Contemporary India Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Social+science Contemporary India
What is manufacturing?
Production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw materials to more valuable products is called manufacturing. For instance, paper is manufactured from wood, sugar from sugarcane, iron and steel from iron-ore and aluminium from bauxite.
Name any three physical factors for the location of an industry.
The three physical factors for the location of an industry are:
(i) Availability of raw material.
(ii) Power
(iii) Labour
Name any three human factors for the location of an industry.
The three human factors for the location of an industry are:
(i) Labour
(ii) Capital
(iii) Transport and communication
What are basic industries? Give an example.
Basic industries are which supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods.
Examples: Iron and steel, copper smelting and aluminium smelting industries.
Name the important raw materials used in manufacturing of cement.
The important raw materials used in manufacturing of cement are:
(i) Limestone
(ii) Silica
(iii) Alumina
(iv) Gypsum
How are integrated steel plants different from mini steel plants? What problems does the industry face? What recent developments have led to a rise in the production capacity?
Differences between integrated steel plants and mini steel plants:
Mini steel plants are smaller, have electric furnaces, use steel scrap and sponge iron. They have re-rollers that use steel ingots as well. They produce mild and alloy steel of given specifications.
An integrated steel plant is large, handles everything in one complex – from putting together raw material to steel making, rolling and shaping.
The following problems are being faced by iron and steel industry:
(a) High costs and limited availability of coking coal
(b) Lower productivity of labour
(c) Irregular supply of energy
(d) Poor infrastructure.
Recent Developments:
Liberalisation and Foreign Direct Investment have given a boost to the industry with the efforts of private entrepreneurs.
How do industries pollute the environment?
Industries have increased pollution and degraded environment. Industries create four types of pollution as mentioned below:
(i) Water Pollution: Water pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and affluents discharged into rivers. The main culprits in this regard are paper, pulp, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries and electroplating industries that let out dyes, detergents, acids, salts and heavy metals like lead and mercury pesticides, fertilisers, synthetic chemicals with carbon, plastics and rubber, etc. into the water bodies.
(ii) Air Pollution: The smoke emitted by the industries pollute air and water badly. The smoke is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries and smelting plants. The burning of fossil fuels in big and small factories is a great cause of air pollution.
(iii) Noise Pollution: Industrial and construction activities, machinery, factory equipment, generators, saws and pneumatic and electric drills makes a lot of noise.
(iv) Thermal Pollution: Thermal pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
Discuss the steps to be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry.
The below mentioned steps should be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry:
(i) Minimising use water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages.
(ii) Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(iii) Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
(iv)Overdrawing of ground water reserves by industry where there is a threat to ground water resources also needs to be regulated legally.
(v)Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers.
Sponsor Area
Solve the puzzle by the following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
|
G |
G |
G |
P |
V |
A |
R |
A |
N |
A |
S |
I |
|
U |
O |
J |
I |
P |
G |
X |
K |
M |
Q |
W |
V |
|
K |
S |
U |
G |
A |
R |
C |
A |
N |
E |
E |
N |
|
O |
T |
T |
O |
N |
O |
Z |
V |
O |
P |
T |
L |
|
A |
U |
E |
L |
U |
B |
H |
I |
L |
A |
I |
U |
|
T |
K |
O |
C |
R |
A |
Q |
N |
T |
R |
L |
C |
|
E |
I |
R |
O |
N |
S |
T |
E |
E |
L |
S |
K |
|
E |
N |
A |
N |
O |
E |
P |
I |
T |
l |
R |
N |
|
G |
A |
N |
U |
J |
D |
R |
A |
G |
D |
T |
O |
|
N |
T |
A |
R |
P |
O |
A |
P |
U |
E |
P |
W |
|
A |
S |
N |
A |
E |
N |
J |
D |
I |
Y |
S |
K |
|
S |
M |
H |
V |
L |
I |
A |
J |
H |
S |
K |
G |
1. Textiles, sugar, vegetable oil and plantation industries deriving raw materials from agriculture are called.....
2. The basic raw material for sugar industry.
3. This fibre is also known as the‘Golden Fibre’.
4. Iron-ore, coking coal and limestone are the chief raw materials of this industry.
5. A public sector steel plant located in Chhattisgarh.
6. Railway diesel engines are manufactured in Uttar Pradesh at this place.

1. Agrobased, 2. Sugarcane, 3. Jute, 4. Iron and steel, 5. Bhilai, 6. Varanasi
Which one of the following statements is true about the manufacturing industries?
