Biology Chapter 11 Transport In Plants
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 11 Political+science Biology
Why the water is forced to move through cell membrane beyond endodermis ?
Why the cortex produces no resistance to movement of water ?
What is transmembrane pathway ?
Why transpiration is more on lower surface than on upper surface of leaves ?
Name the two forces responsible for the rise of water in a capillary tube.
(i) Cohesion force (ii) Adhesion force
Which force is first operative in translocation of water through capillarity : cohesive force or adhesive force ?
What are the two factors which affect osmosis?
1. Concentration gradient. The difference in the concentration on both sides of the semipermeable membrane.
2. Pressure gradient - Pressure difference between two solutions.
Name the plant having more stomata on lower surface than on upper surface.
Name the plant having equal number of stomata on both surfaces.
Name the substance which has maximum imbibition capacity.
Sponsor Area
What is pressure potential ?
If the osmotic potential is - 0.1 then what will be the value of osmotic pressure.
What is the value of water potential to fully turgid cell and why ?
What is the value of water potential to fully turgid cell and why ?
Therefore the water potential becomes zero when solute potential becomes equal to the pressure potential.
Define the terms imbibition imbibant, imbibate and imbibition pressure.
Imbibant : It is the solid substance which absorbs water and swells up.
Imbibate : It is the liquid or water which is imbibed by the imbibant.
Imbibition pressure : The imbibant, after imbibition of water or liquid, exerts the pressure which is called imbibition pressure. The germinating seeds have imbibition pressure of about 1000 atmospheres.
Describe the importance of imbibition.
1. The young cells absorb water by imbibition.
2. The germinating seeds imbibe water resulting in the bursting of seed coat leading to their germination.
3. Roots absorb water by imbibition initially.
4. The imbibitional pressure helps the roots and seeds to push through the soil.
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion?
Factors affecting diffusion :
1. Temperature : The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the temperature. As the temperature increases the rate of diffusion increases.
2. Surface area : More the surface area more will be the rate of diffusion.
3. Concentration gradient: The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the concentration gradient.
4. Pressure - Increase in the pressure increase diffusion rate.
5. Permeability of the membrane separating the solutions. More permeable the mebrane more will be the diffusion.
Describe the significance of diffusion.
1. The cell walls of plant cells remain moist due to diffusion of water molecules from one cell to the other.
2. The ions in the cells get uniformly distributed due to diffusion.
3. Transpiration is also due to diffusion of water vapour from intercellular space of spongy parenchyma into the atmosphere through stomata or cuticle.
4. The exchange of gases occurs through stomata due to diffusion.
5. The aroma or fragrance of flowers spreads due to the diffusion and insects are attracted for pollination.
Define osmosis. Give its types.
Osmosis is of two types :
(a) Exosmosis (b) Endosmosis.
(a) Exosmosis : It is the process by which solvent molecules diffuse from inside to outside across a semipermeable membrane.
(b) Endosmosis : It is the process by which solvent molecules diffuse from outside to inside of a cell across a semi-permeable membrane.
What is the significance of osmosis ?
1. Water molecules diffuse from the soil into root hair by osmosis.
2. Cell to cell movement of water occurs by osmosis.
3. Opening and closing of stomata are due to osmotic changes in guard cells.
4. The flowers remain fully stretched due to osmosis.
5. The plant movements like nyctinasty, seismonasty etc. occur due to the changes in the osmotic pressure.
6. The cells remain fully turgid due to osmosis.
Define the term diffusion pressure deficit (DPD) and also write its relation.
The diffusion pressure of pure water is maximum and it continues to decrease as more and more solute is added into it.
D.P.D = O.P - T.P
Where,
D.P.D. = Diffusion pressure deficit
O.P = Osmotic pressure
T.P = Turgor pressure
Define the terms osmotic pressure and turgor pressure.
Turgor pressure : It is the pressure exerted by protoplast upon the cell membrane of cell wall.
Write note on solute potential.
Ψw = (solute potential) Ψs.
Why walls of xylem vessels have great affinity for the attraction of water ?
List the functions of turgor pressure.
Turgor pressure is resposnsible for -:
1. The opening and closing of stomatal pores.
2. Providing mechanical support to the non-woody stems.
3. Keeping the leaves erect and fully expanded.
4. It helps in cell enlargement.
5. It is responsible for absorption of water as it creates a negative water potential.
What is permanent wilting ?
Give the significance of plasmolysis.
1. It helps in recognition whether the cell is living or dead.
2. It helps in killing weeds. The concentrated solution of NaCl is sprayed over weeds which get killed due to plasmolysis.
3. Plasmolysis is used in preservation of food materials. Pickles and jams have more NaCl and sugar content respectively so that they must remain protected from the attack of fungus, spores, bacteria etc.
4. With the help of plasmolysis, the plants growing in crevices of walls of houses can be killed by adding hypertonic solution.
Sponsor Area
Discuss root pressure responsible for ascent of sap
Root pressure : It is a positive force. It is due to the osmosis of water, from the soil into the root cells and the active pumping of salts into the xylem tissue, which maintains a concentration gradient along which the water will move. It is responsible for the ascent of sap to small heights.
What is wilting ?
What is transpiration flux ?
What is cohesion?
On what properties of water does the ascent of xylem sap depend?
i. Cohesion – It is themutual attraction between water molecules.
ii. Adhesion – It is the attraction of water molecules to polar surfaces (such as the surface of tracheary elements).
iii. Surface Tension – The water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase.
Describe the mechanism of passive water absorption.
The water moves through the apoplast pathway in a passive way. The direction of the movement of water is according to the concentration gradient and hence no energy is required for the same. The water is absorbed in the following way -:
1. Root hairs have low water potential as compared to the soil. Thus, root hairs absorb water from the soil.
2. The water from soil enters into root hairs due to osmosis.
3. The cortical cells just adjoining to epidermal cells with root hair have much more osmotic pressure than root hair cells. Thus, water from epidermal cells diffuses into cortical cells adjoining them. The water diffuses passively through the cortical cells until they reach the casparian stripe which are suberized.
What is absorption lag ?
Describe active absorption.
What are photoactive stomata ?
Write notes on cuticular and lenticular transpiration
Lenticular transpiration : These are the openings in case of stem. These are formed below stomata. Some amount of water is transpires through the lenticels. This type of transpiration is called lenticular transpiration. It is 1% of total transpiration.
Describe the external factors affecting transpiration.
1. Temperature : Rate of transpiration is directly proportional to the temperature. Transpiration rate increases with increase in temperature.
2. Light : More light closes the stomata.
3. Relative humidity : Rate of transpiration is inversely proportional to the relative humidity.
4. Velocity of the wind : The rate of transpiration is directly proportional to the velocity of wind. However, the wind of 40-50 km/hr brings closing of stomata and thus decreases the rate of transpiration.
5. Atmospheric pressure : Rate of transpiration is inversely proportional to the atmospheric pressure.
What is apolast ?
Describe internal factors affecting transpiration.
1.Surface area of leaf - Leves having larger surface are have more transpiration.
2.Thickness of cuticle - Thick cuticle layer lowers the rate of transpiration.
3. Number of stomata - more the number of transpiration more will be the transpiration.
4. Sunken stomata - lowers the rate of transpiration.
What is symplast ?
“Transpiration is a necessary evil.” Discuss.
What is the different between the stomata of dicots and monocots?
1. Stomata distribution - In monocots stomata are equally distributed while in the dicots the stomata is usually found on the lower surface of the leaf.
2. Guard cell shape - In monocots the guard cells are dumbell shaped while in the dicots they are kidney or bean shaped.
Comment upon antitranspirants
Antitranspirants : These are the chemicals which reduce transpiration. These are used to prevent water loss when there is drought. These anti-transpirants are of two types :
Briefly describe the apoplast and symplast pathway.
Symplast pathway - It is the system of the interconnected protoplasts. Neighbouring cells are connected through the cytoplasmivc strands that extend through the plasmodesmata. It involves crossing of the cell membrane.
