Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination And Integration
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Biology
Name the cells that the thyroid gland is composed of.
i. Follicles
ii. Stromal tissue
What is goitre?
Why is the Parathyroid hormone called hypercalcemic hormone?
How do thymosins provide humoral immunity ?
Thymosin help in the production of antibodies which provide the humoral immunity.
What is gluconeogenesis?
What is hyper secretion ?
Name the exact part of uriniferous tubule which is directly influenced by ADH.
What is synergism ?
What are antagonistic hormones?
Sponsor Area
What is ANF?
Which hormone is called hyperglycemic hormone?Why?
What connects the two lobes of thyroid glands?
Which two hormones are secreted by follicular cells?
The follicular cells synthesize the following two hormones :
i. Tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine (T4).
ii Triiodohyronine (T3).
Name the layers of the adrenal cortex.
i. Zona reticularis which is the inner layer
ii Zona Fasciculata which is the middle layer.
iii Zona granulosa which is outer layer.
The glucose homeostasis is maintained by which two hormones?
When thyroxine has negative feed back effect ?
When thyroxine has positive feed back effect ?
Which two hormone maintain the calcium balance in the body?
Which hormones can enter biomembrane to regulate cell activities by acting with the intracellular receptors?
Sponsor Area
Which hormone plays a vital role in immunity?
What are androgens ?
How many hormones are secreted by pars distalis ?
Pars distalis produces six hormones namely:
i. Growth hormone(GH)
ii. Prolactin (PRL)
iii. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
iv. Adenocortocotrophc hormone (ACTH)
v. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
vi. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Which gland has neurosecretory cells? What are those cells called?.
How many hormones are secreted by pars intermedia ?
Name the hormones secreted by pars nervosa.
i. Oxytocin
ii. Vasopressin.
Erythropoietin hormone is produced by?
Erythropoietin is produced by juxtaglomerular cells of kidney.
What are hormone receptors?
The complex formed on binding of the hormone to its receptor are known as hormone receptors.
Briefly state the effects of glucocorticoids.
i. They regulate carbohydrate metabolism.
ii. It stimulates the processes gluconeogenesis, lipolysis and proteolysis.
iii. It inhibits cellular uptake and utilization of amino acids.
iv. Maintain the cardio-vascular system and the kidney functions.
v. Glucocorticoids like cortisols have anti-inflammatory reactions.
vi. They suppress the immune response.
vii. They stimulate the production of RBC.
What is erythropoietin ?
What are 'Islets of Langerhans' ?
Define endocrine system and discuss the types of endocrine glands.
Endocrine system : It consists of endocrine glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried towards distant target organs.
Types of endocrine glands :
1. Pure endocrine glands : These glands only secrete hormones e.g. thyroid gland, pituitary gland etc.
2. Heterocrine glands : These glands secrete both enzymes and hormones. Thus, they act as endocrine and exocrine e.g. pancreas.
Write the functions of androgens.
Androgens are hormones produced by the leydig cells or institial cells of testis. The androgens perform the following function :
1. It regulates the developement , maturationand functions of the male accessory sex organs like epidydimis, vas deferens etc.
2. It regulates muscular growth, growth of facial hair.
3. It plays an important role in the stimulation of the process of spematogenesis.
Define the terms : endocrine glands and hormones.
Endocrine glands : These are ductless glands which produce hormones. The hormones secreted by them are transported by the blood to the different parts of the body.
Hormones : The hormones are chemical informational regulatory molecules secreted by endocrine glands. They non-nutrient chemicals which act as intercellular messengers and are produced in trace amounts.
Explain the types of hormones depending upon their origin.
On the basis of their chemical nature, hormones are divided into four groups :
1. Amino acid derivatives : These hormones are formed from amino acids e.g. epinephrine, norepinephrine etc.
2. Peptide derivatives : These are of derived from peptide, polypeptide and proteins e.g. insulin, glucagon, pituitary, hypothalamic hormones etc
3. Iodothryonines derivatives : e.g. thyroid hormones.
4. Steroid hormones : These are derived from steroids just as cholesterol e.g. testosterone, progestrone etc.
Write hormones secreted by placenta and the entric epithelium of stomach.
i. Placenta : secretes a human chorionic gonadotrophin hormone (hCG). It stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone.
ii. Enteric epithelium of stomach : It secretes gastrin hormone when bolus comes into stomach. The gastrin hormone stimulates gastric glands to secrete the gastric juice.
Write a note on thyroid gland.
Location : It is present in the neck. Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland. It is bilobed and both the lobes are connected by isthmus.
Structure: The thyroid gland is a lobular structure having two lobes. The lobes are connected by a thin flap like connective tissue called isthumus. The thyroid gland has two types of cells called follicular cells and stromal tissues.
Hormones synthesized : The thyroid glands release two hormones which are tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
Functions of the hormones:
1. The thyroid hormones play an important role in the regulation of metabolic rate.
2. they support the rate of red blood cell formation.
3. They control the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
4. They maintain water and electrolyte balance in the body.
5. They regulate the blood calcium levels.
Discussname the hprmones secreted by gasto instentinal tract.
Four major peptides hormone are secreted by the endocrine cells present in the gastro-intestinal tract :
It secretes the following hormones :
1. Gastrin : This hormone acts on the gastric gland and stimulate them to secrete hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen.
2. Secretin : It acts on the exocrine pancreas and stimulates secretion of water and bicarbonates.
3. Cholecystokinin (CCK) : It stimulates gall bladder to release bile and stimulates pancreas to secrete pancreatic juice.
4. Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) - inhibts gastric secretion and motility.
Write the cause, symptoms of Grave’s disease, iodine deficiency goitre, cretinism and myxoedema .
Cause : It is caused due to the excessive secretion of thyroxine.
Symptoms :
The disease is characterised by increased rate of metabolism, bulging of eyeballs, increased blood pressure and excessive perspiration.
2. Iodine Deficiency Goitre :
Cause : It is caused due to the lack of iodine in food.
Symptoms : It causes enlargement of thyroid gland. It occurs mostly to the people of hilly areas.
3. Cretinism :
Cause : It is caused due to hyposecretion of thyroxine in children.
Symptoms :
The person suffering from cretinism shows
stunted growth, mental retardation and low blood pressure.
4. Myxoedema :
Cause : It is caused due to the hyposecretion of thyroxine in adults.
Symptoms :
The affected person shows low metabolic rate, body temperature, mental retardationand weakness.
Describe parathyroid gland and give its functions.
Hormones : These glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) , which is a peptide hormone.
Functions of the hormones :
1. It increases the amount of calcium. It stimulates the resorption of Ca2+ from the digested food and and Ca2+ resorption in the renal tubules. It also the process of demineralization in bones.
2. It decreases the amount of phosphorous in blood.
3. It plays a significant role in maintaining the calcium balance in the body.
Explain the following :
(a) Insulin lowers the blood sugar level.
(b) Hypothalamus and pituitary function as an integrated and coordinated system.
(c)Body growth is greatly accelerated at puberty in the male.
(d) Adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system function as a closely integrated system.
(e) Pituitary gland regulates the reproductive system.
(a) Insulin is reponsible for lowering the blood sugar level by converting excess of glucose to gylcogen which is stored in muscles and liver.
(b) The hormones released by the hypothalamus controls all the secretions of hormones of pituitary gland. The hypothalamus hormones regulate the secretion and production of the pituitart hormones. Pituitary gland regulates the activities of other glands. Thus, pituitary gland and hypothalamus function as an integrated and coordinated system.
(c) At puberty there is an increase in the testosterone secretion by Leydig’s cells. The testosterone hormone plays a major role in body growthand accelerates body growth during puberty.
(d) Adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system are closely integrated systems as the emergency hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline are secreted during danger when nerve impulse reaches adrenal medulla via sympathetic nerves.
(e) Gonadotrophic hormone secreted by pituitary gland controls the male and the female gonads. The gonadotrophins released by the pituitary regulates the reproductive system.
Discuss the abnormalities of parathyroid gland.
Abnormalities of parathyroid gland :
1. Due to hyposecretion : Secretion of the PTH in lesser amount that the normal results in :
(a) Decrease of calcium of blood which causes cramps and convulsions.
(b) It also causes parathyroid tetani which is characterised by sustained contraction of muscles of face, larynx, limbs etc.
2. Due to hypersecretion : Secretion of the hormone in excess amount results in abnormal increase in the amount of calcium in blood. The increased calcium levels may results in easy fractures of bones.
Write notes on the following :
i. Hypothyroidism
ii. Melatonin
The effects of hypothyroidism are:
a. Goitre that is enlargement of tyhrois glands.
b. Hypothyroidiem during pregnancy causes defective developement and maturation of the baby. It may lead to stunted growth that is cretinism. mental retardation, low intelligence quotient, abnormal skin, deaf-mutism etc.
c. In adult women , it leads to irregularity in menstrual cycle.
a. It regulates the 24 hour cycle or the diurnal rhythm of the body.
b. It regulates the normal rhythm of the sleep-wake cycle.
c. It maintains the body temperature.
d. It regulates the skin pigmentation, influences the metabolism, menstrual cycle and the defense capability of the body.
Explain thymus gland.
Location : The thymus gland is a lobular structure located between the lungs and behind sternum on the ventral side of aorta.
Hormone : Secretes thymosin hormone. Thymosin is a peptide hormone.
Functions of the hormones :
1. It plays a major role in the differentiation of T-lymphocytes which provide cell-mediated immunity.
2. It promotes the production of antibodies.
Briefly explain the structure of adrenal gland and hormones secreted by its different parts.
Adrenal gland :
The adrenal glands are present in pairs, one at the anterior part of each kidney. The adrenal gland is made of two kinds of tissues namely
i. Adrenal medulla.
ii Adrenal cortex.
Parts of Adrenal gland :
1. Adrenal cortex : It is the outer part of the adrenal gland. It is further differentiated into three parts :
(a) Zona glomerulosa (Outer zone)
(b) Zona fasciculata (Middle zone)
(c) Zona reticulosa (Inner zone outer to adrenal medulla).
Hormones secreted - Adrenal cortex secretes the following three hormones derived from steroids :
(i) Aldosterone or mineralocorticoids.
(ii) Cortisol or glucocorticoids.
(iii) Sexcorticoids or androgens.
2. Adrenal medulla : It lies inner to cortex.
Hormones secreted- It secretes two hormones namely:
(a) Epinephrine
(b) Norepinephrine.
Write a note on Melanocyte stimulating hormone.
Discuss about functions of aldosterone and Cortisol
1. Aldosterone -
Functions :
a. Regulates the balance of water in the body.
b. It stimulates the reabsorption of Na+, water and excretion of K+.
b. It It helps in the maintenance of electrolytes, body fluid volume, osmotic pressure and blood pressure.
2. Cortisol :
Functions :
a. Maintains the cardio-vascular system as well as kidney functions.
b. Produce anti-inflammatory reactions and suppresses the immune response.
c. It stimulates the producion of RBCs.
Name one abnormalities caused by hypo and hyper secretion of hormones of adrenal cortex.
Abnormalities caused by the hypo or hyper secretion of hormones of adrenal cortex:
i. Disease caused due to hyposecretion of hormones
(a) Addison’s disease : It is caused due to the deficiency of mineralo-corticoids and Cortisol.
Symptoms : It is characterised by low blood sugar level and low blood pressure.
ii. Disease caused due to hypersecretion of hormones
(b) Cushing’s syndrome : It is due to the excess of Cortisol.
Symptoms : It is characterised by high blood sugar level, diabetes, weakness and restlessness.
Write a note on adrenal medulla.
Adrenal medulla : It is the centrally located tissue that lies inner to cortex. It secretes following two hormones :
1. Norepinephrine : It controls heart beat, contraction of arteries, breathing etc. at normal time.
2. Epinephrine : It is released at the time of emergency. It has the following effects.
(a) It increases heart beat and breathing.
(b) It constricts the arteries so that more blood may go into muscles.
(c) It dilates pupil.
(d) It oxidises more food so that more energy is produced.