Manufacturing industries provide employment not only for agriculture, but for secondary and tertiary sectors also
Manufacturing industries reduce our dependency on agriculture
Manufacturing industries can only help in agriculture modernisation
Manufacturing industries create unemployment
A.
Manufacturing industries provide employment not only for agriculture, but for secondary and tertiary sectors also
On the basis of ownership industry can be classified as __________ , __________ , __________ and ___________.
Public sector, private sector, consumer industry, mineral based industry.
Public sector, private sector, joint sector, small scale industry
Public sector, private sector, joint sector, co-operative sector
Agro-based, mineral-based, small scale industry, private sector
C.
Public sector, private sector, joint sector, co-operative sector
Which state of India is famous for cotton textile industry?
Punjab
Maharashtra
Jkarkand
Jammu and Kashmir
B.
Maharashtra
C.
Jkarkand
Which of the following is the famous centre of cotton textiles in India?
Mumbai
Jalandhar
Lucknow
Amritsar
A.
Mumbai
C.
Lucknow
Which state has largest number of jute mills?
Assam
Bihar
Jharkhand
West Bengal
D.
West Bengal
Sponsor Area
Name the most important sugar producing states of India.
Uttar Pradesh
Bihar
Sikkim
West Bengal
A.
Uttar Pradesh
B.
Bihar
Most of the sugar industries are ideally suited to
Private sector
Public sector
Joint sector
Co-operative sector
D.
Co-operative sector
The iron and steel industry is the basic industry because
it provides employment to many people
all other industries–heavy, medium and light depend on it for their machinery
it makes use of iron ore which is a basic ore
all of these
B.
all other industries–heavy, medium and light depend on it for their machinery
Why iron and steel industry is known as a heavy industry?
Because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky
Because it needs heavy investment
Because it needs more land
None of the above
A.
Because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky
What is NTPC?
National Temporary Power Corporation
National Thermal Power Corporation
National Thermal Power Council
None of the above
B.
National Thermal Power Corporation
Classify the following into two groups on the basis of bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods —
(i) Oil, (ii) Knitting needles, (iii) Brassware, (iv) Fuse wires, (v) Watches, (vi) Sewing machines, (vii) Ship building, (viii) Electric bulb, (ix) Paint brushes, (x) Automobiles.
Basis of bulk and weight of raw material:
(i)Heavy Industries-
(a) Brassware
(b) Ship building
(c) Automobiles
(d) Oil
(ii)Light Industries-
(a) Knitting needles
(b) Fuse wires
(c) Electric bulb
(d) Paint brushes
(e) Watches
(f) Sewing machines.
Why the cotton textile industry is concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat?
(i)Availability of raw cotton
(ii)market
(iii)transport including accessible port facilities
(iv)labour
(v)moist climate
Where is the cement industry strategically located and why?
The cement industry is strategically located in Gujarat because it has suitable access to the market in the Gulf countries.
Why is steel needed?
Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods.
Classify industries on the basis of source of raw materials used.
(i)Agro based: cotton, woollen, jute, silk textile, rubber and sugar, tea, coffee, edible oil.
(ii)Mineral based: iron and steel, cement, aluminium, machine tools, petrochemicals.
Diffentiate between private sector and public sector.
|
Private sector |
Public sector |
|
Private sector industries owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals –TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd., Dabur Industries |
Public sector, owned and operated by government agencies – BHEL, SAIL etc. |
|
|
|
|
|
Why is a tendency for the sugar mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states?
(i)The cane produced here has a higher sucrose content.
(ii)The cooler climate also ensures a longer crushing season.
(iii)Moreover, the cooperatives are more successful in these states.
Classify industries on the basis of capital investment.
