Economics Chapter 3 Poverty As A Challenge
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 9 About 2.html Economics
Describe how the poverty line is estimated in India?
(i)Income Method — Under Income method, a minimum per capita income is fixed like in 1999-2000, the income was fixed at Rs. 328 per capita per month, and in urban areas it was Rs. 454. If any family has less than the fixed income, it is considered as below the poverty line. This method is used to distribute food at subsidized price through PDS.
(ii)Expenditure Method —
(a)Under this method the minimum nutritional food requirement for survival is estimated. The total minimum food requirement is firstly measured in calories. The calories is then converted into money value.
(b)A minimum amount which is required for clothes and other requirements is added to the money value of food. This total amount is considered as poverty line.
(c)All the families which spend less than the poverty line are considered as below the poverty line families. In India, the daily minimum nutritional requirement for a person has been fixed at 2400 calories in rural areas, and 2100 calories in urban areas.
Do you think that the present methodology of Poverty estimation is appropriate?
No, the present methodology of poverty estimation is not appropriate.
It is only a quantitative concept. It captures only a limited part of what poverty really means to the people. It is about a ‘minimum’ subsistence level of living rather than a 'reasonable' level of living.
Describe the poverty trends in India since 1973.
|
Poverty ratio (%) |
Number of Poor |
|||||
|
Year |
Rural |
Urban |
Cambined |
Rural |
Urban |
Combined |
|
1973-74 1993-94 |
56.4 37.3 |
49.0 32.4 |
54.9 36.0 |
261 244 |
60 76 |
321 320 |
|
1999-00 |
27.1 |
23.6 |
26.1 |
193 |
67 |
260 |
(i)It is clear from the above table that there is substantial decline in poverty ratio in India from about 55 per cent in 1973 to 36 per cent in 1993.
(ii)The proportion of people below poverty line further came down to about 26 per cent in 2000.
Discuss the major reasons for poverty in India.
The major reasons for poverty in India are discussed below:
(i) One historical reason is the low level of economic development under the British Colonial administration.
(ii)The policies of the Colonial government ruined traditional handicrafts and discouraged development of Industries like textile.
(iii)With the spread of irrigation and the Green Revolution many job opportunities were created in the agricultural sector. But the effects were limited to some parts of India.
(iv)Another reason of high poverty rate has been the huge income inequalities.
(v)One of the major reasons for this is the unequal distribution of land and other reasources.
Identify the social and economic groups which are most vulnerable to poverty in India.
(i)Social groups - Schedule Caste and Schedule Tribe households.
(ii)Economic groups - Rural agricultural labour households and the urban casual labour households.
Give an account of the interstate disparities in poverty in India.
(i)States with Poverty ratio more than the national average: Assam, Bihar, Orissa, U.P. and Tripura are the most poverty ridden states of India. The poverty ratio in these states is much higher than the national average. Bihar and Orissa are the poorest states with poverty ratio of 43 and 47 respectively.
(ii)States with low poverty ratio: Haryana, Punjab, Goa, Himachal Pradesh, and J&K have very low precentage of population living below the poverty line.
(iii)States with poverty ratio less than the national average: There has been a significant decline in poverty ratio in Tamilnadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat and West Bengal. Recent studies show that in 20 states and union territories, the poverty ratio is less than the national average.
Describe global poverty trends.
(i) Fall in global poverty - The World Bank defines poverty as living on less than $ 1 per day. There has been a substantial reduction in global poverty. It has fallen from 28 percent in 1990 to 21 per cent in 2001.
(ii)Regional variation - Although there has been a substantial reduction in global poverty, it is marked with great regional variation. Poverty declined substantially in China and South-East Asian countries as a result of rapid economic growth and massive investment in human resources development. But the pace of reduction of poverty in South Asian countries is very slow.
(iii)Poverty in India - Poverty in India has also declined, but the pace of reduction is very slow. According to World Bank's definition, 35.3% of the total population is still living below the poverty line.
(iv)Poverty in Sub-Saharan Africa - In Sub-Saharan Africa, poverty in fact rose from 41 per cent in 1981 to 46 per cent in 2001. Sub-sahara includes Algeria, libya, Nigeria, China etc.
