Nuclei
The operation of a nuclear reactor is said to be critical, if the multiplication factor (k) has a value
1
1.5
2.1
2.5
A.
1
The multiplication factor (k) is an important reactor parameter and is the ratio of number of neutrons present at the beginning of a particular generation to the number present at the beginning of the next generation. It is a measure of the growth rate of the neutrons in the reactor. For k =l, the operation of the reactor is said to be critical.
Note: If k becomes greater than one, the reaction rate and the reactor power increase exponentially. Unless the factor k is brought down very close to unity, the reactor will become supercritical and can even explode.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Nuclei Chapter
The above is a plot of binding energy per nucleon Eb, against the nuclear mass M; A, B, C, D, E, F correspond to different nuclei. Consider four reactions: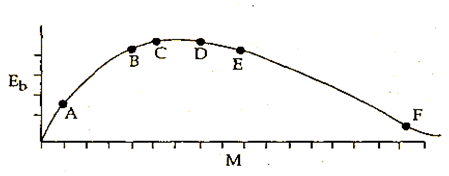
(i) A + B → C + ε (ii) C → A + B + ε
(iii) D + E → F + ε and (iv) F → D + E +ε
where ε is the energy released? In which reaction is ε positive?
This question contains Statement -1 and Statement-2. Of the four choices given after the statements,
Choose the one that best describes the two statements.
Statement – I: Energy is released when heavy nuclei undergo fission or light nuclei undergo fusion.
and
Statement – II: For heavy nuclei, binding energy per nucleon increases with increasing Z while for light nuclei it decreases with increasing Z.
If M0 is the mass of an oxygen isotope 8O17 , Mp and MN are the masses of a proton and a neutron respectively, the nuclear binding energy of the isotope is
In gamma-ray emission from a nucleus
When 3Li7 nuclei are bombarded by protons, and the resultant nuclei are 4Be8 , the emitted particles will be
The ‘rad’ is the correct unit used to report the measurement of
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area