A small scale industry is defined with reference to the maximum investment allowed on the assets of a unit. This limit has changed over a period of time. At present the maximum investment allowed is rupees one crore. If invesment is more than one crore on any industry then it is known as a large scale industry.
Classify industry according to their main role.
(i)Basic or key industries which supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods e.g. iron and steel and copper smelting, aluminum smelting.
(ii)Consumer industries that produce goods for direct use by consumers – sugar, toothpaste, paper, sewing machines, fans etc.
Mention the factors which are responsible for localisation of jute textile mills mainly along the banks of the Hugli river.
(i)Proximity of the jute producing areas.
(ii)Inexpensive water transport, supported by a good network of railways, roadways and waterways to facilitate movement of raw material to the mills.
(iii)Abundant water for processing raw jute,
(iv)Cheap labour from West Bengal and adjoining states of Bihar, Orissa and Uttar Pradesh.
(v)Kolkata as a large urban centre provides banking, insurance and port facilities for export of jute goods.
Discuss Sugar Industry in India.
Sugar Industry:
(i)India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies the first place in the production of gur and khandsari.
(ii)The raw material used in this industry is bulky, and in haulage its sucrose content reduces.
(iii)In 2010-11 there were over 662 sugar mills in the country spread over Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat along with Punjab, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh.
(iv)Sixty per cent mills are in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
(v)This industry is seasonal in nature so, it is ideally suited to the cooperative sector.
Write a brief note on Fertilizer Industry in India.
Fertilizer Industry:
(i)The fertiliser industry is centred around the production of nitrogenous fertilisers (mainly urea), phosphatic fertilisers and ammonium phosphate (DAP) and complex fertilisers which have a combination of nitrogen (N), phosphate (P), and potash (K).
(ii)Potash is entirely imported as the country does not have any reserves of commercially usable potash or potassium compounds in any form.
(iii)India is the third largest producer of nitrogenous fertilisers. There are 57 fertiliser units manufacturing nitrogenous and complex nitrogenous fertilisers, 29 for urea and 9 for producing ammonium sulphate as a byproduct and 68 other small units produce single superphosphate.
(iv)At present, there are 10 public sector undertakings and one in cooperative sector at Hazira in Gujarat under the Fertiliser Corporation of India.
(v)After the Green Revolution the industry expanded to several other parts of the country. Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab and Kerala contribute towards half the fertiliser production
Describe the growth of chemical industry in India.
Chemical industry in India:
(i)The Chemical industry in India is fast growing and diversifying. It contributes approximately 3 per cent of the GDP.
(ii)It is the third largest in Asia and occupies the twelfth place in the world in term of its size. It comprises both large and small scale manufacturing units.
(iii)Rapid growth has been recorded in both inorganic and organic sectors. Inorganic chemicals include sulphuric acid (used to manufacture fertilisers, synthetic fibres, plastics, adhesives, paints, dyes stuffs), nitric acid, alkalies, soda ash (used to make glass, soaps and detergents, paper) and caustic soda.
(iv)Organic chemicals include petrochemicals, which are used for manufacturing of synthetic fibers, synthetic rubber, plastics, dye-stuffs, drugs and pharmaceuticals. Organic chemical plants are located near oil refineries or petrochemical plants.
(v)The chemical industry is its own largest consumer. Basic chemicals undergo processing to further produce other chemicals that are used for industrial application, agriculture or directly for consumer markets.
Write the challenges faced by jute industry. Why the internal demand of Jute has increased?
The internal demand has increased due to the Government policy of mandatory use of jute packaging. The growing global concern for environment friendly, biodegradable materials, has once again opened the opportunity for jute products.
Write six steel towns of India.
The following are the steel towns of India:
(i) Jamshedpur (Jharkhand),
(ii) Bokaro (Jharkhand),
(iii) Bhilai (Chhattisgarh),
(iv) Rourkela (Orissa),
(v) Durgapur (West Bengal).
(vi)Salem(Tamil Nadu)
Distinguish between agro-based industry and mineral-based industry.
|
Agro-based Industry |
Mineral-based Industry |
|
1. These industries derive their raw materials from agriculture. |
1. These industries derive their raw materials from minerals. |
|
|
|
|
2. They mostly produce consumer goods. |
2. These industries produce both consumer and value based goods. |
|
3. Example: Sugar, jute, textile, vegetable oil etc. |
3. Example: Iron and steel, engineering, ship building, machine tools, etc. |
Why manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of economic development?
