Define the following terms in connection with spherical mirrors:
(i) Pole (ii) Centre of curvature (iii) Radius of curvature (iv) Principal axis (v) Linear aperture (vi) Angular aperture (vii) Principle focus (viii) Focal length (ix) Focal plane.
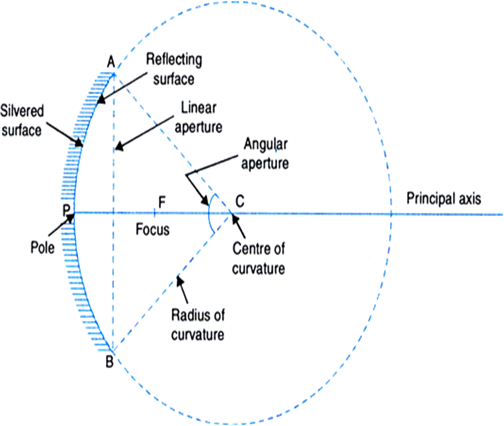
Fig. Characteristics of a concave mirror
(i) Pole: The centre of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is a point which is called the pole. Pole lies on the surface of the mirror.
(ii) Centre of curvature: The centre C of the sphere of which the mirror forms a part is the centre of curvature.
(iii) Radius of curvature: It is the radius R (= AC or BC as shown in the figure) of the sphere of which the reflecting surface of the mirror forms a part.
(iv) Principal axis: The line passing through the pole and the centre of curvature of mirror is called its principal axis.
(v) Linear aperture: It is the diameter AB of the circular boundary of the spherical mirror.
(vi) Angular aperture: It is the angle ACB subtended by the boundary of the spherical mirror at its centre of curvature.
(vii) Principle focus: It is a point F on the principal axis where a beam of light parallel to the principal axis either actually converges to or appears to diverge from, after reflection from a mirror.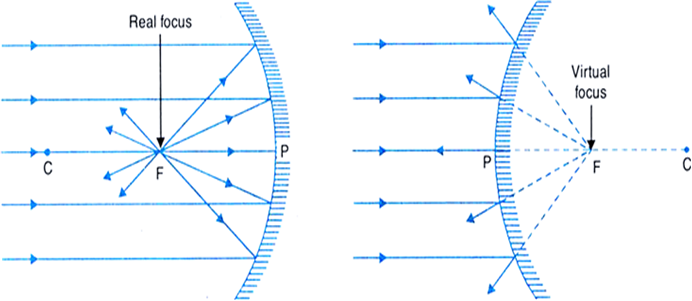
Fig. Principal focus of (a) a concave mirror (b) a convex mirror.
As shown in Fig.(a), when a beam of light is incident on a concave mirror parallel to its principal axis, it actually converges to a point F on the principal axis after reflection. So a concave mirror has a real focus and hence, it is called a converging mirror.
As shown in Fig.(b), when a beam of light is incident on a convex mirror parallel to its principal axis, after reflection, it appears to diverge from a point F (lying behind the mirror) on the principal axis.
So a convex mirror has a virtual focus and hence, it is called a diverging mirror.
(viii) Focal length: The distance f (= PF) between the focus and the pole of the mirror is called the focal length of the mirror.
(ix) Focal plane: The vertical plane, passing through the principal focus and which is perpendicular to the principal axis is called focal plane.
When a parallel beam of light is incident on a concave mirror at a small angle to the principal axis, it is converged to a point in the focal plane of the mirror.
Note: A line joining any point of the spherical mirror to its centre of curvature is always normal to the mirror at that point.





