Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 11 Political%25252bscience Biology
What are the difficulties that you would face in classification of animals, if common fundamental features are not taken into account?
The difficulties that one would face in classification of animals if common fundamental features are not taken into account are as following:
(i) Animal kingdom consists of a large number of organisms. If the common fundamental characteristics are not considered for classification, each organism will have to be placed in a different group. Thus, the study of the organisms would become nearly impossible and it would be very tough.
(ii) Without common fundamental features, it would be very difficult to segregate the organisms into groups.
(iii) Without segregation into groups, comparing different organisms and judging their individual evolutionary significance would be difficult. We would not be able to deduce the evolutionary relationship.
If you are given a specimen, what are the steps that you would follow to classify it?
The steps that we would follow to classify the given specimen will be
(i) First we would classify the specimen according to the level of organisation. The animals can be classified into Cellular and Tissue/Organ level.![]()
(ii) The second criteria for classification would be on the basis of the body symmetry i.e. whether the specimen is of radial symmetry of bilateral symmetry.![]()
(iii) The third classification would be on the basis of the body cavity or coelom. Wheteher the body cavity is present or absent. And whether the coelom is acoelom, pseudocoelom or true coelom![]()
![]()
(iv) The specimen would be classified on the basis of the arrangement or the number of the layers into diploblastic or triploblastic.
(v) The specimen would then be classified on the basis of the presence or the absence of notochord.
How useful is the study of the nature of body cavity and coelom in the classification of animals?
Coelom is the body cavity which is lined by a mesoderm. The presence or absence of body cavity or coelom plays a very important role in the classification of animals.
Animals that having a cavity between body wall and digestive tract are known as coelomates for eg. annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinodermates, and chordates etc.
The animals in which the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm are known as pseudocoelomates. In such animals, mesoderm is scattered in between ectoderm and endoderm. Aschelminthes is an example of pseudocoelomates.
Animals in which the body cavity is absent are known as acoelomates For e.g platyhelminthes.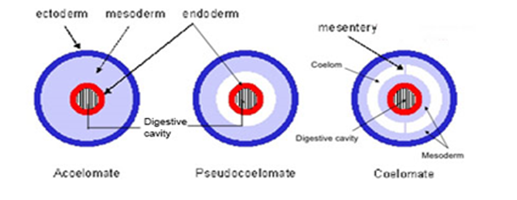
Distinguish between intracellular and extracellular digestion?
|
Intracellular digestion |
Extracellular digestion |
|
Digestion takes place inside the cell. |
Digestion takes place outside the cell |
|
Enzymes are secreted into the food vacuole |
Enzymes are secreted into the digestive cavity. |
|
Less efficient |
More efficient |
|
Found in unicellular animals |
Found in multicellular organisms |
What is the difference between direct and indirect development?
|
Direct development |
Indirect development |
|
In this the embryo develops into a mature individual without involving a larval stage. |
Indirect development encompasses a larval stage that undergoes a metamorphic transition into a juvenile. |
|
Metamorphosis is absent. |
Metamorphosis is present. |
|
It occurs in fishes, reptiles, birds, and mammals |
It occurs in most of the invertebrates and amphibians. |
What are the peculiar features that you find in parasitic platyhelminthes?
Parasitic platyhelminthes have the following peculiar features:
1. They have dorsiventrally flattened body and bear hooks and suckers to attach inside the body of the host. They can absorb nutrition from the host directly through the body surface.
2. Their body is covered with thick covering to protect them from the action of digestive juices of the host.
What are the reasons that you can think of for the arthropods to constitute the largest group of the animal kingdom?
The phylum, Arthropoda, consists of more than two-thirds of the animal species on earth. The reasons for the success of arthropods are as follows.
(i) Jointed legs that allow more mobility on land.
(ii) Hard exoskeleton made of chitin that protects the body from the harsh conditions.
(iii) The hard exoskeleton also reduces water loss from the body making them more adapted to terrestrial conditions.
(iv) The fertilisation is internal which provides protection to the progeny from the external harsh conditions.
Water vascular system is the characteristic of which group of the following:
Porifera
Ctenophora
Echinodermata
Chordata
C.
Echinodermata
Echinodermata it consists of an array of radiating channels, tube feet. The water vascular system helps in locomotion, food capturing and respiration.
“All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates”. Justify the statement.
Chordates are those animals which have a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord and paired pharyngeal gill slits. Chordates are sub classified into four other groups of which vertebrate is one subphyla.
However, Vertebrates are characterized by the presence of the notochord in the embryonic stage, which gets replaced by a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in adults.
Since the notochord is not replaced by the vertebral column in all the chordates, thus, it can be said that all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
How important is the presence of air bladder in Pisces?
Air bladder is a gas filled sac found in fishes. It is of great importance as it helps in maintaining buoyancy and helps them to ascend or descend and stay still in the water current. It is importance but there are organisms like Chondrichthyes which do not possess air bladder. Thus, the presence of the air bladder is not necessary in Pisces.
What are the modifications that are observed in birds that help them fly?
Birds have undergone many structural adaptations to suit their aerial life. Some of these adaptations are as follows:
(i) Streamlined body for rapid and smooth movement and to counter the resistance offered by the air current.
(ii) Covering of feathers for insulation.
(iii) Forelimbs modified into wings and hind limbs used for walking, perching, and swimming.
(iv) Presence of pneumatic bones to reduce weight.
(v) Presence of additional air sacs to supplement respiration.
(vi) Endoskeleton has hollow long bones to reduce weight that favors flying.
(vii) Uricotelic excretion that helps to reduce storage of water to reduce weight.
Could the number of eggs or young ones produced by an oviparous and viviparous mother be equal? Why?
The numbers of eggs produced by an oviparous mother will always be more than the young ones produced by a viviparous mother. This is because in oviparous animals, the development of young ones takes place outside the mother's body. Thus, their eggs are vulnerable because of the harsh environmental conditions and predators. Therefore, to overcome the loss, more eggs are produced by mothers so that even under harsh environmental conditions, some eggs are able to survive and produce young ones.
On the other hand, in viviparous organisms, the development of young ones takes place inside the body of the mother. Since the development takes place inside the body the young one is less exposed to environmental conditions and predators. Therefore, there are more chances of their survival and hence, less number of young ones is produced compared to the number of eggs.
Match the following:
| A. Operculum | (i) Ctenophora |
| B. Parapodia | (ii) Mollusca |
| C. Scales | (iii) Porifera |
| D. Comb plates | (iv) Reptilia |
| E. Radula | (v) Annelida |
| F. Hairs | (vi) Cyclostomata and Chondrichthyes |
| G. Choanocytes | (vii) Mammalia |
| H. Gill slits | (viii) Osteichthyes |
A. Operculum | (i) Osteichthyes |
B. Parapodia | (ii) Annelida |
C. Scales | (iii) Reptilia |
D. Comb plates | (iv) Ctenophora |
E. Radula | (v) Mollusca |
F. Hairs | (vi) Mammalia |
G. Choanocytes | (vii) Porifera |
H. Gill slits | (viii) Cyclostomata and Chondrichthyes |
Prepare a list of some animals that are found parasitic on human beings.
Liver fluke
Fasciola hepatica
Taenia solium
Ascaris lumbricoides
Wuchereria bancrofti
Ancyclostoma
Anopheles
Bedhug
Lice
Sponsor Area
Which of the following pairs of animals has non-glandular skin
Snake and Frog
Chameleon and Turtle
Frog and Pigeon
Crocodile and Tiger
B.
Chameleon and Turtle
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
In cockroaches and prawns excretion of waste material occurs through malpighian tubules.
In ctenophors, locomotion is mediated by comb plates.
In Fasciola flame cells take part in excretion
Earthworms are hermaphrodites and yet cross-fertilization takes place among them.
A.
In cockroaches and prawns excretion of waste material occurs through malpighian tubules.
Give an example of
a. Roundworm
b. Fish possessing poison sting
c. A limbless amphibia
d. An oviparous animal
a. Ascaris
b. Trygon
c. Ichthyophis
d. Platypus
Endoparasites are found inside the host body. Mention the special structures possessed by these to enable them to survive in those conditions.
The special structures possessed by endoparasites are as follows:
1. Hooks and suckers,
2. Dorsoventrally flattened body,
3. High reproductive potential,
4. Indirect development.
Fill up the blank spaces appropriately.
|
Phylum |
Excretory organ |
Circulatory organ |
Respiratory organ |
|
Arthropoda |
a |
b |
trachea |
|
c |
Nephridia |
closed |
skin |
|
vertebrata |
d |
closed |
lung |
|
Phylum |
Excretory organ |
Circulatory organ |
Respiratory organ |
|
Arthropoda |
a. Malphigian tubules, |
b Open |
trachea |
|
cAnnelida |
Nephridia |
closed |
skin |
|
vertebrata |
d. Kidney |
closed |
lung |
On a morning walk with your friend you came across an animal which looks like a snake. But on watching it closely, your friend says it is an earthworm. What helped him in identifying it as an earthworm?
The following characteristic helped to identify it as an earthworm
Body elongated and metamerically segmented, the presence of prostomium, characteristic mode of locomotion.
1.In order to eradicate mosquitoes Housing colony members were asked to keep the surroundings dry, not to let water standing any where and cover the drainage. It was found that the strategy worked and there was decline in the number of mosquitoes.What according to you is the reason for the decline in the number of mosquitoes.?
Mosquito belongs to class Insecta, phylum Arthropoda . Its development is indirect with distinct stages like egg, larva,pupa and adult. It breeds in water. Since water is not provided, it cannot complete its life cycle . This leads to the decline in the number of mosquitoes.
Ravi’s younger brother of class III stated that bats are like birds as they are able to fly.
How will you contradict him and make him understand that bats are mammals and not birds?
Flight is not only the criteria for classifying bat as birds. The features that bat has which prove that it is a mammal and not a bird are:
i. External ears
ii. Body covered with hairs and mammary glands.
iii. They have skin instead of feathers and mouth.
iv. They have teeth instead of the beak.
v. They do not lay eggs but give birth to young ones.
What is metagenesis? Mention an example which exhibits this phenomenon.
The cnidarians exhibit alternation of generations in which one generation is the Polyp form while the other is the Medusa form
What is the role of radula in molluscs?
The radula is a file-like rasping organ found in molluscs. It helps in scraping food. It also used for creating depression in rocks.
What is the importance of pneumatic bones and air sacs in Aves?
Pneumatic bones are hollow and hence are light weight. They help to reduce the weight and hence help the birds in flight. They also provide support.
Which group of chordates possess sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
Cyclostomata. They are also known as the jawless fish.
Sponsor Area
Give one example each of an animal possessing placoid scales and that with cycloid scales.
Placoid scale - are found in Scoliodon
Cycloid scale - are found in Rohu.
Name the animal, which exhibits the phenomenon of bioluminescence. Mention the phylum to which it belongs.
Pleurobrachia and Ctenoplana exhibit the phenomenon of bioluminescence. They belong to the phylum Ctenophora
Differentiate between
Open and Closed circulatory system
| Open Circulatory system | Closed circulatory system |
| 1. The blood flows in spaces called sinuses and cells and tissues are bathed in blood. | 1. The blood flows through a network of blood vessels |
| 2. Inefficient | 2. Efficient |
| 3. Found in Arthropoda and Mollusca | 3. Found in Annelida and mammals. |
Differentiate between
Oviparity and viviparity
| Oviparity | Viviparity |
| 1. The animals lay eggs and young ones hatch from them. | 1. Animals give birth to young ones. |
| 2. Found in reptiles and birds | 2. Found in Mammals |
Differentiate between
Direct and Indirect development
| Direct Development | Indirect Development |
| The youngs ones are completely different from their adult forms. | The young ones resemble their adult form. |
| Occurs in cockroach and frog | Occurs in birds, reptiles and mammals |
Differentiate between :
Acoelomate and Pseudocoelomate
| Acoelomate | Psedocoelomate |
| 1. The body cavity is absent | The mesoderm present is scattered in pouches and the cavity present is considered to be false. |
| Found in Platyhelminthes | Found in Aschelminthes |
Differentiate between
Polyp and Medusa
| Polyp | Medusa |
| Sessile and cylindrical | Motile, free-living and umbrella shaped |
| e.g Hydra | e.g Aurelia |
Differentiate between
Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes
| Chondrichthyes | Osteichthyes |
| They have cartiligionous endoskeleton | They have bony endoskeleton |
| They have placoid scales | They have cycloid scales |
| e.g Scoliodon | e.g Rohu |
Mention two similarities between
a. Aves and mammals
b. Frog and crocodile
c. Turtle and pila
The similarities between the two are:
a. Aves and mammals - They both are warm-blooded animals and have a four-chambered heart.
b. Frog and crocodile - Both can live on land as well as water. Both use lungs for breathing
c. Turtle and Pila - Both have a hard covering protecting their body. Both are oviparous.
Which of the following characteristic features always holds true for the corresponding group of animals?
Viviparous Mamalia Posess a mouth with an upper and lower jaw Chordata 3-chmbered heart with one incompletely divided ventricle Reptilia Cartiliginous- endoskeleton Chondrichthyes
C.
| 3-chmbered heart with one incompletely divided ventricle | Reptilia |
Except for crocodilians, which have a four-chambered heart, all reptiles have a three-chambered heart consisting of two atria and one ventricle. The chamber called the right atrium receives deoxygenated, or 'spent,' blood returning from the body tissues.
Which one of the following characteristics is not shared by birds and mammals?
-
Breathing using lungs
-
Viviparity
-
Warm-blooded nature
-
Ossified endoskeleton
B.
Viviparity
Mammals are viviparous while birds are oviparous.
Which of the following features is not present in the phylum-Arthropoda?
-
Metameric segmentation
-
Parapodia
-
Jointed appendages
-
Chitinous exoskeleton
B.
Parapodia
Parapodia are present in annelids.
Which of the following features is not present in Periplaneta americana?
-
Indeterminate and radical cleavage during embryonic development
-
Exoskeleton composed of N-acetylglucosamine
-
Metamerically segmented body
-
Schizocoelom as body cavity
A.