(i)Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
(ii)Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country.
(iii)It also helps in bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
(iv)Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
(v)Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of furnished goods of higher value are prosperous.
Sponsor Area
Write the problem faced by cotton textiles.
(i)Power supply is erratic
(ii Output of labour is low
(iii)Stiff competition with the synthetic fibre industry.
Describe how agriculture and industry move hand in hand.
(i)For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
(ii)They depend on the latter for raw materials and sell their products such as irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, plastic and PVC pipes, machines and tools, etc. to the farmers.
(iii)Thus, development and competitiveness of manufacturing industry has not only assisted agriculturists in increasing their production but also made the production processes very efficient.
Why Chotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries?
These include:
(i)low cost of iron ore
(ii)high grade raw materials in proximity
(iii)cheap labour and vast growth potential in the home market
Write a note on water pollution.
(i)Water pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and affluents discharged into rivers.
(ii)The main culprits in this regard are paper, pulp, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries and electroplating industries that let out dyes, detergents, acids, salts and heavy metals like lead and mercury pesticides, fertilisers, synthetic chemicals with carbon, plastics and rubber, etc. into the water bodies.
(iii)Fly ash, phospo- gypsum and iron and steel slags are the major solid wastes in India
Explain the impact of IT and Electronic Industries.
(i)A major impact of this industry has been on employment generation. It is encouraging to know that 30 per cent of the people employed in this sector are women.
(ii)This industry has been a major foreign exchange earner in the last two or three years because of its fast growing Business Processes Outsourcing (BPO) sector.
(iii)The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to the success of IT industry in India.
Mention the pro-active approach of NTPC in Preserving the natural enviroment and resources.
This has been possible through:
(i) Optimum utilisation of equipment adopting latest techniques and upgrading existing equipment.
(ii) Minimising waste generation by maximising ash utilisation.
(iii) Providing green belts for nurturing ecological balance and addressing the question of special purpose vehicles for afforestation.
(iv) Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system and liquid waste management.
(v) Ecological monitoring, reviews and online database management for all its power stations.
Why the textile industry occupies unique position in the Indian economy?
(i)It contributes significantly to industrial production (14 per cent), employment generation (35 million persons directly – the second largest after agriculture) and foreign exchange earnings (about 24.6 per cent).
(ii)It contributes 4 per cent towards GDP.
(iii)It is the only industry in the country, which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain i.e., from raw material to the highest value added products.
Centres of cotton, woollen and silk textile industries are marked in the given map by different symbols and numbered from 1 to 28. Identify them and write under each textile industry the sr. no. of the centre, its name and the state in which the centre is located.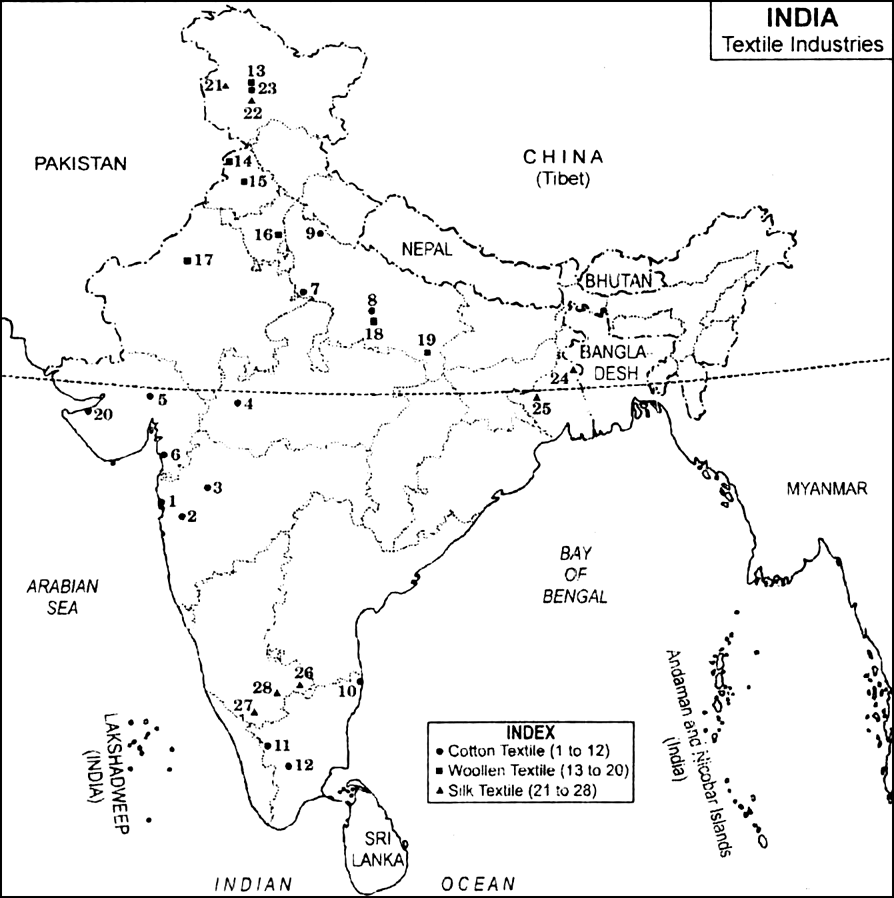
S | Name of the | State in which |
No. | Centre | located |
COTTON TEXTILE | ||
L | Mumbai | Maharashtra |
2. | Pune | Maharashtra |
3. | Aurangabad | Maharashtra |
