Science Chapter 8 Motion
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 9 About 2.html
Why is the atmosphere essential for life?
The atmosphere consists of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour. All these gases are very essential for the survival of organisms. The atmosphere keeps the average temperature of the earth fairly steady and thus makes conditions suitable for the survival of organisms. The atmosphere prevents the sudden increase in temperature during the daylight hours. It also slows down the escape of heat into outer space during the night, keeping the Conditions favourable. Because of all these reasons atmosphere is very important.
Why is water essential for life?
Water is essential for life because
(i) all life processes that take place in the cells require water medium.
(ii) water is needed for transportation of substances from one part of the body to the other in a dissolved form.
(iii) All the reactions in the body or within the cells occur between substances that are dissolved in water.
How are living organisms dependent on the soil? Are organisms that live in water totally independent of soil as a resource?
Living organisms directly or indirectly are dependent on soil. Because for substances and energy (food) all living things depend on green plants. Carnivores (which eat other animals) also depend on animals which eat plants. Plants need soil for their survival. Because soil provides the following things to the plants:
(i) nutrients (minerals) to prepare food through photosynthesis for self and other organisms.
(ii) support.
Thus, ultimately all living organisms are dependent on the soil.
It is not true to say that organisms that live in water are totally independent of soil as a resource. Organisms living in water depend on green plants for materials and energy. Aquatic green plants get dissolved mineral from water. Water bodies get supply of minerals from the soil through rivers, rain water, etc. The minerals locked in rocks cannot be available to organisms until rocks are converted to small particles of soil. If there is no continuous supply of mineral from the soil to water bodies, minerals present in the water will exhaust. The organisms living in water will not be able to survive for a long time. Thus, organisms that live in water are not totally independent of soil as a resource.
You have seen weather reports on television and in newspapers. How do you think we are able to predict the weather?
Prediction of the weather can be done by studying wind patterns which decide rainfall patterns. It also shows areas of low pressure and high pressure. these areas give an idea about the rainfall patteren of the area. For example in large part of India, rains are mostly brought by the South-West or North-East monsoons. This is how the weatherof the area is predicted taking into account the wind pattern.
We know that many human activities lead to increasing levels of pollution of the air, water-bodies and soil. Do you think that isolating these activities to specific and limited areas would help in reducing pollution?
Isolating the activities to specific and limited areas would not help in reducing pollution. Air, water and soil are natural resources and are inter-related. Pollution of one usually leads to the pollution of the other resource. Moreover the pollution cannot be limited to a specific region or area. For example, if air becomes polluted by excessive amount of carbon dioxide, it will cause warming of the air over that land. As a resust air at region will rise this will cause air from nearby areas to move in place of rising a hot air. So, carbon dioxide will spread in the atmosphere affecting other areas too. Similarly increased level of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur in air of an area will diffuse in the atmosphere affecting other places.
The pollution of water bodies of a specific area will cause depletion of oxygen and addition of poisonous substances. It will lead to death of aquatic animals and plants of the particular water-body and affect the related food chains or food webs will be disturbed not at particular area of the nearby areas too. Similarly, if the soil will loose fertility, there will be soil erosion. Thus isolating the activities to specific and limited areas wont help.
Write a note on how forests influence the quality of our air, soil and water resources.
Forests influence the quality of air, soil and water, natural resources in the following ways :
(i) Air - Forests have large number of trees, shrubs and herbs. They take in CO2 and give out oxygen during photosynthesis in daylight. Thus, they maintain the concentration of oxygen and carbon-dioxide in the atmosphere.
(ii) Soil - Forest tree and other plant roots bind the soil particles. They form a vegetation cover over the fertile top soil. Forest trees check the speed of running water and wind and thus protect the soil from erosion.
(iii) Water - Forest trees are large in number and give out enourmous amount of water during transpiration in the form of water vapour. The water vapour helps in the formation of clouds which on precipitation cause rain.
What are the two things which are essential for all forms of life on the earth?
The two things which are essential for all forms of life on the earth
(i) The three resources—the land, the water and the air available on the earth.
