Contemporary India Chapter 7 Lifelines Of National Economy
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Social+science Contemporary India
State any three merits of roadways.
Three merits of roadways are:
(i) Roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
(ii) Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
(iii) Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
Where and why is rail transport the most convenient means of transportation?
Railway transport is the most convenient means of transportation in northern plains.
The northern plains with their vast level land, high population density and rich agricultural resources provided the most favourable condition for their growth.
What is the significance of the border roads?
The significance of Border Roads:
(i) These are very important for strategic point of view in the northern and north eastern border areas of our country.
(ii) These roads have increased accessibility in areas of difficult terrain.
(iii) These roads have helped in the economic development of northern and north eastern areas of India.
What is meant by trade? What is the difference between international and local trade?
The exchange of goods among people, states and countries is referred to as trade.
Trade between two countries is called international trade whereas trade between two places within a country is called local trade. This trade is carried on in cities, towns and villages.
Why are the means of transportation and communication called the lifelines of a nation and its economy?
Means of transport and communication are called the lifelines of a nation for the following reasons:
(i)Roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography and can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
(ii)Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India. Railways also make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
(iii)Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods. It is a fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
(iv)Airways can cover very difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense forests and also long oceanic stretches with great ease.
(v)Long distance communication is far easier without physical movement of the communicator or receiver.
Write a note on the changing nature of the international trade in the last fifteen years.
(i)Exchange of commodities and goods have been superseded by the exchange of information and knowledge.
(ii)India has emerged as a software giant at the international level and it is earning large foreign exchange through the export of information technology.
(iii)India has trade relations with all the major trading blocks and all geographical regions of the world. Among the commodities in export the share of agriculture and allied products has been 9.9 per cent, ores and minerals 4.0%, gems and jewellery 14.7 per cent, petroleum products (including coal) 16.8 per cent in 2010-11.
(iv)The commodities imported to India include petroleum and petroleum products (28.6 per cent), pearls and precious stones (9.4 per cent), chemicals (5.2 per cent), coal, coke and briquettes (2.7 per cent), machinery (6.4 per cent) in 2010-11.
(v)Bulk imports as a group registered a growth accounting for 28.2 per cent of total imports. This group includes fertilizers (3.4 per cent), cereals (14.3 per cent), edible oils (17.4 per cent) and newsprint (Paper board manufacture and newsprint 40.3 per cent) in 2010-11.
Sponsor Area
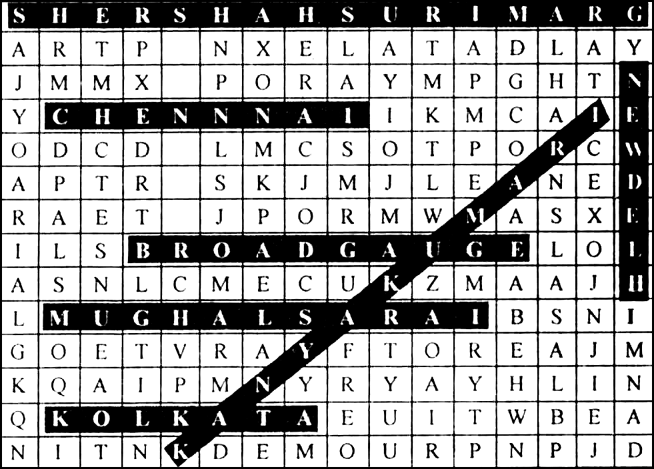
Start your search vertically, horizontally or diagonally and reach various destinations across the country.
