Contemporary World Politics Chapter 2 The End Of Bipolarity
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 12 Computer%2band%2bcommunication%2btechnology Contemporary World Politics
Which among the following statements that describe the nature of Soviet economy is wrong?
A.
(a) Socialism was the dominant ideology.B.
(b) State ownership/control existed over the factors of production.C.
(c) People enjoyed economic freedom.D.
(d) Every aspect of the economy was planned and controlled by the State.B. TRUE
C. FALSE
D. TRUE
Arrange the following in chronological order:
1)
Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
2)
Fall of the Berlin Wall
3)
Disintegration of the Soviet Union
4)
Russian Revolution
1)
Fall of the Berlin Wall
2)
Disintegration of the Soviet Union
3)
Russian Revolution
4)
Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
Tips: -
Russian Revolution (1917)
Soviet invasion of Afghanistan (1979)
Fall ofthe Berlin Wall (1989)
Disintegration ofthe Soviet Union (1991)
Match the following:
| A. Mikhail Gorbachev | (i) Successor of USSR |
| B. Shock Therapy | (ii) Military pact |
| C. Russia | (iii) Introduced reforms |
| D. Boris Yeltsin | (iv) Economic model |
| E. Warsaw | (v) President of Russia |
A. Mikhail Gorbachev | (i) Introduced reforms |
B. Shock Therapy | (ii) Economic model |
C. Russia | (iii) Successor of USSR |
D. Boris Yeltsin | (iv) President of Russia |
E. Warsaw | (v) Military pact |
Fill in the blanks:
a. The Soviet political system was based on ______ ideology.
b. ______was the military alliance started by the USSR.
c. ______ party dominated the Soviet Union’s political system.
d. ______ initiated the reforms in the USSR in 1985.
e. The fall of the ______ symbolised the end of the Cold War.
Mention any three features that distinguish the Soviet economy from that of a capitalist country like the US.
(ii) There was no place for the institution of private property under the Soviet economy.
(iii) State ownership was the dominant form of ownership; land and productive assets were owned and controlled by the Soviet State.
What were the factors that forced Gorbachev to initiate the reforms in the USSR ?
(i) The Soviet system had become very bureaucratic and authoritarian, making life Very difficult for the citizens.
(ii) There was lack of democracy. There was no freedom of speech. As a result of it, people often expressed their dissent in jokes and cartoons.
(iii) There was control of one party i.e., Communist Party of the Soviet Union over all institutions. It was not accountable to the people.
(iv) People in the fifteen republics had no right to manage their own affairs including their cultural affairs.
(v) Russia was one of the fifteen republics but in practice it dominated everything, and people from other regions felt neglected and often suppressed.
(vi) The Soviet Union lagged behind the West in technology, infrastructure and in fulfilling the political or economic aspirations of citizens.
(vii) Low productivity and technology resulted in shortages of all consumer goods. Thus, the Soviet economy had become stagnant.
What were the major consequences of the disintegration of the Soviet Union for countries likeIndia ?
(i) Indo-Russian relations are embedded in a history of trust and common interests and are matched by popular perceptions. Indian heroes from Rajkapoor to Amitabh Bachchan are household names in Russia and many post-Soviet countries.
(ii) Russia and India share a vision of a multipolar world order i.e., the coexistence of several powers in the international system, collective security, greater regionalism and independent foreign policy for all countries and other matters.
(iii) More than 80 bilateral agreements have been signed between India and Russia as a part ofthe Indo-Russian Strategic Agreement of 2001.
Results : (i) As a result of Indo-Russian relations, India benefited on issues like Kashmir, energy supplies, and other matters.
(ii) Russia is able to sell its military hardware to India. It has come to India's assistance during oil crises.
(iii) India is seeking to increase its energy imports from Kazakhstan and Turmenistan. It has sought their cooperation for partnership and investment in oil field.
(iv) India has got cryogenic rocket from Russia.
What was Shock Therapy ? Was this the best way to make a transition from communism to capitalism ?