4. | Indore | Madhya Pradesh |
5. | Ahmedabad | Gujarat |
6. | Surat | Gujarat |
7. | Agra | Uttar Pradesh |
8. | Kanpur | Uttar Pradesh |
9. | Moradabad | Uttar Pradesh |
10 | Chennai | Tamil Nadu |
11 | Coimbatore | Tamil Nadu |
12. | Madurai | Tamil Nadu |
WOOLLEN TEXTILE | ||
13. | Srinagar | Jammu and Kashmir |
14. | Amritsar | Punjab |
S. | Name of the | State in which |
No. | Centre | located |
15. | Ludhiana | Punjab |
16. | Panipat | Haryana |
17. | Bikaner | Rajasthan |
18. | Kanpur | Uttar Pradesh |
19. | Mirzapur | Uttar Pradesh |
20. | Jam Nagar | Gujarat |
SILK TEXTILE | ||
21. | Baramula | Jammu and Kashmir |
22. | Anantnag | Jammu and Kashmir |
23. | Srinagar | Jammu and Kashmir |
24. | Murshidabad | West Bengal |
25. | Bankura | West Bengal |
26. | Kolar | Karnataka |
27. | Mysore | Karnataka |
28. | Bengaluru | Karnataka |
Read the map of India described below and answer the questions that follow: 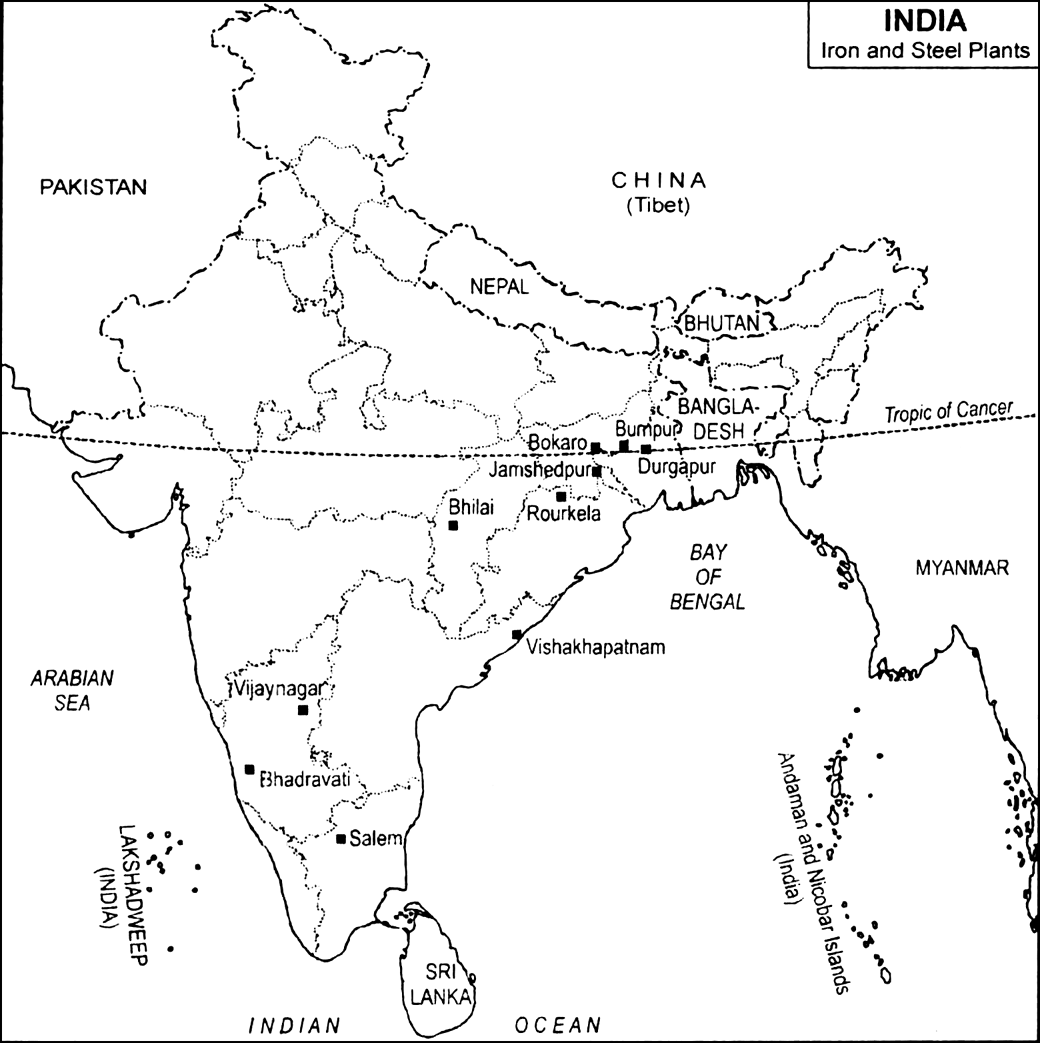
Questions:
Write one iron and steel plant located in Jharkhand, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh and Karnataka.
Iron and steel plants located in the following states:
(i) Jharkhand — Jamshedpur, Bokaro
(ii) West Bengal — Durgapur, Burnpur
(iii) Karnataka — Vijaynagar, Bhadravati
(iv) Chhattisgarh — Bhilai
Read the map given below and answer the question that follows: 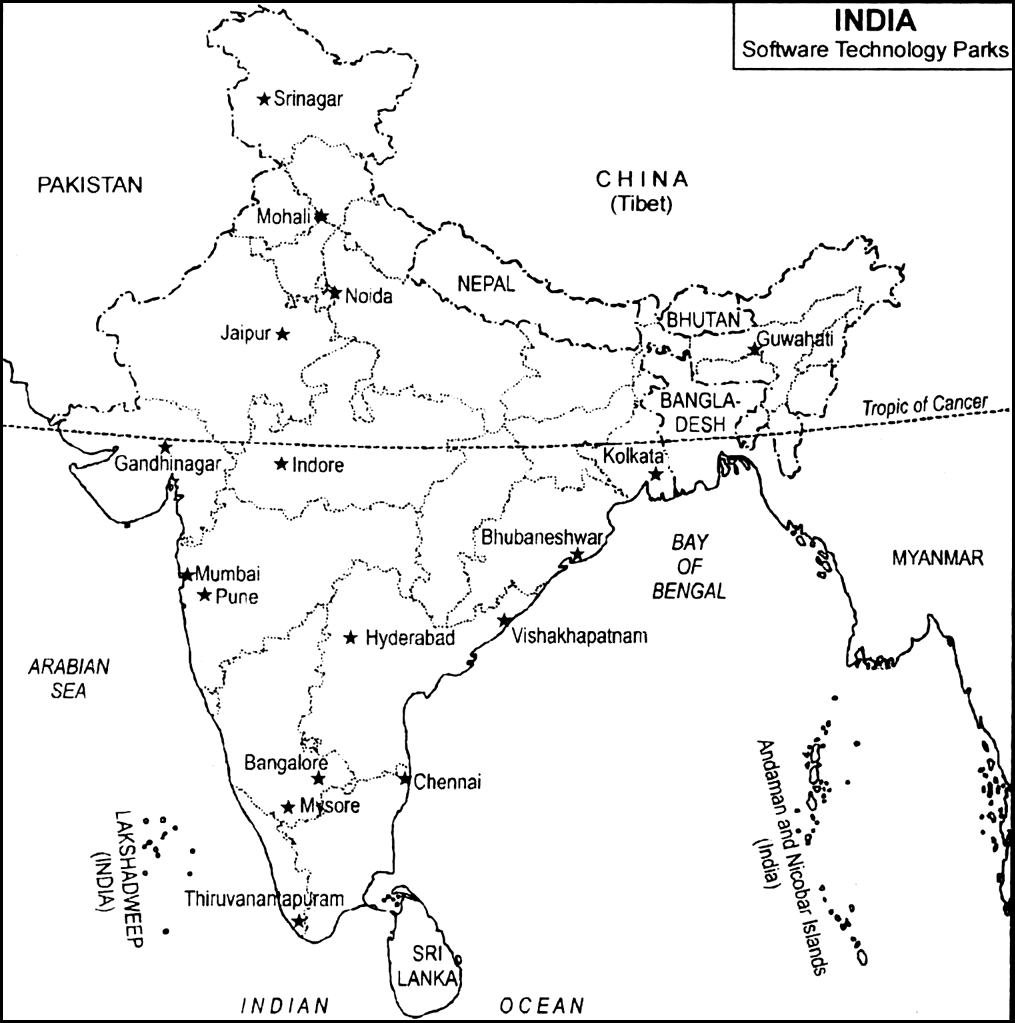
Question:
Write one software technology park located each in Jammu and Kashmir, Assam, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
Software technology parks located in the states mentioned are:
(i) Jammu and Kashmir — Srinagar
(ii) Assam — Guwahati
(iii) Uttar Pradesh — Noida
(iv) Kerala — Thiruvananthapuram
(v) Madhya Pradesh — Indore
(vi) Rajasthan — Jaipur.
Suggest three steps to minimize the environmental degradation cause by the industrial development in India.