|
S |
H |
E |
R |
S |
H |
A |
H |
S |
U |
R |
1 |
M |
A |
R |
G |
|
A |
R |
T |
P |
R |
N |
X |
E |
L. |
A |
T |
A |
D |
L |
A |
Y |
|
J |
M |
M |
X |
1 |
P |
O |
R |
A |
Y |
M |
P |
G |
H |
T |
N |
|
Y |
C |
H |
E |
N |
N |
N |
A |
I |
1 |
K |
M |
C |
A |
I |
E |
|
O |
D |
C |
D |
A |
L |
M |
C |
S |
O |
T |
P |
O |
R |
C |
W |
|
A |
P |
T |
R |
G |
S |
K |
J |
M |
J |
L |
E |
A |
E |
D |
|
|
R |
A |
E |
T |
A |
J |
P |
O |
R |
M |
W |
M |
A |
S |
X |
E |
|
1 |
L |
S |
B |
R |
O |
A |
D |
G |
A |
U |
G |
E |
L |
O |
L |
|
A |
S |
N |
L |
C |
M |
E |
C |
U |
K |
Z |
M |
A |
A |
J |
H |
|
L |
M |
U |
G |
H |
A |
L |
S |
A |
R |
A |
I |
B |
S |
N |
I |
|
G |
O |
E |
T |
V |
R |
A |
Y |
F |
T |
O |
R |
E |
A |
J |
M |
|
K |
Q |
A |
1 |
P |
M |
N |
Y |
R |
Y |
A |
Y |
H |
L |
I |
N |
|
Q |
K |
O |
L |
K |
A |
T |
A |
E |
U |
I |
T |
W |
B |
E |
A |
|
N |
I |
T |
N |
K |
D |
E |
M |
O |
U |
R |
P |
N |
P |
J |
D |
1. Srinagar, 2. Shershah Suri Marg, 3. Mughal Sarai, 4. Chennai, 5. Broad Gauge, 6. Kanyakumari, 7. Kolkata, 8. New Delhi.
Who build and maintain the National Highways?
State Government
National Government
Village Panchayat
District Level Governing Body
B.
National Government
PWD repairs and builds roads in
States and U.Ts.
Districts
Big Cities
Small Cities
A.
States and U.Ts.
National Highway No. 8 connects
Delhi—Mumbai
Delhi—Bengaluru
Chennai—Kolkata
Mumbai—Chennai
A.
Delhi—Mumbai
Which one of the following states has the lowest road density?
Rajasthan
Jammu and Kashmir
Arunachal Pradesh
Kerala
B.
Jammu and Kashmir
Sponsor Area
S.T.D. refers to ___________ .
Subscriber Trunk Dialling
Subscriber Telephone Dialling
Social Telephone Distributor
Speed Telephone Dialling
A.
Subscriber Trunk Dialling
What is the name given to the International Airport at Kolkata?
Jawaharlal Nehru
Indira Gandhi
Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose
Rajiv Gandhi
C.
Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose
Which one of the following is a subsidiary port of Mumbai?
Jawaharlal Nehru
Haldia
Tuticorin
Vishakhapatnam
A.
Jawaharlal Nehru
North-South Corridor connects the following
Srinagar—Kanyakumari
Delhi—Chennai
Patna—Kochi
Shimla—Bengaluru
A.
Srinagar—Kanyakumari
Where is the new port of Haldia located?
Near Mumbai
Near Kandla
Near Kolkata
Near Chennai
C.
Near Kolkata
The authority that certifies both Indian as well as foreign films is the ___________ .
Central Board of Film Certification
Prasar Bharti
National Film Division
National Film Institute
A.
Central Board of Film Certification
Which of the following statements is not correct about Vishakhapatnam port?
It is the deepest landlocked port
It is a well protected port
It was developed to ease volume at the Chennai port
It was originally conceived as an outlet for iron-ore export
C.
It was developed to ease volume at the Chennai port
Write the diffrent modes of transport in India?
Different modes of transport are:
(i) Railways
(ii) Roadways
(iii) Airways
(iv) Waterways
(v) Pipelines
Make the classification of various means of transport.
Transport are classified into three types:
(i) Land
(ii) Water
(iii) Air
Land transport are further classified into:
(a) Roadways
(b) Railways
(c) Pipelines
Water transport are classified into :
(a) Inland
(b) Overseas
Air transport are divided into:
(a) Domestic Airways—Public Undertakings and Private Airlines.
(b) International Airways.
Find out places linked by the National Highway No. 2 and 3.
The places linked by the National Highways:
National Highway No. 2: It is a part of Golden Quadrilateral Super Highway and links cities like Aurangabad, Varanasi, Allahabad, Kanpur, Agra and Delhi.
