Biology Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 11 Political+science Biology
How is nitrogenase enzyme protected ?
What is Hidden hunger in the case of plants?
Which kind of plants harbour nitrogen fixing bacteria in their root nodules ?
When a section of root nodule of a legume is examined it appears pinkish. Why ?
What is active absorption ?
What are Chemoautotrophs ?
Name two sulphur containing amino acids.
What is meant by outer-space of cells?
What are ion channels ?
usually occurs through ion-channels,
What is leghaemoglobin ?
What are bacteroids ?
What are haustoria ?
Sponsor Area
Name the nitrifying bacteria in the soil. Why are they called chemoautotrophs ?
What does 15–15–15, 17–18–19 etc. signify on fertilizer bags ?
What is aeroponics ?
What is the effect of deficiency of silicon on cereals ?
What is plant ash ?
Give the role of minerals.
1. The mineral elements are absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction.
2. The minerals are components of protoplasm. The elements having variable valency bring oxidation and reduction reactions e.g. Fe, Cu.
3. K+ ions help in the opening and closing of stomata.
4. Salts of weak acids and weak bases act as buffers.
5. Minerals maintain osmotic potential of cell sap and permeability of plasmalemma.
6. Minerals also act as cofactors and thus bring catalytic reactions.
7. K+ and boron help in transportation of food in the phloem tissue.
Write a note on nutrient deficiency symptoms in plants.
1. Chlorosis
2. Necrosis
3. Abscission
4. Fall of leaves
5. Leaf curl
6. Wilting
Write a note on hydroponics.
Mention the significance and disdvantages of hydroponics.
1. Through hydroponic gardening; plants can be grown anywhere as long as their growth requirements are met .
2. Plants produced are free from soil pathogens and diseases as no soil is involved.
3. Plants grown are free from harmful chemicals as fertilizers and pesticides are not used.
4. The plants can be produced at those places where there is scarcity of land and the soil is thin or infertile.
5. The plants grown by this method are more healthy.
Disadvantages of hydroponics :
1. The initial set-up is very costly.
2. It needs the help of expert scientists to prepare the required nutrient medium and its maintenance.
Comment upon active absorption of minerals.
What is necrosis.
Sponsor Area
Explain mottled leaf.
Briefly exlpain protein carrier molecules

Mineral absorption through carrier molecules
What is Plant nutrition ?
Write a note on symbiotic nitrogen fixation.
Write the various natural methods involved in the replenishment of the soil fertility.
(1) Weathering of rocks.
(2) Decomposition of fallen leaves, twigs, dead plants and animals and excreta and their convertion to humus.
(3) Biological nitrogen fixation.
Mention the artificial methods involved in the restoration of soil fertility.
(1) By adding farm yard manure or animal excreta to the soil.
(2) By adding fertilizers, manure.
(3) By green manuring.
(4) By crop rotation.
(5) By controlling over-grazing.
List the criteria for essentiality of elements.
1. The essential elements should be necessary for growth and reproduction of the plant. It should be indispensable. The plant should not be able to complete its lifecycle in the deficiency of the element.
2. The element should not be replaceable and its requirement should be specific. The deficiency of the element should not be met by supplying some other element.
3. There should be direct involvement of the element in the metabolism of the plant.
Why do plants need potassium and magnesium ?
Potassium - is involved in maintaining the turgidity of cells and in the activation of enzymes. It helps in the opening and closing of stomata, to determine anion-cation balance in the cells, formation of cell membrane and in translocation of organic solutes in the phloem.
Magnesium- is a constituent of chlorophyll. It is required in fat synthesis and nucleic acid synthesis. It activates enzyme in phosphate metabolism.
Explain chlorosis and give its cause. Describe the role of copper.
Role of copper :
Copper is absorbed as cupric ions (Cu2+). It is essential for the overall metabolism in plants. It is associated with certain enzymes involved in redox reactions.
Name two Macro and micro nutrients
Macronutrients - Nitogen, carbon
Micronutrients - Zinc , molybdenum.
What is the importance of boron in plant life ?
1. Boron is involved in pollen germination and cell elongation, cell differentiation.
2. It is required in the translocation of scarbohydrates.
3. It is required for the uptake of Calcium ions.
4. It helps in membrane functioning.
Name the essential elements :
Write the deficiency symptoms of :
(1) iron (2) zinc and calcium.
(2) Zinc : Due to the deficiency of zinc, young leaves and internodes become extermely small, resulting in little leaf rosette and mottled leaf condition .
Calcium : It's deficiency produces necrosis in the leaf and stem. Plants have a stunted growth with suppressed flowering. Flowers fall immaturely and this process is called premature fall of flower.
In what amount macronutrients and micronutrients are required.
Micronutrients : These are present in amount less than 10m mole kg-1.
Describe the natural method of nitrogen fixation.
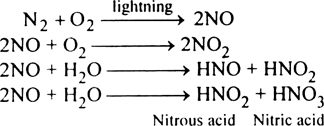
Comment upon ammonification.
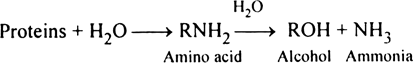
Give a brief account about soil fertility and its depletion.
Soil fertility. It is the ability of soil to provide good growth of plants. It is dependent upon pH value, size of soil particles, presence of minerals, presence of air , optimum temperature etc.
Depletion of soil fertility is due to the following reasons :
1. Non-rotation of crops causes deficiency of minerals.
2. Precipitation of salts due to change of pH value.
3. Leaching of salts.
4. Over use of the land for cropping.
5. Over grazing.
7. Deforestation.
What are protoplasmic elements ?
Give the significance of culture experiment.
Significances of culture experiment :
1. It tells the essentiality of an element.
2. It also tells the toxicity of an element when present in excess amount.
3. It can tell the result of interaction between different elements.
4. It tells us about the effects of the deficiency of a particular element.
Give the term for-
The concentration of the essential element below which plants growth is retarded
Deficiency of which elements cause delay in flowering?
Why is there a need for application of fertilisers ?
Name the elements which are not essential for plants but are essential for animals.
Nitrogen is an essential element for plants and is found in abundance as atmospheric nitrogen. But most plants are unable to use it. Why is it so and in what form do plants utilise nitrogen?
Name the element which is mineral and non-mineral.
What are the forces which operate in passive diffusion ?
Why the cotyledons are removed from seedlings for performing cultural experiments ?
Write the deficiency symptoms of following : Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Sulphur, Potassium, Calcium and Magnesium.
