Economics Chapter 4 Food Security In India
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 9 About 2.html Economics
How is food security ensured in India?
This system has two components:
(i) Buffer Stock (ii) Public Distribution System.
(i)Buffer Stock: Buffer stock is the stock of foodgrains, namely wheat and rice procured by the govt. through Food Corporation of India (FCI). The FCI purchases wheat and rice from the farmers in states where there is surplus production.
The purchased foodgrains are stored in granaries. This is done to distribute foodgrains in the deficit areas and among the poorer strata of society at a price lower than the market price also known as Issue price. This also helps in resolving the problem of shortage of food during adverse weather conditions or during the period of calamity.
(ii)Public Distribution System: The food procured by the FCI is distributed through govt. regulated ration shops among the poorer section of the society. This is called the public distribution system.
Which are the people more prone to food insecurity?
(i)The Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and some sections of the OBC’s who have either poor land bare or very low land productivity are prone to food insecurity.
(ii)The people affected by natural disaster, who have to migrate to other areas in search of work, are also among the most food insecure people.
(iii)A large proportion of pregnant and nursing mothers and children under the age of five years constitute an important segment of the food insecure population.
Which states are more food insecure in India?
States which are more food insecure in India are Eastern and South-Eastern parts of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, parts of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Do you believe that Green Revolution has made India self-sufficient in food grains? How?
Yes, Green Revolution has made India self-sufficient in food grains.
It is through:
(ii)After Independence, India was dependent on other countries for its foodgrain requirements but now our imports of foodgrains are negligible.
(iii)The minimum buffer norms for FCI are 24.3 million tonnes but due to the success of Green Revolution, the stock is much more than the minimum norms.
A section of people in India are still without food. Explain.
A section of people like SCs, STs, OBCs, people affected by natural disasters, women (pregnant and nursing mothers) and children under the age of 5 years in India are still without food.
The food insecure people are disproportionately large in some regions of the country, such as economically backward states with high incidence of poverty, tribal and remote areas, regions more prone to natural disasters etc.
The main reason for this unfortunate is that many poor families do not even have enough money or income to buy food in other words, there is availability of food and accessibility to food, but poor families do not have affordability to food.
What happens to the supply of food when there is a disaster or a calamity?
(i)During the disaster or calamity like earthquake, drought, flood, tsunami etc. there is widespread failure of crops. This adversely affects food production.
(ii)During the disaster or calamity the price goes up.
(iii)During any kind of calamity or disaster happens in a very widespread area or is stretched over a longer time period, it may cause a situation of starvation.
Differentiate between seasonal hunger and chronic hunger?
(i)Seasonal hunger is related to cycles of food growing and harvesting. This is prevalent in rural areas because of the seasonal nature of agricultural activities and in urban areas because of the casual labour. This type of hunger exists when a person is unable to get work for the entire year.
(ii)On the other hand chronic hunger is a consequence of diets persistently in adequate in terms of quantity or quality. Poor people suffer from chronic hunger because of their very low income and in turn inability to buy food even for survival.
What has our government done to provide food security to the poor? Discuss any two schemes launched by the government.
Following are the two schemes launched by the government to provide food security to the poor.
(i)Public Distribution System (PDS): The food procured by the FCI is distributed through government regulated ration shops among the poorer section of the society which is known as PDS. This scheme was launched in 1992.
(ii)Antyodaya Anna Yojana: This scheme was launched in December 2000 for the poorest of the poor by providing them foodgrains up to 35 kg at lowest rates, wheat Rs. 2 per kg and rice at Rs. 3 per kg. The scheme has been further expanded twice by additional 50 lakh BPL families in June 2003 and in August 2004. With th
Why buffer stock is created by the government?
The reasons are:
(i)This is done to distribute foodgrains in the deficit areas and among the poorer strata of society at a price lower than the market price also known as Issue Price.
(ii)This also helps resolve the problem of shortage of food during adverse weather conditions or during the periods of calamity.