This was not the best way to make a transition from communism to capitalism due to the following reasons :
(i) It brought ruin to the economies and disaster upon the people of the entire region.
(ii) In Russia, the large state-controlled industrial complex almost collapsed. There was the largest garage sale in history, as valuable industries were undervalued and sold at throw away prices.
(iii) The value of the ruble- the Russian currency declined.
(iv) People lost all their savings due to high rate of inflation.
(v) The collective farm system disintegrated and people were left without food security. Russia started to import food.
(vi) The old trading structure broke down with no alternative in its place.
(vii) The withdrawal of government subsidies pushed large section of the people into poverty.(viii) Privatisation led to new disparities between rich and poor regions.(ix) The democratic constitutions of these countries were prepared in a haste and therefore, includedmany defects. For example in Central Asia, the presidents had powers and some of them became authoritarian.There was no independence of judiciary in some countries.
Write an essay for or against the following proposition : 'With the disintegration of the second world, India should change its foreign policy and focus more on friendship with the US rather than with traditional friends like Russia'.
On the other hand, after the disintegration of the second world, if India comes closer to US, it may loose help from Russia. It is not sure that we will get support or help from the US because Pakistan is an ally of the US. India may also be forced to give up its policy of non-alignment. Under these circumstances the friendship with Russia will be more useful than with US.
Why is the fall of Berlin wall in 1989 considered as the end of bipolarity?
Who was Gorbachev? What had he tried to do in USSR?
Sponsor Area
Why did the coup take place in USSR in 1991 ?
Which three republics of the USSR had declared in December 1991 to disband the Soviet Union and under whom ?
Who was Vladimir Lenin ?
Who had founded the Bolshevik Communist Party and led the Russian Revolution of 1917?
Who was Joseph Stalin?
Which Baltic republics became members of UN and when?
Explain 'Shock Therapy'.
Name the provinces which had become independent of Yugoslavia after 1991.
Correct the following sentence :
In Russia about 90% of its industries were put to sale to multinational companies. This was called the smallest garage sale in history ?
Which republic state became the successor of the Soviet Union? What was its position in the international sphere?
(i) It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council.
(ii) Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union.
(iii) It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US.
In which region was the nationalist dissatisfaction with the Soviet Union strongest and why?
The reason was that people felt alienated from the central Asians and from each. They felt that they were paying a high price to keep the more backward areas within the Soviet Union.
who was Mikhail Gorbachev?
Match the following:
| A. Mikhail Gorbachev | (i) President of Russia (1991-99) |
| B. Boris Yeltsin | (ii) Collectivisation Programme |
| C. Joseph Stalin | (iii) Founder of Bolshevik Party |
| D. Lenin | (iv) General Secretary of the Communist Party |
A. Mikhail Gorbachev | (i) General Secretary of the Communist Party |
B. Boris Yeltsin | (ii) President of Russia (1991-99) |
C. Joseph Stalin | (iii) Collectivisation Programme |
D. Lenin | (iv) Founder of Bolshevik Party |
Diffentiate between unipolarity and bipolarity
Bipolarity means that there are two superpowers as was the case during the Cold War. The two superpowers were USSR and USA before the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.
What were the step required for transition from socialism to capitalism ?
(i) Private ownership.
(ii) Privatisation of state assets.
(iii) Private farming in place of collective farms.
(iv) Change in trading system from controlled to free trade and foreign direct investment,
(v) Deregulation and currency convertibility.
(vi) Break up of existing trade alliance among the countries of the Soviet bloc and to link themselves with the West.
