Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals And Energy Resources
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Social+science Contemporary India
Distinguish between the following in not more than 30 words.
Ferrous and Non-ferrous minerals.
Ferrous Minerals:
(i)Ferrous minerals account for about threefourths of the total value of the production of metallic minerals.
(ii)They provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical industries.
Non-ferrous Minerals:
(i)India’s reserves and production of non- ferrous minerals is not very satisfactory.
(ii)However, these minerals, which include copper, bauxite, lead, zinc and gold play a vital role in a number of metallurgical, engineering and electrical industries.
Distinguish between the following in not more than 30 words.
conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
Conventional sources include: firewood, cattle dung cake, coal, petroleum, natural gas and electricity (both hydel and thermal).
Non-conventional sources include solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas and atomic energy.
What is a mineral?
Geologists define mineral as a “homogeneous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.” Rocks are the treasure of minerals. Minerals are found in varied forms in nature, ranging from the hardest diamond to the softest talc.
How are minerals formed in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
In igneous and metamorphic rocks minerals may occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints.
The smaller occurrences are called veins and the larger are called lodes. In most cases, they are formed when minerals in liquid/ molten and gaseous forms are forced upward through cavities towards the earth’s surface.
Why do we need to conserve mineral resources?
We need to conserve mineral resources for the resaons mentioned below:
(i)The geological processes of mineral formation are so slow that the rates of replenishment are infinitely small in comparison to the present rates of consumption.