Write notes on:—
Minimum Support Price
Minimum Support Price: When FCI purchases wheat and rice from the farmers in states where there is surplus, production, the farmers are paid a pre-announced price for their crops. This price is called minimum support price.
Write notes on:
Buffer Stock
Buffer Stock: It is the stock of foodgrains namely wheat and rice produced by the government through Food Corporation of India.
Write notes on:
Issue Price
Issue Price: When food grains are distributed in the deficit areas and among the poorer strata of the society at a price lower than the market price is known as Issue Price.
Write notes on:—
Fair Price Shops.
Fair Price Shops: Ration shops are known as Fair Price Shops which keep stock of foodgrains, sugar, kerosene oil for cooking. These items are sold to people at a price lower than the market price.
What are the problems of the functioning of ration shops?
(i)Public distribution system dealers are sometimes found resorting to malpractices like diverting the grains to open market to get better margin, selling poor quality grains at ration shops, irregular opening of the shops etc.
(ii) Food adulterations is another big problem of ration shops.
(iii) Earlier every family, poor and non-poor had a ration card with a fixed quota of items such as wheat, sugar, rice, pulses etc.
(iv)But now with the introduction of three different cards the price for above the poverty line family is almost as high as open market price, so there is little incentive for them.
(v)It is common to find that ration shops regularly have unsold stocks of poor quality grains left. This has proved to be a big problem. When ration shops are unable to sell, a massive stock of foodgrains piles up with the FCI.
Write a note on the role of cooperatives in providing food and related items.
(i)The cooperatives are playing an important role in food security in India especially in the southern and western parts of the country.
(iii)For example, out of all fair price shops running in Tamil Nadu, around 94 per cent are being run by the co-operatives.
(iv)In Delhi, Mother Dairy is making strides in provision of milk and vegetables to consumers at controlled rate decided by Government of Delhi.
(v)Amul is another success story of co-operatives in milk and milk products from Gujarat. It has brought about the 'White Revolution' in the country.
Sponsor Area
Which one is the type of hunger?
Seasonal
Chronic
Both Seasonal and Chronic
- None of these
C.
Both Seasonal and Chronic
What are the special target groups in Annapurna Scheme?
Poorest of the poor
Indigent Senior citizens
Backward Blocks
General public
B.
Indigent Senior citizens
What are the special target groups in Antyodaya Anna Yojana?
Poorest of the poor
Poor and non-poor
Backward Blocks
All of these
A.
Poorest of the poor
Under which Scheme Free Issue Price is launched?
Annapurna Scheme
PDS
Antyodaya Anna Yojana
All of these
A.
Annapurna Scheme
Sponsor Area
What are the special target groups in RPDS?
Backward Blocks
Universal
Poorest of the poor
All of these
A.
Backward Blocks
What is MSP?
Minimum Support Price
Main Supply Price
Maximum Support Price
None of these
A.
Minimum Support Price
What is FCI?
Food Centre of India
Food Corporation of India
Functional Corporation of India
None of these
B.
Food Corporation of India
What are two components of food security system?
PDS, FCI
Buffer Stock, FCI
Buffer Stocks, PDS
None of these
C.
Buffer Stocks, PDS
What is PDS?
-
Public Demand and Supply
-
Public Distribution System
-
Public Demand System
-
Public Dividend Supply
B.
Public Distribution System
What is the main function of FCI?
To provide seeds and other inputs to farmers.
To declare MSP.
To purchase wheat and rice from the farmers.
None of these.
C.
To purchase wheat and rice from the farmers.
Government has opened fair price shops _____________.
To promote education
To remove poverty
To provide essential items to poor at reasonable rate
None of these
C.
To provide essential items to poor at reasonable rate
What is RPDS?
Renewed Public Demand Supply
Revamped Public Distribution System
Revised Public Distribution System
Rural Public Demand and Supply
B.
Revamped Public Distribution System
The ADS has facilitated a network of NGO’s for setting up ____________.
