Science Chapter 7 Diversity In Living Organisms
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 9 About 2.html
What are the advantages of classifying organisms?
Classification is advantageous in the following way:
(i) Classification makes the study of huge varieties of organisms easy.
(ii) It helps us to understand the interrelationship among different groups of organisms.
(iii) It helps in the specific identification of any given organism.
(iv) The study of a few representatives from each distinct group helps us to integrate the idea of life as a whole.
(v) It reveals the relationships among various groups of organisms.
(vi) It provides information about plants and animals, which occur in specific geographical regions.
(vii) It indicates the evolutionary relationship by establishing the gradually increasing complexity of form and structure in different groups of organisms.
How would you choose between two characteristics to be used for developing a hierarchy in classification?
The characteristic which is dependent on the previous one and would decide the variety in the next level should be chosen for developing a hierarchy in classification.
Explain the basis for grouping organisms into five kingdoms.
The basis for grouping organisms into five kingdom are:
(i) Cell structure
(ii) Mode
(iii) Source of nutrition
(iv) Body organisation.
What are the major divisions in the plantae? What is the basis for these divisions?
Major divisions in kingdom plantae are—
(i) Thallophyta
(ii) Bryophyta
(iii) Pteridophyta
(iv) Gymnosperms
(v) Angiosperms.
Basis for classification plantae division :
1. Whether the plant body has well differentiated, distinct components is the basis for the first level of classification.
2. Whether the differentiated plant body has special tissues for the transport of water and other substances within it forms the basis for the second level of classification.
3. Whether the plants bear the seeds forms the next level of classification.
4. Whether the seeds are enclosed within fruits.
How are the criteria for deciding divisions in plants different from the criteria for deciding the subgroups among animals?
The criteria for classification of plant kingdom into divisions depend upon:
(a) differentiation of plant body components,
(b) presence of transport (conduction) tissues,
(c) ability to produce seeds, and
(d) enclouser seeds in fruits.
Animals are organisms which are eukaryotic,
multicellular and heterotrophic. Their cells
do not have cell-walls. Most animals are
mobile. Thus they have different criteria for classification - they are classified based on the
extent and type of the body design
differentiation found.
Explain how animals in vertebrata are classified into further subgroups.
Vertebrates classified into further subgroups on the basis of simple to complex form , the structure of the organs like gills/lungs, heart and function of the organisms .
For example, fishes have two chambered heart, amphibians and reptiles have three chambered heart where as aves and mammals have four chambered heart to keep oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separately.
Name the biggest animal and the tallest tree.
Blue whale is 30 metre long and largest animal.
Redwood trees of California are 100 metre tall and are longest tree.
What is classification?
Arranging the organisms into different groups on the basis of similarities and differences is known as classification.
Why do we classify organisms?
We classify organisms due to the following reasons :
(i) Classification makes the study of huge varieties of organisms easy.
(ii) The study of a few representatives from each distinct group helps us to integrate the idea of life as a whole.
(iii) It reveals the relationships among various groups of organisms.
(iv) It provides information about plants and animals, which occur in specific geographical regions.
(v) It indicates the evolutionary relationship by establishing the gradually increasing complexity of form and structure in different groups of organisms.
Give three examples of the range of variations that you see in life form around you.
Range of Variations:
(i) Life span- insects live for a few days whereas cow, dog and humans etc. live for many years.
(ii) body structure—Organisms like cows, insects plants and humans have different body structures.
(iii) Size—Some organisms are small while the others are big. Even different plants are of different sizes
What was the basis of animal classification done by Aristotle.
Aristotle classified animals according to whether they lived on land, in water or in the air.
Why a method of classification of animals proposed by Aristotle was not accepted ? Explain with example.
Aristotle classified animals on the basis of habitat. For example, corals, whales, octopuses, star fish and sharks lived in sea were placed in one group even when they are very different from each other Except habitat, they do not share other similarities. Thus it was not an efficient way to classify animals and hence was discarded.
What do you mean by ‘characteristics’? Explain with example.
Characteristic is a particular form or a particular function. For example, generally human being has five finger on each hand. Thus, presence of five finger on each hand is a characteristic. Similarly, animals can run but tree like banyan tree cannot run, is also a characteristic.
How hierarchy of classification be built?
Organisms are classified in big groups first on the basis of independent characteristics like the form and function of organism. The characteristic chosen in the next level would be dependent on the previous one and decides the variety of organisms in the next level. Thus, one can build up a whole hierarchy of mutually related characteristics to be used for classification.
Which do you think is a more basic
characteristic for classifying
organisms?
(a) the place where they live.
(b) the kind of cells they are
made of. Why?