Distinguish between hormones and enzymes.
|
Hormones |
Enzymes |
|
These are secreted by endocrine glands. |
These are secreted by exocrine glands. |
|
They are transported by blood. |
They are transported by ducts. |
|
The hormones are needed in less amount. |
The enzymes are needed in more amount. |
|
The hormones may be formed from amino acids, proteins, peptides and steroids. |
Enzymes are only proteinous. |
|
Hormones undergo changes during chemical reaction. |
Enzymes do not undergo any change. |
Discuss the hormones secreted by hypothalamus.
Hormones secreted by hypothalamus are:
1. Thyrotrophin-releasing hormone : It acts on the anterior lobe of pituitary gland and stimulates it to release thyrotrophin or thyroid stimulating hormone.
2. Adrenocorticotrophin releasing-hormone : It acts on the anterior lobe of pituitary gland and stimulates it to release adrenocoticotrophin hormone.
3. Gonadotrophin releasing hormone : It acts anterior lobe of pituitary gland, resulting in the release gonadotrophin hormone.
4. Somatotrophin-releasing hormone : It stimulates anterior lobe of pituitary gland and directs it to release somatotrophin hormone or growth hormone.
5. Growth inhibiting hormone : It inhibits anterior lobe of pituitary gland not to release growth hormone. eg . Somatostatin
Sponsor Area
Describe gonadotrophin hormone.
Gonadotrophin hormone : These are hormones which stimulate the gonadal activity. It is of two types :
(1) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) : It stimulates gonads to form gametes. It is present in both the sexes. In males it regulates spermatogenesis and in females it also stimulates ovary to produce oestrogens and stimulates the growth and development of the ovarial follicles.
(2) Luteinizing hormone : In males the LH results in thesynthesis and secretion of the androgens from the testis.
In females LH induces the ovulation.
Write the name and the source of hormones regulating the following :
(a) Uterine changes in pregnancy.
(b) Urinary elimination of water.
(c) Metamorphosis of tadpoles.
(d) Plasma Ca+2 level.
(e) Na+ and K+ metabolism.
(f) Blood sugar level.
(g) Uterine contractions at the time of child's birth.
|
Activities |
Name of hormone |
Source |
|
(a) Uterine change in pregnancy. |
Progesterone. |
Corpus luteum. |
|
(b) Urinary elimination of water. |
Antidiuretic hormone |
Posterior lobe of pituitary gland. |
|
(c) Metamorphosis of tadpoles |
Thyroxine. |
Thyroid gland. |
|
(d) Plasma Ca+2level. |
Parathormone (PTH) |
Parathyroid gland. Zone glomerulosa of adrenal cortex. |
|
(e) Na+ and K+metabolism. |
Mineralocorticoids. |
Adrenal gland. |
|
(f) Blood sugar level. |
Insulin and glucagon. |
Alfa and beta cells of islests of Langerhans (Pancreas). |
|
(g) Uterine contractions at the time of child's birth. |
Oxytocin |
Posterior lobe of pituitary gland |
Write a note on adrenocroticotrophin hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone.
(1) Adrenocorticotrophin hormone (ACTH) : It stimulates the adrenal gland to release different hormones. It is synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary or the pars digitalis region of pancreas.
(2) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) : It stimulates thyroid gland to secrete various hormones. It is released by the anterior pituitary.
Discuss somatotrophic or growth hormone. State the abnormalities cause due to hyposecretion or hypersecretion of growth hormone?
Somatotrophic or growth hormone : It stimulates growth and development of tissues by increased rate of cell division and protein synthesis. It is released by the anterior lobe of the pituitary or the pars digitalis region.
Abnormalities due to growth hormone :
1. Dwarfism : If GH is secreted in less amount ( hyposecretion), it may cause dwarfism.
2. Gigantism : When growth hormone is secreted in excess it brings abnormality in height. The person grows into a giant with long bones.
3. Acromegaly : If in adults it is secreted in more quantity then it brings enlargement of fingers, chin, toes, arms ,the proportion of the body and the limbs is disrupted. This condition is referred to as acromegaly.
Why is the endocrine system considered a chemical extension of the nervous system ?
For example the hypothalamus, which is a part of nervous system secretes TSH-RH (Thyroid stimulating hormone - releasing hormone). The hormone is transported to pituitary gland where it stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete Thyroid stimulating hormone TSH. The TSH in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxin. Thus, endocrine system and nervous system operate in coordination and many functions of the endocrine system are under control of nervous system. The two are collectively called as neuro-endocrine system. Thus, endocrine system is a chemical extension of nervous system.
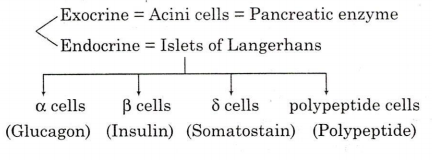
Briefly explain about pancreas.
Pancreas : The pancreas is a is a exocrine as well as endocrine gland. The pancreas has two types of cells :
(a) Pancreatic gland cells : These cells secrete enzymes.
(b) Islets of Langerhans : These are the endocrine part of the pancreas. These cells are further of following types :
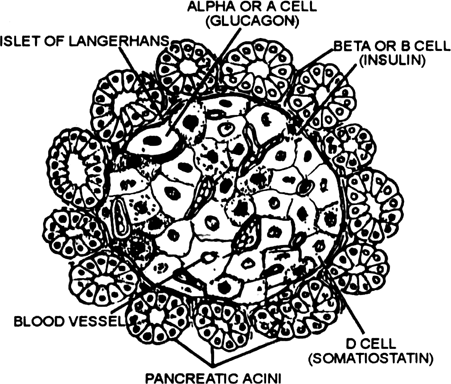
Fig. A part of the section of pancreas to show an islent of Langerhans.
(i) Alfa cells : These secrete glucagon. The glucagon converts glycogen into glucose. This process is called glycogenolysis.
(ii) Beta cells : These secrete insulin. It converts glucose to glycogen in liver. This process is called glycogenesis.
(iii) Delta cells : These secrete somatostanin hormone which controls the rate of absorption of food.
Explain diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes mellitus : It is commonly called sugar disease. It is caused due to the lack of secretion of insulin.
Symptoms : The disease is characterised by the following:
1. Sugar in the urine.
2. Frequent urination.
3. Thirst increases.
5. Ketone bodies are formed and may be excreted with the urine.
6. Weakness.
7. Healing of the wound takes more time.
What are the principal hormones produced by the anterior pituitary? What function does each serve ?
The hormones produced are:
1. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) : It is a proteinaceous hormone. It acts on the thyroid gland and regulates the secretion of the thyroid hormone.
2. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH or Corticotropin hormone) : It is a peptide hormone. It controls functioning of adrenal cortex, especially secretion of glucocorticoids & sex corticoids.
3. Growth hormone, somatotropin hormone (STH) : It is a proteinaceous hormone. It regulates the synthesis of growth of the body.
4. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) : It is a glycoprotein gonadotrophic hormone. It controls spermatogenesis in testes, maturation of graafian follicles and secretion of estrogens in ovaries.
5. Luteinising hormone (LH) : It performs the following functions
(i) In females LH helps in growth and development of graafian follicles, ovulation, growth of ruptured follicle.
(ii) In females LH also helps in secretion of progestrone by corpus luteum.
(iii) IIn males it acts on Leydig’s or interstitial cells of testes to secrete testosterone and other androgens.
6. Prolactin (PRL) : It is a proteinaceous hormone. It stimulates development of mammary glands during pregnancy and lactation after child birth.
Describe the hormones secreted by ovaries.
Ovaries : The ovaries secrete the following hormones :
(1) Estrogen : It is secreted by graafian follicles. Estrogen performs the following functions :
a. It brings ovulation.
b. It brings development of genital ducts.
(2) Progesterone : It is secreted by corpus luteum. The progesterone help in the implantation. The progesterone also maintains the enlargement of uterine wall during pregnancy.
(3) Relaxin : It is secreted by corpus luteum (part of graafian follicle after ovulation) at the end of gestation period. It enlarges the pelvic region during the childbirth.
What hormones are secreted by the posterior pituitary gland ? What function does each serve ? Where are these hormones actually produced ?
The posterior pituitary gland or neurohypophysis or pars nervosa stores and release two hormones :
1. Vasopressin (ADH or Antidiuretic Hormone)
2. Oxytocin
1. Function of Vasopressin hormone. Vasopressin hormone controls urine output. When there is more water in the body then this hormone is secreted in less amount. When amount of water is less inside the body then it is secreted in more amount so the urine output is less. The ADH hormone reduces water loss.
2. Function of Oxytocin :
(i) It acts on smooth muscles and results in their contraction .
(ii) It stimulates rigorous contraction in the uterine walls during the child birth.
(iii) It stimules ejection of milk from the mammary glands.
Give one example of pairs of antagonistic hormones associated with basal metabolism ? How does each pair function?
Antagonistic hormones : These are the hormones which function in opposition to each other. Examples :
1. Insulin and glucagon are antagonistic to each other.
Insulin brings glycogenesis and lowers blood sugar level by changing glucose into glycogen.
Glucagon brings glycogenolysis and raises blood sugar level by changing glycogen into glucose.
Write hormones secreted by placenta and the entric epithelium of stomach.
Enteric epithelium of stomach : It secretes gastrin hormone into stomach. The gastrin hormone stimulates gastric glands to secrete gastric juice.
What two hormones are produced by the adrenal medulla ?
The adrenal medulla is the inner part of adrenal gland which lies above the kidney.
Adrenal medulla produces following two hormones:
1. Adrenaline
2. Nor-adrenaline
1. Adrenaline : It is an emergency hormone because it is produced at the time of emergency or stress. Adrenaline instantly prepares our body for fight or flight. It increases breathing rate, heart rate, B.P. and also helps in releasing RBC from spleen.
2. Nor-adrenaline or Nor-epinephrine : This hormone regulates the heart rate, breathing rate, B.P. at normal time.
From what chemical compounds are all steroid hormones derived ? Mention at least two examples of steroid hormones.
Steroid hormones are manufactured from cholesterol or cholesterol esters.
Examples of Steroid hormones :
I. Testosterone
II. Estrogen
Explain the following :
(1) Insulin lowers the blood sugar level.
(2) Adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system function as a closely integrated system.
(3) Pituitary gland regulates the reproductive system.
(4) Feed back system controls the blood level of many hormones.
(1) Insulin is reponsible for lowering the blood sugar level by converting excess of glucose to gylcogen which is stored in muscles and liver.
(2) Adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system are closely integrated systems as noradrenaline is secreted during danger when nerve impulse reaches adrenal medulla via the sympathetic nerves.
(3) Gonadotrophic hormone secreted by pituitary gland controls spermatogenesis in male and ovulation of mature follicles , growth and development of ovarian follicles and maintenance of corpur luteum in females.
(4) Hormones maintain homeostasis. Hormones produced in body are under the control of hormones secreted by pituitary gland and hormones of pituitary gland are further controlled by hormones of hypothalamus. All this control of hormones is done by feed back mechanism. For example, if thyroxin amount is more in blood then it stimulates hypothalamus to secrete less thyrotropin releasing hormones which decreases thyroxine secretion. On decrease in amount of thyroxine below normal, thyrotrophin releasing hormone accelerates the release of thyroxine secretion. This is feed back control.
In general, how do steroid hormones effect changes in their targets cells ?
The steroid hormones bring changes in their target cells in the following manner :
1. Steroid hormones are lipid soluble hormones and can readily pass through the plasma membrane of a target cell.
2. After reaching the cytoplasm they bind to specific intracellular receptor proteins. They form a complex that enters the nucleus and binds to specific regulatory sites on chromosomes.
3. The binding alters the pattern of gene expression, initiating the tanscription of some genes (DNA), while repressing the transcription of others.
4. This results in the production of specific mRNA translation products such as proteins and usually enzymes, thus causing the required effects.
Write a note on Melanocyte stimulating hormone.
What hormones are produced when the body's blood glucose level drops below normal? How do these hormones act to return the level to normal ? What hormone is produced when the body's blood glucose levels become elevated ? How does this hormone act to return the level to normal?
Hormone released when blood glucose level falls : Glucagon hormone is released when blood glucose level falls. It converts glycogen into glucose in liver. The glucose is released into blood and raises blood glucose level.
