Science Chapter 16 Light
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 8 Social+science
Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see object in the room? Can you see objects outside the room. Explain.
In a dark room we are not able to see the objects around us. The absence of light in a dark room does not enable us to see the objects in the dark room. Whereas, outside the room light is present. This light which falls on the object is reflected back and goes into our eyes. Hence, we see the objects on which the light falls.
Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
|
Regular reflection |
Diffused reflection |
|
(i) It takes place on a smooth surface. (ii) All the reflected rays are parallel to each other. (iii) Reflected rays are in one direction. |
(i) It takes place on a rough surface. (ii) Reflected rays are not parallel. (iii) Reflected rays are scattered in different directions.
|
No, diffused reflection is not due to failure of laws of reflection. Diffused Reflection occurs due to irregularities in the surface.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
Polished wooden table
A polished wooden table will have regular reflection because its surface is smooth.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
Chalk powder
Chalk particles are not smooth. Therefore diffused reflection will take place on it's surface.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
Cardboard surface
Cardboard surface has minute irregularities on it, so it will have a diffused reflection.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
Marble floor with water spread over it
Marble stone with water spread over it will have regular reflection if water is stable. But, if waves are formed due to moving water then diffused reflection will take place.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
Mirror
Regular reflection. Mirror has ultra-smooth surface.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
Piece of paper
Diffused reflection. The surface of a piece of paper has minute irregularities in it.
State the laws of reflection.
Laws of reflection are stated as follows:
(i) Incident ray, reflected ray and normal drawn at the point of incidence, all the three always lie in the same plane.
(ii) Angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incident lie in the same plane.
The below activity will show that the incident ray, reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all the three lie in the same plane. 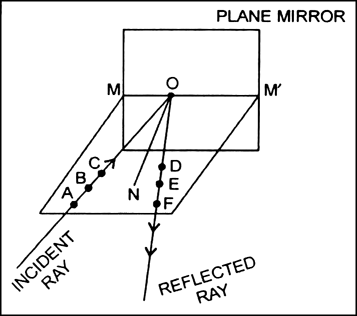
1. Take a white sheet, spread it on a table.
2. Draw a line MM' on it and place a plane mirror vertically on this line.
3. Take a comb and cover all the opening of it except one. Now, let light pass through this opening such that the parallel light rays fall on the mirror.
4. Adjust the set-up in such a way that a pattern of incident and reflected ray is formed.
5. Now mark points A, B, C on incident ray and points D, E, F on its corresponding reflected ray.
6. Remove the mirror and join the points. Extend the line ABC and DEF to meet MM' at O.
7. OA is incident ray and OF is reflected ray. Draw ON perpendicular to MM'.
Therefore, we can see that incident ray, reflected ray and normal at the point of incidence, all lie in one plane.
Image formed by a plane mirror is
virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged
virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged
real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
B.
virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Kaleidoscope operates on the principle of multiple reflection.
Construction of a kaleidoscope:
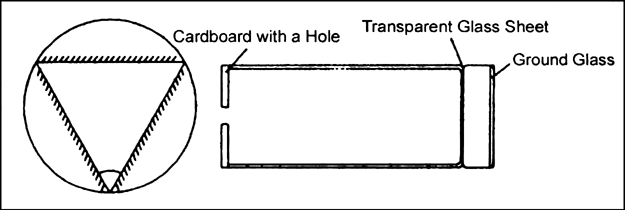
1. A kaleidoscope is constructed using three narrow strips of plane mirrors inclined at angles of 60° enclosed in a tube.
2. One end of tube has a ground glass plate with a clear glass plate on its inner side.
3. A metallic ring separates the two plates and the space is filled with coloured pieces of glass or broken bangles.
4. A cardboard with a hole in the centre is fixed on the other end of the tube.
Sponsor Area
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.

Gurmit wanted to perform the Activity of 'Throwing light on frinds eye' using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teachers advise?
LASER light is harmful for eyes. If our eyes are exposed to this light, it can cause permanent damage to our eyes. Hence, the teacher has asked Gurmit not to perform the activity with LASER light.
Explain how you can take care of your eyes?
Following precautionary measures can be taken to take care of our eyes:
(i) We should atleast always wash our eyes with plane cold water atleast three times a day.
(ii) We should not touch our eyes with dirty hands.
(iii) We should never rub our eyes.
(iv) We should not look at sun directly.