The characteristic of the kind of cells they are made of - is a more basic characteric of classification as habitat or the place where the organisms can live will involve very different groups staying in a similar habitat. Thus, habitat cannot be basic characteristic for the classification of organism into groups. However, the type of cell will give a better lassification.
What is the primary characteristic on which the first division of organism is made?
The primary characteristic on which the first division of organisms is made is the organisation of nucleus. Whether organism has eukaryotic cell i.e., membrane-bound organelle, including nucleus or has prokaryotic cell i.e., has no clearly demarketed nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Sponsor Area
On what basis are plants and animals put into different categories?
Plants and animals are put into different groups on the basis of whether the organisms produce their own food through process of photosynthesis (plants) or organisms get food from outside (animals).
What indicates that the classification of life forms will be closely related to their evolution?
The characteristics that came into existence earlier are likely to be more basic than characteristics that have come into existent later. Therefore the characteristic that came in earlier will be common and found in more organisma as compared to the one which came in later as it is found in fewer. So, we can predict that the organisms having the latter charactristic evolved during the later stages. Thus, the classification of life forms is closely related to their evolution.
What is evolution?
Most life forms that exist today have arisen from a common ancestor by accumulation of changes in body design that allow the organism to possess different characteristics and to survive better. This process is known as evolution.
Which organisms are called primitive and how are they different from the so-called advanced organisms?
The organisms which have ancient body design that that have not changed much over the course of time, are known as primitive or lower organism.
Advanced organisms are those who have accumulated changes and acquired their particular body designs relatively recently.
The difference between the two are :
1. Primitive organisms have simpler body design where as advanced or younger organisms have complex body design.
2. Primitive or lower organism have not changed much whereas the advanced organisms are those who have acquired their particular body designs relatively recently and possess changes.
Will advanced organisms be the same as complex organisms? Why?
Advanced organisms may be same as complex organisms. Since there is a possibility that complexity increases with time and the organisms accumalate changes for better adaptation and survival, therefore we can say that advanced organssims are complex in nature.
List the names of five kingdom of organism. What type of organisms they composed of?
|
Kingdom |
Type of Organisms |
|
1. Monera |
Bacteria and Cyanobacteria |
|
2.Protista |
Bacteria and Cyanobacteria |
|
3. Fungi |
Lack chlorophyll and obtain their food through absorption. |
|
4.Plantae |
All photosynthetic green plants. |
|
5. Animalia |
It is the kingdom of multicellular consumers |
On what basis five kingdom classification is formed?
Five kingdom classification is based on cell structure, mode and source of nutrition and body organisation.
Who proposed division of Monera kingdom ? Name the groups proposed.
Carl Woese proposed the further division of Monera kingdom. He divided the group into Archaebacteria (or Archaea) and Eubacteria (or Bacteria).
Define the term species.
A species includes all organisms that are similar enough to breed and perpetuate. For example dogs, humans etc.
Write down the hierarchic categories which are generally used for classification of animals.
The hierarchial categories are -:
(i) Kingdom. Plant kingdom and animal kingdom.
(ii) Phylum (for animals)/Division (for plants). A group of closely related classes having certain common characters.
(iii) Class. A group of closely related orders having certain common characters.
(iv) Order. A group of closely related families having certain common characters.
(v) Family. A group of closely related genus having certain common characters.
(vi) Genus. A group of closely related species have certain common characters.
(vii) Species. A group of organisms which are similar enough to breed and perpetuate.
What are the characteristic of kingdom Monera?
Characteristics of kingdom Monera:
(i) The organism do not have clearly defined nucleus i.e., nucleus is not enclosed in nuclear membrane.
(ii) Cell organelles are not covered with a membrane.
(iii) Organisms do not show multicellular body design i.e., they are unicellular.
(iv) Some organisms have cell wall other do not have cell wall.
(v) The mode of nutrition may be autotrophic (synthesising their own food) or heterotrophic (getting food from the environment).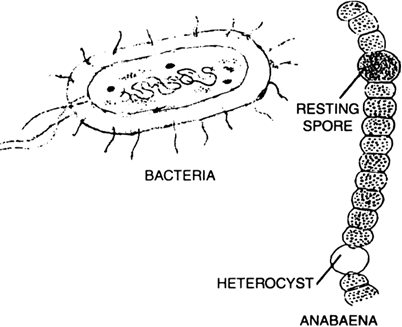
Fig. Monera
Why are blue green algae included under monera and not under plantae?
Blue green algae or cyanobacteria are prokaryotes and have nucleoid with naked DNA, i.e., nuclear material is not enclosed within a nuclear membrane. The cell organelles are also not enclosed with membrane. Blue green algae do not show multicellular body design like plants. All these characters show that the blue green algae belong to the kingdom monera rather than plantae.