AIDS awareness programme
Grain banks in different regions
Educational awareness programme
None of these
B.
Grain banks in different regions
What is the minimum buffer stock norm for the FCI?
The minimum buffer stock norm for the FCI is 243 million tonnes of Wheat and Rice.
Why were the FCI granaries over flowing with foodgrains?
The FCI granaries were over flowing with foodgrains due to more production.
What is meant by food security?
Food security means availability, accessibility and affordability of food to all people at all times.
What is meant by availability of food?
Availability of food means food production within the country, food imports and the previous years stock stored in government granaries.
What is meant by accessibility of food?
Accessibility of food means food is within the reach of every person.
What do you mean by affordability of food?
Affordability of food means that an individual has enough money to buy sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet one's dietary needs.
How is food security affected during calamity?
During calamity production of food grains decreases. It creates a shortage of food in the affected areas which may cause a situation of starvation.
Examine famine.
A Famine is characterised by wide spread deaths due to starvation and epidemics caused by forced use of contaminated water or decaying food and loss of body resistance due to weakening from starvation.
Which year shows a drastic decline in food availability?
Year 1941 shows a drastic decline in food availability.
Sponsor Area
Describe National Food for Work Programme.
National Food for Work Programme:
(i)National Food for Work Programme was launched on November 14, 2004 in 150 most backward districts of the country with the objective of intensifying the generation of supplementary wage employment.
(ii)The programme is open to all rural poor who are in need of wage employment and desire to do manual unskilled work.
(iii)It is implemented as a 100 per cent centrally sponsored scheme and the foodgrains are provided to States free of cost.
What are the dimensions of food security?
(i)Availability of food—It means food production within the country, food imports and the previous years stock stored in government granaries.
(ii)Accessibility—It means food is within reach of very person.
(iii)Affordability—It implies that an individual has enough money to buy sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet ones dietary needs.
State the declaration of world food Summit, 1995.
The 1995 World Food Summit declared,
“Food security at the individual, household, regional, national and global levels exists when all people, at all times, have physical and economical access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs the food preferences for an active and healthy life.'
The declaration further recognises that “poverty eradication is essential to improve access to food”.
Who are food insecure?
Although a large section of people suffer from food and nutrition insecurity in India.
(i)The worst affected groups are landless people with little or no land to depend upon traditional, artisans, providers of traditional services, petty self-employed workers and destitutes including beggars.
(ii)In the urban areas, the food insecure families are those whose working members are generally employed in ill paid occupations and casual labour market.
(iii)These workers are largely engaged in seasonal activities and are paid very low wages that just ensure bare survival.
What do you about Rationing?
The rationing system was revived in the wake of an acute food shortage during 1960s prior to the Green Revolution. In the wake of the high incidence of poverty levels, as reported by the NSSO in the Mid-1970's three food intervention programme were introduced.
(i) PDS (Public Distribution System).
(ii) ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services).
(iii) FFW (Food For Work).
What is the Public Distribution System?
The food procured by the FCI is distributed through government regulated ration shops among the poorer section of the society. This is called the public distribution system (PDS).
Discuss Targeted Public Distribution System.
Targeted Public Distribution System:
(i)Targeted public distribution system was introduced to adopt the principle of targeting the ‘poor in all areas'.
(ii)In order to ensure availability of minimum quantity of food grains to the families living below the poverty line, the govt, launched the TPDS system in June 1997.
(iii)It was intended to benefit about 6 crore poor families in the country for whom a quantum of 72 lakh tonnes of food grains was earmarked annually at the rate of 10 kg per family per month.
State the functions of the FCI.
The functions of the FCI are stated below:
(ii)It also builds the buffer stock.
Explain seasonal hunger.
(i)Seasonal hunger is related to cycles of food growing and harvesting.
(ii)This is prevalent in rural areas because of the seasonal nature of agricultural activities and in urban areas because of the casual labour, e.g., there is less work for casual construction labour during the rainy season.
What is chronic hunger? State any one factor responsible for chronic hunger.