(ii)Mineral resources are, therefore, finite and non-renewable. Rich mineral deposits are our country’s extremely valuable but short-lived possessions.
(iii)Continued extraction of ores leads to increasing costs as mineral extraction comes from greater depths along with decrease in quality.
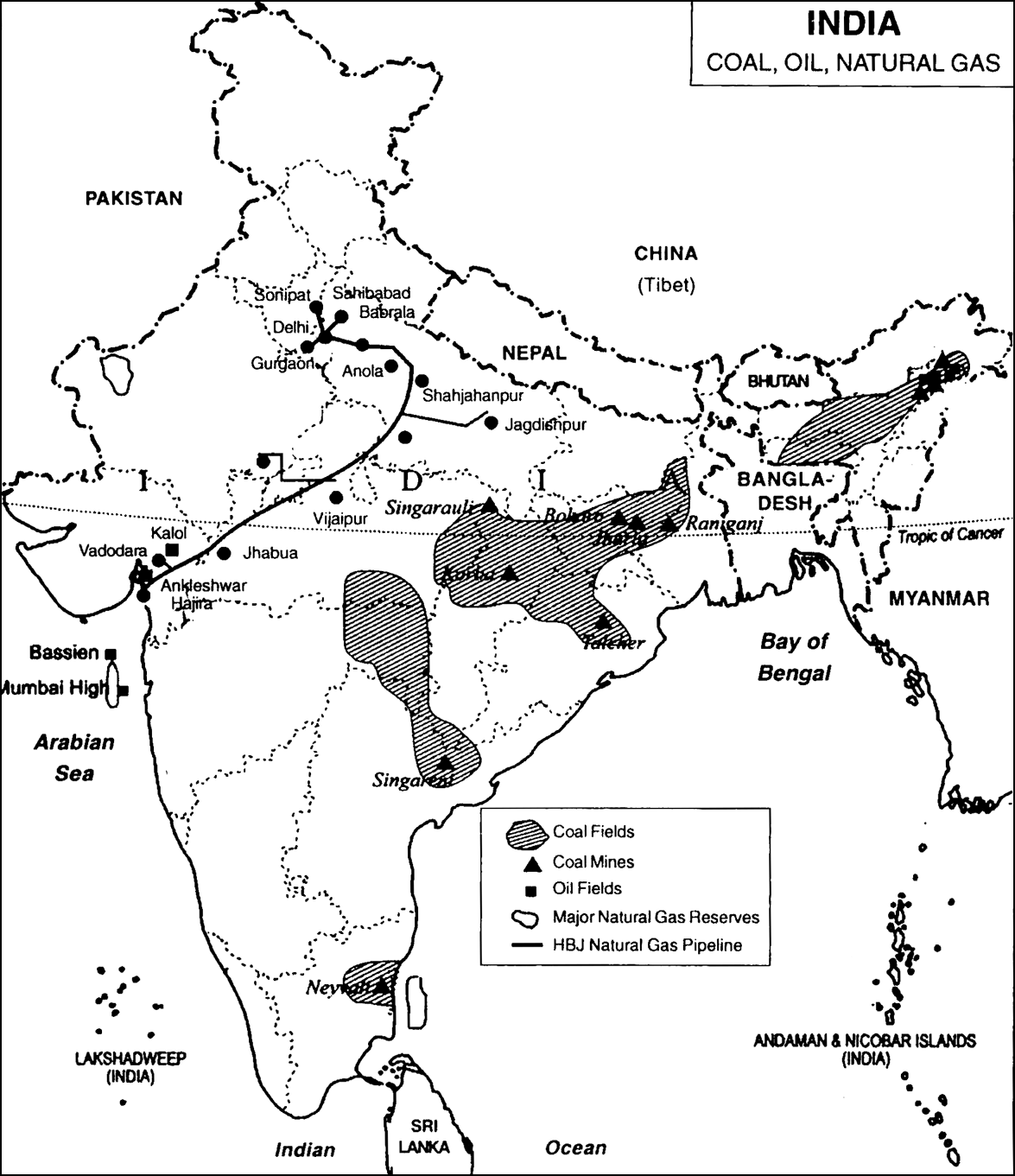
Describe the distribution of coal in India.
(i)The major resources of Gondwana coal, which are metallurgical coal, are located in Damodar valley (West Bengal-Jharkhand). Jharia, Raniganj, Bokaro are important coalfields.
(ii)The Godavari, Mahanadi, Son and Wardha valleys also contain coal deposits.
(iii)Tertiary coals occur in the north eastern states of Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Why do you think that solar energy has a bright future in India?
Solar energy has a bright future in India as:
(i)India is a tropical country.
(ii)It has enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy.
(iii)Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity.
(iv)Solar energy is fast becoming popular in rural and remote areas.
(v)Some big solar power plants are being established in different parts of India which will minimise the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes, which in turn will contribute to environmental conservation and adequate supply of manure in agriculture.
Fill the name of the correct mineral in the crossword below:
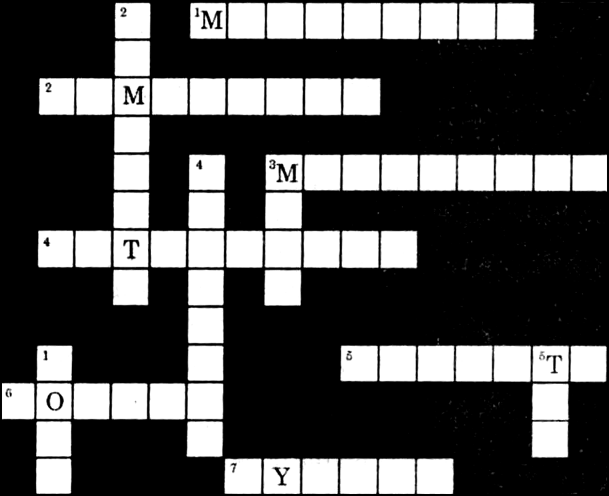
Across:
1. A ferrous mineral (9)
2. Raw material for cement industry (9)
3. Finest iron-ore with magnetic properties (9)
4. Highest quality hard coal (10)
5. Aluminium is obtained from this ore (7)
6. Khetri mines are famous for this mineral (6)
7. Formed due to evaporation (6)
Down:
1. Found in placer deposit (4)
2. Iron-ore mined in Bailadila (8)
3. Indispensable for electrical industry (4)
4. Geological Age of coal found in north east India (8)
5. Formed in veins and lodes (3)

Across: 1. Manganese, 2. Limestone, 3. Magnetite, 4. Anthracite, 5. Bauxite, 6. Copper, 7. Gypsum.
