Science Chapter 8 Cell - Structure And Functions
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 8 Social+science
Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
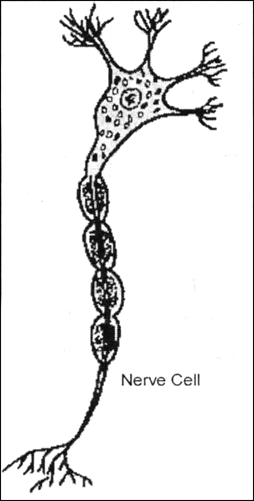
Functions of the nerve cells :
(i) Nerve cells help in the transfer of messages from various body parts to brain and brain to various parts of the body.
(ii) They also help in the control and coordination of the different parts of the body.
Write short notes on the following :
Cytoplasm
It is a jellylike substance which is present between nucleus and cell membrane. There are various other organelles present in the cytoplasm. It is made up of carbohydrates, proteins and water.
Write short notes on the following :
Nucleus of a cell
Nucleus is spherical dense body found in the centre of the cell. Nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from cytoplasm. It acts as control centre of the activities of the cell. Nucleus contains thread-like structures called chromosomes. Nucleus membrane is porous and allows the movement of material between the nucleus and cytoplasm. It also contains the threadlike structure called chromosomes which are genetic material.
Make sketches of animal and plant cell. State three differences between them.
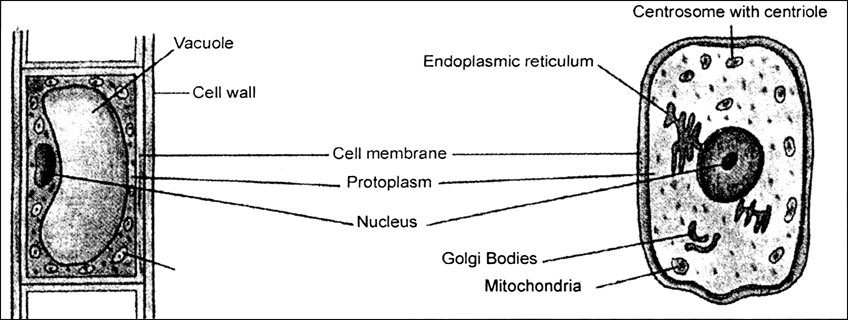
Differences:
| Animal cells | Plant cells |
| Does not have cell walls. | Has cell walls. |
| Chloroplasts are absent. | Chloroplasts are present. |
| Centrosome presents near the nucleus . | Centrosome is not present. |
.
State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes have a well designed nucleus and organelles covered with membranes while prokaryotes do not have a well designed nuclear membrane .
Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their function.
Chromosomes are found in the nucleolus. Their function is to carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
‘Cells are the basic structural units of living organism.’ Explain.
Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms because all organism are composed of cell. The cells are the building block of life.The smallest functional unit of any part is a cell.
Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
Chloroplasts are only found in plant cells because they are required for the food making process of plants called photosynthesis. The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which traps solar energy and utilize it for making food. Since animals do not synthesize food they do not have chlorophyll.
Name three important parts of cell.
The three important parts of cell
(i) Cell membrane, (ii) Cytoplasm, (iii) Nucleus.
Sponsor Area
Name the largest known cell.
An ostrich egg cell in the largest known cell. It is about 170 x 135 mm in size.
Name the largest cell of the human body.
A nerve cell is the longest cell of the human body.
What is pseudopodia?
The finger like projections of different lengths of the body of amoeba is called pseudopodia.
What is protoplasm?
Protoplasm is the living substance of the cell.
It includes the cytoplasm and the
nucleus.
What is nuclear membrane?
Nuclear membrane is the membrane that surrounds the nucleus. It separates the nucleus from cytoplasm. The nuclear membrane is porous membrane is also porous and allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus.
What are prokaryotic cells?
The cells having nuclear material without nuclear membrane are called prokaryotic cells.
What are eukaryotic cells?
The cells having well organised nucleus with a nuclear membrane are called eukaryotic cells.
Name any two organisms having eukaryotic cells.
Two organism having eukaryotic cells are Plants and animals.
Sponsor Area
Mitochondria are called ‘power house’ of the cell. Give reason.
Mitochondria help in the oxidation of food and release energy. Hence they are known as Power House of the cell.
Why Lysosomes are called the ‘Suicidal bags’?
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes. When the cell gets damaged, lysosomes may burst and the enzymes digest their own cell. Therefore, lysosomes are also known as ‘suicide bags’ of a cell. The lysosomes are formed from the golgi bodies.
