Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution whereas haloarenes undergo electrophilic substitution. Account for it.
Haloalkanes undergo nucleophillic substitution reaction due to high electronegativity of the halogen atom, the C—X bond in haloalkanes (alkyl halides) is slightly polar, thereby the C-atom acquires a slight positive charge (≡ C+δ—X–δ). Hence, C-atom is a good target for attack by nucleophiles (electron easily rich species). Therefore, the X-atom of the halo-alkane is replaced by a nucleophile easily.
Nu : + R+δ—Xδ → R—Nu + X–
On the other hand, in haloarenes the halogen atom releases electron to the benzene nucleus relatively electron-rich with respect to halogen atom. As a result, the electrophile attacks at ortho and para position. Hence, haloarenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Chapter
Write structures of the following compounds:
1-Bromo-4-sec butyl-2-methyl benzene.
Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI?
Write structures of different dihalogen derivatives of propane.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
i) A single monochloride.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
i)Three isomeric monochlorides.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
Four isomeric monochlorides.
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions:![]()
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: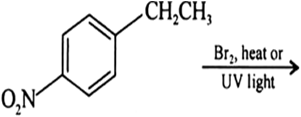
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: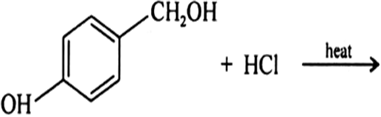
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions: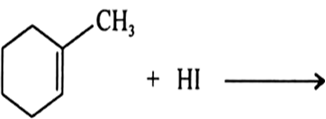
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area