Science Chapter 10 Light - Reflection And Refraction
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 %2525e0%2525a4%2525b8%2525e0%2525a4%2525be%2525e0%2525a4%2525ae%2525e0%2525a4%2525be%2525e0%2525a4%25259c%2525e0%2525a4%2525bf%2525e0%2525a4%252595%252b%2525e0%2525a4%2525b5%2525e0%2525a4%2525bf%2525e0%2525a4%25259c%2525e0%2525a5%25258d%2525e0%2525a4%25259e%2525e0%2525a4%2525be%2525e0%2525a4%2525a8
An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Write four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
(i) Virtual
(ii) Always forms behind the mirror between focus and pole.
(iii) Image is always erect
(iv) Small in size
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
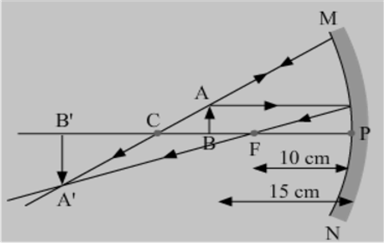
Given
h1 =+4
f = - 10 cm
u = -15 cm
v = ?
h2 = ?
Using the mirror equation,
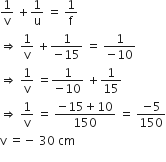
Thus, to obtain a sharp image of the object the screen should be placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror.
Magnification: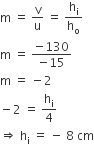
Analyse the following observation table showing a variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in the case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow, without doing any calculations:
| S. No. |
Object distance |
Image distance |
| 1 | -90 | +18 |
| 2 | -60 | +20 |
| 3 | -30 | +30 |
| 4 | -20 | +60 |
| 5 | -18 | 90 |
| 6 | -10 | 100 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens ? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct.How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Take an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
(b) Serial number 6 is not correct as the object distance is between focus and pole so for such cases the image formed is always virtual but in this case, a real image is forming as the image distance is positive.
(c) Approximate value magnification for object distance - 20 cm and image distance + 60 cm is 3.

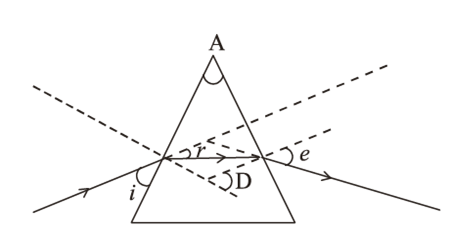
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
Two light rays whose path of reflection are priorly know are:
(i) The incident ray passes through the centre of curvature: In this case, light ray after reflecting from the concave mirror moves back in the same path. This happens because the light ray is incident perpendicularly on the mirror surface.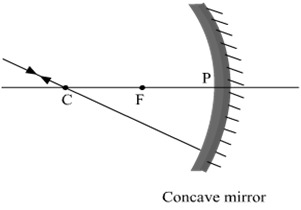
(ii) The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the concave mirror obliquely and making equal angles with the principal axis.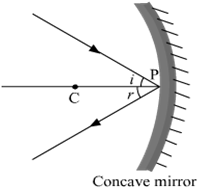
Let an object "a candle" is placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then using above two rays, image of the candle can be located as shown below: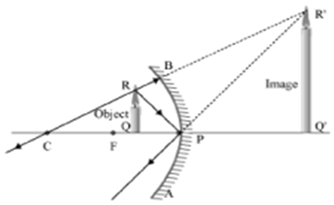
A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object?
Given,
u = -20 cm
m = -3
m = v/(-u)
∴ v =-m xu
= -(-3)(-20 cm) = -60
Distance between the object and the screen is 40 cm
= -60 cm- (-20 cm)=- 40 cm
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that, he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
a) Away from the lens
b) Size increases
c) Intensity decreases
d) About 20 cm
If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer.
To get erect and diminished image mirror used is a convex mirror.
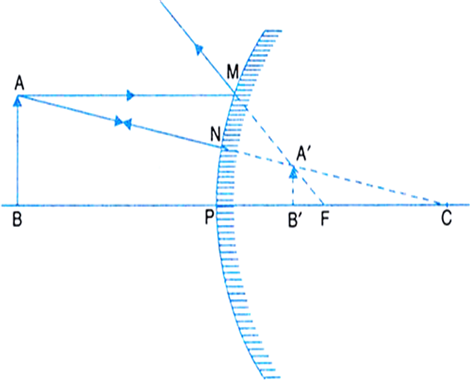
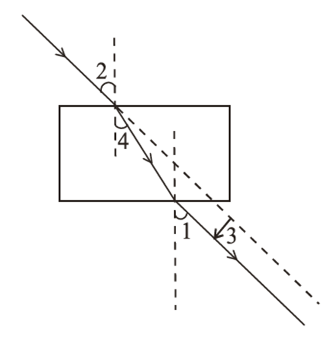
State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term ‘absolute refractive index of a medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
(1) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
(2) For the light of a given colour and for a given pair of media, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant.
This is also known as Snell's Law.
Mathematically it can be written as:
Here, μ is the refractive index of medium B with respect to medium A.
Refractive index of a medium with respect to the vacuum is known as the absolute refractive index.
What is meant by the power of a lens? Write its SI unit. A student uses a lens of focal length of 40 cm and another of –20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens.
The power of lens is defined as the reciprocal of its length. It is denoted by using the letter P.
Unit of Power is Dioptre (D)
Focal length = 40 cm
Focal length = -20 cm
Convex lens P = 1/f = 100/40 = 2.5 D
Concave lens = P = 1/f = -100/20 = -5D
An object of height 4.0 em is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre ‘O’ of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre ‘O’ and principal focus ‘F’ on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object.
Ray diagram:
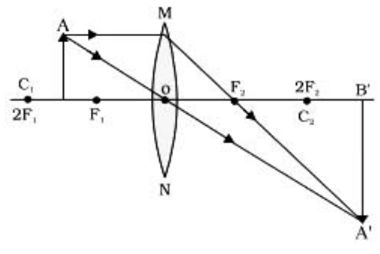
Here, focal length, f = 20 cm,
u = - 30 cm,
h0 = 4 cm
Using, lens formula,
therefore, image distance, v = 60 cm
The image formed is real and inverted.
The ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area