National Highway No. 3: It is a National Highway and links cities like Mumbai, Nasik, Indore, Biora, Shivpuri and Gwalior.
Sponsor Area
Differentiate between personal and mass communication.
|
Personal Communication |
Mass Communication |
|
(i) It is the communication in between two or more persons at a personal level. (ii) It is of two types-oral and written, e.g. telephone, letters. |
(i)Mass communication provides entertainment and creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies. (ii) It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books and films. |
Mention the characteristics of Kandla sea port.
(i)Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port developed soon after Independence to ease the volume of trade on the Mumbai port, in the wake of loss of Karachi port to Pakistan after the Partition.
(ii)Kandla is a tidal port.
(iii)It caters to the convenient handling of exports and imports of highly productive granary and industrial belt stretching across the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Discuss the major sea ports of southern India with their characteristics.
The major seaports of southern India are discussed below:
(i) Kochi Port: It is the extreme south-western port. It is located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbour.
(ii) Tuticorin Port (Tamil Nadu): It has a natural harbour and rich hinterland. It has a flourishing trade handling of a large variety of cargoes to even our neighbouring countries like Sri Lanka, Maldives, etc. and the coastal regions of India.
(iii) Chennai Port: It is one of the oldest artificial ports of lndia. It is the second port next to Mumbai in terms of the volume of trade and cargo.
(iv) Vishakhapatnam Port: It is the deepest landlocked and well-protected port.
Describe the sea ports of eastern India with reference to their features and importance.
The seaports of eastern India are described below:
(i) Paradip Port, Orissa: It specialises in the export of iron-ore.
(ii) Kolkata Port:
(a) It is an inland riverine port.
(b) It serves as a very large and rich hinterland of Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
(c) It is a tidal port and, therefore, requires constant dredging of Hooghly.
(iii) Haldia Port: It was developed as subsiadiary port in order to relieve growing pressure on the Kolkata port.
Explain the importance of pipeline in India.
(i)Pipeline transport network is a new arrival on the transportation map of India. In the past, these were used to transport water to cities and industries.
(ii)Now, these are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big thermal power plants.
(iii)Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into slurry.
(iv)The far inland locations of refineries like Barauni, Mathura, Panipat and gas based fertilizer plants could be thought of only because of pipelines.
(v)Initial cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs are minimal. It rules out trans-shipment losses or delays.
Why the railways are sparsely distributed in Himalayan mountainous regions?
(i)high relief
(ii)sparse population
(iii)lack of economic opportunities
Explain the three important networks of pipeline transportation in the country.
(i)From oil field in upper Assam to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh), via Guwahati, Barauni and Allahabad. It has branches from Barauni to Haldia, via Rajbandh, Rajbandh to Maurigram and Guwahati to Siliguri.
(ii)From Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar in Punjab, via Viramgam, Mathura, Delhi and Sonipat. It has branches to connect Koyali (near Vadodara, Gujarat) Chakshu and other places.
(iii)Gas pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects Jagdishpur in Uttar Pradesh, via Vijaipur in Madhya Pradesh. It has branches to Kota in Rajasthan, Shahajahanpur, Babrala and other places in Uttar Pradesh.
Differentiate between National Highways and State Highways.
|
National Highways |
State Highways |
|
1. National Highways link extreme parts of the country. 2. These are the primary road systems and are laid and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD). |
1. Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as State Highways 2. These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (SPWD) in state and Union Territories. |
Mention the problems suffered by the Indian railways?
(i)Many passengers travel without tickets.
(ii)Thefts and damaging of railway property has not yet stopped completely.
(iii)People stop the trains, pull the chain unnecessarily which causes heavy damage to the railway.
Why there is growing importance of road transport vis-à-vis rail transport?
(i) Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
(ii) Roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
(iii) Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
(iv) Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
(v) It also provides door-to-door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower and used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
Write the point connected by the two corridors.
Explain the different system of communications in India.
(i)India has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia. There is a uniform rate of STD facilities all over India.
(ii)All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country.
(iii)Doordarshan, the national television channel of India, is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world. It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
(iv)India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually. They are of different types depending upon their periodicity. Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects.