Three steps to minimise environmental degradation caused by industrial development in India are mentioned below:
i. By using the natural resources judiciously and minimum usage of electricity.
ii. By treating wastewater through primary, secondary and tertiary treatment.
iii. By planting green belts in and around industries for promoting ecological balance and holding afforestation drives.
Suggest three steps to minimize the environmental degradation caused by the industrial development in India.
Three steps to minimise environmental degradation caused by industrial development in India:
i. By ensuring the optimum use of equipment by adopting latest techniques and upgrading existing equipment.
ii. By treating wastewater through primary, secondary and tertiary treatment.
iii. By planting green belts in and around industries for promoting ecological balance and holding afforestation drives.
Why has the 'Chhotanagpur Plateau Region' the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries? Analyse the reasons.
The reasons:
(i) low cost of iron ore.
(ii) High-grade raw materials in proximity.
(iii) Cheap labour and vast growth potential in the home market.
Describe any five factors responsible for the concentration off iron and steel industry in and around Chhotanagpur Plateau region.
Chotanagpur plateau has the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries. It is largely, because of the relative advantages this region has for the development of this Industry. These include:
(i) low-cost of iron ore
(ii) High-grade raw materials in proximity
(iii) cheap labour
(iv) vast growth potential in the home market
Examine the contribution of manufacturing industry to national economy.
The contribution of manufacturing industries contribute to national economy are-
(i) Manufacturing industries contribute 17 percent of GDP.
(ii) Since 2003 they are growing at the rate of 9-10 percent per annum and has improved employment.
