In figure, ABCD is a square and ∠DEC is an equilateral triangle. Prove that
(i) ∆ADE ≅ ∆BCE
(ii) AE = BE
(iii) ∠DAE = 15°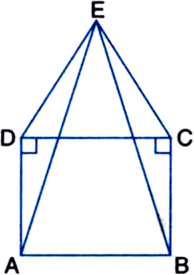
Given: ABCD is a square and ∆DEC is an equilateral triangle.
To Prove:
(i) ∆ADE ≅ ∆BCE
(ii) AE = BE
(iii) ∠DAE = 15°
Proof: (i) In ∆ADE and ∆BCE,
AD = BC
![]()
DE=CE
![]()
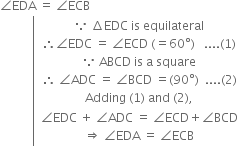
∴ ∆ADE ≅ ∆BCE | SAS congruence rule
(ii) ∵ ∆ADE ≅ ∆BCE | Proved in (1)
∴ AE = BE | CPCT
(iii) In ∆DAE,
∵ DE = DA | Given
∴ ∠DAE = ∠DEA ...(1)
| Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal Also, ∠ADE + ∠DAE + ∠DEA = 180°
| Angle sum property of a triangle
⇒ (∠ADC + ∠EDC) + ∠DAE + ∠DEA = 180°
⇒ (90° + 60°) + ∠DAE + ∠DEA = 180°
⇒ ∠DAE + ∠DEA = 30° ...(2)
From (1) and (2),
∠DAE = 15° = ∠DEA