Down: 1. Gold, 2. Hematite, 3. Mica, 4. Tertiary, 5. Tin.
Why is mica used in toothpaste?
It makes toothpaste white
It makes toothpaste sparkle
It makes toothpaste soft
It makes toothpaste enable to kill germs
B.
It makes toothpaste sparkle
Sponsor Area
The largest producer (state) of copper is __________.
Bihar
Madhya Pradesh
Gujarat
Maharashtra
B.
Madhya Pradesh
Which one of the following belts has large reserve of iron-ore?
Orissa-Jharkhand belt
Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt
Durg-Baster-Chandrapur belt
Maharashtra-Goa belt
B.
Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt
Minerals are needed to be conserved because
they are finite and non-renewable
they are finite and renewable
they are infinite but non-renewable
none of these
A.
they are finite and non-renewable
The finest quality coal with the highest carbon content is
Lignite
Anthracite
Peat
Bituminous
B.
Anthracite
Coal is formed in ___________.
Metamorphic rocks
Igneous rocks
Sedimentary rocks
None of the above
C.
Sedimentary rocks
Why is Neyveli famous for?
Coal deposits
Mica deposits
Iron deposits
Aluminium deposits
A.
Coal deposits
Sponsor Area
In India the major part of petroleum is obtained from
Ankleshwar
Naharkatia
Mumbai High
Kalol
C.
Mumbai High
Which one of the following is a non-conventional source of energy?
Firewood
Coal
Petroleum
Solar energy
D.
Solar energy
Natural gas is considered an eco-friendly fuel because
it emits low carbon dioxide on combustion
it does not emit carbon dioxide on combustion
it emits low carbon monoxide on combustion
none of these
A.
it emits low carbon dioxide on combustion
Thermal power plants make use of
fast flowing water
uranium and thorium
coal, petroleum and natural gas
none of these
C.
coal, petroleum and natural gas
Sunlight, water, wind and biogas are the
conventional sources of energy
non-conventional sources of energy
instant sources of energy
latent sources of energy
B.
non-conventional sources of energy
Describe the importance of minerals in our lives.
(i)Almost everything we use, from a tiny pin to a towering building or a big ship, all are made from minerals.
(ii)The railway lines and the tarmac (paving) of the roads, our implements and machinery too are made from minerals. Cars, buses, trains, aeroplanes are manufactured from minerals and run on power resources derived from the earth.
(iii)Even the food that we eat contains minerals. In all stages of development, human beings have used minerals for their livelihood, decoration, festivities, religious and ceremonial rites.
(a) Write two types of metallic minerals with example.
(b) Mention two minerals in which India is rich and two minerals in which India is deficient.
(a)The two types of metallic minerals are:
(i)Ferrous
(ii)Non-ferrous
Ferrous metals - iron-ore and manganese.
Non-ferrous- copper and bauxite.
(b) Name of minerals in which India is rich are iron-ore and mica.
India is deficient in: Copper and zinc.
What are the three types of iron-ore and three uses of manganese-ore?
Three types of iron-ore are:
(i)Magnetite
(ii)Hematite
(iii)Limonite
Manganese is used in manufacturing bleaching powder, insecticides and paints.
Write four important iron-ore and manganese-ore producing states of India.
Four important Iron-ore producing states in India are:
(i)Chhattisgarh (ii) Jharkhand
(iii)Orissa (iv)Karnataka.
Four important manganese ore producing states in India are:
(i)Karnataka. (ii)Orissa
(iii)Madhya Pradesh (iv)Maharashtra
Which is the next major source of energy after coal in India? Explain its importance.
The next major source of energy after coal in India is petroleum.
The importance of Petroleum:
(i)It provides fuel for heat and lighting, lubricants for machinery and raw materials for a number of manufacturing industries.
(ii)Petroleum refineries act as a “nodal industry” for synthetic textile, fertiliser and numerous chemical industries.
(a) What is the difference between magnetite and hematite.
(b) Where are high grade of hematites found.
(a) Magnetite contains 60 to 70% of iron whereas hematite contains, 50 to 60% of iron.
(b) Very high grade hematites are found in the famous Bailadila range of hills in the Bastar district of Chhattisgarh.
