Contemporary India Chapter 1 Resources And Development
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Social+science Contemporary India
Which one of the following type of resource is iron-ore?
- Renewable
- Biotic
- Flow
- Non-renewable
D.
Non-renewableName three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
(i) Maharashtra
(ii) Gujarat
(iii) Madhya Pradesh.
The name of the crop which is mainly grown in black soil is cotton.
What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main feature of this type of soil.
Alluvial soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coastal plains.
The features of Alluvial soil:
(i)This is the most widely spread and important soil. The entire northern plains of our country are made of alluvial soil.
(ii)Alluvial soils contain adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of several crops like Sugarcane, Paddy, Wheat and Pulses.
(iii)The alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay.
What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
The steps to be taken are:
(i)Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is called contour ploughing.
(ii)Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion. Western and central Himalayas have well developed terrace farming.
(iii)Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind. This method is known as strip cropping.
What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Biotic resources: These are obtained from biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc
Abiotic resources: All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. For example, rocks and metals.
Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased since 1960-61?
Land use pattern in India:
Total geographical area of India is 3.28 million sq km. Land use data, however, is available only for 93 per cent of the total geographical area because the land use reporting for most of the north-east states except Assam has not been done fully. Moreover, some areas of Jammu and Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China have also not been surveyed.
The land under permanent pasture has also decreased. Most of the other than the current fallow lands are either of poor quality or the cost of cultivation of such land is very high. Hence, these lands are cultivated once or twice in about two to three years and if these are included in the net sown area then the percentage of NSA in India comes to about 54 per cent of the total reporting area. The pattern of net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per cent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana and less than 10 per cent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman Nicobar Islands.
Forest area in the country is far lower than the desired 33 per cent of geographical area, as it was outlined in the National Forest Policy (1952). It was considered essential for maintenance of the ecological balance. The livelihood of millions of people who live on the fringes of these forests depends upon it.
Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it, has resulted in land degradation.
How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Technical and economic development has led to more consumption of resources:
(i) Technical and economic development has led to more consumption of resources. Higher level of technological development needs more and more resources for production activities. For example water resources are being over exploited to expand irrigated area.
(ii)Human beings have fallen into modern line of consumption. A new middle class which has emerged on account of economic development has increased trend of consumption over the year.
(iii) Information technology has brought boom in human choices, interests, hobbies, life-style and status-symbols.
A developed nation in the world is
Bangladesh
Nepal
United States of America
Sri Lanka
C.
United States of America
Which one of the following is a non - renewable resource?
Cotton
Thermal electricity
Wood
Livestock
B.
Thermal electricity
Sponsor Area
Pasture is a
Land owned by all countries of the world
Land can be used only for growing rice
Land covered with natural grasses
Land covered with mud
C.
Land covered with natural grasses
Gully erosion makes soil
Unfit for cultivation
Very fit for cultivation
Fit for culitvation
Makes soil very rich
A.
Unfit for cultivation
Soil formed by intensive leaching is
Alluvial soil
Red soil
Laterite soil
Desert soil
C.
Laterite soil
Fallow land refers to
Land not under cultivation
Land with many gullies
A fertile land
Cultivable land not cultivated for a season to regain its fertility
D.
Cultivable land not cultivated for a season to regain its fertility
Which one of the following statements correctly defines the term, ‘Resource’? - Things that we buy from the market
- All those elements that fulfil our needs.
- Everything available in our environment which can be used to fulfil our needs, technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable.
- Technologically accessible things.
C.
Everything available in our environment which can be used to fulfil our needs, technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable.Which is not a characteristic of a Resource?
- It is technologically accessible
- It is economically feasible
- It is culturally acceptable
- It is not naturally available
D.
It is not naturally availableWhich one of the following is not a natural resource?
Land
Buildings
Water
Minerals
B.
Buildings
Sponsor Area
Terrace cultivation is mainly used to
restrict soil erosion
develop deposition
escalate fertility
increase irrigation facility
A.
restrict soil erosion
Which one of the following is responsible for soil erosion in farms?
Rivers and wind work
Defective methods of farming
Running water
Moving glaciers
B.
Defective methods of farming
The global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and degradation are the result of
Accumulation of resources in a few hands
Judicious use of resources
Indiscriminate exploitation of natural resources
All of these
C.
Indiscriminate exploitation of natural resources
In which state the net sown area is less than 10% of the area of the land?
Arunachal Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Bihar
Orissa
A.