(v)Poverty in Russia - The poverty has also resurfaced in some of the former socialist countries like Russia, where officially. It was not existent earlier.
|
Country |
% of Population below $1 a day |
|
1. Nigeria |
70.8 |
|
2. Bangladesh |
36.0 |
|
3. India |
35.3 |
|
4. Pakistan |
17.0 |
|
5. China |
16.6 |
|
6. Brazil |
8.2 |
|
7. Indonesia |
7.5 |
|
8. Sri Lanka |
5.6 |
The above table shows the poverty situation in some of the countries of the world.
Describe current government strategy of poverty alleviation.
It is also based on many schemes and programmes. Some of them have been mentioned below:
(i)National Food for work programme (NEWP) - This programme was launched in 2004 in 150 most backward districts of country. The programme is open to all rural poor who are in need of wage employment and desire to do manual unskilled work.
(ii)Prime Minister Rozgar Yozana (PMRY) - This scheme was started in 1993. It aims at creating self-employment opportunities for educated unemployed youth in rural areas and small towns.
(iii)Rural Employment Generation Programme (REGP) - It was launched in 1995. It aims at creating self-employment opportunities in rural areas and small towns
What do you understand by human poverty?
Human poverty is an inefficiency to get minimum basic needs such as, food, clothes and shelter.
Who are the poorest of the poor?
The women, children and old people are the poorest of the poor.
What are the main features of the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005?
(i)The NREGAs 2005 was passed in September 2005.
(ii)The act provides 100 days assured employment to every rural household in 200 districts.
(iii)The central government will also establish National Employment Guarantee funds.
(iv)Later, the scheme will be extended to 600 districts. One third of the proposed Jobs would be reserved for women.
(v)Under the programme, if an applicant is not provided employment within 15 days, he / she will be entitled to a daily unemployment allowance.
Sponsor Area
Which state has the lowest percentage of poor in India?
Punjab
Jammu and Kashmir
Himachal Pradesh
Kerala
B.
Jammu and Kashmir
When was National Rural Employment Guarantee Act passed?
September, 2005
August, 2004
December, 2005
January, 2005
A.
September, 2005
Which country has the largest concentration of the poor?
China
India
Japan
Sub-Saharan Africa
D.
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sponsor Area
What is NSSO?
National Sarva Siksha Organisation.
National Sample Survey Organisation.
National Statistics Survey Organisation.
None of these.
B.
National Sample Survey Organisation.
Which of the following is used to measure poverty?
Education and Health
Education and Literacy rate
Income and Consumption level
All the above
C.
Income and Consumption level
What is SGSY?
Swarana Jayanti Gramodaya Swarozgar Yojana.
Swarana Jayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana
Swarozgar Gram Swarana Jayanti Yojana
None of these
B.
Swarana Jayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana
How is poverty defined by World Bank?
All those who live on less than $ 8 per day are considered living below poverty line.
All those person who live on less than $ 10 per day are considered living below poverty line.
All those person who live on less than $ 1 per day are considered living below poverty line.
None of these.
C.
All those person who live on less than $ 1 per day are considered living below poverty line.
In which region of the world poverty line has risen up?
Europe
Asia
Sub-Saharan Africa
All the above
C.
Sub-Saharan Africa
What is MNREGA?
Mumbai Nation Rural Employment Guarantee Act.
Mahatma Rural Employment Guarantee Act.
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act.
None of these.
C.
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act.
Which of the following is historical reason for the low level of economic development?
Fata of monsoon
Low development of industry
Over dependent on agriculture
The policies of the colonial government.
D.
The policies of the colonial government.
The current anti poverty strategy of the govt. is based broadly on two planks.
Promotion of economic growth, targeted anti-poverty programmes.
Economic growth education.
Education, targeted anti-poverty programme.
None of these.
A.
Promotion of economic growth, targeted anti-poverty programmes.
What is Vulnerability?
Vulnerability to poverty is a measure which describes the greater probabilities of certain communities, or individual of becoming or remaining poor in the coming year.
What average Calories have been fixed for Rural and Urban Areas by the Goverment?
For the rural area 2400 calories and for the urban area 2100 calories have been fixed for per person per day in India.
Who estimates the Poverty Line?
The poverty line is estimated periodically normally every five year by conducting sample survey. These surveys are carried out by the National Sample Survey Organisation. (NSSO).
Enlist three section of poor people.