Discuss the significance of coal in India.
(i)It provides a substantial part of the nation’s energy needs.
(ii)It is used for power generation, to supply energy to industry as well as for domestic needs.
(iii)India is highly dependent on coal for meeting its commercial energy requirements.
Explain the various types of coal.
The various types of coal are:
(i) Lignite: Lignite is a low grade brown coal, which is soft with high moisture content.
(ii) Bituminous: Coal that has been buried deep and subjected to increased temperatures is bituminous coal. It is the most popular coal in commercial use. Metallurgical coal is high grade bituminous coal which has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces.
(iii) Anthracite: Anthracite is the highest quality hard coal.
Describe the usage of manganese.
(i)Manganese is mainly used in the manufacturing of steel and ferro-manganese alloy.
(ii)Nearly 10 kg of manganese is required to manufacture one tonne of steel.
(iii)It is also used in manufacturing bleaching powder, insecticides and paints.
Why and where copper is mainly used? Which regions are the leading producers of copper in India?
The Balaghat mines in Madhya Pradesh, Khetri mines in Rajasthan and Singhbhum district of Jharkhand are leading producers of copper.
What do you mean by geothermal energy? Write any two experimental projects which have been setup to harness geothermal energy.
Two experimental projects have been set up in India to harness geothermal energy.
One is located in the Parvati valley near Manikarn in Himachal Pradesh and the other is located in the Puga Valley, Ladakh.
‘India is fortunate to have fairly rich and varied mineral resources.’ Examine.
(i)Broadly speaking, peninsular rocks contain most of the reserves of coal, metallic minerals, mica and many other non-metallic minerals.
(ii)Sedimentary rocks on the western and eastern flanks of the peninsula, in Gujarat and Assam have most of the petroleum deposits.
(iii)Rajasthan with the rock systems of the peninsula, has reserves of many non-ferrous minerals.
(iv)The vast alluvial plains of north India are almost devoid of economic minerals.
(v)These variations exist largely because of the differences in the geological structure, processes and time involved in the formation of minerals.
Why there is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development?
(i)Energy is a basic requirement for economic development.Every sector of the national economy – agriculture, industry, transport, commercial and domestic – needs inputs of energy.
(ii)The economic development plans implemented since Independence necessarily required increasing amounts of energy to remain operational.
(iii)As a result, consumption of energy in all forms has been steadily rising all over the country
How is electricity generated by tidel energy? Mention the region in India which provide ideal condition to it.
In India the Gulf of Khambhat, the Gulf of Kuchchh in Gujarat on the western coast and Gangetic delta in Sunderban regions of West Bengal provide ideal conditions for utilising tidal energy.
Write any six nuclear power stations in India.
The six nuclear power stations in India are mentioned below :
(i) Tarapur
(ii) Rawatbhata
(iii) Kalpakkam
(iv) Naruara
(v) Kakrapara
(vi) Kaiga
What steps should be taken to conserve the minerals?
(i)A concerted effort has to be made in order to use our mineral resources in a planned and sustainable manner.
(ii)Improved technologies need to be constantly evolved to allow use of low grade ores at low costs.
(iii)Recycling of metals, using scrap metals and other substitutes are steps in conserving our mineral resources for the future.
Tips: -
V. Imp.
Differentiate between natural gas and biogas.
Natural Gas:
(i)Natural gas is an important clean energy resource found in association with or without petroleum.
(ii)It is used as a source of energy as well as an industrial raw material in the petrochemical industry.
(iii)Natural gas is considered an environment friendly fuel because of low carbon dioxide emissions and is, therefore, the fuel for the present century
Biogas:
(i)Shrubs, farm waste, animal and human waste are used to produce biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas.
(ii)The plants using cattle dung are known as ‘Gobar gas plants’ in rural India. These provide twin benefits to the farmer in the form of energy and improved quality of manure. Biogas is by far the most efficient use of cattle dung.
(iii)It improves the quality of manure and also prevents the loss of trees and manure due to burning of fuel wood and cow dung cakes
Why aluminium is an important metal?