Name the groups of organism which come under kingdom monera.
Bacteria, Cyanobacteria (blue green algae) and mycoplasma come under the kingdom monera.
What are mycoplasm?
Mycoplasms are the smallest and the simplest organisms. They belon to the kingdom Monera. They are prokaryotic having nucleoid. Their body can change shape easily. They are heterotrophs.
What are the characteristics of kingdom protista? Give examples.
Characteristics of Kingdom Protista:
(i) They are unicellular eukaryotic organism i.e., they have membrane bound nucleus and organelles.
(ii) Some of these organism use appendages such as hair like cilia or whip-like flagella for moving around.
(iii) Their mode of nutrition can be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
Examples:Unicellular algae (like Chlamydomonas, Chlorela), diatoms and protozoans like amoeba.
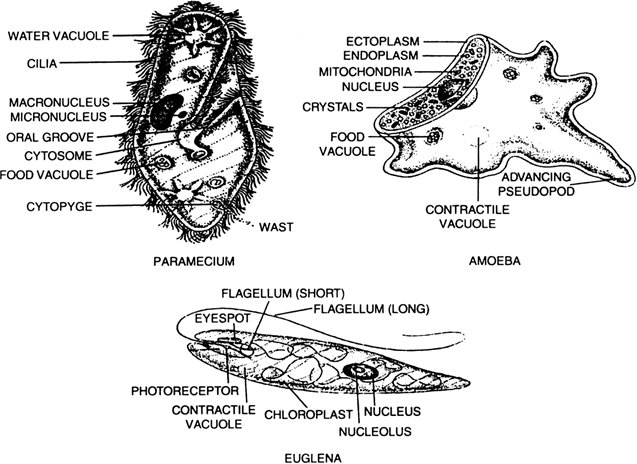
Give one example of each protesta having cilia and flagella.
The examples of protista having
i. Cilia is Paramecium
ii. Flagella is Euglena
What are the characteristics of fungi? Give examples.
Characteristics of Fungi:
(i) They are heterotrophic.
(ii) The organisms are saprophyte i.e., they use decaying organic material as food or may be parasite.
(iii) They have membrane bound nucleus.
(iv) They have cell walls made of chitin.
(v) Some of them have the capacity to become multicellular organisms at certain stages in their lives.
(vi) Some of the fungal species have symbiotic relationship where they are mutually dependent on the blue-greem algae. These are called lichens.
Examples: Rhizopus, Yeast, Agaricus (mushrooms), Penicillium.
Fungi
Sponsor Area
List the similarities between plants and animals.
The similarities between plants and animals are:
(i) Both plants and animals are made up of cells.
(ii) Both contain living substance protoplasm.
(iii) Certain life processes i.e., respiration, digestion, reproduction, assimilation etc. take place in both the groups in an identical manner.
(iv) Both show response to external stimuli.
(v) Growth is present in both the groups.
(vi) Both reproduce and pass on their hereditary characters to the offspring by the same mechanism.
What are the three differences between plants and animals.
|
Plants |
Animals |
|
1. Most of the plants are stationary and do not move from one place to another. |
1. Most of the animals are mobile i.e., they can move from one place to another. |
|
2. They are autotrophic and make their own food as they have chlorophyll. |
2. They are heterotrophic and cannot make their own food. They do not have chlorophyll. |
|
3. Most of the plants continue growing throughout their life. The growth may be in length (Height) or producing spreading branches. |
3. Animals stop growing especially in length (Height) after attaining certain maturity. |
|
4. Plant cells have cell walls as outer most covering. |
4. Animal cell do not have cell walls. |
What is the criterion for classification of organisms as belonging to kingdom Monera or Protista?
The criterion for the classification of organisms under the kingdom monera and protista is:
The organisms which are unicellular and do not have a membrane bound nucleus and organelles are put under Monera.
While the unicellular organisms which have membrane bound definite nucleus and organelles are classified as Protista.
In the hierarchy of classification, which grouping will have the smallest number of organisms with a maximum of characteristics in common and which will have the largest number of organisms?
In the hierarchy of classification -
Species will have the smallest number of organism with a maximum of characteristics in common.
Kingdom will have the largest number of organisms.
On what basis classification plants depend?
Classification among plants:
(i) The first level of classification depends on whether the plant body has well differentiated, distinct components like root, stem and leaf.
(ii) The next level based on whether the differentiated plant body has special tissues for the transport of water and other substances within it.
(iii)The next level of classification depends on whether the plant bear seeds and seeds are enclosed within fruits.
What are Thallophytes?