Chronic hunger is a consequence of diets persistently inadequate in terms of quantity and quality.
Very low income is one of the basic cause of chronic hunger.
Mention the significance of Academy of Development Science (ADS).
The significance of Academy of Development Science (ADS) are mentioned below :
(i)Academy of Development Science (ADS) has facilitated a network of NGOs for setting up grain banks in different regions.
(ii)ADS organises training and capacity building programmes on food security for NGOs.
(iii)Grain Banks are now slowly taking shape in different parts of Maharashtra.
(iv)ADS efforts to set up Grain Banks, to facilitate replication through other NGOs and to influence the Government’s policy on food security are thus paying rich dividends.
(v)The ADS Grain Bank programme is acknowledged as a successful and innovative food security intervention.
What are the significance of Public Distribution System?
The characteristics of Public Distribution System are given below:
(i)The Public Distribution System, including the minimum support price and procurement has contributed to an increase in foodgrain production and provided income security to farmers in certain regions.
(ii)Public Distribution System has been instrumental in averting widespread hunger and famine by supplying food from surplus regions of the country to the deficit ones.
(iii)The Public Distribution System has proved to be the most effective instrument of government policy over the years in stabilising prices and making food available to consumers at affordable prices.
“In most of the years, the food stock in buffer stock remained consistently higher than the buffer norms.” State the reasons.
(i) The increase in the MSP has induced to farmers to produce food grains.
(ii)Most of the food grain producing states put pressure on the central government to purchase food grains from the farmers.
(iii)There is no proper distribution system and the PDS has also failed to solve the problem of buffer stocks.
'In the wake of the high incidence of poverty levels as reported by the NSSO in the mid-1970's three important food intervention programmes were introduced'.
Mention these programmes.
These programmes are:
(ii)Public Distribution System - The food procured by the FCI is distributed through govt. regulated ration shops among the poorer section of the society. This is called the PDS.
(iii)Integrated child development service - Integrated child development service was introduced in 1975. Under this basic necessities were provided to childern.
What do know about Co-operative Societies?
The Co-operative societies are the societies which are run by the local people, who are democratically elected.
These societies provide people the basic necessities of life like food grains, vegetables, milk etc. at reasonable rates.
Write the names of any three Co-operative Societies working in different states of India.
The Co-operative Societies are:
(i)Mother dairy-Delhi.
(ii)Academy of Development Science-Maharashtra.
(iii)Amul-Gujarat.
State the factors on which the food security depends.
The factors are:
(i)Public Distribution System
(ii)Buffer stock
(ii)Food Production
Mention the criticism associated with Public Distribution System in India.
The Public Distribution System has faced severe criticism on several grounds.
(i)Instances of hunger are prevalent despite overflowing granaries.
(ii)FCI go-downs are overflowing with grains, with some rotting away and some being eaten by rats.
How does ‘buffer stock’ ensure food security?
Buffer stock ensures food security in following ways:
(i)It distributes foodgrains in the deficit areas and among the poorer strata of society at a price lower than the market price.
(ii) It also helps to resolve the problem of shortage of food during adverse weather conditions or during the periods of calamity.
Describe in short the measures adopted by India after Independence to achieve self-sufficiency in food grains.
After Independence, Indian policy makers adopted all measures to achieve self-sufficiency in food grains.
(i)India adopted a new strategy in agriculture, which resulted in the ‘Green Revolution’ especially in the production of wheat and rice.
(ii)The increase in food grains was, however, disproportionate. The highest rate of growth was achieved in Punjab and Haryana, where foodgrain production jumped from 7.23 million tonnes in 1964-65 to reach an all time high of 30.33 million tonnes in 1995-96.
(iii)Tamilnadu and Andhra Pradesh, on the other hand recorded significant increases in rice yield.
What were the impacts of Green Revolution?
The impacts of Green revolution are the following:
(i)The Green Revolution has made India self-sufficient in food grains.