Differentiate between the following
(f) Guttation and Tranpiration.
| Transpiration | Guttation |
| 1. Water loss is in the form of water vapour. | 1. Water loss is in the form of water droplets. |
| 2. Occurs through stomata | 2. Occurs through hydathodes. |
| 3. Occurs usually during day | 3. Occurs during the night. |
| 4. Transpiration pull is involved | 4. Root pressure in involved |
Distinguish between stomata and hydathodes.
|
Stomata |
Hydathodes |
|
1. Stomata are A tiny pore in a plant leaf surrounded by a pair of guard cells that regulate its opening and closure, and serves as the site for gas exchange. |
1. A pore that exudes water on the surface or margin of a leaf of higher plants |
|
2. Water is lost in the form of water vapour |
2. Water is lost in its liquid form. |
|
3. Carry out the process of transpiration. |
3. Carry out the process of guttation. |
|
4. Usually open during the day and closed during the night. |
4. Open all time. |
Difference between semipermeable and selectively permeable membrane
the movement of salute particles. e.g egg membrane, animal bladder, parchment paper.
Selectively or Differentially permeable membranes allow selective passage of solutes along
with solvent, through them. Example Plasma membrane of the cell.
Why is imbibition considered to be diffusion?
Difference between active and passive water absorption
Differentiate between the following
(b) Transpiration and Evaporation.
|
Transpiration |
Evaporation |
|
1. It is a physiological process and occurs in plants. 2. The water vapours diffuse through cucticle or through the stomata. 3. Living cells are involved. 4. Various forces such as vapour pressure, diffusion pressure, osmotic pressure, etc. are involved. 5. It is a slow process. 6. It is dependent upon anatomy of root, stem and leaves. |
1. It is a physical process and occurs on any free surface. 2. Any liquid can evaporate. The living epidemis and stomata are not required. 3. It can occur from both living and non-living surfaces. 4. No such forces are involved. 5. It is a fast process. 6. It is independent of anatomy of leaf, stem and roots. |
What is the mode of absorption by epiphytic roots ?
Which two things are reponsible for the movement of water up a plant
(i) Root pressure.
(ii) Transpiration pull.
In what way does the concept of water potential help in explaining water movement ?
Water potential is the potential energy of water which helps in the movement of water. Pure water has the highest water potential , pure water has a water potential equal to zero. When solute is added to the water it decreases its water potential. As we know that the cell having greater water potential has more concentration of water thus we can say that the movement of water will take place from high water potential to low water potential, as diffusion of water takes place from its high concentration to low concentration. Thus the concept of water potential help us to understand in which direction the water will move.
Loss of water decreases or increases Ψw? Comment.
Is there a general mechanism to explain opening and closing of stomata? Justify your answer.
The opening and closing of stomata is operated by turgor changes in guard cells. When the guard cell absorb water they become turgid and the stomata opens. The opening and closing of stomatal pore is aided by the differential thickening of the guard cell's inner and outer membrane and the orientation of the microfibrils in the cell.
When the guard cell absorb water then the thin outer walls bulge out and force the inner walls into a crescent shape, thus opening the stomatal pore. The radial orientation of cellulose microfibrils rather than longitudinally enable the stoma to open. When the lose water they lose turgidity , the elastic inner walls regain their original shape, the guard cells become flaccid and the stoma closes.
One way in which osmotic pressure is different from the osmotic potential.
Osmotic pressure is equivalent to the osmotic potential but osmotic pressure is the positive pressure apllied whereas the osmotic potential is negative.
What cause the opening and closing of guard cells of stomata during transpiration ?
The change in the turgidity of guard cells results in closing or opening of stomata. The inner and outer walls of the guard cells differ in thickness, the inner walls are thick while the outer are thin. When the guard cells absorb water their turgidity increases, thus the thin outer walls bulge out and force the inner walls into a crescent shape. The change in shape is aided due to the radial orientation of the microfibrils in the cell walls of the guard cells. These microfibrills help the guard cells to bulge out thus opening the stomata. During tranpiration the loss of water makes the guard cells lose turgidity, the elastic inner walls regain their original shape, the guard cells become flaccid and the stomata closes.
Sponsor Area
What is the relation between water potential , solute potential and Pressure potential
where
Does transpiration bring any useful function in plant ?
1. Ascent of sap - It is the pulling force that helps in the movement of water up the plant.
2. Cooling effect - cools the leaf surfaces sometimes upto 10 to 15 degrees.
3. Transport minerals from the soil to all parts of the plants.
4. Maintains the shape and structure of the plants by keeping the cells turgid.
5. Supplies water for photosynthesis.
Give the water potential for the following :
a. Pure water
b. Fully turgid cells
c. Concentrated solution
a. Pure water - Zero
b. Fully turgid cells - Zero
c. Concentrated solution - Negative.
Write short notes on :
Plasmolysis
In which direction water flows regarding water potential.
Describe the role of osmotic potential in regulating water potential of plant cells.
Describe osmosis as a special case of diffusion.
1. In osmosis only water or solvent molecules diffuse from their higher concentration to lower concentration, while in diffusion all type of matter can diffuse i.e. diffusion of gases, solids as well as of liquids.
2. In osmosis diffusion of solvent molecules or water molecules occur through semipermeable membrane. In simple diffusion semipermeable membrane is not required.
Thus osmosis is a special case of diffusion in which only solvent or water molecule diffuse from low to high concentration through semipermeable membrane.
What type of molecules undergo facilitated diffusion ?
Comment upon the rate of diffusion. Name the factors that affect the rate of diffusion.
Give the comparison among simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion and active transportation.
|
Simple Diffusion |
Facilitated Diffusion |
Active Transport |
|
1. Membrane proteins are not required . 2. It is not selective. 3. Saturation does not occur. 4. It does not occur against concentration gradient. 5. ATP is not required. |
1. Membrane proteins are required. 2. It is selective. 3. Saturation occurs. 4. Not against the concentration gradient. 5. ATP is not required. |
1 . Membrane proteins are required. 2. It is selective. 3. Saturation occurs 4. Against the concentration gradient. 5. It needs ATP. |
What is the role of special proteins in diffusion?
Difference between the following
(c) Osmotic Pressure and Osmotic Potential
| Osmotic Pressure | Osmotic Potential |
| 1.Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane. | 1.Osmotic potential is defined as the ability of a solution to draw water in when separated from another solution by a semi-permeable |
| 2. It is expressed in bars with a positive sign. | 2. It is expressed in bars with a negative sign. |
Explain pressure flow hypothesis of translocation of sugars in plants.
Describe the role played by protein pumps during active transport in plants.
The protein pumps are involved in the active transport of substances like minerals. They are present in the membrane of the cell or organelles. The proteins pumps help in the transfer of molecules from their lower concentration to the region of their higher concentration by using energy.
Explain why xylem transport is unidirectional and phloem transport bi-directional.
The leaves carry out photosynthesis and act as the source of the food. The phloem conducts the food from the source to the sink (the part of the plant requiring or storing food). But, the source and sink may be reversed depending on the season, or the plant’s needs. During spring, the food stored in the sink is mobilised toward the growing buds of the plant, through the phloem. Thus, the movement of food in the phloem is bidirectional (i.e., upward and downward) as the realtion of source and sink is variable.
However, the transport of water in the xylem takes place only from the roots to the leaves. Therefore, the movement of water and nutrients in the xylem is unidirectional.
Difference between Diffusion and Osmosis
|
Diffusion |
Osmosis |
|
1.It is the process of movement of the molecules from high concentration to low concentration until molecules get uniformly distributed. |
1.It is the process of diffusion of only solvent of water molecules from its higher concentration to lower concentration via semi permeable membrane. |
|
2. Semi permeable membrane is not needed. |
2. Semi permeable membrane is essential. |
|
3. It involves the movement of both solute and solvent |
3. Osmosis involves movement of solvent molecules only.
|
What essential role does the root endodermis play during mineral absorption in plants?