Why chloroplasts are called the ‘kitchens’ of the cell?
Chloroplasts contain the green piment chlorophyll. These pigment are important for photosynthesis as they trap the solar energy and produce food from it. So, chloroplasts are the ‘kitchens of the cells’.
Why do grass look green, papaya yellow and edible part of water melon red?
The grass looks green because of the presence of chloroplast which have green pigment called chlorophyll. Papaya and watermelon are of yellow and red colour respectively because of the presence of chromoplasts having pigments with different colours.
Why is it said that ‘a cell without nucleus is without any future’?
It is said because the nucleus controls all the metabolic activities directly or indirectly. It controls the formation of various cell organelles by controlling the synthesis of proteins. It also contains the genes which are the hereditary units. A cell without a nucleus cannot perform tha vital activities, hence, it has no future.
Name the three main components of the cell. Briefly explain one of them.
There are three main components of a cell :
(i) Cell membrane, (ii) Cytoplasm, (iii) Nucleus.
Cytoplasm- The cytoplasm and nucleus are enclosed within the cell membrane. The cell membrane is also called Plasma membrane. It membrane separates cells from one another. The plasma membrane is porous and allows the movement of substances or material both inward and outward.
Write the functions of cell wall.
Functions of cell wall are :
(i) It provides rigidity to the plant cell.
(ii) It prevents drying of cells.
(iii) It provides shape to the plant cell.
Write any two functions of protoplasm.
Two functions of protoplasm
(i) It controls all the functions of a cell .
(ii) It is the house for all the cell organelles..
Write the functions of cytoplasm.
Functions of cytoplasm are :
(i) It is a physical basis of all metabolic activities.
(ii) Various cell organelles perform specific functions in the cytoplasm.
(iii) It provides turgidity.
Write the functions of mitochondria, golgi bodies and ribosomes.
Mitochondria : It performs the function of respiration and provides the cell with energy. It is called the power house of cell.
Golgi bodies : These collect and distribute substances made in cell, synthesis and secretions of many materials.
Ribosomes : They help in the synthesis of proteins.
Explain the variation of size of cells.
Cells vary in their size. Some cells are very small like bacterial cell whose size is about 0.5 micrometre. Nerve cell is about 1 metre long. Ostrich egg is the largest cell measuring 170 mm ×130 mm.
Differentiate between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell.
|
Prokaryotic Cell |
Eukaryotic Cell |
|
1. Nucleus is not bound by a nuclear membrane 2. Cell size is generally small (1–10 μm). |
1. Nucleus is bound by a nuclear membrane. 2. Cell is generally large (5–100 μm). |
Explain various types of organisms on the basis of number of cells.
There are two types of organisms on the basis of number of cells:
(i) Unicellular : The organisms contain only single cell in the body are called unicellular organisms. For example : amoeba and paramecium.
(ii) Multicellular : The organisms made up of more than one cells, are called multicellular organisms. For example human, tree, dog, etc.
In the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Each living cell along with its components like protoplasm and various organelles, has the capacity to perform basic functions of life. If this organisation of a cell is destroyed, then cell will not be able to perform certain basic functions and it may lead to its death in the future.
Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
The plasma membrane allows or permits the entry and exists of some materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents movement of some other materials. The cell membrane, therefore, is called a selectively permeable membrane.
What is an organ system?
(a) Give two examples of organ systems in animals.
(b) Name the two main organ systems in plants.
A group of interconnected organs which works together to do a big job for the organism, is called an organ system.
(a) Various organ systems of animals (including human beings) are Digestive system, Respiratory system, Circulatory system, Nervous system etc.
(b) The plants have two main organ systems : Root system and shoot system.
A, B, C and D are basic parts of all the cells. The part A contains thread like structures called E which transfer the characteristics from parents to their offsprings into the cell and out of the cell. The part B provides energy to the cell. The part C is found in plant cell but not in animal cell. The part D is a transparent, jelley–like material. What could A, B, C, D and E be?
A : Nucleus
B : Mitochondria
C : Cell membrane
D : Cytoplasm
E : Chromosomes.
How do you differentiate protoplasm from cytoplasm?
Protoplasm : The cytoplasm surrounded by the cell membrane and enclosing the nucleus together constitute the protoplasm. In other words the cell membrane, the cytoplasm and the nucleus constitute protoplasm.
Cytoplasm : It is jelly like substance occupied most of the inside of the cell. It occupies the space between the cell membrane and the nucleus. All the life functions take place in the cytoplasm. It contains many important tiny structures called the organelles, which performs the various life functions.
Write the functions of cell organelles.
