Explain how Newton’s second law can be used to define the unit of force. Define the SI unit of force.
Measurement of force from Newton’s second law.
Consider a force F acts on a body of mass m and changes its velocity from u to v in t seconds.
Then
Initial momentum of the body, p1 = mu
Final momentum of the body, p2 = mv
Change of momentum = p2 - p1
= mv - mu
= m(v - u)
Time taken = t![]() Rate of change of momentum =
Rate of change of momentum =
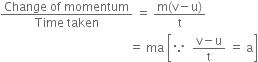
According to Newton’s second law, the rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the applied force.
So,
![]()
Here,
k is a constant.
The unit of force is so chosen that k is equal to one.
If m = 1, a = 1 and F = 1, then k = 1.
Therefore, F = ma
![]() Force = Mass x Acceleration
Force = Mass x Acceleration
SI unit of force is Newton.
One newton is that force which produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2 in a body of mass 1 kg.
1 newton = 1kg x 1 m/s2 or 1N = 1kg m/s2
Thus, force is measured using the second law of motion.
If the mass and acceleration of a body are known, we can determine the force acting on it.