(ii) The energy which is provided by the sun.
What is biosphere?
The life-supporting zone of the earth where the atmosphere, the hydrosphere and the lithosphere interact and make life possible is known as the biosphere.
What are the physical components?
Physical components consists of geographical conditions such as the temperature, rainfall, soil, seasons and the climate.
What is biotic component?
The biotic component means the living organism which are present in the environment.
Does there exist any relationship between the climate and biotic components? If yes, explain with example.
The climate and the biotic components are related. The biotic components effect the climate conditions. For example, presence of more trees in a region results in cooling of the place and it also controls the rainfall of that area. Human beings also affect the climate. The humn activities like use of fuels and CFCs etc increases the teperature and thus affects the climate of the region.
What percentage of oxygen and nitrogen is present in the air?
About 20% oxygen and about 78% nitrogen is present in the air.
Name the pollutants by which industries pollute air.
Industrial air pollutants are S02, CO2, oxides of nitrogen, H2S, fumes of acids, dust, particles of unburnt carbon, lead, asbestos and even cement.
How is balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen maintained in the environment?
Oxygen is required by all living beings for respiration and also for burning materials. Thus, it is used up in the breathing and burning. Oxygen is given out by the plants during the process of photosynthesis.
The plants take up carbon-dioxide during photosynthesis. The carbon dioxide is released by the animals during the process of respiration. Thus the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide is maintained.
What are the two main ways in which oxygen is consumed and carbon dioxide is produced?
The two ways in which the oxygen is consumed and carbon is produced are :
(i) Respiration - in which oxygen is taken up and broken down into glucose molecules to produce energy for life activities. During this process carbon-dioxide is released.
(ii) Combustion - in which fuels are burnt in presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide. Forest fires also consume oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
What are the two ways in which carbon dioxide is fixed to keep its percentage almost constant?
Carbon dioxide percentage is kept almost costant by the following ways:
(i) By photosynthesis - green plants convert carbon dioxide into glucose in the presence of sunlight.
(ii) Many marine animals (like unio and pila) use carbonates dissolved in sea-water to make their shells.
Sponsor Area
What is the role of the atmosphere in climate control?
The atmosphere controls the climate in the following ways -:
i. It keeps the average temperature of the earth fairly steady.
ii. It prevents the sudden increase in temperature during the daylight hours.
ii. It slows down the escape of heat into outer space during the night and thus maintain a optimum temperature.
What are the two factors that cause changes in our atmosphere?
The factors that cause changes in the atmosphere are :
(i) Heating of air and
(ii) Formation of water vapour.
What causes the direction of the wind from the sea to the land during the day time?
During the day land gets heated faster than the water bodies that is the sea. The heated air above the aland rises creating a low pressure area. To fill in the low pressure area the cool air above the sea moves into the area of low pressure. The movement of awind from one area to the other creates wind. This movement of air from sea to land causes the wind to move in the direction from sea to land.
What can you say about:
(i) The appearance of areas of low and high pressure in coastal areas at night?
(ii) The direction in which air would flow at night in coastal areas?
(i) During night the land cools faster than the sea Since, sea water cools down slower than the land, the air remains warm and rises up, creating a region of low pressure above the sea. As the land cools faster the air above land also becomes coll and a region of high pressure is developed over land.
(ii) At night, the air flows from the land to the sea.
Which are the winds that brings about rain in the most part of India?
The south-west or north-east monsoons brings rain in most part of India.
What is air pollution?
Presence of undesired substances like oxides of nitrogen and sulphur, suspended particles like unburnt carbon particles and hydrocarbons in increased quantity which degrade the quality of the air is called air pollution
What causes acid rain?
When fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum products are burnt, they produce oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. When these gases are precipitated along with the rains , they make the rain acidic in nature. This causes acid rain.
How does smog form?
Presence of high levels of all suspended particles like unburnt carbon particles and hydrocarbons makes the visibility low, especially in cold weather when water also condenses out of air. This is known as smog.