(v) We should read book, watch T.V., read from black board from a suitable distance.
(vi) Consult an eye specialist if you have any irritation, redness in our eyes.
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Given,
But, we know that
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
That is, i = r
Therefore,
So, the angle of incidence of the ray will be 45°.
How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
Infinite images of the candle will be formed.
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown in the figure. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror. 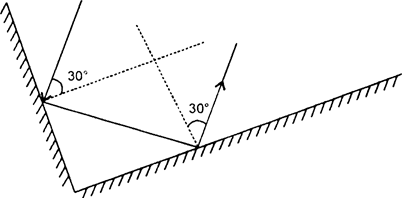
The emergent ray from mirror B will reflect at 60o.

Bhoojo stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in figure. Can he see himself in the mirror ? Also can he see image of objects situated at P, Q and R?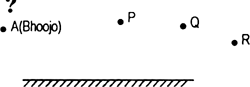
Bhoojo can’t see his image himself because he is not standing in front of the mirror. However, he will be able to see P and Q because, the reflected rays from P and Q reaches his eyes.
Bhoojo cannot see R because the reflected rays will not reach his eyes. 
Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror, (figure).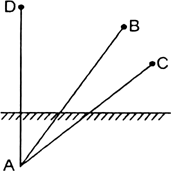

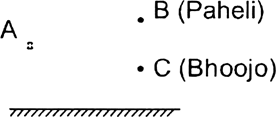
Can Paheli at B see this image?
Yes, Paheli can see the image at B because the reflected ray from A will reach B.
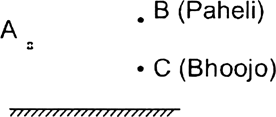
Can Bhoojo at C see this image?
Yes, Bhoojo can see the image because his eyes will receive the reflected ray from A.
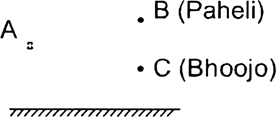
When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?
There won't be any change in the image A. Position of image A will remain fixed even if Paheli moves from B to C.
Write down five English alphabets which do not show lateral inversion on suffering reflection from a plane mirror.
English alphabets which do not show lateral inversion on suffering from a plane mirror are A, H, O, T, U.
You are standing at a distance of 1 m from a plane mirror. What is the distance between you and your image?
2 m is the distance between you and the image formed.
What is a mirror?
A surface typically of glass, which reflects a clear image is known as mirror.
Mirror is a smooth and shiny surface.
What is reflection?
The processs of throwing back the light falling on a surface is known as Reflection.
What kind of surfaces reflect light?
Smooth, polished surfaces reflect maximum light. Usually all surfaces reflect light. But, the amount of reflected light depends on the smoothness and roughness of the surface.
What is incident ray?
The ray of light, which strikes the reflecting surface is known as incident ray.
What is reflecting ray?
Ray of light, that comes back from the surface after reflection is known as reflected ray.
What is angle of incidence?
Angle formed between the incident ray and normal is called angle of incidence.
What is angle of reflection?
The angle formed between the reflecting ray and normal is called angle of reflection.
State second law of reflection?
The second law of reflection states that:
Angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
What kind of image is formed by a plane mirror?
Plane mirror forms a virtual and erect image.
Sponsor Area
Where is the image formed by the plane mirror?
The image is formed behind the mirror in a plane mirror.
What is the size of the image formed in a plane mirror?
The size of the image formed in a plane mirror is same as that of the object, in front of the mirror.
At what distance is the image formed behind the plane mirror?
In a plane mirror, the image is formed at the same distance, as is the object in front of the mirror.
What is the phenomenon called where left side appears to be right and vice-versa in a plane mirror?
Lateral inversion.
What kind of lens is present in the human eye?
The human eye contains a convex lens made of a transparent, soft and flexible material like a jelly made of proteins.
What is the range of vision of a normal human eye?
The range of vision of a normal human eye is from infinity to about 25 centimetres.
What type of photosensitive cells are present on the retina of the eye?
Cones and rods are present on the retina of the eye.
What is blind spot?
At the junction of the optic nerve and the retina, there are no sensory cells. So, due to the absence of rods ans cones, no vision is possible at this spot. Hence, this spot is called blindspot.
What is the function of eyelids?
Eye-lids shut out light when not required. It prevents any unwanted object from entring the eyes.
What is meant by reflection? What type of surface reflects most of the light falling on it?