Indeterminate and radical cleavage during embryonic development
Cockroach has determinate cleavage during emembryonic development and it develops into nymph, which is a fully developed cockroach.
The eyes of Octopus and eyes of cat show different patterns of structure, yet they perform a similar function. This is an example of
-
homologous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
-
homologous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution
-
analogous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
-
analogous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution
C.
analogous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
The analogous organs are not anatomically similar structures through they perform similar structure though they perform similar functions, Hence, analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution different structures evolving for the same function and hence, having similarity.
Homologous organs developed along different due to adaptations to different needs. This is divergent evolution and the structures are homologous.
A senentary sea anemone gets attached to the shell lining of hermit crab. The association is
-
ectoparasitism
-
symbiosis
-
commensalism
-
amensalism
C.
commensalism
This type of mutualisn to called protocooperation. In this type, the sea anemone grows on the back of the hermit crab. It protects the crab with the help of its nematocysts. Ectoparasites live on the outside of host., e.g., Human body louse. In this interaction, the parasite gets the benefits at the expense of the host.
Commensalism is an association between organisms in which one or both the species are benefitted and neither species is harmed. In amensalism, one species is harmed whereas the other is unaffected. Predation parasitism and commensalism share a common characteristic, the interacting species live closely together.
A jawless fish, which lays eggs in fresh water and whose ammocoetes larvae after metamorphosis return to the ocean is:
-
Eptatretus
-
Myxine
-
Neomyxine
-
Petromyzon
D.
Petromyzon
Petromyzon(the lamprey) belongs to the section Agnatha of the sub-phylum-Vertebrata. They have long, greenish brown, cylindrical body with smooth scaleless, slimy skin, jawless mouth, etc. They lay eggs in freshwater but their ammocoete larvae(lower) after metamorphosis return to the ocean.
The chitinous exoskeleton of arthropods is formed by the polymerisation of
-
Keratin sulphate and chondraitin sulphate
-
D-glucosamine
-
N-acetyl glucosamine
-
lipoglycans
C.
N-acetyl glucosamine
The chitinous exoskeleton of arthropods is formed by the polymerisation of N-acetyl glucosamine, which is a derivative of glucose. It is also a characteristic component of the cell wall of fungi, the radulae of molluscs and the beaks and internal shells of cephalopods including squid and octopuses.
Metagenesis refers to
-
Presence of different morphic forms
-
Alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
-
Occurrence of a drastic change in form during post-embyonic development
-
Presence of a segmented body and parthenogenetic mode of reproduction
B.
Alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
Metagenesis is an organisation refers to the reproduction characterised by the alteration of a sexual generation and a generation that reproduces asexually, i.e., alternation of generations.
Five Kingdom system of classification suggested by RH Whittaker is not based on
-
presence or absence of a well-defined nucleus
-
mode of reproduction
-
Mode of nutrition
-
Complexity of body organisation
A.
presence or absence of a well-defined nucleus
RH Whittaker's classification is nor based on presence or absence of a well - defined nucleus. He gave five kingdom classification and used five criteria for delimiting kingdoms.
These are
both come under body organisation
(i) Complexity of cell structure
(ii) Complexity of body structure
(iii) Mode of nutrition
(iv) Ecological life cycle including mode of reproduction
(v)Phylogenetic relationship.
He divided organisms into five kingdoms as follows:
Kingdom - Monera
Kingdom - Protista
Kingdom - Fungi
Kingdom - Plantae
Kingdom - Animalia
Body having meshwork of cells, internal cavities lined with food filtering flagellated cells and indirect development are the characteristic of phylum
-
Coelenterate
-
Porifera
-
Mollusca
-
Protozoa
B.
Porifera
In Porifera (sponges), bodies are asymmetrical. Body lacks tissues or organs, but from a meshwork of cells surrounding channels that open to the outside through pores, and that expand into internal cavities lined with food filtering flagellated cells (choanocytes).
Select the taxon mentioned that represents both marine and freshwater species
-
Echinoderms
-
Ctenophora
-
Cephalochordata
-
Cnidaria
D.
Cnidaria
Cnidarian members are found both in fresh water and marine environments, while members of Ctenophora, Cephalochordata and Echinodermata are found exclusively in the marine environment.
Which one of the following living organisms completely lacks a cell wall?
-
Cyanobacteria
-
Sea-fan (Gorgonia)
-
Saccharomyces
-
Blue-Green algae
B.
Sea-fan (Gorgonia)
Sea-fan (Gorgonia) belongs to Kingdom-Animalia Phylom, Cnidaria and order: Gorgonacea. As it is on the animal, thus it lacks cell wall cyanobacteria of B we green algae (kingdom Monera) have a cell wall which is composed of peptidoglycan.
Saccharomyces is a genus of kingdom fungi which includes many species of yeast. Their cell wall is mode up of chitin
Planaria possess high capacity of
-
metamorphosis
-
regeneration
-
alternation of generation
-
bioluminescence
B.
regeneration
Planaria are the type of flatworms belonging to phylum-Platyhelminthes. They are the simplest from of multicellular animal. The have a high capacity of regeneration of new tissue at the wound site via cell proliferation ( blastema formation) and the remodelling of pre-existing tissue to restore symmetry and proportion. This is due rieoblast cells.
The cells are usually scattered through out the body and are able to participate in any type of development. The regenerative capacity of different body sections is an indicator of the presence of different numbers of neoblast cells.
A marine cartilaginous fish that can produce electric current is
-
Pristis
-
Torpedo
-
Trygon
-
Scoltodon
B.
Torpedo
Torpedo is a marine cartilaginous fish which produces 8-220 volt electric charge (current) depending on species. Their electric organs are modified lateral muscle plates innervatted by carnrial nerves.
Trygon (sting ray) resembles electric ray in many aspects but is devoid of electricity discharging (or producing) organs.
Scoliodon (dog fish) is known for its great sense of smell. Pristis or common saw fish (also known as carpenters shark) is charactesised by a long, narrow, flattened rostrum lined with sharp transverse teeth to resembles a saw.
In which one of the following, the genus name, its two characters and its phylum are not correctly matched, whereas the remaining three are correct?
-
Genus Name Two characters Phylum pila (i)
(ii)Body segmented
Mouth with RadulaMollusca -
Genus Name Two characters Phylum Asterias (i)
(ii)Spiny skinned
Water vascular systemEchinodermatac -
Genus Name Two characters Phylum Sycon (i)
(ii)Pore bearing
Canal systemPorifera -
Genus Name Two characters Phylum Periplaneta (i)
(ii)Jointed appendages
Chitinous exoskeletonArthropoda
A.
| Genus Name | Two characters | Phylum | |
| pila | (i) (ii) |
Body segmented Mouth with Radula |
Mollusca |
Molluscs are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, soft-bodied animals. Thier soft body is covered by a calcareous shell and is unsegmented with a distinct head, muscular foot and visceral hump.
e.g., Pila (apple snail), Sepia (cuttle fish), Pinctada (pearl oyster), etc.
Which one of the following pairs is wrongly matched?
-
Ginkgo – Archegonia
-
Salvinia – Prothallus
-
Viroids – RNA
-
Mustard – Synergids
B.
Salvinia – Prothallus
Salvinia is a heterosporoues water fern. The microsporangia and megasporangia are borne within special reproductive structure called sporocarps. These are borne terminally in clusters on the segment of submerged leaves. Sporocarps are strictly monosporangiate, i.e., they bear either only microsporangia or megasporangia.
Viroids are single stranded RNA molecules. The female reproductive organ is archegonia in gymnosperms.
Which one of the following categories of animals, is correctly described with no single exception in it?
-
All reptiles possess scales, have a three chambered heart and are cold blooded (poikilothermal)
-
All bony fishes have four pairs of gills and an operculum on each side
-
All sponges are marine and have collared cells
-
All mammals are viviparous and possess diaphragm for breathing
B.
All bony fishes have four pairs of gills and an operculum on each side
Prototherian mammals are oviparous. Sponges are aquatic mostly marine some freshwater have cellular grade of organization. Choanocytes or collar cells are characteristics of porifers. Four pair of gills occur in bony fishes. The gills are covered over by operculum on either side.
All reptiles posses scales, are cold blood but have three-chambered and four-chambered heart.
Which of the following characteristics is mainly responsible for diversification of insects on land?
-
Segmentation
-
Bilateral symmetry
-
Exoskeleton
-
Eyes
C.
Exoskeleton
Exoskeleton of insects is primarily made of proteins (sclerotin) and chitin interwoven and linked together to form strong flexible bundles. The ratio of the components of exoskeleton varies from insects to there habitats. The rigid and strong nature of exoskeleton allones insects to become complex and diversify with regards to size, shape, colour and adaptable modifications.
Which of the following endoparasites of humans does show viviparity?
-
Ancylostoma duodenale
-
Enterobius vermicularis
-
Trichinella spiralis
-
Ascaris lumbricoides
C.
Trichinella spiralis
Trichinella spiralis, a nematode parasite copulates in intestine, after which males dies and females produces larvae which enters into the blood circulation to reach the muscles. The production of larvae indicates vivipary. Ancylostoma, Enterobius and Ascaris are all egg laying endoparasites.
Which of the following animals is not viviparous?
-
Flying fox(bat)
-
Elephant
-
Platypus
-
Whale
C.
Platypus
Mammals are broadly classified into two broad categories:
(i) Protheria are egg laying mammals
(ii) Theria are placental mammals, which can be further divided into Metatheria and Eutheria.
Platypus is a protheric mammal or oviparous whereas bats, elephant and whale belongs to Eutheria as they produce fully formed young ones.
Which one of the following groups of animals is correctly matched with its one characteristic feature without even a single exception?
-
Chordata - possess a mouth provided with an upper and a lower jaw
-
Chondrichthyes - possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
-
Mammalia - give birth to young ones
-
Reptillia - Possess 3 - chambered heart with one incompletely divided ventricle
B.
Chondrichthyes - possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
The members of the class - Chondrichthyes are marine animals with a streamlined body and have a cartilaginous endoskeleton.
Uricotelic mode of passing out nitrogenous wastes is found in
-
birds and annelids
-
amphibians and reptiles
-
insects and amphibians
-
reptiles and birds
D.
reptiles and birds
Reptile, birds, land snails and insects excrete nitrogenous waste as uric acid in the formed pellet of paste with a minimum loss of water and called uricotelic animals.
One very special feature in the earthworm pheretima is that
-
the typhlosole greatly increases the effective absorption area of the digested food in the intestine
-
the S- shaped setae embedded in the integument are the defensive weapons used against the enemies
-
It has a long dorsal tubular heart
-
fertilisation of eggs occurs inside the body
A.
the typhlosole greatly increases the effective absorption area of the digested food in the intestine
A pair of short and conical intestinal caecae project from the intestine on the 26th segment. The characteristic feature of the interesting between 26-35 segments is the presence of an internal median fold of dorsal wall called typhlosole. This increases the effective area of absorption in the intestine.
In which one of the following the genus name, its tow characters and its class/ phylum are correctly matched?
-
GenusTwo charactersClass/phylumSalaman drai).A tympanum represents earAmphibia
-
Genus
Two characters
Class/phylum
Pteropus
i)Skin possesses hair
ii)Oviparous
Mammalia
-
Genus
Two characters
Class/phylum
Aurelia
i)Cnidoblas
ii)Organ level of organization
Colenterata
-
Genus
Two characters
Class/phylum
Ascaris
i)Body segmented Annelida
ii) Females distinct
Annelida
A.
|
Genus
|
Two characters
|
Class/phylum
|
|
Salaman dra
|
i).A tympanum represents ear
|
Amphibia
|
Salamandra is a member of the class -amphibia. A tympanum represents the ear.
Which one of the following statements is totally wrong about the occurrence of the notochord, while the other three are correct?
-
It is present only in larval tail in Ascidians
-
It is replaced by a vertebral coloumn in adult frog
-
It is absent throughout life in humans from the very beginning
-
It is present throughout life in Amphioxus
C.
It is absent throughout life in humans from the very beginning
The notochord is a flexible, rod -shaped body found in the embryo of all chordates. It is composed of cells derived from the mesoderm. It represents the primitive axis of the embryo. In some chordates, it persists throughout life as the main axial support of the body (e.g. Amphibians), while in most vertebrates including humans it becomes the vertebral body of the vertebral column.
The pathogen Microsporum responsible for ringworm disease in humans belongs to the same kingdom of organisms as that of
-
Taenia, a tapewarm
-
Wuchereria, a filarial worm
-
Rhizopus, a mould
-
Ascaris, a round worm
C.
Rhizopus, a mould
Many fungi belonging to the genera-Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton are responsible for ringworms which is one of the most common infectious diseases in man. Microsporum is a member of the class- Deuteromycetes (Fungi imperfecti) of Kingdom - Fungi, Rhizopus (bread mould) is a member of the class - Zygomycetes (conjugation fungi) of Kingdom - Fungi.
Sponsor Area
The figure shows four animals (A),(B) (C) and (D). Select the correct answer with respect to common characteristics of two animals.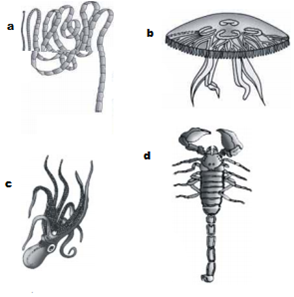
-
(A) and (D) respire mainly through the body wall
-
(B) and (C) shows radial symmetry
-
(A) and (B) have cnidoblasts for self -defence
-
(C) and (D) have a true coelom
D.
(C) and (D) have a true coelom
From phylum - Arthropoda a phylum -Chordata, all are acoelomate. In option (c), Octopus, a mollusc, is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomate animal. In option (D), scorpion an arthropod, is bilaterally symmetrical triploblastic, segmented and coelomate animals.
One example of animals having a single opening to the outside that serves both as mouth as well as anus is
-
Octopus
-
Asterias
-
Ascidia
-
Fasciola
D.