Deficiency symptoms of Nitrogen:
1. Deficiency of nitrogen interferes with protein synthesis and hence all forms of growth are affected.
2. An early symptom is yellowing of leaves and development of chlorosis.
3. Older leaves turn light brown in colour and gradually dry.
4. Flowering is delayed or completely suppressed.
Deficiency symptoms of Phosphorous :
The deficiency of phosphorus causes :
1. disruption of general metabolism
2. abnormalities in the shape and size of chloroplast.
Deficiency symptoms of Sulphur :
1. Deficiency symptoms first appear in young leaves.
2. They become reduced, chlorotic followed by anthocyanin pigmentation in certain species.
3. Root system becomes extensive and stems become hard and woody.
Deficiency symptoms of Potassiam :
1. Deficiency symptoms are first observed on the older, lower leaves. Spots of dead tissue on older leaves are seen.
2. Potassium deficiency in cereal crops develop weak stalk. These plants easily bent to the ground by wind or rain.
Deficiency symptoms of Calcium :
1. Calcium deficiency brings about decomposition of root epidermis, roots become mucous, the growing zone and lateral roots rapidly die off.
2. Its deficiency terminates growth of meristematic regions.
3. Margins of younger leaves show chlorosis which become nacrotic.
4. Twig or stalk just below the tip and seed head is often unable to stand erect.
Deficiency symptoms of Magnesium :
1. Extensive interveinal chlorosis of the leaves resulting in defoliation;
2. Yellowing of the leaves start from basal to younger ones;
(i) Manganese (ii) Copper (iii) Zinc
1. Manganese (Mn) :
Physiological role.
i. As a Cofactor : Mangenese primarily functions as activator of several enzymes involved in photosynthesis.
ii. It helps in the splitting of water and liberation of oxygen
iii. Synthesis of chlorophyll : It is also involved in the synthesis of chlorophyll.
Deficiency symptoms
Deficiency of manganese causes chlorosis, nacrosis in the interveinal areas of leaves, the veins remain green, the chloroplasts are devoid of chlorophyll and starch grains become yellow green in colour, vacuolated and finally disintegrate.
2. Copper :
Physiological role.
Copper is a component of many enzymes involved in redox reactions. It plays a as a key role in the electron transport chain in photosynthesis.
Deficiency symptoms.
i. Deficiency of copper causes necrosis.
ii. Under severe conditions the whole plant may appear wilted and the leaves may be lost.
3. Zinc :
Physiological functions.
Zinc plays an important role in the activation of many enzymes especially carboxylases
It is involved in the synthesis of auxin. s
Deficiency symptoms.
Deficiency of zinc causes
(i) shortening of internodes with the result plant become stunted;
(ii) reduction in the size of leaves so that the leaves become very small.
(iii) chlorosis of older leaves starting at tip and extending to the margins.
Explain with examples :
(1) Macronutrients,
(2) Micronutrients,
(3) Toxic elements ,
(4) Essential elements.
(i) Macronutrients are generally present in plant tissues in large amounts in excess of 10m mole kg–1 of dry matter. For example - Carbon, hydrogen, nitogen, phosphorous, and oxygen
(b) Micronutrients : Micronutrients or trace elements are needed in less than 10mmole kg–1 of dry matter eg. iron, manganese, copper, molybdenum, zinc, boron, chlorine and nickel.
(c) Toxic elements : Any mineral ion or element which reduces dry weight by 10% of plant is called toxic element. Toxicity of element differs from plant to plant. The elements when present in large amounts much more than what is needed becomes toxic.
(d) Essential elements : These are the elements which are essential for the growth of the plants. The plant cannot complete their lifecycle in the absence of it. They are C, H, O, N, P, S, K, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, Cu, Mo, Zn, B, CI and NL
What is Foliar Nutrition ? Describe its advantages.
Foliar Nutrition—In this type of process fertilizers, growth hormones, mineral nutrients and several other chemical substances are directly applied to the plants on their leaves. They are dissolved in water and sprayed on the leaves of plants. Such an application of nutrients is called foliar nutrition.
Advantages of Foliar Nutrition—The foliar nutrition has several advantages—
1. It reaches the desired tissues more quickly as compared to the soil nutrients.
2. It is more economical means of fertilizing crop plants particularly costly micronutrients.
3. It is a useful method for accelerating growth and development during flowering and fruiting.
Define the followings :
(1) Nutrients (2) Micronutrients
(3) Macronutrients (4) Active absorption
(5) Passive absorption
6) Symplastic pathway
(1) Nutrients. The chemical substance that works as a raw material for body building and maintaining its function is termed nutrient.
(2) Micronutrients. These are needed in very small amounts, equal to or less than 0. lmg per gram of dry matter.
(3) Macronutrients. These must be present in plant tissues in concentrations of 1 to 10 mg per gram of dry matter.
(4) Active absorption. It is the movement of ions or molecules against concentration gradient or towards concentration gradient by taking energy directly or indirectly through metabolism.
(5) Passive absorption. It is the movement of minerals from higher concentration to lower concentration by physical processes not involving direct expenditure of energy.
(6) Symplastic pathway. It is the movement of ions across the cytoplasm of cortex, endodermis of pericycle through plasmodesmata.
Write short notes on :
(a) Reductive amination
(b) Transamination.
(a) Reductive amination. In this process ammonia reacts with ![]() -Ketoglutaric acid and forms glutamic acid as indicated below :
-Ketoglutaric acid and forms glutamic acid as indicated below : 
(b) Transamination. This process involves the transfer of amino groups from one amino acid to the keto group of a keto acid. Glutamic acid is the main amino acid from which the transfer of NH2 group takes place and the other 17 amino acids are formed through transamination. The enzyme required for such raction is called transaminase.
Make a list of macronutrients and mention one major function of any four of them.
The macronutrients are: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulphur, potassium, calcium and magnesium.
Functions of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen :
These are the components of protoplasm and all organic componds found in plants.
Functions of nitrogen.
It plays a major constituent of proteins, nucleic acids, vitamins and hormones.
Functions of phosphorous.
Phosphate plays a key role in energy metabolism. Incorporated into ATP it is part and parcel of the universal energy currency of all types of living systems.
Fuctions of sulphur.
Sulphur is present in amino-acids - cysteine and methionine.
Sponsor Area
Name the four broad categories of essential elements.