Analyse the map and answer the questions given below :
Political Map ofthe Commonwealth of Independent States, 1947
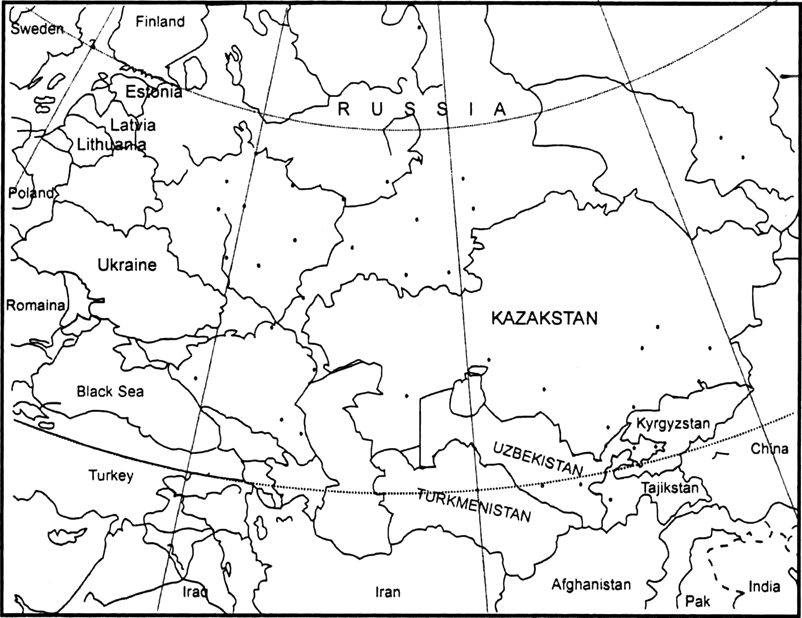
(i) Name the three Baltic republics that became UN members in September 1991 and locate themby marking 1,2,3.
(ii) Which republics are the producer of oil and gas ?
(ii) Azerbaijan, Kazakstan, Russia, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
How did post-communist regimes including Russia revive its economies in 2000.
What is the main source of economic benefit for the central Asian Republics ? Why has it turned a zone of competition among Russia, US and China ?
USA : After 9/11 incident, the US wanted military bases which could be used during wars in Afghanistan and Iraq.
Russia : Russia perceives these states as its 'Near Abroad' and want to have them under Russian influence.
China : It has interests due to oil resources and have started settling arounds its border to conduct trade.
Explain the reasons that led to the disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991.
(i) Economic stagnation: The Soviet economy used much of its resources in maintaining a nuclear and military arsenal and the development of its satellite states in Eastern Europe and within the Soviet system.This led to huge expenditure and economic stagnation.
(ii) Knowledge about the advance of the West: The citizens became more knowledgeable about theeconomic advance of the West. They came to know about the disparities between their system and the systemof the West.
(iii) Stagnation in administration and political sphere: The Communist Party had ruled the Soviet Union for 70 years but was not accountable to the people. The administration was bureaucratic and authoritarian. There was no place for dissent. There was too much corruption. There was no system to correct mistakes.Party leaders enjoyed more privileges than ordinary citizens.
Why had the Soviet Union collapsed inspite of Gorbachev's accurate diagnosis of the problem and his attempt to implement reforms?
(i) Some sections of Soviet society felt that Gorbachev should have moved much faster. They were disappointed and impatient with his methods. They benefited too slowly.
(ii) The members of the Communist Party, on the other hand, felt that their power and privileges were being eroded and Gorbachev was moving very quickly.
Thus, there were two different reactions about Gorbachev's policy. Under these circumstances, he lost support on all sides and divided public opinion. In the meantime, rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty in Russia, the Baltic republics, Ukraine, Georgia and others led to disintegration of the USSR.
What were the effects of disintegration of USSR ?
(i) End of Cold War confrontations: With the collapse of the Soviet Union, the ideological dispute that socialism was better than capitalism or vice versa was over. As a result of it, the arms race too came to an end.
(ii) Change in power relations: The US became the sole superpower. Capitalist economy was now the dominant economic system internationally. World Bank and International Monetary Fund became powerful advisors to countries since they gave loans for their transition to capitalism.
(iii) Emergence of many new countries: Some new countries emerged on the international scene. The Baltic and East European states wanted to join the European Union. They became part of North Atlantic Treaty Organisation. Thus, many new states emerged, each with its own identity, interests and economic and political problems.