Arunachal Pradesh
C.
Bihar
In which state deforestation due to mining has caused land degradation?
Jharkhand
Kerala
Punjab
Uttar Pradesh
A.
Jharkhand
B.
Kerala
Which one of the following is not the community owned resource?
Grazing grounds
Burial grounds
Village ponds
Privately owned house
D.
Privately owned house
Which one of the following is not a renewable resource?
Solar energy
Wind energy
Forests
Fossils Fuels
D.
Fossils Fuels
Which of the following method will not help in soil conservation?
Contour ploughing
Strip cropping
Creating shelter belts
Ploughing up and down the slopes
D.
Ploughing up and down the slopes
Which one of the following states has mostly laterite soil?
Uttar Pradesh
Bihar
Rajasthan
Madhya Pardesh
D.
Madhya Pardesh
Make the classification of resources.
The classification of resources:
(a) On the basis of origin – biotic and abiotic
(b) On the basis of exhaustibility – renewable and non-renewable
(c) On the basis of ownership – individual, community, national and international
(d) On the basis of status of development – potential, developed stock and reserves.
Discuss renewable resources with example.
Renewable Resources: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources.
For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. The renewable resource may further be divided into continuous or flow.
Mention any three measures for conservation of resources.
Three measures for conservation of resources are mentioned below:
(i) Judicious utilisation of resources.
(ii) Preventing wastage of resources.
(iii) Use of alternatives or substitutes in the case of non-renewable resources.
Explain the complex process involved in resource planning in India.
(i) identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
(ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
(iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Distinguish between human made resources and natural resources. Write any two.
|
Natural Resources |
Human made Resources |
|
(i) Resources which are gifts of nature. (ii) It is of two types-biotic and abiotic, e.g., biotic—plants and animals, abiotic— rocks and metals. |
(i) Resources which are created by man. (ii) These are developed by man using his skill and knowledge by utilising natural resources, e.g., machines, technology. |
Define resources. State its characteristics.
Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs is defined as resources.
The characteristics:
(i)it is technologically accessible
(ii)It is economically feasible
(iii)It is culturally acceptable
Explain the co-relation between technology and resources.
Mention the main characteristics of black soil in India.
The characteristics of black soil:
(i)These soils are black in colour and are also known as regur soils.
(ii)Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil.
(iii)It is believed that climatic condition along with the parent rock material are the important factors for the formation of black soil.
(iv)This type of soil is typical of the Deccan trap (Basalt) region spread over northwest Deccan plateau and is made up of lava flows.
(v)The black soils are made up of extremely fine i.e. clayey material. They are well-known for their capacity to hold moisture.
Explain the problems associated with indiscrimate usage of resources.
Indiscriminate usage of resources have led to the following major problems:
(i)Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few individuals.
(ii)Accumulation of resources in few hands, which, in turn, divided the society into two segments i.e. haves and have nots or rich and poor.
(iii)Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as, global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
Write the names of different soil found in India.
(i)Alluvial soils
(ii)Black soil
(iii)Red and Yellow soils
(iv)Laterite soil
(v)Arid soil
(vi)Forest soil
Describe national resources.
Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. We might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area upto 12 nautical miles (19.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation.
Describe the factors responsible for soil formation.
The factors responsible for soil formation are:
(i) Relief, parent rock or bed rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil.
(ii) Various forces of nature such as change in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers, etc. contribute to the formation of soil.
(iii) Chemical and organic changes which take place in the soil are equally important. Soil also consists of organic (humus) and inorganic materials.
Read the data given below carefully and answer the questions that follow:
|
Land Use |
Percentage of Land |
|
|
Forest Net sown area Fallow land Land not available for cultivation Land under pasture and tree crops Culturable waste land |
22.5 46.6 7.7 13.8 4.8 4.6 |
|
|
Total |
100 |
|
(i) What percentage of land is dedicated to each of the net sown area and fallow land?
(ii) What is the main difference between the net sown area and fallow land?
(i) 46.6% of land is dedicated to the net sown area and 7.7% to the fallow land.
(ii) Fallow land is cultivated once in two or three years while net sown area is cultivated more than once in a year.
Exaplain the ways of land degradation in various state of India.
Land degradation:
(i)Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Orissa deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation.
(ii)In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
(iii)In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
(iv)The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere.