The endodermal cells have transport proteins which act as control points, to adjust the quantity and types of solutes that reach the xylem. The suberin layer of the endodermis allows unidirectional active transport of the ions and the symplastic movement of water.
How does water is absorbed by the roots ? Discuss different pathways for its translocation.
The root hair absorb water a
Transportation : Once water is absorbed it is translocated into deeper layers of root by different pathways as :
(i) Apoplast pathway (ii) Symplast pathway
(i) Apoplast pathway : It is the pathway which occurs through cell walls. It is non living pathway.
The apoplastic pathway is continuous through walls as well as through intercellular spaces. It does not involve crossing of cell membrane. It does not provide any barrier. Mass flow of water through apoplastic pathway is mainly due to cohesive and adhesive forces.
The casparian strips of endodermis provide check to apoplastic pathway and water has to cross the cell membrane and pass through cytoplasm. The pathway becomes symplast.
(ii) Symplast Pathway : It occurs through interconnected protoplasts. The protoplasts of adjacent cells are connected via plasmodesmata.
The symplastic pathway is slow because of cell membranes and their organelles Symplastic movement may be aided by streaming movement of cytoplasm as in leaf of Hydrilla.
(iii) Vacuolar symplast pathway : It is the movement of water in the xylem vessels.
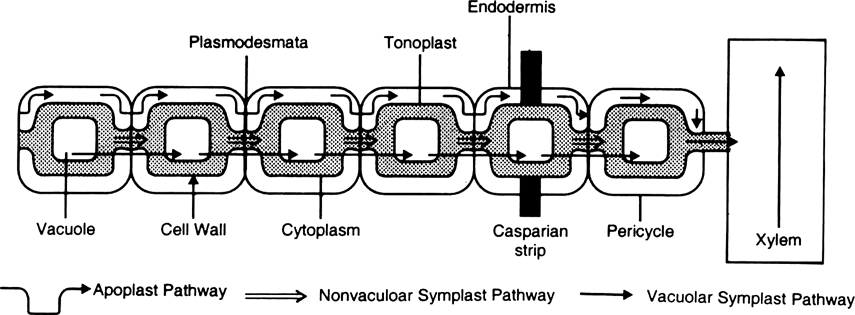
Three pathways of water movement inside the root.
Difference between Imbibition and Osmosis
|
Imbibition |
Osmosis |
|
1. It involves the absorption water by a solid substance wihtout getting dissolved. |
1. It involves the movement of water or solvent from its higher chemical potential to lower chemical potential. |
|
2. It does not need semi-permeable membrane. |
2. A semi-permeable membrane is required in osmosis. |
|
3. Heat is produced |
3. Heat is not produced. |
|
4. It is due to presence of colloidal particles.
|
4. It requires the presence of solute particles in solution form.
|
Explain transpiration and photosynthesis are complementary to each other.
Photosynthesis : It is the process of manufacture of food from C02 and water by the green parts of plant.
It is the transpiration which creates a transpiration pull for absorption of water and minerals The water is raw material for photosynthesis. If water availability is limited then photosynthesis also becomes limited. Actively photosynthetic plant needs proper supply of water. C4 plants were evolved only to use minimum amount of water and maximum use of C02 and they are double efficient to C3 plants.
C4 plant loses half the amount of water as compared to C3 plants for fraction of same amount of C02.
Thus it appears to be a compromise between transpiration and photosynthesis.
What is translocation ?
How is mycorrhizal association helpful in absorption of water and minerals in plants?
Mycorrhiza : It is the symbiotic association between roots of some plants and fungi. The hyphae provide a very large surface area and absorb mineral ions and water from soil. This is not possible for roots. The fungi provides mineral and water to roots. The hyphae secrete chemicals which protect the roots from pathogens. Thus mycorrhizal association is helpful in absorption of water and minerals in plant cells.
Where unidirectional translocation occurs?
What happens when pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or solution ?
Briefly describe water potential. What are the factors affecting it ?
Water potential : This term was given by Slatyer and Taylor (1960). It is the difference in free energy or chemical potential per unit molal volume of water in a solution over its pure state at same temperature and pressure. It is denoted by Psi or Ψw and is expressed in Pascals (Pa). T
The water potential of pure water is always taken as zero at standard temperature and pressure.
Water potential (Ψw) is expressed as the sum of solute potential (Ψs) and pressure potential (Ψp).
Ψw = Ψs + Ψp
Factors affecting the water potential are as followwing:
i. Solute concentration - The dissolution of solute in water decreses its water potential. All mixtures have a water potential less than zero. More the solute more negative will be the water potential.
ii. Pressure - If pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is aaplied to a pure water or solution, its water potential increases.
What are porins ? What role do they play in diffusion ?
Explain why pure water has maximum water potential.
What is symport ?
Distinguish between imbibition and diffusion.
|
Imbibition |
Diffusion |
|
1. It is the proces by which solid absorbs water and swells up without getting dissolved. 2. In this only water or liquid is absorbed. 3. Imbibant is required. 4. Due to imbibition pressure is increased.
|
1. It is the diffusion of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration. 2. This may occur in water, liquids, solids and gases. 3. Imbibant is not required . 4. The pressure is reduced after diffusion.
|
What is mass flow or bulk flow ?
Differentiate between apoplast pathway and symplast pathway.
|
Apoplast pathway |
Symplast pathway |
|
1. Apoplast is the system of adjacent walls and continuous through the plant except at casparian strips. 2. There is no role of plasmodesmata. 3. It occurs through cell wall and intercellular spaces. Cell membrane is not crossed. 4. It is fast. 5. It is not aided by streaming movement of cytoplasm. 6. It does not involve osmosis. |
1. It is the system of interconnected protoplasts. 2. Continuity of protoplasm from one cell to another cell is through plasmodesmata. 3. It occurs through cell membrane. 4. It is slow. 5. It is aided by streaming movements of cytoplasm. 6. It involves osmosis. |
(a) With the help of well-labelled diagrams, describe the process of plasmolysis in plants, giving appropriate examples.
When a cell is kept in a hypertonic solution, the concentration of the solution outside the cell is more. The concentration gradient makes the water from the cells moves out by the process of exosmosis. The water is lost from the cytoplasm and the vacuole. As the water is lost from the cell the cell membrane of the plant cells shrinks away from its cell wall. This condition of the cell is called as plasmolysed. 
(b) Explain what will happen to a plant cell if it is kept in a solution having higher water potential.
What role does root pressure play in water movements in plants?
Root pressure only provides a moderate push in the overall movement of water or water transport. It does not play a major role in the movement of water up the tall trees.
The main contribution of the root pressure is to re-establish the continuous flow of water molecules in the xylem which often break under the enormous tensions created by transpiration.
Describe transpiration pull model of water transport in plants. What are the factors influencing transpiration? How is it useful to plants?
In plants, the water is lost in the form of water vapour from the stomata of the leaves. As the film of water is continuous over the cells, thus a transpirational pull is generated by the loss of water from the stomatal pores of leaves. This is called the cohesion-tension model of water transport.
During daytime, the water lost through transpiration (by the leaves to the surroundings) causes the guard cells and other epidermal cells to become flaccid. They, in turn, take water from the xylem. This creates a negative pressure or tension in the xylem vessels, from the surfaces of the leaves to the tips of the roots, through the stem. As a result, the water present in the xylem is pulled as a single column from the stem. The cohesion and adhesion forces of the water molecules and the cell walls of the xylem vessels prevent the water column from disrupting.
Factors affecting transpiration
The rate of transpiration depends on the following factors:
External factors -
i. Temperature
ii. Humidity
iii. Light
iv. Wind speed
Internal factors
i. Number and distribution of stomata,
ii. Percent of open stomata
iii. Water status of the plant
iv. Canopy structure.
Transpiration is useful to the plants in the following way:
i. Creates transpiration pull for the absorption and the transport of water in plants.
ii. supplies water for photosynthesis.
iii. Transports minerals and nutrients to the plants.
iv. Has a cooling effect on the leaf surface.
v. Maintains the shape and structure of the plants cells by keeping them turgid.
