Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money And Credit
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Social+science Understanding Economic Development
In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower. Explain.
The situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower:
(i)The borrower had to pay interest on principal as well as on interest to lenders.
(ii)The lenders can go against the defaulT borrower in the court to recover his principal amount and interest thereupon.
(iii) Sometimes, the lender can sell the security or the assets as collateral pledged with the banks or co-operative society or any informal agency of credit.
How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants ? Explain with an example of your own.
Double coincidence of wants is an essential feature in a barter system where goods are directly exchanged without the use of money. But on other hand in an economy where money is in use, money by providing the crucial intermediate step eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want.
For example: It is no longer necessary for the shoemaker to look for a farmer who will buy this shoes and at the same time sell him rice. All he has to do is find a buyer for his shoes. Once he has exchanged his shoes for money he can purchase rice or any commodity in the market.
How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.
In this way, banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers).
Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits. The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Look at a 10 Rupee note. What is written on top? Can you explain this statement?
On the top of a 10 Rupee note “Reserve Bank of India, Guaranteed by the Central Government is written.”
It implies that the notes are issued by Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the Central Government. This means that the currency is authorised or guaranteed by the Central Government and no one can refuse payment made in it.
In what ways does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of banks? Why is this necessary?
The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
For instance, we have seen that the banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive. The RBI monitors that the banks actually maintain the cash balance. Similarly, the RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small scale industries and small borrowers etc. Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom and at what interest rate etc.
The supervision of RBI is necessary for the following reasons :
(i)It ensures safety to the bank deposits of people.
(ii)It helps in collection of economic data all over the country.
(iii)It contains corrupt practices from creeping within banks.
(iv)Information forwarded by banks to RBI helps Ministry of Finance in drafting and presentation of National Budget every year.
Analyse the role of credit for development.
The role of credit for development:
(i)Credit is available normally from two sources. These can be either formal sources or informal sources.
(ii)Terms of credit vary substantially between formal and informal lenders. At present, it is the richer households who receive credit from formal sources whereas the poor have to depend on the informal sources. It is essential in modern economy to make terms of credit flexible with formal sources of credit e.g. Banks etc. in order to safeguard interests of the poor sections of society in India.
(iii) In prevailing situations, if credit can be made available to the poor people on terms and conditions that are appropriate and reasonable, these millions of small entrepreneurs with their millions of small pursuits can add up to create the biggest development wonder.
Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender? Discuss.
Manav will decide to borrow from the bank or the moneylender on the following basis:
(i)Difference between rate of interest charged by formal and informal sources at the desired time.
(ii)Perusal upon terms of credit viz. paper work, security, collateral etc. made necessary by respective sources.
(iii)Mode of payment viz. size of instalment, frequency (monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or annually) or full repayment at the end of certain period i.e. two years, three years and so on. Apart from this his own capacity to repayment after thorough analysis of information collected.
In India, about 80 per cent of farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(a) Why might banks be unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b) What are the other sources from which the small farmers can borrow?
(c) Explain with an example how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmer.(d) Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
(a) Small farmers have no collateral against loans. Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid. That is why banks have no interest to lend to small farmers.
(b)These small farmers take loans from informal lenders including moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends etc.
(c)The terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmers because of the crop failure. In this situation credit pushes the farmers into debt trap.
(d)The idea is to organise rural poor, in particular women, into small Self Help Groups (SHGs) and pool (collect) their savings.
Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
(i)This would lead to higher incomes and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(ii)They could grow crops, do business, set up small-scale industries etc.
(iii)They could set up new industries or trade in goods. Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development.
Why is money accepted as a medium of exchange in India?
Money is accepted as a medium of exchange because:
(i)The currency is authorised by the government of the country.
(ii)The Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government. As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency.
(iii)Moreover the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in setting transactions in India.
Sponsor Area
Answer the questions asked below:
(i)Why are transactions are made in money?
(ii)Why is money is called a medium of exchange?
(iii)What is the most significant feature of the barter system?
(i) Because money is easily acceptable. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want.
(ii) Because it acts as an intermediate in the exchange process.
(iii) Double coincidence of wants.