Hormone released when blood glucose level elevated : Insulin is the hormone released when blood glucose level is elevated. It converts glucose into glycogen in liver and thus reduces level of glucose in the blood.
Distinguish between hormones and enzymes.
|
Hormones |
Enzymes |
|
|
1. Glands |
These are secreted by endocrine glands. |
These are secreted by exocrine glands. |
|
2. Transportation |
They are transported by blood. |
They are transported by ducts. |
|
3. Amount : |
The hormones are needed in less amount. |
The enzymes are needed in more amount. |
|
4. Chemical nature: |
The hormones may be formed from amino acids, proteins, peptides and steroids. |
Enzymes are only proteinous. |
|
5. Change of nature : |
Hormones undergo changes during chemical reaction. |
Enzymes do not undergo any change. |
What is diabetes ? Which hormonal deficiency results in this disease ? How does this affect an individual ability to use glucose? What are some possible treatments for diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes : It is disease which occurs due to the elevation of blood sugar level. It is characterized by the excretion of extra sugar in urine.
It is due to the deficiency of insulin hormone. The deficiency of insulin leads to increase in the glucose level in the blood as it does not convert excess of glucose in glucogen. This raises blood-glucose level. Somatostatin inhibits secretion of insulin and glucagon.
Treatment of diabetes :
1. Minimize intake of sugar and starch products.
2. Patients should take insulin tablets/ injections.
3. Daily walking for 5-6 km is good for diabetic patients.
Which endocrine glands are controlled by the secretion of other glands.
Hypothalamus controls the secretion of the hormones of the pituitary glands. Hormone like Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) Thyroid stimulating hormone releasing hormone (TSH-RH) regulates the pituitary hormones like Growth hormone (GH) and TSH respectively.
The pituitary gland hormones regulate the secretion of the hormones of the other glands. Pituitary secretes hormones like
i. TSH -Thyroid stimulating hormone which acts on thyroid glands.
ii. ACTH-Adrenocorticotropic hormones which act on the adrenal gland.
How is communication among the parts of an organism is accomplished ?
Endocrine system is controlled by brain. Hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones which excite synthesis of various hormones from pituitary gland. The hormones of pituitary gland regulate hormonal release from thyroid, adrenal gland, gonads etc.
Hormonal response is selective but specific.
Give examples on .
(1) Hyperglycemic hormone and hypoglycemic hormone.
(2) Hvpercalcemic hormone
(3) Gonadotrophic hormones
(4) Progestatinal hormones
(5) Blood pressure lowering hormone
(6) Androgens and estrogens.
(1) Hyperglycemic hormone - Glucagon.
Hypoglycemic hormone - Insulin hormone.
(2) Hypercalcemic hormone - PTH or Parathyroid hormone.
(3) Gonadotrophic hormone - FSH (Follicular stimulating Hormone) or LH (Luteinizing hormone)
(4) Progestational hormone - Progesterone.
(5) Blood pressure lowering hormone - ANF (Atrial natriuretic factor ).
(6) Androgens : Testosterone in males
Estrogens : Estrogen and progesterone.
Which hormonal deficiency is responsible for the following :
(1) Diabetes mellitus (2) Goitre (3) Cretinism.
The hormonal deficiency responsible of the following are:
(1) Diabetes mellitus : Deficiency of insulin .
(2) Goitre : Deficiency of Thyroid hormone.
(3) Cretinism : Deficiency of thyroxine.
Match column I with column II.
| A. Tn | (i) Thyroid |
| B. PTH | (ii) Thyroid |
| C. GNRH | (iii) Pituitary |
| D. LH | (iv) Parathyroid |
A. Tn | (i) Thyroid |
B. PTH | (ii) Parathyroid |
C. GNRH | (iii) Thyroid |
D. LH | (iv) Pituitary |
Match column I with column II
| A. Smooth muscle | (i) Myoglobin |
| B. Tropomyosin | (ii) Thin filament |
| C. Red muscle | (iii) Sutures |
| D. Skull | (iv) Involuntary |
A. Smooth muscle | (i) Thin filament |
B. Tropomyosin | (ii) Involuntary |
C. Red muscle | (iii) Myoglobin |
D. Skull | (iv) Sutures |
Write short notes on the functions of the following hormones.
(a) Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
(b) Thyroid hormones
(c) Thymosins
(d) Androgens
(e) Estrogens
(f) Insulin and Glucagon.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is relesed by the parathyroid glands. It is a peptide hormone.
Function - The PTH performs the following function:
i. Increases the Ca2+ level in the blood and maintains the calcium balance in the body.
ii. It acts on bones and stimulates the process of demineralisation.
iii. It stimulate the reabsorption of the Ca2+ by the renal tubules.
iv. It increases the calcium absorption from the digested food.
(b) Thyroid hormones :
Thyroxine/ Tetraiodothyonine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are collectively known as thyroid hoemones. They are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid gland and are peptide hormones.
Functions - They perform the following functions.
i. Regulate the basal metabolic rate
ii. Support the red blood cells formation.
iii. Control the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
iv. Maintain the water and electrolyte balance.
v. Regulate the blood calcium levels.
(c) Thymosins
Thymosins are released by the thymus gland. They are peptide hormones.
Functions - They peform the following functions.
i. Play a major role in the differentiation of T-lymphocytes.
ii. Promote the production of antibodies.
(d) Androgens
Androgens are the secreted by the Leydig cells or interstitial cells. Androgens are a group of hormones that consist mainly testosterone.
Function - They perform the following functions.
i. Regulate the development, maturation and functions of the male accessor sex organs in males.
ii. Stimulate development of secondary sexual characters in males.
iii. Stimulate the process of spematogenesis.
iv. Produce anabolic effect on protein and carbohydrate metabolism.
(e) Estrogens
Estrogen is secreted by ovary. It is a steroid hormone synthesied by ovarian follicles.
Functions - They perform the following functions:
Stimulate the growth and activity of female secondary sex organs. and regulate the female sexual behaviour
(f) Insulin and Glucagon
These are released by the pancreas. The insulin hormone is synthesized by the beta-cells and the glucagon is synthesized by the alpha-cells.
Functions : They perform the following functions.
i. They maintain the glucose homeostasis.
ii. The glucagon acts on the liver cells and result in glycogenolysis and thus in the increased glucose levels in the blood. It also reduces the glucose uptake and utilisation.
iii. Insulin decreases the blood glucose level and enhaces cellular glucose uptake and utilisation.
List the hormones secreted by the following
(1) Hypothalamus ,(2) Pituiltary gland , (3) Thyroid gland
(4) Parathyroid gland , (5) Adrenal gland, (6) pancreas
(7) Testis, (8) Ovary, (9) Thymus
(10) Atrium, (11) Kidney , (12) G–1 Tract.
(1) Hypothalamus :
It secretes following hormones:
(a) Hypothalamus: Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus include:
(1) Releasing hormones: These hormones stimulate the secretions of the pituitary hormone. Examples of these hormones are:
(i) Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone
(ii) Thyrotrophin-releasing hormone
(iii) Somatotropin-releasing hormone
(iv) Adrenocorticotrophin-releasing hormone
(2) Inhibiting hormones: These hormones inhibit the secretions of the pituitary hormone. Examples of these hormones are:
(i) Somatostatin
(ii) Growth-inhibiting hormone
(iii) Melanocyte-inhibiting hormone
(2) Pituitary gland :
Pituitary gland is divided into.
(i) Adeno hypophysis (ii) Neuro hypophysis
Hormones secreted by the adenohypophysis are:
(i) Growth hormone (GH)
(ii) Prolactin
(iii) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
(iv) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
(v) Luteinizing hormone (LH)
(vi) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
(vii) Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
Hormones secreted by the neurohypophysis are:
(i) Oxytocin
(ii) Vasopressin
(3) Thyroid gland :
Follicle cells of thyroid gland secrete two hormones.
Tetraidothyronine (T4)
Tridothysonine (T3)
C cells of thyroid also secrete thyrocalcitonin.
(4) Parathyroid gland : It secretes parathyroid hormone .
(5) Adrenal gland :
The adrenal gland has outer
(i) Adrenal cortex
(ii) Adrenal medulla.
(i) Adrenal cortex has three parts :
(a) Outer part or zona glomerulosa : It secretes mineral corticoids.
(b) Middle part or zona fasciculata : It secretes glucocorticoids,.
(c) Inner part or zona reticularis : Both middle and inner part secrete sex corticoids.
(ii) Adrenal medulla :
It secretes
i. epinephrine or adrenaline hormone
ii. noradrenaline or norepinephrine hormone.
(6) Pancreas : Its cells called Islets of Langerhans are of two types :
(a) α cells : These secrete glucagon hormone. (b) β cells : These secrete insulin.
(7) Testis: It has interstitial cells or cells of leydig which secrete androgens mainly testosterone.
(8) Ovary: The graafian follicle secretes estrogen hormone.
Corpus luteum secretes progesterone and relaxin hormone.
(9) Thymus :
It secretes thymosin hormone.
(10) Atrium : The atrial wall secretes atrial natiuretic factor (ANF)
(11) Kidney : The juxtaglomerular cells of kidney produce erythropoietrin hormone.
(12) G–1 Tract :
It secretes following hormones.
(i) secretin
(ii) cholecystokinin (CCK)
(iii) enterogastrone or gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
(iv) Villikinin
(v) Duocrinin
(vi) Enterocrinin.
Briefly mention the mechanism of FSH.
Mechanism of FSH :
(1) FSH is secreted by anterior lobe of pituitary gland.
(2) FSH binds to its receptor to form FSH -receptor complex.
(3) FSH receptor complex generates second messenger cAMP
(4) cAMP brings biochemical responses.
(5) The biochemical chages lead to the physiological responses. Due to biochemical responses graafian follicle are matured and they secrete estrogen while in case of male it brings formation of sperms.
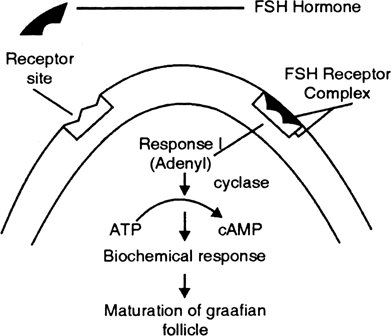
Mechanism of FSH hormone
Diagrammatically indicate the location of the various endocrineglands in our body.
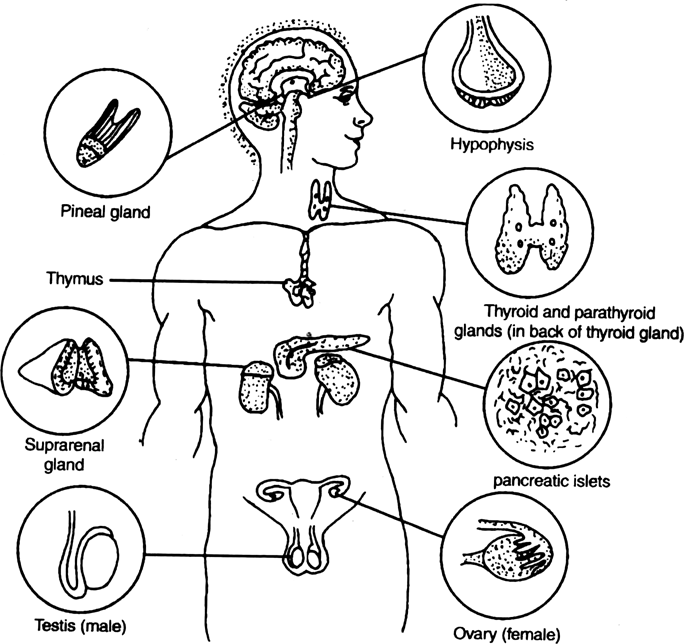
The endocrine glands and their locations in the body
Define the following:
(a) Exocrine gland
(b) Endocrine gland
(c) Hormone
(b) Endocrine gland : Endocrine glands are glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood rather than through a duct. They are ductless.
(c)Hormone : Hormones are non-nutrient chemicals which act as intercellular messengers and are produced in trace amounts.