Essential elements can be grouped into four broad categories on the basis of their diverse functions. These categories are :
1. Structural elements
2. Energy related molecules
3. Activators or inhibitors of enzymes.
4. Elements which alter the osmotic potential.
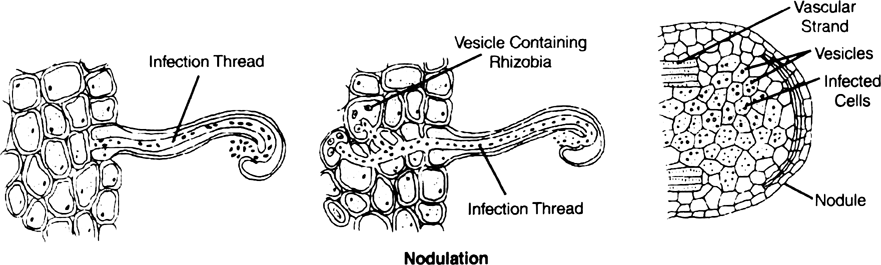
Describe how nodulation occurs ?
Nodulation : It is the process of formation of nodules. It can be described in in following points.
1. Rhizobiua multiply and colonise the surroundings of roots and get attached to the epidermal and root hair cells.
2. The root hairs curl and bacteria invede it.
3. An infection thread is produced that carries the bacteria to the cortex of the root.
4. Bacteria is then released into the cells and this leads to the differentiation of specialised nitrogen fixing cells.
5. The nodule establishes a direct vascular connection with the root for exchange of nutrients.
Name at least five different deficiency symptoms in plants. Describe them and correlate them with concerned mineral deficiency.
2. Die back: It is the withering of stem from apex downward. It is due to the deficiency of copper.
3. Necrosis : It is the death of the tissues. The leaf tips develop dead areas or necrotic areas. It may be also due to Ca, Mg, Ni, Cu and K.
4. Whiptail disease : It occurs in cauliflower. It is due to the deficiency of Mo.
5. Little leaf disease: It is due to the deficiency of Zn. It also causes rosette of apple and peaches.
What do you understand by heterotrophic mode of nutrition ?
Heterotrophic nutrition : It is the nutrition in which organisms do not manufacture their own food but take food from external sources such as other living organisms or from dead and decaying matter. For example - animals are heterotrophic
Why is that in certain plants deficiency symptoms appear first in younger parts of the plant while in others they do so in mature organs?
If the element is mobile, then the deficiency appears in the older tissues first as the biomolecules in the older tissue are broken down to release the element which is then transported to the young tissues. For example, nitrogen being a mobile, its deficiency appear in senescent or older leaves.
If the element is immobile then the deficiency first appears in the young parts as the these are not transported from the older tissues. Deficiency of the immmobile element calcium is first seen in young parts.
What are the conditions necessary for fixation of atmospheric N2 by Rhizobium ? What is their role in N2 fixation.
Conditions for N2 fixation : There are following conditions necessary for N2 fixation :
(1) A strong reducing agent like NADPH : It supplies hydrogen to N2.
(2) ATP as source of energy : It provides energy. For fixation of NH3 molecules, 8 ATP molecules are needed.
(3) The enzyme system : Nitrogenase is necessary for N2 fixation.
(4) Compound for trapping ammonia : Ammonia is very toxic and needs to be trapped in the form of amino acids.
(5) Leghaemoglobin : It is O2 scavenger and maintains anaerobic environment otherwise in the presence of O2 the enzyme nitrogenase is toxicated.
Describe the passive mineral absorption.
Passive mineral absorption : It is the absorption which occurs without expenditure of energy. It occurs by following methods :
(A) Diffusion (B) Mass flow
(A) Diffusion : It is the movement of minerals down the concentration gradient .
Types of Diffusion : It is of Two types as :
(a) Passive Diffusion : It occurs either by dissolving of minerals in matrix cell membrane or through pores. It is a physical process which needs no energy. Water, 02, C02, etc. diffuse by passive diffusion. Sodium in Nitella is absorbed by passive diffusion.
(b) Facilitated diffusion : It occurs by special protein molecules.
(B) Mass flow : Large amount of water is absorbed daily by the plant. Along with the water minerals from soil are absorbed into roots. More the rate of transpiration, more would be water absorption and thus more minerals pass into the roots and then ascend upwards into stem.
All elements that are present in plant need not be essential to its survival. Comment.
i. The element must be absolutely esential for supporting the normal growth and reproduction. The plant should be unable to complete its lifecycle in the absene of the element.
ii. The element requirement should be specific and not replaceble by another element.
iii. The element must be directly involved in the metabolism of the plant.
Since, all the elements do not meet all the criteria, they are not considered to be essential to the plant.
Why is purification of water and nutrient salts so important in studies involving mineral nutrition using hydroponics?
The purification of water and nutrient salts in hydroponics is very important because of the following reasons:
1. Impure water contains impurities, which will interfere in the growth of plant and make the study for the essntiality difficult.
2. Impurities may be toxic to the plant.
3. Impurities may compete with other minerals.
4. Impurities may inhibit some enzymes.
Therefore, only pure water and nutrients should be taken for hydroponics.
How are the minerals absorbed by the plants?
Absorption of minerals : The minerals are absorbed by the plants in two ways.
1. Passive absorption through the apoplast pathway - The movement of ions generally take place through the ion channels that is the transmembrane protein that function as selective pores. It does not require energy.
2. Active absorption through the symplast pathway - It requires the expenditure of energy. The ions are slowly into the inner space.
Which of the following statements are true? If false, correct them.
1. Boron deficiency leads to stout axis.
2. Every mineral element that is present in the cell is needed by cell.
3. Nitrogen as a nutrient is highly immobile in the plants.
4. It is very easy to establish the essentiality of micronutrients, because they are required in traces.
1. True. Boron deficiency leads to stout axis.
2. False. Every mineral element present in the cell is not needed by the plant.
3. False. Nitrogen is highly mobile.
4. False. It is very difficult to establish essentiality of micronutrients because they are required in traces.
If a plant shows a symptom which could develop due to the deficiency of more than one nutrient how would you find out experimentally, the real deficit mineral?
To find out if the deficiency symptom is due to the deficiency of which nutrient , in the case when more than one nutrient can cause the symptom, a number of wide mouthed bottles is taken. Each is fitted with split cork.
One of them has the normal culture and is called control. While the other bottles have deficiency of one mineral each. For example necrosis is caused by the deficiency of Ca, Mg or K.
Thus three bottles having defieciency of Ca, Mg and K respectively is taken and the plant is grown in each.
The plants in the three bottles are checked if they have developed chlorosis. If the symptom is corrected by the supply of the particular mineral. Then it is concluded that the deficiency was because of that mineral.
What are the steps involved in formation of root nodule
Steps of root nodules :
(1) Rhizobium bacteria makes contact with a susceptible root hair and divide near it.
(2) After successful infection of the root hair causes the root hair curls,
(3) Infected thread carries the bacteria to the inner cortex. The bacteria modifies into rod-shaped bacteroids and cause inner cortical and pericycle cells to divide. Division and growth of cortical and pericycle cells lead to the nodule formation,
(4) A mature nodule forms with vascular tissues continuous with those of the root.
