Economics Chapter 2 People As Resource
Sponsor Area
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Social Science Economics
What do you understand by ‘people as resource’?
‘People as Resource’ is a way of referring to a country's working people in term of their existing productive skills and abilities. People as a resource contribute to the creation of the Gross National Product. People as resource is the positive side of a large population that is often overlooked.
How is human resources different from other resources like land and physical capital?
Following are the differences between human resources and land and physical capital resources:
|
Human Resources |
Land and Physical Capital Resources |
|
(i)Human resource is a primary factor of production as it can make use of land and capital. (ii)Human resource is an active factor of production. (iii)It includes education, health etc. |
(i)Land and physical capital resources are secondary factors of production as they cannot become useful on their own. (ii)These are passive factor of production. (iii)These includes building, land etc. |
What is the role of education in human capital formation?
Following are the role of education in human capital formation:
(i) Education bears fruits in term of good job and salary.
(ii)Education increases the efficiency of the workers.
(iii) Education helps in increasing the mental horizon of the people.
(iv) Education enhances the national income, cultural richness and increase the efficiency of governance.
(v) Education encourages economic development through greater participation of the people in the affairs of the country.
What is the role of health in human capital formation?
Following are the role of health in human capital formation:
(i)The health of a person helps him to realise his potential and ability to fight illness.
(ii)Good health increases the efficiency of a worker.
(iii)Good health increases the learning capacity of a worker.
(iv)Health does not mean survival only. It involves not only the physical fitness of the individual but also his mental.
(v)Health is an indispensable basis for realising one's well being.
What part does health play in the individual's working life?
Health play an important role in the individual's working life in the following ways:
(i)Good health increases the efficiency of a worker.
(ii)The health of an individual helps him to realise his potential and the ability to fight illness.
(iii)An unhealthy person becomes a liability for an organisation indeed; health is an indispensable basis for realising one’s well being.
What are the various activities undertaken in the primary, secondary and the tertiary sector?
(i)Primary Sector Activities - Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishing, poultry farming and mining activities are the main primary sector activities.
(ii)Secondary Sector Activities - Quarrying and manufacturing are the main activities of secondary sector.
(iii)Tertiary Sector Activities - Trade, transport, communication, banking, education, health, insurance services are the main activities of Tertiary sector activities.
What is the difference between economic activities and non-economic activities?
The difference are:
|
Economic Activities |
Non-Economic Activities |
|
(i)Economic activities add value to the national income. |
(i) Non-Economic activities do not add any value of the national income. (ii) Non-Economic activities do not contribute to the flow of goods and services in an economy. (iii) Increase in non-economic activities is not an indicator of the economic progressing. ( |
Why are women employed in low paid work?
The main reasons for women being employed in low paid work are:
(i)Literacy rate among women is very low.
(ii)Various activities relating to legal protection of women is meagre.
(iii)Most of the women are not ready to work outside their domestic domain.
(iv)Most of the women are unskilled workers.
(v)Women cannot be as regular as men in their duties as they are more attached to home duties.
How will you explain the term unemployment?
Unemployment:
(i)Unemployment is said to exist when people who are willing to work at the going wages cannot find job.
(ii)Unemployment in a country refers to that situation where in large number of working population is willing to work at the existing rate of wages but due to several reasons they fail to get any work.
(iii)The working population includes people from 15 to 59 years. Boys and girls below the age of 15 years and men and women above the age of 59 do not fall in the category of working population.
What is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment?
|
Seasonal Unemployment |
Disguised |
|
(i) Seasonal unemployment happens when people are not able to find jobs during some months of the year. |
(i) In case of disguised unemployment people appear to be employed. |
Why is educated unemployment, a peculiar problem of India?
(i)This is a phenomenon urban areas.
(ii)There is unemployment among technically qualified persons on one hand, while there is dearth of technical skills required for economic growth.
(iii)A study showed that unemployment among graduates and post graduates has increased faster than among the matriculates.
(iv)A paradoxical manpower situation is witnessed as surplus manpower in certain categories coexists with the shortage of manpower in others.
(v)Many youth with matriculation, graduation and post graduation degrees are not able to find job.
In which field do you think India can build the maximum employment opportunity? Explain.
India can build the maximum employment opportunity in the field of primary sector by providing modern methods of production as most of the population is engaged in agriculture sector.
Can you suggest some measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed?
The suggestions are mentioned below:
(i) Emphasis should be laid on skill development.
(ii)Technical education should be provided.