Discuss the factors responsible for ascent of xylem sap in plants.
The transpirational pull is mainly responsible for the ascent of xylem sap in plants.
This ascent of water is facilitated by the following physical factors:
i. Cohesion - It is the mutual attraction between water molecules
ii. Surface tension - It is responsible for the greater attraction between water molecules in liquid phase than in gaseous phase.
ii. Adhesion - Attraction of water molecules to polar surfaces like the tracheary elements.
iv. Capillarity -Ability of water to rise in thin tubes
These physical properties give water high tensile strength, i.e., an ability to resist a pulling force and high capillarity, i.e., the ability to rise in thin tubes. The thin tubes of xylem work like capillary tubes.
Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through stomatal opening. through the same stomatal opening. carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements using the following options
-
Both processes can happen together because the diffusion coefficient of water and CO2 is different
-
The above processes happen only during night time
-
One process occurs during day time and other at night
-
Both processes cannot happen simultaneously
A.
Both processes can happen together because the diffusion coefficient of water and CO2 is different
Diffusion of water vaour and C02 are an independent process. Their diffusion depends on the difference in their ppartial pressure in the atmosphere as well as inside the leaves.
Which of the following criteria dows not pertain to facilitate transport?
-
Requirement of special membrane proteins
-
High selectivity
-
Transport saturation
-
Uphill transport
D.
Uphill transport
Facilitated transport is a form a passive transport in which materials are moved across the plasma membrane by a transport protein down. Their concentration gradient. It requires integral membrane proteins and highly selective biological membranes to cross.
Saturation occurs in facilitated, diffusion because not enough carriers may be available to handle all the free solute molecules. The rate of movement may reach a maximum. Uphill transport is a process in which diffusion of a component occurs from a less concentrated permeable stream.
Sponsor Area
Roots play insignificant role in absorption of water in
-
Sunflower
-
Pistia
-
Pea
-
Wheat
B.
Pistia
Pistia is a hydrophyte where absorption of water by root is insignificant.
Tracheids differ from other treachery elements
-
having Casparian strips
-
being imperforate
-
lacking nucleus
-
being lignified
B.
being imperforate
Tracheids and vessels both are called tracheary elements because their main function is conduction of sap. They differ from each other in being inspectorate. Tracheids are the specific cells which pit to support upwards and lateral conduction of water sap. Tracheid are comparatively short and single cell, while vessels have more than one cell and up to 10 cm long.
Root pressure develops due to
-
active absorption
-
low osmotic potential in soil
-
passive absorption
-
increase in transpiration
A.
active absorption
Root pressure is the positive pressure that develops in the roots of plants by the active absorption of nutrients from the soil. When the nutrients are actively absorbed by root hairs, water (along with minerals) increase the pressure in the xylem. This pressure pushes water up to smell heights.
A column of water within xylem vessels of tall trees does not break under its weight because of
-
Dissolved sugars in water
-
Tensile strength of water
-
Lignification of xylem vessels
-
Positive root pressure
B.
Tensile strength of water
A column of water within xylem vessels of tall tree does break under its weight because of high tensile strenght of water, i.e. an ability to resist a pulling force. This high tensile property depends on cohesion, adhesion and surface tension property of water. Due to these forces only transpiration drive ascent of xylem sap occurs.
A protoplast is a cell
-
without plasma membrane
-
without nucleus
-
undergoing division
-
without cell wall
D.
without cell wall
A protoplast is a cell without cell wall. It is a plant, bacterial or fungal cell that had its cell wall completely or partially removed using either mechanical or enzymatic means.
Which one of the following is correctly matched?
-
Passive transport of nutrients - ATP
-
Apoplast - Plasmodesmata
-
Potassium-Readily immobilization
-
Bakane of rice seedlings-F Skoog
C.
Potassium-Readily immobilization
Active transport of nutrients require ATP. Symplast is translocation through plasmodesmata. Bakane disease of rice was found by Hori (1918) to be due to Gibberella fujikuroi. None of the options is correct.
Options (C) may be correct is statement be read as 'Potassium readily mobilization' instead of 'potassium readily immobilization.
Approximately seventy percent of carbon dioxide absorbed by the blood will be transported to the lungs
-
as bicarbonate ion
-
in the form of dissolved gas molecules
-
by binding to RBC
-
as carbamino - haemoglobin
A.
as bicarbonate ion
Because of its high solubility, about 7% of carbon dioxide gets dissolved in the blood plasma and is carried to the wings in the same way. The largest fraction of carbon dioxide, i.e., (about 70% ) is converted to bicarbonates (HCO3-) and transported in the plasma.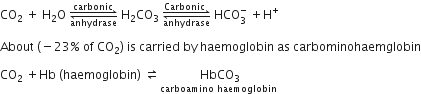
Transpiration and root pressure cause water to rise in plant by?
-
pulling it upward
-
pulling and pushing it, respectively
-
pulling it upward
-
pushing and pulling it, respectively
B.
pulling and pushing it, respectively
Transpiration causes water to rise in plants by pulling through xylem elements.
Root pressure causes water to rise in plants by pushing water in xylem components.
So, the rise of water in plants is done by pulling and pushing via transpiration and root pressure respectively.
In a ring girdled plant
-
the shoot dies first
-
the root dies first
-
the shoot and root die together
-
Neither root nor shoot will die
B.
the root dies first
In a ring girdled plant, the root dies first. A ring of bark is cut from the stem. It also removes phloem. Nutrients collect above the ring where the bark also swells up and may give rise to adventitious roots. Growth is vigorous above the root. The tissues below the ring not only show stoppage of growth but also begin to shrivel (contract). Roots begin to starve first if the ring is not healed, after sometime roots will die, which will kill the whole plant.
Which one gives the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements?
-
Transpiration
-
Potassium influx and efflux
-
Starch hydrolysis
-
Guard cell photosynthesis
B.
Potassium influx and efflux
Levitt in 1954 proposed active potassium transport theory, which is the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements. It is a explained below as:
Which one gives the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements?
-
Transpiration
-
Potassium influx and efflux
-
Starch hydrolysis
-
Guard cell photosynthesis
B.
Potassium influx and efflux
Levitt in 1954 proposed active potassium transport theory, which is the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements. It is explained below as: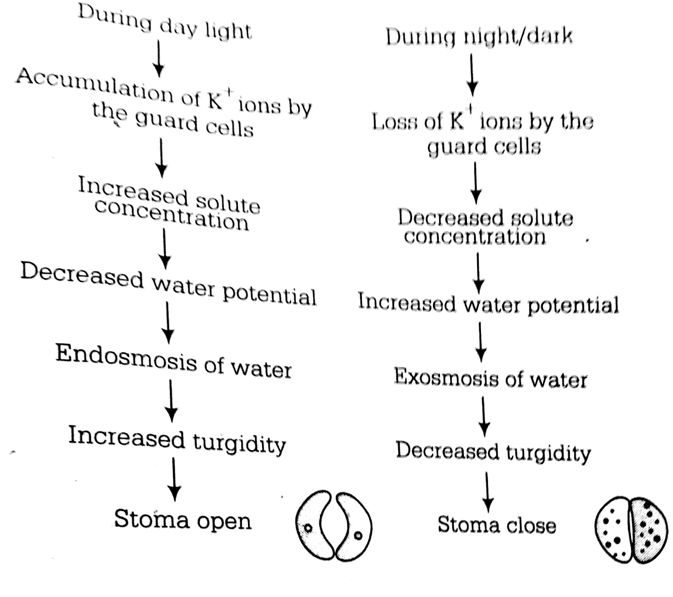
The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another is called
-
inversion
-
duplication
-
translocation
-
crossing over
C.
translocation
The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another called translocation.