Explain with examples: macronutrients, micronutrients, beneficial elements, toxic elements and essential elements.
Macronutrients - Those nutrients that are needed by the plants in large quantities are known as macronutrients. They are generally present in the plant tissues in large amounts i.e. in excess of 10 mmole Kg-1 of dry matter. For e.g - carbon, hydrogen etc.
Micronutrients - Are the elements which are needed by the plants in very small quantities i.e less than 10 Kg-1 of dry matter. For e.g. zinc, boron etc.
Beneficial elements - The elements are plant nutrients that may not be essential, but are beneficial to plants. For e.g/ - Selenium is beneficial to higher plants.
Toxic elements: Micronutrients are required by plants in small quantities. An excess of these nutrients may induce toxicity in plants. For example, when manganese is present in large amounts, it induces deficiencies of iron, magnesium, and calcium by interfering with their metabolism.
Essential element - The elements that are absolutely necessary for plant growth and reproduction. The requirement of these elements is specific and non-replaceable. For example carbon, magnesium , phosphorous , zinc etc.
In which of the following, all three are macronutrients
-
Iron, copper, molybdenum
-
Molybdenum, magnesium, manganese
-
Nitrogen, nickel, phosphorous
-
Boron, zinc, manganese
C.
Nitrogen, nickel, phosphorous
Option c is the most appropriate as it has two macronutrients.
The first stable product of fixation of atmospheric nitrogen in leguminous plants is
-
NO2-
-
ammonia
-
NO3-
-
glutamate
B.
ammonia
The process of conversion of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia is termed as nitrogen fixation.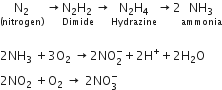
In reductive animation, ammonia reacts with alpha-ketoglutaric acid and forms glutamic acid alpha-ketoglutaric acid +NH4+ +NADPH
During biological nitrogen fixation inactivation of nitrogenase by oxygen poisoning is prevented by
-
Leghaemogolobin
-
Xanthophyll
-
Carotene
-
Cytochrome
A.
Leghaemogolobin
During biological nitrogen fixation, inactivation of nitrogenase by oxygen poisioning is prevented by leghaemoglobin.
It is a red-pigment that is filled outside the peribacteroid space in the cytosol of nodule cells. It has the ability to combine very rapidly with oxygen and thus acts a very efficient O2 scavenger.
Best defined function of manganese in green plants is
-
Photolysis of water
-
Calvin cycle
-
Nitrogen fixation
-
Water absorption
A.
Photolysis of water
Photolysis of water requires light energy, an Oxygen-Evolving Complex (OEC) and electron carrier 1/2. OEC complex was formerly called Z-enzyme. It has four Mn ions. Light energy brings about changes in Mn (Mn+2, Mn3+, Mn+4) which helps in removing electrons from OH- component of water forming oxygen. Liberation of oxygen also requires Cl- and Ca+2.
Consumption of which one of the following foods can prevent the kind of blindness associated with vitamin ‘A’ deficiency?
-
‘Flaver Savr’ tomato
-
Canolla
-
Golden rice
-
Bt-Brinjal
C.
Golden rice
Golden rice is a variety of Oryza sativa (rice) produced through genetic engineering to biosynthesize Beta-acetone, a precursor of vitamin-A in the edible part of rice (i.e., endosperm). The research that led golden rice was conducted with the goal of helping children who suffer from vitamin-A deficiency. Because many children in countries where there is a dietary deficiency in vitamin-A rely on rice as a staple food, the genetic modification of rice to produce the vitamin-A precursor beta-carotene is seen as a simple and less expensive alternative to vitamin supplements.
For its action, nitrogenase requires
-
high input of energy
-
light
-
Mn2+
-
super oxygen radicals
A.
high input of energy
The enzyme nitrogenase is a Mo-Fe protein and catalyses the conversion of atmospheric N2 to NH3 as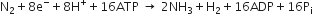
Enzyme nitrogenase functions under anaerobic condition and the pigment leghaemoglobin protect it from oxygen.
Minerals known to be required in large amounts for plant growth include
-
phosphorus, potassium, sulphur, calcium
-
calcium, magnesium, manganese, copper
-
potassium, phosphorus, selenium, boron
-
magnesium, sulphur, iron, zinc
A.
phosphorus, potassium, sulphur, calcium
Minerals known to be required in large amounts for plant growth are macronutrients. According to question, option (a) is correct, i.e., phosphorus, potassium, sulphur, calcium.
Macronutrients are consumed in large quantities and are required for plant tissue from 0.2% to 0.4% (on dry matter weight basis). Following are the rest of the macronutrients as:
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, magnesium, silicon.
Which one of the following elements in plants is not remboilised?
-
Calcium
-
Potassium
-
Sulphur
-
Phosphorus
A.
Calcium
An element like calcium are a part of a structural component of the cell and hence, are not released. The deficiency symptoms tend to appear first in the young tissue whenever the elements are not demobilised.
Which one of the following is not an essential mineral elements for plants while the remaining three are?
-
Iron
-
Manganes
-
Cadmium
-
Phosphorus
C.
Cadmium
Cadmium is not essential elements to plants
An element playing important role in nitrogen fixation is
-
Molybdenum
-
copper
-
manganese
-
zinc
A.
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is absorbed as molybdate by plants. It is involved in nitrogen metabolism including nitrogen fixation. It is a component of enzyme nitrogenase and acts as an enzyme activator. Its deficiency cause chlorosis and necrosis, whiptail of cauliflower and premature leaf fall.
Copper is absorbed by the plant in ionic form. Its deficiency causes necrosis, die back in Citrus, reclamation in legumes.
Manganese is absorbed by the plants as a bivalent ion. It acts as the enzyme activator. Its deficiency causes interveinal chlorosis as well as yellowing of starch and their subsequent degenerate.
Zinc is needed for biosynthesis of IAA and also acts as the enzyme activator. Its deficiency causes chlorosis, little leaf, rosette, the white bud of maize and mottling of leaves.
which one of the following is not a micronutrient?
-
Molybdenum
-
Magnesium
-
Zinc
-
Boron
A.
Molybdenum
The essential elements, which are required by plants in comparatively large amounts are called as macro elements, e.g, C,H, O, N, P,K,Ca,S,Mg,Fe. The elements, which are required in very small amount by the plants are called micro elements, e.g, Zn, Mn, B, Cu, Mo and Cl
The free-living, anaerobic nitrogen - fixer is
-
Beijerinckia
-
Rhodospirillum
-
Rhizobium
-
Azotobacter
B.