(iii)Vocational education should be introduced.
(iv)The problem of the educated unemployed can be mitigated by providing them professional education.
(v) The problem of the educated unemployed can be mitigated by providing help to the educated unemployed for starting modern techniques of farming.
Can you imagine some village which initially had no job opportunities but later came up with many?
(i)There was a village inhabited by several families. Each family produced enough to feed its members. Each family met its needs by the members making their own clothes and teaching their own children.
(ii)One of the families decided to send one of its sons to an agriculture college. The boy got his admission in the nearby college of agriculture.
(iii)After some time he became qualified in agro-engineering and came back to the village. He proved to be so creative that he could design an improved type of plough, which increased the yield of wheat. Thus a new job of agro-engineer was created and filled in the village. Inspired by this success all the families after some time held a meeting in the village.
(iv)They all wanted to have a better future for their children too. They requested to Panchayat to open a school in the village. The Panchayat with the help of govt. opened a school. A teacher was recruited from a nearby town.
(v)After some time one of the families gave training to his daughter in tailoring. She started stitching clothes for all the families at the village. Overtime, this village, which formally had no job opportunities in the beginning, had many opportunities like teacher, tailor, agro-engineer and many more.
Which capital would you consider the best—land, labour, physical capital and human capital? Why?
Among land, labour, physical capital and human capital, the human capital is the best because human capital can make use of land, labour and physical capital.
Land and capital cannot become useful on its own.
Population can be as ______________ for the economy.
Asset
Liability
Both asset and liability
None of these
C.
Both asset and liability
In which field the investment formulates human capital?
Education
Health
Training
All of these
D.
All of these
Sponsor Area
What type of unemployment exists in rural areas of India?
Seasonal
Disguised
Both seasonal and disguised
Voluntary
C.
Both seasonal and disguised
Which one is an example of Primary sector?
Agriculture
Manufacturing
Communication
Trade
A.
Agriculture
Which one is the example an Secondary sector?
Agriculture
Manufacturing
Communication
Banking
B.
Manufacturing
Sponsor Area
In India, how many doctors were there in 2001?
7,01,500
4,03,600
4,03,600
5,03,900
D.
5,03,900
What is GDP?
Germany, Nepal, Pakistan
Gross National Product
Gross Net Product
None of these
B.
Gross National Product
What is unemployment?
A situation under which a person is under paid
A situation under which a person is not working
A situation under which people are willing to work at the prevailing wages but cannot find a job
A situation under which a person is unemployed for a particular season
C.
A situation under which people are willing to work at the prevailing wages but cannot find a job
What is national income?
It is an average income of each and every citizen of a country
It is a sum total of goods and services produced by each household
It is gross domestic purchase
It is a sum total of goods and services produced in a country
D.
It is a sum total of goods and services produced in a country
What is CHC?
Common Heath Centre
Community Help Centre
Community Help Centre
None of these
C.
Community Help Centre
What is PHC?
Primary Health Club
Primary Help Club
Primary Help Centre
Primary Health Centre
D.
Primary Health Centre
What is ‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’?
It is to promote adult education
Under this free and compulsory education will be provided to all
It is an employment programme of the central govt
It is a scheme under which elementary education is to be provided to all children in the age group of 6-14 years.
D.
It is a scheme under which elementary education is to be provided to all children in the age group of 6-14 years.
What is seasonal unemployment?
People appear to be employed but they are not
People are willing to work at the prevailing wages cannot find job
When people are not able to find jobs during some months of year
None of these
C.
When people are not able to find jobs during some months of year
Which are of the following is not an activity of tertiary sector?
Transport
Banking
Manufacturing
Tourism
C.
Manufacturing
Has the literacy rate of the population increased since 1951?
Yes, the literacy rate of the population has increased. The literacy rate have increased from 18% in 1951 to 65% in 2001.
Why are women less educated than men?
Women are less educated than men because women are not encouraged to attend school as compared to men.
Is the increase in number of colleges adequate to admit the increasing number of students?
No, because in comparision to the increase of students the number of colleges are not increasing.
Do you think we should have more number of universities?
Yes, we should have more number of universities.
What is the increase noticed among the teachers in the year 1998-99?
In 1950-51 the number of teachers was 24,000 and it was 3,42,000 in 1998-99.
What is your idea about future colleges and universities?
It will remain more or less constant due to the non-availability of employement in Govt Sector.
Students will prefer professional education as there are more employement opportunities with the professional education.
What are two types of rural unemployment?