Mention in brief the wind power in India.
(i)The largest wind farm cluster is located in Tamil Nadu from Nagarcoil to Madurai.
(ii)Apart from these, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep have important wind farms.
(iii)Nagarcoil and Jaisalmer are well known for effective use of wind energy in the country.
What are the impacts of mining on the health of the miners and the environment?
The impacts of mining:
(i)The dust and noxious fumes inhaled by miners make them vulnerable to pulmonary diseases.
(ii)The risk of collapsing mine roofs, inundation and fires in coalmines are a constant threat to miners.
(iii)The water sources in the region get contaminated due to mining.
(iv)Dumping of waste and slurry leads to degradation of land, soil, and increase in stream and river pollution.
Why Mica is an indispensable minerals and where are its deposits found?
Mica is indispensable minerals due to its excellent di-electric strength, low power loss factor, insulating properties and resistance to high voltage.
Mica deposits are found in the northern edge of the Chota Nagpur plateau. Koderma Gaya – Hazaribagh belt of Jharkhand is the leading producer.
Write the distribution of bauxite in India.
Sponsor Area
(a) Mark three iron ore belts.
(b) Show three sites of iron ore mines and write the names of sites.
(c) Identify names and location of three exporting ports of iron-ore.
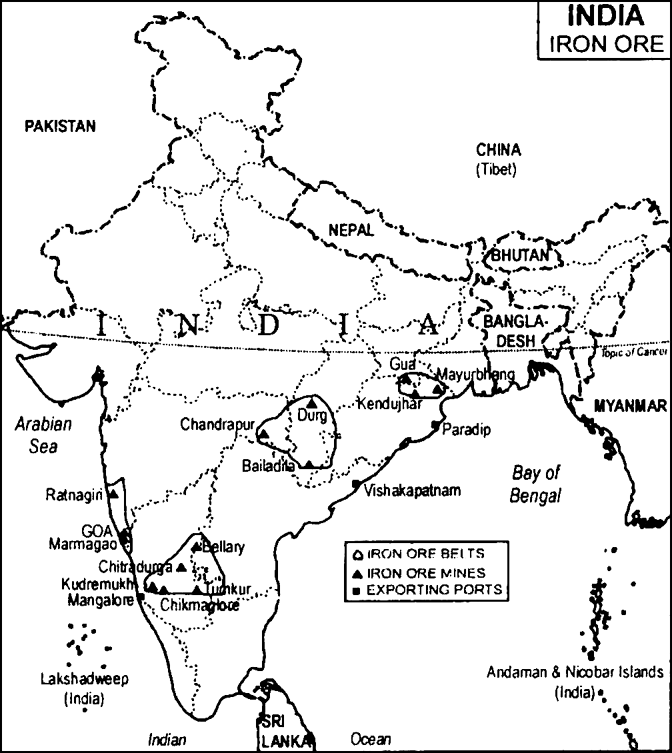
(a) Iron-ore belts: Iron ore belts have been marked on western coastside which extend from Ratnagiri to Marmagao.
Another belt is extended between Orissa and Bellary to Chikmaglore districts of Karnataka. One belt is extended centrol India near Durg to Bailadila and fourth belt of iron are is extended between Gua, Kendujhar in Orissa.
(b) Iron ore mines sites: Iron mines cites are Ratnagiri, Goa, Chitradurga, Tumkur, Chikmaglore, Kendujhar.
(c) Exporting Ports: Marmagao, Mangalore, Vishakhapatnam, Paradip.
On the outline map of India locate and mark (with their names).
(i) Three fields of Mica.
(ii) Three fields of Bauxite
(iii) Three fields of Manganese.
