Describe Galileo’s experiments with inclined planes and state the conclusion.
Galileo deduced that objects move with constant speed when no force acts on them, by observing the motion of objects on inclined planes.
i) Galileo studied the motion of marbles on an inclined plane, in his first experiment.
He observed that when a marble rolls down an inclined plane, its velocity increases, as shown in Fig.9.6 (a).
Here the marble falls under the unbalanced force of gravity.
The velocity of the marble decreases when it rolls up the inclined plane (against the force of gravity), as shown in Fig.9.6(b).
From these observations, Galileo argued that the velocity of a marble rolling on flat horizontal surface should remain constant.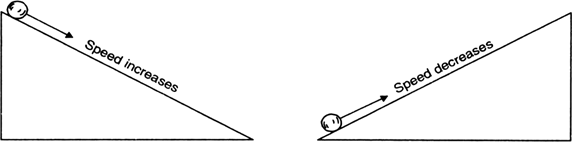
Fig. Motion of a marble (a) down the inclined plane and (b) up the inclined plane.
The above experiments suggest that an unbalanced force (external force) is required to change the motion of an object while no unbalanced force is needed to keep an object moving with a constant velocity.
From the observations above,
Galileo concluded the following law of inertia:
1. A body moving with a certain speed along a straight line path will continue to move with the same speed along the same straight line path, unless acted upon by an external force.