Fasciola
Fasciola hepatica (sheep liver fluke) belongs to phylum - Platyhelminthes. These worms have an incomplete alimentary canal, there is a single opening for both ingestion and egestion. This is also called as blind sac body pain.
Which one of the following statements about all the four of Spongilla, leech, dolphin and penguin is correct?
-
Penguin is homoiothermic while the remaining three are poikilothermic
-
Leech is a fresh water from while all other are marine
-
Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three
-
All are bilaterally symmetrical
C.
Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three
Spongilla belongs to phylum- Porifera, in which, choanocytes are the characteristic cells, these are absent in leech, dolphin and penguin. These distinctive cells line the interior body walls of sponges. These cells have a central flagellum that is surrounded by a collar of microvilli Choanocytes are versatile cells. Their flagella beat to create the active pumping of water through the sponge, while the collars of choanocytes are the primary area where nutrients absorbed into the sponge.
Which one of the following statements about certainly given animals is correct?
-
Roundworms (Aschelminthes) are pseudocoelomates
-
Molluscs are acoelomates
-
insects are pseudocoelomates
-
Flatworms (Platyhelminthes) are coelomates
A.
Roundworms (Aschelminthes) are pseudocoelomates
Roundworms (Phylum-Aschelminthes) are pseudocoelomates, false coelom is derived from embryonic blastocoel.
Flatworms (phylum-Platyhelminthes) are acoelomate animals.
Molluscs and insects (phylum - Arthropoda) are coelomate animals.
Which one of the following kinds of animals are tribalistic?
-
Flatworms
-
Sponges
-
Ctenophores
-
Plumule
A.
Flatworms
Flatworms (phylum-Platyhelminthes) are triploblastic animals. The cells of the body wall arranged in three layers. Spongers, ctenophores and corals are diploblastic animals.
Crocodile and penguin are similar to whale and dogfish in which one of the following features?
-
possess a solid single -stranded central nervous system
-
lay eggs and guard them till they hatch
-
possess a bony skeleton
-
have gill slits at some stage
D.
have gill slits at some stage
Crocodile, penguin, whale and dogfish, all are chordates. So, all of these have gill slits at some stage of development.
Which one onf the following groups of animals is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic?
-
Coelenterates (cnidarians)
-
Aschelminthes (roundworms)
-
ctenophores
-
Sponges
B.
Aschelminthes (roundworms)
Aschelminthes are bilateral symmetrical and triploblastic animals, eg, Ascaris.
Coelenterates are radially symmetrical and diploblastic animals, eg, Obelia.
Ctenophores are biradial symmetrical and diploblastic animals, eg, Ctenoplana.
Sponges are asymmetrical or radially symmetrical and diploblastic animals, eg, sycon.
A change in the amount of yolk and its distribution in the egg will effect
-
formation of a zygote
-
the pattern of cleavage
-
number of blastomeres produced
-
fertilization
B.
the pattern of cleavage
The mode of cleavage is determined by the amount of yolk and its distribution.
(I) Holoblastic - The cleavage, in which the segmentation lines pass through the entire egg, dividing it completely, eg, frog, human egg, etc.
(II) Meroblastic -The lines of segmentation do not completely pass through the egg and remain confined to a part of the egg, eg , insects, birds, reptiles.
Which one of the following pairs of animal comprises' jawless fishes'
-
Lampreys and eels
-
Mackerels and rohu
-
Lampreys and hag fishes
-
Guppies and hag fishes
C.
Lampreys and hag fishes
Lampreys and myxine (hagfish) belong to the class- Cyclostomata, group-Agnatha of Vertebrata. Agnatha has mouth without jaws. In these, the mouth is ventral, Suctorial and circular.
Which one of the followings in birds, indicates their reptilian ancestry?
-
Scales on their hind limbs
-
Four chambered heart
-
Two special chambers crop and gizzard in their digestive tract
-
Eggs with a calcareous shell
D.
Eggs with a calcareous shell
Nearly a century ago, T H Huxley called birds ' glorified reptiles' thereby meaning that birds have evolved from some reptilian ancestor. Both birds and reptiles lay the same type of eggs, which are deposited outside water. Eggs are large and telolecithal.The ovum is surrounded by albumen, an egg membrane and a thick hard calcareous shell, which are all secreted by special glands located in the walls of the oviduct.
Birds like mammals have a completely four-chambered heart with double circulation, in which there is no mixing of pure and impure blood., All birds have horny epidermal scales confined to the lower parts of their legs and feet, which are exactly like the epidermal scales of the reptiles. Besides birds are covered by feathers, which are homologous to the reptilian horny scales as they have a similar origin and develop from similar germ buds.
Cellulose is the major component of cell walls of
-
Pythium
-
Xanthomonas
-
Pseudomonas
-
Saccharomyces
A.
Pythium
Fungal cell wall contains 80-90% carbohydrates, the remainder being proteins can lipids. The typical feature of fungal cells wall is presence of chitin but cellulose does occur in cell walls of Oomycetes (eg, Pythium) and hyphochytridiomycetes.
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of phylum-Annelida?
-
Closed circulatory system
-
Segmentation
-
Pseudocoelom
-
Ventral nerve cord
C.
Pseudocoelom
Name of the phylum-Annelida was first coined by Lamarck. The body of annelids is elongated, bilaterally symmetrical triploblastic, truely coelomate and metamerically segmented into similar metameres. The coelom is true, schizocoelous. Blood vascular system is closed. The nervous system is with a pair of cerebral ganglia and a double ventral nerve cord bearing ganglia and lateral nerves in each segment.
The blood vascular system consisting of blood vessels and capillaries. Blood is composed of fluid plasma and colourless corpuscles, physiologically comparable to the leucocytes of vertebrates.
Pseudocoelom is the body cavity of Aschelminthes.
Which one of the following phyla is correctly matched with its two general characteristics?
-
Arthropoda - Body divided into head, thorax and abdomen and respiration by tracheae.
-
Chordata - Notochord at some stage and separate anal and urinary openings to the outside
-
Echinodermata - Pentamerous radial symmetry and mostly internal fertilisation
-
Mollusca - Normally oviparous and development
A.
Arthropoda - Body divided into head, thorax and abdomen and respiration by tracheae.
Arthropoda is the largest phylum of the animal kingdom. The body of an arthropod is divisible into head, thorax and abdomen. Head and thorax often fused to form a cephalothorax. The respiration takes place by general body surface, gills tracheae or book lungs.
Molluscs are dioecious or monoecious, one or more gonads with conducts, opening into renal ducts or to the exterior. The fertilisation is external or internal, development direct or through free larval forms.
Echinoderma has pentamerous radial symmetry derived from an original bilateral symmetry. The fertilization is external, development indirect through free - swimming larvals forms.
Chordates are sharply distinguished from non-chordates by the presence of notochord, dorsal tubular central nervous system and phayngeal gills slits.
What is common between parrot, platypus and kangaroo?
-
Homeothermy
-
Toothless jaws
-
Functional post-anal tail
-
Ovoparity
A.
Homeothermy
Parrot (Birds), Platypus and kangaroo (both mammal) are homeothermic animals.
Which one of the following is a matching set of a phylum and its three examples?
-
Cnidaria — Bonellia, Physalia, Aurelia
-
Platyhelminthes — Planaria, Schistosoma, Enterobius
-
Mollusca — Loligo, Teredo, Octopus
-
Porifera — Spongilla, Euplectella, pennatula
C.
Mollusca — Loligo, Teredo, Octopus
Loligo, Teredo and Octopus are the members of phylum Mollusca.
Loligo is commonly called squid or sea arrow and is gregarious, fast swimmer in the open water of the sea and is carnivorous, feeding on crabs and fishes.
Octopus (Devil fish) is found at the bottom of the sea. It is nocturnal and feeds on crabs, fishes and other molluscs.
Teredo or shipworm is a marine bivalve which has small anterior shell and long slender body with a smell foot functioning as adhesive structure.
Metameric segmentation is the characteristic of
-
Platyhelminthes and Arthropoda
-
Echinodermata and Annelida
-
Annelida and Arthropoda
-
Mollusca and Chordata
C.
Annelida and Arthropoda
Metameric segmentation is the characteristic of Annelida (e.g., earthworm) and Arthropoda (e.g. Cockroach).
In earthworm body consists of 100-120 ring-like segments or somites called metameres. It shows true segmentation i.e., external segmentation corresponds with internal segmentation.
Cockroach also shows the metameric segmentation. Its anterior few segments are specialized to form head. Such metamerism is called heteronomous metamerism.
Metameric segmentation is absent in platyhelminthes, Echinodermata, Mollusca etc.
Biradial symmetry and lack of cnidoblasts are the characteristics of
-
Starfish and sea anemone
-
Ctenoplana and Beroe
-
Aurelia and Paramecium
-
Hydra and starfish
B.
Ctenoplana and Beroe
Ctenoplana and Beroe lack cnidoblasts and have biradial symmetry. These belong to phylum Ctenophora.
Hydra Sea anemone, Aurelia are coelenterates which have cnidoblasts. Although sea anemone has biradial symmetry.
In which one of the following sets of animals do all the four give birth to young ones?
-
Lion, bat, whale, ostrich
-
Platypus, penguin, bat, hippopotamus
-
Shrew, bat, cat, kiwi
-
Kangaroo, hedgehog, dolphin, loris
D.
Kangaroo, hedgehog, dolphin, loris
Kangaroo, Hedge Hog, Dolphin and Loris are all mammals. These give birth to young ones.
Two commons characters found in centipede, cockroach and crab are
-
compound eyes and anal cerci
-
jointed legs and chitinous exoskeleton
-
green gland and tracheae
-
book lungs and antennae
B.
jointed legs and chitinous exoskeleton
Crab, centipede and cockroach belong to phylum Arthropoda. These have jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton.
Which of the following represents order of 'Horse'?
-
Equidae
-
Perissodactyla
-
Caballus
-
Ferus
B.
Perissodactyla
In case of poriferans the spongocoel is lined with flagellated cells called :
-
Ostia
-
Oscula
-
Choanocytes
-
Mesenchymal cells
C.
Choanocytes
Choanocytes (collar cells) form lining of spongocoel in poriferans (sponges). Flagella in collar cells provide circulation to water in water canal system.
Which among these is the correct combination of aquatic mammals?
-
Seals, Dolphins, Sharks
-
Dolphins, Seals, Trygon
-
Whales, Dolphins, Seals
-
Trygon, Whales, Seals
C.
Whales, Dolphins, Seals
Sharks and Trygon (sting ray) are the members of chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) while whale, and Seals are aquatic mammals belong to class mammalia
An important characteristic that Hemichordates share with Chordates is
-
Absence of notochord
-
Ventral tubular nerve cord
-
Pharynx with gill slits
-
Pharynx without gill slits
C.
Pharynx with gill slits
Pharyngeal gill slits are present in hemichordates as well as in chordates. Notochord is present in chordates only. Ventral tubular nerve cord is characteristic feature of non-chordates
Which one of these animals is not a homeotherm?
Macropus
Chelone
Psittacula
Camelus
B.
Chelone
Homeotherm are animals that maintain constant body temperature, irrespective of surrounding temperature.
Birds and mammals are homeotherms. Chelone (Turtle) belongs to class reptilia which is Poikilotherm or cold blood.
Which of the following features is used to identify a male cockroach from a female cockroach?
Presence of a boat-shaped sternum on the 9th abdominal segment
Presence of caudal styles
Presence of anal cerci
Forewings with darker tegmina
B.
Presence of caudal styles
Males bear a pair of short, thread-like anal styles which are absent in females.
Anal/caudal styles arise from 9th abdominal segment in the male cockroach.
Which of the following animals does not undergo metamorphosis?
Earthworm
Tunicate
Starfish
Moth
A.
Earthworm
Metamorphosis refers to the transformation of a larva into an adult.
The animal that performs metamorphosis is said to have indirect development.
In earthworm, development is direct which means no larval stage and hence no metamorphosis.
Torsion of visceral mass is seen in animals belonging to the class
Cephalopoda
Scaphopoda
Amphineura
Gastropoda
D.
Gastropoda
Animals of class-Gastropoda of phylum-Mollusca undergo twisting of torsion of the visceral mass during development, leading to the conversion of the symmetrical embryo into an asymmetrical adult.
Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| A. | Pinocytosis | 1. | Euglena Gracillis |
| B. | Hotozoic | 2. | Paramecium |
| C. | Parasitic | 3. | Amoeba Proteus |
| D. | Mixotrophic | 4. | Monocystis |
A B C D 3 2 4 1 A B C D 2 3 4 1 A B C D 4 3 1 2 A B C D 1 4 2 3
A.
| A | B | C | D |
| 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
Organ of Jacobson helps in
Touch
Vision
Smell
Hearing
C.
Smell
Jacobson's organ is an axillary olfactory sense organ that is found in many animals. In mammals, the sensory neurons of Jacobson's organ detect specific chemical compounds contained within scents that are often but not always, large non-volatile molecules. It is well developed in snakes (and Lizards)
Notochord originates from
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
Endoderm
None of these
A.
Mesoderm
Notochord originates from mesoderm germ layer.
Which of the given option is correct regarding the statements?
Statement I: Cephalochordata bears notochord all along the body throughout life.
Statements II: Urochordate bears vertebral column only in the tail region throughout the life.
I wrong, II correct
I correct, II wrong
Both I and II are wrong
Both are correct
B.
I correct, II wrong
Cephalochordate has notochord all along the body through out life. But urochordates have a notochord in the tail region in their larval stage only.
Which of the following cells in earthworm play a role similar to liver in vertebrates?
Amoebocytes
Mucocytes
Chloragogen cells
Epidermal cells
C.
Chloragogen cells
Chlorogogen cells are excretory in function. The chlorogogen cells take up excretory matter from the blood capillaries of the gut and from the coelomic fluid of the coelom. They also store glycogen and fat. So, these cells are analogous to the liver of vertebrates.