The bouncing back of the incident light when it strikes on a reflecting surface is known as reflection of light
The reflecting surface should have highly polished shiny surfaces. This would enable the surface to reflect most of the light falling on them.
How do we see various objects?
When light falls on any object, the incident light is reflected back depending on the smoothness of the surface. The reflected light reaches our eyes, and it enables us to see the objects.
Write the laws of reflection. Draw a suitable diagram also.
Laws of reflection are:
(i) The ray of incidence, ray of reflection and normal drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting surface, all the three, lie in the same plane.
(ii) Angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of reflection.
The below diagram illustrates the law of reflection: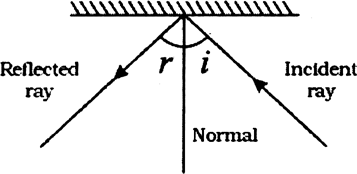
What do you mean by following:
(i) Incident ray,
(ii) Reflected ray.
Incident ray: The light ray that strikes any surface is called incident ray.
Reflected ray: The light ray that comes back from the surface, after reflection in a different direction, is called reflected ray.
What do you mean by angle of incidence and angle of reflection?
Angle of incidence: The angle formed between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence.
Angle of reflection: The angle formed between the reflected ray and the normal is called angle of reflection.
Angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
What is a mirror? What kind of image is formed in a mirror?
Mirror is a smooth surface which is polished from its back and can form the image of the object which is placed in front of it. The most familiar type of mirror is the plane mirror, which has a flat screen surface.
The image formed by a mirror is a virtual and erect and is of same size as that of the object infront of it.
What do you mean by lateral inversion? Draw a diagram also.
When an object is placed in front of the mirror, it's image is formed. The process where the right hand side of the object appears to be the left side in the image and right appears on the left is known as lateral inversion.
The english alphabet F shows lateral inversion.
State four characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
The characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror are:
(i) is always virtual and erect.
(ii) is of the same size as the object.
(iii) is formed at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
(iv) is laterally inverted.
What phenomenon is depicted in the given diagram? Explain the phenomenon and label A and B in the diagram.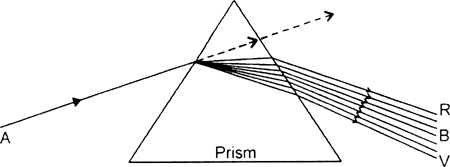
The phenomenon depicted in the diagram is known as dispersion of light.
When a ray of white light passes through the prism, it asplits into seven colours of light rays.
A : White light beam
B : spectrum formed on splitting up of white light.
Why is normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?
The maximum accommodation of a normal eye is reached when the object is at a distance of about 25 cm from the eye. After this limit, the ciliary muscles cannot make the eye-lens bulge more. Hence, an object which is placed at a distance of less than 25 cm cannot be seen clearly by a normal human eye.
Why does it take some time to see objects in a dim room when you are the room from bright sunlight outside?
When a person is out in the bright sunlight, iris causes the pupil to contract so that only small portion of light enters the eye and rods of the retina are also adjusted in the same way. And, suddenly when a person enters into a dimly-lit room, each iris takes some time to increase the diameter of the pupil, so that more amount of light can enter the eyes to see the object clearly. The rod cells of the retina also take some time to adjust themselves to get the picture of the object in dim light.
How can we see the moving picture?
The moving pictures or a continuous film that we see is a compilation of several shots taken at different times.
Our retina retains the image for 1/6th of a second. If the images flashes at a rate faster than 16 per second, then a moving picture of any object can be seen.
So, the shots of pictures are flased at a rate of 24 per second. Hence, it enables us to see the picture.
How do ciliary muscles affect the functioning of eye?
Ciliary muscles are capable of contracting and relaxing. Therefore, they are able to change the thickness of eye lens, thereby changing its focal length. Changing focal length helps us to see the nearby and far-off objects distinctly.
Therefore, power of accomodation of the eye is due to the function of ciliary muscles.
Even though the image formed on retina is inverted, how do we see erect objects?
The inverted image which is formed on the retina is conveyed to brain in the form of electric impulses with the help of optical nerves. Brain is able to perceive an erect image of object with the help of electrical impulses.
Explain in brief the perception of colour.
Human eye contains large number of rods and cones which are sensitive to light. Rods respond to the intensity of light and cones respond to the colour of the light. A person becomes blind due to the absence of cone cells in the eye.
Cone cells helps in perceiving the color. This is called perception of colour.
