Contemporary India Chapter 3 Water Resources
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Social+science Contemporary India
The longest dam in the world is
Hirakund
Bhakra Dam
Nagarjuna Sagar Dam
Tungabhadra Dam
A.
Hirakund
Which purpose is served by the Multipurpose Projects?
To irrigate the land
To fill land
To uproot the people
To make the land better
A.
To irrigate the land
B.
To fill land
Which is not the source of irrigation in India?
Canals
Ocean currents
Tubewells
Ponds
B.
Ocean currents
C.
Tubewells
Which of the following is not true with reference to water scarcity?
Water scarcity is also due to unequal access to water
Only 1/10 of the earth’s surface is covered with water
Water scarcity is also caused by over exploitation of water resources
The regions having low annual rainfall faces the problem of water scarcity
B.
Only 1/10 of the earth’s surface is covered with water
Sponsor Area
Which of the following is not true with reference to rain water harvesting?
It solves the problem of water scarcity
It is an environmental friendly technique
It is very cheap
It can also be used to generate electric power
D.
It can also be used to generate electric power
In western Rajasthan the practice of roof top rain water harvesting is declining because of the
abundant rainfall
recharged water table
availability of water from Rajasthan Canal
none of these
C.
availability of water from Rajasthan Canal
The total renewable water resources of India are estimated at
1,897 sq. km. per annum
1,978 sq. km. per annum
1,978 sq. km. per annum
none of these
A.
1,897 sq. km. per annum
What is the basic cause of new social movements like the Narmada Bachao Andolan and Tehri Dam Andolan?
A large scale displacement of local communities
The dams built on these rivers will provide power only to cities
Many industries will be submerged under these dams
The building of dam will lead to water scarcity
A.
A large scale displacement of local communities
Match the following options:
| A. Bhakhra Nangal | (i) Narmada |
| B. Hirakud | (ii) Kaveri |
| C. Mettur | (iii) Mahanadi |
| D. Sardar Sarovar | (iv) Satluj |
A. Bhakhra Nangal | (i) Satluj |
B. Hirakud | (ii) Mahanadi |
C. Mettur | (iii) Kaveri |
D. Sardar Sarovar
| (iv) Narmada |
Which of the following statements is not correct about multi-purpose projects?
They affect natural flow of rivers causing poor sediment flow and excessive sedimentation at the bottom of reservoir
Local and landless people get the maximum benefit from these projects
Dams fragment rivers making it difficult for acquatic fauna to migrate, especially for spawning
They have been the cause of many new social movements like “Tehri Dam Andolan” and “Narmada Bachao Andolan”
B.
Local and landless people get the maximum benefit from these projects
Sponsor Area
Salal Hydro Electric Project is in which of the following states?
Jammu and Kashmir
Orissa
Punjab
Himachal Pradesh
A.
Jammu and Kashmir
When does water stress occur? How can we conserve water?
Water stress occurs when water availability is between 1000 and 1600 cubic metre per person per year.
Water can be conserved by:
(i) developing natural reservoir like ponds, tanks lakes and etc.
(ii) practising rainwater harvesting.
How industries pollutes water resources.
Most industries require large amounts of water for their work. When involved in a series of processes, the water comes into contact with heavy metals, harmful chemicals, radioactive waste and even organic sludge.These are either dumped into open oceans or rivers.
What do you mean by dam? How does a dam is classified?
Dams are classified according to structure, intended purpose or height.
Mention the problems faced by the people of Rajasthan due to water scarcity?
The problems:
(i) The women are compelled to use ‘matkas’ (earthen pots) for collecting and storing water.
(ii) They have to travel long distances to get water.
(iii) They are forced to bring rain water.
Why does some area inspite of having ample water suffer from scarcity?
Names two rivers of north India and sources of their pollution.
The two rivers are:
Ganga and Yamuna.
Sources of their pollution:
(i)Sewage
(ii)Fertilizers from agricultural
(iii)Industrial discharge
Mention the reaons for objections to big dams.
