Moving Charges And Magnetism
Draw the field lines of (a) a bar magnet (b) a current carrying finite solenoid, and (c) an electric dipole.
What basic difference do you notice between the magnetic and electric field lines? How do you explain this difference?
The field lines of (a) a bar magent, (b) a current carrying finite solenoid and (c) electric dipole are shown below.
At large distances, the field lines are very similar. The curves labelled (i) and (ii) are closed Gaussian surfaces.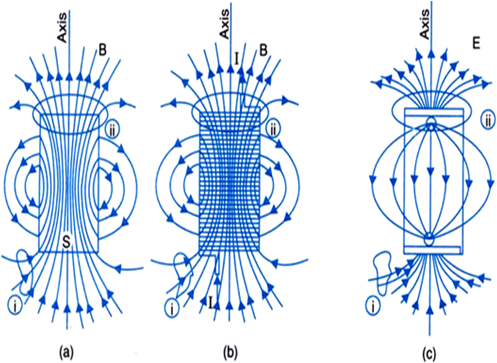
There is a basic difference between magnetic and electric field lines. In case of the electric field of an electric dipole, the electric lines of force originate from positive charge and end at the negative charge.
In case of a bar magnet, the magnetic field lines are closed loops, i.e., magnetic field lines do not start or end anywhere.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Moving Charges And Magnetism Chapter
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 x 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω; N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 x 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants k are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of (a) current sensitivity and (b) voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area