List the hormones secreted by the following:
(k) Kidney
The kidney release the hormone Erythropoietin
Which of the following pairs of hormones are not antagonistic (having opposite effects) to each other?
-
Insulin Glucagon -
Aldosterone Atrial Natriuretic Factor -
Relaxin Inhibin -
Parathormone Calcitonin
C.
| Relaxin | Inhibin |
Relaxin relaxes pubic symphysis during parturition while inhibin decreases the secretion of FSH from anterior pituitary
A pregnant female delivers a baby, who suffer from stunted growth, mental retardation low intelligence quotient and abnormal skin. This is the result of
-
deficiency of iodine in diet
-
low secretion of growth hormone
-
cancer of the thyroid glad
-
over secretion of pars distalis
A.
deficiency of iodine in diet
Hypothyroidism during pregnancy causes defective development and maturation of the growing foetus leading to stunted growth. Low secretion of GH results in stunted growth. Low secretion of GH result in stunted growth resulting in pituitary dwarfism. Paras distalis or anterior pituitary producers Growth hormone. prolactin (PRL), thyroid stimulation hormone (TSH), Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH), Luteinising Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
Which of the following statement is correct in relation to the endocrine system?
-
Adenohypophysis is under the direct neural regulation of the hypothalamus.
-
Organs in the body like gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney and live
-
Non-nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that acts as intercellular messengers are known as hormones.
-
Releasing and inhibitory hormones are produced by the pituitary gland.
C.
Non-nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that acts as intercellular messengers are known as hormones.
Hormones are non-nutrient chemicals, which act as intracellular messengers and are produced in trace amounts. Endocrine cells are present in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract, e.g., gastrin, secretin, GIP. Atrial wall of our heart secretes a peptide hormone called ANF (Atrial Natriuretic Factor), RH/ IH are produced by the hypothalamus. Adenohypophysis is not directly under neural control, it is under the control of hypothalamic hormones, brought by portal system.
Sponsor Area
Which one of the following hormones is not involved in sugar metabolism?
-
Cortisone
-
Aldosterone
-
Insulin
-
Glucagon
B.
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is not involved in sugar metabolism. It is a steroid hormone (mineralocorticoid) produced by the outer section(zona glomerulosa) of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It plays a central role in the adrenal gland. It plays a central role in the regulation of blood pressure mainly by acting on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron, increasing reabsorption of ions and water in the kidney, to cause the conservation of sodium, secretion of potassium, increase in water retention and decrease in blood pressure and blood volume.
Which one of the following hormones though synthesised elsewhere, is stored and released by the master gland?
-
Antidiuretic hormone
-
Luteinizing hormone
-
Prolactin
-
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
A.
Antidiuretic hormone
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) or vasopressin is a peptide hormone synthesised in the hypothalamus, but stored and released from the posterior pituitary lobe.
A person entering an empty room suddenly finds a snake right in front on opening the door. Which one of the following is likely to happen in his neurohormonal control system?
-
Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal medulla
-
Neurotransmitters diffuse rapidly across the cleft and transmit a nerve impulse
-
Hypothalamus activates the parasympathetic division of brain
-
Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal cortex
A.
Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal medulla
Epinephrine and nor-epinephrine are secreted by adrenal medulla (under the control of sympathetic nervous system) in response to stress of any kind or during the emergency situations. These are also called emergency hormones or hormones of flight, fight and fright (triple F hormone).
Which one of the following pairs of hormones are the examples of those that can easily pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind to a receptor inside it(mostly the nucleus)
-
Insulin and glucagon
-
Thyroxin and insulin
-
Somartostatin and oxytocin
-
Cortisol and testosterone
D.
Cortisol and testosterone
Cortisol and testosterone are lipid soluble hormones, which can directly pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind with interacellular receptors.
What is correct to say about the hormone action in humans?
-
Glucagon is secreted by
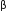 -cells of Islets of Langerhans and stimulates glycogenolysis
-cells of Islets of Langerhans and stimulates glycogenolysis -
Secretion of thymosine is stimulated with ageing
-
In females, FSH first binds with specific receptors on ovarian cell membrane
-
FSH stimulates the secretion of oestrogen and progesterone
C.
In females, FSH first binds with specific receptors on ovarian cell membrane
FSH hormone is one of the gonadotropins secreted by anterior lobe of pituitary. It is a proteinaceous hormone, so binds with extra cellular or membrane bound receptors.
Identify the hormone with its correct matching of source and function.
-
Oxytocin - posterior pituitary, growth and maintenance of mammary glands.
-
Melatonin - pineal gland, regulates the normal rhythm of sleep-wake cycle
-
Progesterone - corpus luteum, stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs
-
Atrial natriuretic factor - ventricular wall increases the blood pressure
B.
Melatonin - pineal gland, regulates the normal rhythm of sleep-wake cycle
Melatonin is a hormone present in animals, plants and microbes. In animals melatonin allowing the regulation of the circadian rhythms. Oxytocin is a neurohypophysial hormone which stimulates the muscle contraction (smooth muscle) in the wall uterus during childbirth. Progesterone is a female hormone produced by the ovaries during the release of a mature egg from an overly during ovulation.
ANF stimulates the secretion of Na and H2O by the kidneys and helps in regulating blood pressure.
Fight or flight reactions cause activation of
-
the parathyroid glands, leading to increased metabolic rate
-
the kidney, leading to suppression of reninangiotensin - aldosterone pathway
-
the adrenal medulla, leading to increased secretion epinephrine and norepinephrine
-
the pancreas leading to a reduction in the blood sugar levels
C.
the adrenal medulla, leading to increased secretion epinephrine and norepinephrine
Fight or flight reaction is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to an emergency. Emergency hormone are secreted by adrenal medulla of adrenal gland secretes adrenaline (epinephrine) and nor alternative (norepinephrine) hormones which stimulate sweating, heart beat and breathing rate. These also cause dilation of coronary artery ( for increasing inspiratory volume)and pupil (for better vision)
Which one of the following pairs of chemical substances, is correctly categorised?
-
Calcitonin and thymosin - Thyroid hormones
-
Pepsin and prolactin - Two digestive enzymes secreted in stomach
-
Troponin and myosin - Complex proteins in striated muscles
-
Secretin and rhodopsin - Polypeptide hormones
C.
Troponin and myosin - Complex proteins in striated muscles
Striated muscle consists of large number of muscle fibres called myofibrils. Myofibrils are made up of actin and myosin protein. The actin or secondary myofilaments also possess troponin and tropomyosin protein.
Thymosin hormone is secreted from thymus gland. Prolactin is a hormone secreted from anterior lobe of pituitary.
Rhodopsin is a pigment found in rod cells of eye.
Erythropoiesis starts in
-
kidney
-
liver
-
spleen
-
red bone marrow
C.
spleen
The process of formation of erythrocytes is erythropoiesis, which is part of haemopoiesis (formation of blood).
The production of blood during different stages is as follows:
During few early weeks of embryonic life-yolk sac.
Some later stages (After 3-4 months) - liver (mainly) along with spleen and lymph nodes.
Later part of gestation and after birth (After 7 months) - red bone marrow (till 5 yrs)
Bone marrow of long bones (20-25 yrs).
Membranous bones like vertebrae, etc.
A chemical signal that has both endocrine and neural roles is?
-
melatonin
-
calcitionin
-
epinephrine
-
cortisol
C.
epinephrine
Epinephrine secreted from the medulla of adrenal gland acts as both, an endocrine hormone and as a neurotransmitter (produced at the ends of sympathetic never fibres).
Epinephrine as hormone accelerates metabolic rate for preparing us to face emergency situations.
As neurotransmitter, it transmits nerve impulse across a synaptic left. Calcitonin is released when Ca2+ level increases, melatonin causes concentration of pigment in melanocytes and cortisol is a glucocorticoid.
Match the source gland with its respective hormone as well as the function.
-
Source gland Hormone Function Posterior pituitary Vasopressin Stimulates resorption of water in the distal tubules in the nephron -
Source gland Hormone Function Corpus luteum Oestrogen Supports pregnancy -
Source gland Hormone Function Thyroid Thyroxine Regulates blood calcium level -
Source gland Hormone Function Anterior pituitary Oxytocin Contraction of uterus muscles during child birth
A.
| Source gland | Hormone | Function |
| Posterior pituitary | Vasopressin | Stimulates resorption of water in the distal tubules in the nephron |
The pituitary gland is located in a bony cavity called sella tursica and is attached to hypothalamus by a stalk. It is divided anatomically into an adenohypophysis and a neurohypophysis. The latter is also called pars nervosa or posterior pituitary. It stores and releases two hormone called oxytocin and vasopressin, which are actually synthesized by the hypothalamus and are transported axonally to neurohypophysis. Vasopressin acts mainly at the kidney and stimulates resorption of water and electrolytes by the distal tubules in the nephron and thereby reduces loss of water through urine (diuresis). Hence, it is also called as anti-diuretic hormone (ADH).
The 24 hour (diurnal) rhythm of our body such as the sleep -wake cycle is regulated by the hormone
-
Calcitonin
-
prolactin
-
adrenaline
-
melatonin
D.
melatonin
Melatonin, also know as chemically N-acetyl 5- methoxy tryptamine is a naturally occurring compound found in animals, plants and microbes. In animals, circulating levels of the hormone melatonin vary in a daily cycle, thereby allowing the entrainment of the circadian rhythms of several biological functions.
Injury to the adrenal cortex is not likely to affect the secretion of which one of the following?
-
Aldosterone
-
Both androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone
-
Adrenalin
-
Cortisol
C.
Adrenalin
The adrenal medulla synthesises two hormones - adrenalin (epinephrine) and nor - adrenaline (non-epinephrine). These hormones are proteinaceous in nature and derived from amino acid tyrosine. Thus, injury to adrenal cortex will not affect the secretion of adrenaline.
Which one of the following pairs is incorrectly matched?
-
Glucagon - Beta cells (source)
-
Somatostatin - Delta cells (source)
-
Corpus luteum - Relaxin (secretion)
-
Insulin - Diabetes mellitus (disease)
A.
Glucagon - Beta cells (source)
In pancreatic islets, alpha or A -cells constitute about 15% of pancreatic islets cells and secrete glucagon. Its molecule consists of a single polypeptide chain of 29 amino acid residues. Glucagon intensifies glycogenolysis, deamination and gluconeogenesis, and inhibits glycogenesis in liver cells. It also intensifies lipolysis in adipose tissue. Thus, it is a promoter of catabolic metabolism.
The nerve centres which control the body temperature and the urge for eating are contained in
-
hypothalamus
-
pons
-
cerebellum
-
thalamus
A.
hypothalamus
Hypothalamus is the part of the sides and floor of the brain derived from the forebrain. It lies at the base of the thalamus. The hypothalamus contains a number of centres, which control body temperature, urge for eating and drinking. it also contains several groups of neurosecretory cells, which secrete hormones called, hypothalamic hormones.
Toxic agents present in food which interfere with thyroxine synthesis lead to the development of
-
toxic goitre
-
cretinism
-
simple goitre
-
thyrotoxicosis
C.
simple goitre
toxic agents in food which interfere with thyroxine synthesis will lead to simple goitre thyrotoxicosis and toxic goitre is under the category of hyperthyroidism.
Select the correct matching of a hormone its source and function.
-
Hormone
Source
Function
Vasopressin
Posterior Pituitary
Increases loss of water through urine
-
Hormone
Source
Function
Norepinephrine
Adrenal medulla
Increases heartbeat, rate of respiration and alertness
-
Hormone
Source
Function
Glucagon
Beta-cells of Islets of Langerhans
Stimulates glycogenolysis
-
Hormone
Source
Function
Prolactin
Posterior pituitary
Regulates growth of mammary glands and milk formation in females
B.
|
Hormone |
Source |
Function |
|
Norepinephrine |
Adrenal medulla |
Increases heartbeat, rate of respiration and alertness |
Hormone noradrenaline or norepinephrine is secreted by the cells of adrenal medulla, under normal condition, It maintains the blood pressure. It causes contraction of essentially all the blood vessels of the body. This result an increased activity of the heart raised blood pressure, stimulated respiration, positive oxygen consumption, etc.