The reasons for objections:
(i)The dams that were constructed to control floods have triggered floods due to sedimentation in the reservoir.
(i)The big dams have mostly been unsuccessful in controlling floods at the time of excessive rainfall.
(ii) The floods have not only devastated life and property but have also caused extremely soil erosion.
(iii) Sedimentation also meant that the flood plains were deprived of silt, a natural fertiliser, further adding on to the problem of land degradation.
(iv) It was also observed that the multipurpose projects or big dams induced earthquakes, caused water borne diseases and pests and pollution resulting from excessive use of water.
Tips: -
V. Imp.
Why did the Krishna-Godavari dispute arise? What does it about?
The Krishna-Godavari dispute had arisen due to objections raised by Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh goverments.
It is regarding the diversion of more water at Koyna by the Maharashtra government for a multipurpose project. This would reduce downstream flow in their states with adverse consequences for agriculture and industry
Why are dams built nowadays?
What have caused water scarcity in India?
Water scarcity in India is caused by:
(i)over- exploitation
(ii)excessive use
(iii)unequal access to water among different social groups.
Why do we need to harvest rain water?
We need to harvest rain water to:
(i) increase the level of ground water.
(ii) meet the increasing demand for water.
(iii) avoid flooding of roads.
Tips: -
Imp.
Write the significance of Tankas in Rajasthan.
(i)In the semi-arid and arid regions of Rajasthan, particularly in Bikaner, Phalodi and Barmer, almost all the houses traditionally had underground tanks or tankas for storing drinking water.
(ii)The tanks could be as large as a big room; one household in Phalodi had a tank that was 6.1 metres deep, 4.27 metres long and 2.44 metres wide.
(iii)The tankas were part of the well-developed rooftop rainwater harvesting system and were built inside the main house or the courtyard. They were connected to the sloping roofs of the houses through a pipe. Rain falling on the rooftops would travel down the pipe and was stored in these underground ‘tankas’.
(iv)The first spell of rain was usually not collected as this would clean the roofs and the pipes. The rainwater from the subsequent showers was then collected.
(v)The rainwater can be stored in the tankas till the next rainfall making it an extremely reliable source of drinking water when all other sources are dried up, particularly in the summers.
Write the popular sources of irrigation in India.
The popular sources of irrigation in India are:
(i) canals
(ii) wells and tubewells
(iii) tanks
Explain the technique practiced in Meghalaya to harvest water.
It is a 200-year-old system of tapping stream and spring water by using bamboo pipes which is still prevalent. About 18-20 litres of water enters the bamboo pipe system, gets transported over hundreds of metres, and finally reduces to 20-80 drops per minute at the site of the plant.
Describe the Bamboo-Drip Irrigation System of Meghalya.
The Bamboo-Drip Irrigation System is very popular in Meghalaya.
(i)It is a 200 year old system of tapping stream and spring water by using bamboo pipes.
(ii) Bamboo pipes are used to divert perennial springs on the hill tops to the lower reaches by gravity.
(iii)The channel sections, made of bamboo, divert water to the plant site where it is distributed into branches, again made and laid out with different forms of bamboo pipes. The flow of water into the pipes is controlled by manipulating the pipe positions.
(iv)If the pipes pass a road, they are taken high above the land.
(v)Reduced channel sections and diversion units are used at the last stage of water application. The last channel section enables water to be dropped near the roots of the plant.
Explain briefly about Narmada Bachao Andolan or Save Narmada Movement.
Narmada Bachao Andolan or Save Narmada Movement is a Non Governmental Organisation (NGO).
(i)It mobilised tribal people, farmers, environmentalists and human rights activists against the Sardar Sarovar Dam being built across the Narmada river in Gujarat.
(ii)It originally focused on the environmental issues related to trees that would be submerged under the dam water.
(iii)Recently it has re-focused the aim to enable poor citizens, especially the oustees (displaced people) to get full rehabilitation facilities from the government.
Mention the hydraulic structures constructed in Ancient India.
