Light - Reflection and Refraction
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
Two light rays whose path of reflection are priorly know are:
(i) The incident ray passes through the centre of curvature: In this case, light ray after reflecting from the concave mirror moves back in the same path. This happens because the light ray is incident perpendicularly on the mirror surface.
(ii) The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the concave mirror obliquely and making equal angles with the principal axis.
Let an object "a candle" is placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then using above two rays, image of the candle can be located as shown below:
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Light - Reflection and Refraction Chapter
A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object?
In the following diagram the correctly marked angles are: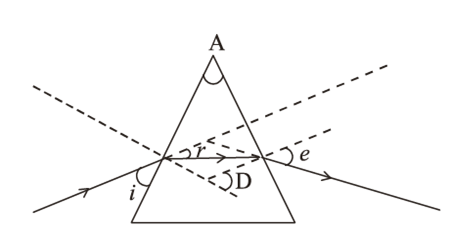
The correct sequencing of the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence, the angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 is: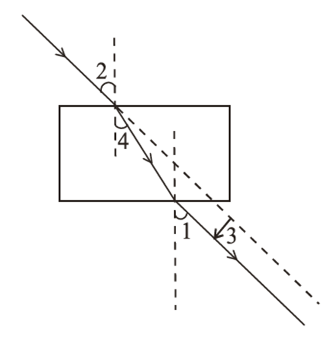
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that, he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area