Feeling the tremors of an earthquake a scared resident of the seventh floor of a multistoryed building starts climbing down the stairs rapidly. Which hormone initiated this action?
-
Thyroxin
-
Adrenaline
-
Glucagon
-
Gastrin
B.
Adrenaline
Adrenalin hormone is responsible for the action, as adrenalin hormone is known as 3F hormone. 
A person is having problems with calcium and phosphorus metabolism in his body. Which one of following glands may not be functioning properly?
-
Parathyroid
-
Parotid
-
Pancreas
-
Thyroid
A.
Parathyroid
The parathormone secreted by parathyroid hormone regulates the calcium and phosphate balance between the blood and other tissues.
Compared to a bull a bullock is docile because of
-
higher levels of thyroxin
-
higher levels of cortisone
-
lower levels of blood testosterone
-
lower levels of adrenaline/ noradrenaline in its blood
C.
lower levels of blood testosterone
Testis are degenerated in bullock due to which testosterone level in blood is reduced. This hormone promotes the growth of many body tissues such as muscles.
A steroid hormone which regulates glucose metabolism is
-
cortisol
-
corticosterone
-
11-deoxycorticosterone
-
cortisone
A.
cortisol
Cortisol or hydrocortisone is the principal glucocorticoid hormone (corticosterone is more abundant in some small mammals). It regulates the glucose metabolism and promotes gluconeogenesis, especially during starvation and raises blood pressure. Cortisone is an inactive form of cortisol.
Which one of the following is not a second messenger in hormone action?
-
cGMP
-
Calcium
-
Sodium
-
cAMP
C.
Sodium
Second messengers are the organic molecules and sometimes the metal ions, acting as intracellular signals, whose production or release usually amplifies a signal such as a hormone, received at the cell surface.
Sodium (Na) is not a second messenger to be discovered.
In addition to cyclic AMP, Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate (CGMP) functions as a second messenger in certain cases.
Calcium ions (Ca++) also act as second messenger in phospholipase  second messenger system.
second messenger system.
Which of the following is an accumulation and release centre of neurohormones?
-
Posterior pituitary lobe
-
Intermediate lobe of the pituitary
-
Hypothalamus
-
Anterior pituitary lobe
C.
Hypothalamus
Almost all secretion by the pituitary gland are controlled by hormonal signal from hypothalamus. The neurohormones are secreted and accumulated by hypothalamus.
Which hormone causes dilation of blood vessels, increased oxygen consumption and glycogenolysis?
-
ACTH
-
Insulin
-
Adrenalin
-
Glucagon
C.
Adrenalin
Adrenaline (epinephrine) is a hormone produced by adrenal medulla and is secreted in great amounts during emotional states. It elevates the glucose level in blood stream (by glucogenesis) which is accompanied by an increase in oxygen consumption, body temperature, heat production. Adrenaline also causes an increase in the flow of blood by dilating the blood vessels.
Insulin regulates the glucose level in blood.
ACTH (Adreno Corticotropic Hormone) is secreted by the anterior pituitary and stimulates the adrenal cortex.
Glucagon is a polypeptide hormone secreted by the alpha cells of islets of langerhans of pancreas. It acts to promote glycogenolysis.
A temporary endocrine gland in the human body is
-
Pineal gland
-
Corpus cardiacum
-
Corpus luteum
-
Corpus allatum
C.
Corpus luteum
Corpus luteum is the temporary endocrine structure formed in the ovary after ovulation. It is responsible for the release of the hormones like progesterone, oestrogen etc.
GnRH, a hypothalamic hormone, needed in reproduction, acts on
-
Anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and oxytocin
-
Anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and FSH
-
Posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of oxytocin and FSH
-
Posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and relaxin
B.
Anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and FSH
A decrease in blood pressure/volume will not cause the release of
-
Renin
-
Atrial Natriuretic Factor
-
Aldosterone
-
ADH
B.
Atrial Natriuretic Factor
A decrease in blood pressure / volume stimulates the release of renin, aldosterone, and ADH while increase in blood pressure / volume stimulates the release of Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF) which cause vasodilation and also inhibits RAAS (Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System) mechanism that decreases the blood volume/pressure.
Hypersecretion of Growth Hormone in adults does not cause further increase in height, because
-
Growth Hormone becomes inactive in adults
-
Epiphyseal plates close after adolescence
-
Bones loose their sensitivity to Growth Hormone in adults
-
Muscle fibres do not grow in size after birth
B.
Epiphyseal plates close after adolescence
Epiphyseal plate is responsible for the growth of bone which close after adolescence so hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults does not cause further increase in height.
Which of the following is an amino acid derived hormone?
Epinephrine
Ecdysone
Estriol
Estradiol
A.
Epinephrine
Epinephrine is derived from tyrosine amino acid by the removal of the carboxyl group. It is a catecholamine.
Which of the following gastric cells indirectly help in erythropoiesis?
Chief cells
Mucous cells
Parietal cells
Goblet cells
C.
Parietal cells
Parietal or oxyntic cell is a source of HCl and intrinsic factor. HCl converts iron present in diet from ferric to ferrous form so that it can be absorbed easily and used during erythropoiesis.
Intrinsic factor is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12 and its deficiency causes pernicious anaemia.
Endemic goitre is a state of
normal thyroid function
moderate thyroid function
increased thyroid function
decreased thyroid function
D.
decreased thyroid function
Goitre is a swelling of the neck due to enlargement of the thyroid gland. This may be due to a lack of dietary iodine, which occurs due to decreases thyroid function, which is necessary for the production of thyroxine hormone.
This was the casue of endemic goitre formerly common in regions, where the people lacked in their diet iodine.
Hormone responsible for the secretion of milk after parturition is
ACTH
LH
ICSH
Prolactin
D.
Prolactin
Prolactin or luteotrophic hormone or luteotropin is a hormone, synthesised and stored in the anterior pituitary gland, that stimulates milk production after childbirth and also stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum in the ovary.
Gigantism and acromegaly are due to
Hypothyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Hypopituitarism
Hyperpituitarism
D.
Hyperpituitarism
Hypersecretion of Growth Hormone (GH) or Somatotropin Hormone (STH) from adenohypophysis of pituitary gland causes gigantism in children and acromegaly in adulthood. Gigantism involves excessive growth (lengthening) of bones with enlargement of internal organs as well. Acromegaly causes abnormal thickening of bones (due to ossification of periosteum) especially at face and margins of hand and feet.
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of
K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
B.
Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
D.
Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
Which of the following hormone secretes a gastric secretion?
Entero gastrone
Gastrin
CCK-PZ
Villikinin
B.
Gastrin
Gastrin hormone is secreted by gastric glands to release gastric juice. Enterogastrone is secreted by the duodenal epithelium which inhibits the secretion of gastric juice.
Steroid hormones work as
They enter into target cells and binds with specific receptor and ativate4s specific genes to form protein
They bind to cell membrane
They catalyse formation of cAMP
None of the above
B.
They bind to cell membrane
A steroid hormone is lipid soluble, so easily pass through the plasma membrane.
Adrenaline and noradrenaline are hormones that act as
Energy producing agents
Food storage materials
Neurotransmitters
Energy storing substances
C.
Neurotransmitters
There are four neurotransmitters identified in vertebrates acetylcholine, serotonin, adrenaline and noradrenaline.
Which one of the following hormones is released by the posterior lobe of pituitary gland?
FSH
ADH
ACTH
MSH
B.
ADH
Anti Diuretic Hormone (ADH) is released by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland which is also called vasopressin. It increases the reabsorption of water by kidneys.
Which hormone produces the calorigenic effect?
Thyroxine
FSH
Insulin
All of these
A.
Thyroxine
Calorigenic effect refers to the substance or process that produces heat or energy or that increase the consumption of O2
Which of the following act as an antigen, but do not induce antibody production?
Haustra
Histones
Haptens
None of these
C.
Haptens
The hapten is a low weight molecular that can be made immunogenic conjugation to a suitable carrier.
If the free energy change of a reaction is greater than zero, then the reaction is
Spontaneous
Non-spontaneous
At equilibrium
Endothermic
B.
Non-spontaneous
An endergonic reaction (also called a non-spontaneous reaction) is a chemical reaction in which the standard change in free energy is positive and energy is absorbed.
The contraction of gall bladder is due to
Gastrin
Secretin
Cholecystokinin
Enterogastrone
C.
Cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin (also called pancreozymin) is a hormone of the mucosa of the small intestine. It is related in response to chyme. It causes the pancreas to release pancreatic enzymes and gallbladder to eject bile.
Apoenzyme is
Protein
Carbohydrate
Vitamin
Amino acid
A.
Protein
Enzymes are proteinaceous molecules Simple enzymes are composed of only protein, while holoenzymes are composed of protein part (apoenzyme) and non-protein part (prosthetic group).
Follicle Stimulating Hormone is secreted by
anterior lobe of pituitary
hypothalamus
gonads
poterior lobe of pituitary
A.
anterior lobe of pituitary
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) is a glycoprotein secreted from anterior lobe of pituitary. It is secreted in both males and females. In males, it stimulates spermatogenesis and development of seminiferous tubules and in females, it stimulates formation and growth of ovarian follicle in ovary.
Which of the following is the largest gland in an adult man?
Thymus
Liver
Thyroid
Pancreas
B.
Liver
| Liver | Thyroid Gland | Pancreas | Thymus gland |
| Endodermal in origin | Length- 3 to 7 cm; Weight- 25gms | Length- 12- 15 cms; Weight- 50- 70 gm | Weight- at birth- 10 to 12 gms; at puberty- 20 to 30 gms; at old age- 3 to 6 gms |
| Largest gland in human body | Largest endocrine gland | Heterocrine (mixed) gland | Has immunological functions |
| Secretes bile which is used in the emulsification and absorption of fats. | Location- below larynx | Hormones secreted are insulin, glucagon and somatostatin | After puberty it is not clearly visible. |
| Produces heparin, plasma protein (albumin, fibrinogen and prothrombin) etc. | Produces thyroxine (T4)- controlsbasal metabolic rate of the body |
During emergency which of the following hormone is secreted?
Aldosterone
Thyroxine
Adrenalin
Calcitonin
C.
Adrenalin
| Adrenalin | Aldosterone | Thyroxine | Calcitonin |
| Secreted by Chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla | Secreted by adrenal cortex | Produced in manufactured and synthesized from iodine | Secreted by parafollicular cells of thyroid |
| Controlled by Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) | Mineralocorticoid or salt retaining hormone | Also called tri-iodothyronine hormone | Also called Thyrocalcitonin (TCT) hormone. |
| Also called 'emergency hormone' | Function is in conservation of sodium and water and dimination of potassium. | Function is to control metabolism, regulating tissue growth and development. | Main role is to lower the amount of calcium and phosphate in the blood. |
The function of pineal body is to
lighten the skin colours
control sexual behaviour
regulates the period of puberty
All of the above
D.
All of the above
The pineal gland is a small mass of tissues near the centre of the mammalian brain. It secretes melatonin hormone, a modified amino acid. It contains light sensitive cells and has nervous connections from the eyes. It also regulates sexual behaviour and period of puberty.
The reabsorption of water in the kidney is under the control of
LH
ADH
STH
ACTH
B.
ADH
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) controls the tubular permeability and concentration of sodium in the extracellular fluid. It regulates the osmotic pressure of body fluids by causing the kidneys to increase water reabsorption.
It associates with the renal pressure system and then regulates the fluid volume of body through the agency of hypothalamic osmoreceptors.
Which is gonadotropin hormone
GH
MSH
ADH
FSH and LH
D.
FSH and LH
Gonadotropins or gonadotropic hormones are as follows.
(a) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) : It stimulates growth of ovarian follicles and their secretion of oestrogen in the female and spermatogenesis in the male.
(b) Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone (ICSH) : It activates the Leydig's cells of the testis to secrete androgens. In female it stimulates the corpus luteum of the ovary to secrete progesterone. In female ICSH is termed as LH (Luteinizing Hormone).