(v)India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short films; video feature films and video short films.
Which part of the country has special provisions for air services and why?
It is because the north-eastern part of the country is marked with the presence of big rivers, dissected relief, dense forests and frequent floods and international frontiers.
Write the name of international airports in Delhi and Kolkata. Mention the advantages of airways.
The name:
International Airport in Delhi—Indira Gandhi International Airport.
International Airport in Kolkata—Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport.
The advantages of airways:
(i)The air travel is the fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport.
(ii)It can cover very difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense forests and also long oceanic stretches with great ease.
Write a note on National Highways in India.
National Highways:
(i) National Highways link extreme parts of the country.
(ii)These are the primary road systems and are laid and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD). A number of major National Highways run in North-South and East-West directions.
(iii)The historical Sher-Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway No.1, between Delhi and Amritsar.
Describe the significance of Radio and Television in India.
(i)All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country.
(ii)Doordarshan, the national television channel of India, is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world. It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports, etc. for people of different age groups
'Transport, communication and trade are complimentary to each other'. Explain.
Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication system.
Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
Mention the three types of railway gauges.
Three types of railway gauges:
(i) Broad Gauge
(ii) Metre Gauge
(iii) Narrow Gauge
Describe the waterways which have been declared as the National Waterways by the Government.
(i)The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km)-N.W. No.1
(ii)The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km)-N.W. No.2
(iii)The West-Coast Canal in Kerala (Kottapurma-Kollam, Udyogamandal and Champakkara canals-205 km) – N.W. No.3
(iv)Specified stretches of Godavari and Krishna rivers along with Kakinada Puducherry stretch of canals (1078 km) – N.W. No.4
(v)Specified stretches of river Brahmani along with Matai river, delta channels of Mahanadi and Brahmani rivers and East Coast Canal (588 km) – N.W. No.5
Explain the various types of roads in India.
The various types of roads in India are explained below:
(i) Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways: It is a network of six lane super highways including North-South Corridor and East-West Corridor. It is a major road development project that connects Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai and Delhi. National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) is implementing this gigantic project.
(ii)National Highways: National Highways link extreme parts of the country. These are the primary road systems and are laid and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD).
(iii)State Highways: Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as State Highways. These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (PWD) in State and Union Territories.
(iv)District Roads: These roads connect the district headquarters with other places of the district. These roads are maintained by the Zila Parishad.
(v)Border Roads: Border Roads Organisation, a Government of India undertaking constructs and maintains roads in the bordering areas of the country. These roads have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain and have helped in the economic development of these area.
State the significance of railways in India.
(i)Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
(ii)Railways also make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
(iii)Apart from an important means of transport the Indian Railways have been a great integrating force for more than 150 years.
(iv)Railways in India bind the economic life of the country as well as accelerate the development of the industry and agriculture.
(v)The Indian Railway have a network of 7,133 stations spread over a route length of 64,460 km with a fleet of 9,213 locomotives, 53,220 passenger service vehicles, 6,493 other coach vehicles and 2,29,381 wagons.
Differentiate between transport and communication.
|
Transport |
Communication |
|
1. Means of transport carry people and goods from one place to another within the shortest time. 2. The major modes of transport are the railways, the roadways, waterways, the airways and the pipelines. 3. The means of transport make possible interaction between people, increase commerce and trade and maintain supply and demand forces of the market in balanced state. |
1. Means of communication carry messages from people in a place to people in another place. Physical movement is not required. 2. The means of communication are posts and telegraph, telephone, fax, teleprinters, print media, radio, television, wireless and satellite. 3. Means of communication create mass awakening towards world happenings. |
Expalin tourism as a trade in India.
Tourism in India has grown substantially over the last three decades.
(i)More than 15 million people are directly engaged in the tourism industry. Tourism also promotes national integration, provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
(ii)It also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage.
(iii)Foreign tourists visit India for heritage tourism, eco tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, medical tourism and business tourism.
(iv)Rajasthan, Goa, Jammu and Kashmir and temple towns of south India are important destination of foreign tourists in India.
(v)There is a vast potential for development of tourism in the north-eastern states and the interior parts of Himalayas, but to strategic reasons these have not been encouraged so far.