How is our atmosphere different from the atmosphere on Venus and Mars?
Atmosphere of the our atmosphere consists of a mixture of many gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour that helps life to exist on the earth.
The major component of the atmosphere found on the Venus and Mars is carbon dioxide (95-97%), thus it does not support life.
How does the atmosphere act as a blanket?
Our atmosphere acts as a blanket because:
(i) It keeps the average temperature of the earth fairly constant during the day.
(ii) The atmosphere prevents the sudden increase in temperature during the daylight hours.
(iii) During the night, it slows down the escape of heat into outer space nad maintain ptimum temperature.
What causes winds?
The uneven cooling of land and sea and the building of the low and high pressure area causes the air to move from a high pressure are to a low pressure area. This movemnet of the air from one region to the other region caused winds.
How are clouds formed?
A large amount of water evaporates from the water bodies and goes into the air. Some amount of water vapour also gets into the air due to various biological activities. The hot air rises up carrying the water vapour with it. As the air rises up, it gets cooled. Cooling causes the water vapour in the air to condense in the form of tiny droplets around dust and other suspended particles in the air. This leads to the formation of clouds.
List any three human activities that you think would lead to air pollution.
Man made sources of air pollution:
(i) Use of diesel and petrol in vehicles.
(ii) Burning of coal in factories, engines and thermal power stations.
(iii) Deforestation.
Do all organisms require water? Give reasons.
Yes, all organisms require water. Water is very essential as :
(i) all cellular processes take place in a water medium in the body.
(ii) all the substances are transported from one part of the body to the other by water in dissolved or suspended form.
(iii) All the reactions that take place in the body occur in water as medium.
Why do terrestrial life-form require fresh water?
The bodies of terrestrial organisms cannot tolerate the high amounts of dissolved salts present in saline water. So, they need fresh water for life processes like cellular reactions, transportation and excretion processes etc.
What are the sources of water pollution?
The sources of water pollution are -:
(i) Fertilizers and pesticides used on farms.
(ii) Industries which use water for cooling and which dump the industrial wastes in the water bodies.
(iii) Sewage from the towns and cities.
(iv) Water released from dams.
When water is said to be polluted?
The addition of undesirable substances to the water bodies which cause any change in physical, chemical or biological quality of water making it unsuitable for living organisms or for use, is called water pollution.
List water pollutants.
Some water pollutaants are :
(i) Microorganisms e.g., protozoans, bacteria and viruses
(ii) Eggs or larvae of disease causing vectors like mosquitos.
(iii) Oil spills.
(iv) Fertilizers and pesticides.
(v) Radioactive wastes.
(vi) Industrial wastes.
(vii) Sewage disposals and domestic wastes.
When do we use the term water pollution. Give examples.
The term water pollution is used when there is :
(i) Addition of undesirable substances to water bodies. For example, addition of industrial wastes containing poisonous salts like mercury salts, pesticides, insecticides, etc. Addition of disease causing organisms, like cholera causing bacteria through sewage.
(ii) The removal of desirable substances from water bodies. For example, depletion of dissolved oxygen and nutrients which adversely affects aquatic animals and plants.
(iii) A change in temperature of water in water bodies which adversely affects the organisms living in the water bodies.
Pesticides and insecticides are sprayed in fields then how they reach water bodies to pollute?
The pesticides and insecticides sprayed in the fileds are carried away by rain water. These chemicals are washed away with the rain or irrigational water into the nearby water bodies like ponds, lakes or rivers.
Why do organisms need water?
Organisms need water for
(i) Cellular processes - as all the processes take place in a water medium.
(ii) Transportation of substances - water is used for the transportation of substances from one part of the body to the other.
(iii) Reactions - All the reactions that occur in the cell or body occur between substances dissolved in water.
Sponsor Area
What is the major source of fresh water in the city / town I village where you live?
River/well.
Do you know of any activity which may be polluting this water source?
The activity which pollutes the water resource are:
River. The sewage from the town and the cities are dumped into the water bodies and lead to its pollution.