Match the following and select the correct option.
| List I | List II |
| A. Cyclostomes | 1. Hemichordata |
| B. Ayes | 2. Urochordata |
| C. Tunicates | 3. Agantha |
| D. Balanoglossus | 4. Pisces |
| E. Osteichthyes | 5. Tetrapod |
A B C D E 3 5 2 1 4 A B C D E 3 1 5 2 4 A B C D E 1 2 3 4 5 A B C D E 2 3 4 1 5
A.
| A | B | C | D | E |
| 3 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
Chondrichthyes is characterised by
Placoid scale
Placoid scale and ventral mouth
Ventral mouth
Ctenoid scale and ventral mouth
B.
Placoid scale and ventral mouth
Chodrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes) are marine. Their mouth is ventral and they have cartilaginous endoskeleton. Dermal placoid scales are present, e.g. Scoliodon, Pristis, etc.
Ichthyology is study of
Aves
Amphibians
Reptiles
Fishes
D.
Fishes
Study of amphibians and reptiles is called Herpetology.
Study of aves is called Ornithology.
Study of fishes is called Ichthyology.
Select incorrect pair
Porifera – Choanocytes
Coelenterata – Nematocysts
Annelida – Segmentation
Monera – Eukaryote
D.
Monera – Eukaryote
Kingdom - Monera includes all prokaryotes (autotrophic of heterotrophic) viz, mycoplasmas, bacteria, Actinoomycetes (mycelial bacteria) and photosynthetic vyanobacterial while all unicellular eukaryotic organisms like flagellates, diatoms, dinoflagellates, slime moulds, sarcondina etc. are included in Kingdom - Protista.
Bilateral symmetry, metameric segmentation, coelom and open circulatory system are the features of
Annelida
Arthropoda
Mollusca
Echinodermata
C.
Mollusca
The members of phylum-Arthropoda show bilateral symmetry, three germ layers in body wall, external metamerism, jointed and paired appendages, haemoocel and open type of circulatory system with dorsal heart.
Correctly matched set of phylum, class and example is
Protozoa-Mastigophora-Entamoeba
Mollusca=-Bivalvia-c-Pmcrcdc
Arthropoda-Diplopoda-Scolopendra
Chordata-Cyclostomata-Phrynosoma
B.
Mollusca=-Bivalvia-c-Pmcrcdc
Pinctada sp. is the bivalve molluscs, commonly known as pearl oysters. These belong to sub-class-Lamellibranchia, class-Bivalvia or Pelycipoda, phylum-Mollusca and Kingdom-Animalia.
The most primitive vertebrates are
Ostracoderms
Cephalochordates
Placoderms
Cyclostomes
A.
Ostracoderms
Class-Ostracodermi of vertebrata includes most primitive vertebrates, e.g., Cephalaspis and Drepanaspis.
Sponsor Area
Branch of zoology dealing with the study of fishes is called
Arthrology
Ichthyology
Saurology
Herpetology
B.
Ichthyology
| Branch of Zoology | Area |
| Arthrology | Study of Joints |
| Ichthyology | Study of Fishes |
| Saurology | Study of Lizards |
| Herpetology | Study of Reptiles |
Theory of continuity of germplasm was propounded by
Mendel
Lamarck
Weismann
Haeckel
C.
Weismann
Theory of continuity of germplasm was proposed by August Weismann (1892), a German Biologist, he suggested that the changes occurring in germplasm are inherited by offsprings, whereas in somatoplasm are not transmitted to next generation.
Food storage in Leucosolenia occur by
Ostia
Osculam
Thesocyte
Spongocoel
C.
Thesocyte
It occurs by thesocyte which have lobose pseudopodia and are filled with food reserves, thus acting as storage cells.
The structure present in all adult vertebrates is
Notochord
Dorsal tubular nerve cord
Pharyngeal gill slits
All of these
B.
Dorsal tubular nerve cord
Dorsal tubular nerve cord is the characteristic feature of all adult vertebrate. It is a gel-like substance and is remnant of the notochord.
Which one of the following is not a vertebrate?
Sea cow
Sea lion
Sea horse
Sea hare
D.
Sea hare
See hare belongs to phyllum-Mollusca and is not a vertebrate.
Consider the following statements and Choose correct ones from given options.
(I) Shark do not have any bone in its body.
(II) Water snake and salamander belongs to same class and have largest RBC.
(III) Silver fish is a true fish while cuttle and star fishes are mollusks and echinoderms respectively.
(IV) Ornithorhynchus is a connecting link between reptiles and mammals.
I, II and IV
I and IV
I, II and III
III and IV
B.
I and IV
• Shark is a member of Chondrichthyes class, which is a cartilaginous fish.
• Water-snake is a reptile and salamander is an amphibian having largest RBC in the Animal Kingdom.
• Silverfish (Lepisma) is an arthropod, cuttlefish (Sepia) is a mollusc and starfish(Asterias) is an Echinodermata. So none of them is a true fish (Pisces).
• Omnithorhychus is a mammal which is also known as duck-billed platypus. It is a member of Monotremata order which is a connecting link between reptiles and mammals.
A horse and a donkey can breed to produce mule which is an infertile animal. The infertility is because horse and donkey belong to different.
Class
Order
Species
Genus
C.
Species
A horse (Equus ferus caballus) and a donkey (Equus africanus asinus) can breed to produce mule, which is an infertile animal. The infertility is because horse and donkey belong to different species. Mule are medium weight animals that are more hardworking and long-lived than horse and donkey.
Match the following Columns.
| Column I (organism) | Column II (Connecting Link) |
| A. Echina | 1. Between Annelida and Mollusca |
| B. Peripatus | 2. Between Reptiles and Mammals |
| C. Neopilina | 3. Between Annelida and Arthropoda |
| D. Protopterus | 4. Between Pisces and Amphibian |
A – 4; B – 3; C – 2; D – 1
A – 2; B – 3; C – 1; D – 4
A – 3; B – 1; C – 2; D – 4
A – 4; B – 2; C – 1; D – 3
B.
A – 2; B – 3; C – 1; D – 4
| Organism | Connecting Link |
| Echidna | Between Reptile and Mammals |
| Peripatus | Between Annelida and Arthropoda |
| Neopilina | Between Annelida and Mollusca |
| Protopterus | Between Pisces and Amphibia. |
Slime-mould belongs to
kingdom-Protista
Kingdom-Monera
Kingdom-Fungi
Kingdom-Plantae
A.
kingdom-Protista
Slime-moulds are also called fungus-like protists, which share characteristics of both animal and fungi.
A connecting link between plant and animal kingdom is
Paramecium
Chlamydomonas
Chlorella
Euglena
D.
Euglena
Euglena can be considered as both plants as well as an animal. It can perform photosynthesis in presence of light. But in the absence of light, it opts holozoic mode nutrition which is the feature of animals. Thus, Euglena is considered as connecting link between plant and animal kingdom.
Chondrichthyes is characterised by
Placoid scale
Ventral mouth
Ctenoid scale and ventral mouth
Placoid scale and ventral mouth
D.
Placoid scale and ventral mouth
Chondrichthyes is one of the classes of super-class-Pisces, sub-phylum-Vertebrata and phylum Chordata. The members of class-Chondrichthyes are marine animals with a streamlined body and have a cartilaginous endoskeleton. Mouth is located ventrally. The skin is tough, containing minute placoid scales. The teeth are modified placoid scales which are backwardly directed, e.g., Dog fish (Scoliodon), sawfish (Pristis), great white shark (Carcharodorus sting ray (Trygon), etc.
Animals of class-Mammalia have
Seven cervical vertebrae
Seven cranial nerve
Single ventricular chamber
Fourteen cervical vertebrae
A.
Seven cervical vertebrae
The number of cervical vertebrae is seven in almost all mammals including human beings.
The echinoderms are
arborial insects
marine animals
terrestrial insects
freshwater forms
B.
marine animals
All members of Phylum- Echinodermata are marine. Therefore, Echinoderms are marine, spiny skinned animals. They have water vascular system for locomotion, eg, starfish, Antedon.
Arboreal insects lives on trees. Freshwater forms are animals or plants living in fresh water of ponds, eg, Hydrilla.
Tube feet is the locomotory organ in
starfish
jelly fish
silver fish
Scoliodon
A.
starfish
Tube feet are extensible tubular processes bearing suckers and present in rows on the under surface of Echinoderms. These are connected internally with water vascular system. Each tube foot has an ampulla, a podium and a sucker. These are sensory structures that take part in adhesion, locomotion, respiration and food capturing.
Jelly fish is a member of Phylum- Coelenterata. Scoiliodon is a fish and silver fish is an arthropod.
Sea gulls excrete excess of NaCl from
liver
lungs
nasal activity
kidney
C.
nasal activity
Sea gulls have salt glands which excrete large loads of salt taken with their food and with the water they drink. Sea water contains 3% salt which is three times saltier than a bird's body fluid.
Salt glands are located above each eye and consists of several lobes arranged parallely. Salts are secreted into many radially arranged tubules then flows into a central canal that leads into the nose.
Connecting link between annelids and molluscs is
Neopilina
Peripatus
Periplaneta
Limulus
A.
Neopilina
Neopilina (mollusc) is considered as a connecting link between Annelida and Mollusca.
Ruminants belong to order
Proboscida
Artiodactyla
Marsupials
Edentata
B.
Artiodactyla
Ruminants have the habit of chewing the cud. Stomach of ruminants have four parts, ie, rumen, reticulum, omassum, abomassum. They belong to Order- Artiodactyla of Class- Mammalia, eg, cow, sheep, goat.
Elephants belong to Order- Proboscidea of Class- Mammalia.
Marsupials are the members of subclass- Metatheria, in which a pouch marsupium is present for keeping and nourishing the young ones, eg, kangaroo.
Which of the following have notochord throughout life?
Birds
Fish
Snake
Amphioxus
D.
Amphioxus
In chordates and sub- phylum Cephalochordates, notochord is present throughout life. In vertebrates, it is replaced by vertebral column.
During unfavourable conditions, the sponges form
cyst
encyst
spicule
Gemmule
D.
Gemmule
Unfavourable conditions such as high temperature, dry conditions, sponges body gets divided into numerous small spore like bodies called gemmules.
In Amoeba, cysts are formed during unfavourable conditions.
Spicules are endoskeleton of sponge body.
Shell of molluscs is derived from
foot
mantle
ctenidia
placoid
B.
mantle
Molluscs are soft bodied, unsegmented animals covered by a shell. Mantle is present between the shell and body wall, which secretes the shell.
Which of the following cell type is capable of giving rise to other cell types in sponges?
Thesocytes
Pinacocytes
Cnidocytes
Archaeocytes
D.
Archaeocytes
Archaeocytes are the totipotent cells, which provide great regenerating power to sponges. Sex cells (sperm and ova arise from undifferentiated archaeocytes).
Thesocytes are the amoebocytes with reserve food granules.
Pinacocytes are the polygonal flat cells present as outer layer of cells, called pinacoderm lining the spongocoel or body cavity in Leucosolenia.
Cnidocytes occur in entire epidermis except that of basal disc and are found only in cnidarians. These are spherical or oval cells.
Animals having a built in thermostat to maintain constant body temperature are known as
biothermic
poikilothermic
oligothermic
homeothermic
D.
homeothermic
Homeothermic are the animals having a nearly uniform or constant body temperature. These animals are known as warm blooded animals, eg, birds, man.
Poikilothermic are those, having a variable temperature which fluctuates with that of environment. They are called the cold blooded animals, eg, reptiles, amphibians.
The intermediate host of Schistosoma is
Snail
mosquito
housefly
sheep
A.
Snail
Schistosoma mansoni is the common human blood fluke. It belongs to class- Trematoda of Platylhelminthes. Blood fluke is digentic, primary host is man and secondary host id snail.
Sheep is the primary host of Fasciola hepatics (sheep liver fluke), causing 'liver rot'. Its secondary host is also the snail.
Mosquito and housefly are not found to be the intermediate host of any animal.
In Mollusca, eye is present over a stalk, called
ostracum
operculum
ommatophores
osphradium
C.
ommatophores
In Mollusca, each eye is located upon a stumpy peduncle called ommatophore.
Mantle, a loose skin fold, dorsally covers Mollusca body and encloses a mantle cavity. It further contains rectum, genital duct, a penis and a small chemoreceptor called Osphradium.
The large, oval aperture or mouth of the shell can be tightly closed by a thick, plate- like operculum attached to the foot.
Tuberllarians are free living
nematodes
cestodes
flat worms
trematodes
C.
flat worms
Tuberllaria is a Class of Phylum- Platyhelminthes. These are free living flat worms and are majorly aquatic. It consists of cilia, unsegmented body, mouth ventral, suckers absent with tango, chemo and photoreceptors, eg, Planaria.
Trematoda is a Class of Phylum- Platyhelminthes. Also known a s flukes, body is without cilia, unsegmented with suckers and hooks, eg, Fasciola etc.
Cestoda is also one of the Class of Phylum- Platyhelminthes. Commonly called tapeworms; are generally without cilia and sense organs, body is segmented, digestive system absent, eg, Taenia.
The characteristic larva of Phylum- 'Coelenterata' is
planula
cysticercus
rhabdiform
wriggler
A.
planula
Coelenterata or Cnidaria shows both sexual and asexual reproduction. The larval stages are planula (Obelia) and ephyra (Aurelia).
Cysticercus is a bladder worm and the third level stage in Taenia. It is visible after the hexacanth is released in the stomach of pig, which goes in the blood circulation and on reaching muscles appears as bladderworm.
Rhabditiform is the first larval stage in Ascaris. It is a non- infective juvenile stage which rests for a week and completes first moult within egg and becomes second stage which is infective.
Wriggler is the larva of mosquito. It is free swimming, active, aquatic larva performing wriggling movements. It has life span of 3- 4 days.
The excretory material of bony fish is
urea
protein
ammonia
amino acid
A.
urea
The excretory and osmoregulatory organs of fishes are the gills and kidney. Excretion in bony fishes is ureotelic (ie, they excrete urea but some fresh water bony fishes are ammonotelic (ie, excrete ammonia).