They are:
(i)landless labourer
(ii)Urban casual labourers
(iii)Rural agriculture labourers
What are the new indicator of poverty?
Now a days poverty is looked through other social indicators like illiteracy level, lack of general resistance due to malnutrition, lack of access to health care, lack of job opportunities, lack of access to safe drinking water, sanitation etc.
What is social exclusion of Poverty?
According to this concept, poverty must be seen in term of the poor having to live only in a poor surrounding with other poor people excluded from enjoying social quality of better off people in better surrounding.
Why do different Countries use different poverty line? State an example.
Each country uses an imaginary line that is considered appropriate for its existing level of development and its accepted minimum social norms.
For example, a person not having a car in the United States may be considered poor. In India, owning of a car is still considered a luxury.
Mention any four states which has highest poverty and four states with lowest poverty in India.
The states with highest poverty are: Orissa, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and Assam.
The lowest poverty states are: Goa, J&K, Punjab and Himachal Pradesh.
What is the situation of people in developing countries living in extreme economic poverty?
The situation of people in developing countries living in extreme economic poverty had fallen from 28 per cent in 1990 to 21 per cent in 2001.
Describe ‘National Food for Work Programme (NFWP)’.
National Food for Work Programme was launched in 2004 in 150 most backward districts of the country.
The programme is open to all rural poor who are in need of wage employment and desire to do manual unskilled work. It is implemented as a 100 per cent centrally sponsored scheme and food grains are provided free of cost to the states.
Mention ‘Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana' (PMRY).
Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana was started in 1993.
The aim of the programme is to create self employment opportunities for educated unemployed youths in rural areas and small towns. They are helped in setting up small business and industries.
What is ‘Rural Employment Generation Programme (REGP)’?
The Rural Employment Generation Programme was launched in 1995. The aim of the programme is to create self-employment opportunities in rural areas and small towns. A target for creating 25 lakh new jobs has been set for the programme under the Tenth Five Year Plan.
What do you know about ‘Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY)’?
The Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana was launched in 1999.
The programme aims at bringing the assisted poor families above the poverty line by organising them into self help groups through a mix of bank credit and govt. subsidy.
Discuss ‘Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana (PMGY)’.
The Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana was launched in 2000.
Under this additional central assistance is given to states for basic services such as primary health, primary education, rural shelter, rural drinking water and rural electrification.
How does the social scientists see poverty?
Social scientists see poverty through variety of indicators.
They look through poverty mainly from social indicators like illiteracy level, lack of general resistance due to malnutrition, lack of access to health care, lack of access to safe drinking water, sanitation, lack of job opportunities etc.
Mention the major dimensions of poverty.
Following are the major dimensions of poverty:
(i)Poverty means hunger and lack of shelter.
(ii)Poverty also means lack of clean water and sanitation facilities.
(iii)It is a situation in which parents are not able to send their children to school.
(iv)It is a situation in which sick people cannot afford treatment.
(v)Poverty means lack of a regular job at a minimum decent level.
What is the main factor responsible for the reduction of poverty in the following states?
(i) West Bengal
(ii) Kerala
(iii) Punjab
iv) Tamil Nadu
The factor responsible are:
(i)West Bengal — Poverty has been reduced through land reform measures.
(ii)Kerala — Poverty has been reduced through human resource development.
(iii)Punjab — Poverty has been reduced due to high agricultural growth rate.
(iv)Tamilnadu — Poverty has been reduced through proper PDS.
‘Poverty reduction is expected to make better progress in the next ten to fifteen years.’ State the reasons.
The resaons are:
(i)Increasing stress on universal free elementary education.
(ii)Declining population growth.
(iii)Increasing empowerment of the women.
'The result of Poverty alleviation programmes have been mixed.’ Mention the reasons.
The resaons are:
(i)Over population and Corruption.
(ii)Less effectiveness is the lack of proper implementation and right targeting.
(iii)There has been a lot of overlapping of schemes.
Sponsor Area
'There is a strong link between economic growth and poverty reduction.’ Describe with examples.
The growth rate jumped from the average of about 3.5 per cent a year in the 1970s to about 6 per cent during the 1980s and 1990s. The higher growth rates have helped significantly in the reduction of poverty.
