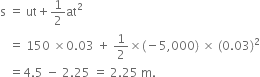A bullet of mass ‘a’ and velocity ‘b’ is fired into a large block of mass ‘c’. The final velocity of the system is
Here,
Mass of the bullet, m = 10 g = 0.01 kg
Initial velocity, u = 150 ms-1
Final velocity, v =0 m/s
Time taken for the bullet to reach the target, t = 0.03 s
The distance of penetration of the bullet into the block,