(v)It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country
Distinguish between stock and reserve with one example of each.
|
Stock |
Reserve |
|
1. Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these, are included among stock. |
1. Reserves are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing technical ‘know-how’ but their use has not been started. 2. Examples; forests, reservoirs. |
What is meant by sustainable economic development?
Sustainable economic development means ‘development should take place without damaging the environment, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations.’
Sponsor Area
Describe land as resources.
Land resources:
(i)We live on land, we perform our economic activities on land and we use it in different ways. Thus, land is a natural resource of utmost importance.
(ii)It supports natural vegetation, wild life, human life, economic activities, transport and communication systems.
(iii)However, land is an asset of a finite magnitude, therefore, it is important to use the available land for various purposes with careful planning.
Distinguish between the renewable and Non-renewable resources.
|
Renewable Resources |
Non-Renewable Resources |
||
|
1. The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources. 2. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. 3. The renewable resource may further be divided into continuous or flow.
|
1. These occur over a very long geological time. 2. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. 3. These resources take millions of years in their formation.
|
Describe the characteristics of laterite soils and places where they are found.
(i)The laterite soil develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall. This is the result of intense leaching due to heavy rain.
(ii)Humus content of the soil is low because most of the micro organisms, particularly the decomposers, like bacteria, get destroyed due to high temperature.
(iii)Laterite soils are suitable for cultivation with adequate doses of manures and fertilizers.
(iv)These soils are mainly found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and the hilly areas of Orissa and Assam.
(v)After adopting appropriate soil conservation techniques particularly in the hilly areas of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, this soil is very useful for growing tea and coffee. Red laterite soils in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Kerala are more suitable for crops like cashew nut.
Differentiate between sheet erosion and gully erosion.
Sheet Erosion: When water flows as a sheet down a slope and as a result, the top part of the land is washed away, such an erosion is called sheet erosion.
Gully Erosion: When the running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies, then such an erosion is called gully erosion. The Chambal ravines are the result of such gully erosion.
Differentiate between Bangar and Khadar soil.
|
Bangar Soil |
Khadar Soil |
|
(i) Bangar is the old alluvium. In other words, Bangar is older than Khadar. (ii) Bangar often contains kankar nodules with calcium carbonates in sub-soil. (iii) Bangar is not renewed frequently. Hence, it is less fertile. (iv) Bangar is found away from the river and higher than ground level. |
(i) Khadar is the new alluvium. In other words, Khadar is younger in age. (ii) Khadar is finer, more sandy and free from kankar nodules. (iii) Khadar is renewed frequently and is more fertile. (iv) Khadar is found near river channels in deltas and in flood plains. |
Distinguish the alluvial soil found in the upper course of rivers and that found in the lower courses.
|
Alluvial soil in the upper course |
Alluvial soil in the lower course |
|
(i) The soil particles are bigger in size. (ii) The soils are coarse. (iii) The soils in the upper course is less fertile. |
(i) The soil particles are smaller in size. (ii) The soils are less coarse. (iii) The soils in the lower course is more fertile. |
Explain Agenda-21.
It is the declaration signed by world leaders in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), which took place at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
It aims at achieving global sustainable development. It is an agenda to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities. One major objective of the Agenda 21 is that every local government should draw its own local Agenda 21.
Write a note on importance of resource planning in India.
Resource planning:
(i)Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources. It has importance in a country like India, which has enormous diversity in the availability of resources.
(ii)There are regions which are rich in certain types of resources but are deficient in some other resources.
(iii)There are some regions which can be considered self sufficient in terms of the availability of resources and there are some regions which have acute shortage of some vital resources. For example, the states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits.
(iv)Arunachal Pradesh has abundance of water resources but lacks in infrastructural development. The state of Rajasthan is very well endowed with solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources.
(v)The cold desert of Ladakh is relatively isolated from the rest of the country. It has very rich cultural heritage but it is deficient in water, infrastructure and some vital minerals. This calls for balanced resource planning at the national, state, regional and local levels.
What is soil erosion? Mention the causes.
The causes:
(i)Human activities like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc.
(ii) Natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion.
Explain the ways to solve the problems of land degradation.
There are many ways to solve the problems of land degradation.
(i)Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent.
(ii)Planting of shelter belts of plants, control on over grazing, stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes are some of the methods to check land degradation.
(iii)Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
Write a note on 'Soil as a Resource'.
Soil as a Resource in India:
(i)Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. It is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms on the earth.
(ii)The soil is a living system. It takes millions of years to form soil upto a few centimeters in depth. Relief, parent rock or bedrock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are the important factors in the formation of soil.