Damage to thymus in a child may lead to
a reduction in haemoglobin content of blood
a reduction in stem cell production
loss of antibody mediated immunity
loss of cell mediated immunity
D.
loss of cell mediated immunity
Thymus gland is located in the upper part of thorax near the heart. It is a bilobed, pinkish gland. It secretes thymosin hormone, thymic humoral factor and thymopoietin.
Proliferation of lymphocytes and differentiation of these lymphocytes into a variety of clones are induced by these factors. These clones are differentially specialized to destroy different specific category of antigens and pathogens. Therefore, thymus gland brings fourth T- lymphocytes for cell mediated immunity.
Parkinson's disease (characterized by tremors and progressive rigidity of limbs) is caused by degeneration of brain neurons that are involved in movement control and make use of neurotransmitter
acetylcholine
norepinephrine
dopamine
GABA
C.
dopamine
A dopamine deficiency is due to low level of dopamine in the body. It leads to a problem with the receptors in the brain and develops into Parkinson's disease or depression.
Acetylcholine is a major neurotransmitter responsible for memory and learning. It can lead to diseases such as dementia and Alzheimer's.
Norepinephrine promotes arousal and alertness. Increased levels of norepinephrine leads to excessive activity of sympathetic nervous system, and it can further lead to obesity, metabolic syndrome and high blood pressure.
GABA or Gamma- Amino Butyric Acid deficiency can lead to depression, anxiety, insomnia etc.
Which of the following is both exocrine and endocrine gland
Liver
Pancreas
Thyroid
Adrenal
B.
Pancreas
Pancreas are partially exocrine and partially endocrine gland.
Moulting hormone is secreted by
corpora cardiacum
prothoracic gland
corpora allata
neurosecretory hormone
B.
prothoracic gland
Moulting hormone (ecdysone) is secreted by prothoracic gland. These glands are paired, bilateral sheet of cells in the thorax. In Periplaneta, this endocrine gland is X-shaped. This gland is stimulated by prothoracicotropic hormone. Ecdysone, by causing transformation from larval to pupal stage, initiates post embryonic growth in insects.
Deoxyribonuclease and ribonuclease are secreted by
liver
stomach
pancrease
kidney
C.
pancrease
Deoxyribonuclease and ribonuclease are secreted by pancreas. These enzymes act on DNA and RNA and convert them to deoxyribonucleotides and ribonucleotides, respectively. The optimum pH required by pancreatic juice to secrete these enzymes is 7-8 (alkaline).
Blood calcium level can be increased by the administration of
glucagon
thyroxine
parathormone
caleitonin
C.
parathormone
Parathyroid hormones are released when the level of ca is less in blood it increases level of ca in the blood while calcitocine hormones reciprocates the effect.
Gonadotropin releasing hormone is transferred to anterior pituitary by
left coronary artery
hypophysial portal veins
axons of neurosecretory cells
nuclei of hypothalamus
B.
hypophysial portal veins
Hypothalamus is connected to the anterior lobe of pituitary gland by hypophysial portal veins. The latter carry blood containing neurohormones (releasing factors) from the hypothalamus to the anterior lobe of the pituitary.
When kidney of a person is damaged, he/she invariably suffers from anaemia because
RBCs pass through the glomerulus
sufficient erythropoietin is not produced
haemoglobin is not synthesised sufficiently
iron and vitamin B12 are not able to bind to haemoglobin
B.
sufficient erythropoietin is not produced
Erythropoietin is a glycoprotein produced by the kidney, which regulates red blood cell formation in the bone marrow. During kidney damage, enough erythropoietin required for adequate RBCs production is not synthesised resulting in anaemia
Which one of the following is not derived from plants
Opioids
Cocaine
DDT
Cannabinoid
C.
DDT
DDT (Dichloro diphenyl trichloroethane) is a colourless, crystalline, tasteless and almost odourless organochloride known for its insecticidal properties. DDT is not derived from any plant rather it is prepared by the chemical reactions of some chemical compounds.
Opioids (opiates) are the analgesic drugs that are derived from latex of unripe fruits of poppy plant, Papaver somniferum. Similarly, cocaine and cannabinoids are the drugs derived from Erythroxylon coca (Coca plant) and Cannabis sativa (Hemp plant) respectively
Assertion: ADH and RAAS work in response to low blood volume and blood pressure.
Reason: ANF works in response to high blood volume and blood pressure.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) and RAAS (Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System) work in response to low blood volume and low blood pressure.
ADH increases the reabsorption of water in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct, and thus results in an increase in blood volume and blood pressure.
RAAS is operated by JGA (Juxtaglomerular apparatus). It increases blood volume and blood pressure by two ways: Firstly, it induces the proximal convoluted tubules to reabsorb more NaCl and water and secondly, it stimulates the adrenal gland to release a hormone, called aldosterone that induces the distal convoluted tubule to absorb more Na' and water.
ANF (Atrial Natriuretic Factor) works in response to high blood volume and high blood pressure. It opposes the regulation by RAAS. The walls of the atria of the heart release ANF in response to an increase in blood volume and blood pressure. ANF inhibits release of renin from the JGA and thereby inhibits NaCl reabsorption by the collecting duct and reduces aldosterone release from the adrenal gland.
Thus ADH, RAAS and ANF regulate the functions of kidneys and control body fluid osmolarity, salt concentration, blood pressure and blood volume.
Select the correct statement about hormones and their actions.
Parathyroid hormone increases K absorption of the body.
Insulin and glucagon helps to maintain blood sugar levels.
Old aged people have weak immunity due to increased activity of thymus.
Osteoporosis in women occurs due to increased levels of oestrogens.
B.
Insulin and glucagon helps to maintain blood sugar levels.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates the reabsorption of Ca by renal tubules and increases Ca2+ absorption from digested food. It means PTH increases the blood Ca2+ level.
Old aged persons have weak immunity because thymus is degenerated in old individuals resulting in a decreased production of thymosin and poor immunity.
Oestoporosis in women occurs due to decreased level of estrogen.
Which of the following pairs of hormones can easily pass through the cell membrane and binds to a receptor inside it (mostly in the nucleus)
Insulin, glucagon
Thyroxine, insulin
Somatostatin, oxytocin
Cortisol, testosterone
D.
Cortisol, testosterone
Cortisol and testosterone are steroidal in nature. Steroid hormones are lipid soluble and easily pass through cell membrane of a target cell into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm they bind to specific intracellular receptors (proteins) to form a hormone receptor complex that enters the nucleus.
Assertion: The immune responses of old persons become weak.
Reason: Thymus is degenerated in old individuals resulting in a decreased production of thymosin
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Adrenocorticotropic-Releasing Hormones (ARH) excite the anterior lobe of
pituitary gland to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
Reason: ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete its glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid hormones.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion : Hormone calcitonin has antagonistic effect to that of parathormone.
Reason : Calcitonin decreases blood calcium level while parathormone increases blood calcium level.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Calcitonin or thyrocalcitonin is secreted by parafollicular cells of thyroid stroma. It retards bone dissolution and stimulates excretion of calcium in urine. Thus, it lowers calcium level in extra cellular fluid (ECF).
Parathornone is secreted by chief cells of parathyroid gland and is also known as Collip's hormone. It maintains blood calcium level by increasing its absorption from food in intestine and its reabsorption from nephrons in the kidney. Maintenance of proper calcium level is in fact, a combined function of parathormone and calcitonin. When calcium level falls below normal, then parathormone maintains it by promoting its absorption, reabsorption and also by demineralization of bones. When blood calcium level exceeds above normal, then calcitonin hormonen increases excretion of calcium in urine.
A patient of diabetes mellitus excretes glucose in urine even when he is kept in a carbohydrate free diet. It is because
fats are catabolised in adipose tissues to form glucose
amino acids are catabolised in kidney to form glucose
amino acids are discharged in blood stream from liver
glycogen from muscles is released in blood stream.
A.
fats are catabolised in adipose tissues to form glucose
A patient of diabetes mellitus is unable to produce or fail to utilize insulin hormone. Thus, he is unable to store glucose in the form of glycogen. Hence, he started to excrete glucose in the urine. A patient is kept in carbohydrate free diet yet he excretes glocose in urine because high level of glucose not only depends on dietary carbohydrates but also on glycogenolysis (degradation of glycogen in liver) and gluconeogenesis (breakdown of fats into glucose in adipose tissues and coversion of muscle lactate into glucose via cori cycle).
Which of the following match is correct?
Hormone Effect Oxytocin Milk ejection hormone Glucagon Decreases blood sugar level Adrenaline Decreases heart rate Thyroxine Decreases BMR
A.
| Hormone | Effect |
| Oxytocin | Milk ejection hormone |
Oxytocin is a hormone that causes both contraction of smooth muscle in the uterus during birth and expulsion of milk from the mammary glands during suckling. It is produced in the neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus but is stored and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland.
Glucagon is a hormone, secreted by the (or A) cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas, that increases the concentration of glucose in the blood by stimulating the metabolic breakdown of glycogen. It thus antagonizes the effects of insulin.
Adrenaline (epinephrine) is a hormone produced by the medulla of the adrenal glands, that increases heart activity, improves the power and prolongs the action of muscles, and increases the rate and depth of breathing to prepare the body for 'fright, flight, or fight'. At the same time it inhibits digestion and excretion.
Thyroxine is secreted by thyroid gland. It controls the rate of all metabolic processes in the body and influence physical development and activity of the nervous system.
Which of the following statements regarding glucagon is false?
It is secreted by -cells of Langerhans
It acts antagonistically to insulin
It decreases blood sugar level
The gland responsible for its secretion is heterocrine gland.
C.
It decreases blood sugar level
Glucagon is a hormone, secreted by the - cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas, that increases the concentration of glucose in the blood by stimulating the metabolic breakdown of glycogen. It thus antagonizes the effects of insulin.
Assertion: Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by a vein.
Reason: This attachment hypophysial portal vein.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
D.
If both assertion and reason are false.
Pituitary gland or hypophysis is situated in a depression, the sella turcica of sphenoid bone of the skull. It is directly attached to the hypothalamus by a stalk, the infundibulum. Hypophysial portal veins carry blood containing neurohormones (releasing factors) from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary.
Assertion: Rabies is acute infectious disease of warm blooded mammals characterised by
involvement of central nervous system resulting in paralysis and finally death.
Reason: This is caused due to neurotropic filterable bacteria in saliva of rabid animals.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Rabies (hydrophobia) is an acute viral disease of the central nervous system that affects all warm-blooded animals and is usually transmitted to humans by a bite from an infected dog. Symptoms appear after an incubation period ranging from 10 days to over a year and include malaise, fever, difficulty in breathing, salivation, periods of intense excitement, and painful muscle spasms of the throat induced by swallowing. In the later stages ofthe disease the mere sight ofwater induces convulsions and paralysis, death occurs within 4-5 days.
Assertion : Aldosterone is a steroid hormone and is important in the control of sodium and potassium ion concentration in mammals.
Reason : It upgrades sodium ion concentration in the ECF by promoting reabsorption of sodium ions from renal tubules and excretion of potassium ions in urine.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone or mineralocorticoid produced by the outer-section ie, zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland to regulate sodium and potassium balance in the blood. It is produced in the cortex of adrenal gland (above the kidneys). It helps in regulating blood pressure. It sends signals to the organs like kidney and colon, that can increase the amount of sodium that the body sends into the blood stream or the amount of potassium released in the urine. It also helps to maintain body's pH and electrolyte levels.
Which one of the following four secretions is correctly matched with its source, target and nature of action?
Secretion Source Target Action Gastrin Stomach lining Oxyntic cells Production of HCl Inhibin Sertoli cells Hypothalamus Inhibition of secretion of gonadotropin releasing hormone Enterokinase Duodenum Gall bladder Release of bile juice Atrial Natiuretic Factor (ANF) Sinu atrial node (SAN) M- cells of Atria Juxta- glomerular apparatus (JGA) Inhibition of release of renin
D.
| Atrial Natiuretic Factor (ANF) | Sinu atrial node (SAN) M- cells of Atria | Juxta- glomerular apparatus (JGA) | Inhibition of release of renin |
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is released by wails of the cardiac atrium in response to high sodium concentration, high extracellular fluid volume, or high blood volume. It then acts via various mechanisms to excrete Na, and to cause vasodilation in the circulatory system. It also decreases Na resorption in the renal distal convoluted tubule and cortical collecting duct. It also inhibits renin secretion.
