Contemporary India Chapter 4 Agriculture
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Social+science Contemporary India
Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
The important beverage crop is Tea.
The geographical conditions required for growth of Tea:
(i)The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter.
(ii)Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year.
(iii)Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves.
(iv)Tea is processed within the tea garden to restore its freshness.
Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
Rice is the staple food crop of a majority of the people in India.
Rice is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions.
Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
The various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers are mentioned below:
(i)Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire and disease.
(ii)Establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies and banks for providing loan facilities to the farmers at lower rates of interest.
(iii)Kissan Credit Card (KCC), Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) schemes is introduced by the Government of India for the benefit of the farmers.
(iv)Moreover, special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers have been introduced on the radio and television.
(v)The government had also announced minimum support price, remunerative and procurement prices for important crops to check the exploitation of farmers by speculators and middlemen.
The land under cultivation has got reduced day by day. Can you imagine its consequences?
Consequences of reduction of agricultural land:
(i)India will turn in to food deficit from food surplus country.
(ii)India will face shortage of raw material for its agriculture based industries.
(iii)The poor farmers will become poorer and it will also lead to sharp rise in prices of the agricultural items.
Suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Considering the importance of agriculture in India, the Government of India has made concerted efforts to increase agricultural production.
(i)Establishment of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), agricultural universities, veterinary services and animal breeding centres, horticulture development, research and development in the field of meteorology and weather forecast, etc. are given priority for improving Indian agriculture.
(ii)Food security policy has enabled the poor to have access to food. The focus of the policy is on growth in agriculture production and on fixing the support price for procurement of wheat and rice, to maintain their stocks. Food Corporation of India (FCI) is responsible for procuring and stocking foodgrains, whereas distribution is ensured by public distribution system (PDS). The FCI procures foodgrains from the farmers at the government announced minimum support price (MSP).
(iii)The Green Revolution based on the use of package technology and the White Revolution (Operation Flood) are some of the strategies initiated to increase agricultural production.
Describe the impact of globalisation on Indian agriculture.
(i)Despite being an important producer of rice, cotton, rubber, tea, coffee, jute and spices our agricultural products are not able to compete with the developed countries because of the highly subsidised agriculture in those countries.
(ii)Today, Indian agriculture finds itself at the crossroads. To make agriculture successful and profitable, proper thrust should be given to the improvement of the condition of marginal and small farmers. The green revolution promised much. But today it’s under controversies. It is being alleged that it has caused land degradation due to overuse of chemicals, drying aquifers and vanishing biodiversity.
(iii)A few economists think that Indian farmers have a bleak future if they continue growing foodgrains on the holdings that grow smaller and smaller as the population rises. Indian farmers should diversify their cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops. This will increase incomes and reduce environmental degradation simultaneously. Because fruits, medicinal herbs, flowers, vegetables, bio-diesel crops like jatropha and jojoba need much less irrigation than rice or sugarcane. India’s diverse climate can be harnessed to grow a wide range of high-value crops.
Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
It is a kharif crop which requires high temperature, (above 25°C) and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm. In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation.
Rice is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. Development of dense network of canal irrigation and tubewells have made it possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall such as Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan.
Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
1. The two staple food crops of India.
2. This is the summer cropping season of India.
3. Pulses like arhar, moong, gram, urad contain ....
4. It is a coarse grain.
5. The two important beverages in India are...
6. One of the four major fibres grown on black soil.

(i) Rice and Wheat, (ii) Kharif, (iii) Protein, (iv) Jowar, (v) Tea and Coffee, (vi) Cotton.
Sponsor Area
Wheat requires annual rainfall between
50 and 75 cm
about 200 cm
200 and 300 cm
less than 20 cm
A.
50 and 75 cm
Which of the following conditions can ruin tea crop?
Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year
Frost free climate
Deep fertile well drained soil
Clayey soil which has high water holding capacity
D.
Clayey soil which has high water holding capacity
The largest jowar producing state of India is
Uttar Pradesh
Maharashtra
Bihar
Haryana
B.
Maharashtra
Who initiated the Bhoodan Movement?
Baba Amte
Vinoba Bhave
Acharya Narendra Dev
Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan
B.
Vinoba Bhave
Sponsor Area
What was the ‘Gramdan’?
Gifting of pulses
Distribution of villages
Donation
None of these
B.
Distribution of villages
Bhoodan-Gramdan movement is also known as
Green Revolution
White Revolution
Blood-less Revolution
None of these
C.