Moulting hormone is secreted by
corpora cardacum
corpora allata
neurosecretory hormone
prothoracic gland
D.
prothoracic gland
Prothoracic gland is also known as moult gland in some arthropods and Y organ or ventral gland in crustaceans. It secretes moulting hormone called ecdysone or ecdysome, which is steroid and stimulates moulting or ecdysis during metamorphosis in insects.
In sea anemone, the symmetry is
radial
bilateral
spherical
absent
A.
radial
In radial symmetry, body is divided into two similar halves by more than two planes passing through the main axis.
Cnidarians or coelenterates such as Hydra, sea anemone, Aurelia, Obelia etc are radially symmetrical animals with cell- tissue grade of body organizations.
Solenocytes are associated with
respiration
digestion
excretion
nutrition
C.
excretion
Solenocytes or flame cells are the excretory organs of Phylum- Platyhelminthes.
Connecting link between annelids and molluscs is
Neopilina
Peripatus
Periplaneta
Limulus
A.
Neopilina
Neopilina (mollusc) is considered as a connecting link between Annelida and Mollusca.
Shell of molluscs is derived from
foot
mantle
ctenidia
placoid
B.
mantle
Molluscs are the soft bodied, unsegmented animals covered by a shell. Mantle is the dorsal body wall which covers the organs of digestion, reproduction and movement. In between the shell and body wall is a covering called mantle, which secretes the shell.
chloragogen cells help in
respiration
reproduction
circulation
nutrition
D.
nutrition
Chloragogen cells or yellow cells are present in the region of intestine in Pheretima. The exact function of these cells is not fully known but it is believed that they are concerned with storage of reserve food and also excretory in function. Chloragogen cells are analogous to liver of vertebrates.
'Sea fan' belongs to
Coelenterata
Porifera
Echinodermata
Mollusca
A.
Coelenterata
Sea fan is common name of Gorgonia. It belongs to phylum-Coelenterata, class-Anthozoa and order-Gorgonacea.
Trochophore is the larva of
Neopilina
Chiton
Pila
All of these
D.
All of these
Trochophore is cilliated, larval stage of polychaetes, mollsucs and rotifers. Neopilina, Chiton and Pila belong to phylum--Mollusca. Molluscan development is either direct or with metamorphosis through the trochophore stage.
Food storage in Leucosolenia occur by
ostia
osculum
thesocyte
spongocoel
C.
thesocyte
Food storage in Leucosolenia occurs by thesocyte. Thesocytes have lobose pseudopodia and are filled with food reserves, thus, acting as storage cells.
Chloragogen cells of earthworms are analogous to vertebrate
lungs
liver
gut
kidneys
B.
liver
Chloragogen cells of earthworm are analogous to liver of vertebrates which is used to store nutrition.
Class Crustacea differs from lnsecta in having
two pairs of antennae
jointed foot
chitinous cuticle
none of the above
A.
two pairs of antennae
The main characteristics of class Crustacea and Insecta are as follows :
(1) Class Crustacea : Mostly aquatic with gills, two pairs of antennae and at least three pairs of jaws, appendages mostly biramous and always more than four in the trunk region. Example : prawn, crab, lobster etc.
(2) Class Insecta : Hexapod arthropods with a pair of antennae and three pairs of Jaws. Example : cockroach, grasshopper, bees,housefly etc.
Which of the following character is present essentialy in chordates
Ventral spinal chord
Dorsal heart
Pharyngeal gill slits
Blood flow in forward direction in ventral blood vessels
C.
Pharyngeal gill slits
Chordate animals, at some time in their life history, exhibit the following three diagnostic
charcters :
(1) Presence of notochord.
(2) Presence of dorsal tubular nerve cord.
(3) Presence of gill clefts during development.
Beside these, some other characters are :
(4) Ventral heart.
(5) Hepatic portal system.
Number of cranial nerves in frog
10 pairs
9 pairs
12 pairs
none of these
A.
10 pairs
Ten pairs of cranial nerves are present in anamniotes such as fishes and amphibians (e.g., Frog). Twelve pairs of cranial nerves are present in amniotes, reptiles, birds and mammals including rabbit and humans.
In contrast to annelids the platyhelminthes show
radial symmetry
presence of pseudocoel
bilateral symmetry
absence of body cavity
D.
absence of body cavity
Platyhelminthes does not have coelomic or pseudocoelomic cavity for digestion of food as found in higher organisms. These group of organisms are known to obtain their digested food directly.
Mantle, foot and shell are the characteristics of
Nautilus
Echinus
Limulus
Euplectella
A.
Nautilus
Mantle, foot and shell are characteristics of a mollusc. Nautilus is a mollusc, it is a tetrabranch cephalopod. The shell is external and coiled over the head. Nauctilus is always active at night and rests on bottom during day.
Third cleavage of frog's development is
equatorial
vertical
latitudinal
none of these
C.
latitudinal
First and second cleavage in frog are holoblastic, complete, equal, vertical, whereas third cleavage is holoblastic, complete, unequal, latitudinal or horizontal and near the animal pole. It results in the formation of 8 cells of three are black micromeres which have less or no yolk, so divide faster and 4 are colourless macromeres
The main excretory organ of prawn is
green gland
flame cell
Malphigian tubule
nephridia
A.
green gland
The main excretory organs of prawn are paired green glands. They are located within the second antennae, which are the second pair of appendages, attached to the anterior part of the body. Each green gland consists of on endsac, labyrinth and a bladder.
Flame cell is a specialized excretory cell found in the simplest freshwater invertebrates, including flatworms, rotifers and nemerteans. It functions like a kidney, removing wate material.
The Malphigian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids and tardigrades. It consist of branching tubules extending from the alimentary canal that absorbs solutes, water and wates from surrounding hemolymph.
Nephridium is an invertebrate organ which occurs in pairs and performs a function similar to the vertebrate kidney.
Which of the following is not an insect?
Locust
Lepisma
Termites
Spider
D.
Spider
Spider is not an insect. It belongs to the Order Araneae of the Class-Arachnida. It bears four pairs of walking legs unlike insects (have three pairs of walking legs) Loust, Lepisma and Termites are come in the category of insects.
Which cells are found only in sponges?
Amoeboid cells
Choanocytes
Pigment cells
Gland cells
B.
Choanocytes
Choanocytes are found only in sponges. The choanocyte is an ovoid cell with free ends bearing a transparent contractile collar. The collar surrounds a single, long flagellum. Choanocytes are used in feeding and for ensuring flow of water within the animal's body.
Which of the following assists in the locomotion of the organism stated
Epithelium of' Pheretima
Trichocysts of Paramecium
Pedicellaria of Star fish
Posterior sucker of Hirudinaria
D.
Posterior sucker of Hirudinaria
Hirudinaria belongs to class Hirudinea of phylum-Annelida.
It has definite number of body segments (26 + 7= 33). It feeds on blood (sanguivorous) and has anticoagulant hirudin in its saliva. Hirudinaria have a posterior sucker for locomotion. Leech creep by looping and swim by undulations of body.
The scientist, who described the birds as glorified reptiles, was
Romer
Huxley
Mendel
Robert Hooke
B.
Huxley
Huxley stated that birds are glorified reptiles. The missing link Archaeopteryx is a fossil lizard bird. It was founded by Andreas Wagner (1861) from upper Jurassic limestone rocks of Solenbofen in Bowaria, Germany
In frog, the vertebra with an anterior convex surface (i.e., double convexties) is
atlas
urostyle
8th vertebra
9th vertebra
D.
9th vertebra
The 9th or sacral vertebra is acoelous and highly specialised the anterior face is convex for this give greater strength them, it would be given if its anterior end are hollowed out the transverse process are stout and downwardly directed. The ileum of the pelvic girdle articulates with the transverse process of 9th vertibrae.
What is left when bath sponges dries up
Spicules
Spongin fibres
Tentacles
Holdfast
B.
Spongin fibres
Euspongia is called bath spongia. The sponge are classified on the basis of skeleton which is made up of spongin fibere. After the bath sponge dries only the skeleton is left.
A definite number of segments are found in
slug
earthworm
leech
tapeworm
C.
leech
Leech belongs to Phylum- Annelid. A definite number of segments, ie, 33 segments are found in leech.
The red colour of 'red sea' is due to which of the following blue-green algae?
Chlamydomonas nivalis
Anabaena
Microcystis
Trichodesmium
D.
Trichodesmium
Trichodesmium is a diazotroph, ie, it fixes atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, a nutrient used by other organisms.
Red Sea looks reddish because of the presence of cyanobacteria Trichodesmium erythraeum which turns the normaly blue- green water a reddish- brown water.
Some salient features and phyla of organisms are given below. Select the option which shows correct combination of organism, its phylum and salient features.
Hydra coelenterate Bilateral symmetry Cnidoblasts present Planaria Platyhelminthes Bilateral symmetry High Regeneration Capacity Ancylostoma Annelida Bilateral symmetry Elongated and Worm shaped Octopus Mollusca Radial symmetry External skeleton of
shell present
B.
| Planaria | Platyhelminthes | Bilateral symmetry | High Regeneration Capacity |
Hydra shows radial symmetry, Ancylostoma is an aschelminth. Octopus shows bilateral symmetry and also lacks an external skeleton of shell.
Cochineal insects have proved very useful for
rodents control
Parthenium control
cactus prevention
Eicchornia prevention
C.
cactus prevention
In India and Australia, the overgrowth of cacti was checked by the introduction of cochineal insect (Cactoblastis cactorum).
Select the option that correctly matches characteristic features with the group of three animals.
Skeleton ofspicules - Sycon, Adamsia, Spongilla
Excretion by flame cells - Taenia, Fasciola, Ancylostoma
Mouth contains radula - Dentalium, Octopus, Ophiura
Jointed appendages - Limulus, Apis, Laccifer
D.
Jointed appendages - Limulus, Apis, Laccifer
In poriferans, the body is supported by a skeleton made up of spicules or spongin fibres. Sycon and Spongilla are examples of poriferans, whereas Adamsia is a coelenterate.
In platyhelminths, specialised cells called flame cells help in excretion. Taenia and Fasciola are platyhelminths whereas Ancylostoma is an aschelminth.
In molluscs, mouth contains a file-like rasping organ for feeding called radula. Dentalium and Octopus are molluscs whereas Ophiura is an echinoderm.
Arthropods have jointed appendages. Limulus, Apis and Laccifer all three are arthropods
The formation of canal system in sponges is due to
reproduction
porous walls
folding of inner walls
gastro- vascular system
C.
folding of inner walls
Canal system is a system of passages connecting various cavities of the animal body as in sponges. It serves the function of food collection, respiration and excretion.
It has less number of cells and thin body wall initially. But when the system gets complicated, the number of flagellated cells increases and the force to draw water current increases. It results in more number of cells and thick body wall. Thick body wall is folded forming regularly arranged in-pushings and out-pushings leading to the formation of canals.
Benthoic animals are those, which
are deep dweller in sea
are floating (free) organisms
are submerged in sea
float on the sea surface
A.
are deep dweller in sea
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the very bottom of the sea. It includes the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The term 'benthic' was originally used for those animals which live on sea bottom.
Assertion: Cephalisation is advantageous to an animal.
Reason: Cephalisation improves the appearance of an animal.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
Cephalisation is the concentration of nervous tissue and sense organs in or towards the anterior end forming a distinct head. It provides greater prominence and domination of the head over the rest of the body. However, it does not improve the appearance of the animal.
Retrogressive metamorphosis occurs in
Hemichordata
Cephalochordata
Urochordata
Vertebrata
C.
Urochordata
In retrogressive metamorphosis, degeneration is shown by larva to form less developed adult. It is a type of metamorphosis seen in Herdmania (Urochordate). It involves transformation of an active, free swimming larva with advanced characters into sedentary and simple adult.
Which of the following waste products in grasshopper is not excreted and is used in other metabolic activities
Carbon dioxide
Water
Uric acid
Faeces
B.
Water
Excretory organs of grasshopper are the Malpighian tubules and the main excretory product is uric acid. Malpighian tubules of insects such as grasshoppers not only help to excrete the waste but also function to conserve water, which is then used in other metabolic activities. In the Malpighian tubules, bicarbonates of potassium and sodium, water and uric acid are formed during the process, of excretion. A large amount of water and bicarbonates of potassium and sodium are reabsorbed by the cells of Malpighian tubules and then transferred to the blood (haemolymph). Uric acid is carried to the alimentary canal of the insect and is finally passed out through anus.
Select the animal that exhibits retrogressive metamorphosis
Bufo
Limulus
Amphioxus
Herdmania
D.
Herdmania
Retrogressive metamorphosis occurs in Urochordates (e.g., Herdmania, Ascidia, Doliolum etc.), in which better developed (advanced) larva changes to less developed (primitive) adult.
Assertion: The nymph of a cockroach undergoes moulting several times.
Reason: There is gradual metamorphosis in cockroach.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Gradual metamorphosis occurs in many insects such as cockroaches. In gradual metamorphosis, there are three stages: egg, nymph and adult. As nymphs, they moult several times (13 times in cockroach), but once they become adults they do not moult again. Nymphs are similar in shape to the adults, but smaller in size and without wings.
Assertion: Branchiostoma and Balanoglossus are bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic animals.
Reason: They are exclusively marine and possess notochord.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
Balanoglossus (Phylum-Hemichordata) and Branchiostoma (= Amphioxus, Subphylum - Cephalochordata) both are bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic animals. Both are marine animals. Balanoglossus does not possess a notochord whereas Branchiostoma being a chordate possesses notochord that persists throughout life.
Assertion: Cephalisation is advantageous to an animal.
Reason: It improves the appearance of the animal.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
Cephalisation is the concentration of nervous tissues and sense organs in or towards the anterior end forming a distinct head. It provides greater prominence and domination of the head over the rest of the body. It does not improve the appearance of the animal.
Assertion: Blood in cockroach is colourless haemolymph with no respiratory pigment.