What is meant by density of roads? Mention the problems faced by road transportation in India.
Road transportation in India faces the following problems:
(i)Keeping in view the volume of traffic and passengers, the road network is inadequate.
(ii)About half of the roads are unmetalled and this limits their usage during the rainy season.
(iii)The National Highways are inadequate too.
(iv)Moreover, the roadways are highly congested in cities and most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
Write the commodities imported to India.
How the distribution pattern of the Railway network in the country has been largely influenced by physiographic, economic and administrative factors?
The distribution pattern of the Railway network in the country has been largely influenced by physiographic, economic and administrative factors:
(i)The northern plains with their vast level land, high population density and rich agricultural resources provided the most favourable condition for their growth.
(ii)However, a large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges across their wide beds posed some obstacles.
(iii)In the hilly terrains of the peninsular region, railway tracts are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels.
(iv)The Himalayan mountainous regions too are unfavourable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
(v)Likewise, it was difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plain of western Rajasthan, swamps of Gujarat, forested tracks of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Jharkhand.
Name the current zones of Indian Railways with their headquarters.
Kindly locate the headquarters of Indian Railway zones on the map of India.
|
Current Indian Railway Zones |
Headquarters |
Current Indian Railway Zones |
Headquarters |
|
1. Northern Railway 2. North Central Railway 3. North East Railway 4. Eastern Central Railway 5. North East Frontier Railway 6. Eastern Railways 7. South East Railway 8. South East Central Railway |
Delhi Allahabad Gorakhpur Hazipur Guwahati Kolkata Kolkata Bilaspur |
9. East Coast Railway 10. Southern Railway 11. South Central Railway 12. South West Railway 13. Central Railway 14. Western Railway 15. West Central Railway 16. North West Railway |
Bhubaneshwar Chennai Secunderabad Hubli Mumbai Mumbai Jabalpur Jaipur |

'Efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for fast development'. Explain.
(i)Goods and services do not move from supply locales to demand locales on their own. The movement of these goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations necessitates the need for transport.
(ii)Some people are engaged in facilitating these movements. These are known to be traders who make the products come to the consumers by transportation.
(iii)Thus, the pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movement over space.
Which one of the following regions is associated with Konkan railway?
North Eastern
Eastern Coastal Plains
Sahyadri and the Western Coast
Central highlands and Northern plains
C.
Sahyadri and the Western Coast
Expalin the features of two major means of mass communication in India.
(i)All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country.
(ii)Doordarshan, the national television channel of India, is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world. It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports, etc. for people of different age groups
'International trade is considered the economic barometer for a country'. Discuss.
(i)Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity.
(ii)As the resources are space bound, no country can survive without international trade. Export and import are the components of trade.
(iii)The balance of trade of a country is the difference between its export and import. When the value of export exceeds the value of imports, it is called a favourable balance of trade. On the contrary, if the value of imports exceeds the value of exports, it is termed as unfavourable balance of trade.