Explain the functions of money.
Functions of Money are explained below:
(A)Primary Functions:
(i) Medium of Exchange, (ii) Measure of Value.
(B)Secondary Functions:
(i) Store of Value
(ii)Standard for Deferred Payments
(iii)Transfer of Value
Mention the requirement which the borrower has to fulfil before taking a housing loan.
The requirements are:
(i)The borrower has to submit a certificate of his source of income.
(ii)He has to produce documents of his employment records.
(iii)The papers of the new house has to be handed over to the banks as collateral security.
Mention the chracteristics of cheque payments.
(i)For payment through cheque, the payer who has an account with the bank, makes out a cheque for a specific amount.
(ii)A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
(iii)Cheque payments share the essential features of money.
(iv)The facility of cheques against demand deposits makes it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash.
(v)Since cheque payments are accepted widely as a means of payment, along with currency, they constitute money in the modern economy.
Write two formal and informal sources of rural credit in India.
Formal sources of rural credit in India are:
(i)Cooperative Societies.
(ii)Commercial Banks.
Informal sources of rural credit in India are:
(i) Relatives and friends.
(ii)Local moneylenders.
Dintinguish between formal sector and informal sector loans.
The distinctions:
(i)Formal sector loans are such loans which are taken either from the banks or the co-operatives. While informal sector loans are those which are taken from moneylenders, traders, employers, relative and friends.
(ii)In the case of informal sector of loans, the rate of interest is quite high. On the other hand the rate of interest in informal sector is very low.
(iii) In formal sector of loans, there is no exploitation unlike the informal sector of loans. In the informal sector, the trader would buy the produce of the farmers at lower price but a bank would never resort to such tactics.
Explain the loan activities of Banks.
(i)Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. This is kept as provision to pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money from the bank on any given day.
(ii)Since, on any particular day, only some of its many depositors come to withdraw cash, the bank is able to manage with this cash.
(iii)Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities.
(iv)Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people. In this way, banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers).
(v)Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits. The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Describe why deposits are called demand deposits.
Banks accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount as interest. People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require.
Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Answer the questions that follow:
(i)Write the modern forms of money.
(ii)Name the organisation which issue currency notes in India on behalf of the central government.
(iii)Describe debt trap. Mention any two factors responsible for the debt trap.
(i)Paper notes, coins and demand deposits are the modern forms money.
(ii) The Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
(iii) It is situation which pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.
Factors:
(i) Failure of crops.
(ii) Using credit for non-productive purposes.
Write any three limitations of the barter system.
The limitations of the barter system:
(i)Lack of Double Coincidence of Wants: Barter system can work only when both buyer and seller are ready to exchange each other’s goods.
(ii)Lack of Common Measure of Value: In the barter system, all commodities are not of equal value and there is no common measure (unit) of value of goods and services, in which exchange ratios can be expressed.
(iii)Lack of Standard of Deferred Payment: The borrower may not be able to arrange goods of exactly same quality at the time of repayment.
Write the advantages of money.
The advantages of money:
(i)Removes the coincidence of wants.
(ii)Takes less storage space and is easier to carry.
(iii)Liquidity of currency is easier.
Discuss the advantages of Self Help Group?
The advantages of Self Help Group:
(i)The SHGs help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(ii)They can get timely loans for a variety of purposes and at a reasonable interest rate. Moreover, SHGs are the building blocks of organisation of the rural poor.
(iii)Not only does it help women to become financially self-reliant, the regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc
Explain the working of Self Help Group.
(i)A typical SHG has 15-20 members, usually belonging to one neighbourhood, who meet and save regularly.
(ii)Saving per member varies from Rs 25 to Rs 100 or more, depending on the ability of the people to save. Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
(iii)The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the moneylender charges. After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank.
(iv)Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create selfemployment opportunities for the members.
(v)Most of the important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members. The group decides as regards the loans to be granted — the purpose, amount, interest to be charged, repayment schedule etc. Also, it is the group which is responsible for the repayment of the loan.
Write the advantages of depositing money in the banks.
The advantages:
(i) People can earn interest on the deposited money.