Economic growth widens opportunities and provides the resources needed to invest in human development. This also encourages people to send their children, including the girl child to schools in the hope of getting better economic returns from investing in education.
Name any two social groups which are most vulnerable to poverty.
The groups are:
(i) Scheduled Castes (SC)
(ii) Scheduled Tribes (ST).
Which Act ensures a poor person of 100 days employment?
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act.
“The Current anti-Poverty strategy of the govt. is based broadly on two planks'. Name the two planks.
The planks are:
(i)Promotion of economic growth.
(ii)Targeted anti-poverty programmes.
Name the organisation which is responsible for estimating poverty.
National Sample Survey Organisation.
Mention any four countries which have high percentage of population living below poverty.
The countries:
(i) India (ii) Bangladesh (iii) Nigeria (iv) Pakistan.
Define mass poverty.
Mass poverty is a situation in which a large section of people in economy are deprived of the basic necessities.
State any two indicators of poverty.
The indicators are:
(i)Level of income
(ii)Level of consumption.
Suggest any three measures to remove poverty in India.
The measures are:
(i)Population Control.
(ii)Creation of more employment opportunities.
(iii)More emphasis on small, rural and cottage industries.
Discuss the following term with reference to textbook :
(i) Landless
(ii) Unemployment
(iii) Size of families
(iv) Illiteracy
(v) Poor health/Malnutrition
(vi) Child labour
(vii) Helplessness.
(i)Landless: Landless is that person who does not own any land.
(ii)Unemployment: Unemployment is a situation in which those people who are able and willing to work at existing wage rate can not get work. Ram Saran and Lakha Singh's families are unemployed or under employed.
(iii)Size of Families: By the size of families we mean the number of persons in a family. Generally the size of poor families like Ram Saran and Lakha Singh is very large.
(iv)Illiteracy: Who can not read, write are treated as illiterate. Poor persons are generally illiterate.
(v)Poor health/Malnutrition: Poor health mean who have no access to health care and remain ill. Malnutrition means under nourished.
(vi)Child Labour: Working of the under age child is known as child labour which is prohibited by the government. But there always exists child labour in the poor families.
(vii)Helplessness: The poor are helpless. They have even to work at lower wages than minimum wages.
Describe the concept of social exclusion of poverty with example.
Social Exclusion:
(i)According to this concept, poverty must be seen in terms of the poor having to live only in a poor surrounding with other poor people, excluded from enjoying social equality of better off people in better surroundings.
(ii)Social exclusion can be both a cause as well as a consequence of poverty in the usual sence.
(iii)Broadly, it is a process through which individuals or groups are excluded from facilities, benefits and opportunities that other (their ‘betters’) enjoy.
(iv)A typical example is the wroking of the caste system in India in which people belonging to certain castes are excluded from equal opportunities.
(v)Social exclusion thus may lead to, but can cause more damage than having a very low income.
Examine the ‘Vulnerability’ of poverty.
Vulnerability:
(i)Vulnerability to poverty is a measure, which describes the greater probability of certain communities (say, members of a backward caste) or individuals (such as a widow or a physically handicapped person) of becoming or remaining poor in the coming years.
(ii)Vulnerability is determined by the option available to different communities for finding alternative leaving in terms of assets, education, health and job opportunities.
(iii)Further, it is analysed on the basis of the greater risks there groups face at the time of natural disasters, terrorism etc.
(iv)Additional analysis is made of their social and economic ability to handle these risks.
(v)In fact, vulnerability describes the greater probability of being more adversely affected then other people when bad time comes for everybody. Whether a flood or an earthquake or simply a fall in the availability of jobs.
Mention any three features of Public Distribution System (PDS).
The the features of PDS are mentioned below:
(i) It is used as an important activity of the state to ensure food security to the people, particularly the poor ones.
(ii)The prices of the goods sold through PDS in fair prices shops is lesser than that of the market price. The cost of this price difference is borne by the government.
(iii)This system controls unscrupulous rise in prices for essential goods in the markets.
What do you think would be the “minimum necessary level” in your locality?
I think ‘minimum necessary level’ in our locality is Rs. 800 per month.