It is a chromosomal abnormality caused by rearrangement of part between non-homologous chromosomes.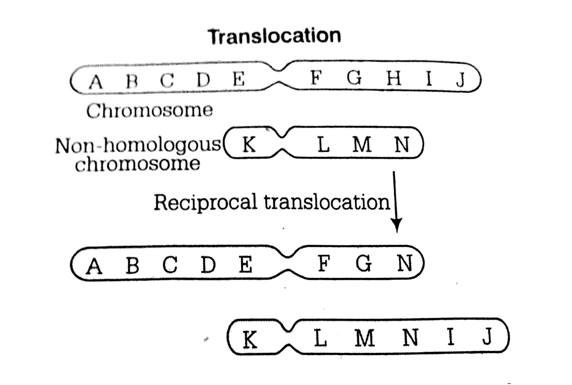
The function of leghemoglobin in the root nodules of legumes is
-
oxygen removal
-
nodule differentiation
-
expression of nif gene
-
inhibition of nitrogenase activity
A.
oxygen removal
Leghaemoglobin is an oxygen scavenger. It protects the nitrogen-fixing enzyme nitrogenase.
Guttation is the result of
-
diffusion
-
transpiration
-
osmosis
-
root pressure
D.
root pressure
Loss of water in the liquid state from uninjured parts of plants is known as guttation. It is due to root pressure.
Carrier ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substance like
-
amino acids and glucose
-
glucose and fatty acids
-
fatty acids and glycerol
-
fructose and some amino acids
A.
amino acids and glucose
Active transport occurs with the help of energy, usually against a concentration gradient. For this, cell membrane possess carriers and gated channels. Active transports of one substance are often accompanied by permeation of other substances. The phenomenon is called secondary active transport. It is of two main types- Co-transport (eg, glucose and some amino acid along with inward pushing of excess Na+) and counters transport (Ca2+ and H+ movement outwardly as excess Na+ passes inwardly).
Guard cell help in
-
protection against grazing
-
transpiration
-
guttation
-
fighting against infection
B.
transpiration
Guard cells help in transpiration. Each stomatal opening is surrounded by two specialized epidermal cells, called guard cells. Because of their small size guard cells are rapidly influenced by turgor change and thus regulate the opening and closing of stomata.
The rupture and fractionation do not usually occur in the water column in vessel/tracheids during the ascent of sap because of
-
lignified thick walls
-
cohesion and adhesion
-
weak gravitational pull
-
tranpiration pull
B.
cohesion and adhesion
The Vertical conduction of water from root to aerial parts of the plant is called ascent of sap. The water molecules remain joined to each other due to a force of attraction called cohesion force. This attraction is due to the presence of hydrogen bonds between them. The magnitude of this force is very high, therefore, the continuous water column in the xylem cannot be broken easily due to the force of gravity or other obstructions offered by internal tissues in the upward movement of water. This adhesive property of water, ie, the attraction between the water molecules and the walls of xylem ensures the continuity of water column in xylem.
Due to transpiration water evaporates to outer atmosphere through stomata. As a result leaf cells develop low water potential and water from leaf veins moves into leaf cells. They xylem of the main stem. A pressure (pull) is thus, exerted by all the leaves on the stems, which is called transpiration pull. This is strong enough to pull up the column of water to a great height.
Passage cells are thin-walled cells found in
-
endodermis of roots facilitating rapid transport of water from cortex to pericycle
-
phloem elements that serve as entry points for substance for transport to other plant parts
-
testa of seeds to enable emergence of growing embryonic axis during seed germination
-
central region of style through which the pollen tube grows towards the ovary
A.
endodermis of roots facilitating rapid transport of water from cortex to pericycle
In roots, endodermis is the innermost layer of cortex. Some of the endodermal cells present opposite to the xylem patches are thin walled and are called passage cells or transfusion cells. Passage cells help in transfer of water and dissolved salts from cortex directly into the xylem and ultimately to the pericycle.
Two cells A and B are contiguous. Cell A has osmotic pressure 10 atm, turgor pressure 7 atm and diffusion pressure deficit 3 atm. Cell B has osmotic pressure 8 atm, turgor pressure 3 atm and diffusion pressure deficit 5 atm. The result will be
-
Movement of water from cell B to A
-
No movement of water
-
Equilibrium between the two
-
Movement of water from cell A to B
D.
Movement of water from cell A to B
The water moves from lower DPD to higher DPD.
The translocation of organic solutes in sieve tube members is supported by
-
root pressure and transpiration pull
-
P-proteins
-
mass flow involving a carrier and ATP
-
cytoplasmic streaming
C.
mass flow involving a carrier and ATP
According to mass flow hypothesis, the transport of organic solutes takes place from source to sink this transport also depends on metabolic energy.
According to cytoplasmic streaming hypothesis (put forward by de Vries 1885) the transport of organic solutes takes place by combination of diffusion and cytoplasmic streaming.
Cytoplasmic streaming carry organic solutes from one end the other end of sieve tube.
P proteins has a role as defence against phloem-feeding insects and sealing of damaged sieve tubes.
Protein is absent in monocots and gymnosperms.
Which of the following is made up of dead cells?
-
Xylem parenchyma
-
Collenchyma
-
Phellem
-
Phloem
C.
Phellem
Cork cambium undergoes periclinal division and cuts off thick walled suberised dead cork cells towards outside and it cuts off thin walled living cells i.e., phelloderm on inner side.
Which of the following facilitates opening of stomatal aperture?
-
Contraction of outer wall of guard cells
-
Decrease in turgidity of guard cells
-
Radial orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
-
Longitudinal orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
C.
Radial orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
Which of the following elements is responsible for maintaining turgor in cells?
Magnesium
Sodium
Calcium
Potassium
D.
Potassium
Potassium helps in maintaining turgidity of cells. Plants require potassium ion (K+) for protein synthesis and for the opening and closing stomata, which regulated by proton pumps to make surrounding guard cell either turgid or flaccid.
Stomatal movement is not affected by
Temperature
Light
CO2 concentration
O2 concentration
D.
O2 concentration
Light, temperature and concentration of CO2 affect opening and closing of stomata while they are not affected by O2 concentration.
Some functions of the nutrient element are given below
- Important constituent of proteins involved in ETS.
- Activator of catalase.
- Important constituent of cytochrome
- Essential for chlorophyll synthesis
The concerned nutrient is
Cu
Fe
Ca
Mo
B.
Fe
Iron (Fe) is the concerned nutrient associated with the above-given functions.
Tyloses an outgrowth from ray or axial parenchyma cell into the lumen of a vessel, which partially or completely blocks the cavity are present in
Periderm
Heart wood
Sap wood
Secondary cortex
B.
Heart wood
Tyloses are found in the heartwood, sometimes the xylem parenchyma develops balloon-like structure to which are called tyloses, block the luman of the xylem.
In which form does the food is transported in plants?
Sucrose
Fructose
Glucose
Lactose
A.
Sucrose
Translocation is the movement of organic nutrients from the region of source or supply to the region of sink or utilisation. It mainly occurs through phloem and is translocated in the form of sucrose. Sucrose is a disaccharide, relatively inactive and highly soluble sugar.
In plants, water supply is due to
osmosis
imbibition
guttation
adhesion force
D.
adhesion force
Adhesion force is the force between walls and water.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water from its pure or dilute solution into a stronger solution when the two are seperated by a semi- permeable membrane.
Imbibition is the absorption of water by the solid particles of an adsorbant without forming a solution.
Guttation is the loss of water in the form of liquid droplets from the leaves and other parts of an uninjured or intact plant.
Most accepted theory for ascent of sap is
capillary theory
root pressure theory
pulsation theory
transpiration pull
D.
transpiration pull
Transpiration pull or the suction force is the force which aids in drawing the water upward from roots to leaves. In leaves, some amount of water is used for photsynthesis and excess of water is released into atmosphere through openings called as stomata.
Root Pressure Theory is the transverse osmotic pressure within the cells of a root system that causes sap to rise through a plant stem to the leaves.