Sponsor Area
Describe signifant tensions and conflicts which occurred in the former Soviet republics. What are their results?
(i) In Russia, two republics Chechnya and Dagestan had violent secessionist movements.
(ii) In central Asia, Tajikistan witnessed a civil war that went on for 10 years till 2001.
(iii) In Azerbaijan's province of Nagorno-Karabakh, some local Armenians want to secede and join Armenia.
(iv) In Georgia civil war broke out as the two provinces demanded independence.
(v) There are movements against the existing regimes in Ukraine, Kyrgyzstan and Georgia.
(vi) There are river disputes in the region.
Results: All these tensions and conflicts have led to instability, making life difficult for ordinary citizen.
Analyse India's relationship with the USSR during the Cold War.
(i) Economic: Russia gave aid and technical assistance for steel plants like Bhilai, Bokaro,Visakhapatnam and machinery plants like Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd. The Soviet Union accepted Indian currency for trade when India was short of foreign exchange.
(ii) Political: The Soviet Union supported India's stand on Kashmir issue in the UN. It supported India during the war with Pakistan in 1971.
(iii) Military: India received most of its military hardware from the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union entered into various agreements allowing India to jointly produce military equipment.
(iv) Culture: Hindi films and Indian culture became popular in the Soviet Union. A large number of Indian writers and artists visited the USSR.
Highlight any one major distinction between the Soviet economy and the Capitalist economy.
Soviet economy was planned and controlled by the state while Capitalist economy is liberal.
How was the U.S. benefited by the Soviet disintegration ?
(i) It established US hegemony in the world.
(ii)Capitalist economy model followed by US became accepted norms.
Suppose there had been no Cold War, how would that situation have affected India’s foreign policy ?
OR
If the Soviet Union has not disintegrated and the world had remained bipolar, how would that situation have affected the world politics ?
If the Cold War had not taken place , it would have affected Indian foreign policy in the following ways:
(i) India would have vigorously pursued independent foreign policy .
(ii) Since the rivalry between many major powers would have increased hatred and enmity, India would have been compelled to join the arms race to become a strong nation to defend its independence and sovereignty.
(iii) Indian would have the become a super power in Asia because of her large territory, human resource and strategic location.
Or
If the Soviet Union had not disintegrated, it would definitely have affected the following developments.
(i) Cold War confrontations would not have ended and United Nations would not have become the sole super power of the World.
(ii) Most of the countries which were part of erstwhile USSR would have never got independence.
(iii) Accumulation of nuclear weapons would have continued endlessly.
State any two features of the Soviet System.
The features:
(i) It was very bureaucratic and authoritarian.
(ii) It had tight control over all institution and was unaccountable to the people.
Describe any four consequences of Shock Therapy.
The consequences are:
(i) Collective farms were replaced by private farming and capitalism in agriculture.
(ii) Privatisation of state assets and corporate ownership patterns were immediately brought in.
(iii) Development began to be envisaged through more trade and sudden and complete switch to free trade was considered essential.
(iv) It also involved a breakup of the existing trade alliance among the countries among the countries of the Soviet bloc.
What was Cuban Missile Crisis? Describe its main events.
OR
Explain any three reasons for the disintegration of the USSR.
The reasons:
(i) The Soviet System, however, became very bureaucratic and authoritarian, making life very difficult for its citizens.
(ii) The one- party system represented by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union had tight control over all the Institutions and was unaccountable to the people.
(iii) Russia was only one of the fifteen republics that together constituted the USSR, in reality Russia dominated everything, and people from other regions felt neglected and often suppressed.
Explain any two reasons for the disintegration of the U. S. S. R.
Reasons for disintegration:
(i) The Soviet system became very bureaucratic and authoritarian, making life very difficult for its citizens.
(ii) Although Russia was only one of the fifteen republics that together constituted the USSR, in reality Russia dominated everything and people from other regions felt neglected and suppressed.
What was the Soviet System? Assess any four features of the Soviet System.
Or
Examine the relevance of the Non- aligned Movement after the Cold War era.