(i)In the first century B.C., Sringaverapura near Allahabad had sophisticated water harvesting system channelling the flood water of the river Ganga.
(ii)During the time of Chandragupta Maurya, dams, lakes and irrigation systems were extensively built.
(iii)Evidences of sophisticated irrigation works have also been found in Kalinga, (Odisha), Nagarjunakonda (Andhra Pradesh), Bennur (Karnataka), Kolhapur (Maharashtra), etc.
(iv)In the 11th Century, Bhopal Lake, one of the largest artificial lakes of its time was built.
(v)In the 14th Century, the tank in Hauz Khas, Delhi was constructed by Iltutmish for supplying water to Siri Fort area.
How the Industrialisation and urbanisation in post-independent India have caused water scarcity?
(i)This ever increasing number of industries has made matters worse by exerting pressure on existing freshwater resources.
(ii)Industries, apart from being heavy users of water, also require power to run them.
(iii)Moreover, multiplying urban centres with large and dense populations and urban lifestyles have not only added to water and energy requirements but have further aggravated the problem.
(iv)As the housing societies or colonies in the cities have their own groundwater pumping devices to meet their water needs.
(v)Not surprisingly, the fragile water resources are being over - exploited and have caused their depletion in several of these cities.
Why were the multi-purpose projects launched after Independence in India?
This was thought to integrate development of agriculture and the village economy with rapid industrialisation and growth of the urban economy.
Enlist few Multi-purpose projects with river and state on which it is built in India.
Multi-purpose projects with river and state in India:
|
Names of the Projects |
Rivers |
Beneficiaries |
|
1. Damodar Valley Project 2. Bhakhra Nangal 3. Hirakund Project 4. Kosi Project 5. Chambal Valley Project 6. Tungabhadra Project 7. Nagarjuna Sagar Project 8. Narmada Valley Project 9. Indira Gandhi Canal (Rajasthan Canal) |
Damodar Satluj Mahanadi Kosi Chambal Tungabhadra Krishna Narmada Beas, Satluj |
Jharkhand, West Bengal Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan Orissa Bihar and (Nepal) Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh Andhra Pradesh Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan. |
(any five projects)
Why in recent years, multi-purpose projects and large dams have come under great scrutiny and opposition?
(i)Regulating and damming of rivers affect their natural flow causing poor sediment flow and excessive sedimentation at the bottom of the reservoir, resulting in rockier stream beds and poorer habitats for the rivers’ aquatic life.
(ii)Dams also fragment rivers making it difficult for aquatic fauna to migrate, especially for spawning.
(iii)The reservoirs that are created on the floodplains also submerge the existing vegetation and soil leading to its decomposition over a period of time.
Which scarcity of resource is represented in the picture and how?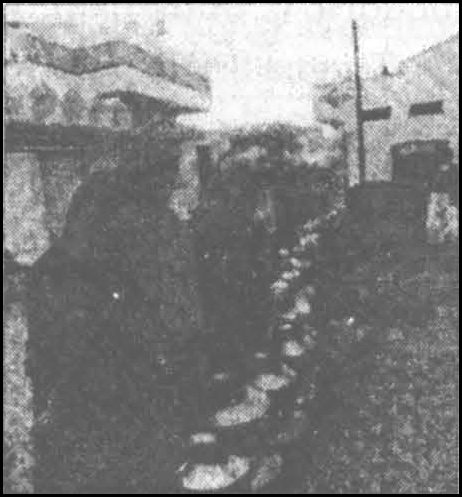 
Water scarcity is reprensented by a long queue of women with empty pots.
Sponsor Area
Which of the following statements is true for India?
Industries use maximum water.
Inter state water disputes have emerged based on the sharing of multipurpose project water.
The people who are displaced due to dam construction are given proper rehabilitation.
There is compulsory water harvesting methods used in all cities.
B.
Inter state water disputes have emerged based on the sharing of multipurpose project water.
The traditional methods of water storage is
Presence of Hauz Khas tank in Siri Fort area in Delhi
Inundation canals
Bamboo drips
Rooftop water harvesting
A.