Rhodospirillum
Rhodospirillum is free - living, anaerobic, nitrogen fixer. Both Beijerinckia and Azotobacter are free-living, nitrogen - fixing, aerobic microbes. Rhizobium is a symbiotic, nitrogen-fixer.
Leguminous plants are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen through the process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Which one of the following statement is not correct during the process of nitrogen fixation?
-
Leghaemoglobin scavenges oxygen and is pinkish in colour
-
Nodules act as a site for nitrogen fixation
-
The enzyme nitrogenase catalyse the conversion of atmospheric N2 to NH3
-
Nitrogenase is insensitive to oxygen
D.
Nitrogenase is insensitive to oxygen
Root nodules of leguminous plants harbour symbiotic bacteria, Rhizobium, which fixes atmospheric nitrogen and provides the plant with most or all of its nitrogen requirements. In return, they have access to a rich supply of carbohydrate. The fixation of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) occurs within the nodules, using the enzyme nitrogen cut this enzyme is very sensitive to oxygen and gets inhibited in oxygen rich environment. This problem is solved by leghaemoglobin, a pinkish-red, oxygen-binding, iron-containing protein present in root nodules. It functions as oxygen buffer, scavenges oxygen and provides the enzyme nitrogenase, a low oxygen environment in which nitrogen fixation can occur.
Manganese is required in
-
nucleic acid synthesis
-
plant cell wall formation
-
photolysis of water during photosynthesis
-
chlorophyll synthesis
C.
photolysis of water during photosynthesis
In plants, manganese is absorbed in the form of manganous ions (Mn2+). It activates many enzymes involved in photosynthesis, respiration and nitrogen metabolism. The best-defined function of manganese is in the splitting of water to liberate oxygen during photosynthesis, ie, photolysis of water.
Which of the following is a symbiotic nitrogen fixer?
-
Glomus
-
Azotobacter
-
Frankia
-
Azolla
C.
Frankia
Casuarina tree has nitrogen-fixing root nodules that harbour a filaments streptomycete like symbiotic nitrogen-fixing organism, called Frankia.
Nitrogen-fixation in root nodules of Alnus is brought about by
-
Bradyrhizobium
-
Clostridium
-
Frankia
-
Azorhizobium
C.
Frankia
Nitrogen is the most critical element. The atmosphere is the greatest reservoir of nitrogen. Molecular nitrogen cannot be utilised directly by plants. It has to be fixed or converted into compounds prior to utilisation. symbiotic nitrogen fixation is accomplished by Rhizobium species, which occurs on the roots of leguminous plants. Certain non-leguminous plants also form nodules to fix nitrogen. The best-known example in the temperate region is alder (Alnus sp.). The bacteria involved in nodule formation is an Actinomycetes, the frankia.
Clostridium is anaerobic saprotrophic free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Bradyhizobium is symbiont in plants of parasponia and soybean.
The azohizobium forms both stem and root nodules in Sesbania (aquatic plant).
The two subunits of ribosome remain united at a critical ion level of
-
Copper
-
Manganese
-
Manganese
-
calcium
C.
Manganese
Magnesium is required in leaves, growing areas of root and stem protein synthesis hence, withdrawn from ageing. It is a constituent of chlorophyll, middle lamella, and connects with phosphate transfer in respiration, binding of ribosomes and DNA and RNA synthesis.
Manganese activates enzymes of respiration, photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism performing oxidation, reduction decarboxylation. photolysis of water etc.
Copper is an activator of plastocyanin cytochrome oxidase, RuBP carboxylase and many other enzymes. It functions in electron transfer, maintenance of carbohydrate/nitrogen balance, chlorophyll synthesis etc.
Calcium is a constituent of middle lamella, an activator of enzymes connected with chromosome formation and many aspects of metabolism.
Which one of the following elements is not an essential micronutrient for plant growth?
-
Mn
-
Zn
-
Cu
-
Ca
D.
Ca
Ca is essential macronutrient for plant growth. It is constituent of middle lamella, activator of enzymes, connected with chromosome formation and many aspects of metabolism
Examination of blood of a person suspected of having anaemia, shows large, immature, nucleated erythrocytes without haemoglobin. Supplementing his diet with which of the following is likely to alleviate his symptoms?
-
Thiamine
-
Folic acid and cobalamine
-
Riboflavin
-
Iron compounds
D.
Iron compounds
Anaemia refers to any condition in which there is an abnormally low haemoglobin concentration and/or blood cell count. The most common cause is deficiency of iron which is an essential element of haemoglobin molecule.
Thus, the iron compounds in the diet will help to alleviate the symptoms of anaemia.
Thiamine (vitamin B1), deficiency causes beri-beri.
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) deficiency causes cheilosis and skin diseases.
Sulphur is an important nutrient for optimum growth and productivity in
-
pulse crops
-
cereals
-
fibre crops
-
oilseed crops
A.
pulse crops
Sulphur is constituent of certain amino acids. The amino acids form the protein by polymerisation. The pulses are rich in protein.
The first stable product of fixation of atmospheric nitrogen in the leguminous plant is
NO2-
ammonia
NO3-
glutamate
B.
ammonia
The fixation of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia is given as
The process in which atmospheric nitrogen rates concerted into inorganic nitrogenous (nitrate, ammonia) compounds through microorganisms is called biological nitrogen fixing.
Macromolecule chitin is
Nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
Phosphorous containing polysaccharide
Sulphur containing polysaccharide
Simple polysacchaaride
A.
Nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
Macromolecules chitin is an example of complex structural hetero plysaccharide. It has nitrogen-containing glucose derivatives such as N-acetyl glucosamine.
Following are the two statements regarding the origin of life.
- The earliest organisms that appeared on the earth were non-green and presumably an aerobes.
- The first autotrophic organisms were the chemoautotrophs that never released oxygen of the above statements which on of the following options is correct?
II is correct, but I is false
Both I and II are correct
Both I and II are false
I is correct, but II is false
B.
Both I and II are correct
The earliest organisms that appeared on earth were anaerobic chemoautotrophs. Chemoautotrophs were the first autotrophic organisms. They were unable to perform photolysis of water and never released oxygen, e.g. sulphur bacteria
The structures present in the roots to absorb water and minerals is
Epidermal extensions
Hypodermis
Endodermis
Epidermal appendages
A.
Epidermal extensions
Epidermal extensions are always unicellular, while epidermal appendages may be uni or multicellular. Root hairs are epidermal extensions formed by outward elongated bulging of a wall of epidermal cells.
Sponsor Area
Nitrogen-fixation in root nodules of Alnus is brought about by
Bradyrhizobium
Clostridium
Frankia
Azorhizobium
C.