The two types are:
(i) Disguised unemployment.
(ii) Seasonal unemployment.
What are the two types of urban unemployment?
They are:
(i)Educated unemployment.
(ii)Industrial unemployment.
How will you invest in human capital?
We will invest in human capital through education, training, medical care etc.
What kind of people are considered an asset in economy?
Healthy and educated people are considered an asset in economy.
Define infant mortality rate
Infant mortality rate is the death of a child under one year of age.
What is birth rate?
Birth rate is number of babies born for every 1,000 people during a particular period of time.
What is meant by death rate?
Death rate is the number of people per 1,000 who die during a particular period of time.
What are the main sources of human Capital Formation?
The sources are:
(i) Education
(ii) Health facilities.
Discuss the quality of population.
The quality of population depends upon the health of a person, life expectancy, skill formation acquired and the literacy rate.
The quality of population decides the growth rate of the country. Literate and healthy people are considered an asset for the economy. On the other hand illiterate and unhealthy people turns out to be liability.
'Country like Japan did not have any natural resources, still they are developed countries'. State the reasons.
(i)Japan have invested in human capital especially in the field of education and health.
(ii)The skilled and trained people have made efficient use of other resources like land and capital.
(iii)Efficiency and technology evolved by people have made there countries developed.
State any three factors on which the quality of population depends.
The factors are:
(ii)Health
(ii)Life expectancy
(iii)Education
Describe ‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’.
‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan is a step towards providing elementary education to all children in the age group of 6-14 by 2010.
It is a time bound initiative of the central govt. in partnership with the states, the local goverment and the community for achieving the goal of universalisation of elementary education.
Enlist the following activities into primary, secondary and tertiary activities.
Banking, insurance, dairy, quarrying, mining, communication, education, fishing, poultry farming, Agriculture, manufacturing, forestry, tourism and trade.
|
Primary |
Secondary |
Tertiary |
|
(i) Dairy (ii) Mining (iii) Fishing (iv) Poultry Farming (v) Agriculture (vi) Forestry |
(i) Quarrying (ii) Manufacturing |
(i) Banking (ii) Insurance (iii) Communication (iv) Education (v) Tourism (vi) Trade |
Sponsor Area
Mention the objectives of the Tenth Five Year Plan with reference to education.
(i)The Tenth Five Year Plan endeavoured to increase the enrolment in higher education of the 18-23 year age group from the present 6-9 percent, by the end of the plan period.
(ii)The Tenth Five Year Plan also focuses on distant education, convergence of formal, non-formal, distant and IT education institutions.
(iii)The strategy focus on increasing access, quality, adoption of states-specific curriculum modification, vocationalisation and networking on the use of information technology.
Differentiate between disguised unemployment and educated unemployment.
The difference:
|
Disguised Unemployment |
Educated Unemployment |
|
(i) Disguised unemployment is that kind of unemployment under which people appear to be employed, but they are not. (ii) It is mainly found in rural areas. |
(i) Educated unemployment is that kind of unemployment under which people are educated but are unable to find a job. (ii) It is mainly found in urban areas. |
What are the causes for seasonal unemployment?
The causes are:
(i)Lack of multiple cropping.
(ii)Lack of small scale and cottage industries in rural areas.
(iii)Lack of commercialisation of agriculture.
Why investment in human resource is important?
This investment on people is the same as investment in land and capital.
What are the implication of umemployment?
The implication of unemployment are:
(i)Unemployment leads to wastage of manpower resource. People who are an asset for the economy turn into a liability.
(ii)There is a feeling of hopelessness and despair among the youth. People do not have enough money to support their family.
(iii)Inability of educated people who are willing to work to find gainful employment implies a great social waste.
(iv)Unemployment tends to increase economic overload. The dependence of the unemployed on the working population increases.
(v)The quality as life of an individual as well as of society is adversely affected.
Mention the steps taken by the goverment to promote education.
The steps taken by the goverment to promote education are mentioned below:
(i)Goverment has launched various schemes for providing universal access, retention and quality in elementary education, with a special emphasis on girls.
(ii)The expenditure on education as a percentage of GDP has been increased from 0.64 percent in 1951-52 to 3.98 percent in 2002.
(iii)The plan outlay on education has been increased from about Rs. 151 crore in the first plan to about Rs. 43,825 crore in the 10th Five Year Plan.
(iv)Vocational streams have been developed to equip large number of high school students with occupations related to knowledge and skills.
(v)There is also an establishment of schools like the Navodaya Vidyalaya in each district of the country.
