Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Explain the reason for the following:
Tertiary butyl iodide forms tertiary butyl alcohol with water, but with an alkali solution, it yields isobutylene (2-methyl propene).
Tertiary butyl iodide forms tertiary butyl alcohol with water due to SN1 mechanism. This reaction is carried out in polar solvents like water and alcohol. The reaction between tert-butyl iodide and hydroxide ion yields tert-butyl alcohol.In the case of alkali, solvent racemisation takes place. Due to the racemisation, the attack of the nucleophile may be accomplished from either side resulting in a mixture of the product. Hence isobutylene is formed.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Chapter
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
i)Three isomeric monochlorides.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
Four isomeric monochlorides.
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions:![]()
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: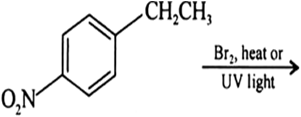
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: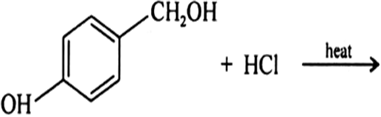
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: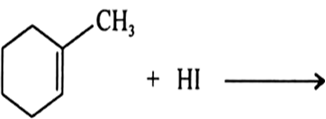
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: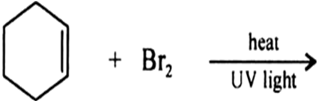
Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points:
Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloro-methane, Dibromomethane.
Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points:
1-chloropropane, Isopropyl chloride, 1-chlorobutane.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area