Define the term “osmotic pressure”. Describe how the molecular mass of a substance can be determined on the basis of osmotic pressure measurement.
Answer:
Osmotic pressure: Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure that should be applied to the more concentrated solution to prevent osmosis.
osmotic pressure is proportional to the molarity, C of the solution at a given temperature T.
Thus: Π = C R T
Here Π is the osmotic pressure and R is the gas constant.
Determination of osmotic pressure: Barkley and Hartley’s method: The apparatus consists of a porous pot containing copper ferrocyanide deposited in its wall (acts as semipermeable membrane) and fitted into a bronze cylinder to which is fitted a piston and a pressure gauge (to read the applied pressure).
The pot is fitted with a capillary indicator on left and water reservoir on right. Pot is filled with water while the cylinder is filled with a solution whose osmotic pressure is to be measured. Water tends to pass into the solution through the semipermeable membrane with the result that the water level in the indicator falls down. External pressure is now applied with piston so as to maintain a constant level in the indicator. This external pressure is osmotic pressure.
If the membrane used was a slightly, leaky, then the measured valued of osmotic pressure will not be definite.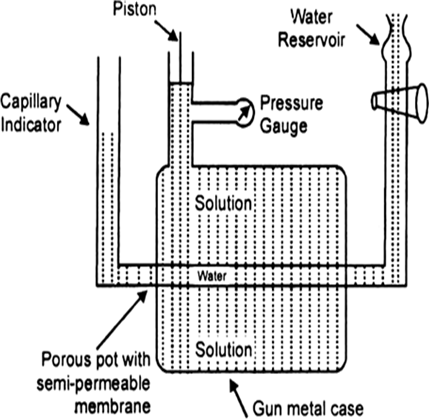
Fig. Barkley and Hartley’s apparatus.