Mention the steps taken by the government to Improve the literacy level in India.
The steps taken by the government to Improve the literacy level in India are mentioned below:
(i)The Primary School system has expanded to over 5,00,000 villages in India.
(ii)Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan is a significant step towards providing elementary education to all children in the age group of 6-14 years by 2010. It is a time bound initiative of the central government, in partnership with the states, the local government and the community for achieving the goal of universalisation of elementary education.
(iii) Mid-day meal scheme has been implemented to encourage attendance and retention of childern, and improve their nutritional status.
(iv)Along with it, bridge coverage and back to school camps have been initiated to increase the enrolment in elementary education.
Describe peculiarities of literacy in India.
The peculiarities of literacy in India are:
(i)The literacy rates have increased from about 18 percent in 1951 to around 65 percent in 2001.
(ii)A vast difference is noticed across different sections of the population.
(iii)Literacy among males is nearly 50 percent higher than females, and it is about 50 percent higher in urban areas as compared to the rural areas.
(iv)According to the census of 2001, a person aged 7 years and above, who can read and write with understanding in any language is treated as literate.
(iv)Literacy rates vary from 96 percent in some districts of Kerala to a below 30 percent in some parts of Madhya Pradesh and Bihar.
State the factors responsible for unemployment in India.
(i)Rise of Population - Population of India has been continuously rising. From a population of about 361 million in 1951, it has risen to around 1027 million in 2001, but due to slow economic growth employment opportunities have not risen at the same pace.
(ii)Underdevelopment of cottage and small scale industry - In India rural sector is facing problems of disguised and seasonal unemployment. This is due to under development of the cottage and the small scale industry.
(iii)Over dependence on agriculture - Even after more than 50 years of Independence, more than 60 percent of our population still depends upon the primary sector for its livelihood.
Mention any three schemes launched by the Govt. of India to tackle unemployment.
The schemes launched by the Govt. of India to tackle unemployment are mentioned below:
(i)National Rural Employment Programme (1980-81).
(ii)Jawahar Rozgar Yojana (1989) etc.
(iii)Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (2005).
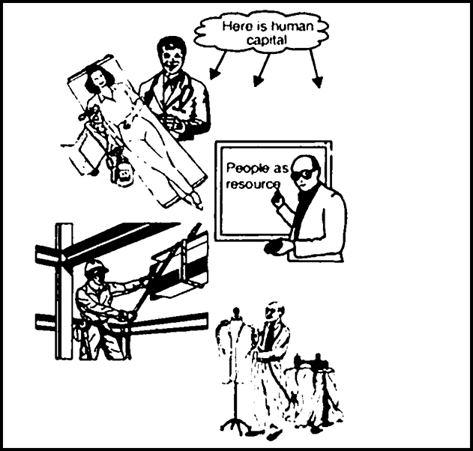

Observing the photograph can you describe how a doctor, teacher, engineer and a tailor are an asset to the economy?
A doctor, teacher, engineer and a tailor are an asset to the economy because all of them do human capital formation through their work.
(i)A doctor cures the patients and makes them able to do work.
(ii)A teacher enables the people to read, write and understand. By this process they become able to get work in the different fields.
(iii)An engineer formulates human capital by making roads, bridges and building.
(iv)A tailor converts cloth into different wears to the people.
Thus all of them contribute to the economic development of the country.
Mentioned the differences you noticed between the two friends Vilas and Sakal in the chapter.
We noticed the following differences between the two friends Vilas and Sakal:
(ii)Sakal was a healthy boy whereas Vilas turned out to be a patient of arthritis.
(iii)Sakal earned a sound salary while Vilas had only a meagre income.
(iv)Sakal secured a job in the private firm, contrary to it, Vilas survived by selling fish in the nearby market.
Visit a village or colony located near to your residential area and note down the various activities undertaken by the people of that village or colony.
If this is not possible, ask your neighbour what is their profession? In which of the three sectors will you categorise their work?
I asked my neighbour and came to know that they are doing the following professions:
(i) Mr. Rakesh is a farmer.
(ii) Mr. Sohan Lai works in a bank.
(iii) Mr Subhash works in a factory.
Thus the work of Rakesh, Sohan Lai and Subhash will be categorised in the Primary sector, Tertiary sector and Secondary sector respectively.
State whether these activities are economic or non-economic activities.
Vilas sells fish in the village market.
Economic activity.
Say whether these activities are economic or non-economic activities.
Vilas cooks food for his family.