Functions of cell organelles are
(i) Mitochondria : It performs the function of respiration and produces energy.
(ii) Endoplasmic-reticulum : It is a network of membrane, it provides large surface area for life function to take place.
(iii) Chloroplasts : These are green in colour, contain green pigment chlorophyll which help in manufacturing of food in plants.
(iv) Golgi complex : These collect and distribute materials made in the cell.
(v) Centrioles and centrosome : It helps in cell division in animal cells.
(vi) Ribosomes : They help in protein synthesis.
(vii) Vacuoles : They are used for storage of waste material.
What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
If the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down, then following things may happen :
(i) There will be no difference between the contents of the cell and its external environment.
(ii) Ruptured plasma membrane will allow free movement of all the substances in and out of the cell.
(iii) The cell will lose its shape as the plasma membrane provide shape to the cell.
(iv) All the metabolic activities of the cell will get affected , may even stop and cell may die .
What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no golgi apparatus?
the function of Golgi apparatus is to tranfer the substances made in the cell to different part of the cell. Therefore, if there are no golgi apparatus then the substances will not be disrtibuted and transported to other parts. The cell may even die due to lack of the materials.
What is the difference between the plasma membrane and cell wall? Give the functions of each.
| Plasma membrane | Cell wall |
| Its is living. | It is non-living |
| Found in all the cells | Found in plant cells, bacteria, and fungi. Absent in animal cells. |
| Selectively permeable | Freely permeable. |
Functions of Plasma Membrane :
(i) It gives shape and rigidity to the cell.
(ii) It helps in maintaining the chemical composition of the cell.
(iii) It helps in cellular movement or locomotion as in amoeba.
Functions of Cell Wall :
(i) It provides support to a plant cell.
(ii) It determines the shape of the cell and prevents it from drying.
Cells in which nuclear membrane is absent from the nucleus are called _______cells.
prokaryotic
Sponsor Area
Match the following option:
| A. Structural unit of body | (i) Mitochondria |
| B. Cell wall | (ii) Chloroplast |
| C. Power house of the cell | (iii) Nucleus |
| D. Kitchen of the cell | (iv) Cell |
| E. Control unit of the cell | (v) Plant cell |
A. Structural unit of body | (i) Cell |
B. Cell wall | (ii) Plant cell |
C. Power house of the cell | (iii) Mitochondria |
D. Kitchen of the cell | (iv) Chloroplast |
E. Control unit of the cell | (v) Nucleus |
Ribosomes are the centre for
fat synthesis
protein synthesis
starch synthesis
sugar synthesis
B.
protein synthesis
Out of the following, which animal is unicellular?
Amoeba
Paramecium
Bacteria
All of the above
D.
All of the above
Draw a labelled diagram of a plant cell and compare it with animal cell.
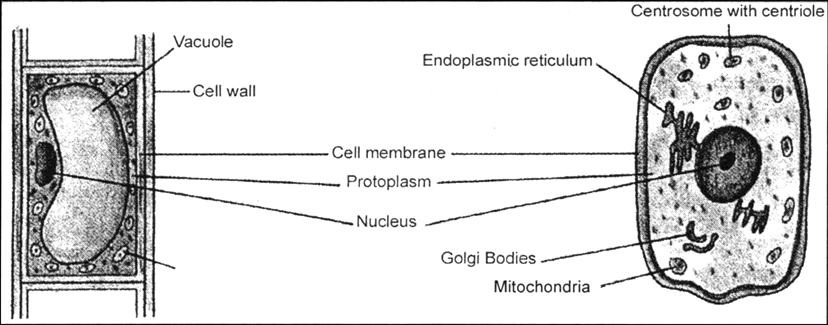
(i) Plant cell contains a rigid cell wall while animal cell has no cell wall.
(ii) Plant cell has plastids while animal cell does not have plastids.
(iii) Plant cell has big vacuole while animal cell has small vacuole.
Draw a diagram of (a) Amoeba, (b) Paramecium. Name the locomotion organisms in both of them.
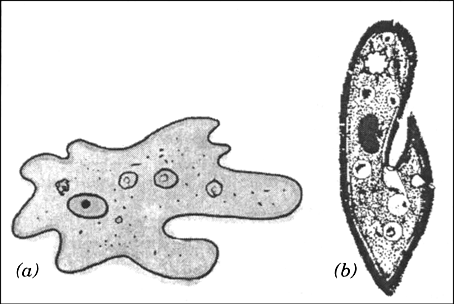
(a) Amoeba, (b) Paramecium
Amoeba moves with the help of pseudopodia while Paramecium moves through cilia.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area