Highways are shown on the given political outline map of lndia. Identify the Highways and write the names of terminal cities marked A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H.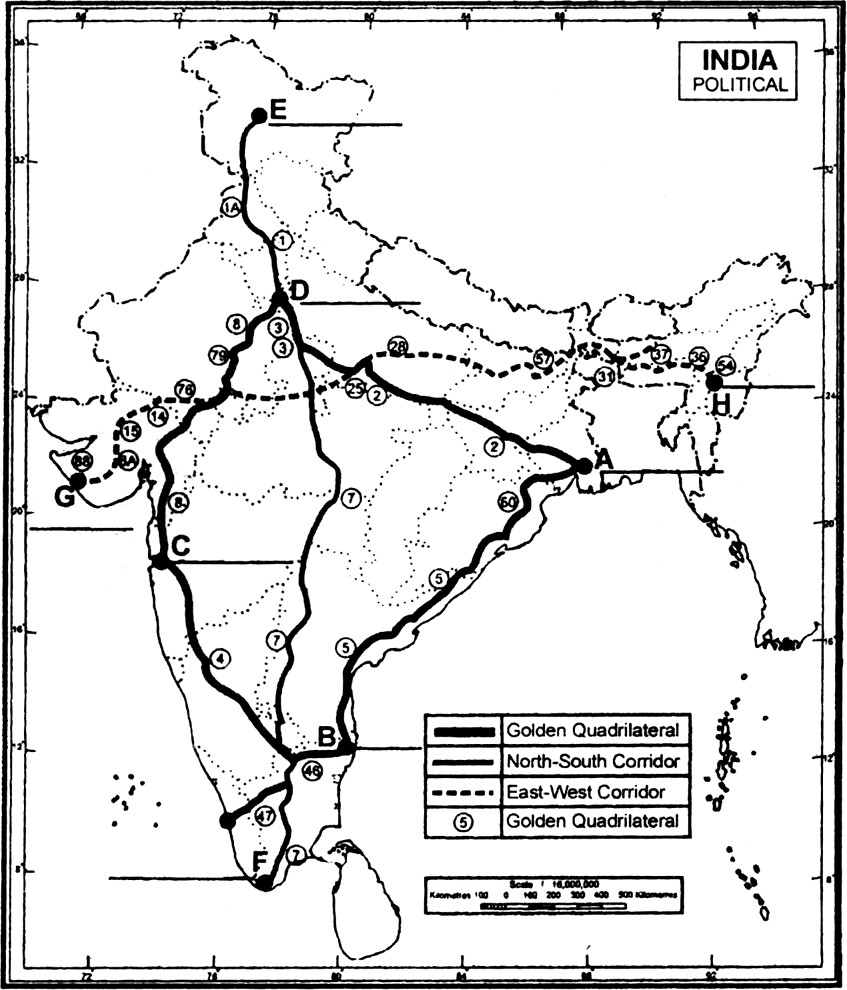
|
A—Kolkata |
B—Chennai |
|
C—Mumbai |
D—Delhi |
|
E—Srinagar |
F—Kannyakumari |
|
G—Porbandar |
H—Silchar |
Read the map given below, showing national highway development project and answer the questions that follow:
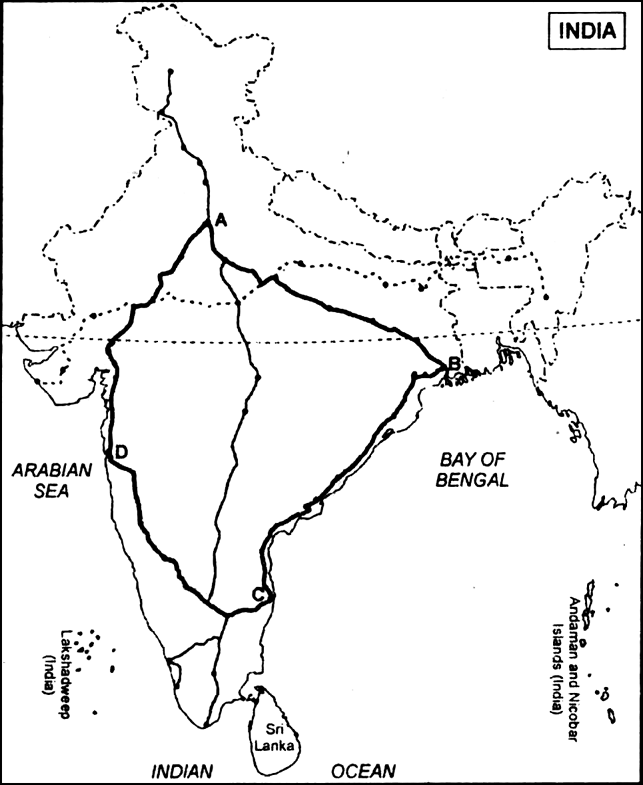
(i) Name the Expressway National Highway that will join A, B, C and D stations.
(ii) Write the city related to C and D stations.
(iii) What is the major objective of these Super Highways?
(i) Golden Quadrilateral.
(ii) C—Chennai, D—Mumbai.
(iii)The major objective of these Super Highways is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India.