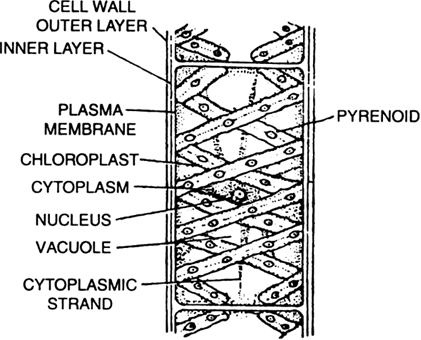
Thallophyta are plants that do not have well differentiated body. The plants in this group are commonly called algae which are predominantly aquatic.
What are algae? Give example.
Algae or thallophyta are a classification of the plant kingdom. Algae have the following characteristics:
(i) Plants which have thaloid body i.e., body is not differentiated into root, stem and leaf.
(ii) Plant cells contain pigment like chlorophyll and other pigment and are autotrophic.
(iii) They are prdominantly aquatic.
Example. Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Cladophora, Ulva and Chara.
Thallophyta-Algae.
What are bryophytes? Give examples.
Bryophyta.
i. These are also called the amphibians of the plant kingdom.
ii. Plant body may be thalloid or leafy. True roots are absent instead rhizoids develop.
iii. No specialised conducting tissue in figure. These grow on damp walls and on the bark of tree.
iv. It includes two groups.
(a) Liverwort
(b) Mosses.
Examples. Marchantia, Riccia, Sphagnum etc.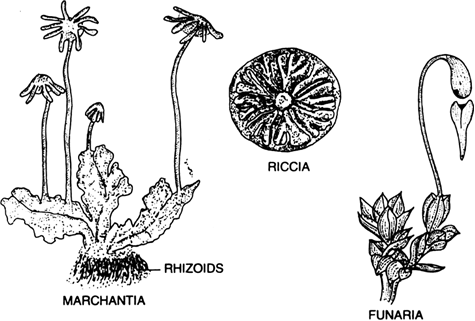
What are Pteridophyta?
Pteridophyta are group of plants that have body differentiated into roots, stem and leaves. They possess a specialised tissue for the conduction of water and other substances from one part of the plant body to another. Example, Marsilea, ferns and horse tail.
What are the characteristics of:
(i) Subkingdom cryptogamae and (ii) Subkingdom phanerogamae?
(i) Cryptogamae. These are also known as lower plants / flowerless or seedless plants. These plants have hidden reproductive organs. They do not bear external flowers or seeds.
(ii) Phanerogamae. These bear seeds. Sex organs are multicellular and embryo develops from a fertilized egg. Plant body is differentiated into stem, leaves and roots. Vascular system (xylem and phloem) is well developed.
Which plant groups belong to cryptogamae.
Plants groups that belong to cryptogramae are
(i) Thallophyta (ii) Bryophyta (iii) Pteridophyta.
What are phanerogams? What are its two subdivision?
Phanerogamsare plants which includes plants with well differentiated reproductive tissues that make seeds. Seeds are the result of the reproductive process. They have embryo along with stored food, which provides nutrition to the growing embryo during germination. This group is further classified, based on whether the seeds are naked or enclosed in fruits into two groups that is gymnosperms and angiosperms.
What are Gymnosperms?
Gymnosperms. These are the plants in which seeds are naked that is they are not covered within fruits. These are regarded as lower flowering plants. They are perenial, evergreen and woody.
Examples. Pinus, Cycas, Cadrus, Thuja etc.
Cycas Pinus
What are seeds?
Seeds are the fertilized ripened ovule of a flowering plant containing an embryo and capable normally of germination to produce a new plant. They are the unit of reproduction of a flowering plant, capable of developing into another such plant.
What are angiosperms?
Angiosperms. These are plants with covered seeds (seeds enclosed in fruits). These are the highest forms of plants. All are flower, seed and fruit bearing.
i. The seeds develop inside an organ which is modifies to become fruit.
ii. They bear flowers.
iii. Plants embryos have cotyledons which are known as seed leaves.
iv. Two big groups of angiosperms are included in this. They are:
(i) Dicotyledons (embryo of the seed bears two cotyledons) e.g., Pea, Gram, Mustard etc.
(ii) Monocotyledons (embryo of the seed bears single cotyledon) e.g., Wheat, Maize, Paphiopedilum etc.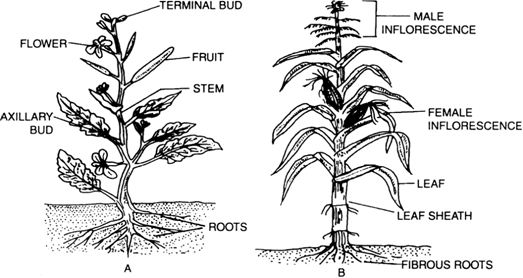
Give one point of difference between Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
Gymnosperms have naked seeds which are not enclosed in fruits. Angiosperms have seeds enclosed by a fruit.