Pulsation theory or Vital force theory was not accepted because living cells are not involved in the ascent of sap as water continue to rise upwards in the plant.
Capillarity Theory is the capillarity movement of water due to adhesion and cohesion forces balanced by downward pull of gravity.
Which of the following theory gives the latest explanation for the closure of stomata?
ABA theory
Munch Theory
Starch glucose theory
Active K+ transport theory
D.
Active K+ transport theory
As per 'Active K+ transport mechanism' accumulation of K+ ions occurs in the guard cells during the day inresponse to light. It increases the turgidity of guard cells, consequently stomata open.
During night, ions move out of the guard cells into surrounding epidermal cells consequently guard cells become flaccid and stomata close.
Root hair absorbs water from soil through
turgor pressure
ion exchange
osmosis
DPD
C.
osmosis
Root hair absorbs water from soil through osmosis. Osmosis is a process in which solvent moves through a semi- permeable membrane from a place of higher diffusion pressure to a place of lower diffusion pressure.
Who said that 'transpiration is a necessary evil'
Curtis
Andersen
Steward
J.C. Bose
A.
Curtis
Curtis (1926) called transpiration as necessary evil because it provides some beneficial aspects but on the other hand, many functioning and energy gets wasted from absorption of water upto the stage of transpiration.
Transpiration would be lowest when
wind velocity is high
enough water is in the soil
atmospheric RH is high
high temperature and light
C.
atmospheric RH is high
When atmospheric RH is high, the temperature of atmosphere will be low. This will reduce the rate of evaporation and also reduces the rate of transpiration.
Which of the following exhibits a direct porportionality to transpiration
Light and RH
Temperature and RH
Temperature and wind
RH and wind
C.
Temperature and wind
Temperature and wind have the direct proportional to the transpiration. When the winds faster and dry and temperature is high, the rate of water evaporation will also high, increasing the rate of transpiration.
Water in plants is transported by
cambium
phloem
xylem
epidermis
B.
phloem
The water absorbed by root hairs is transported to other parts of the plant through xylem. Phloem transfers food prepared in leaves to the other parts. Cambium is responsible for secondary growth while epidermis is the outermost protective layer of cells.
The most important force which pulls water up in tall trees is
imbibition force
osmotic force
cohesive force
electromagnetic force
C.
cohesive force
The most important force which pulls water up in the tall trees is the cohesive (inter-molecular) force between HO molecules. It also helps in maintaining the continuity of water column in tall trees.
The light phase of photosynthesis is called
Hill reaction
photo action
pigment action
chlorophyllous process
A.
Hill reaction
Hill reaction, also called as light reaction is a photochemical reaction. In this, reduced enzymes and phosphate bond energy (ATP) are produced.
Potometer works on the principle of
amount of water absorbed equals the maount transpired
osmotic pressure
root pressure
potential difference between the tip of the tube and that of the plant
A.
amount of water absorbed equals the maount transpired
Evaporation of water in the form of vapours from aerial parts of a living plant is known as transpiration. Measurement of transpiration can be done with the help of potometer. It works on the principle of amount of water absorbed equals the amount of water transpired.
Which one of the following does'nt help in molecule transport?
Diffusion
Osmosis
Surface tension
Active transport
C.
Surface tension
Surface tension does not help in molecule transport. The process of diffusion and osmosis transport molecules is without using energy but in case of active transport energy (ATP) is used.
Potometer is used to measure
ascent of sap
root pressure
transpiration
photosynthesis
C.
transpiration
Potometer is used to measure transpiration rate. These are of four types-
- Simple
- Ganong's
- Bose's
- Farmer's potometer
The real forces responsible for the movement of water from one cell to another cell is mainly
Osmotic Pressure (OP)
Turgor Pressure (TP)
Diffusion Pressure Deficit (DPD)
imbibition
C.
Diffusion Pressure Deficit (DPD)
The net force with which water is drawn into a cell is equal to difference of OP and TP, known as diffusion pressure deficit or suction pressure. DPD of pure water is maximum (= 1236 atm) solvent moves from cell of low DPD to high DPD. DPD, or SP= OP-TP.
The magnitude of root pressure ranges from
2-5 atm
0.1-0.2 atm
1-5 atm
4-6 atm
C.
1-5 atm
The term root pressure was coined by Stephen Hales (1727). The evidences that support the existence of this phenomenon are bleeding and guttation. The magnitude of root pressure is 1-2 atm and very rarely 5 atm.
Assertion: Translocation of sugar from source (leaf) to sink is defined as pressure flow hypothesis.
Reason: Translocation of the solute is facilitated through living phloem sieve tube cells.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
The accepted mechanism for the translocation of sugars from source to sink is called pressure flow hypothesis. The glucose is prepared at the source by photosynthesis, it is converted to sucrose (a disaccharide). The sugar is then moved in the form of sucrose into the companion cells and then into living phloem, sieve tube cells by active transport.
A plasmolysed cell can be deplasmolysed by placing it in
isotonic solution
saturated solution
pure water or hypotonic solution
hypertonic solution
C.
pure water or hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution is the solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater inside the cell than outside of it.
Hypertonic Solution is the solution where the concentration of solutes is greater outside the cell than inside it.
Isotonic Solution refers to two solutions having the same osmotic pressure across a semi- permeable membrane.
Saturated Solution is a chemical solution containing the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved in the solvent.
Which one of the following is correct for the transmembrane proteins in lipid bilayer of plasma membrane?
They are absent in animal cells
They act as channel proteins
They are absent in plant cells
They are only externally located
B.
They act as channel proteins
The tunnel proteins or transmembrane proteins run throughout the lipid bilayer and individually or in group form channels for the passage of water and water soluble substances. The channels however, possess selective properties for passage of different ions and other polar substances.
Assertion: Light is one of the important factor in transpiration.
Reason: It induces stomatal opening and closing. Therefore, transpiration increases in light and
decreases in dark.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Light has got no direct effect on the rate of transpiration but indirectly it affects the rate in two ways firstly by controlling the stomatal opening and secondly by affecting the temperature. With the increase in the light intensity the rate of transpiration increases because the stomata get opened and the temperature increases. The rate of transpiration increases markedly in light and decreases in dark. There is a close relationship between the opening of stomata and presence of light.
Which of the following helps in ascent of sap?
Root pressure
Transpiration
Capillarity
All of these
D.
All of these
Water is mainly absorbed by roots which goes upwards so as to replace water loss in transpiration and to be used in photosynthesis. This upward movement of water from roots to leaves through stem against force of gravity is cal led ascent of sap.
There are many theories in order to understand the ascent of sap.
- Root Pressure Theory- Root pressure is developed when rate of absorption is more than rate of transpiration and so water is pushed up in the tracheary elements.
- Capillary Force Theory- According to this, xylem vessels act as minute capillaries and water rises in these capillaries due to capillary action or surface tension.
- Transpiration Pull Theory- Due to water loss by transpiration suction pressure is increased and water is absorbed from adjacent xylem vessels of leaves and thus sap in under tension.
Grafting is successful in dicots but not in monocots because the dicots have
vascular bundles arranged in a ring
cambium for secondary growth
vessels with elements arranged end to end
cork cambium
B.
cambium for secondary growth
Grafting is the technique of joining parts of two plants so as to form a composite plant. Grafting is carried out during period of active growth and rapid healing between two related plants having vascular cambium. One plant has strong root system and the other plant possesses better flower or fruit yield. The former is called stock and the latter is known as scion or graft. Vascular cambium are the lateral meristem found in those vascular plants that exhibit secondary growth. It forms secondary xylem and secondary phloem mostly by periclinal division.
In the sieve elements, which one of the following is the most likely function of P-proteins
Deposition of callose on sieve plates
Providing energy for active translocation
Autolytic enzymes
Sealing mechanism on wounding
D.