Well. Washing and bathing near the well leads to the pollution of water.
What is soil?
Soil is a mixture. It contains small particles of rock of different sizes, humus and microscopic life.
What factors decide the type of soil?
Type of soil depends upon:
(i) the average size of soil particles,
(ii) the amount of humus and
(iii) the microscopic organisms found in it.
What factors decide which plants will thrive on that soil?
The factors which determine which plants will thrive on the soil are :
(i) the nutrient content of the soil,
(ii) the amount of humus present in the soil and
(iii) the depth of the soil.
What is humus? What is its function in the soil?
Humus is the bits of decayed organisms present in the soil. It usually gives the soil a blackish colour.
Function. Humus is the major factor in deciding the soil structure because:
(i) it causes the soil to become more porous.
(ii) allows water and air to penetrate deep into the soil making available for the roots of the plants.
What is top soil?
Top soil. The topmost layer of the soil which contains soil particles, humus and living organisms is called top soil.
What is soil pollution?
Soil Pollution is the removal of useful components from the soil and addition of substances that affect fertility of the soil adversely and kill the diversity of soil organisms is called soil pollution.
What are the causes of soil erosion?
The causes of soil erosion are :
(i) Deforestation - The roots of the plants hold the soil particles tightly and the plants slow down the speed of flowing water thus preventing the soil from erosion.
(ii) Leaving land uncultivated for long time will cause the soil to erode.
(iii) Excessive grazing will remove the vegetation cover of the land and cause soil erosion.
(iv) Flood or heavy rains can wash away the soil and cause soil erosion.
(v) High speed winds can also carry away the top layer of the soil and cause its erosion.
List three measures for prevention of soil erosion.
Measures that can be adopted for the prevention of soil erosion are:
(i) Intensive cropping, and use of proper drainage canals in the fields.
(ii) Terrace farming to retard the speed of flowing water in hilly or sloping areas.
(iii) Trees should be planted. Grasses should also on lands with no vegetation cover.
(iv) Indiscriminate cutting down of forest should be avoided.
What measures one should take to maintain the fertility of the soil?
Following are the measures that one should take for maintaining the fertility of the soil :
(i) Crop rotation - which ensures efficient use of nutrients by all the plants.
(ii) Growing of leguminous plants as one of the crop which increases the nutrient content of the soil by fixing nitrogen.
(iii) Leaving the soil uncultivated for one or two seasons.- This helps the soil to regain its richness.
(iv) Using manure - Being organic in nature it impreoves the fertility and quality of the soil.
Why is replenishment of soil essential ? Describe two natural ways of soil replenishment.
Growing of crops year after year results in the depletion of certain nutrients. The soil becomes deficient every year. If these nutrients are not replenished, the soil will become unfit for cultivation and land may become barren. Hence, replenishment of soil is essential.
The two natural ways of soil replenishment are:
(i) Crop rotation i.e., rotation of crops. In this practice, different crops having varied requirements of nutrients are grown on the same land during different seasons. So that the soil is not depleted of any particular nutrient all the time, often a legume crop e.g., pea, gram, pulses etc. are grown alternately to replenish the soil.
(ii) Leaving the agricultural land uncultivated for one or two seasons.This helps the soil to regain its richness.
Is it necessary to replenish forests?
It is very necessary to replenish forests as forest control the following things:
(i) Rainfall. Trees give out enormous amount of water during transpiration. This water vapour helps in the formation of rain clouds. If trees are killed and not replenished , it will reduce the rainfall in the area
(ii) Soil erosion. If trees are cut at a large rate the soil becomes uncovered. The top soil which is rich in organic matter will be washed away by water or carried away by wind. It may lead to the formation of a desert.erosion may lead to the formation of desert.
(iii) Carbon dioxide-oxygen balance. Forests have very large number of trees. They give out O2 and take in CO2 in day time during photosynthesis. Thus they help in maintaining carbon dioxide-oxygen balance in the atmosphere.
(iv) Natural growth of trees. Forests cannot be grown in a few days or months. Trees take years together to grow their heights.