Blood-less Revolution
What is India’s position with respect to production of sugarcane?
It is the second largest producer after Brazil
It is the largest producer
It is the second largest producer after Egypt
It is the second largest producer after Australia
A.
It is the second largest producer after Brazil
Which one of the following is associated with PDS (Public Distribution System)?
A plan to increase the production of various crops
A scheme that provides foodgrains to the villagers at minimum price
A programme that provides foodgrains at subsidised price in rural and urban areas
It is an insurance scheme
C.
A programme that provides foodgrains at subsidised price in rural and urban areas
Rice cultivation requires
high temperature, high humidity and annual rainfall above 100 cm
low temperature, low humidity and less rainfall
moderate temperature, high humidity and annual rainfall more than 200 cm
high temperature, zero humidity and no rainfall
A.
high temperature, high humidity and annual rainfall above 100 cm
Under globalisation, our agricultural products are not able to compete with the developed countries because of the
highly subsidised agriculture in those countries
high quality products in these countries
- high export duties
lack of awareness
A.
highly subsidised agriculture in those countries
Which one out of the following is the adverse effect of the Green Revolution?
Production get increased
Quality of production increases
Land degradation due to overuse of chemicals
Great increase in the farmers' income
C.
Land degradation due to overuse of chemicals
Which one of the following types of farming is practised in the areas of high population?
Intensive subsistence farming
Plantation farming
Commercial farming
Primitive subsistence farming
A.
Intensive subsistence farming
Tips: -
M. Imp.
Name any three Agro-based industries in India.
The Agro-based industries in India are:
(i)Tea
(ii)Coffe
(iii)Sugar
Mention the region in India where various form of slash and burn cultivation is practiced.
It is jhumming in north-eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland; Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in Bastar district of Chhattishgarh, and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
The slash and burn cultivation is also called ‘Bewar’ or ‘Dahiya’ in Madhya Pradesh, ‘Podu’ or ‘Penda’ in Andhra Pradesh, ‘Pama Dabi’ or ‘Koman’ or Bringa’ in Odisha, ‘Kumari’ in Western Ghats, ‘Valre’ or ‘Waltre’ in South-eastern Rajasthan, ‘Khil’ in the Himalayan belt, and ‘Kuruwa’ in Jharkhand.
Write in brief about production of Maize in India.
(i)Maize is used both as food and fodder.
(ii)It is a kharif crop which requires temperature between 21°C to 27°C and grows well in old alluvial soil.
(iii)In some states like Bihar maize is grown in rabi season also.
(iv)Use of modern inputs such as HYV seeds, fertilisers and irrigation have contributed to the increasing production of maize.
(v)Major maize-producing states are Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Madhya Pradesh.
Differentiate between commercial agriculture and plantation agriculture.
|
Commercial Agriculture |
Plantation Agriculture |
|
|
1The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs. 2. High yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides are used in order to obtain higher productivity. 3. The degree of commercialisation of agriculture varies from one region to another. For example, rice is a commercial crop in Haryana and Punjab, but in Odisha, it is a subsistence crop. |
1. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area. 2. The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry. 3. Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers. |
|
Differentiate between Primitive subsistence farming and Intensive subsistence farming.
|
Primitive Subsistence farming |
Intensive Subsistence farming |
|
1. It is practised on small patches of land. 2. Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks, and family or community labour are used. 3. In this type of farming, farmers depend on the monsoons and natural fertility of the soil. 4. Land productivity in this type of agriculture is low. |
1. It is practised on bigger land holdings. 2. Modern inputs like HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides, etc., to obtain higher productivity are used. 3. In intensive subsistence, irrigation facilities like tubewells and canal irrigation is used. 4. Land productivity is high as it is meant for commercial purposes. |
Distinguish between kharif crops and rabi crops.
|
Kharif Crop |
Rabi Crop |
|
1.Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September-October. 2. Important crops grown during this season are paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur (arhar), moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean.
|
1. Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June. 2. Some of the important rabi crops are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard.
|
Differentiate between commercial agriculture and Prmitive subsistence farming.
|
Commercial Farming |
Primitive subsistence Farming |
|
1. The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs. 2. High yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides are used in order to obtain higher productivity. 3. The degree of commercialisation of agriculture varies from one region to another. For example, rice is a commercial crop in Haryana and Punjab, but in Odisha, it is a subsistence crop. |
1.Primitive subsistence agriculture is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks, and family/community labour. 2. This type of farming depends upon monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown. 3. It is a ‘slash and burn’ agriculture. Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family. |
Differentiate between the tea and coffee.
|
Tea |
Coffee |
|
1. The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. |
1. Indian coffee is known in the world for its good quality. The Arabica variety initially brought from Yemen is produced in the country 2. Intially its cultivation was introduced on the Baba Budan Hills and even today its cultivation is confined to the Nilgiri in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
|
Tips: -
M. Imp.
Which were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after Independence.
Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari, etc. were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after Independence.
Tips: -
V. Imp.
Explain the importance of agriculture in India.
(i)Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities.
(ii)Agriculture is a primary activity, which produces most of the food that we consume.
(iii)Besides food grains, it also produces raw material for various industries.
Explain any two features of Intensive subsistence farming in India.
(i)This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii)It is labour intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
Sponsor Area
Name major fiber crops grown in India and the source from where its derived.
The first three are derived from the crops grown in the soil, the latter is obtained from cocoons of the silkworms fed on green leaves specially mulberry.
Name two most important food crops of India and the region where its produced.
Two most important food crops of India are rice and wheat.
Rice: Rice is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. Development of dense network of canal irrigation and tubewells have made it possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall such as Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan.
Wheat: There are two important wheat-growing zones in the country – the Ganga-Satluj plains in the northwest and black soil region of the Deccan. The major wheat-producing states are Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan and parts of Madhya Pradesh.
What is meant by sericulture?
Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk fibre is known as sericulture.
Name a crop which is a commercial as well as subsistence crop in India.
Write a note on millets grown in India.
(i)Though, these are known as coarse grains, they have very high nutritional value. For example, ragi is very rich in iron, calcium, other micro nutrients and roughage.
(ii)Jowar is the third most important food crop with respect to area and production. It is a rain-fed crop mostly grown in the moist areas which hardly needs irrigation.
(iii)Major Jowar producing States were Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
(iv)Bajra grows well on sandy soils and shallow black soil. Major Bajra producing States were: Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat and Haryana.
(v)Ragi is a crop of dry regions and grows well on red, black, sandy, loamy and shallow black soils. Major ragi producing states are: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Jharkhand and Arunachal Pradesh.
Mention the significances of pulses in India.
(i)These are the major source of protein in a vegetarian diet. Major pulses that are grown in India are tur (arhar), urad, moong, masur, peas and gram.
(ii)Pulses need less moisture and survive even in dry conditions.
(iii)Being leguminous crops, all these crops except arhar help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air.
(iv)Therefore, these are mostly grown in rotation with other crops.
(v)Major pulse producing states in India are Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra and Karnataka.
Explain the characteristics of jute grown in India.
(i)Jute grows well on well-drained fertile soils in the flood plains where soils are renewed every year.
(ii)High temperature is required during the time of growth. West Bengal, Bihar, Assam, Odisha and Meghalaya are the major jute producing states.
(iii)It is used in making gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets and other artefacts. Due to its high cost, it is losing market to synthetic fibres and packing materials, particularly the nylon.
Tips: -
Imp.
Who was declared as the spiritual heir of M. K. Gandhi?
Tips: -
M. Imp.
Describe the objectives of India's food security policy.
India’s food security policy:
(i)It has a primary objective to ensure availability of foodgrains to the common people at an affordable price.
(ii)It has enabled the poor to have access to food.
(iii)The focus of the policy is on growth in agriculture production and on fixing the support price for procurement of wheat and rice, to maintain their stocks.
(iv)Food Corporation of India (FCI) is responsible for procuring and stocking foodgrains, whereas distribution is ensured by public distribution system (PDS).
(v)The FCI procures foodgrains from the farmers at the government announced minimum support price (MSP).
Explain the types of farming system practised in India.
The types of farming system practised in India are:
(i)Primitive Subsistence Farming: This type of farming is still practised in few pockets of India. This type of farming depends upon monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.
(ii)Intensive Subsistence Farming: This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land. It is labour intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii)Commercial Farming: The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity. The degree of commercialisation of agriculture varies from one region to another.
Suggest what Indian farmers can do to increase income without affecting environment.
Describe the factors responsible for the decline in the production of foodgrains in India.
The factors responsible for the decline in the production of foodgrains in India :
(i)There has been a gradual shift from cultivation of food crops to cultivation of fruits, vegetables, oilseeds. This has led to the reduction is net area under cereals and pulses.
(ii)The competition for land between non-agricultural uses such as housing etc. has resulted in reduction in the net sown area.