Table: Estimates of Poverty in India.
|
Poverty ratio (%) |
Number of poor (in millions) |
|||||
|
Year |
Rural |
Urban |
Combined |
Rural |
Urban |
Combined |
|
1973-74 |
56.4 |
49.0 |
54.9 |
261 |
60 |
321 |
|
1993-94 |
37.3 |
32.4 |
36.0 |
244 |
76 |
320 |
|
1999-00 |
27.1 |
23.6 |
26.1 |
193 |
67 |
260 |
Source : Economic Survey 2002-03. Ministry of Finance, Government of India. Study the Table and answer the following questions:
(i) Even if poverty ratio declined between 1973-74 and 1993-94, why did the number of poor remain at about 320 million?
(ii) Are the dynamics of poverty reduction the same in rural and urban India?
(i) Even if poverty ratio declined between 1973-74 and 1993-94, the number of poor remained at about 320 million because of rapid increase in population.
(ii) No, the dynamics of poverty reduction are not the same in rural and urban India.
Observe some of the poor families around you and try to find the following:
(i)Which social and economic group do they belong to?
(ii)Who are the earning members in the family?
(iii)What is the condition of the old people in the family?
(iv)Are all the children (boys and girls) attending schools?
(ii) A few members are the earning members in the family.
(iii) The condition of the old people in the family is most vulnerable.
(iv) All the children (boys and girls) are not attending the schools. Most girls are still at home.
Graph: Poverty Ratio in Selected Indian States, 1999-2000.
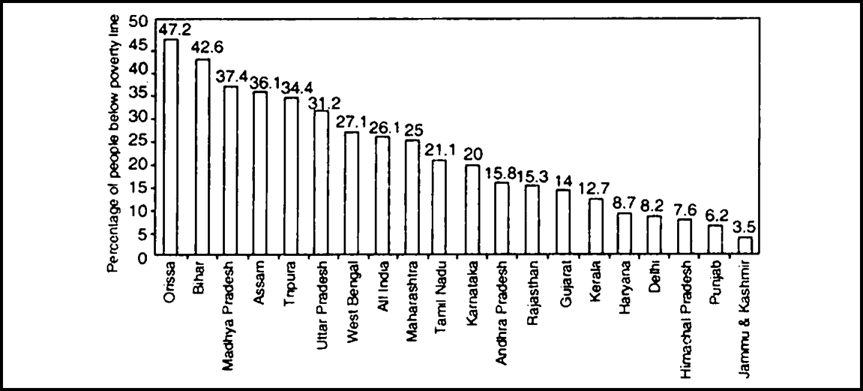
Source: Economic Survey 2001-02, Ministry of Finance, Government of India. Study the Graph 3.2 and do the following:
(i) Identify the three states where the poverty ratio is the highest.
(ii) Identify the three states where poverty ratio is the lowest.
(i)The poverty ratio is the highest in states like Orissa, Bihar and Madhya Pradesh.
(ii)The poverty ratio is the lowest in the states like Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab and Himachal Pradesh.
Graph: Number of poor by region ($ 1 per day) in millions.
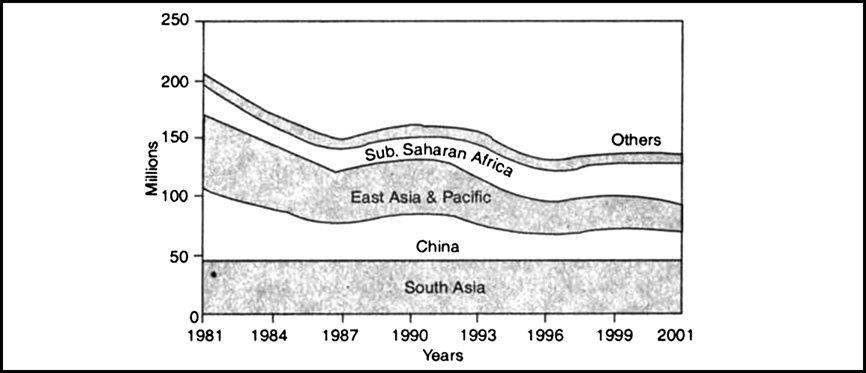
Sources: World Development Indicators 2005. The World Bank. Study the Graph and do the following:
(i) Identify the areas of the world, where poverty ratios have declined.
(ii) Identify the area of the globe which has the largest concentration of the poor.
(i)Poverty ratios have declined in South Asia and Pacific.
(ii)South Asia has the largest concentration of the poor.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





