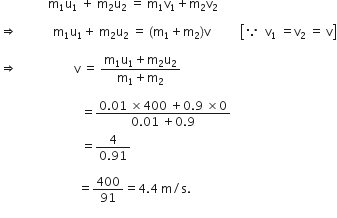A bullet of mass 10 g moving with a velocity of 400 m/s gets embedded in a freely suspended wooden block of mass 900 g. What is the velocity acquired by the block?
Let the final velocity of the bag along with the bullet embedded in it be v.
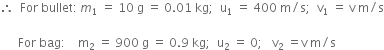
Now, According to the law of conservation of momentum,
Total momentum before collision = Total momentum after collision
That is,