Gastrin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the enteroendocrinc cells of the stomach. It plays an important role in the control of gastric acid secretion.
Inhibin hormone is secreted from corpus luteum, placenta and testes. It supplements the effect of excess sex hormones for depressing gonadotrophic activity (FSH, LH, ICSH) target of inhibin is anterior lobe of pituitary.
Duodenal enterokinase converts trypsinogcn to activate trypsin which, in turn, activates the other pancreatic enzymes.
Tadpoles of frog can be made to grow as giant sized tadpoles, if they are
administered antithyroid substance like thiourea
administered large amounts of thyroxine
reared on a diet rich in egg yolk
reared on a diet rich in both egg yolk and glucose.
A.
administered antithyroid substance like thiourea
Thyroxine, the principal hormone, of thyroid gland, is required for tissue differentiation and metamorphosis (the rapid transformation from the larval to the adult form) in amphibians. Thyroxine triggers a response from the hypothalamus, (probably by a genetic mechanism) followed by the production and release of TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone), thus metamorphosis begins and tadpoles metamorphose into frogs. Thiourea is an organic compound of carbon, nitrogen, sulphur and hydrogen, with the formula CSN2H4, or (NH2)2CS. It is similar to urea, except that oxygen atom is replaced by a sulphur atom.
Which one of the following four glands is correctly matched with the accompanying description ?
Thyroid - hyperactivity in young children causes cretinism
Thymus - starts undergoing atrophy after puberty
Parathyroid - secretes parathormone which promotes movement of calcium ions from blood into bones during calcification
Pancreas - Delta cells of the Islets of Langerhans secrete a hormone which stimulates glycolysis in liver
B.
Thymus - starts undergoing atrophy after puberty
The thymus gland is located behind the sternum and between lungs. It is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to shrink slowly and become replaced by fat.
The thyroid gland is a vital hormone gland. It plays an important role in the metabolism growth and development of the human body. It helps to regulate many body functions by constantly releasing a steady amount of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. Cretinism is a type of mental retardation and bodily malformation caused by severe, uncorrected thyroid deficiency.
The major function of parathyroid gland is to maintain the body's calcium and phosphate levels within a very narrow range, so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. It secretes parathyroid hormone. It also enhances the excretion of phosphate by the kidneys and its uptake by the cells.
Pancreas is an organ present in abdomen. It plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into fuel for the body's cells. Delta cells is a type of cell found in Islets of Langerhans in pancreas. They form somatostatin, a hormone that inhibits the release of numerous hormones in the body.
Assertion: Our body secretes adrenaline in intense cold.
Reason: Adrenaline raises metabolic rate.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Adrenaline is a catecholamine hormone, also known as epinephrine, secreted by the mammalian adrenal medulla as well as the adrenergic nerve endings. Its secretion is stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system under conditions of stress. Adrenaline stimulates blood flow to skeletal muscles and increases blood glucose levels. It also raises metabolic rate.
The source of somatostatin is same as that of
thyroxine and calcitonin
insulin and glucagon
somatotropin and prolactin
vasopresin and oxytocin
D.
vasopresin and oxytocin
The source of somatostatin is same as that of vasopressin and oxytocin. Somatostatin is produced from hypothalamus (somatostatin neuron) and oxytocin and vasopressin are also produced in the nuclei of hypothalamus, though later they are stored and released from posterior pituitary.

Assertion: Diabetes insipidus is marked by excessive urination and too much thirst of water.
Reason: Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is secreted by the posterior lobe of pituitary gland,
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
B.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
Diabetes insipidus is an uncommon disorder that causes an imbalance of water in the body. This imbalance leads to intense thirst even after drinking fluids (polydipsia), and excretion of large amounts of urine (polyuria).
Diabetes insipidus occurs when your body can't regulate how it handles fluids. Normally, your kidneys remove excess body fluids from your bloodstream. This fluid waste is temporarily stored in your bladder as urine, before you urinate.
Which is not a gonadal hormone
Progesterone
Testosterone
Adrenalin
Estrogen
C.
Adrenalin
Adrenaline is produced in the medulla in the adrenal glands as well as some of the central nervous system's neurons. Within a couple of minutes during a stressful situation, adrenaline is quickly released into the blood, sending impulses to organs to create a specific response.
Adrenal gland is derived from
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
both (a) and (b)
D.
both (a) and (b)
Adrenal gland consists of two different parts, ie, cortex and medulla. Cortex (outer) is the major (80%) part which is derived from mesoderm while medulla (inner) is derived from ectoderm.
Which endocrine gland becomes inactive in old age
Adrenal
Thymus
Pineal
Pituitary
B.
Thymus
A critical immune organ called the thymus shrinks rapidly with age, putting older individuals at greater risk for life-threatening infections. A new study reveals that thymus atrophy may stem from a decline in its ability to protect against DNA damage from free radicals. The damage accelerates metabolic dysfunction in the organ, progressively reducing its production of pathogen-fighting T cells.
Secretin hormone is secreted by :
liver
pancreas
intestine
Brunner's glands
D.
Brunner's glands
Secretin is a hormone secreted by Brunner's glands in the wall of duodenum and jejunum under stimulus of acidic food coming from the stomach. The acidity is due of HCl.
Liver secretes and synthesizes 4 hormones. They are Insulin, Growth Factor- 1 (IGF-1), Angiotensinogen and Thromopoietin.
Pancreas secrete hormones such as insulin, somatostatin, gastrin and glucagon.
Hormones secreted by pancreas are:
ACTH
oxytocin
LH and FSH
insulin and glucagon
D.
insulin and glucagon
- cells of islets of Langerhans of pancreas produce the hormone insulin. It's chief physiological action is to adjust blood glucose by decreasing the levei i.e., opposite to that of glucagon which is a product of - cells of pancreas.
Neurohypophysis secretes
ADH and oxytocin
oxytocin and estrogen
vasopressin and GH
vasopressin and estrogen
A.
ADH and oxytocin
Neurohypophysis is the posterior lobe of pituitary. It consists of supporting cells called pituicytes. Its hypothalamic neurons secrete two octapeptide hormones namely antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin.
Physiologically active thyroxine exists in which of the following form ?
Unbound
Bound to albumin
Bound to globulin
All of the above
A.
Unbound
Once the thyroxine is in the circulation, it binds to albumin. Only the free unbound form of thyroxine is physiologically active.
The most accepted theory of ageing is :
less RBC in blood
thymus gland becomes non-functional
brain cells die with ageing
all of the above
B.
thymus gland becomes non-functional
Ageing is a progressive deterioration in structure and function of cells and tissues with age. According to the immunity theory of ageing due to decline of thymus, immunity decreases resulting in more diseases, damage and destruction of cells and tissues.
The specific region of hypothalamus, responsible for physiological sweat secretion, is
para-ventricular nucleus
supra-optic nucleus
median eminence
pars distalis
A.
para-ventricular nucleus
The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) has emerged as one of the most important autonomic control centers in the brain, with neurons playing essential roles in controlling stress, metabolism, growth, reproduction, immune, and other more traditional autonomic functions (gastrointestinal, renal and cardiovascular).
Endemic goitre is a state of
increased thyroid function
normal thyroid function
decreased thyroid function
moderate thyroid function
A.
increased thyroid function
The most common type of goitre is endemic goitre, caused by iodine deficiency. Iodine is an essential nutrient that is required for the production of thyroid hormone. When iodine intake is low, thyroid hormone production is low, and in response the pituitary gland secretes greater quantities of the hormone thyrotropin or thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). This excess thyrotropin stimulates not only thyroid hormone production but also thyroid growth.
Islets of Langerhans are found as
anterior pituitary
kidney cortex
spleen
endocrine pancreas
D.
endocrine pancreas
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine, ie, hormone producing cells. It was discovered by Paul Langerhans. They consist of 1 to 2% of the pancreas volume and receive 10- 15% of its blood flow. These are irregularly shaped patches of endocrine tissue located within the pancreas of most vertebrates.
Which of the following is the function of adrenalin?
Helps in gastric juice secretion
Increases heart rate and blood pressure
Increases blood calcium
Helps in milk secretion
B.
Increases heart rate and blood pressure
Adrenalin is a natural stimulant made in the adrenal gland of the kidney. Its biological name is epinephrine. It is carried in the blood stream and affects the autonomous nervous system. It control the functions such as, the heart rate, dilation of the pupil, secretion of sweat and saliva, altering body's metabolism etc.
The hormone responsible for 'Fight and Flight' response is
adrenalin
thyroxin
ADH
oxytocin
A.
adrenalin
Adrenalin is a natural stimulant made in the adrenal gland of the kidney. Its biological name is epinephrine. Adrenalin is carried in the blood stream and affects the autonomous nervous system, which control functions such as, the heart rate, dialation of the pupils and secretion of sweat and saliva. Adrenalin is the body's activator and is released in response to anxiety.
ACTH is secreted from
adrenal cortex
pituitary
adrenal medulla
thyroid
B.
pituitary
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is secreted from pituitary gland. It controls structure and functioning of adrenal cortex especially secretion of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoides.
The cause of cretinism is
hypothyroidism
hypoparathyroidism
hyperthyroidism
hyperparathyroidism
A.
hypothyroidism
Cretinism refers to severe hypothyroidism in an infant or child.This person has slow body growth and mental development of reduced metabolic rate. Myxoedema is caused by deficiency of thyroid hormone in adults.
Which of the following is a minerelocorticoid?
Testosterone
Progesterone
Adrenalin
Aldosterone
D.
Aldosterone
Mineralocorticoides are responsible for regulation of mineral metabolism. Aldosterone is one of the important mineralocorticoides in humans. Its main function is to regulate the sodium content of the body.
Which one of the following is not a second messenger in hormone action?
Calcium
Sodium
cAMP
cGMP
B.
Sodium
Secondary messengers are molecules that relay signals received at receptors on the cell surface such as the arrival of protein hormones, growth factors, etc to target molecules in the cytosol and/ or nucleus. Ca+, cAMP and cGMP are secondary messenger in hormone action.
Goitre can occur as a consequence of all the following except
iodine deficiency
pituitary adenoma
Grave's disease
excessive intake of exogenous thyroxin
D.
excessive intake of exogenous thyroxin
Thyroxine is the main hormone secreted into the bloodstream by the thyroid gland. It is the inactive form and most of it is converted to an active form called triiodothyronine by organs such as the liver and kidneys.
The genetic deficiency of ADH-receptor leads to
diabetes mellitus
glycosuria
diabetes insipidus
nephrogenic diabetes
D.
nephrogenic diabetes
It's a hormone made by the hypothalamus in the brain and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. It tells kidneys how much water to conserve. ADH constantly regulates and balances the amount of water in your blood. Higher water concentration increases the volume and pressure of your blood.
Tetany is caused by
hyperparathyroidism
hypoparathyroidism
hyperthyroidism
hypothyroidism
B.
hypoparathyroidism
Tetany is caused due to hypoparathyroidism. It causes the lowering blood calcium level. This increases the excitibility of nerves and muscles which results in sustained contraction of muscles of larynx, face, hands and feet.
Which the following is a gastrointestine hormone?
Prolactin
Enterogastrone
GH
FSH
B.
Enterogastrone
Gastrointestinal hormones are the hormones secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the stomach, pancreas and small intestine. Enterogastrone hormone produced by small intestine slows down secretion of gastric juice. Enterokinase is an enzyme in intestinal juice that activates trypsinogen to trypsin.
Which one of the following statement is incorrect?
Glucagon is secreted by pancreas
Androgen is produced by ovary
Thyroxine is secreted by thyroid
Oxytocin is secreted by pituitary
B.
Androgen is produced by ovary
Leydig cells or interstitial cells of testes secrete androgens or male sex hormones. They are found in the connective tissues around seminiferous tubules. Androgens are responsible for the development of male secondary sex organs and accessory/external male sex characters.