Sealing mechanism on wounding
Sieve elements are a component of phloem tissue and are responsible for conduction of food in plants. A sieve tube element has peripheral layer of cytoplasm without any nucleus. The central part is occupied by a network of canals which contain fibrils of p-protein. The protein is vibratite and is believed to actively participate in the transport of nutrients. One general property of its ability to form a gel and it functions as a puncture repair substance forming a plug at any site of damage in sieve element, thus preventing loss of food materials being translocated by the phloem. Thus it is believed to have scaling function on wounding.
A scion is grafted to a stock. The quality of fruits produced will be determined by the genotype of
stock
scion
both stock and scion
neither stock nor scion.
B.
scion
Grafting is the technique ofjoining parts of two plants so as to form a composite plant. One plant has a strong root system called the stock, and the other plant having better flower or fruit yield is known as scion. When a scion is grafted to a stock the root system of the plant has the genotype of stock and fruits produced show genotypes of the scion
Assertion: When the ambient temperature is high and soil contains excess of water, the plants tend to lose water in the form of droplets from lenticels.
Reason: Root pressure regulates the rate of loss of water form lenticels
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
A.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
When the ambient temperature is high and soil contains excess water, the rate of transpiration is increased i.e.. loss of water takes place from leaves through stomata. Lenticular transpiration is only 0.1 % of the total transpiration. It however continues day and night because lenticels have no mechanism of closure. The lcnticcls connect the atmospheric air with the cortical tissue ofstem through interccllular spaces present amongst the complementary cells. Root pressure regulates the rate of loss of water from the stomata in some plants. High temperature may cause desiccation and closure of stomata. Root pressure is a positive pressure that develops in the xylem sap of the roots of some plants.
Assertion: In angiosperms the conduction of water is more efficient because their xylem has vessels.
Reason: Conduction of water by vessel elements is an active process with energy supplied by xylem parenchyma rich in mitochondria
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
C.
If assertion is true but reason is false
Xylem is the main conducting tissue in plants. It consists of 4 different components-tracheids, trachea or vessels, xylem fibre and xylem parenchyma.
Tracheids are elongated cells with tapering end. They arc generally present in ferns and gymnosperms for conduction of water. In angiosperms, vessels are composite structure as these are formed by dissolution of end walls of row of cells i.e., vessels elements. So angiosperms, have more efficient system of conduction due to presence of vessels. Conduction of water by vessel elements is also known as ascent of sap. Water absorbed by roots, goes upward to replace the water loss by transpiration. The most accepted theory for ascent of sap is transpiration pull theory i.e., when water is lost by transpiration from the leaves, a tension is created in the xylem and due to this water absorbed by roots hair is passed through vessels to the leaves. The xylem parenchyma are mainly for storage function but sometimes help in conduction.
Companion cell in plants are associated with
vessels
sieve elements
sperms
guard cells
B.
sieve elements
Companion cell A type of cell found within the phloem of flowering plants. Each companion cell is usually closely associated with a sieve element. Its function is uncertain, though it appears to regulate the activity of the adjacent sieve element and to take part in loading and unloading sugar into the sieve element. In gymnosperms a similar function is attributed to albuminous cells, which are found closely associated with gymnosperm sieve elements
Assertion : Long distance flow of photoassimilates in plants occurs through sieve tubes.
Reason : Mature sieve tubes have parietal cytoplasm and perforated sieve plates.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
A.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
The main function of sieve tube is the transport of food products from green and storage organs of the plant to other organs of the plant. The sieve clements are sieve tubes arranged one above the other and have sieve plates (obligue or transverse perforated septa) on their end walls. The cytoplasm occur in the form of a thin living layer along the inner side of cellulose wall. The nucleus disappears in mature sieve elements.
The plant undergoes wilting when
xylem is blocked
cambium is blocked
phloem is blocked
some roots are reduced in number
A.
xylem is blocked
Wilting The condition that arises in plants when more water is lost by evaporation than is absorbed from the soil. This causes the cells to lose their turgor and the plant structure droops. Plants can normally recover from wilting if water is added to the soil, but permanent wilting and possible death can result if the plant does not have access to water for a long period of time. In certain plants wilting is important as a mechanism to avoid overheating: when the leaves droop they are taken out of direct contact with the sun's rays. When the sun sets the plant can begin to transpire at the normal rate and the cells of the leaves regain their turgor.
Xylem is responsible for transport of water. If xylem is blocked, plant will undergo wilting
Vascular bundles of roots are
conjoint
concentric
bicollateral
radial
D.
radial
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in vascular tissue, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will include supporting and protective tissues.
In a stem or root this means that the xylem is closer to the centre of the stem or root while the phloem is closer to the exterior. In a leaf, the adaxial surface of the leaf will usually be the upper side, with the abaxial surface the lower side.
Ectophloic siphonostele is found in
Osmunda and Equisetum
Marsilea and Botrychium
Adiantum and Cucurbitaceae
Dicksonia and Maiden hair fern
A.
Osmunda and Equisetum
Ectophloic siphonostele is a monostele version of siphonostele. In this, a circular ring of xylem exists around the pith, and outside of xylem a ring of phloem is observed. It is found in flora section of the ecosystem.
Lenticular transpiration takes place in
fruits
woody stems
leaves
all of these
B.
woody stems
Transpiration always occurs against the gravity. Transpiration involves mainly the xylem cells which become active during absorption process by the roots.
Lenticular transpiration is the type of transpiration which occurs through the small pores called as lenticels present in the bark.
When the cell is fully turgid, its
DPD = OP
DPD = zero
WP = TP
OP = zero
C.
WP = TP
A fully stretched cell wall is exerting a restraining inward force called wall pressure on cell contents. This wall pressure is balanced by an equal but oppositely directed-force called turgor pressure in the cell contents, and when the cell wall can stretch no further, the cell is said to be fully turgid. Hence, when the cell is fully turgid its,
Wall Pressure (WP) = Turgor Pressure (TP).
What is the difference between pinocytosis and phagocytosis?
Pinocytosis is the process where substance is directly ingested as it is in dissolved form and ready for cellular absorption. It is done by the process of invagination.
Phagocytosis is the process where particles are broken down into simpler substance with the help of enzymes for absorption. It is mainly done by pseudopodia.
Graham's law is correlated with
diffusion
osmoregulation
osmosis
absorption
A.
diffusion
Graham's law of effusion (also called Graham's law of diffusion) was formulated by Scottish physical chemist Thomas Graham in 1848. Graham found experimentally that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass of its particles.
A plant cell becomes turgid due to
plasmolysis
exosmosis
endosmosis
electrolysis
C.
endosmosis
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a differentially permeable membrane. Endosmosis leads to diffusion of water into the cell and thus, cell becomes turgid.
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium due to water loss from osmosis.
Living. cells placed in isotonic solution (0.9% saline) retain their size and shape. This is based on the concept of
osmosis
diffusion
facilitated diffusion
transpiration
A.
osmosis
When living cells are placed in isotonic solution, they retain their shape and size as such because no osmotic movement of water molecules takes place.
If a plant cell is placed in hypertonic solution, the cell gets plasmolysed due to exosmosis. On the other hand, if a plasmolysed cell is placed in hypotonic solution, endosmosis occurs and the cell gets deplasmolysed.
In higher plants, continuity of cytoplasm from one cell to its neighbouring cells is established through
apoplast
chloroplast
leucoplast
symplast
D.
symplast
Symplast refers to the interconnected protoplasts and their plasmodesmata which effectively result in the cells of different plant organs forming a continuum.
Apoplast is the space outside the plasma membrane within which material can diffuse freely.
Chloroplasts are small organelles inside the cells of plants and algae. They absorb light to make sugar in a process called photosynthesis.
Leucoplast is a colourless organelle found in plant cells, used for the storage of starch or oil.
Which of the following criteria does not pertain to facilitated transport?
Requirement of special membrane proteins
High selectivity
Transport saturation
Uphill transport
D.
