Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Explain the following terms:
(i) Nucleophile (ii) Nucleophilic reagent and (iii) Nucleophilic substitution.
i) A nucleophile is a chemical species that donates an electron pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in realtion to a reaction.
ii) a nucleophilic reagent defined as the molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bind can act as nucleophiles. For example OH- Cl-, CN- etc
iii) Nucleophilic substitution reaction:- A nucleophile react with haloalkane having a partial positive on the carbon atom bonded to halogen. a substitution reaction take place and atom attached to the substrate departs as leaving atom or ion. Since the substitution reaction is initiated by a nucleophile it is called substitution reaction.For example nucleophillic substitution reaction of alkyl halides.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Chapter
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
i) A single monochloride.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
i)Three isomeric monochlorides.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
Four isomeric monochlorides.
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions:![]()
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: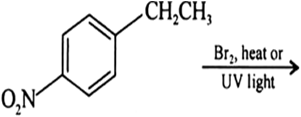
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: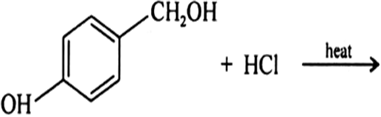
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: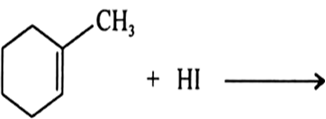
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: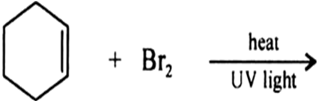
Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points:
Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloro-methane, Dibromomethane.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area