(iii) They have reduced the dependence on agriculture.
Describe any three factors that control industrial location.
The factors that control industrial location are-
(i) Availability of raw materials
(ii) Labour
(iii) Power and Market
Which one of the following cities has emerged as the ‘electronic capital’ of India?
-
Delhi
-
Kolkata
-
Bangalore
-
Hyderabad
B.
Kolkata
C.
Bangalore
Why is iron and steel industry called a heavy industry? Give three reasons.
Iron and steel industry is called as a heavy industry because-
(i) The raw materials and finished goods are heavy and bulky.
(ii) The transportation costs are heavy
(iii) Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4:2:1.
Explain with examples the interdependence of agriculture and industries.
Agriculture and industries are interrelated to each other and move hand in hand which are explained in the following points :
(i.) Agriculture serves as a major source of raw materials to many industries.
(ii.) Industries obtain raw materials from agriculture and produce finished products. For example, Jute, sugar, cotton textiles etc.
(iii.) Manufacturing industries which are involved in the production of tools, equipment's have helped in modernizing agriculture.
(iv.) Industries are also involved in producing fertilizers, pesticides, plastics and other tools for the farmers.
Explain any two main challenges faced by the jute industry in India. Explain any three objectives of National Jute Policy.
Following are the challenges faced by jute industries in India :
(i.) Prices of jute textiles are so low that industrialists hesitate to set up these industries.
(ii.) International demand of jute goods is falling sharply which is not an encouragement for these industries.
The government has taken the following steps to boost Jute production :
(i.) Government has made it compulsory in the country to use jute packaging.
(ii.) In 2005, our government formulated the National Jute policy with the following aims:
To expand production
To enhance quality
To provide good prices to the farmers
To enhance yield per hectare.
Why has aluminium metal great importance?
Aluminium is of great importance because of the following reasons:-
- It is a good conductor of electricity, which makes it ideal for use in electrical wiring, light bulbs and telephone wires.
Suggest any three steps to minimise the environmental degradation caused by the industrial development in India.
Industrial pollution can be controlled by the following ways:-
- Industrial plants should be set up in distant areas away from human settlements.
- Industries should encourage sustainability and recycling of their products.
- Industries need to take up preventive measures to check pollution such as, treatment of industrial effluents, limited use of ground water, reduction of smoke by adopting certain measures like use of gas or oil in place of coal etc.
'Consumption of energy in all forms has been rising all over the country. There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy saving'. Suggest and explain any three measures to solve this burning problem.
There is an urgent need to develop sustainable path of energy development because of the following reasons:-
- Energy ensures and sustains economic development. It is needed to cook, to provide light and heat, to propel vehicles and to drive machinery in industries.
- Be it agricultural sector, industrial, transport, commercial or even domestic sector they require energy sources to remain operational and to ensure production. With the increase in population, rising demands, greater industrialization, increased consumption, changes in transportation our energy requirements have and will increase.
- We have to judiciously use our limited sources of energy and conserve them because of their growing consumption and their potential scarcity.
Suggest any three steps to minimise the environmental degradation caused by the industrial development in India.
Industrial pollution can be controlled by the following ways:-
- Industrial plants should be set up in distant areas away from human settlements.
- Industries should encourage sustainability and recycling of their products.
- Industries need to take up preventive measures to check pollution such as, treatment of industrial effluents, limited use of ground water, reduction of smoke by adopting certain measures like use of gas or oil in place of coal etc.
Explain any three objectives of the ‘National Jute Policy, 2005’.
In 2005, the Government formulated the National Jute Policy with the objective of increasing productivity, improving quality, ensuring good prices to jute farmers and enhancing the yield per hectare. The jute industry faced tough competition from synthetic substitutes and competitors such as Bangladesh and Brazil. The growing global concern for environment-friendly, biodegradable materials also led to the Government policy of mandatory use of jute packaging.
Why is India not able to perform to her full potential in iron and steel production? Explain any three reasons.
The following are three important reasons why India has not been able to perform to her full potential in iron and steel production:
i. High cost of production and limited availability of coking coal
ii. Lower productivity of labour
iii. Irregular supply of energy
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area