Sponsor Area
Read the given map and answer the questions that follow: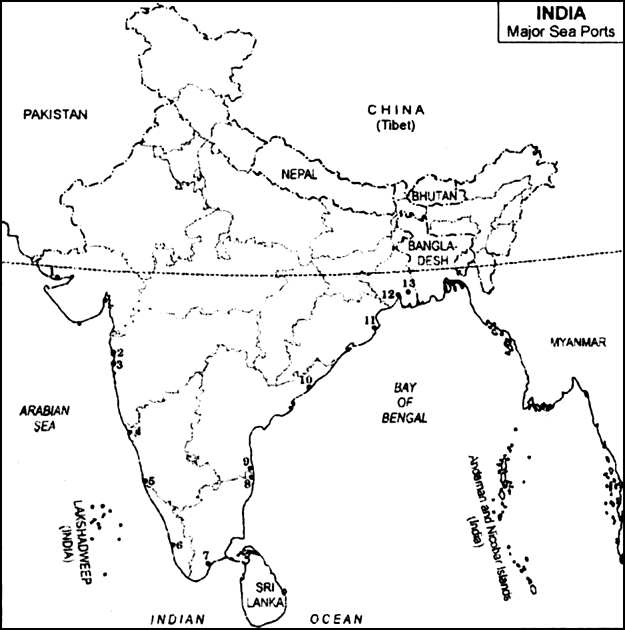
(i) Name the sea ports which have been developed to ease the volume of trade on each of the following ports:
(a)Mumbai
(b)Kolkata
(ii) Write against each serial number, the name of major sea ports and the states in which it is located.
(i) The sea ports which have been developed to ease the volume of trade:
(a) Jawahar Lal Nehru Port was developed to reduce pressure on Mumbai.
(b) Haldia Port was developed to reduce pressure on Kolkata.
(ii)
|
Major Sea Ports |
States |
Ma jor Sea Ports |
States |
|
1. Kandla 2. Mumbai 3. Jawahar Lal Nehru 4. Marmagao 5. New Mangalore 6. Kochi |
Gujarat Maharashtra Maharashtra Goa Karnataka Kerala |
7. Tuticorin 8. Chennai 9. Ennore 10. Vishakhapatnam 11. Paradip 12. Haldia 13. Kolkata |
Tamil Nadu Tamil Nadu Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh Orissa West Bengal West Bengal |
Classify communication services into two categories. Explain main features of each.
Communication services can be classified into two categories—personal communication and mass communication.
i. Personal communication: It refers to communication between two or more people or among groups of people. Personal communication may take place through various means such as mobile, letters and social networking sites.
ii. Mass Communication: Mass communication is a means to provide people with information on current affairs, to create awareness among them and to entertain them. Some means of mass communication are radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books and films.
“Roadways still have an edge over railways in India.” Support the statement with arguments.
Roadways still have an edge over railways in India for the following reasons:
i. It is because it is still the most common means of transport in the country.
ii. The construction costs of roadways are much lower than the construction costs of railways.
iii. While it is difficult to lay down railway lines in hilly tracts or mountainous regions, roads can be easily built in dissecting tracts of land.
iv. Roads today connect even the smallest village to a large town. Railways have yet not been able to connect villages to cities.
v. Roadways are economical in transporting few people and a small quantity of goods over short distances. Roads provide a link between various railway stations.
Describe any three features of waterways in India.
The three features of waterways in India:
i. They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
ii. They are fuel efficient and environment-friendly means of transport.
iii. Around 95% of the country’s trade volume is moved by sea.
Why was Jawaharlal Nehru port developed?
Jawaharlal Nehru Port was developed with a view to decongest the Mumbai port.
Describe three major problems faced by the road transport in India.
The problems faced:
(i) The road network is inadequate, keeping in view the volume of traffic and passengers.
(ii) Roadways are highly congested in cities and most of the bridges and culverts are old or narrow.
(iii) About half of the roads are unmetalled and this limits their usage during the rainy season.
Why is a dense and efficient network of transport and communication a perequisite for the development of local, national and global trade of today? Give your opinion.
The opinions:
(i) This is necessary to carry raw materials to production centres and from manufacturing hubs to markets in as little time as possible to achieve efficiency, especially for perishable goods.