Uphill transport
Facilitated transport is a form of passive transport in which materials are moved across the plasma membrane by a transport protein down. Their concentration gradient. It requires integral membrane proteins and highly selective biological membranes to cross. Saturation occurs in facilitated, diffusion because not enough carriers may be available to handle all the free solute molecules. The rate of movement may reach a maximum. Uphill transport is a process in which diffusion of a component occurs from a less concentrated stream to a more concentrated permeable stream.
In which one of the following, expenditure of energy is required?
Osmosis
Diffusion
Active transport
Passive transport
C.
Active transport
Active transport is the only phenomenon of transportation which uses energy in the form of ATP to pump molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (i.e., low to high concentration). This is mainly carried out by the carrier proteins in the plasma membrane.
Diffusion is the transport of solvent or solute molecules (i.e., across a membrane). Osmosis (i.e., net movement of solvent molecules across a semi-permeable membrane) and passive transport (i.e., movement of biomolecules or other substances across cell membrane) does not require the expenditure of energy for the transportation of molecules or ions.
Guttation is a process of loss of water in
liquid form containing dissolved minerals
liquid form without dissolved minerals
vapour form with minerals
vapour form without minerals
A.
liquid form containing dissolved minerals
Guttation isa process of loss of water in the form of liquid from the uninjured margins of the development of root pressure through a special type of stomata called hydrathod. It usually occurs during night. Guttation water contain many dissolved minerals. It occurs only in some plants like grasses, Colocasia, tomato, etc.
Engulfing ofsolid materials by cells is called
pinocytosis
phagocytosis
active transport
autolysis
B.
phagocytosis
The process of engulfing of solid material by infolding of plasma membrane is called phagocytosis.
The process of engulfing of liquid material by infoldings of plasma membrane is called pinocytosis.
Active transport is the movement of moecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration gradient, i.e. moving from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.
Autolysis or self- digestion refers to the destruction of a cell through the action of its own enzymes.
Pick the reaction from the following, where a water molecule is removed and reduction of NAD+ does not occur in the reactions of respiration.
I. Succinic acid Fumaric acid
II. Malic acid Oxaloacetic acid
III. 2-phosphoglycerate phosphoenol pyruvic acid
IV. Pyruvic acid Acetyl Co-A
The correct answer is
I, IV
I, II
II, III
I, III
D.
I, III
I and III reactions in which water is removed, but NAD+ is not reduced.
(I) Succinic acid Fumaric acid
NAD+ FADH+ + H2O
(III) 2- Phosphoglycerate 2- Phosphoenol pyruvic acid + H2O
The II and IV reaction occur in the following way:
(II) Malic acid Oxaloacetic acid
NAD+ + H2O + NADH
(IV) Pyruvic acid Acetyl Co- A
NAD+ NAD+ + CO2 + H2
With reference to water potential of a plant cell, the relationship is represented by
A.
The difference between the free energy of water molecule in pure water and the energy of water in any other system is termed as water potential. Movement of water occurs from region of high water potential to low potential i.e.
Here, = water potential; = metric potential; = solute potential; = pressure potential
Identify the wrong statement.
The degree of decrease of chemical potential of water depends on concentration of solute
Bacteria and fungal spores are killed when they enter into pickels and jams due to plasmolysis
The process of water excudation is called transpiration
Reverse plasmolysis will occur when flaccid cells are placed in hypotonic solution
C.
The process of water excudation is called transpiration
Transpiration is the process of loss of water vapours from plant body surface.
Guttation is the process of excudation of xylem sap on the edges of leaves. It takes place by hydathodes.
Match the following columns and choose the correct option from the codes given below
| Column I (Type of Pressure in a cell) | Column II (Characteristics) |
| A. Osmotic pressure | 1. Provide turgidity to cells, tissues and softer organs |
| B. Turgor pressure | 2. Control entry of water into cells |
| C. Wall pressure | 3. Prevents bursting of cells and limits expansion |
| D. Diffusion pressure deficit | 4. Helps in retaining water inside cells |
A - 1; B - 3; C - 2; D - 4
A - 2; B - 4; C - 1; D - 3
A - 3; B - 2; C - 4; D - 1
A - 4; B - 1; C - 3; D - 2
D.
A - 4; B - 1; C - 3; D - 2
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Osmotic pressure | 4. Helps in retaining water inside cells |
| B. Turgor pressure | 1. Provide turgidity to cells, tissues and softer organs. |
| C. Wall pressure | 3. Prevents bursting of cells and limits expansion |
| D. Diffusion pressure deficit | 2. Control entry of water into cells |
A plant cell is placed in a solution whose solute concentration is twice as great as the concentration of the cell cytoplasm. The plasma membrance is selectively permeable, allowing water but not solutes to pass through. What will happen to the cell?
The cell will swell because of endosmosis
The cell will shrivel because of exosmosis
The cell will shrivel because of active transport of water
No change will occur because of hard impervious cell wall present
B.
The cell will shrivel because of exosmosis
The cell will shrivel because of exosmosis. Exosmosis will occur as the concentration inside the cell is half than outside, hence, water will move from the cytoplasm to the surrounding medium causing the cell to shrivel.
Read the following statements with respects to rate of transpiration.
I. In dry atmosphere, the relative humidity is low so, the rate of transpiration increases.
II. Slow breeze promotes the rate of transpiration.
III. ABA promotes transpiration.
IV. A high salt concentration in soil water increases transpiration.
Choose the incorrect options.
I and II
II and III
III and IV
I and IV
C.
III and IV
Statement III and IV are incorrect as Abscisic Acid (ABA) inhibits transpiration. This hormone functions in various plant developmental processess, including bud dormancy and ABA-mediated signalling also plays an important part in plant responses to environmental stress and plant pathogens. A high salt concentration in soil reduces the rate of transpiration due to less water absorption.
Diffusion Pressure Deficit (DPD) is equal to the Osmotic pressure substracted by
Osmotic Pressure (OP)
Turgor Pressure (TP)
Suction Pressure (SP)
Water Potential ()
B.
Turgor Pressure (TP)
The amount by which the diffusion pressure of a solution is lower than that of its solvent is known as Diffusion Pressure Deficit or DPD. It is also called suction pressure. At fully turgid condition.
DPD (SP) = OP - WP
The right equation for water potential is
D.
Water potential is a measure of how freely water molecules can move in a particular environment or system. It is represented by a Greek letter Psi or .
Sunken stomata are present in
mesophyte
xerophyte
epiphytes
All of these
B.
xerophyte
A sunken stomata is a stomata in a small pit, which protects the escaping water vapor from air currents, decreasing water loss from the leaf. It is commonly found in plants in arid environments as one of their adaptations to preserve water such as in xerophytes.
In plants, water supply is due to
osmosis
imbibition
guttation
adhesion force
D.
adhesion force
Diffusion of water from its pure state or dilute solution into a solution or stronger solution when the two are separated by a semipermeable membrane is termed as osmosis. In plants water supply is due to osmosis.
Most accepted theory for ascent of sap is
capillarity theory
root pressure theory
pulsation theory
transpiration pull theory
D.
transpiration pull theory
Transpiration pull is the tension, which develops due to transpiration. It has been demonstrated and evidenced, that rate of water absorption and hence, ascent of sap closely follows the rate of transpiration.
Cohesion and Transpiration pull theory, given by Dixon and Jolly (1894) is the most accepted theory tor ascent of sap.
Transpiration differ from evaporation in
rate of water loss
transpiration is a physiological process whereas evaporation is physical process
transpiration is a physical process while evaporation is physiological process
frequency of water loss
B.
transpiration is a physiological process whereas evaporation is physical process
Transpiration differ from evaporation because the transpiration is a physiological process while evaporation is a physical process. Transpiration is influenced by pH, CO2 and hormone whereas the evaporation is not influenced by pH, CO2 and hormones.
An antitranspirant is
cobalt chloride
mercury
potassium
phenyl mercuric acetate
D.
phenyl mercuric acetate
Antitranspirants are the substances that are employed for reducing the rate of transpiration eg, phenyl mercuric acetate, salicylic acid reduce the degree of stomatal opening.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area