(iii)Various forces of nature such as change in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of the decomposers, etc. contribute to the formation of soil.
(iv)Chemical and organic changes which take place in the soil are equally important.
(v)Soil also consists of organic (humus) and inorganic materials.
Classify resources on the basis of their status of development.
On the basis of the status of development resources can be classified into four types.
(i) Potential resources: These include resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised. For example, solar and wind energy in Rajasthan and Gujarat respectively.
(ii) Developed resources: These include resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilization. For example coal, iron, manganese, etc.
(iii) Stock: Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access them are called stock. For example, geothermal energy.
(iv) Reserves: Resources which can be put into use with the help of existing technical ‘know-how’ but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future requirements. For example, water in dams, forests, etc.
Write a note on Earth Summit.
In June 1992, more than 100 heads of states had met in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, for the first International Earth Summit.
The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socioeconomic development at the global level. The assembled leaders signed the Declaration on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity. The Rio Convention endorsed the global Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Classify the resources on the basis of ownership.
On the basis of ownership resources can be classified into four types.
(i) Individual resources: These are owned privately by individuals. For example, plots, houses, plantation, pasture lands, ponds, are owned by individuals.
(ii) Community owned resources: The resources which are accessible to all the members of the community are called community owned resources. For example, grazing grounds, burial grounds, picnic spots, play grounds, etc.
(iii) National resources: All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area upto 12 nautical miles from the coast belong to the nation.
(iv) International resources : There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
On the outline map of India, identify the soil types marked by 1-6 and write their names in the blank space.
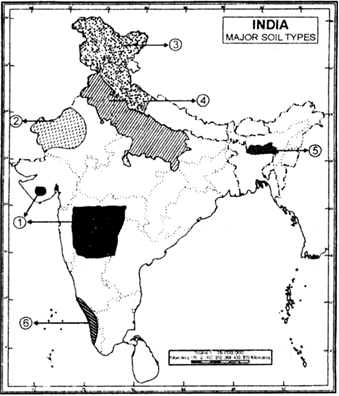
(1) Black soil
(2) Desert (Arid) soil
(3) Mountainous soil
(4) Alluvial soil
(5) Red and yellow soil
(6) Laterite soil.
Which of the following is not a measure for soil conservation?
Strip cropping
Terrace cultivation
Shelter belts
Overdraining of ground water
Overdraining of ground water
Which of the following is not important in soil formation? Relief
Parent rock
Climate
Duration of day
Relief
Parent rock
Climate
Duration of day
Duration of day
'The process of transformation of things has an interdependent relationship.' Explain.
The process of transformation of things available in our environment involves an inter- dependent relationship between nature, technology and institutions. Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development.
Which soil is also called Regur Soil? Which crop is ideal for it?
Black soil are also known as regur soils.
Black soil is ideal for growing cotton.
Describe the features of forest soils.
Forest soils:
(i)These soils are found in the hilly and mountainous areas where sufficient rain forests are available.
(ii)The soils texture varies according to the mountain environment where they are formed.
(iii)They are loamy and silty in valley sides and coarse grained in the upper slopes.
(iv)In the snow covered areas of Himalayas, these soils experience denudation and are acidic with low humus content.
(v)The soils found in the lower parts of the valleys particularly on the river terraces and alluvial fans are fertile.
What is the state of India's environment as depicted by the Sukhomajri and the district of Jhabhua.
State of India’s Environment
(i)The village of Sukhomajri and the district of Jhabua have shown that it is possible to reverse land degradation. Tree density in Sukhomajri increased from 13 per hectare in 1976 to 1,272 per hectare in 1992;
(ii)Regeneration of the environment leads to economic well-being, as a result of greater resource availability, improved agriculture and animal care, and consequently, increased incomes. Average annual household income in Sukhomajri ranged from Rs 10,000-15,000 between 1979 and 1984;
Describe land utilization.
Land resources are used for the following purposes:
(i)Forests
(ii)Land not available for cultivation:
(a) Barren and waste land
(b) Land put to non-agricultural uses, e.g. buildings, roads, factories, etc.
(iii)Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land):
(a) Permanent pastures and grazing land,
(b) Land under miscellaneous tree crops groves (not included in net sown area),
(c) Cultruable waste land (left uncultivated for more than 5 agricultural years).
(iv)Fallow lands:
(a) Current fallow-(left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year),
(b) Other than current fallow-(left uncultivated for the past 1 to 5 agricultural years).