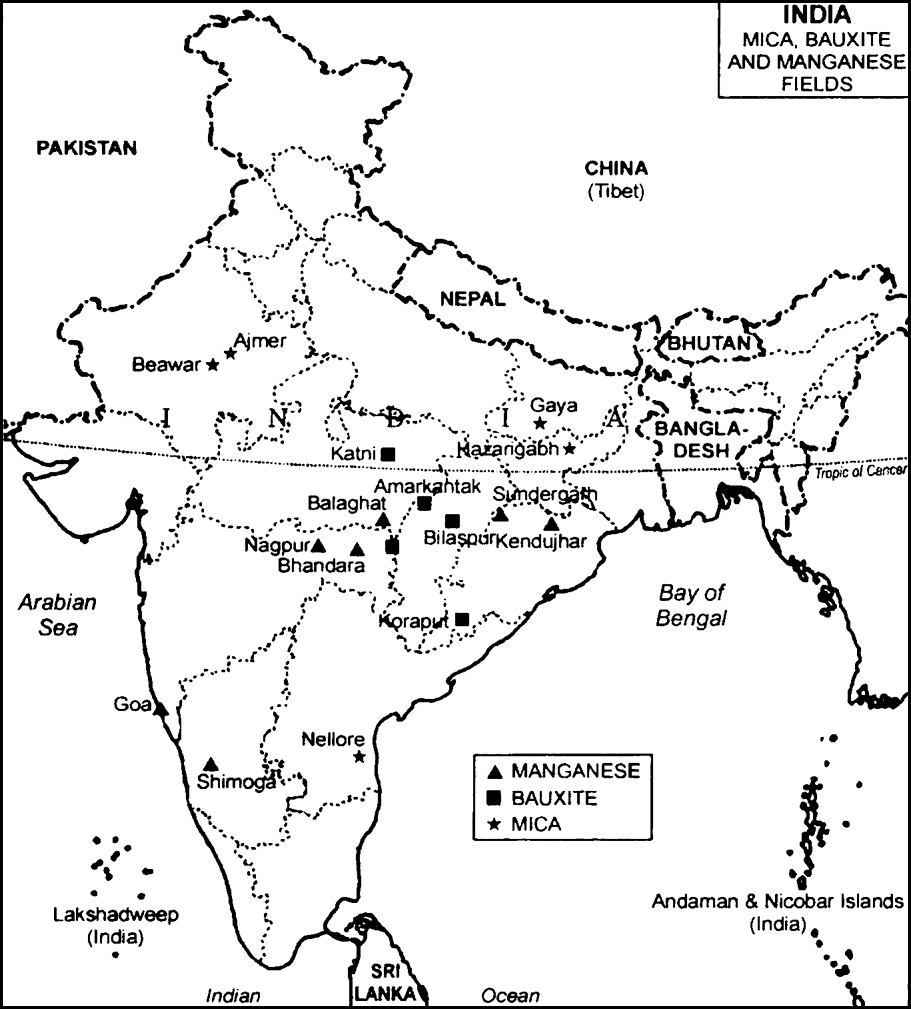
Hints: Mica: 1. Ajmer, 2. Beawar, 3. Gaya, 4. Hazaribagh, 5. Nellore.
Bauxite: 1. Katni, 2. Bilaspur, 3. Amarkantak, 4. Maikal hill.
Manganese: 1. Sundergarh, 2. Balaghat, 3. Nagpur, 4. Bhandara, 5. Kendujhar, 6. Shimoga, 7. Goa.
Why there is a pressing need to use renewable energy in India?
(i)The growing consumption of energy has resulted in the country becoming increasingly dependent on fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas.
(ii)Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in future, which in turn has serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
(iii)Moreover, increasing use of fossil fuels also causes serious environmental problems.
Match the following options:
| A. Beds of layers | (i) Common salts, magnesium |
| B. Alluvial place deposits | (ii) Gypsum, potash salt |
| C. Veins and lodes | (iii) Bauxite |
| D. Result of evaporation in deserts | (iv) Coal and iron ore |
| E. Ocean waters and ocean beds | (v) Manganese nodule |
| F. Residual mass of weathered material | (vi) Gold, silver etc. |
A. Beds of layers | (i) Coal and iron ore |
B. Alluvial place deposits | (ii) Manganese nodule |
C. Veins and lodes | (iii) Gypsum, potash salt |
E. Ocean waters and ocean beds | (v) Manganese nodule |
F. Residual mass of weathered material | (vi) Common salts, magnesium |
Why has aluminium metal great importance?