It is, therefore, necessary to replenish forests at proper time, i.e., we must plan and grow trees and avoid indiscriminate cutting down of forests.
How does explosion of population create problems?
Explosion of population causes the following problems:
(i) Due to increase in population there is increase in demand of space, food and other necessities. To meet the demand, forests, fields, hills etc. are used indiscriminately.
(ii) Overpopulation leads to overuse of the resources. The rate of use is much more than the rate of their formation. thus. it depletes the resources.
How is soil formed?
The following are the factors or processes result in the formation of the soil:
(i) The sun. The sun causes heating of rocks during the day. As a result they expand. The rocks cool down at night and contract. Since, all parts of the rock do not expand and contract at the same rate, it results in the formation of cracks. Finally huge rocks break up into smaller pieces which forms the soil. .
(ii) Water. It acts in two ways :
(a) It gets into cracks of rock formed due to uneven heating by the sun. In winter, this water freezes and cause widening of cracks. It is because water expands on freezing (ice). This leads to the breaking of the roacks.
(b) Running water wears away hard rocks over a long period. Water flowing at high speed carries rock pieces alongwith it and cause these rock pieces to rub against each other. As a result the rocks wear down to smaller particles. The running water carries these particles far away from their parent rock and deposits them down its path.
(c) Wind. Strong winds and storms also erode rocks down. The strong wind carries small rock pieces and sand from one place to the other like water.
(d) Living organisms. The Lichens (symbiotic association of fungi and algae) grow on the surface of rock. They release certain substances that cause the rock surface to powder down to form a thin layer of soil.
On this thin layer of soil small plants like moss grow. They cause the rock to break up further. The roots of big plants/trees sometimes go into cracks in the rock. As these roots grow bigger the cracks are widen.
All these processes lead to the formation of soil.
What is soil erosion?
Removal of useful components of the soil and addition of the substances that affect the soil quality adversely and kills the diversity of the organisms living in the soil is called as soil erosion.
What are the methods of preventing or reducing soil erosion.
The following are some methods which can prevent or reduce soil erosion:
(i) Keeping the vegetation cover on the ground which reduces soil erosion by wind and water.
(ii) Avoid overgrazing.
(iii) Afforestation, the roots of trees check the flow of running water. Trees also check speed of strong winds. Thus, prevent erosion of soil.
(iv) Intensive cropping.
What is biogeochemical?
The cycling of minerals (elements) between non-living and living components of the environment is known as biogeochemical.
List the main elements/substances of biogeochemical cycles.
The main elements/substances are carbon (C), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), sulphur (S), phosphorus (P) and water.
Name the group of plants which has nitrogen fixing bacteria in the root nodules.
Leguminous plants such as pea, gram, bean etc have the nitogen fixing bacteria in their roots.
What is the name of the organism found in the nodule of leguminous plants?
Rhizobium bacteria.
What do you mean by biological fixation of nitrogen?
The fixation of free (atmospheric) nitrogen by bacteria and blue green algae is known as biological fixation of nitrogen. The nitrogen fixing bacteria like rhizobium is found in the roots of the leguminous plants.
Which of the following can fix free nitrogen?
(a) Virus (b) Fungi (c) Blue green algae (d) Protozoa.
(c) Blue green algae.
Name the main reservoir of gaseous carbon and main deposition of biological carbon.
The main reservoir of gaseous carbon is atmosphere.
Biological carbon is majorly deposited in the sea. .
How do forests play an important role in maintaining the water cycle?
Trees of forests absorb water from the soil. the water evaporate through transpiration from the plants . Thesis water vapour in the atmosphere condense into droplets. These droplets fall as rain. Thus the water cycle is maintained.
‘Organisms play a vital role in nitrogen fixation’. Write the names of two such organisms.
The two organisms which play vital role in nitrogen fixation are:
(i) Rhizobium (bacteria) and Blue green Algae—fixation of free atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
(ii) Nitrosomonas (nitrifying bacteria) convert ammonia to nitrites and Nitrobactor convert nitrites into nitrates.