The Soviet system gave primacy to the state and the institution of the party. This system centred around the Communist Party and no other political party was allowed. The economy was planned and controlled by the state.
Features of the Soviet system:
(i) The Soviet System was very bureaucratic and authoritarian.
(ii) Lack of democracy and the absence of freedom of speech.
(iii) Tight control over all institutions and was unaccountable to the people.
(iv) Russia dominated everything and people from other regions felt neglected and often suppressed.
OR
Non-alignment, after the cold war in 1991, both as an international movement and as the core of Indian‘s foreign policy, lost some of its earlier relevance and effectiveness.
(i) However, Non alignment contained some core value and enduring ideas.
(ii) It was based on the recognition that decolonized states share a historical affiliation and can become a powerful force it they come together.
(iii) It meant that the poor and often very small countries of the world need not become followers of any of the big powers, that they could pursue an independent foreign policy.
(v) It was also based on a resolve to democratize the international system by thinking about an alternative world order to redress existing inequalities.
These core ideas remain relevant even after the cold war has ended.
Mention any two characteristics of the Soviet Political System.
The characteristics were-
(i) It was very bureaucratic and authoritarian.
(ii) The communist Party had tight control over all the institutions and was unaccountable to the people.
For how many years did the Civil War continue in Tajikistan? When did it come to an end?
Civil war continued for ten years in Tajikistan. It came to an end in 2001.
What is cold war? Why did the Super Powers depend on military alliances with smaller countries?
OR
Explain any six consequences of the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
The Cold War referred to the competition, the tensions and series of confrontations between the United States and Soviet Union, backed by their respective allies.
The Super Powers depend on military alliances with smaller countries because the smaller states were helpful for the superpowers in gaining access to:
(i) Vital resources such as oil or minerals
(ii) Territory, from where the superpowers could launch their weapons and troops.
(iii) Location from where they could spy on each other.
(iv) Economic support, in that many small allies together could to pay for military expenses.
OR
The consequences of the disintegration of the Soviet Union are:
(i) It meant the end of Cold War confrontations.
(ii) The ideological dispute over whether the socialist system would beat the capitalist system was not an issue any more.
(iii) Power relations in the world politics changed and, therefore, the relative influence of ideas and institutions also changed.
(iv) Politically, the notion of liberal democracy emerged as the best way to organise political life.
(v) The end of Soviet bloc meant the emergence of many new countries.
(vi) The central Asian countries wanted to take advantage of their geographical locations and continue their close ties with Russia and also to establish ties with the West, the US, China and others.
Define ‘Shock Therapy’.
The model of transition in Russia, Central Asia and east Europe that was influenced by the world Bank and the IMF is known as ‘Shock Therapy’.
Examine any six factors which led to the disintegration of the former Soviet Union.
OR
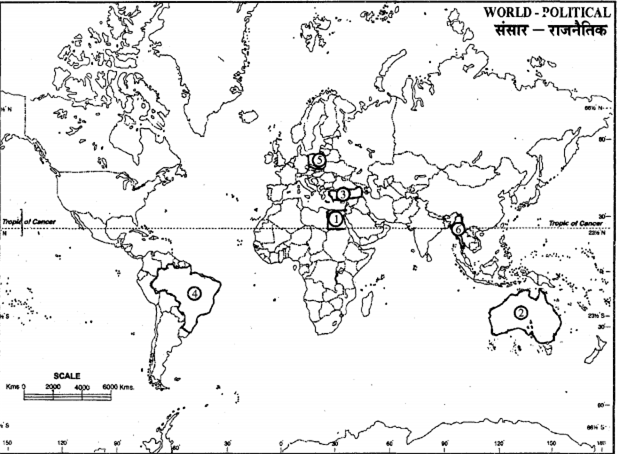
Study the political outline map of the world given below in which six diferent countries have been marked as (1) , (2) , (3) , (4) , (5) and (6) . Identity these countries and name them. Also classify them as the First World, Second World and Third World countries. Write your answer in the Answer-Book as per the folowing format:
| No. Of the Country | Name of the country | First/Second/Third World |
The factors which led to the disintegration of the former Soviet Union are:
(i) The Soviet system gave primacy to the state and the institution of the party.