(ii) People have the provisions to withdraw the money as and when they require.
(iii) People can also make payments through cheques.
Of all the loans taken by urban households in 2010, what percentage was formal and what percentage was informal?
|
Nature of Household |
Informal Sources of Credit |
Formal Sources of Credit |
|
1 Poor households |
85% |
15% |
|
2. Households with few assets |
53% |
47% |
|
3. Well-off households |
28% |
72% |
|
4. Rich households |
90% |
10% |
Read the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
Sources of Credit for Rural households in India in 2003
(i)Which are the two major sources of credit for rural households in India?
(ii) Which one of them is the most dominant source of credit for rural households?
(iii) Why is it the most dominant source of credit?
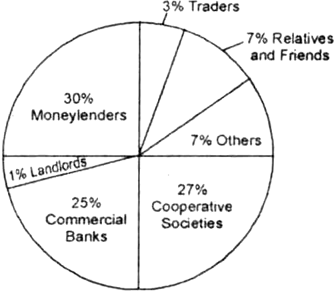
(i) Moneylenders and cooperative societies.
(ii) Moneylenders.
(iii) It is because, small farmers are poor, semi-literate or illiterate and cannot fulfil the conditions of collaterals.
Mention the two froms of modern money. Why are they considered as money?
Two forms of modern money are:
(i) Paper notes
(ii) Coins
They are considered as money because they are authorised by the government of the country.
'Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the development'. Explain.
Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development:
(i)Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
(ii)Hence, borrowers have less income left for themselves.
(iii)In certain cases, the high interest rate for borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower.
(iv)This could lead to increasing debt and debt trap.
(v)Also, people who might wish to start an enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing.
Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
We need to expand formal sources of credit in India for the reasons mentioned below:
(i) To reduce dependence on informal sources of credit because the latter charge high interest rates and do not benefit the borrower much.
(ii) Cheap and affordable credit is essential for country’s development.
(iii) Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers. Thus, it is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words
The basic behind the SHGs is to provide a financial resource for the poor through organizing the rural poor especially women, into small Self Help Groups. They also provide timely loans at a responsible interest rate without collateral.
The main objectives of the SHGs are:
(i) To organize rural poor especially women into small Self Help Groups.
(ii) To collect savings of their members.
(iii) To provide loans without collateral.
(iv) To provide timely loans for a variety of purposes.
(v) To provide loans at responsible rate of interest and easy terms.
(vi) Provide platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such education, health, nutrition, domestic violence etc.
What are the reasons why the banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers?
The banks might not be willing to lend certain borrowers for the following reasons:
(i) Banks require proper documents and collateral as security against loans. Some persons fail to meet these requirements.
(ii) The borrowers who have not repaid previous loans, the banks might not be willing to lend them further.
(iii) The banks might not be willing to lend those entrepreneurs who are going to invest in the business with high risks.
What is the meaning of 'barter system'?
The system in which goods are directly exchanged without the use of money.
Sponsor Area
Which one of the following is a formal source of credit?
-
Traders
-
Cooperative societies
-
Money-lenders
-
Friends and relatives
B.
Cooperative societies
Which one of the following is the appropriate meaning of collateral?
-
It is the sum total of money borrowed from banks
-
The amount borrowed from friends
-
It is an asset of the borrower used as guarantee to a lender
-
The amount invested in a business
C.
It is an asset of the borrower used as guarantee to a lender
How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants? Explain with an example.
In an economy where money is in use, money by providing the crucial intermediate step eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants. It is no longer n necessary for the shoe manufacturer to look for a farmer who will buy his shoes and the same time sell him wheat. All he has to do is find a buyer for his shoes. Once he has exchanged his shoes for money, he can purchase wheat or any other commodity in the market. Since money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called a medium of exchange.
How is money used as a medium of exchange? Explain with examples.
Money acts as a medium of exchange in the ways mentioned below:
(i) Solves the problem of double co-incidence of wants
(ii) Acts as an intermediate in exchange process
(iii) Has a store value
What is money? Why is modern money currency accepted as a medium of exchange?
Money is that which acts as an intermediate in the exchange process.