Because it is a good conductor of electricity and thus is used in the electrical equipment industry.
‘Consumption of energy in all forms has been rising all over the country. There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy saving’. Suggest and explain any three measures to solve this burning problem.
Three measures which need to be taken to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy saving are:
i. By judiciously using and conserving energy resources.
ii. By taking measures such as switching off electricity when not in use, using car pooling and travelling by public transport.
iii. By using non-conventional means of energy such as wind energy and solar energy.
How can solar energy solve the energy problem to some extent in India? Give your opinion.
India is a tropical country. It has enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. Solar energy is fast becoming popular in rural and remote areas. Some big solar power plants are being established in different parts of India which will minimise the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes, which in turn will contribute to environmental conservation and adequate supply of manure in agriculture.
Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India? Assess the importance of its different forms.
Coal is the most abundantly used fossil fuel in the country. It provides a substantial part of the nation’s energy needs.
(i) Lignite-It is a low-grade brown coal, which is soft with high moisture content and used for electricity generation.
(ii) Bituminous coal- The coal that has been buried deep and subjected to increased temperature is bituminous coal. It is the most popular coal in commercial use.
(iii) Anthracite- It is the highest quality hard coal and considered a metallurgical coal which has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces.
How can biogas solve the energy problem mainly in rural India? Give your suggestions.
The plants using cattle dung are known as ‘Gobar gas plants’ in rural india. These provide twin benefits to the farmer in the form of energy and improved quality of manure. Biogas has higher thermal efficiency in comparision to kerosene, dung cake and charcoal. Biogas is by far the most efficient use of cattle dung. It improves the quality of manure and also prevents the loss of trees and manure due to burning of fuel wood and cow dung cakes.
Which one of the following minerals is a fossil fuel?
-
Barium
-
Coal
-
Zircon
-
Uranium
A.
Barium
B.
Coal
Explain any three steps to be taken to conserve the energy resources.
Three steps to be taken to conserve the energy resources are –
(i) Use of public transport system instead of individual vehicles.
(ii) Switching off electricity when it is not in use.
(iii) Use of power saving devices and non-conventional sources of energy.
What are the two main ways of generating electricity? How are they different from each other? Explain.
Electricity is generated mainly in two ways-
(i) Hydro electricity is generated by fast flowing running water, which is a renewable resource. India has a number of multi-purpose projects like the Bhakra Nangal, Damodar Valley Corporation etc. producing hydroelectric power.
(ii) Thermal electricity is generated by burning fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas. The thermal power stations use non-renewable fossil fuels for generating electricity.There are over 310 thermal power plants in India.
Name the non-metallic mineral which can be split easily into thin sheets. Mention its uses.
Mica is the non-metallic mineral which can be split easily into thin sheets.
Due to its excellent di-electric strength, low power loss factor, insulating properties and resistance to high voltage, mica is one of the most indispensable minerals used in electric and electronic industries.
Why is there a pressing need for using renewable energy sources in India? Explain any five reasons.
There is a pressing need to use renewable energy resources in India because-
(i) The growing consumption of energy has resulted in the country becoming increasingly dependent on fossils fuels such as coal, oil and gas.
(ii) Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages.
(iii) Uncertainties about the security of energy supply in future.
(iv) The serious repercussions it has on the growth of the national economy.
(v) Increasing use of fossil fuels also causes serious environmental problems.
Which one of the following is a non-metallic mineral?
-
Lead
-
Copper
-
Tin
-
Limestone
D.
Limestone
Why is conservation of mineral resources essential? Explain any three methods of conserving mineral resources.
The geological processes of mineral formation are so slow that rates of replenishment are infinitely small in comparison to the present rates of consumption.
Mineral resources are, therefore, finite and non-renewable.
The methods for conservation:
(i) Improved technologies need to be constantly evolved to allow use of low grade ores at low coasts.
(ii) Recycling of metals, using scrap metals and other substitutes.
(iii) Usage of mineral resources in planned and sustainable manner.
Describe any three characteristics of 'Odisha-Jharkhand belt' of iron one in India.