Which of the following statement is correct in relation to the endocrine system?
Adenohypophysis is under direct neural regulation of the hypothalamus
Organs in the body like gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney and liver do not produce any hormones
Non- nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that act as intercellular messenger are known as hormones
Releasing and inhibitory hormones are produced by the pituitary gland
C.
Non- nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that act as intercellular messenger are known as hormones
Hormones are non nutrient chemicals, which act as intracellular messengers and are produced in trace amounts. Endocrine cells are present in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract, e.g., gastrin, secretin, GIP. Atrial wall of our heart secretes a peptide hormone called ANF (Atrial Natriuretic Factor), RH/IH are produced by hypothalamus. Adenohypophysis is not directly under neural control, it is under the control of hypothalamic hormones, brought by portal system.
Select the answer which correctly matches the endocrine gland with the hormone it secretes and its function/deficiency symptom
Endocrine gland Hormone Function/ deficiency symptoms Anterior pituitary Oxytocin Stimulates uterus contraction during child birth Posterior pituitary Growth Hormone (GH) Oversecretion stimulates abnormal growth Thyroid gland Thyroxine Lack of iodine in diet results in goitre Corpus luteum Testosterone Stimulates spermatogenesis
C.
| Thyroid gland | Thyroxine | Lack of iodine in diet results in goitre |
Lack of iodine in diet results in goitre. Oxytocin is produced by neurohypophysis, which stimulates uterus contraction during child birth. Anterior pituitary secretes Growth Hormones (GH) its over secretion stimulates abnormal growth. Testosterone is secreted by Leydig cells of testes in males.
Which of the following pituitary hormones is secreted without the involvement of a Releasing Hormone (RH)?
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Oxytocin
Prolactin
C.
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a mammalian neurohypophysial hormone produced by hypothalamus and stored and secreted by posterior lobe of pituitary gland. It acts as a neuromodulator in the brain. It is secreted by the pituitary without the involvement of a Releasing Hormone (RH).
TSH, FSH and prolactin are secreted with the involvement of releasing hormones to release thyrotroph, gonadotroph and lactotroph cells triggers respectively the anterior lobe of pituitary to release their particular hormones such as thyroid releasing hormone, gonadotropin releasing hormone and prolactin releasing hormone, respectively.
Which of the following hormones is a derivative of fatty acid?
Gastrin
Thyroxin
Estrogen
Prostaglandins
D.
Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins are a group of hormone like lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from unsaturated fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. It is a local hormone (i.e., autocrine or paracrine) because their target cells are in the close vicinity of the site of secretion.
Other hormones such as estrogen is primarily a steroid hormone, thyroxin is a thyrosine-based hormone and gastrin is a peptide hormone.
Cells die at the time of release of secretory materials in
holocrine gland
apocrine gland
merocrine gland
mixed or apocrine gland
A.
holocrine gland
Halocrine gland is a type of exocrine gland, the secretions of halocrine gland are produced in the cytoplasm of the cell and released by the rupture of the plasma membrane, which destroy the cell and results in the secretion of the product into the lumen. Halocrine secretion is the most damaging type of secretion.
Melatonin is produced from
pineal gland
adrenal gland
parathyroid gland
ovary
A.
pineal gland
Pineal gland secretes a hormone called melatonin. This hormone plays a very important role in the regulation of a 24 hour (diurnal) rhythm of our body. It also influences metabolism, pigmentation, the menstrual cycle as well as our defense capability.
Adrenal gland is composed of two types of tissues, adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex. Adrenal medulla, secretes hormones adrenaline or epinephrine and noradrenaline or norepinephrine. Adrenal cortex secretes many hormones called as corticoids.
The parathyroid glands secrete a peptide hormone called parathyroid hormone. This hormone increases the Ca2+ levels in the blood.
Ovary produces two groups of steroid hormones called oestrogen and progesterone.
Zymogenic cells of gastric gland secrete
pepsinogen
trypsin
pepsin
chymotrypsin
A.
pepsinogen
The peptic cells or chief cells or zymogenic cells of gastric gland secrete pepsinogen. The enzyme pepsinogen has no proteolytic activity. It is the inactive precursor of pepsin. The proenzyme pepsinogen on exposure to HCl gets converted into the active enzyme pepsin which is the proteolytic enzyme of the stomach.
Pancreatic acinar cells (exocrine part of pancreas) produce pancreatic juice that contains protein-digesting enzymes, namely trypsin, chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase and carbohydrases like pancreatic a-amylase and lipase.
Which one of the following is called intra-specific chemical messenger?
Pheromones
Prostaglandins
Corticotrophin
Catecholamines
A.
Pheromones
Pheromone is a chemical substance produced and released into the environment by an animal, especially a mammal or an insect, affecting the behaviour or physiology of others of its species.There are alarm pheromones, food trail pheromones, sex pheromones and many other that affect behaviour or physiology.
Which one of the following secretes glucagon?
Beta () cells of islets of Langerhans
Alpha () cells of islets of Langerhans
Acidophilic cells of adenohypophysis
Basophilic cells of adenohypophysis
B.
Alpha () cells of islets of Langerhans
The islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine cells. Hormones produced in the islets of Langerhans are secreted directly into the blood flow by five types of cells, mentioned as follows.
Alpha cells secrete glucagon.
Beta cells secrete insulin and amylin delta cells secrete somatosatin.
Gamma cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide and epsilon cells secrete ghrelin.
Which one of the following enzymes is responsible for the conversion of norepinephrine to epinephrine?
Catecholamine-O-methyltransferase
Phenylalanine-N-methyltransferase
DOPA decarboxylase
Monoamine oxidase
A.
Catecholamine-O-methyltransferase
Phenylalanine-N-methyltransferase (PNMT) is an enzyme found in the adrenal medulla that converts nor-epinephrine to epinephrine. It is a protein whose encoding gene is found on chromosome 17 in humans. It catalyses the transfer of a methyl group from SAM (S-adenosyl-L-methionine) which is a factor to nor-epinephrine, converting it into epinephrine.
The hormone that stimulates the release of pancreatic juice is
secretin
glucagon
inhibin
insulin
A.
secretin
To regulate the digestive function of the pancreas, the endocrine system uses two hormones, i.e. secretin and cholecystokinin.
Secretin is produced from the cells in the lining of the duodenum in response to acidic chyme emerging from the stomach. It stimulates the pancreas to produce and secrete pancreatic juice containing a high concentration of bicarbonate ions.
Match the following Columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Hyperthyroidism | 1. Myxedema |
| B. Hyposecretion of glucocorticoids | 2. Addison's disease |
| C. Hypothyroidism- I | 3. Increased metabolic rate |
| D. Hyperparathyroidism |
4. Cushing's syndrome 5. Kidney stone |
A- 3; B- 2; C- 1; D- 5
A- 3; B- 4; C- 1; D- 2
A- 1; B- 4; C- 3; D- 2
A- 1; B- 2; C- 3; D- 5
A.
A- 3; B- 2; C- 1; D- 5
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Hyperthyroidism | 3. Increased metabolic rate |
| B. Hyposecretion of glucocorticoids | 2. Addison's disease |
| C. Hypothyroidism- I | 1. Myxedema |
| D. Hyperparathyroidism | 5. Kidney stone |
What would not take place if chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla undergoes oncogenesis?
High blood sugar and glucosuria
High BMR
Pheochromocytomas
Low blood pressure
D.
Low blood pressure
Chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla are responsible for secreting epinephrine and norepinephrine. Their tumour will lead to hypersecretion of epinephrine causing high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, glycosuria, high BMR, nervousness and sweating and pheochromocytomas.
Glands in a vertebrate body originate from
ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm
ectoderm and endoderm
mesoderm
ectoderm
D.
ectoderm
Glands in a vertebrate body originate from ectoderm. Glands are the modification of epidermis of skin. The ectoderm also gives rise to the neural crest (ganglion, sensory cell, etc) and neural tube (brain, spinal cord etc).
Statement I:- An injury to the anterior pituitary affects the growth of a person.
Statement II:- Injury to adrenal cortex is not likely to affect secretion of cortisol.
Choose the correct option
Statement I is correct but II is incorrect
Statement II is correct but I is incorrect
Both statement are correct
Both statements are incorrect
A.
Statement I is correct but II is incorrect
Statement I is correct as an injury to the anterior pituitary affects the growth because somatotropin or growth hormone is the major hormone secreted from this region. It is the most important stimulant of proper normal growth of body.
Statement II is incorrect and can be corrected as an injury to adrenal cortex is not likely to affect secretion of adrenaline and noradrenaline. It is because, that these hormones are secreted by adrenal medulla of adrenal gland.
Which gland is worked opposite to pressure?
Adrenal
parathyroid
Pineal
Thyroid
A.
Adrenal
Adrenal gland secretes adrenaline hormone which is sympathomimetic and it works opposite to pressure.
In human beings, which hormone acts as a mild growth hormone?
Prolactin
Oestrogen
Progesterone
Cortisol
A.
Prolactin
Prolactin is the lactogenic hormone. It stimulates mammary growth and differentiation and milk production. Therefore, it indirectly controls growth.
Acromegaly is due to hypersecretion of
insulin
thyroxine
growth hormone
None of these
C.
growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) is secreted by anterior pituitary gland. It works with thyroid hormone and controls the normal growth. Hypersecretion (over production) of growth hormones in children causes the bones to grow unusually long. This results in a condition known as gigantism. But in adults, hypersecretion of growth hormone causes the bones of hands and face to thicken. This results in a condition called as acromegaly.
Sella turcica is found
near pituitary
in bones
in joints
near thyroid
A.
near pituitary
Sella turcica is found near pituitary gland. The pituitary is a small gland, laying in sella turcica of sphenoid bone and attached to hypothalamus of slender stalk.
Posterior pituitary gland
produces and store hormones
stores 6 trophic honnones
stores and releases ADH and oxytocin
release and store growth and thyroid stimulating hormone
C.
stores and releases ADH and oxytocin
Posterior pituitary gland is the back portion of the pituitary. It is a small gland in the head called the master gland. It does not synthesize any hormone but stores and releases two hormones ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) and Oxytocin.
Antidiuretic hormone is released in response to a fall in the water content of blood plasma and leads to an increase in the permeability to water of the distal and collective tubules of the nephron in the kidney so that water is retained in the blood plasma.
Oxytocin causes contraction of the uterus during birth and the ejection of milk from the nipple.
Gonadotrophins are secreted from
gonads
anterior pituitary
posterior pituitary
antidiuretic hormone
B.
anterior pituitary
Gonadotropic hormones, eg, gonadotrophins are of two types : Follicular stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone. These hormones are secreted from anterior pituitary gland. Gonads secrete sex hormones and posterior pituitary gland secretes oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone.
During emergency, which of the following hormone is secreted ?
Aldosterone
Thyroxine
Adrenalin
Calcitonin
C.
Adrenalin
Adrenalin is called as an emergency hormone as it contributes the 'fright, fight and flight reactions', which occurs in condition of emergency.
Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid or salt retaining hormorie secreted by adrenal cortex.
Thyroxin (tri-iodothyronin) is manufactured in thyroid gland and is synthesized from iodine.
Calcitonin or thyrocalcitonin (TCT) is a non-iodised hormone, secreted by parafollicular cells of thyroid.
The islets of Langerhans are found in
pancreas
stomach
liver
alimentary canal
A.
pancreas
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells. There are 3 types of cells-
(i) Alpha cells (32-38%) secreting glucagon
(ii) Beta cells (60-70%), secreting insulin
(iii) Delta and F-cells (2-8%), secreting somatostatin.
ADH controls water permeability of
collecting tube
distal convoluted tubule
proximal convoluted tubule
bowman's capsule
B.
distal convoluted tubule
ADH or vasopressin is effective in reabsorption of water by changing permeability of DCT (distal collecting tubules) or collecting ducts.
Acromegaly is due to hypersecretion of
thyroxin
prolactin
insulin
growth hormone
D.
growth hormone
Acromegaly is caused by the overproduction of growth hormone. It is characterised by gradual, marked enlargement, or elongation of the bones of the face, jaw extremities.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