The reasons for accepting modern money currency as a medium of exchange-
(i) It is authorised by the government of the country.
(ii) It is a unit of account.
(iii) It has a store value.
Why is cheap and affordable credit important for the country’s development? Explain three reasons.
The reasons:
(i) Cheap and affordable credit leads to higher incomes and encourage people to invest in agriculture, engage in business and set up small scale industries.
(ii) Cheap credit reduces the dependence on informal sources.
(iii) Affordable credit also ends the cycle of debt trap and lead to sustainable economic activity.
Why do banks keep a small proportion of the deposits as cash with themselves?
A. To extend loan to the poor.
B. To extend loan facility.
C. To pay salary to their staff.
D. To pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money.
D. To pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money.
Why are most of the poor households deprived from the formal sector of loans?
Poor households are deprived of the formal sector of loans because they lack proper documents and collateral such as house, livestock or any other property as a guarantee to obtain a bank loan.
How can the formal sector loans be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers? Suggest any five measures.
The formal sector credit in India includes loans from banks and cooperatives. RBI supervises their functions of providing loans. These formal sector credits can be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers through the following way:
i. Formal sector credit needs to be expanded in India so as to save people and especially poor farmers and workers from exploitation of the informal sector credit.
ii. Provide credit at a reasonable rate of interest to fulfil various needs of the people by providing cheap and affordable credit.
iii. This credit can be distributed equally which helps in benefiting the poor. This can help in promoting agricultural activities and small-scale industries.
iv. The absence of collateral and documentation with rural borrowers would ease the formalities to obtain credit from the formal sector. Provide flexible loans in terms of
timelines, interest rates and procedural requirements to rural borrowers.
v. Awareness among rural borrowers against the exploitation of informal sector credit facilities. The need to keep them aware regarding the high rate of interest and debt traps of moneylenders.
How does money act as a medium of exchange?
By providing the crucial intermediate step that eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants.
Why is modern currency accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own? Find out the reason.
The reasons:
i. It is authorised by the government.
ii. The cuurency notes in India is issued by Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the central central government.
iii. The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
How do banks play an important role in the economy of India? Explain.
The role of banks in an economy of India:
(i) Deposits - Banks accepts the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount as interest. People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
(ii) Loans - Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.
(iii) Credits - A large number of transaction in our day- to-day activities involve credits in some form or the other. Credit, loans refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, good or services in return for the promise of future payment. Credit, therefore plays a vital and positive role.
What are the two forms of modern currency?
The two forms of modern currency are paper notes and coins.
'Money has made transactions easy.' Justify.
In an economy where money is in use, money by providing the crucial intermediate step eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants. It is no longer n necessary for the shoe manufacturer to look for a farmer who will buy his shoes and the same time sell him wheat. All he has to do is find a buyer for his shoes. Once he has exchanged his shoes for money, he can purchase wheat or any other commodity in the market. Since money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called a medium of exchange.
Which one of the following is not a feature of money?
-
Medium of exchange
-
Lack of divisibility
-
A store of value
-
A unit of account
B.
Lack of divisibility
Explain any four terms of credit with examples.
Four terms of credit are-
(i) Interest rate- Every loan agreement specifies an interest rate which the borrower must pay to the lender along with the repayment of the principal.
(ii) Collateral- It is an asset that the borrower owns such as land, building, vehicle, live stocks deposits with the banks and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
(iii) Documentation-It is related to identification such as employment records and salary.
(iv) Mode of repayment- This refers to the manner in which loan would be repaid.
Which one of the following refers to investment?
-
The money spent on religious ceremonies
-
The money spent on social customs
-
The money spent to buy assets such as land
-
The money spent on household goods
C.
The money spent to buy assets such as land
Explain with an example, how credit plays a vital and positive role for development.
The role of credits-
(i) Credits help to increase earnings and therefore the persons is better off than before.
(ii) Peoples grow crop, do business and set up small-scale industries.
(iii) People set up new industries and trade in goods.
Which government body supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India? Explain its functioning.
The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India. It functions are-
(i) The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
(ii) It sees that banks lend not only to profit-making businesses and traders but also small cultivators, small-scale businesses and small borrowers.