(ii) Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh recorded significant increase in rice yield.
(iii) The highest rate of growth was achieved in Punjab and Haryana.
(iv) The increase in the production of food grains helped the Government to build the buffer stock.
(v) Because of the Green Revolution, there was an increase in the production of rice and wheat.
Explain the current status of the Public Distribution System (PDS).
(i)Public Distribution System is the most important step taken by the government of India towards ensuring food security.
(ii)In the beginning the coverage of PDS was universal with no discrimination between the poor and non-poor. Over the years, the policy related to PDS has been revised to make it more efficient and targeted.
(iii) In 1992 Revamped Public Distribution System (RPDs) was introduced in 1700 blocks in the country. The target was to provide the benefits of PDs to remote and backward areas.
(iv) From June 1997, in a renewed attempt, Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDs) was introduced to adopt the principle of targeting the ‘poor in all areas'. It was for the first time that a differential price policy was adopted for poor and non-poor.
(v) Further, in 2000 two special schemes were launched viz, Antyodaya Anna Yojana, (AAY) and the Annapurna Scheme (APS) with special target groups of ‘poorest of the poor’ and ‘Indigent Senior Citizens’, respectively. The functioning of these two schemes was linked with the existing network of the PDS.
Table: Production of Rice in the Province of Bengal.
|
Year |
Production (Lakh tonnes) |
Imports (Lakh tonnes) |
Exports (Lakh tonnes) |
Total Availability (Lakh tonnes) |
|
1938 1939 1940 1941 1942 1943 |
85 79 82 68 93 76 |
– 04 03 02 – 03 |
– – – – 01 – |
85 83 85 70 92 79 |
Source : Sen, A.K. 1981 Page 61,
1. Some people say that the Bengal famine happened because there was shortage of rice. Study the table and find out whether you agree with the statement?
2. Which year shows a drastic decline in food availability?
1. By studying the table, we did not agree with the statement because in the year of famine total availability of rice was sufficient.
2. 1941.
Picture 4.1 Starvation victims arriving at a relief centre, 1945.

Picture 4.2 During the Bengal Famine of 1943, a family leaves its village in China gong district in Bengal.
Questions:
(a) What do you see in Picture 4.1?
(b) Which age group is seen in the first picture?
(c) Can you say that the family shown in the Picture 4.2 is a poor family? Why?
(d) Can you imagine the source of livelihood of the people, (shown in two pictures) before the occurrence of famine ? (In the context of a village)
(e) Find out what type of help is given to the victims of natural calamity at a relief camp.
(f) Have you ever helped such victims (in the form of money, food, clothes, medicines etc.)?
(b)Old age group is seen in the first Picture.
(c)The family shown in the Picture 4.2 is a poor family because this family is leaving its village due to poverty.
(d)The source of livelihood of the people before the occurrence of famine could be agriculture and its allied activities.
(e)The victims of a natural calamity at relief camp is given in kind of food, clothes, medicines and money etc.
(f)Yes, I have helped such victims in the form of money.
Why is agriculture a seasonal activity?
Agriculture is a seasonal activity because it does provide employement for the whole year.
Why is Ramu unemployed for about four months in a year?
Ramu is unemployed for about four months in a year because agriculture being a seasonal activity does not provide employement for the whole year.
What does Ramu do when he is unemployed?
Ramu looks for work in other activities when he is unemployed.
Who are supplementing income in Ramu’s family?
Ramu’s wife Sunhari and his son are supplementing income in his family.
Why does Ramu face difficulty when he is unable to have work?
Ramu faces difficulty when he is unable to have work because during this period some times his small kids have to sleep without food.
When is Ramu food insecure?
Ramu is food insecure during four months when he remains unemployed because of the seasonal nature of agriculture work.
Does Ahmad have regular income from rickshaw-pulling?
No, Ahmad does not have a regular income from rickshaw-pulling.
How does the yellow card help Ahmad run his family even with small earning from rickshaw-pulling?