You are given an assortment of plants on your laboratory table. What characters will you look for in order to label a particular specimen as : (i) Angiosperm (ii) Moss (iii) Alga.
(i) Angiosperm:
(a) Presence of flowers, seeds covered seeds and fruits.
(b) Presence of root, stem and leaves.
(c) Presence of xylem vessels.
(ii) Moss:
(a) Absence of roots.
(b) Presence of rhizoids.
(c) Leaves one cell thick.
(d) Presence of green thallus.
(iii) Alga:
(a) Green in colour.
(b) Filamentous or single celled.
(c) Food stored as starch.
(d) Aquatic.
Why do bryophytes called as amphibians of the plant kingdom?
Bryophytes are called amphibians amongst the plants because they are found on land but need water for reproductive process:
(a) The plant body of bryophytes are devoid of vascular tissues, roots, cuticle, etc. therefore, live in moist habitats in order to obtain water directly or through rhizoids and prevent desiccation.
(b) Like amphibians of animal kingdom, the sperms require an external supply of water for swimming and reaching the eggs for fertilizing the same.
How are pteridophytes different from the phanerogams?
These are differences between pteridophytes and phanerogams:
|
Pteridophytes |
Phanerogams |
|
1. Pteridophytes have naked embryos that are called spores. 2. The reproductive organs are inconspicuous, therefore called cryptogamae (those with hidden reproductive organs). |
1. Phanerogams produce seeds which consists of embryo and stored food. 2. They have well differentiated reproductive tissues which after reproductive process produce seeds. |
How do gymnosperms and angiosperms differ from each other?
These ate differences between Gymnosperm and Angiosperm:
|
Gymnosperm |
Angiosperm |
|
1. They produce cones formed of sporophylls. The sporophylls carry male nd female sex organs. 2. The plants bear naked seeds. |
1. They produce flowers which carry male and female sex organs. 2. The seeds develop in an organ which modifies into fruit, i.e., seeds are found covered within a fruit. |
List important features of members of animal kingdom.
Characteristics of the members of kingdom animalia:
(i) These organisms are eukaryotic and do not have cell walls.
(ii) They are multicellular.
(iii) They are heterotrophic.
(iv) Most of the animals are mobile.
Draw outline classification of Animal (Animalia) kingdom upto phylum level in order of hierarchy.
Outline classification of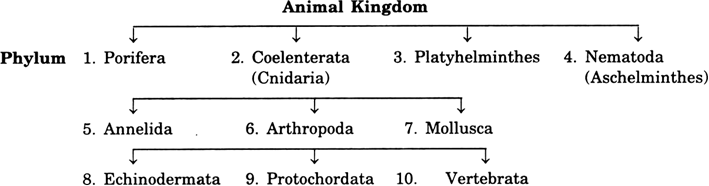
List the salient features of Phylum Porifera of Animal Kingdom?
(1) Phylum Porifera
Main Features:
i. They have pores all over their body.
ii. The are non motile and attached to some solid support.
iii. Animals of this phylum are known as sponges. They have a characteristic canal system for water passage not found in any other kind of animals.
iv. Their skeleton is made up of calcareous or siliceous spicules or spongin fibres.
v Reproduction is both asexual by budding and gemules and sexual reproduction through fertilization.
vi. Body has very minimum differentiation and division into tissues.
Examples. Sycon, Spongilla and Euplectella.
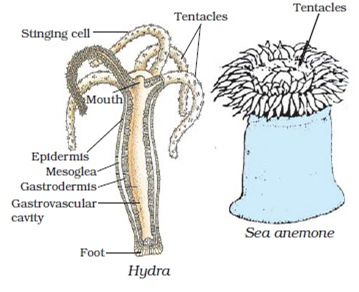
List the salient features of Phylum Cnidaria (Coelenterata) of Animal Kingdom?
Phylum Cnidaria (Coelenterata)
Main Features :
(i) The body of animals of this phylum is Radially Symmetrical.
(ii) The body bears tentacles supplied with special stinging cells called cnidoblasts.
(iii) There is a cavity in the body.
(iv) The body is made of two layers of cells.
(v) Some coelenterates live in colony (Obelia) while others live solitary (Hydra).
(vi) Animals of this phylum exist in two types known as Zooids—Polyps and Medusae. Polyps are always fixed but Medusae are free swimming.
(vii) Reproduction is usually asexual (budding) in polyp form and sexual in medusae form.