(iii)Fertilisers, pesticides and insecticides which once showed dramatic results, are now being held responsible for degrading the soils.
(iv)Periodic scarcity of water has led to reduction in area under irrigation. Inefficient water management has led to water logging and salinity.
(v)The unsustainable pumping has reduced water storage in aquifers. Consequently, many wells and tubewells have run dry. This has pushed the marginal and small farmers out of cultivation
Write the geographical conditions required for the cultivation of wheat. With the help of outline map of India, indicate the wheat growing areas/states.
Wheat: This rabi crop requires a cool growing season and a bright sunshine at the time of ripening. It requires 50 to 75 cm of annual rainfall evenlydistributed over the growing season.
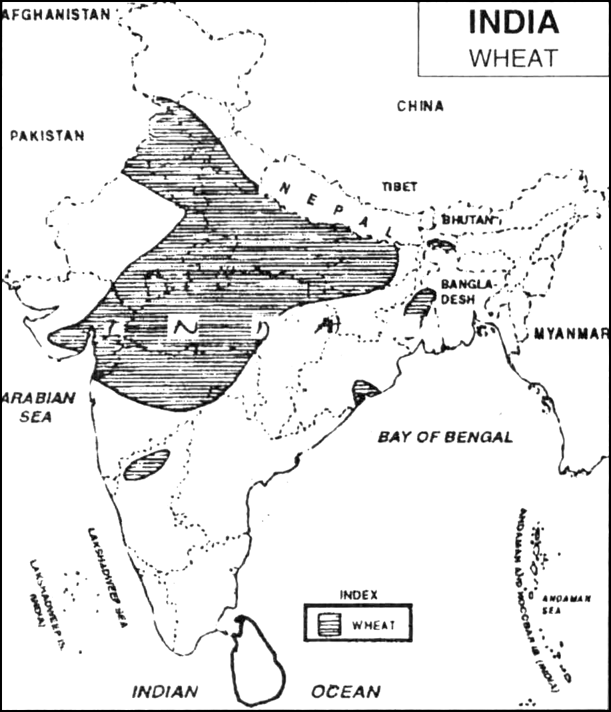
There are two important wheat-growing zones in the country – the Ganga-Satluj plains in the northwest and black soil region of the Deccan. The major wheat-producing states are Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan and parts of Madhya Pradesh.
Mention the geographical conditions required for the cultivation of sugarcane. Show the main growing areas or regions of sugarcane in India.
Sugarcane: It is a tropical as well as a subtropical crop. It grows well in hot and humid climate with a temperature of 21°C to 27°C and an annual rainfall between 75cm. and 100cm. Irrigation is required in the regions of low rainfall. It can be grown on a variety of soils and needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting.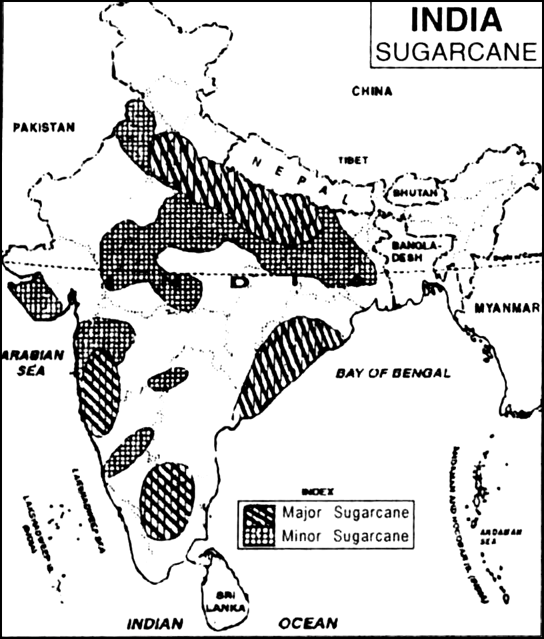
The major sugarcane-producing states are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana.
Explain Rubber as the non-food crop in India.
(i)Rubber is an equatorial crop, but under special conditions, it is also grown in tropical and sub-tropical areas.
(ii)It requires moist and humid climate with rainfall of more than 200 cm. and temperature above 25°C. Rubber is an important industrial raw material.
(iii)It is mainly grown in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andaman and Nicobar islands and Garo hills of Meghalaya.
Describe the division of consumers in India and the difficulties associated with it.
The division of consumers in India and the difficulties associated with it:
(i)The consumers in India are divided into two categories : below poverty line (BPL) and above poverty line (APL), with the issue price being different for each category.
