Give some examples to illustrate Newton’s third law of motion.
Illustration's of Newton's third Law of motion:
(i) While walking we press the ground with our feet in the backward direction (action), as shown in Fig. 9.18.
The ground exerts an equal and opposite force on us. The horizontal component of this force of reaction enables us to move forward. 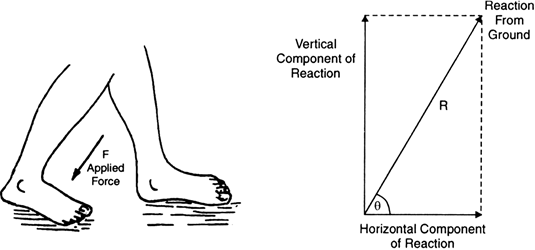
Fig. Action and reaction force acting while we walk on the ground.
(ii) While swimming, a person pushes water with his hands and feet in the backward direction (action). Water pushes the person with an equal force in the forward direction, which is the reaction force.
(iii) When a gun is fired, the exploding gases, which come out because of a chemical reaction, exert a forward force on the bullet. The bullet exerts an equal and opposite reaction force on the gases. This results in the recoil of the gun, as shown in fig. below
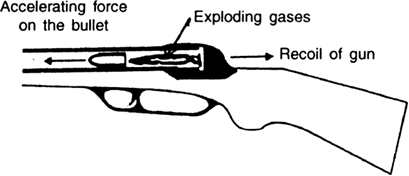
Fig. A forward force on the bullet and recoil of gun.
(iv) When a sailor jumps out of a rowing boat, the boat moves backwards. As the sailor jumps forward, he applies a forward force (action) on boat and the boat moves backwards due to the force of reaction.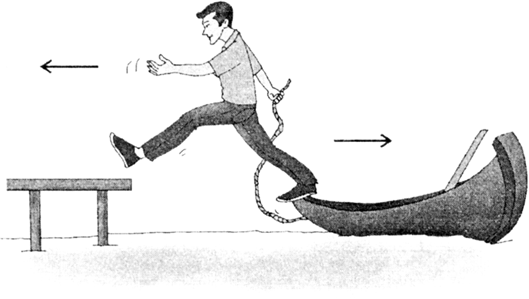
Fig. 9.21. As the sailor jumps in forward direction, the boat moves backwards.