What is the function of decomposers in Biogeochemical cycles?
In Biogeochemical cycles, decomposers play a major role. hey decompose the dead bodies (of plant and animals) and excreta of both plants and animals. These bacteria convert the complex sunstances into the simpler forms. The compounds are released into nutrient pool (soil, water bodies, atmosphere) and the elements are put back into circulation by plants through reabsorption from the soil.
List four points which one should know regarding cycling of materials.
The points one should know regarding the cycling of material are:
(i) The source of the element.
(ii) The form in which it is available.
(iii) The form in which it is converted during cycling.
(iv) The form in which it is released into the nutrient pool.
List the important steps involved in nitrogen cycle in the biosphere.
The imporatnat steps involved in nitrogen cycle :
(i) Nitrogen fixation - and assimilation of free atmospheric nitrogen by Rhizobium or blue-green algae.
(ii) Nitrogen is converted to its oxides during lightning and in the prsence of high temperature and pressure. These oxides dissolve to give nitric and nitrous acid and fall on land along with rain.
(ii) Ammonification - conversion of ammonia to nitrites by Nitrosomonas (nitrifying bacteria).
(iii) Nitrification - conversion of nitrites to nitrates by Nitrobactor.
(iv) Denitrification - break down of nitrates to free nitrogen by Pseudomonas (denitrifying bacteria).
In what ways cycling of materials and flow of energy in the environment differ?
Cycling of materials and flow of energy in biosphere differ mainly in following ways :
(i) Flow of energy is unidirectional, i.e., from non-living to living things.
Unlike energy cycle the material cycle through living and non-living components of the biosphere.
(ii) Energy once trapped get lost as heat during its passage through trophic levels of food chain. Therefore, constant supply of energy from the sun is necessary.
The amount of various elements/minerals cycling through living and non-living components more or less remains constant.
Briefly describe the nitrogen cycle in the environment.
Or
Draw a neat labelled diagram to show nitrogen cycle in nature.
Nitrogen exists as free nitrogen in the atmosphere. In air N2 is about 78%. This free nitrogen is fixed into compounds of ammonia and nitrates. Most of the organisms cannot utilize nitrogen as molecular nitrogen.
Fixation of Nitrogen. Fixation of free nitrogen into compounds takes place by following means :
(a) Certain blue green algae and bacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
(b) Nitrogen—fixing bacteria found in the nodules of roots of legumes such as gram, bean, pulses etc., fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen containing compounds.
(c) Lightening also helps in the formation of nitrogen containing compounds.
Nitrogen containing fertilizers produced artificially in factories are the fixed form of nitrogen.
Plants take compounds containing nitrogen from the soil. Form plants nitrogen passes into food web. Decay of dead plants, animals and excreta like urine, faeces, causes return of nitrogen compounds to the soil. Denitrifying bacteria and fire cause liberation of free nitrogen in the atmosphere.
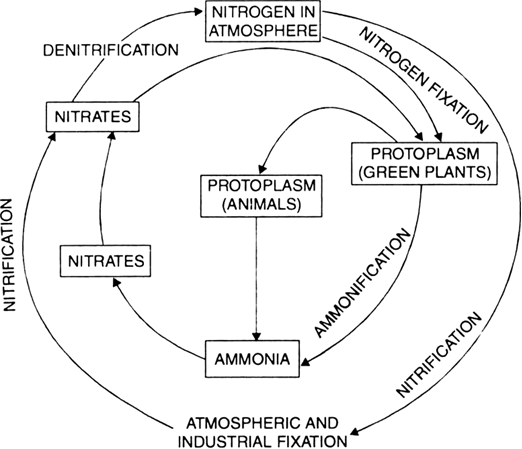
Nitrogen cycle.