Presence of Hauz Khas tank in Siri Fort area in Delhi
Match the following information given in the columns:
|
S.No. |
Name of the dam |
River on ivhich it is built |
State in which it is located |
|
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. |
Bhakhra-Nangal Gandhi Sagar Hirakud Mettur Nagarjun Sagar Tungbhadra |
Krishna Mahanadi Satluj Tungbhadra Kaveri Chambal |
Tamil Nadu Himachal Pradesh Madhya Pradesh Orissa Karnataka Andhra Pradesh |
|
S.No. |
Name of the dam |
River on ivhich it is built |
State in which it is located |
|
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. |
Bhakhra-Nangal Gandhi Sagar Hirakud Mettur Nagarjun Sagar Tungbhadra |
Satluj Chambal Mahanadi Kaveri Krishna Tungbhadra |
Himachal Pradesh Madhya Pradesh Orissa Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh Karnataka |
Map the sketch to harvest roof top water.
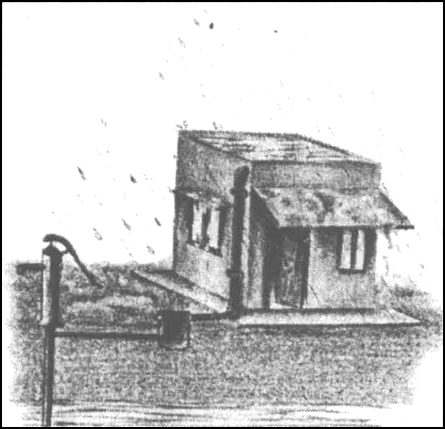
(a) Recharge through Hand Pump
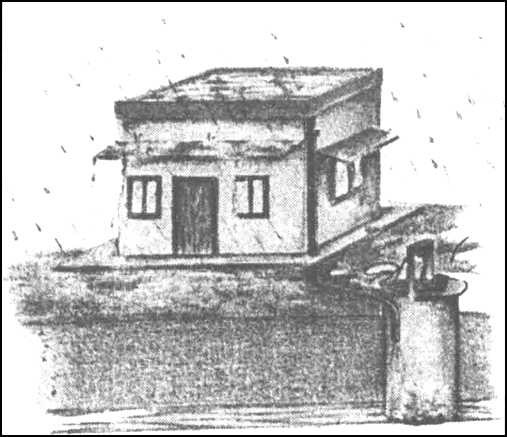
(b) Recharge through Abandoned Dugwell
Based on the information given below classify each of the situations as ‘suffering from water scarcity’ or ‘not suffering from water scarcity’.
(a) Region with high annual rainfall.
(b) Region having high annual rainfall and large population.
(c) Region having high annual rainfall but water is highly polluted.
(d) Region having low rainfall and low population.
(a) Not suffering from water scarcity
(b) Suffering from water scarcity
(c) Suffering from water scarcity
(d) Not suffering from water scarcity
Which one of the following statements is not an argument in favour of multipurpose river projects?
Multi-purpose projects bring water to those areas which suffer from water scarcity.
Multi-purpose projects by regulating water flow helps to control floods.
Multi-purpose projects lead to large scale displacements and loss of livelihood.
Multi-purpose projects generate electricity for our industries and our homes.
C.
Multi-purpose projects lead to large scale displacements and loss of livelihood.
Here are some false statements. Identify the mistakes and rewrite them correctly.
(a) Multiplying urban centres with large and dense populations and urban lifestyles have helped in proper utilisation of water resources.
(b) Regulating and damming of rivers does not affect the river’s natural flow and its sediment flow.
(c) In Gujarat, the Sabarmati basin farmers were not agitated when higher priority was given to water supply in urban areas, particularly during droughts.
(d) Today in Rajasthan, the practice of rooftop rainwater water harvesting has gained popularity despite high water availability due to the Rajasthan Canal.
(a) Multiplying urban centres with large and dense populations and urban lifestyles have caused the over exploitation of water resources.