(v)Net sown area:
Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as gross cropped area.
Which one of the following is not true about resources.
Resources are renewable and non-renewable both
Resources need to be planned before utilization.
- Wasteful consumption of resources need not be stopped as it is essential for high standard of living.
- Resources are unequally distributed on earth.
C.
Wasteful consumption of resources need not be stopped as it is essential for high standard of living.Which one of the following is a characteristic of red soil in India?
- it is formed due to diffusion of iron in crystalline metamorphic rocks
- it is formed due to leaching
- it is rich in lime and potash
- the lower horizons are occupied by kankar formations
A.
it is formed due to diffusion of iron in crystalline metamorphic rocksOn the political map of india identify the soil types in (I), (II), (III) and (IV).
(I) ____________
(II) ____________
(III) ____________
(IV) ____________
(I) Black Soil (II) Red and Yellow (III) Mountainous and Forest soil (IV) Alluvial soil.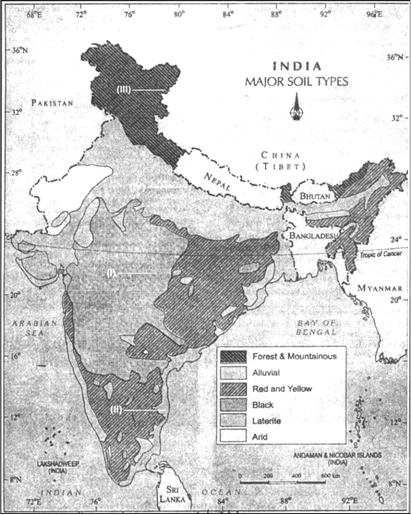
Mention the factors responsible for soil formation.
Factors responsible for soil formation are:
(i) Colour
(ii)Thickness
(iii)Texture
(iv)Age
(v) Chemical and physical properties
Differentiate between potential resources and stock resources with examples.
The difference:
Potential Resources: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised due to lack of capital or other reasons.
For example, the western parts of India, particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far, these have not been developed properly.
Stock Resources: Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these, are included among stock.
For example, water is a compound of two inflammable gases; hydrogen and oxygen, which can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have the required technical ‘know-how’ to use them for this purpose. Hence, it can be considered as stock.
Explain degradation of land by human activities.
Land degradation by human activities:
(i)We have sowed our land with the past generations and will have to do so with the future generations too.
(ii)Ninety-five per cent of our basic needs for food, shelter and clothing are obtained from land.
(iii)Human activities have not only brought about degradation of land but have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to land.
(iv)At present, there are about 130 million hactares of degraded land in India. Approximately, 28 per cent of it belongs to the category of forest degraded area, 56 per cent of it is water eroded area and the rest is affected by saline and alkaline deposits.
(v)Some human activities and quarrying too have contributed significantly in land degradation.
Suggest any two ways to check soil erosion by rivers.
(i) Reducing flow of river water
(ii) Constructing small bandhs
Fill the crosswords given below:
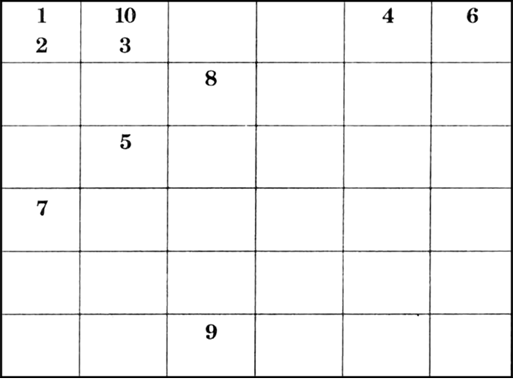
Across:
1. The other name of black soil. (1)
3. Develops on crystalline igneous rocks. (3)
5. Erosion of top soil as water flows over large areas. (5)
7. The club advocated resource conservation for the first time at international level. (4)
9. Deccan plateau is made up of. (4)
Down:
2. Soil that develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rain fall. (8)
4. Subset of the stock (8)
6. Obtained from biosphere and have life. (6)
8. An example of ravine. (7)
10. Denudation of soil cover. (7)
Across: 1. Regur, 3. Red soil, 5. Sheet erosion, 7. Club of Rome, 9. Lava.
Down: 2. Laterite, 4. Reserves, 6. Biotic, 8. Chambal, 10. Soil erosion.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





