Let C be the circle with centre at(1,1) and radius 1. If T is the circle centred at (0,y) passing through origin and touching the circle externally, then the radius of T is equal to
-

-

-
1/2
-
1/4
D.
1/4
Let the coordinate of the centre of T be (0, K)
Distance between their centre
So, the radius of circle T is k i.e, 1/4






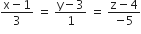 in the plane 2x-y+z+3 =0 is the line
in the plane 2x-y+z+3 =0 is the line







 get reflected upon reaching X -axis, the equation of the reflected ray is
get reflected upon reaching X -axis, the equation of the reflected ray is 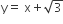
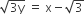


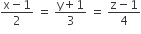 and
and 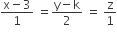 intersect, then k is equal to
intersect, then k is equal to