(ii) This system centred around the Communist Party and no other political party was allowed.
(iii) The Soviet System was very bureaucratic and authoritarian.
(iv) Lack of democracy and the absence of freedom of speech.
(v) Tight control over all institutions and was unaccountable to the people.
(vi) Russia dominated everything and people from other regions felt neglected and often suppressed.
0R
| No. Of the Country | Name of the country | First/Second/Third World |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Egypt Australia Turkey Brazil Poland Myanmar |
III I I III II III |
Describe any six factors responsible for the disintegration of U.S.S.R.
OR
What is meant by New International Economic Order? Mention any four reforms of the global trading system proposed by UNCTAD in 1972.
The factors responsible for Disintegration of U.S.S.R:
(i) Internal weaknesses of Soviet political and economic institutions.
(ii) Economic stagnation for many years led to severe consumer shortages.
(iii) Soviet Union became stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well.
(iv) The Communist Party that had ruled for 70 years was not accountable to the people.
(v) Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration and rampant corruption.
(vi) The inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made and the unwillingness to allow more openness in government and the centralisation of authority in vast land.
OR
The Non-aligned countries were categoried as the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) – and the challenge they faced was to be more developed. Economic development was also vital for the independence of the new countries. Without sustained development, a country could not be truly free and then be dependent on richer countries. The idea of a New International Economic Order (NIEO) originated with this realization.
Reforms of the global trading system proposed by UNCTAD in 1972.
(i) To give the LDC‟s control over their natural resources exploited by the developed Western countries.
(ii) To obtain access to Western markets so that the LDCs could sell their products and therefore, make trade more beneficial for the poorer countries.
(iii) To reduce the cost of technology from the Western countries, and
(iv) To provide the LDCs with a greater role in international economic institutions.
Which one of the following statements about the Berlin wall is false ?
-
It symbolized the division between the Capitalist ;and the Communist world.
-
It was built immediately after the Second World War.
-
It was broken by the people on 9th November, 1989.
-
It marked the unification of the two parts of Germany.
B.
It was built immediately after the Second World War.
Read the passage given below carefully and answer the following questions ;
Each of these countries was required to make a total shift to a capitalist economy, which meant rooting out completely any structures evolved during this period. Above all, it meant that private ownership was to be the dominant pattern of ownership of property. Privatization of state assets and corporate ownership patterns were to be immediately brought in. Collective farms were to be replaced by private farming and capitalism in agriculture. This transition ruled out any alternate or ‘third way’.
(i) Name any two countries which were required to make a total shift.
(ii) Why were the collective farms to be replaced by private farming ?
(iii) Since the ‘third way’ had been ruled out, what were the only two ways of controlling the economy ?
(i) Armenia (ii) Georgia
(ii) Due to the end of state controlled economy and introduction of privatization and liberalisation.
(iii) Two ways – (i) State controlled economy (socialism) (ii) Capitalism.
Highlight any three positive and three negative features each of the Soviet System in the Soviet Union.
OR
How far it is correct to say the international alliances during the Cold War era were determined by the requirements of the superpowers and the calculations of the smaller states ? Explain.
Positive features:
i. Soviet System was more developed than rest of the world except U.S.A.
ii. Minimum standard of living was insured for all the citizens
iii. The Govt. subsidized the basic needs including health, education etc.
iv. There was no unemployment.
Negative features:
i. System was very bureaucratic and authoritarian.
ii. Lack of democracy and absence of freedom in many fields.
iii. There was only one party system.
iv. The party did not recognize the aspirations and feelings of people
OR
The smaller states were helpful for the superpowers in gaining access to
(i) vital resources, such as oil and minerals,
(ii) territory, from where the superpowers could launch their weapons and troops,
(iii) locations from where they could spy on each other, and
(iv) economic support, in that many small allies together could help pay for military expenses.