(a) What is dispersion of white light? What is the cause of such dispersion? Draw a diagram, to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism.
Draw a suitable diagram also.
(b) A glass prism is able to produce a spectrum when white light passes through it but a glass slab does not produce any spectrum. Explain why?
(a)
(i) The splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a transparent medium like a glass prism is called dispersion of light.
(ii) The dispersion of white light occurs because the angle of refraction for different colours of light is different when passing through the glass prims.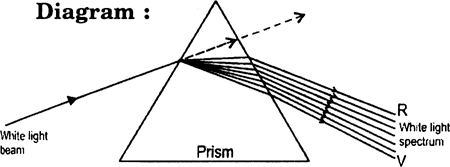
(b) The refraction of light takes place at the two slant surfaces in a prism. The dispersion of white light occurs at the first surface of prism where its constituent colours are deviated through different angles. On the second surface of the prism, the white light suffers refraction and splits into seven colors.
But, in a rectangular glass block, the refraction of light takes place at the two parallel surfaces. At the first surfaces although the white light splits into its constituent colours on refraction, but these split colours on suffering refraction at the second surface emerge out in form of a parallel beam, which gives an impression of white light.
What is meant by the ‘persistence of vision’ ? We are able to see the movie picture in a cinema hall. How does this happen?
Persistence of vision refers to the optical illusion whereby multiple discrete images blend into a single image in the human mind. Human eye has the ability to see the image of an object even after the removal of the object for a short duration of time.
Persistence of vision enables us to see the movies in a cinema hall. The individual shots that are captured is projected at a rate of about 24 frames per second. Under these conditions, the image of one picture persists on the retina of the eye till the image of the next picture falls on the screen and so on. Due to this, the slightly different images of the successive pictures present on the film merge smoothly with one another and gives us the feeling of moving images.
What are the uses of a plane mirror?
Uses of a plane mirror are:
(i) to see our reflections in it, at our homes.
(ii) used to reflect light on a particular object.
(iii) used for signalling by scouts and army.
(iv) used to form multiple images in show windows.
(v) used to reflect sun rays in appliances like solar cooker etc.
(vi) Toys like kaleidoscope are made on the concept of multiple reflection. Periscopes used by navy is based on the concept of multiple reflection for spying in sea.
Write various measures to save our eyes.
Describe how does human eye work?
The following steps are involved in the functioning of the eye.
1. A light ray which is incident on the object is reflected back and it enters our eyes through cornea. Cornea is called window to the world. Cornea is transparent.
2. Behind the cornea, there is a dark muscular structure called Iris. Iris is that part of the eye which gives eyes it's distinctive color.
3. In the iris, there is a small opening called the pupil. Size of the pupil is controlled by iris.
4. Behind the pupil of the eye is a lens which is thicker at the centre. Lens focuses the image of the object on the retina.
5. Retina converts these optical images into optical pulses. These optical pulses are then sent to brain through optical nerves.
6. The amount of light entering the eye through cornea is controlled by Iris. It expands when light is bright and thus enables controlled amount of light to enter the pupil. In dark it contracts and increases the size of pupil to allow more light to enter the eye.
Sponsor Area
Match the following options:
| A. Cornea | (i) No image formed |
| B. Pupil | (ii) Front part of eye |
| C. Blind spot | (iii) Small opening in the cornea |
| D. Rods | (iv) Sensitive for bright light |
| E. Cones | (v) Sensitive for dim light |
A. Cornea | (i) Front part of eye |
B. Pupil | (ii) Small opening in the cornea |
C. Blind spot | (iii) No image formed |
D. Rods | (iv) Sensitive for dim light |
E. Cones | (v) Sensitive for bright light |
Match the following options:
| A. Iris | (i) Image formed |
| B. Retina | (ii) Controls the size of pupil |
| C. Rainbow | (iii) Spectrume |
| D. Band of seven colours | (iv) Dispersion of light |
A. Iris | (i) Controls the size of pupil |
B. Retina | (ii) Image formed |
C. Rainbow | (iii) Dispersion of light |
D. Band of seven colours | (iv) Spectrume |
The image formed by a plane mirror is
real and inverted
real and erect
virtual and inverted
virtual and erect
D.
virtual and erect
The size of an image formed by a plane mirror is
the same as the size of the object
large than the size of the object
smaller than the size of the object
double times the size of the object
A.
the same as the size of the object
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