Importance of Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen is an important constituent of tissues, proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, amino acids. Atmosphere contains about 78 per cent nitrogen but plants and animals cannot use nitrogen in this form. Plants take nitrogen in the form of nitrates—the usable form. From plants, through food nitrogen travels to animals. If nitrogen in the form of proteins, amino acids, enzymes etc. remains locked up in the bodies of organisms, there will be shortage of usable form of nitrogen. Therefore, circulation of nitrogen in nature is very essential.
Draw a labelled diagram to show the oxygen cycle in nature.
Or
Draw a neat labelled diagram to show the oxygen cycle in nature.
Or
Describe oxygen cycle in nature.
Oxygen cycle. Oxygen in gaseous form is present in atmosphere (21 per cent).
In water bodies, it is present in dissolved form. From these sources, plants, animals and decomposers take molecular O2 for respiration.
Burning of fuels such as coal, wood, petroleum also use atmospheric O2.
Green plants utilize CO2 and H2O during photosynthesis and release molecular O2 in air and water.
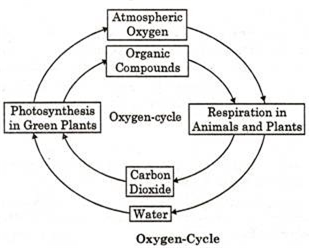
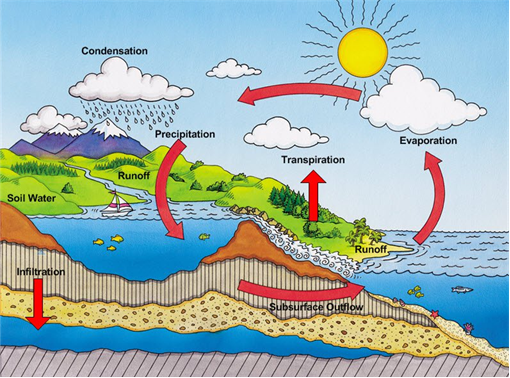
Describe water cycle.
Water cycle. Water is one of the most important physical components which is essential for survival of life on earth. The water from the water bodies on evaporation move up. As the vapours rises up in the atmosphere they become cooler and condense and form clouds and which fall down as rain. After rain it passes through rivers and gets collected again in the ocean. The circulation of water in this manner is known as water cycle. The cycle is also performed through living beings like absorption and transpiration of water by plants and drinking by animals. Animals loose water during respiration and evaporation or perspiration. They loose water through excretion.
What will happen, if decomposers are eliminated completely from the earth surface? Write important points.
If the decomposers are eliminated from the earth's surface it will lead to the following conditions:
(i) Dead bodies of animals and plants and other dead organic matter will remain undecomposed.
(ii) After some time, the dead bodies of organisms will occupy the whole space available on this earth.
(iii) There will be no recycling of matter between biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem because all the matter will remain locked up in the dead bodies.
Thus existence of life on the earth will become impossible.
Define the following terms:
(i) Autotrophs (ii) Heterotrophs
(iii) Decomposers (iv) Producers.
(i) Autotrophs. Organisms which can synthesis their own food by the process of photosynthesis are called autotrophs. All green plants are autotrophs.
(ii) Heterotrophs. Organisms which depend on plants or animals for their food are called heterotrophs. They cannot make their own food. All the animals are heterotrophs.
(iii) Decomposers. These are bacteria and fungi (microorganisms) which decompose dead organic matter. They depend on the dead and decaying matter for food.
(iv) Producers. These are the organisms which produce food. All green plants (autotrophs) are producers.
What is green house effect?
The increase in the temperature of the Earth due to the increase in the concentration of gases like Caarbon-dioxide , methane etc is called green house effect. It is the heating of the atmosphere due to the absorption of infrared radiations by CO2 molecules.
State, why a car parked in the sunshine with its windows closed is found much more hot inside than outside?
The inside of a car with its windows closed is hotter than outside due to green house effect as the glass in the windows absorb infrared radiations of the sun but do not allow them to escape or reflect back, thus increasing the temperature of the car on the inside.
Burning of fossils fuels causes pollution. Comment.