(ii)However, this categorisation is not perfect and a number of deserving poor have been excluded from the BPL category.
(iii)Moreover, some of the so called APL slip back to BPL, because of the failure of even one crop and it is administratively difficult to accommodate such shifts.
Why despite increase in GDP growth rate sufficient employment opportunities is not generated in agriculture?
(i)The growth rate in agriculture is decelerating which is an alarming situation. Today, Indian farmers are facing a big challenge from international competition.
(ii)At the same time our government is going ahead with reduction in the public investment in agriculture sector particularly in irrigation, power, rural roads, market and mechanisation.
(iii)Subsidy on fertilisers is decreased leading to increase in the cost of production.
(iv)Moreover, reduction in import duties on agricultural products have proved detrimental to agriculture in the country.
(v)Farmers are withdrawing their investment from agriculture causing a downfall in the employment in agriculture.
The crops grown in Rabi season are the following
Wheat, peas, barley and mustard
Rice, jute, maize, soyabean
Pulses, melons, vegetables
Sugarcane and tobacco
A.
Wheat, peas, barley and mustard
Mark the characteristic of commercial farming
Plots of land are fragmented
Transport and communication plays an important role
The yield is usually low
The pressure of population is high on land
B.
Transport and communication plays an important role
Wheat is mainly grown in
Punjab, Bihar, Orissa, Bengal
Punjab, Rajasthan, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh
Maharashtra, Punjab, Bihar
Kerala, Andhra, Rajasthan
B.
Punjab, Rajasthan, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh
Solve the puzzle for following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
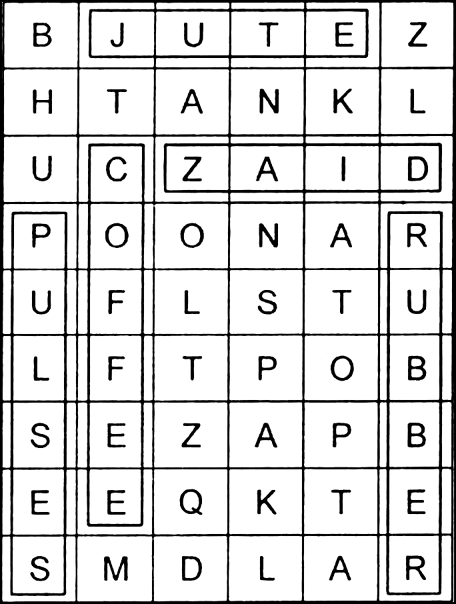
(a) A leguminous crop.
(b) Known as golden fiber.
(c) An equatorial crop.
(d) Its cultivation was initially introduced on Baba Budan Hills.
(e) Shorts season during the summer months.
(a) Pulses (b) Jute
(c) Rubber (d) Coffee
(e) Zaid
|
Crop |
Soil |
Climate |
Distribution . |
|
Rice – – Maize – |
– – Black soil – – |
– – – – Moist and humid rainfall >200 cm temperature >25 degree. |
– – Hills of Daijeeling, Tamil Nadu, Kerala – – |
|
Crop |
Soil |
Climate |
Distribution |
|
1. Rice |
Alluvial soils with clayey subsoil. |
Temperature: High above 25°C; High humidity. Rainfall: Above 100 cm. |
Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar and Punjab. |
|
2. Cotton |
Light, well drained Alluvial soil, Black cotton soil. |
Temperature: 21°C to 27°C, 210 frost free days. Rainfall: 50-80 cm. |
Gujarat, Maharashtra, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. |
|
3. Coffee |
Loamy soil with humus on well drained hills. Red and laterite soil. |
Temperature: 18°C to 28°C. Rainfall: 125 to 200 cm. |
Hills of Daijeeling, Tamil nadu, Kerala. |
|
4. Maize |
Nitrogen-rich loamy soil. |
Temperature: 21°C to 27°C; cannot stand frost at any stage. Rainfall: 50 cm to 100 cm. Sunshine promotes growth. |
Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Punjab. |
|
5. Rubber |
Deep, alluvial soil with good drainage. |
Moist and humid rainfall.. Temperature: More than 25 degree. |
Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. |
Why was the cotton textile industry concentrated in the cotton growing belt in the early years? Explain.
In the early years the cotton textile industry were concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharastra and Gujurat.
The reasons:
(i) availability of raw cotton
(ii) transport including accessible port facilities
(iii) labour
(iv) market
(v) moist climate
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