Examples. Hydra (sea anemones) Obelia, Aurelia and Jelly fish.
List the features of Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) of the Animal Kingdom?
Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
Main Features:
(i) Their body is dorsoventrally flat and leaf-like or ribbon like.
(ii) Body symmetry is bilateral that is left and right half have the same design.
(iii) They are mostly hermaphrodite.
(iv) Body cavity or true coelom is absent.
(v) There are three layers of cells from which differentiated tissues can be formed. So, animals are triploblastic.
(vi) They are either free living or parasitic.
Examples. Planaria, Fasciola (liver fluke) and Taenia solium (tape worm) are parasitic.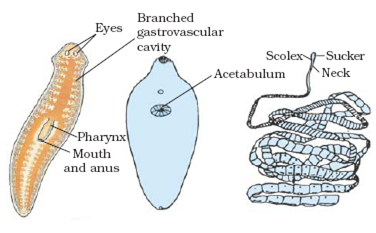
List the features of Phylum Nematoda fo the Animal Kingdom.
Phylum Nematoda (Aschelminthes) (round or thread worms)
Main Features:
(i) Most of the Aschelminthes are small cylindrical or round worms.
(ii) Body cavity is not a true coelom. A pseudocoelom is present.
(iii) Body is bilaterally symetrical and triploblastic.
(iv) Sexes are separate.
(v) There are tissues but no real organs.
Examples. Ascaris (round worm), Ancylostoma (hook worm) and Wuchereria (filarial worm) causes elephantiasis.
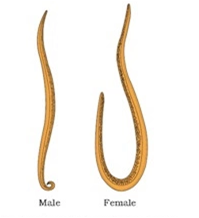
Ascaris
List the features of Phylum Annelida of the Animal kingdom.
Phylum Annelida (segmented worm)
Main Features:
(i) They have elongated and segmented body.
(ii) Body bears lateral appendages for locomotion in the form of chitinous Setae or Parapodia.
(iii) The body is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic.
(iv) Reproduction by sexual means. Sex may be separate or hermaphrodite (both sexes in the same individual).
(v) They are the first animals with true coelom (body cavity).
Examples. Pheretima (earthworm), Hirudinaria (cattle leech) and Nereis.
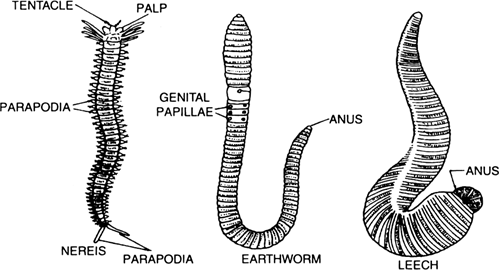
Annelida.
List the features of Phylum Arthropoda of the Animal kingdom.
Phylum Arthropoda (animals with jointed feet/appandages) -This is the largest group of animals.
Main Features:
(i) They possess jointed legs/appendages.
(ii) They have chitinous exoskeleton.
(iii) The body is segmented and may divisible into two regions—Cephalothorax (head and thorax joined) and Abdomen or into three regions—Head, Thorax and Abdomen.
(iv) Body cavity is reduced and is known as Haemocoel (cavity filled with blood).
(v) These animals are bilaterally symmetrical.
(vi) There is an open circulatory system i.e., the blood does not flow in definite blood vessels.
Examples. Apis (honey bee), Musca, Anopheles (mosquito), Palaemon (Prawn), Crabs etc.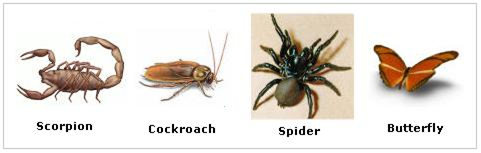
List the features of Phylum Mollusca.
Main Features of the phylum mollusca are as follows:
(i) They have unsegmented or soft body.with little segmentation.
(ii) The body is divided into three regions—head, dorsal visceral mass and ventral foot.
(iii) Body is bilateral symmetrical.
(iv) The coelomic cavity is reduced.
(v) They have open circulatory system and kidney like organs for excretion.
(vi) Some molluscs have hard calcareous shell, an outer covering of the body.
(vii) Respiration is by gills called ctenidia.