Fossil fuels such as coal, wood, petroleum oil, natural gas are burnt to provide a source of energy. Their combustion not only produces energy and carbon dioxide but other poisonous gases like carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen and smoke particles also. All these gases cause atmospheric pollution. Thus the burning of the fossil fuel causes pollution.
Sponsor Area
What are aerosols? How are these dangerous?
The solid particles or liquid droplets dispersed in air are called aerosols. The aerosols deplete the ozone and thus are very dangerous..
What is the role of plants in controlling air pollution and flood?
The plants clean the air. They produce the most important gas oxygen. They maintain a balance between the CO2 and oxygen. The burning of fossil fuels has caused air pollution by increasing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere. Photosynthesis of plants use the CO2 and thus control air pollution. Plants make the soil more compact as their roots hold together the soil particles and they lower the speed of the water and thus protection from floods.
Write a note on air pollutants containing nitrogen.
The burning of fossil fuels produces oxides of nitrogen which cause air pollutions. The oxides of nitrogen are dangerous to breathe and when dissolved in the rain they make the rain acidic which is very harmful for different organisms.
What is the function of ozone layer?
The ozone layer protects the earth from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiations from the sun. The ozone layer absorbs the harmful radiation of the sun and prevents them from reaching the Earth's surface.
“Ozone present in stratosphere is essential for life on earth but its presence very near to the earth's surface is harmful”. Comment.
Ozone present in the stratosphere protects us from the harmful UV radiation of the sun. But, it is a poisonous gas with a chlorine like odour and causes respiratory problems, therefore its presence very near to the earth's surface can be harmful for the organisms.
Explain the following phenomenon (i) Acid rain (ii) Ozone depletion (iii) Global warming or green house effect.
(i) Acid Rain. The oxides of nitrogen and sulphur present in air as pollutant get dissolved in rain water to form nitric acid and sulphuric acid respectively. The presence of these makes the rain acidic. The acid rain damages monuments, statues and buildings. It also causes gradual degradation of soil and a decline in forest and agricultural productivity.
(ii) Ozone depletion. Reduction in thickness of ozone layer or holes in the ozone layer of atmosphere is known as depletion of ozone. Depletion of ozone layer is mainly caused by Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). (CFCs) are used in refrigerators, fire extinguishers and aerosol sprayers. These break the ozone molecules and lead to its depletion. Due to depletion of ozone layer, more UV radiation reaches the earth and causes skin cancer, damage to eyes and immune system.
(iii) Global warming or Green house effect. Certain gases such as CO2 and CH4 (methane) when present in sufficient amount trap the heat of the sun and increase the temperature of the Earth. This increase in temperature of earth is known as global warming and the phenomenon is called green house effect.
Global warming may cause :
(i) melting of ice caps of mountains and glaciers resulting in floods and rise in sea level.
(ii) variation in weather.
Write the harmful effects of ozone depletion.
Harmful effects of ozone layer depletion are
(i) Due to depletion of ozone layer, the ultra violet (UV) radiation will reach the earth. UV radiations cause skin cancer, damage to eyes and immune system.
(ii) UV radiation kills microorganisms, such as bacteria, even useful ones.
(iii) Ozone layer depletion may lead to variation in rainfall, ecological disturbances and changes in the global food supply.
What are the different states in which water is found during the water cycle?
Water is found during the water cycle in three states, namely solid (ice or snow), liquid and vapour.
Name two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
Proteins and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are the two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
List any three human activities which would lead to an increase in the carbon dioxide content of air.
The following activities of human beings may increase carbon dioxide content of air:
(i) Burning of fossil fuels such as petrol, diesel and coal in various activities like transportation and industrial processes.
(ii) Burning of wood and charcoal for heating, cooking, etc.
(iii) Deforestation that reduces the green plant and tree population, consequently utilisation of atmospheric CO2 during photosynthesis.
What are the two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere?
Oxygen is found in the atmosphere in the form of
(i) a diatomic molecule having two atoms of oxygen, with chemical formula O2.
(ii) a triatomic i.e., containing three atoms of oxygen, with a chemical formula O3, called ozone.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