Frankia
Nitrogen is the most critical element. The atmosphere is the greatest reservoir of nitrogen. Molecular nitrogen cannot be utilized directly by plants. It has to be fixed or converted into compounds prior to utilization, Symbiotic nitrogen fixation is accomplished by Rhizobium species, which occurs on the roots of leguminous plants. Certain non-leguminous plants also form nodules to fix nitrogen. The best known example in temperate region is alder (Alnus sp.). The bacteria involved in nodule formation is an Actinomycetes, the Frankia.
Clostridium is anaerobic, saprotrophic, free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Bradyrhizobium is symbiont in plants of parasponia and soyabean.
The Azorhizobium forms both stem and root nodules in Sesbania (aquatic plant).
Many elements are found in living organisms either free or in form of compounds. One of the following is negligible is living organisms
Silicon
Magnesium
Iron
Sodium
A.
Silicon
Silicon is a micronutrient/trac element which is found only in few organisms.
Which of the following is non-symbiotic nitrogen fixer organism?
VAM
Azotobacter
Anabaena
Rhizobium
B.
Azotobacter
Anabaena, Nostoc and Aulosira are symbiotic Rhizobium Nitrogen fixing microbes, while.
Which of the following is responsible for biological nitrogen-fixation?
Nife gene
Nitrogenase
Yeast alanin tRNA synthetase
RNA synthetase
A.
Nife gene
VAM is a symbiotic relationship between fungi and higher plants. Nif gene is responsible for biological nitrogen fixation, which directs the synthesis of the nitrogenase enzyme.
‘Sun basket’ is
The device to utilize sun rays directly to meet the requirement of heat energy
The sufficient amount of sunlight stored in a cell
A device of taking a sunbath
All of the above
B.
The sufficient amount of sunlight stored in a cell
Green plants are called sun basket because they store solar energy by converting it into chemical energy with the help of chloroplast by the process called photosynthesis.
Chlorosis is produced in the leaves due to the deficiency of Fe, Mg, Mn, S or N of these essential elements, those that are exclusive constituents of chlorophyll molecule are
Fe, S
N,S
Mg, S
Mg, N
D.
Mg, N
Magnesium is present in the central position of tetrapyrrole ring of the chlorophyll molecule. Porphyrin is a cyclic tetrapyrrole ring made up of four nitrogen-containing pyrrole rings arranged in a cyclic fashion in the chlorophyll molecule.
Heterocysts are present in
Riccia
Ulothrix
Albugo
Nostoc
D.
Nostoc
Heterocysts are modified vegetative cells specified for nitrogen fixation. These are found in blue-green algae, e.g., Nostoc.
A plant requires magnesium (Mg) for
Holding cells together
Protein synthesis
Chlorophyll synthesis
Cell wall development
C.
Chlorophyll synthesis
Magnesium is an important constituent of chlorophyll molecule.
Which is essential for root hair growth?
Zinc
Calcium
Molybdenum
Sulphur
B.
Calcium
| Element | Essential for |
| Zinc | Auxin synthesis |
| Calcium | Root hair growth |
| Molybdenum | Nitrogen fixation |
| Sulphur | Protein synthesis |
Molybdenum causes
mottling
wilting
reclamation
chlorosis
A.
mottling
Molybdenum causes mottling because of this element deficiency results in sulfite toxicity. Appearance of green and non- green patches.
Hydroponics is a
soilless culture
airless culture
waterless culture
none of these
A.
soilless culture
Hydroponics refers to soil-less cultures of plants and growing them on mineral solution
Lathyrism is caused by
dal
moth dal
khesari dal
Glycine
C.
khesari dal
Lathyrism is a neurological disease causd by khesari dal (Lathyrus odoratus). It carries an ODAP, also known as β-N-oxalyl-amino-L-alanine, or BOAA which is a neurotoxin (glutamate analogue).
The enzyme responsible for atmospheric nitrogen fixation is
nitrogenase
hydrogenase
oxygenase
carboxylase
A.
nitrogenase
Enzyme nitrogenase plays a key role in N, fixations and remains active only during anaerobic condition. It is made up of two protein subunits :
i) non-heme iron protein or Fe-protein or dinitrogen reductase.
ii) Iron molybdenum protein or Mo-Fe protein or dinitrogenase
Insects captured by insectivorous plants fulfil their requirements of
enzymes
oxygen
nitrogen
water
C.
nitrogen
The insectivorous plants grow in nitrogen deficient soil and their nitrogen requirement is fulfilled by capturing and digesting the insects.
The deficiencies of micro-nutrients, not only affects growth of plants but also vital functions such as photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron flow. Among the list given below, which group of three elements shall affect most, both photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron transport ?
Cu, Mn, Fe
Co, Ni, Mo
Mn, Co, Ca
Ca, K, Na
A.
Cu, Mn, Fe
Micronutrients are minerals obtained from the soil and present in plant tissues at concentrations usually less than 3 mol g-1 dry matter. Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn) and Iron (Fe) are the micronutrients which affect both photosynthesis and mitochondrial electron transport as they are the main constituents of various electron carriers.
The non- photosynthetic, non- symbiotic N2 fixing bacteria are
Rhodobacter
Spirillum
Azotobacter
All of these
C.
Azotobacter
Azotobacter, Beijerinkia are non photosynthetic, non symbiotic and aerobic nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Clostridium is free living, anaerobic nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Which of the following element plays an important role in nitrogen fixation
Zinc
Molybdenum
Manganese
Copper
B.
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a component of nitrogenase and thus brings about fixation of gaseous nitrogen. It also act as enzyme activator of nitrate reductase.
Which one of the following elements is almost non-essential for plants?
Ca
Mo
Zn
Na
D.
Na
Sodium and Iodine are not required by most of the plants.
Sodium (Na) is required by very limited plants as it helps to concentrate carbon- dioxide, but mostly plants use a trace amount to produce metabolism.
Which of the following genera is associated with coralloid roots?
Cycas
Taxus
Pinus
Sequoia
A.
Cycas
Roots in Cycas are of two types- normal and coralloid roots. Coralloid roots are irregular, negatively geotropic, dichotomously branched coral like roots which do not possess root hairs and root caps. Coralloid roots have a symbiotic association with blue-green algae like Nostoc and Anabaena species
Which of the following is a group of micronutrients for plants?
Fe, Mn, Cu, Mo, Zn
Fe, Mn, Cu, O, C
Cu, B, Cl, Fe, Ca
Ca, Mg, Fe
A.