They were also important for ideological reasons. The loyalty of allies suggested that the superpowers were winning the war of ideas as well, that liberal democracy and capitalism were better than socialism and communism, or vice versa.
How far can Shock Therapy be called the best way to make the transition from communism to Capitalism?
It was the best way because it had privatised state-owned assets, replaced collective farms with private agriculture, introduced free trade and Foreign Direct Investments.
Why did the one-party system, represented by the Communist Party, become a source of dissent and dissatisfaction among the Soviet people?
Reasons:
(i) Lack of democracy and absence of freedom of speech.
(ii) The Soviet system had become very bureaucratic and authoritarian.
Describe any three features of the Soviet system.
Or
What circumstance compelled the super-powers to have military alliances with smaller countries? Describe.
The Features:
(i) The Soviet political system centered around the communist party and no other political party was allowed.
(ii) Economy was planned and controlled by the state. State ownership was the dominant form of ownership: land and productive assets were owned and controlled by the Soviet state.
(iii) It had a domestic, consumer industry that produced everything from pin to cars.The Soviet state ensured a minimum standard of living for all citizens,and the government subsidised basic necessities including health, education, child-care and other welfare schemes.
Or
The smaller states were helpful for the superpowers in gaining access to:
(i) Vital resources such as oil or minerals
(ii) Territory, from where the superpowers could launch their weapons and troops.
(iii) Location from where they could spy on each other.
(iv) Economic support, in that many small allies together could to pay for military expenses.
(v) They were also important for ideological reasons.
(vi) The loyalty of allies suggested that the superpowers were winning the war of ideas also.
In what three ways did the collapse of the Soviet Union affect the world politics ? Explain.
Ways in which the collapse of Soviet Union affected the world politics:-
(i) End of the Cold War confrontations.End of the ideological conflict between
socialists and capitalist system.
(ii) Power relations in world politics changed and the relative influence of ideas and institutions also changed.
(iii)The emergence of new independent countries with their own independent aspirations and choices.
State any one special feature of Indo-Russian friendship.
Special feature of India – Soviet Friendship:
(i) Russia is important for India’s nuclear energy requirement and space
industry
(ii) The Indian military gets most of the hardware from Russia
Starting in the 1960s, the two super powers signed which two significant
agreements to control arms ?
(i) Limited Test Ban Treaty
(ii) Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)
What is meant by alliance building as a component of traditional security Policy?
State its advantages. An alliance is a coalition of States that coordinate their actions to deter or to
defend against military attack. Most alliances are in writing.
ADVANTAGES
(i) Alliances are formed to increase the effective power relative to another
country or alliance.
(ii) They are based on national interest.
Why did the Soviet Union, the second most powerful country in the world,
disintegrate? Explain any six reasons.
Disintegration Soviet Union
(i) Internal weakness of Soviet political and economic institutions.
(ii) Economic stagnation.
(iii) Soviet resources were mainly used to maintain its nuclear and military arsenals.
(iv) Awareness among Soviet people about the economic advancement of the West.
(v) Stagnation in political and administrative fields.
(vi) The Communist Party was not answerable to the people.
(vii) Ordinary people were alienated from the government.
(viii) Poor administration, rampant corruption, inability to correct mistakes.
(ix) Lack of openness and centralisation of authority. (x) Government lost popular backing
(xi) Rise of nationalism and desire for sovereignty within the Soviet republics.
(xii) Gorbachov’srule in reforming the economy and other reforms.
How did the Soviet Union suddenly disintegrate? Explain any six reasons.
Reasons for disintegration:
i) Internal weakness of Soviet political and economical institutions.
ii) Soviet Union used much of its resources in maintaining Nuclear and military arsenals.
iii) Communist party was not accountable to the people.
iv) Ordinary people became more knowledgeable about the technology.
v) Corruption was rampant. vi) The Soviet Union had became stagnant in administrative and political sense.
vii) The system was unwilling to allow openness.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