Reason: Respiration in cockroach occurs through diffusion in haemolymph.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
The colourless blood or haemolymph of cockroach has a clear plasma and numerous white corpuscles called haemocytes. Being devoid of any respiratory pigment, it does not serve for gaseous exchange. Its plasma contains about 70% water. Rest of it is composed of amino acids, uric acid, proteins, sugars, fats, and salts of sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium. Transportation of these materials between different parts of body is the main function of haemolymph.
In all terrestrial insects, like cockroach, every tissue of body is in direct contact with atmospheric air for gaseous exchange. A complicated system of numerous shiny, transparent and branched air tubes or tracheae is found for this purpose in the haemocoel cavity. Atmospheric air enters into and escapes out from this system through ten pairs of slit-like apertures called stigmata or spiracles, located on lateral sides of body
Assertion : In Pleurobrachia, eight comb like ciliary plates called comb plates are present on the body that help in locomotion.
Reason : Pleurobrachia reproduces sexually and its life cycle includes cydippid larva.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Ctenophores are characterized by eight rows of cilia, which are used for locomotion. The cilia in each row are arranged to form a stack of combs, also called comb plates, ctenes; thus the name ctenophore comes from the Greek, menaing 'Comb bearer'.
Choose the correct pair
Coconut, cucurbits - dioecious
Honeybee, Rotifers - parthenogenesis
Ornithorhyncus, Whale - viviparity
Frog, Peacock - external fertilisation
B.
Honeybee, Rotifers - parthenogenesis
Coconut and cucurbits are monoecious plants. Ornithorhynchus is an egg-laying mammal. Whale is a viviparous mammal. Frog shows external fertilisation. It takes place in water. Peacock shows internal fertilisation
Select the incorrect statement.
Periplaneta has compound eyes.
Earthworm shows segmentation.
Ascaris shows sexual dimorphism.
Liver fluke has a complete alimentary canal
D.
Liver fluke has a complete alimentary canal
Liver fluke has an incomplete alimentary canal.
Refer the given figure of digestive system of earthworm and identify the part labelled X.
Intestinal caecae
Typhlosole
Gizzard
Pharynx.
C.
Gizzard
The gizzard is a part of earthwarm's digestive system whuich uses stones that the earthworm eats to grind the food completely.
Lactic acid is produced by Rhizopus species
R. oryzae
R. stolonifer
R. nodosus
R. sexualis
C.
R. nodosus
Rhizopus species causing fermentation are :
(i) R. oryzae - Alcoholic fermentation
(ii) R. nodosus - Lactic acid fermentation
(iii) R. stolonifer (R. nigricans) - Fumaric acid fermentation.
Which of the following is non symbiotic bio-fertilizer
YAM
Anabaena
Azotobacter
Rhizobium
C.
Azotobacter
Anabaena, Nostoc, Aulosira etc., are agriculturally very important as non-symbiotic bacteria also called free living nitrogen fixing bacteria. VAM, Azotobacter and Rhizobium are symbiotic organisms.
During the life-cycle, Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke) infects its intermediate host and primary host at the following larval stages respectively
redia and miracidium
cercaria and redia
metacercaria and cercaria
miracidium and metacercaria.
D.
miracidium and metacercaria.
Life cycle of F. hepatica is complete and completed in two hosts. Primary host, in which the adult fluke lives, is sheep. While the intermediate host, in which numerous larval stages are passed, is a snail (Lymnaea, Planorbis, etc.). This type of life cycle, involving two different kinds of hosts, is termed digenetic.
Miracidium larva is the larval stage involved in life cycle. When suitable conditions become available, the encapsulated embryo, in 4-15 days, differentiates into a miracidium larva. It hatches out and swims in water. Metacercaria develops into adult fluke only inside its definitive host or sheep. The latter gets infection by grazing on leaves and grass blades to which the cysts are attached. Metacercaria survives action of host's gastric juice as its cyst is insoluble in it. Cyst wall finally dissolves in proximal part of intestine and liberates the larva.
Which of the following does not come under the Class Mammals?
Flying fox
Hedgehog
Manatee
Lamprey
D.
Lamprey
Lamprey (or Petromyzon) belongs to class cyclostomata. The lamprey has about 1m long greenish brown, cylindrical body with smooth, scaleless, slimy skin; anterior circular, jawless mouth; a single dorsal naris; seven pairs of circular gill slits; 2 dorsal tins and a tail tin. It's life cycle includes two quite different phases. The larval phase (called ammocoete) is a fresh water sedentary, filter feeding and microphagus creature reminiscent of the lancet. The fish like adult lives in the sea and is parasitic on fishes.
Assertion: Cephalization is advantageous to an animal.
Reason: It improves the appearance of the animal
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Cephalization is the concentration of nervous tissues and sense organs in or towards I the anterior end forming a distinct head. It provides greater prominence and domination of the head over the rest of the body. It does not improve the appearance of the animal.
Assertion : Torison can be seen in ctenidium.
Reason : Ctenidium acts as the respiratory organ.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Ctenidium is a monopectinate gill situated on the right side of the branchial chamber. It helps in respiration by beating of cilia, thus creating water current. It is innervated by nerves from the left pleural and supra-intestinal ganglia. It basically indicates that it is an organ of the left side but has shifted to the right side during development (torsion).
Torsion or twisting is a development of gastropods, which rotates the visceropallium anticlockwise through out 180° from its initial position, so that mantle cavity with its pallial complex, is brought in front of the body in adult.
Which one of the following animals is correctly matched with its one characteristic and the taxon
Animal Characteristic Taxon Millipede Ventral nerve cord Arachnida Duckbill platypus Oviparous Mammalia Silverfish Pectoral and pelvic fin Chordata Sea anemone Triploblastic Cnidaria
B.
| Duckbill platypus | Oviparous | Mammalia |
Millipede: Millipedes belongs to Phylum Arthropoda. Millipedes arc called thousand leggers because of possession of numerous legs. Inspite of this they move very slowly.
Duckbill platypus: It is an egg laying mammal of Phylum Chordata and Class Mammalia.
Silverfish : Lepisma saccharina is commonly known as silver fish because of its glistening silvery white fish like body. It belongs to the insect Order Thysanura.
Sea anemone : Sea anemone (Admasia), belongs to Phylum Cnidaria shows commensalism. It is found attached to the empty shell of gastropods occupied by hermit crab. Its body wall is two layered i.e.. outer epidermis and inner gastrodermis. In between these two layers is present mesogloea.
All mammals without any exception are characterised by
viviparity and biconcave red blood cells
extra-abdominal testes and a four chambered heart
heterodont teeth and 12 pairs of cranial nerves
a muscular diaphragm and milk producing glands.
D.
a muscular diaphragm and milk producing glands.
All mammals without any exception are characterized by a muscular diaphragm and milk producing glands.
Which one of the following pairs of the kind of cells and their secretion is correctly matched
Oxyntic cells a secretion with pH between 2.0 and 3.0 Alpha cells of islets of Langerhans secretion that decreases blood sugar level Kupffer cells a digestive enzyme that hydrolyses nucleic acids Sebaceous glands a secretion that evaporates for cooling
D.
| Sebaceous glands | a secretion that evaporates for cooling |
Oxyntic (or parietal) cell is present in the wall of the stomach that produce HCI which forms the part of gastric juice. Oxyntic cell also produce intrinsic factor which is involved in the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine. The pH of gastric acid is 2-3 in the stomach of the lumen. The acidity being maintained by the proton pump, a H+/ K+ ATPase.
Alpha cell ofislets of langerhans secrete glucagon hormone which raises blood glucose level by stimulating liver to convert glycogen to glucose and by stimulating the conservation of fatty acids and amino acids to glucose.
Kupffer cells arc specialized macrophages that disposes of old blood cells and particulate matter. Kupffer cells, named after Karl Wilhem Von Kupffer, are found in the bloodstreams and in the liver, attached to the walls of the sinusoids.
Sebaceous gland is a simple or branched glands in the skin that secrete an oily substance, sebum which is fatty mildly antiseptic material that protects, lubricates, and waterproofs the skin and hair and help prevent dessication.
A lizard-like member of reptilia is sitting on a tree with its tail coiled around a twig. This animal could be
Hemidactylus showing sexual dimorphism
Varamus showing mimicry
garden lizard (Calotes) showing camouflage
Chamaeleon showing protective colouration
D.
Chamaeleon showing protective colouration
Chamaeleon (or girgit) is a lizard like member of reptilia which is famous for changing its colour according to its surroundings. The phenomenon is called metachrosis. Chamaeleon lives on trees in south India and is insectivorous and can catch an insects about 20 cm away by eversible tongue. Its tails is long cylindrical and prehensile (means able to grasp or grab by wrapping around).
Which one of the following features is common in silverfish, scorpion, dragonfly and prawn?
Two pairs of legs and segmented body
Living chitinous cuticle and two pairs of antennae
Jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton
Closed blood carcular system
C.
Jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton
Silverfish, scorpion, dragonfly and prawn all fall under Phylum Arthropods which have joint appendages and chitinous exoskeleton as the characteristic feature.
Which one feature is common to leech, cockroach and scorpion
Nephridia
Cephalisation
Ventral nerve cord
Antenna
C.
Ventral nerve cord
Ventral nerve chord is the characteristic of lower chordates like leech, cockroach and scorpion
Assertion : The duck-billed Platypus and the spiny ant-eater, both are egg-laying animals yet they are grouped under mammals.
Reason : Both of them have seven cervical vertebrae and 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
Mammal characteristics include the presence of hair and milk or mammary gland and presence of 7 cervical vertebrae and 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
The duck-billed platypus and the spiny anteater are mammals that lay eggs rather than give live birth to young ones. The platypus has a bill like a duck. fur like a mammal and webbed feet. It lays eggs that look like reptile eggs. Its young feed from the mother's mammary glands.The spiny anteater's covering looks like that of the porcupine. It has a long tongue to catch insects and a bill. It lays several eggs which it keeps in a pouch on its side.
Tube-within-a-tube body plan is shown by
coelenterates
platyhelminthes
aschelminthes (nemathelminthes)
porifers
C.
aschelminthes (nemathelminthes)
a) This body plan is present in all advanced animals.
b) The digestive system is complete and has opeaning at both the end.
c) Example- Animals of phylum Annelida onwards.
True coelom appeared first in the course of evolution in
Aschelminthes
Chordata
Echinodermata
Annelida
D.
Annelida
Phylum Annelida shows evidence for first true coelomates. Species belonging to annelida eg. Nereis, hirudinaria etc. Show presence of all three germ layers viz. Ectoderm, Endoderm and Mesoderm. The cavity (coelom) is lined by the cells of Mesoderm. Annelids are schizocoelomates. Mesoderm splits and forms the schizocoelom. In schizocoelomates the opening of the embryonic gut first develops into mouth and later forms the anus.
Shifting of ammonotelism to ureotelism is seen in
fishes
protopterus
frog
snake
C.
frog
In the tadpoles, the end product of nitroger metabolism is ammonia which is easily disposed off by diffusion in water. After metamorphosis, however the frog excrete most of their nitrogen in the form of urea and only small amount as ammonia.
Which of the following is not found in vertebrates
Bilateral symmetry
Gill opening
Body scales
Cnidoblasts
D.
Cnidoblasts
Cnidoblasts (nematoblast) are specialised and modified interstitial cells which are found in coelenterates. These are the organs of defence and offence.
Which of the following is a viral disease in silkworm ?
Flacherie
Grasserie
Muscardine
Pebrine
B.
Grasserie
The viral disease common in silkworm is Grasserie disease. It is also called jaundice of silkworm.
Flacherie is a bacterial disease. Muscardine is caused by fungus and Pebrine is a protozoan parasitic disease of silkworm.
Which of the following is not the example of marine fishes ?
Labeo
Mugil
Hilsa
Sardines
A.
Labeo
Marine fishery deals with ocean fishes. Sea fishing in India is confined to a narrow coastal region, leaving the off-shore and deep-sea regions unexplored. Some of the important marine fishes are Cat fish, Ribbon fish, mugil, hilsa, bombay duck, Sardines etc. Labeo is a fresh water fish.
Which artery is absent in frog
Right systemic arch
Phrenic artery
Carotid artery
Renal artery
B.
Phrenic artery
Phrenic artery is present in mammals which carries blood to diaphragm. In frog diaphragm is absent, therefore, there is no phrenic artery.
Blind sac body plan is shown by
roundworms
annelids
coelenterates
arthropods
C.
coelenterates
Blind sac body plan is found in coelenterates and flatworms. In this type of body plan, animals have a single opening that acts as both mouth and anus. eg, Hydra.
The typhlosole in earthworm is related with
excretion
absorption
respiration
reproduction
B.
absorption
A typhlosole is an internal fold of the intestine or intestine inner wall. Typhlosoles occur in bivalve mollusks, lampreys and some annelids and echinoderms.
It is a highly glandular, vascular longitudinal ridge increasing the area for absorption of digested food.
Mesoglia is seen in between
ectoderm and endoderm
ectoderm and mesoderm
mesoderm and endoderm
just below mesoderm
A.
ectoderm and endoderm
The coelenterates are diploblastic animals. They have two germ layers, the ectoderm and endoderm. Between these two layers, a thin, delicate, transparent and non-cellular mesogloea is present. Mesoglea is present in Diploblastic animals (a) between ectoderm and endoderm. However, in triploblastic animals (b) mesoderm is present between ectoderm and endoderm.

Green gland is the excretory organ of
prawn
butterfly
snail
earthworm
A.
prawn
In many higher crustaceans the excretory glands are located in the head. They are called antennal glands or maxillary glands, depending on whether they open at the base of the antennae or at the maxillae. If the tubule adjacent to the excretory pore is green, the gland is called a green gland.
Malphigian tubules is the excretory organ of butterflies. It is mainly to keep a constant level of salts and water in the haemolymph or blood of the butterfly. It is also to get rid of toxic compounds that are produced during metabolism.
Nephridium is the excretory organ of snails and earthworm. In Snails, it basically removes the nitrogenous waste and maintains the internal water balance. In earthworm, carbon dioxide is excreted out from the body through its moist skin by the process of diffusion.