(ii) It enables goods to reach newer markets and allows people greater accessibility to goods and services. Efficient transport network enables markets to expand to hinterland.
(iii) Technology has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
'Road transport and Rail transport in India are not competitive but complementary to each other.' Justify the statement.
Mention any two inland waterways of India. Write three characteristics of each.
Two inland waterways of India are-
(i) The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri.
(ii) The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia
(A) Characteristics of Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri-
(i) The waterway is 891 km long.
(ii) It is also known as National Waterway No.2
(iii) It facilitates national security.
(B) Characteristics Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia-
(i) It is known as National Waterway No.1
(ii) It is 1620 km long.
(iii) It provides pilgrimage.
Why are efficient means of transport pre-requisites for the fast development of the country? Explain.
Efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for the fast development of the country because:
(a) Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
(b) Waterways are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
(c) Railways make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business and transportation of goods over longer distances.
Explain any three reasons for dense railway network in the North Indian Plains.
The reasons for the dense railway network in the Northern Indian Plains are-
(i) Vast level land.
(ii) High population density.
(iii) Rich agricultural resources.
Mention any four merits and any two demerits of air transport.
The merits of air transport -
(i) Air travel provides the fastest, most comfortable mode of transport.
(ii) It can cover very difficult terrains like mountains, dreary deserts, dense forests and long oceanic stretches with great ease.
(iii) It provides services to inaccessible areas and hilly terrains like the north-eastern states and the interior parts of J&k, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
(iv) Air transport plays a vital role during natural and man-made calamities like floods, droughts, earthquakes and other disasters.
The demerits of air transport-
(i) It is not within the reach of common people.
(ii) It is limited to larger cities.
Name the river which is related to 'National Waterways' No. 1.
The Ganga river, between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km) - N.W. No. 1
Why do the movement of goods and services from one place to another require fast and efficient means of transport. Explain with examples.
Reasons for fast and efficient means of transport :
(i.) It is necessary to carry raw materials to production centers and from manufacturing hubs to markets in as little time as possible to achieve efficiency. This is particularly true for perishable goods.
(ii.) It enables goods to reach newer markets and allows people greater accessibility to goods and services. Efficient transport network enables markets to expand to hinterland.
(iii.) Communication opens new avenues of commerce. Modern communication tools like internet allow commercial transactions to take place over large distances, facilitating electronic commerce and banking across countries and contributing to integration of markets.
Evaluate any three features of 'Golden Quadrilateral' Super Highways.
The features of Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways:-
This have beenplanned to meet the requirement of a fast movement of traffic.
The govt. has launched a major road development project linking Delhi- Kolkata- Chennai- Mumbai and Delhi by 6- lane Super Highways..
The North-South corridor linking Srinagar and kanyakumari, and East-West corridor connecting Silcher (Assam) and Porbandar are parts of this project.
Classify communication services into two categories. Explain main features of each.
The communication service can be classified into two categories:-
(a.) Mass communication
- The sender and the receiver may be a person, group or the whole population.
- It provides entertainment as well as creates awareness among the masses.
- The means of mass communication are : television, internet, radio ,newspaper etc.
(b.) Personal communication
- The sender and the receiver is a person.
- It is a necessary communication between individuals as man is a social animal.
- Means of personal communication are : mobile, social network site's, letters etc.
'Roadways still have an edge over railways in India.' Support the statement with arguments.
Advantages of roadways are as follows:-
- The construction cost of roads is much lower as compared to railway lines.
- Roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
- Road transport is economical as it can transport less people and smaller amount of goods over short distances.
- Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport as they provide a link between railway stations, airports and sea ports.
How are means of transport and communication complementary to each other? Explain with three examples.
Means of transport and communication are complementary to each other in the following
three ways:
i. Transport and communication establish links between production centres and consumption centres and provide the links through which these two centres carry out trade.
ii. Such networks connect the remote pockets of the country with other parts. Hence, effective distribution of produced goods becomes possible.
iii. The movement of raw material becomes much more efficient if there are elaborate means of transport and communications available.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