Non-economic activity.
Say whether these activities are economic or non-economic activities.
Sakal works in the private firm.
Economic activity.
Say whether these activities are economic or non-economic activities.
Sakal looks after his younger brother and sister.
Non-economic activity.
Source : Census of India 2001. Series I India, Paper 1 of 2001.
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
1. Has the literacy rates of the population increased since 1951?
2. In which year India has the highest literacy rates?
3. Why literacy rate is high among the males of India?
4. Why are women less educated than men?
5. How would you calculate literacy rate in India?
6. What is your projection about India's literacy rate in 2010?
1. Yes, the literacy rates of the population has increased since 1951.
2. India has the highest literacy rate in the year 2001.
3. The literacy rate is high among the males of India because of their regular form of education.
4. Women are less educated than men because they are not encouraged to acquire education.
5. Literacy rate in India is calculated by the ratio of educated population and total population multiplied by 100.
6. My projection about India's literacy rate in 2010 is about 80 percent.
Number of Institutions of Higher Education, Enrolment and Faculty.
|
Year |
Number of Colleges |
Number of Universities |
Students |
Teachers |
|
1950—51 |
750 |
30 |
2,63,000 |
24,000 |
|
1990—91 |
7,346 |
177 |
49,25,000 |
2,72,000 |
|
1996—97 |
9,703 |
214 |
67,55,000 |
3,21,000 |
|
1998—99 |
11,089 |
238 |
74,17,000 |
3,42,000 |
Source: UGC Annual Report 1996-97 and 1998-99 and Selected Educational Statistics, Ministry of HRD.
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following questions:
1. Is the increase in number of colleges adequate to admit the increasing number of students?
2. Do you think we should have more number of universities?
3. What is the increase noticed among the teachers in the year 1998-99?
4. What is your idea about future colleges and universities?
1. No, the increase in number of colleges is not adequate to admit the increasing number of students.
2. Yes, I think we should have more number of universities.
3. The increase noticed among the teachers in the year 1998-99 as compared to the year 1950-51 is 3,18,000.
4. Our idea about future colleges and universities is that they will definitely face many problems related with admissions, shortage of staff, infrastructure etc.
Health infrastructure over the years.
|
1951 |
1981 |
2001 |
||
|
|
SC/PHC/CHC |
725 |
57,363 |
1,63,181 |
|
|
Dispensaries and Hospitals |
9,209 |
23,555 |
43,322 |
|
|
Beds |
1,17,198 |
5,69,495 |
8,70,161 |
|
|
Doctors (Allopathy) |
61,800 |
2,68,700 |
5,03,900 |
|
|
Nursing Personnel |
18,054 |
1,43,887 |
7,37,000 |
SC : Sub-Centre, PHC : Primary Health Centre, CHC : Community Health Centre.
Source : National Health Policy, 2002.
Study the Table 2.2 and answer the following questions:
1. What is the percentage increase in dispensaries from 1951 to 2001?
2. What is the percentage increase in doctors and nursing personnel from 1951 to 2001?
3. Do you think the increase in the number of doctors and nurses adequate for India? If not, why?
4. What other facilities would you like to provide in a hospital?
5. Discuss about the hospital you have visited.
6. Can you draw graph using this table?
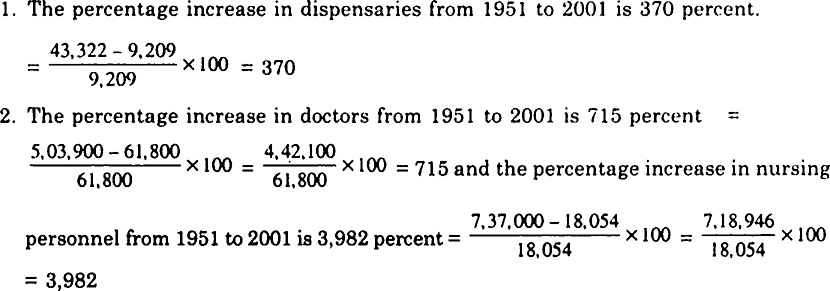
3.The increase in the number of doctors and nurses is not adequate for India because the population of India is growing rapidly.
4.I would like to provide other facilities like X-Ray machines, Ultra sound, MRI etc. in every hospitals with additional doctors.
5.I have visited the hospital in nearby my residence area. There I found long rows of patients and shortage of doctors, beds, nursing personnels, machines and other modern facilities.
6.Self Attempt
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
Sponsor Area