Practical Geometry
Construct an isosceles triangle in which the lengths of each of its equal sides
is 6.5 cm and the angle between them is 110°.
An isosceles triangle PQR has to be constructed with PQ = QR = 6.5 cm. A rough sketch of the required triangle can be drawn as follows.
The steps of construction are as follows.
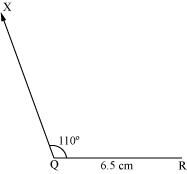
(i) Draw the line segment QR of length 6.5 cm.
![]()
(ii) At point Q, draw a ray QX making an angle 110° with QR.
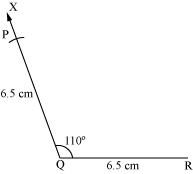
(iii) Taking Q as centre, draw an arc of 6.5 cm radius. It intersects QX at point P.
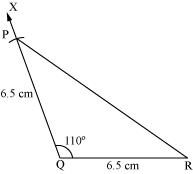
(iv) Join P to R to obtain the required triangle PQR.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Practical Geometry Chapter
Let l be a line and P be a point not on l. Through P, draw a line m parallel to l. Now join P to any point Q on l. Choose any other point R on m. Through R, draw a line parallel to PQ. Let this meet l at S. What shape do the two sets of parallel lines enclose?
Construct ΔXYZ in which XY = 4.5 cm, YZ = 5 cm and ZX = 6 cm.
Construct an equilateral triangle of side 5.5 cm.
Draw ΔPQR with PQ = 4 cm, QR = 3.5 cm and PR = 4 cm. What type of
triangle is this?
Construct ΔABC such that AB = 2.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 6.5 cm. Measure ∠B.
Construct ΔDEF such that DE = 5 cm, DF = 3 cm and m∠EDF = 90°.
Construct an isosceles triangle in which the lengths of each of its equal sides
is 6.5 cm and the angle between them is 110°.
Construct ΔABC with BC = 7.5 cm, AC = 5 cm and m∠C = 60°.
Construct ΔABC, given m∠A = 60°, m∠B = 30° and AB = 5.8 cm.
Construct ΔPQR if PQ = 5 cm, m∠PQR = 105° and m∠QRP = 40°.
(Hint: Recall angle sum property of a triangle).
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area