(b) Regulating and damming of rivers affect their natural flow and causes the sediment to settle at the bottom of the reservoir.
(c) In Gujarat, the Sabarmati basin farmers were agitated when higher priority was given to water supply in urban areas, particularly during droughts.
(d) Today in Rajasthan, the practice of rooftop rainwater harvesting is on the decline due to the Rajasthan canal.
Explain how water becomes a renewable resource.
The earth’s surface is covered with water, but only a small proportion of it accounts for freshwater that can be put to use. This freshwater is mainly obtained from surface run off and ground water that is continually being renewed and recharged through the hydrological cycle. All water moves within the hydrological cycle ensuring that water is a renewable resource.
What is water scarcity and what are its main causes?
The unavailability of potable water is known as water scarcity.
The water scarcity in most cases is caused by over- exploitation, excessive use and unequal access to water among different social groups.
Compare the advantages and disadvantages of multi-purpose river projects.
Multipurpose river projects help in irrigation, electricity production, flood control, inland navigation and fish breeding.
At the same time the multi-purpose river projects also destroy local flora and fauna. Many native villages get submerged, and people lose their livelihood, with little or no hope of rehabilitation.
Discuss how rainwater harvesting in semi-arid regions of Rajasthan is carried out.
Rain water harvesting was commonly practised to store drinking water, particularly in Rajasthan.
(i) In the semi-arid and arid regions of Rajasthan, particularly in Bikaner, Phalodi and Barmer, almost all the houses traditionally had underground tanks or tankas for storing drinking water.
(ii) The tanks could be as large as a big room; one household in Phalodi had a tank that was 6.1 metres deep, 4.27 metres long and 2.44 metres wide. The tankas were part of the well-developed rooftop rainwater harvesting system and were built inside the main house or the courtyard.
(iii) They were connected to the sloping roofs of the houses through a pipe. Rain falling on the rooftops would travel down the pipe and was stored in these underground ‘tankas’. The first spell of rain was usually not collected as this would clean the roofs and the pipes. The rainwater from the subsequent showers was then collected.
(iv) The rainwater can be stored in the tankas till the next rainfall making it an extremely reliable source of drinking water when all other sources are dried up, particularly in the summers.
(v) Rainwater, or palar pani, as commonly referred to in these parts, is considered the purest form of natural water. Many houses constructed underground rooms adjoining the ‘tanka’ to beat the summer heat as it would keep the room cool.
Describe how modern adaptations of traditional rainwater harvesting methods are being carried out to conserve and store water.
Fortunately, in many parts of rural and urban India, modern adaptations of traditional rainwater harvesting methods are being carried out to conserve and store water.
(i) In Gendathur, a remote backward village in Mysore, Karnataka, villagers have installed, in their household’s rooftop, rainwater harvesting system to meet their water needs. Nearly 200 households have installed this system and the village has earned the rare distinction of being rich in rainwater. Gendathur receives an annual precipitation of 1,000 mm, and with 80 per cent of collection efficiency and of about 10 fillings, every house can collect and use about 50,000 litres of water annually. From the 20 houses, the net amount of rainwater harvested annually amounts to 1,00,000 litres.
(ii) Tamil Nadu has made roof top rainwater harvesting structure compulsory to all the houses across the state. There are legal provisions to punish the defaulters.
(iii) In Meghalaya, a 200-year-old system of tapping stream and spring water by using bamboo pipes, is prevalent. About 18-20 litres of water enters the bamboo pipe system, gets transported over hundreds of metres, and finally reduces to 20-80 drops per minute ate the site of the plant.
Roof top rain water harvesting is the most common practice in Shillong, Meghalaya. It is interesting because Cherapunjee and Mawsynram situated at a distance of 55 km. from Shillong receive the highest rainfall in the world, yet the state capital Shillong faces acute shortage of water. Nearly every household in the city has a roof top rain water harvesting structure. Nearly 15-25 per cent of the total water requirement of the household comes from roof top water harvesting.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