Examples. Pila (snail), Unio (fresh water mussel) and Octopus.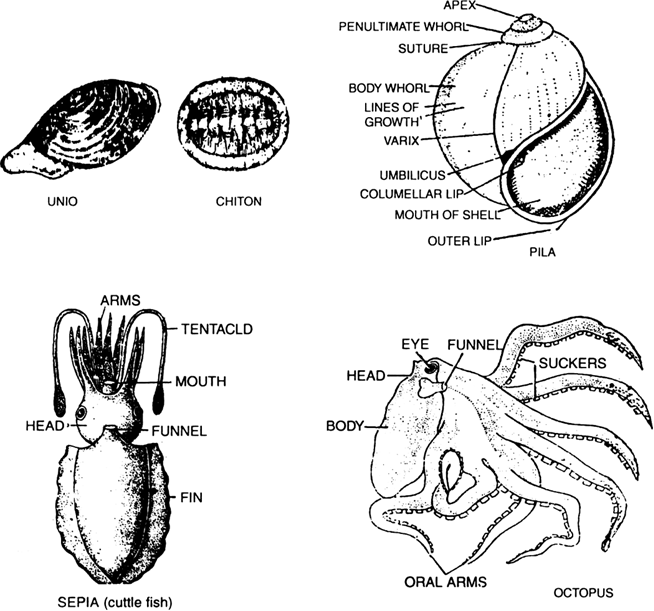
List the features of Phylum Echinodermata.
Phylum Echinodermata (spiny skinned animals)
Main Features are as follows:
(i) They are marine and free living.
(ii) They are triploblastic, and have a coelomic cavity.
(iii) Body surface is covered all over by spines
(iv) Body cavity is modified into a water-vascular system and has a peculiar water-driven tube system which is connected tubefeet for locomotion.
(v) Sexes are separate.
(vi) They have hard calcareous structures that is used as a skeleton.
Examples. Asterias (star fish), Echinus (sea urchin), Antedon (feather star) etc.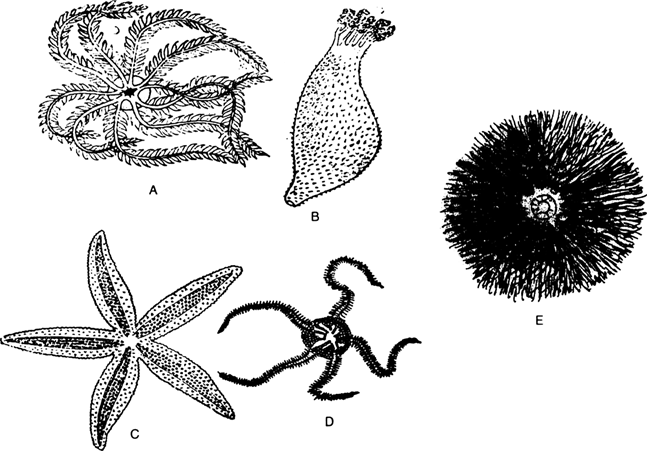
A Antedon
B. Holothuria
C. Starfish
D. Ophioderma
E. Echinus
List the features of Phyllum Protochordata of the Animal kingdom.
Phyllum Protochordata:
Main Features:
(i) The animals are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and have a coelom.
(ii) They have a notochord, at least some stages during their lives. The notochord run along the back of the animal separating the nervous tissue from the gut. It provide support and a place for muscles to attach.
(iii) Protochordates are marine animals.
Examples are Balanglossus, Herdemania, Amphioxus, etc.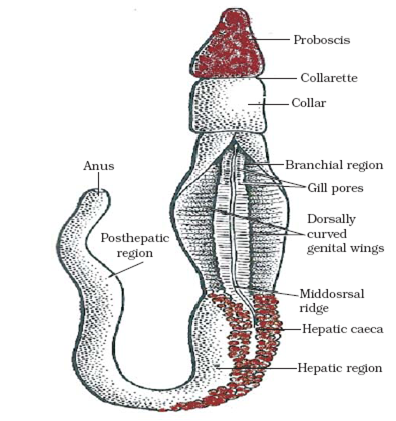
List the features of Vertebrata of the Animal kingdom.
The features of the kingdom vertebrata are-:
(i) They have true vertebral column and internal skeleton. They have a notochord.
(ii) Vertebrates are bilaterally symmetrical body.
(iii) They have dorsal nerve cord.
(iv) They are triploblastic.
(v) They are coelomate and segmented
(vi) They have a complex differentiation of body tissue and organs.
State any two charactericts features of animals.
Characteristic features of Animals:
(i) They are mobile and have a heterotrophic mode of nutrition i.e., they depend on plants or other animals for food.
(ii) They stop growing after maturity.
Give one point of difference between:
i) Bony and cartilaginous fishes.
(ii) Bilateral and radial symmetry.
(iii) Notochord and nerve cord.
(i) Bony and cartilaginous fishes.
Body of a bony is covered with cycloid or ctenoid scales whereas skin of cartilaginous fish is covered with Placoid scales.
(ii) Bilateral and radial symmetry.