Fe, Mn, Cu, Mo, Zn
Micronutrients or trace elements are needed in very small amounts (less than 10 m mole kg-1 of dry matter). These are 8 in number and include Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Copper (Cu), Molybdenum (Mo), Zinc (Zn), Boron (B), Chlorine (Cl) and Nickel (Ni).
Assertion: Nitrogen is one of the most essential elements of human body.
Reason: All types of prokaryotic organisms are able to fix nitrogen.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
Nitrogen is one of the most essential elements of human body. It is a constituent of a number of organic compounds like amino acids, proteins, nucleotides, nucleic acids, many vitamins, hormones etc. Biological N2 fixation is a very important natural process which is performed by two types of prokaryotes - bacteria and cyanobacteria. They include both free living and symbiotic forms.
Assertion: Soil particles, particularly clay and organic matter in soil, contain negative charges that attract positively-charged ions such as Ca2+, K+ and Mg2+.
Reason: Essential elements derived from soil are termed as mineral elements while those derived from air or water are known as nonmineral elements.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Mineral nutrients are absorbed by plants primarily in ionic form from the soil while non-mineral nutrients are absorbed either from the soil or from the atmosphere as a component of compounds.
Assertion : Atmospheric nitrogen gas is always fixed by nitrogen-fixing micro-organisms.
Reason : Decomposers release nitrogen gas from dead bodies of plants and animals.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
D.
If both assertion and reason are false
Nitrogen fixation is a process by which nitrogen in the Earth's atmosphere is converted into ammonia (NH3) or related nitrogenous compounds. Nitrogen- fixing bacteria is a micro- organisms which is capable of transforming atmospheric nitrogen into fixed nitrogen. More than 90 percent of all nitrogen fixation is effected by these organisms, which thus play an important role in the nitrogen cycle. Decomposers are the organisms that break down dead or decaying organisms. They use organic substrates in order to obtain their energy, carbon and nutrients for growth and development.
Which of the following is used as a best genetic vector in plants?
Bacillus thurengiensis
Agrobacterium tumifaciens
Pseudomonas putida
All of the above
B.
Agrobacterium tumifaciens
Agrobacterium tumifaciens is used as a best genetic vector in plants.
Which of the following sugars is not plants?
sucrose
glucose
lactose
fructose
C.
lactose
Sucrose, Glucose and Fructose are found in plants. Sucrose is the commercial sugar which is obtained from sugarcane. Glucose is the main respiratory substrate in plants and animals. Fructose is commonly known as fruiting sugar. Lactose or milk sugar is found in sugar. It is the reducing sugar which is formed in the mammary glands of mammals through condensation of two hexose molecules.
Which one of the following is not a microelement for plants?
Cu
B
Zn
Cr
D.
Cr
Plants require many organic and inorganic nutrients to complete their life-cycle. It has been established that some elements are required by plants in relatively large amount and are called major elements or macronutrients, e.g., Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Sulphur (S), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg).
Microelements or minor elements or trace elements are required by plants in very small amount, less than 1 ppm. eg. Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Boron (B), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn), Molybdenum (Mo), Chlorine (Cl). Thus Chromium (Cr) is not a microelement.
Which of the following is correct set of micronutrient for plants?
Mg, Si, Fe, Cu, Ca
Cu, Fe, Zn, B, Mn
Mg, Fe, Zn, B, Mn
Mo, Zn, Cl, Mg, Ca
B.
Cu, Fe, Zn, B, Mn
Plants require nutrients for proper growth and development. There are 16 elements which are required for plant and are termed as essential elements. They are as follows:
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Sulphur (S), Potassium (K), Magnesium (Mg), Calcium (Ca), Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Boron (B), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn), Molybdenum (Mo) and Chlorine (Cl).
The essential elements are categorised into 2 groups,
- Macro- nutrients: These are required by plants in large quantities. eg, C, H, O, N, S, P, K, Ca and Mg.
- Micro- nutrients: These are required by plants in very small quantities. eg, Fe, Cu, B, Mn, Ni, Mo and Cl.
Hydroponics is
nutrient less culture
water less culture
soilless culture
none of these
C.
soilless culture
Hydroponics is a subset of hydroculture, which is a method of growing plants without soil by using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent. It is useful in areas having thin, infertile and dry soils. They conserve water. It can regulate pH optimum for a particular crop, control soil borne pathogens, avoid problems of weeding and obtain consistently better yield.
Leghaemoglobin helps in
imparting colour to floral petals
protecting nitrogenase from O2
destroying bacteria
transport of food in plants
B.
protecting nitrogenase from O2
Leghaemoglobin is a pinkish pigment present inside the root nodules of nitrogen fixing plants like legumes. It is an oxygen scavenger and is related to blood pigment haemoglobin. It protects nitrogen fixing enzyme nitrogenase from oxygen. The most important bacteria present inside the nodules is Rhizobium.
Which among the following is a rootless plant?
Nymphaea
Sagittaria
Ceratophyllum
Vallisneria
C.
Ceratophyllum
All the given options are hydrophytes in nature which grow in extremely wet or watery conditions. But among them only in Ceratophyllum roots are completely absent even in embryonic stage. They remain under water completely Nymphaea is a rooted hydrophyte with floating leaves.
Vallisneria is rooted submerged hydrophyte and Sagittaria is rooted emergent hydrophyte.
Assertion : Plants absorb sulphur in the form of sulphate ions.
Reason : Sulphur bacteria are required for the formation of sulphate.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Organic sulphur is made available to the plant through biological oxidation through the activity of certain microorganisms. Sulphur is transformed from the organic form to the sulfate ion, the form of sulphur that higher plants absorb. Soil microorganisms oxidize not only organic sulphur but also sulphide minerals such as ferrous sulphide. The elemental sulphur is then oxidized to sulphate by sulphur bacteria.
The function of leghaemoglobin during biological nitrogen fixation in root nodules of legumes is to
convert atmospheric N2 to NH3
convert ammonia to nitrite
transport oxygen for activity of nitrogenase
protect nitrogenase from oxygen
D.
protect nitrogenase from oxygen
Rhizobium is the nitrogen fixing bacteria present in root nodules of leguminous plants. Roots of a legume secrete chemical attractants flavonoids and betaines. Bacteria collect over the root hairs, release nod factors that causes curling of root hairs around the bacteria, degradations of cell wall and formation of an infection thread enclosing bacteria. The infected cortical cells differentiate and start dividing. It produces swelling of nodules and the infected cells enlarge. Bacteria stop dividing and form irregular polyhedral structures called bacteroids. The host cells develops a pinkish coloured pigment called leghaemoglobin. It is an oxygen scavenger and protects nitrogenase from oxygen. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation requires co-operations of 'Nod' genes of legumes, 'nod' 'nif' and 'fix' genes of bacteria.