With the help of yellow card, Ahmad gets sufficient quantity of wheat, rice, sugar and kerosene oil at half of the market price which helps him to run his family even with small earnings from rickshaw-pulling.
Visit some farms in a nearby village and collect the details of food crops cultivated by the farmers.
I visited some farms in a nearby village and collected the details of following food crops cultivated by the farmers:
(i) Wheat
(ii) Rice
(iii) Maize.
Graph: Production of Foodgrains in India (Million Tonnes).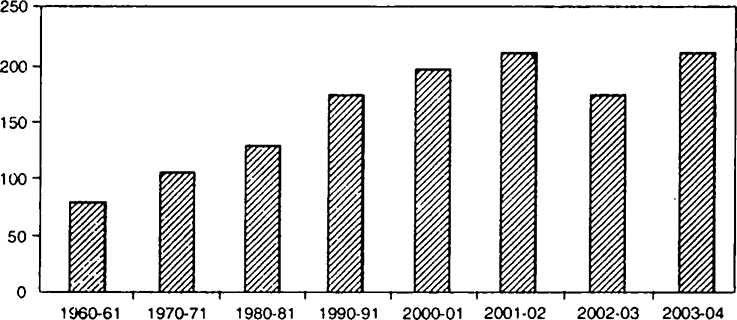
Source: Economic Survey 2011-12
Study the above graph and answer the following questions:
(a) In which year did our country cross the 200 million tonnes per year mark in foodgrain production?
(b) In which decade did India experience the highest decadal increase in foodgrain production?
(c) Is production increase consistent in India since 2000-01?
(b) In the 1990-91 decade, India experienced the highest decadal increase in foodgrain production.
(c) No, the production increase is not consistent in India since 2000-01.
Visit your area's ration shop and get the following details:
1. When does the ration shop open?
2. What are the items sold at the ration shop?
3. Compare the prices of rice and sugar from the ration shop with the prices at any other grocery shop. (for families below poverty line)
4. Find out:
(i) Do you have a ration card?
(ii) What has your family recently bought with this card from the ration shop?
(iii) Are there any problems that they face?
(iv) Why are ration shops necessary?
1. The ration shop opens at 9.30 a.m.
2. Wheat, rice, sugar, kerosene etc. are sold at the ration shop.
3. Wheat and rice are sold at Rs. 12 and Rs. 18 per kg. respectively at other grocery shop, whereas below poverty line gets them at Rs. 2.50 and Rs. 3.50 per kg respectively.
4. (i) Yes, we have a ration card.
(ii) Our family has recently bought wheat with this card from the ration shop.
(iii) No, there are no problems that they face.
(iv)Ration shops are necessary for making food affordable to the poorer sections of the society.
Graph: Central Foodgrains (Wheat + Rice) Stock and Minimum Buffer Norm (Million Tonnes).
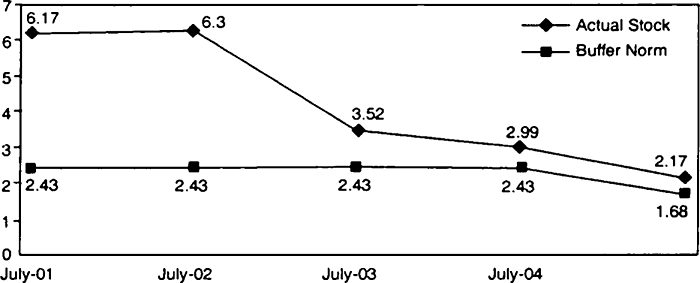
Source : Economic Survey 2004-05.
Study the above graph and answer the following questions:
(i) In which recent year foodgrain stock with the government was maximum?
(ii) What is the minimum buffer stock norm for the FCI?
(iii) Why were the FCI granaries overflowing with foodgrains?
(ii)The minimum buffer stock norm for the FCI is 24.3 million tonnes.
(iii)The FCI granaries were overflowing with foodgrains because of good support price offered to the farmers.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area