An animal is said to have bilateral symmetry, if it has two equal but opposite right and left halves when it is cut lengthwise in the middle vertical plane. For example, frog.
An animal is said to have radial symmetry, if it is symmetrical with respect to any plane passing through its longitudinal axis. Any plane passing longitudinally through any diameter divides the body into equal halves. For eample, Hydra shows a radial symmetry.
(iii) Notochord and nerve cord.
Notochord is skeletal rod (of large vacuolated cells packed within a firm sheath). It lies lengthwise between C.N.S. (central nervous system) and gut. It is present in some stage of development of all chordates. In adult vertebrates, it is replaced by vertebrate (vertebral column).
A nerve cord is a solid strand of nervous tissue, forming part of central nervous system, especially of invertebrates. Nerve cells are distributed all over the nerve cord and are not confined to ganglionic swellings.
The major difference between the two is that—Notochord is part of skeleton system (so known as skeletar rod) where Nerve Cord is part of nervous system.
Sponsor Area
How do poriferan animals differ from coelentrate?
|
Poriferan |
Coelentrate |
|
1. There are pores called ostia all over the body and a large opening at the top. 2. There canal system for circulating water throughout the body. 3. External skeleton is present. 4. The body design show minimal differentiation. 5. Tentacles are absent. |
1. There is only one opening. 2. There is no water canal system in the body. 3. Skeleton is absent. 4. They show more body design differentiation. 5. Tentacles are present. |
How do annelied animals differ from arthropods?
These are differences between annelied animals and arthropods:
|
Annelid animals |
Arthropods |
|
1. They have the true body cavily (coelomic cavity). The coelomic cavity is not blood filled. 2. Body bears lateral appendages for locomotion in the form of chitineous setae or parapodia. 3. Annelids like earthworm and leech do not have chitinous exoskeleton. |
1. The coelomic cavity is blood filled. 2. They have jointed legs for locomotion. 3. They have chitinous exoskeleton. |
What are the differences between amphibians and reptiles?
These are differences between amphibians and reptiles:
|
Amphibians |
Reptiles |
|
1. Animals of this group can live both on land and in water. 2. They lack scales on the body. 3. Their eggs do not have tough covering. 4. They lay their eggs in water. 5. Water is necessary for fertilisation. |
1. Animals can live either on land or in water. 2. They have scales. 3. Their eggs have tough covering. 4. They do not need to lay their eggs in water. 5. Water is not required for fertilisation. |
What are the differences between animals belonging to the Aves group and those in the mammalia group?
|
Aves |
Mammals |
|
1. They beak. 2. Their body is covered with feathers. 3. Forelimbs are modified into wings for flight. 4. They lay eggs. 5. They do not have mammary gland to produce milk for young ones. |
1. They do not have beak. 2. Their body is covered with hair. 3. Forelimbs are not modified into wings. 4. They produce live young ones. 5. They have mammary glands to produce milk for young ones. |
What is the advantage of using scientific names instead of common or popular names?
Millions of animals and plants are named differently in different languages in different parts of the world. The names used for one organism differs from place to place. For example Argemone a common weed has as many as ten to twelve Hindi names alone. Some call it ‘Firangi Dhatura’, ‘Sial Kanta’, ‘Pila Dhatura’, ‘Bharband’, ‘Kandhari’, etc. same thing is applicable to other animals and plants. Sometimes the common names are misleading. Same name may be used for different organism in different parts. To avoid this confusion we use scientific names . The scietific name gives the organism a unique identity which is followed universally , thus a mango ( Magnifera indica) will have the same name in any part of the world, Hence, confusion is avoided.
Who proposed binomial nomenclature ? What are the rules that are followed during writing scientific names?
Carolus Linnaeus proposed binomial nomenclature.
The rules that are to be followed while writing the scientific names are-:
1. The name of the genus should begin with a
capital letter.
2. The name of the species should begin with a
small letter.
3. When printed, the scientific name should be in italics.
4. When written by hand, the genus name and the species name have should be underlined separately.
What are the two components of a scientific name?
The scientific name is composed of
(i) Genus name (generic) and
(ii) Species name (specific).
It is conventional to write the generic name and with a capital and the specific name with a small letter. Generally, the scientific. When printed scientific names are in italic or in bold (black) type.
Example - Azadirachta indica (neem ) , Solanum tuberosum (Potato) etc.
List the conventions that are followed while writing the scientific names.
Conventions followed while writing the scientific names are:
(i) The name of the genus should begin with a capital letter.
(ii) The name of the species should begin with a small letter.
(iii) When printed, the scientific name ishould be in italics.
(iv) When written by hand, the genus name and the species name should be underlined separately.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area