabsorbed; the ascending limb is impermeable to water, but salts are absorbed.
Statement I is correct, but Statement II is incorrect
Statement II is correct, but Statement I is incorrect
Both statements are correct
Both statements are incorrect
A.
Statement I is correct, but Statement II is incorrect
The cellophane tube is surrounded by a fluid having same composition as plasma except nitrogenous wastes. The porous cellophane membrane of the tube allows the passage of molecule based on concentration gradient. It is impermeable to large molecules but permeable to micromolecules.
Which among the following statements is correct with respect to functional structure of glomerular membrane?
I. The endothelium is perforated by small holes called fenestral.
II. The basement membrane is present inside the endothelium and is composed of meshwork of collagen.
III. The epithelium of visceral layer has cells, which are of peculiar shape and are called podocytes.
IV. The shapes between pedicels are called slit pores through which glomerular filterate filters.
Choose the correct option
I, II and III
I, III and IV
I, II and IV
II, III and IV
B.
I, III and IV
Statement II is incorrect and can be corrected as the basement membrane is present outside the endothelium and is composed of meshwork of collagen. This Glomerular Basement Membrane (GBM) of the kidney is the basal lamina layer of the glomerulus.
The glomerulus capillary endothelial cells, the GBM and the filtration slits between the podocytes perform the filtration function of the glomerulus, separating the blood in the capillaries from the filtrate that forms in Bowman's capsule.
Final excretion in urine of which substance is
amino acid
urea
glucose and glycogen
uric acid
D.
uric acid
In the process of excretion, DCT or Distal Convoluted Tubule extracts the wastes like uric acid during the formation of urine. It takes place during tubular secretion or augmentation.
Kidney stones are crystals of
sodium chloride
silica
calcium oxalate
potassium chloride
C.
calcium oxalate
Kidney stones are commonly crystals of calcium oxalate and the patients are therefore, advised to avoid spinach, rhubarb and asparagus in their diet.
If Henle's loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which of the following is to be expected?
The urine will be more concentrated
The urine will be more dilute
There will be no urine formation
There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed
C.
There will be no urine formation
The main function of the Henle's loop is to absorb water from the tubular lumen, thus making the urine concentrated. If loop of Henle becomes absent then the urine becomes more dilute.
The reabsorption of water in the kidney is under the control of
LH
ADH
STH
ACTH
B.
ADH
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) controls the tubular permeability and concentration of sodium in the extracellular fluid. It associates with the renal pressure system and then regulates the fluid volume of body through the agency of hypothalamic osmoreceptors.
The lining of intestine and kidneys in humans is :
keratinized
brush border
ciliated
none of these
B.
brush border
Microvilli are finger like extensions of the cell surface membrane of animal cells such as epithelial tells in intestine and kidney's nephron. They can just be seen with a light microscope as the fringe across the top of cell is called as brush border.
The yellow colour of urine is due to the presence of
urea
uric acid
urochrome
bilirubin
C.
urochrome
Urochrome is a yellow coloured pigment in urine responsible for its yellow colour. It is derived from destruction of haemoglobin by reticuloendothelial cells.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area