The parasite, which completes its life cycle in a single host is
Fasciola hepatica
Plasmodium vivax
Taenia solium
Ascaris lumbricoides
D.
Ascaris lumbricoides
Ascaris lumbricoides completes its life cycle in a single host. It is one of the most familier endoparasite of man. It inhabits the small intestine more frequently of children than of adults.
Water vascular system is present in which of the following phylum?
Porifera
Cnidaria
Ctenophora
Echinodermata
D.
Echinodermata
The water vascular system is a hydraulic system used by echinoderms, such as sea stars and sea urchins, for locomotion, food and waste transportation, and respiration. It is composed of canals connecting numerous tube feet.
In which triploblastic animal, coelom is absent?
Platyhelminthes
Aschelminthes
Annelids
Arthropoda
A.
Platyhelminthes
The members of Phylum- Platyhelminthes are triploblastic and acoelomate, ie, without any body cavity. The spaces between various organs are filled with special mesodermal tissue, the mesenchyma.
In which of the following phyla, compound eyes are present?
Annelida
Arthropoda
Mollusca
Echinodermata
B.
Arthropoda
Compound eyes are present in Phylum- Arthropoda. Each eye consists of about visual elements or units called ommatidia.
Which one of the following is the infective stage of Ascaris lumbricoides?
Unsegmented egg
Egg with first stage larva
Egg with second stage larva
Free third stage larva
C.
Egg with second stage larva
Ascaris has no intermediate host and man acquires infection by directly ingesting Ascaris eggs containing the infective second stage rhabditoid larva with contaminated food or water.
Name two internal characteristic features of class-Mammalia
The internal characteristic features of Class- Mammalia are:
(i) Body cavity is divided by a muscular diaphragm between thorax and abdomen.
(ii) Body is maintained at a hugh and constant temperature by means of internal regulation.
State the advantages of composite fish culture.
In this system, both local and imported fish, a combination of five or six fish species is used in a single fish pond. These species are selected so that they do not compete for food among them by having different types of food habitats.
Advantages:
- Increases the yield of fish.
- Helps in maximum fish production.
- Availability for consumption.
- Can help farmers increase their financial position.
- Also creates employment for skilled and unskilled youths.
'Water vascular' system is found in
sea-anemone
sea-pen
sea-cucumber
sea-horse
C.
sea-cucumber
The water vascular system is a hydraulic system used by echinoderms such as starfish, sea cucumber, etc, for locomotion, food and water transportation and respiration. The system is composed of canals connecting numerous tube feet. They move by alternately contracting muscles that force water into the tube feet, causing them to extend and push against the ground, then relasing to allow the feet to retract.
Retrogressive metamorphosis occurs in
Hemichordata
Cephalochordata
Urochordata
Vertebrata
C.
Urochordata
Metamorphosis is a change from the juvenile to adult stage in which larval stage is quite different from the adult stage.
In retrogressive metamorphosis, the larva possesses advanced characters which are lost during the development and the adult is either sedentary or degenerated with primitive characters.
Urochordate adults, being sedentary show degenerative characters, while the free swimming tadpole larva shows advanced chordate characters which are lost during metamorphosis. Parasitic crustaceans, like Sacculina and copepod parasites and stylopids and scale insects (Insecta) also show retrogressive metamorphosis.
'Organ of Jacobson' helps in
touch
vision
smell
hear
C.
smell
Jacobson's organ, also called vomeronasal organ, an organ of chemoreception is a part of the olfactory system of amphibians, reptiles, and mammals, although it does not occur in all tetrapod groups. It was discovered by Frederick Ruysch and later by Ludwig Jacobson mis 1813.
Cysticercus stage is formed in
Taenia
Plasmodium
Leishmania
Wuchereria
A.
Taenia
Taenia is a genus of tapeworm that includes some important parasites of livestock. Members of the genus are responsible for taeniasis and cysticercosis in humans. They are morphologically characterised by a ribbon-like body composed of a series of segments called proglottids. The anterior end of the body is the scolex.
Which of the following is a catadromous fish?
Hilsa sp.
Mystus sp.
Anguilla sp.
Channa sp.
C.
Anguilla sp.
Anguilla sp, is a catadromous fish found on the Eastern coast of North America. It has a snake-like body with a small sharp pointed head. It has sharp pointed teeth but no pelvic fins. It is very similar to the European eel, but the two species differ in number of chromosomes and vertebrae.
Which of the following animal belongs to class-Crustacea?
Cockroach
Cyclops
Grasshopper
Mosquito
B.
Cyclops
Cyclops are crustaceans and related to lobsters, crabs and shrimp. They are invertebrates with a hard outer shell. They have five pairs of legs and a divided tail-like appendage called a furca. They are small about 2-3 mm long with one black or red eye in the middle of their head.
Radula is found in
Pila sp.
Chiton sp.
Lamellidens sp.
Pinctada sp.
A.
Pila sp.
Radula is a tongue-like organ of molluscs (Pila) consisting of a horny strip whose surface is studded with rows horny teeth for rasping food. In some species, it is modified for scraping or boring.
the scientific name of Asian Tiger Mosquito
Aedes aegypti
Aedes albopictus
Aedes taeniorhynchus
Aedes albolineatus
A.
Aedes aegypti
Aedes albopictus, from the mosquito family, also known as tiger mosquito or forest mosquito, is a mosquito native to the tropical and subtropical areas of Southeast Asia; however, in the past few decades, this species has spread to many countries through the transport of goods and international travel.
Aedes albopictus is the scientific name of Asian tiger mosquito.
Ornithorhynchus is an example of
dinosaur
monotreme mammal
marsupial mammal
eutherian mammal
B.
monotreme mammal
Ornitlwrhyncus anatinus (Duckbilled platypus) is a monotreme mammal, which belongs to sub-class-Prototheria (primitive egg laying mammals), order-Monotremata (living prototherians).
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
Sycon - Canal system
Star fish - Radial symmetry
Ascaris - Flame cell
Prawn - Haemocoel
C.
Ascaris - Flame cell
Fame cells are excretory organs of platyhelminthes. The excretory organ of Ascaris is protonephridia.
Which one of the following animal phyla does not possess a coelom?
Platyhelminthes
Annelida
Mollusca
Echinodermata
A.
Platyhelminthes
The animals of phylum-Platyhelminthes are triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, acoelomate and mostly parasitic.
The scientific name of the moth which produce tasar is
Bombyx mori
Antherae mylitta
Antherae assamensi
Philosomia ricini
C.
Antherae assamensi
Tasar silkworm (Antherae assamensis) is found in China, India and Sri Lanka. This moth does not easily interbreed so, the cocoon are collected from wild areas.
Muga silk worm feeds on
Shorea
Terminalia
Machilus
Marus
C.
Machilus
Muga silkworm (Antheraea assama) belongs to family Saturniidae and is native to Asom (India). Its caterpillars feed on Machilus, cinnamon plants. Silk produced by this moth is known as muga silk.
Which one of the following animal phyla possesses spicule?
Annelida
Mollusca
Porifera
Platyhelminthes
C.
Porifera
Members of phylum-Porifera are characterised by porous body, spongocoel and presence of calcareous/siliceous spicules or proteinaceous spongin fibres or both.
Fin rot of fish is caused by
Aeromonas
Pseudomonas
Branchiomyces
Xenopsylla
B.
Pseudomonas
Fin rot disease of fish is caused by a bacterial infection (e.g., Aeromonas or Psudomonas infection). It is a common symptom of a bacterial disease that affects variety of fishes. Sometimes fin rot begins after an injury to the fish's fins or tail.
In most simple type of canal system of Porifera, water flows through which one of the following ways?
Ostia Spongocoel Osculum Exterior
Spongocoel Ostia Osculum Exterior
Osculum Spongocoel Ostia Exterior
Osculum Ostia Spongocoel Exterior
A.
Ostia Spongocoel Osculum Exterior
The ascon type is the simplest type of canal system found in asconoid sponges like Leucosolenia. The course of water current in ascon type of canal system looks like
Ingressing water spongocoel To outside.
Select the wrong statement.
Isogametes are similar in structure, function and behaviour
Anisogametes differ either in structure, function and behaviour
In oomycetes female gamete is smaller and motile, while male gamete is larger and non-motile
Chlamydomonas exhibits both isogamy and anisogamy and Fucus shows oogamy
C.
In oomycetes female gamete is smaller and motile, while male gamete is larger and non-motile
Oomycetes or egg fungus include water moulds, white rusts and downy mildews. In these, female gamete is smaller and motile, whereas male gamete is larger and non-motile.
Isogametes are found in algae like Ulothrix, Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, etc., which are similar in structure, function and behaviour.
Anisogametes are found in Chlamydomonas in which one gamete is larger and non-motile and the other one is motile and smaller.
Oogamy is the fusion of non-motile egg with motile sperm. The gametes, differ both morphologically as well as physiologically. It occurs in Chlamydomonas, Fucus Chara, Volvox, etc.
One of the representative of Phylum - Arthropoda is
cuttlefish
silverfish
pufferfish
flying fish
B.
silverfish
Silverfish - Arthropoda
Cuttlefish - Mollusca
Putterfish - Chordata (Phylum)
Class - Pisces
Flying fish - Pisces.
The body of Rohu fish is covered by
cycloid scale, but the tail of homocercal
placoid scale, but the tail of heterocercal
cycloid scale, but the tail of heterocerca
placoid scale, but the tail is homocercal
A.
cycloid scale, but the tail of homocercal
Rohu (Labeo rohita) is a carp, which belongs to Class- Osteichytes (bony fishes). The body of rohu or exoskeleton is covered with dermal scales like cycloid scale and the tail fin is always homocercal type (i.e., has equal lobes) or diphycercal type while, the cartilaginous fishes such as Scoliodon has tough skin containing minute placoid scales and the tail fin is heterocercal type (i.e., has unequal lobes).
Which one is an example of living fossil?
Coral
Ascidia
Octopus
King crab
D.
King crab
King crab or horse shoe crab are a superfamily of crab-like decaped crustaceans chiefly found in cold seas. They are generally thought to be derived from hermit crab (the ancestors). It is considered as a living fossil because it has been on earth for millions of years.
Which one of the following matching pairs is incorrect?
Mollusca - Pseudocoel
Cnidaria - Nematocyst
Annelida - Chloragogen cells
Echinodermata - Water vascular system
A.
Mollusca - Pseudocoel
Molluscs are coelomate animals. In such animals, body cavity is lined by mesoderm. Whereas, in some animals body cavity is not lined by mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is persent as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such animals are called pseudocoelomates, e.g. Aschelminthes.
Which one of the following matching pairs is incorrect?
Shell fish - Pisces
Silver fish - Arthropoda
Cuttle fish - Mollusca
Star fish - Echinodermata
A.
Shell fish - Pisces
Shell fish is the term used for exoskeleton bearing aquatic invertebrates including various species of molluscs crustaceans and echinoderms. They are used as food.
Which one of the following group of animals is homeothermic?
Reptiles
Amphibians
Birds
Fishes
C.
Birds
Birds, humans and other mammals can maintain their body temperature irrespective of external temperature variation, i.e. they are warm blooded (homeothermic) animals. While, all reptiles, insects, amphibians and fishes are cold-blooded (poikilothermic) animals. These animals cannot control their body temperature, i.e. their body temperature varies considerably.
Which one of the followings is not a characteristic feature of mammals?
Diphyodont tooth
Ten pairs of cranial nerves
Seven cervical vertebrae
Left aortic arch in the circulatory system
B.
Ten pairs of cranial nerves
Mammals have 12 pairs of cranial nerves not 10. These are:
1. Olfactory
2. Optic
3. Oculomotor
4. Trochlear
5. Tnigeminal
6. Abducent
7. Facial
8. Vestibulocochlear
9. Glossopharyngeal
10. Vagus
11. Accessory
12. Hypoglossal
Antelope cervicapra is
a mammal
commonly known as black back
an animal under data deficient category of wildlife
a threatened Indian wildlife
A.
a mammal
B.
commonly known as black back
D.
a threatened Indian wildlife
Antelope cervicapra (the blackbuck) is an ungulate species of antelope native to the Indian sub continent that has been classified as near threatened by IUCN since 2003. It is a mammal belonging to Order Artiodactyla.
The largest type of nematocysts in Hydra is
Holotrichous isorhizas
Atrichous isorhizas
Desmonemes
Stenoteles
D.
Stenoteles
Stenoteles or penetrants are the largest type of nematocysts in Hydra. The thread tube is open at the end. When discharged, it release thread tube by which a poisnous fluid, hypotoxin is injected paralysing the prey.
Which of the following represents the class of Tubifex?
Echiurida
Archiannetida
Hirudinea
Oligochaeta
D.
Oligochaeta
Tubifex belongs to the class-oligochaeta of Phylum - Annelida. These worms are often found in the delicate tubes in the mud.
Select the mismatch from those given below.
Noctiluca bioluminescence
Gonyaulax catenella saxitoxin
Pyrodinum red tide
Ceratium-zygotic meiosis
C.
Pyrodinum red tide
Some dinoflagellates proliferates in large numbers and cause red tide of the sea. Eg. Gonyaulax and Gymnodinium
Receptacle of antheridiophore and archegoniophore of Marchantia respectively are
8 lobed, 9 rays
6 lobed, 4 rays
9 lobed, 5 rays
2 lobed, 6 rays
A.
8 lobed, 9 rays
Sexually, Marchantia is dioecious with sex organs borne on stalked upright receptacle or gametophore. Gametophore of male is antheridiophore and that of female is archaegoniophore. Former is 8-lobed and latter has 9 cylindircal processes or rays.
Bioluminescence is a characteristic feature of
Diatoms
Dinoflagellates
Slime moulds
Euglenoid
B.
Dinoflagellates
Bioluminescence is the property of a living organism to emit light. Some marine dinoflagellates show bioluminescence i.e., emitting light, Noctiluca, Pyrodinium, Pyrocystis, etc.
Haemocyanin pigment is found in which of the following animal group?