Odisha - Jharkhand Belt:
(i.) In Odisha, high grade haematite ore is found in Badampahar mines in the Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar districts. In the adjoining Singhbhum district of Jharkhand; haematite iron ore is mined in Goa and Noamundi.
(ii.) This belt contains high grade hematite ore found in Kendujhar and Mayurbhanj mines; exported via Paradwip Port.
(iii.) Badampahar mines in the Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar districts of Orissa have high grade hematite ore. Additionally, hematite iron ore is mined in Gua and Noamundi in Singhbhum district of Jharkhand.
'Energy saved is energy produced.' Assess the statement.
Conservation of energy is essential because it protects our environment from green house gas emission and also saves valuable resources from getting depleted. If we save energy then only more energy can be produced. It is essential to use non- conventional sources of energy.
Following are some measures to conserve energy resources:
(i.) We should try to use more and more public transport system instead of private vehicles.
(ii.) Electronic devices must be switched off when not in use.
(iii.) It is necessary to use more and more power saving devices.
(iv.) Reduce consumption of non- renewable sources of energy.
(v.) If possible solar power should be used to generate electricity.
Where do minerals occur in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Major metallic minerals like tin, copper, zinc and lead etc. are obtained from these veins and lodes. In igneous and metamorphic rocks minerals occur in the veins and the lodes
'Minerals are unevenly distributed in India.' Support the statement with examples.
India is blessed with plenty of metallic and non-metallic mineral resources. However, they are unevenly distributed due to differences or variations in geological structures, processes and time involved in the formation of minerals. For instance,
1. majority of coal reserves, metallic minerals, mica and many other non-metallic minerals.
2. sedimentary rocks in Gujarat and Assam have petroleum deposits.
4. the alluvial plains of North India are mostly devoid of mineral resources.
Describe any three characteristics of the Drug-Bastar-Chandrapur Iron-ore belt in India.
Three characteristics of Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur iron-ore belt in India are as follows :
1.Lies in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra.
2.Very high grade hematites are found in the famous Bailadila range of hills in the Bastar district of Chattisgarh.
3.The range of hills comprise of 14 deposits of super high grade hematite iron ore.
Examine any five factors affecting the location of industries in India.
1. Raw Material:
The earliest industries in India developed near the sources of raw material.
2. Energy:
The iron and steel industry has been traditionally tied with the coal resources, as it uses coking coal for fuel. Similarly, the electro- metallurgical and electro-chemical industries, being power intensive, have been located where electricity is easily available.
3. Transport:
Transport is required for carrying raw materials to manufacturing units and finished products to the market.
4. Labour:
The availability of both unskilled and skilled, or technically qualified manpower, is an important factor in the location of industries.
5. Water:
Water is required to produce hydel power and in the process of manufacturing for cleaning, cooling, washing, etc. The industries which heavily depend on water, for one purpose or the other, include iron and steel (for cooling), textile (for bleaching and washing), paper and pulp, chemical, jute, food processing, leather and atomic power.
Analyse the role of chemical industries in the Indian economy.
The given below points enumerate the contribution of chemical industry to Indian economy.
(i) Chemical industry contributes to 3% of GDP and is the third largest in Asia.
(ii) It includes large and small scale units in both organic and inorganic sector.
(iii) Chemicals are used by most of the industries viz . fertiliser industries, petrochemical industries, synthetic fibre industries etc. at one stage or the other.
The dependency on chemical industries in terms of contribution to GDP, establishing large scale and small units in both organic and inorganic sector and use of chemicals by other industries make it a fast growing and diversifying industry
Why is it necessary to conserve mineral resources? Suggest any four ways to conserve mineral resources.
The following are the reasons why mineral resources need to be conserved:
i. The formation of minerals takes a long geological period of millions of years.
ii. Minerals are finite and limited in supply.
iii. Many of them such as coal and petroleum are non-renewable and exhaustible.
The following are the four ways in which mineral resources can be conserved:
i. Minerals should be used in a planned, judicious and sustainable manner.
ii. Technology should be upgraded to allow the use of low grade ore at low costs.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area