Assertion: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in legume root nodules survive in oxygen-depleted cells of nodules.
Reason: Legheamoglobin completely removes oxygen from the nodule cells.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Symbiotic hemoglobin (leghemoglobin) is a hemeprotein found in micromolar concentrations in infected cells of legume roots. This is an essential component for nitrogen fixation by legumes. Leghemoglobin is produced as a result of symbiotic association between bacteroid and plant.
Nif genes occur in
Rhizobium
Aspergillus
Penicillium
Streptococcus
A.
Rhizobium
The nif genes are genes encoding enzymes involved in the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen into a form of nitrogen available to living organisms. The primary enzyme encoded by the nif genes is the nitrogenase complex which is in charge of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to other nitrogen forms such as ammonia which the organism can use for various purposes. Besides the nitrogenase enzyme, the nif genes also encode a number of regulatory proteins involved in nitrogen fixation. The nif genes are found in both free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria and in symbiotic bacteria associated with various plants.
The 'Repeating Unit' of glycogen is
fructose
mannose
glucose
galactose
C.
glucose
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in humans, animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
VAM is
symbiotic bacteria
saprophytic bacteria
saprophytic fungi
symbiotic fungi
D.
symbiotic fungi
The symbiotic relationship between fungal hyphae and root of higher plant is known as mycorrhiza.
Endomycorrhiza (also called VAM) occurring in about 80% of vascular plants. In this association the penetrating hyphae form finely branched haustorial branches or coils vesicles.
The first stable product of fixation of atmospheric nitrogen in leguminous plants is
NO2-
ammonia
NO3-
glutamate
B.
ammonia
The process of conversion of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia is termed as nitrogen fixation.
(Nitrogen) N2 (Dimide) N2H2 (Hydrazine) N2H4 (Ammonia) 2NH3
2NH3 + 3O2 2NO-2 + 2H+ + 2H2O
2NO2 + O2 2NO-3
In reductive animation ammonia reacts with -ketoglutaric acid and forms glutamic acid
- ketoglutaric acid + NH+4 + NADPH Glutamate + H2O + NADP
Natural reservoir of phosphorus is
sea water
animal bones
rock
fossils
C.
rock
The natural reservoir of phosphosus is rock, which contains phosphorus in the form of phosphates. Sea water, animal bones and fossils are reservoir of carbon.
Nitrogenase enzyme is a
magnesium-iron protein
molybdenum-iron protein
iron-copper protein
nickel-iron protein
B.
molybdenum-iron protein
Biological nitrogen fixation is catalyzed by nitrogenase, an enzyme composed of two component proteins called the Fe protein and the Mo-Fe protein. It is found in certain bacteria and blue-green algae. Some of these bacteria are free-living while others are symbiotic. It catalyses the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, the first stable product of nitrogen fixation. It is highly sensitive to the molecular oxygen.
Necrosis (die-back) ofthe tip of young leaves is caused due to the deficiency of
iron
manganese
zinc
copper
D.
copper
Read the following deficiency symptoms of micronutrients in plants.
I. Loosening of inflorescence in Cauliflower.
II. Apical necrosis of young leaves (reclamation disease).
III. Bronze colour in leaves
IV. Upper half a lamina falls down (whiptail disease)
V. Legume cotyledons with brownish spots (marsh spot disease)
Pick out the symptoms caused by the deficiency of molybdenium and choose the correct option.
II, IV and V
I, III and IV
III and II
I and IV
D.
I and IV
Molybdenum is a micronutrient found everywhere in plants more commonly in roots. Its major functions include nitrogen metabolism, ascorbic acid synthesis and oxidation reduction reaction. Its deficiency causes mottled chlorosis with marginal necrosis, whiptail diseases, etc.
Which of the following is correctly matched for the deficiency symptom produced by them?
Molybdenum - Disturbance in iron metabolism
Sodium - Interfere with healthy growth of nails and hair
Protein - Convulsions and hallucinations
Riboflavin - Beri beri
A.
Molybdenum - Disturbance in iron metabolism
Molybdenum is the part of several enzymes essential for the synthesis of haemoglobin and absorption of iron. Its deficiency leads to disturbance in iron metabolism, which affects growth of the body.
Heterocysts in Anabaena is helpful in
secondary growth
nitrogen-fixation
ion uptake
gaseous exchange
B.
nitrogen-fixation
Anabaena is free living filamentous cyanobacteria that contains many vegetative cells, which are photosynthesis and a few thick walled cells heterocytes. The latter does not contain any photosynthetic pigments and acts as the site of nitrogen-fixation.
The statement given below are the deficiency symptoms of a certain element. Identify the element with the help of options that follow.
I. Stunted growth
II. Tissue necrosis
III. Curling appear first in young leaves
IV. Premature flower abscission
Choose the correct option
magnesium
boron
calcium
nitrogen
C.
calcium
Calcium deficiency symptoms appear initially as localized tissue necrosis leading to stunted plant growth, necrotic leaf margins on young leaves or curling of the leaves, and eventual death of terminal buds and root tips. The major function of this element are
(i) selective permeability of cell membrane
(ii) organisation of mitotic spindle
(iii) metabolism
(iv) meristematic activity
The nitrifying bacteria that convert the ammonia to nitrates are
Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter
Azotobacter
Rhizobium sp.
Thiobacillus denitrificans
A.
Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter
Nitrification is the phenomenon of conversion of ammonium to nitrate by nitriflying bacteria like Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter, etc. It occurs in two steps-
2NH3 + 3O2 2NO-2 + 2H+ + 2H2O + Energy
2NO-2 + O2 2NO-3 + Energy
Insectivorous plant is
Cuscuta
Drosera
Striga
None of the above
B.
Drosera
Drosera (an insectivorous plant) found in nitrogen poor habitats capture the animals as a source of nitrogen.
Nodules with nitrogen-fixing bacteria are found in
cotton
gram
mustard
wheat
B.
gram
Leguminous plants such as grams, beans, peas soyabeans, peanuts, alfalfa and clover contain root nodules. Later are formed due to symbiotic association between roots of leguminous plane and bacterium Rhizobium. The plants furnish anaerobic conditions and growth nutrients for the bacteria and the bacteria fix nitrogen to the plant.
Mycorrhiza is an example of
endoparasitism
decomposers
symbiotic relationship
ectoparasitism
C.
symbiotic relationship
Mycorrhiza is a resultof symbiosis between the roots of higher plants and fungi. In this association, plants provide space and prepared food material to fungi in exchange of this, fungi help in absorption of minerals and water to plants.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