Annelida
Insects
Lower invertebrates
Platyheliminthes
C.
Lower invertebrates
Haemocyanin is a protein, which transports oxygen in the body of some invertebrates like molluscs, crustaceans, arthropods, etc. Unlike Hb, it has a copper base, thus, have less affinity towards oxygen compared with haemoglobin.
The eggs of the amphibians are
Mesolecithal
Telolecithal
Centrolecithal
Homolecithal
B.
Telolecithal
Based on the quantity of yolk in the cytoplasm of the eggs, it is classified into:-
(i) Homolecithal (uniformaly distributed yolk
(ii) Telolecitha (yolk is concentrated in the vegetal half) e.g., In amphibians.
(iii) Mesolecithal (Yolk is very large, occupies most of the space).
(iv) Centrolecithal (Yolk localised at the centre).
Aristotle's lentern is
pedicellariae in Pycnopodia
arval form in Antedon
pressure equalisation plate in Asterias
masticatory organ in the digestive tract of sea urchin
D.
masticatory organ in the digestive tract of sea urchin
Aristotle's lantern is a masticatory organ found in the digestive tract of sea urchin. It is made up of five ossicles, which in tum are made up of 250 skeletal elements.
Ornithorhynchus is a connecting link between
fishes and amphibians
Annelida and Arthropoda
Annelida and Mollusca
reptiles and mammals
D.
reptiles and mammals
Ornithorhynchus is a connecting link between reptiles and mammals. They bear hair and mammary glands (like-mammals), but also possess some of the reptilian characteristics such as egg laying, presence of cloaca and some skeletal similarities.
A fish introduced into a water body to control mosquito population is
Gambusia
Labeo
Notopterus
Fistularia
A.
Gambusia
Gambusia is a small fish that is introduced into a water body to control mosquito population. It is a fresh water fish. It feeds on larvae of mosquitoes.
Identify the incorrect match
Mulberry silk - Bombyx mori
Tasar silk - Antheraea pernyi
Muga silk - Antheraea assama
Eri silk - Attacus ricini
B.
Tasar silk - Antheraea pernyi
Tasar silk is obtained from Antheraea paphia that belongs to Family - Saturniidae. It is common in India, China and Sri Lanka. Antheraea pernyi is oak silkworm. It also produces good quality silk.
All chordates at one or other stage possess
two pairs of pentadactyl limbs
pharyngeal gill slits
movable jaw
vertebral column
B.
pharyngeal gill slits
In all the chordates, at some stage of their life history, a series of paired lateral gill clefts or gill slits perforate through the pharyngeal wall of the gut behind the mouth. They serve primarily for the passage of water from pharynx to outside.
Mammals have
biconvex RBCs to increase the surface area
biconcave RBCs to increase the surface area
spherical RBCs to increase the surface area
no RBCs
B.
biconcave RBCs to increase the surface area
RBCs of all mammals are mostly biconcave and circular (except camel and llama RBCs, which are oval). Mature mammalian RBCs do not have cell organelles including nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, centrioles and ER.
Mehli's gland in tapeworm is associated with
respiration
reproduction
excretion
circulation
B.
reproduction
Mehli's gland in tapeworm is associated with reproduction. It is situated distally in the proglottid. The ootype is surround by numerous unicellular shell gland called Mehli's gland.
Which of the following animals has a tetramorphic colony?
Velella
Physalia
Obelia
Porpita
B.
Physalia
Physalia is tetramorphic in nature, it consists of
(i) a small dactylozooid with a long slender tantacle.
(ii) a gastrozooid with mouth but no tentacle.
(iii) a branched gonozooid, which bears both male and female gonophores.
(iv) a large dactylozooid with an enormous nematocyst bearing fishing tentacle.
Select the correct set of animals of Class- Mammalia.
Lion, bat, whale, ostrich
Whale, bat, kangaroo, hippopotamus
Lion, hippopotamus, penguin, bat
Hippopotamus, penguin, whale, kangaroo
B.
Whale, bat, kangaroo, hippopotamus
Whale, Bat, Kangaroo and Hippopotamus belongs to Class- Mammalia. Characteritics of the mammals in this class are-
- Have mammary glands.
- Have four chambered heart.
- Posses diaphragm.
- Have sebaceous (fat secreting glands), sudoriferus (sweat), and scent glands.
- Have heterodont dentation.
Respiration in Ascaris is
aerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
Both (a) and (b)
None of the above
C.
Both (a) and (b)
Respiration in Ascaris is both anaerobic and aerobic. It occurs in different conditions.
In the process of anaerobic respiration, glycogen undergoes glycolysis to yield carbon dioxide, fatty acids and energy. The main fatty acids which are produced include valerianic butyric and caproic acids. These are excreted through cuticle and these impart a characteristic smell like that of a canned pineapple.
Comb jelly is member of phylum
Mollusca
Echinodermata
Coelenterata
Ctenophora
D.
Ctenophora
Comb jelly belongs to Phylum - Ctenophora. It comprise a phylum of invertebrate animals that live in marine waters. They are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia.
Jaws present in which of the following?
Herdmania
Fishes
Petromyzon
Amphioxus
B.
Fishes
Jaws are present in fishes, for eg, Gnathostoma.
Which of the following is not insect?
Spider
Grasshopper
Fly
Bee
A.
Spider
Spider belongs to Class- Arachanida. It has 4 pairs of leg and their body is divisible into cephalothorax and abdomen.
Grasshoppers belong to Sub- order Caelifera. They have powerful hind legs which allow them to escape from threats.
Flies belong to Order- Diptera. They have a pair of functional wings for flight and a pair of vestigial hindwings for balance.
Bees are flying insects. They have their role in pollination.
Microlecithal eggs are present in
Insects
Aves
Fishes
Mammals
D.
Mammals
Microlecithal eggs are found in mammals and these are small sized egg with very small amount of yolk.
Digestion in Leucosolenia and other sponges is
only extracellular
only intracellular
first extracellular, then intracellular
first intracellular, then extracellular
B.
only intracellular
Digestion occurs in food vacuoles only, hence, it is completely intracellular.
A cysticerous in pig muscles can remain alive for
six months
one year
six years
one month
C.
six years
Cysticerci remain alive for 5-6 years and are then calcified by the host (pig).
Tube within tube plan is exhibited by which of the following groups of animals?
Arthropods
Cephalochordates
Annelids
Mollusca
C.
Annelids
Annelids have straight alimentary canal representing a tube within a tube plan. In deuterostomatic animals anus develops earlier during embryonic development from
blastopore (e.g., all chordates and echinoderm invertebrates).
Molluscan blood contains
haemoglobin
haemozoin
haemocyanin
All of these
C.
haemocyanin
Haemocyanin is the characteristic respiratory pigment of only Mollusca and some arthropods.
Moulting in snakes is done by shedding
comified cells
stratified germinativum
epidermis
dermis
A.
comified cells
Stratum comeum is keratinized layer and is shed by snakes annually.
Leveret is young one of
eagle
hawk
deer
None of these
D.
None of these
Leveret is young one of a mammal (hare).
Which one is not diploblastic?
Sponge
Cnidarian
Nematoda
Tenophora
C.
Nematoda
Diploblastic animals have two primary germ layers ectoderm and endoderm as in Porifera, Coelenterata and Ctenophora. Sponges belong to Phylum- Porifera, Cindarian belongs to Phylum- Coelenterata and tenophora belongs to Phylum- Ctenophora.
Which of the following is made up of a single bone in mammals?
Dentary
Hyoid
Upper jaw
All of these
A.
Dentary
Dentary is a tooth bearing membrane bone. In mammals, it is the lower jaw, consisting of single membrane bone on each side fused together in front.
Gemmule formation in sponges are useful in
asexual reproduction
sexual reproduction
parthenogenesis
parthenocarpy
A.
asexual reproduction
Gemmules are asexual reproductive bodies of. sponges. These are formed by endogenous budding in all fresh water and some marine sponges.
Sexual reproduction involves viable male and female gametes.
Development of egg into an adult without fertilization is called parthenogenesis. It is common in honey bees.
Parthenocarpy is the development of seedless fruits.
During its life cycie, Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke) infects its intermediate host and primary host at the following larval stages respectively
metacercaria and ceracaria
miracidium and metacercaria
redia and miracidium
cercaria and redia
B.
miracidium and metacercaria
Liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) is a digenetic endoparasite, i.e., its life cycle completes within two hosts.
The primary host is sheep and the secondary or intermediate host is freshwater gastropod, snail. It infects its intermediate host at miracidium stage and its primary host at metacercaria stage.
Sycon belongs to a group of animals which are best described as
multicellular with a gastrovascular system
multicellular having tissue organisation, but no body cavity
unicellular or acellular
multicellular without any tissue organisation
D.
multicellular without any tissue organisation
Sycon belongs to Phylum- Porifera. These are the primitive group of multicellular animals. They have no tissue grade of organisation, and represent cell aggregated body plan.
Water vascular system is characteristic of
Protozoa
Porifera
Annelida
Echinodermata
D.
Echinodermata
Ambulacral system or water vascular system is a characteristic feature of echinoderms. This system comprises the system of canals and tube feet. Tube feet are also a characteristic feature of echinoderms, which help in adhesion, respiration, food capturing and locomotion.
Which one of the following animals lay eggs yet the female secretes milk?
Bat
Kangaroo
Platypus
Ostrich
C.
Platypus
Duckbilled platypus (Ornithorhyncus anatinus) is a semi-aquatic prototherian found in Australia and Tasmania. In these, the females lay eggs but yet produce milk and possess mammary glands without teats. Milk collects in two abdominal grooves from where the young ones obtainit through lapping.
A sponge harmful to oyster industry is
Cliona
Euspongia
Hyalonema
Spongilla
A.
Cliona
Boring sponges, such as Cliona, attach themselves to shells of oysters, clams, barnacles etc, boring them so full of holes that their contained animals are destroyed and in time, the shells are entirely broken up. Lime of these shells gets dissolved into sea water to be used over again by other animals. Sometimes, these boring sponges may prove great nuisance to oyster beds.
In sea anemone, the symmetry is
radial
bilateral
spherical
absent
A.
radial
In radial symmetry, body is divided into similar halves by more than two planes passing through one main axis. Eg. Cnidarians or coelenterates such as Hydra, sea anemone, Aurelia, Obelia) are radially symmetrical animals with cell-tissue grade of body organization.
Which of the following cell type is capable of giving rise to other cell types in sponges ?
Thesocytes
Pinacocytes
Cnidocytes
Archaeocytes
D.
Archaeocytes
Archaeocytes are the totipotent cells, which provide great regenerating power to sponges. Sex cells such as sperm and ova cells arise from undifferentiated archaeocytes.
Thesocytes store food granules.
Pinacocytes are the polygonal flat cells present as outer layer of cells, called pinacoderm lining the spongocoel or body cavity in Leucosolenia.
Cnidocytes occur in entire epidermis except that of basal disc and are found only in cnidarians. Cnidocytes are spherical or oval cells.
Malpighian tubµles are
excretory organs of insects
excretory organs of frog
respiratory organs of insects
endocrine glands of insects
A.
excretory organs of insects
Excretory organs of insects are called as malpighian tubules. They absorb excretory substances from haemolymph and fat bodies and pass into the proctodaeum. Uric acid is the excretory product of insects.
Trachea is the respiratory organ of insects. It opens outside by ten pairs of spiracles, present in thoracic and abdominal parts.
Endocrine glands of insects consist of corpora allata, corpora cardiaca and prothoracic gland. They regulate metamorphosis in insects through different hormonal secretion.
Excretory organ of frog is kidney.
The characteristic larva of phylum Coelenterata is
planula
cysticercus
rhabditiform
wriggler
A.
planula
The characteritics larva of Phylum- Coelenterata is Planula (Obelia) and Ephyra (Aurelia).
Cysticercus is the third larval stage seen in Taenia besides oncosphere, hexacanth (other two larval stages).
Rhabditiform is the first larval stage in Ascaris, which is formed within 10-14 days.
Wriggler is the larva of mosquito.
Apis dorsata refers to
rock bee
little bee
Indian bee
European bee
A.
rock bee
Apis dorsata is the scientific name of rock bee. It is found in the region of South and Southeast Asia. It is around 17- 20 mm long. Nests are mainly built in exposed places such as on tree limbs, buildings etc.
Which of the following is not a character of Chordata?
Dorsal tubular nerve cord
Pharyngeal gill slits
Presence of notochord
Presence of spinal cord
D.
Presence of spinal cord
Presence of spinal cord is not a characteristic feature of all chordates.
Salamandra atra is
ovoviviparous
oviparous
sexuaily sterile
parthenogenetic
A.
ovoviviparous
The Salamandra atra is ovoviviparous. The male discharge sperms in a capsule known as spermatophore. It is picked up by a female to fertilize her eggs internally. The female give birth to larvae and develops completely in water.
Flying fish is
Torpedo
Scoliodon
Anguilla
Exocoetus
D.
Exocoetus
Flying fish (Exocoetus) is a carnivorous fish. It is known as flying fish because it can leap into air by powerful tail and remain in air due to gliding slowly by means of large pectoral fins.
Ecdysone is secreted from:
insecta
trematoda
nematoda
polycheta
A.
insecta
Ecdysone is a steroid hormone. It controls moulting and metamorphosis in insects. It is a major insect moulting hormone.
The group of anamniota includes:
reptiles and birds
birds and mammals
fishes and amphibians
reptiles, and mammals
C.
fishes and amphibians
Anamniote are an informal group comprising the fishes and the amphibians. Amnion is an extraembryonic membrane that surrounds an embryo in reptiles, birds and mammals. Anamniotes are vertebrate animals as they lack amnion membrane e.g., fishes and amphibians.
The excretory material of bony fish is:
urea
protein
ammonia
amino acid
A.
urea
The excretory and osmoregulatory organs of the fishes are the gills and kidney. Excretion in bony fishes is ureotelic (i.e., they excrete urea) but some freshwater bony fishes are ammonotelic (i.e., excrete ammonia).
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