(iii) Banks have to periodically submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom and at what interest rates.
Highlight the inherent problem in double coincidence of wants.
Double coincidence of wants means that when someone wants to exchange his goods with another person the latter must also be willing to exchange his good with the first person.
'Banks are efficient medium of exchange.' Support the statement with arguments.
People deposit their money with banks by opening a bank account. Banks keep the money safe and provides interest on the deposited amount. The deposited money can be withdrawn from banks as when required on demand. Bank deposits also facilitate easy transfer of money through cheques, demand drafts and internet banking.
Banks keep only 15% of their total cash deposits to meet the everyday withdrawal demands of their customers. Major portion of the remaining deposits are used to give loans to people at specific rate of interest.
' 'Self Help Groups' help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral.' Examine the statement.
Self help groups (SHG) have helped borrowers to borrow money without collateral in the following ways :
(i.) Self help groups have organised rural poor more so women in collecting their money and in extending loans to its members.
(ii.) SHG charge less rate of interest as compared with any other form of rural banking or even those charged by moneylenders.
(iii.) These groups gradually can seek loans from the bank so as to create employment opportunities for its members.
(iv.) Banks have been extending loans to these groups to meet their needs like buying fertilizers, seeds, raw materials etc.
(v.) These SHG have emerged as building blocks for the rural poor as it is the group as a whole which is responsible for the repayment of the loan. In case, of non repayment it is taken up in a serious manner by the group members.
How is the maximum retail price printed on packets beneficial for you?
It is very important as it sets a limit beyond which the sellers cannot sell the product. otherwise they would easily exploit the consumers.
How does the use of money make it easier to exchange things? Give an example.
Money acts as medium of exchange as it facilitates exchange through a common medium i.e. currency. With money as a medium, the two components of a transaction namely, sale and purchase can be easily separated.
Explain any thee loan activities of banks in India.
1. Banks provide loans for various economic activities
2. Banks keep only a small propotions of the deposits with them as cash
3. These deposits are used to meet the loan requirement.Why are most of the poor households deprived from the formal sector of loans?
Poor households even now prefer to get credit from informal means rather than the formal sector due to the following reasons:-
Relatives and money lenders are easily accessible. Still in India several rural areas do not have a bank closeby.
Norms or rules for lending out money is much strict in formal sector as compared to the informal sector.
How can the formal sector loans be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers? Suggest any five measures.
The formal sector loans can be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers in the following ways:-
- Formal sector credit includes loans from banks and cooperatives which are regulated by RBI.
- The rate of interest in formal sector is very low compared to informal sector.
- Informal sector tries to exploit and cheat the poor people by charging high rate of interest and unreasonable terms of credit, but on the other hand, banks encourage the poor people to come together as Self Help Groups (SHGs) to inculcate into them the habit of savings and get easy loans from the banks.
- The difficult terms and conditions underlying the loans should be relaxed so that the poor do not resort to private money lenders who often charge exorbitant rate of interest.
‘Cheap and affordable credit is essential for poor households both in rural and urban areas’. In the light of the above statement, explain the social and economic values attached to it.
Credit means loans. It refers to a sort of agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future repayment.
i. Cheap and affordable credit for poor households is essential for a country’s economic development and material growth. It is required for a variety of important economic activities such as big or small investments, setting up of businesses and buying of cars and houses.
ii. In the rural hinterland, credit helps in the development of agriculture by helping farmers purchase seeds, fertilisers, pesticides and farming machinery.
iii. Some people may also avail of credit to provide for marriage or illness.
What are the two categories of sources of credit? Mention four features of each.
The two categories of credit sources are ‘formal’ and ‘informal’.
The following are four features of formal sources of credit:
i. The most important in this category are banks and cooperative societies. Loans can be obtained from these.
ii. The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of these formal sources. Informal sources of credit:
i. In the informal field, money can be borrowed from a person, friend, relative, moneylender, trader and employer.
ii. There is no regulatory or supervisory body in this sector.
iii. Loans from this sector of credit do not require any collateral.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





